From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A preservative is a substance that is added to products such as foods, pharmaceuticals, paints, biological samples, wood, etc. to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. In general preservation is implemented in two modes, chemical and physical. Chemical preservation entails adding chemical compounds to the product. Physical preservation entails refrigeration and drying.[1] Artificial preservatives are man-made. They are used in foods, cosmetics, and many other products. Artificial preservatives reduce the risk of foodborne infections, decrease microbial spoilage, and preserve fresh attributes and nutritional quality. Some physical techniques for preservation include dehydration, UV-C radiation, freeze-drying, and refrigeration. Generally both chemical preservatives and physical preservation are combined.
The most commonly used antimicrobial preservative is lactic acid. Common antimicrobial preservatives are presented in the table.[2][3][4] Nitrates and nitrites are also antimicrobial.[5][6] The detailed mechanism of these chemical compounds range from inhibiting growth of the bacteria to the inhibition of specific enzymes.
The oxidation process spoils most food, especially those with a high fat content. Fats quickly turn rancid when exposed to oxygen. Antioxidants prevent or inhibit the oxidation process. The most common antioxidant additives are ascorbic acid (vitamin C ) and ascorbates.[7] Thus, antioxidants are commonly added to oils, cheese, and chips.[2] Other antioxidants include the phenol derivatives BHA, BHT, TBHQ and propyl gallate. These agents suppress the formation of hydroperoxides.[3] Other preservatives include ethanol and methylchloroisothiazolinone.
A variety of agents are added to sequester (deactivate) metal ions that otherwise catalyze the oxidation of fats. Common sequestering agents are disodium EDTA, citric acid (and citrates), tartaric acid, and lecithin.[1]
Traditional preservatives such as sodium benzoate have raised health concerns. Benzoate was shown in a study to cause hypersensitivity in some athsma sufferers. This has caused reexamination of natural preservatives which occur vegetables.[8]
The use of food preservatives varies greatly depending on country. Many developing countries that do not have strong governments to regulate food additives face either harmful levels of preservatives in foods, or a complete avoidance of foods that are considered unnatural or foreign. These countries have also proven useful in case studies surrounding chemical preservatives, as they have been only recently introduced.[10] In urban slums of highly populated countries the knowledge about contents of food tends to be extremely low, despite consumption of these imported foods.[11]
In the U.S., the FDA standards do not currently require fruit and vegetable product labels to reflect the type of chemical preservative(s) used on the produce.[citation needed]
The increasing demand for ready-to-eat fresh food products has led to challenges for food distributors regarding the safety and quality of their foods. Artificial preservatives meet some of these challenges by preserving freshness for longer periods of time, but these preservatives can cause negative side-effects as well. Sodium nitrite is a preservative used in lunch meats, hams, sausages, hot dogs, and bacon to prevent botulism. It serves the important function of controlling the bacteria that cause botulism, but sodium nitrite can react with proteins, or during cooking at high heats, to form carcinogenic N-nitrosamines.[6] It has also been linked to cancer in lab animals.[14] The commonly used sodium benzoate has been found to extend the shelf life of bottled tomato paste to 40 weeks without loss of quality.[7] However, it can form the carcinogen benzene when combined with vitamin C.[citation needed] Many food manufacturers have reformed their products to eliminate this combination, but a risk still exists.[14] Consumption of sodium benzoate may also cause hyperactivity. For over 30 years, there has been a debate about whether or not preservatives and other food additives can cause hyperactivity. Studies have found that there may be increases in hyperactivity amongst children who consume artificial colorings and benzoate preservatives, but these studies were not entirely conclusive. Hyperactivity only increased moderately, and it was not determined if the preservatives, colorings, or a combination of the two were responsible for the increase.[15]
Antimicrobial additives
Antimicrobial preservatives prevent degradation by bacteria. This method is the most traditional and ancient type of preserving—ancient methods such as pickling and adding honey prevent microorganism growth by modifying the pH level. Today, synthetic preservatives are used instead.The most commonly used antimicrobial preservative is lactic acid. Common antimicrobial preservatives are presented in the table.[2][3][4] Nitrates and nitrites are also antimicrobial.[5][6] The detailed mechanism of these chemical compounds range from inhibiting growth of the bacteria to the inhibition of specific enzymes.
| E number | chemical compound | comment |
|---|---|---|
| E201 – E203 | benzoic acid, sodium benzoate | used in acidic foods such as jams, salad dressing, juices, pickles, carbonated drinks |
| E214 – E219 | hydroxybenzoate and derivatives | stable at a broad pH range |
| E270 | lactic acid | - |
| E249 – E250 | nitrite | used in meats to prevent botulism toxin |
| E251 – E252 | nitrate | used in meats |
| E280 – E283 | propionic acid and sodium propionate | baked goods |
| E220 – E227 | sulfur dioxide and sulfites | common for fruits |
| E200 – E203 | sorbic acid and sodium sorbate | common for cheese, wine, baked goods |
Antioxidants

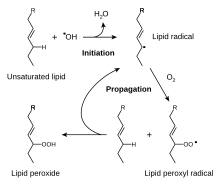
The free radical pathway for the first phase of the oxidative rancidification of fats. This process is slowed by antioxidants.
The oxidation process spoils most food, especially those with a high fat content. Fats quickly turn rancid when exposed to oxygen. Antioxidants prevent or inhibit the oxidation process. The most common antioxidant additives are ascorbic acid (vitamin C ) and ascorbates.[7] Thus, antioxidants are commonly added to oils, cheese, and chips.[2] Other antioxidants include the phenol derivatives BHA, BHT, TBHQ and propyl gallate. These agents suppress the formation of hydroperoxides.[3] Other preservatives include ethanol and methylchloroisothiazolinone.
| E number | chemical compound | comment |
|---|---|---|
| E300-304 | ascorbic acid sodium ascorbate | cheese, chips, |
| E321 | butylated hydroxytoluene, butylated hydroxyanisole | also used in food packaging |
| E310-312 | gallic acid and sodium gallate | oxygen scavenger |
| E220 – E227 | sulfur dioxide and sulfites | beverages, wine |
| E306 – E309 | tocopherols | vitamin E activity |
A variety of agents are added to sequester (deactivate) metal ions that otherwise catalyze the oxidation of fats. Common sequestering agents are disodium EDTA, citric acid (and citrates), tartaric acid, and lecithin.[1]
Nonsynthetic compounds for food preservation
Citric and ascorbic acids target enzymes that degrade fruits and vegetables, e.g., phenolase which turns surfaces of cut apples and potatoes brown. Ascorbic acid and tocopherol, which are vitamins, are common preservatives. Smoking entails exposing food to a variety of phenols, which are antioxidants. Natural preservatives include rosemary extract, hops, salt, sugar, vinegar, alcohol, diatomaceous earth and castor oil.Traditional preservatives such as sodium benzoate have raised health concerns. Benzoate was shown in a study to cause hypersensitivity in some athsma sufferers. This has caused reexamination of natural preservatives which occur vegetables.[8]
History
The preservation of foods has evolved greatly over the centuries, and has been instrumental in increasing food security. The use of preservatives other than traditional oils, salts, etc. in food began in the late 19th century, but was not widespread until the 20th century.[9]The use of food preservatives varies greatly depending on country. Many developing countries that do not have strong governments to regulate food additives face either harmful levels of preservatives in foods, or a complete avoidance of foods that are considered unnatural or foreign. These countries have also proven useful in case studies surrounding chemical preservatives, as they have been only recently introduced.[10] In urban slums of highly populated countries the knowledge about contents of food tends to be extremely low, despite consumption of these imported foods.[11]
Public Awareness of Food Preservatives
Public awareness of food preservatives is uneven.[12] Americans have a perception that food-borne illnesses happen more often in other counties. This may be true, but the occurrence of illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths are still high. It is estimated by the Center for Disease Control (CDC) that each year there are 76 million illnesses, 325,000 hospitalizations, and 5,000 deaths linked to food-borne illness.[13]In the U.S., the FDA standards do not currently require fruit and vegetable product labels to reflect the type of chemical preservative(s) used on the produce.[citation needed]
The increasing demand for ready-to-eat fresh food products has led to challenges for food distributors regarding the safety and quality of their foods. Artificial preservatives meet some of these challenges by preserving freshness for longer periods of time, but these preservatives can cause negative side-effects as well. Sodium nitrite is a preservative used in lunch meats, hams, sausages, hot dogs, and bacon to prevent botulism. It serves the important function of controlling the bacteria that cause botulism, but sodium nitrite can react with proteins, or during cooking at high heats, to form carcinogenic N-nitrosamines.[6] It has also been linked to cancer in lab animals.[14] The commonly used sodium benzoate has been found to extend the shelf life of bottled tomato paste to 40 weeks without loss of quality.[7] However, it can form the carcinogen benzene when combined with vitamin C.[citation needed] Many food manufacturers have reformed their products to eliminate this combination, but a risk still exists.[14] Consumption of sodium benzoate may also cause hyperactivity. For over 30 years, there has been a debate about whether or not preservatives and other food additives can cause hyperactivity. Studies have found that there may be increases in hyperactivity amongst children who consume artificial colorings and benzoate preservatives, but these studies were not entirely conclusive. Hyperactivity only increased moderately, and it was not determined if the preservatives, colorings, or a combination of the two were responsible for the increase.[15]
