From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
| International standard |
- RFC 1945 HTTP/1.0 (1996)
- RFC 2068 HTTP/1.1 (1997)
- RFC 2616 HTTP/1.1 (1999)
- RFC 7230 HTTP/1.1: Message Syntax and Routing (2014)
- RFC 7231 HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content (2014)
- RFC 7232 HTTP/1.1: Conditional Requests (2014)
- RFC 7233 HTTP/1.1: Range Requests (2014)
- RFC 7234 HTTP/1.1: Caching (2014)
- RFC 7235 HTTP/1.1: Authentication (2014)
- RFC 7540 HTTP/2 (2015)
- RFC 7541 HTTP/2: HPACK Header Compression (2015)
- RFC 8164 HTTP/2: Opportunistic Security for HTTP/2 (2017)
- RFC 8336 HTTP/2: The ORIGIN HTTP/2 Frame (2018)
- RFC 8441 HTTP/2: Bootstrapping WebSockets with HTTP/2 (2018)
- RFC 8740 HTTP/2: Using TLS 1.3 with HTTP/2 (2020)
- RFC 9114 HTTP/3
|
|---|
| Developed by | initially CERN; IETF, W3C |
|---|
| Introduced | 1991; 31 years ago |
|---|
| Website | https://httpwg.org/specs/ |
|---|
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser.
Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN
in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a
client and a server using the first HTTP protocol version that was
named 0.9.
That first version of HTTP protocol soon evolved into a more
elaborated version that was the first draft toward a far future version
1.0.
Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later and it was a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving to the IETF.
HTTP/1 was finalized and fully documented (as version 1.0) in 1996. It evolved (as version 1.1) in 1997 and then its specifications were updated in 1999 and in 2014.
Its secure variant named HTTPS is used by more than 79% of websites.
HTTP/2 is a more efficient expression of HTTP's semantics "on the wire", and was published in 2015; used by more than 46% of websites, now supported by almost all web browsers (96% of users) and major web servers over Transport Layer Security (TLS) using an Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation (ALPN) extension where TLS 1.2 or newer is required.
HTTP/3 is the successor to HTTP/2, published in 2022; used by 25% of websites, it is now supported by many web browsers (73% of users). HTTP/3 uses QUIC instead of TCP
for the underlying transport protocol. Like HTTP/2, it does not
obsolesce previous major versions of the protocol. Support for HTTP/3
was added to Cloudflare and Google Chrome first, and is also enabled in Firefox.
HTTP/3 has lower latency for real-world web pages, if enabled on the
server, load faster than with HTTP/2, and even faster than HTTP/1.1, in
some cases over 3× faster than HTTP/1.1 (which is still commonly only
enabled).
Technical overview

URL beginning with the HTTP scheme and the
WWW domain name label
HTTP functions as a request–response protocol in the client–server model. A web browser, for example, may be the client whereas a process, named web server, running on a computer hosting one or more websites may be the server. The client submits an HTTP request message to the server. The server, which provides resources such as HTML files and other content or performs other functions on behalf of the client, returns a response
message to the client. The response contains completion status
information about the request and may also contain requested content in
its message body.
A web browser is an example of a user agent (UA). Other types of user agent include the indexing software used by search providers (web crawlers), voice browsers, mobile apps, and other software that accesses, consumes, or displays web content.
HTTP is designed to permit intermediate network elements
to improve or enable communications between clients and servers.
High-traffic websites often benefit from web cache servers that deliver content on behalf of upstream servers
to improve response time. Web browsers cache previously accessed web
resources and reuse them, whenever possible, to reduce network traffic.
HTTP proxy servers at private network
boundaries can facilitate communication for clients without a globally
routable address, by relaying messages with external servers.
To allow intermediate HTTP nodes (proxy servers, web caches, etc.) to accomplish their functions, some of the HTTP headers (found in HTTP requests/responses) are managed hop-by-hop whereas other HTTP headers are managed end-to-end (managed only by the source client and by the target web server).
HTTP is an application layer protocol designed within the framework of the Internet protocol suite. Its definition presumes an underlying and reliable transport layer protocol, thus Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is commonly used. However, HTTP can be adapted to use unreliable protocols such as the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), for example in HTTPU and Simple Service Discovery Protocol (SSDP).
HTTP resources are identified and located on the network by Uniform Resource Locators (URLs), using the Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI's) schemes http and https. As defined in RFC 3986, URIs are encoded as hyperlinks in HTML documents, so as to form interlinked hypertext documents.
In HTTP/1.0 a separate connection to the same server is made for every resource request.
In HTTP/1.1 instead a TCP connection can be reused to make multiple resource requests (i.e. of HTML pages, frames, images, scripts, stylesheets, etc.).
HTTP/1.1 communications therefore experience less latency as the establishment of TCP connections presents considerable overhead, specially under high traffic conditions.
HTTP/2
is a revision of previous HTTP/1.1 in order to maintain the same
client–server model and the same protocol methods but with these
differences in order:
- to use a compressed binary representation of metadata (HTTP
headers) instead of a textual one, so that headers require much less
space;
- to use a single TCP/IP (usually encrypted) connection per accessed server domain instead of 2 to 8 TCP/IP connections;
- to use one or more bidirectional streams per TCP/IP connection in
which HTTP requests and responses are broken down and transmitted in
small packets to almost solve the problem of the HOLB (head of line blocking).
- to add a push capability to allow server application to send data to
clients whenever new data is available (without forcing clients to
request periodically new data to server by using polling methods).
HTTP/2 communications therefore experience much less latency and, in most cases, even more speed than HTTP/1.1 communications.
HTTP/3 is a revision of previous HTTP/2 in order to use QUIC
+ UDP transport protocols instead of TCP/IP connections also to
slightly improve the average speed of communications and to avoid the
occasional (very rare) problem of TCP/IP connection congestion that can temporarily block or slow down the data flow of all its streams (another form of "head of line blocking").
History
The term hypertext was coined by Ted Nelson in 1965 in the Xanadu Project, which was in turn inspired by Vannevar Bush's 1930s vision of the microfilm-based information retrieval and management "memex" system described in his 1945 essay "As We May Think". Tim Berners-Lee and his team at CERN are credited with inventing the original HTTP, along with HTML and the associated technology for a web server and a client user interface called web browser.
Berners-Lee designed HTTP in order to help with the adoption of his
other idea: the "WorldWideWeb" project, which was first proposed in
1989, now known as the World Wide Web.
The first web server went live in 1990. The protocol used had only one method, namely GET, which would request a page from a server. The response from the server was always an HTML page.
Summary of HTTP milestone versions
| Version
|
Year introduced
|
Current status
|
| HTTP/0.9
|
1991
|
Obsolete
|
| HTTP/1.0
|
1996
|
Obsolete
|
| HTTP/1.1
|
1997
|
Standard
|
| HTTP/2
|
2015
|
Standard
|
| HTTP/3
|
2022
|
Standard
|
- HTTP/0.9
- In 1991, the first documented official version of HTTP was written
as a plain document, less than 700 words long, and this version was
named HTTP/0.9. HTTP/0.9 supported only GET method, allowing clients to
only retrieve HTML documents from the server, but not supporting any
other file formats or information upload.
- HTTP/1.0-draft
- Since 1992, a new document was written to specify the evolution of
the basic protocol towards its next full version. It supported both the
simple request method of the 0.9 version and the full GET request that
included the client HTTP version. This was the first of the many
unofficial HTTP/1.0 drafts that preceded the final work on HTTP/1.0.
- W3C HTTP Working Group
- After having decided that new features of HTTP protocol were required and that they had to be fully documented as official RFCs, in early 1995 the HTTP Working Group (HTTP WG, led by Dave Raggett)
was constituted with the aim to standardize and expand the protocol
with extended operations, extended negotiation, richer meta-information,
tied with a security protocol which became more efficient by adding
additional methods and header fields.
- The HTTP WG planned to revise and publish new versions of the
protocol as HTTP/1.0 and HTTP/1.1 within 1995, but, because of the many
revisions, that timeline lasted much more than one year.
- The HTTP WG planned also to specify a far future version of HTTP
called HTTP-NG (HTTP Next Generation) that would have solved all
remaining problems, of previous versions, related to performances, low
latency responses, etc. but this work started only a few years later and
it was never completed.
- HTTP/1.0
- In May 1996, RFC 1945
was published as a final HTTP/1.0 revision of what had been used in
previous 4 years as a pre-standard HTTP/1.0-draft which was already used
by many web browsers and web servers.
- In early 1996 developers started to even include unofficial
extensions of the HTTP/1.0 protocol (i.e. keep-alive connections, etc.)
into their products by using drafts of the upcoming HTTP/1.1
specifications.
- HTTP/1.1
- Since early 1996, major web browsers and web server developers also
started to implement new features specified by pre-standard HTTP/1.1
drafts specifications. End-user adoption of the new versions of
browsers and servers was rapid. In March 1996, one web hosting company
reported that over 40% of browsers in use on the Internet used the new
HTTP/1.1 header "Host" to enable virtual hosting.
That same web hosting company reported that by June 1996, 65% of all
browsers accessing their servers were pre-standard HTTP/1.1 compliant.
- In January 1997, RFC 2068 was officially released as HTTP/1.1 specifications.
- In June 1999, RFC 2616 was released to include all improvements and updates based on previous (obsolete) HTTP/1.1 specifications.
- W3C HTTP-NG Working Group
- Resuming the old 1995 plan of previous HTTP Working Group, in 1997 an HTTP-NG Working Group
was formed to develop a new HTTP protocol named HTTP-NG (HTTP New
Generation). A few proposals / drafts were produced for the new
protocol to use multiplexing
of HTTP transactions inside a single TCP/IP connection, but in 1999,
the group stopped its activity passing the technical problems to IETF.
- IETF HTTP Working Group restarted
- In 2007, the IETF HTTP Working Group
(HTTP WG bis or HTTPbis) was restarted firstly to revise and clarify
previous HTTP/1.1 specifications and secondly to write and refine future
HTTP/2 specifications (named httpbis).
- HTTP/1.1 Final Update
- In June 2014, the HTTP Working Group released an updated six-part HTTP/1.1 specification obsoleting RFC 2616:
- RFC 7230, HTTP/1.1: Message Syntax and Routing
- RFC 7231, HTTP/1.1: Semantics and Content
- RFC 7232, HTTP/1.1: Conditional Requests
- RFC 7233, HTTP/1.1: Range Requests
- RFC 7234, HTTP/1.1: Caching
- RFC 7235, HTTP/1.1: Authentication
- SPDY: an unofficial HTTP protocol developed by Google
- In 2009, Google, a private company, announced that it had developed and tested a new HTTP binary protocol named SPDY. The implicit aim was to greately speed up web traffic (specially between future web browsers and its servers).
- SPDY was indeed much faster than HTTP/1.1 in many tests and so it was quickly adopted by Chromium and then by other major web browsers.
- Some of the ideas about multiplexing HTTP streams over a single
TCP/IP connection were taken from various sources, including the work of
W3C HTTP-NG Working Group.
- HTTP/2
- In January–March 2012, HTTP Working Group (HTTPbis) announced the
need to start to focus on a new HTTP/2 protocol (while finishing the
revision of HTTP/1.1 specifications), maybe taking in consideration
ideas and work done for SPDY.
- After a few months about what to do to develop a new version of HTTP, it was decided to derive it from SPDY.
- In May 2015, HTTP/2 was published as RFC 7540 and quickly adopted by all web browsers already supporting SPDY and more slowly by web servers.
- HTTP/0.9 Deprecation
- In RFC 7230 Appendix-A, HTTP/0.9 was deprecated for servers supporting HTTP/1.1 version (and higher):
Since
HTTP/0.9 did not support header fields in a request, there is no
mechanism for it to support name-based virtual hosts (selection of
resource by inspection of the Host header field). Any server that implements name-based virtual hosts ought to disable support for HTTP/0.9.
Most requests that appear to be HTTP/0.9 are, in fact, badly
constructed HTTP/1.x requests caused by a client failing to properly
encode the request-target.
- Since 2016 many product managers and developers of user agents
(browsers, etc.) and web servers have begun planning to gradually
deprecate and dismiss support for HTTP/0.9 protocol, mainly for the
following reasons:
- it is so simple that an RFC document was never written (there is only the original document);
- it has no HTTP headers and lacks many other features that nowadays are required for minimal security reasons;
- it has not been widespread since 1999..2000 (because of HTTP/1.0 and
HTTP/1.1) and is commonly used only by some very old network hardware,
i.e. routers, etc.
- HTTP/3
- In 2020, HTTP/3 first drafts have been published and major web browsers and web servers started to adopt it.
- On 6 June 2022, IETF standardized HTTP/3 as RFC 9114.
- Overall updates and refactoring
- In June 2022, a batch of RFCs was published, deprecating many of the
previous documents and introducing a few minor changes and a
refactoring of HTTP semantics description into a separate document.
HTTP data exchange
HTTP is a stateless application-level protocol and it requires a reliable network transport connection to exchange data between client and server. In HTTP implementations, TCP/IP connections are used using well known ports (typically port 80 if the connection is unencrypted or port 443 if the connection is encrypted, see also List of TCP and UDP port numbers). In HTTP/2, a TCP/IP connection plus multiple protocol channels are used. In HTTP/3, the application transport protocol QUIC over UDP is used.
Request and response messages through connections
Data is exchanged through a sequence of request–response messages which are exchanged by a session layer transport connection.
An HTTP client initially tries to connect to a server establishing a
connection (real or virtual). An HTTP(S) server listening on that port
accepts the connection and then waits for a client's request message.
The client sends its request to the server. Upon receiving the request,
the server sends back an HTTP response message (header plus a body if it
is required). The body of this message is typically the requested
resource, although an error message or other information may also be
returned. At any time (for many reasons) client or server can close the
connection. Closing a connection is usually advertised in advance by
using one or more HTTP headers in the last request/response message sent
to server or client.
Persistent connections
In HTTP/0.9, the TCP/IP connection is always closed after server response has been sent, so it is never persistent.
In HTTP/1.0, as stated in RFC 1945, the TCP/IP connection should always be closed by server after a response has been sent.
In HTTP/1.1 a keep-alive-mechanism was officially
introduced so that a connection could be reused for more than one
request/response. Such persistent connections reduce request latency perceptibly because the client does not need to re-negotiate the TCP 3-Way-Handshake connection
after the first request has been sent. Another positive side effect is
that, in general, the connection becomes faster with time due to TCP's slow-start-mechanism.
HTTP/1.1 added also HTTP pipelining
in order to further reduce lag time when using persistent connections
by allowing clients to send multiple requests before waiting for each
response. This optimization was never considered really safe because a
few web servers and many proxy servers, specially transparent proxy servers placed in Internet / Intranets
between clients and servers, did not handle pipelined requests properly
(they served only the first request discarding the others, they closed
the connection because they saw more data after the first request or
some proxies even returned responses out of order etc.). Besides this
only HEAD and some GET requests (i.e. limited to real file requests and
so with URLs without query string used as a command, etc.) could be pipelined in a safe and idempotent
mode. After many years of struggling with the problems introduced by
enabling pipelining, this feature was first disabled and then removed
from most browsers also because of the announced adoption of HTTP/2.
HTTP/2 extended the usage of persistent connections by
multiplexing many concurrent requests/responses through a single TCP/IP
connection.
HTTP/3 does not use TCP/IP connections but QUIC + UDP (see also: technical overview).
Content retrieval optimizations
- HTTP/0.9
- a requested resource was always sent entirely.
- HTTP/1.0
- HTTP/1.0 added headers to manage resources cached by client in order
to allow conditional GET requests; in practice a server has to return
the entire content of the requested resource only if its last modified
time is not known by client or if it changed since last full response to
GET request. One of these headers, "Content-Encoding", was added to
specify whether the returned content of a resource was or was not compressed.
- If the total length of the content of a resource was not known in
advance (i.e. because it was dynamically generated, etc.) then the
header
"Content-Length: number" was not present in HTTP
headers and the client assumed that when server closed the connection,
the content had been entirely sent. This mechanism could not
distinguish between a resource transfer successfully completed and an
interrupted one (because of a server / network error or something else). - HTTP/1.1
- HTTP/1.1 introduced:
- new headers to better manage the conditional retrieval of cached resources.
- chunked transfer encoding
to allow content to be streamed in chunks in order to reliably send it
even when the server does not know in advance its length (i.e. because
it is dynamically generated, etc.).
- byte range serving,
where a client can request only one or more portions (ranges of bytes)
of a resource (i.e. the first part, a part in the middle or in the end
of the entire content, etc.) and the server usually sends only the
requested part(s). This is useful to resume an interrupted download
(when a file is really big), when only a part of a content has to be
shown or dynamically added to the already visible part by a browser
(i.e. only the first or the following n comments of a web page) in order
to spare time, bandwidth and system resources, etc.
- HTTP/2, HTTP/3
- Both HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 have kept the above mentioned features of HTTP/1.1.
HTTP authentication
HTTP provides multiple authentication schemes such as basic access authentication and digest access authentication
which operate via a challenge–response mechanism whereby the server
identifies and issues a challenge before serving the requested content.
HTTP provides a general framework for access control and
authentication, via an extensible set of challenge–response
authentication schemes, which can be used by a server to challenge a
client request and by a client to provide authentication information.
Above mechanism belong to HTTP protocol and it is managed by
client and server HTTP software (if configured to require authentication
before allowing client access to one or more web resources), not by web
application that usually use a web application session.
Authentication realms
The
HTTP Authentication specification also provides an arbitrary,
implementation-specific construct for further dividing resources common
to a given root URI.
The realm value string, if present, is combined with the canonical root
URI to form the protection space component of the challenge. This in
effect allows the server to define separate authentication scopes under
one root URI.
HTTP application session
HTTP is a stateless protocol.
A stateless protocol does not require the web server to retain
information or status about each user for the duration of multiple
requests.
Some web applications need to manage user sessions, so they implement states, or server side sessions, using for instance HTTP cookies or hidden variables within web forms.
To start an application user session, an interactive authentication via web application login must be performed. To stop a user session a logout operation must be requested by user. These kind of operations do not use HTTP authentication but a custom managed web application authentication.
HTTP/1.1 request messages
Request messages are sent by a client to a target server.
Request syntax
A client sends request messages to the server, which consist of:
- a request line, consisting of the case-sensitive request method, a space, the requested URL, another space, the protocol version, a carriage return, and a line feed, e.g.:
GET /images/logo.png HTTP/1.1
- zero or more request header fields
(at least 1 or more headers in case of HTTP/1.1), each consisting of
the case-insensitive field name, a colon, optional leading whitespace, the field value, an optional trailing whitespace and ending with a carriage return and a line feed, e.g.:
Host: www.example.com
Accept-Language: en
- an empty line, consisting of a carriage return and a line feed;
- an optional message body.
In the HTTP/1.1 protocol, all header fields except Host: hostname are optional.
A request line containing only the path name is accepted by
servers to maintain compatibility with HTTP clients before the HTTP/1.0
specification in RFC 1945.
Request methods
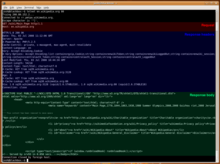
An HTTP/1.1 request made using telnet. The
request message,
response header section, and response body are highlighted.
HTTP defines methods (sometimes referred to as verbs, but nowhere in the specification does it mention verb)
to indicate the desired action to be performed on the identified
resource. What this resource represents, whether pre-existing data or
data that is generated dynamically, depends on the implementation of the
server. Often, the resource corresponds to a file or the output of an
executable residing on the server. The HTTP/1.0 specification defined the GET, HEAD, and POST methods, and the HTTP/1.1 specification
added five new methods: PUT, DELETE, CONNECT, OPTIONS, and TRACE. Any
client can use any method and the server can be configured to support
any combination of methods. If a method is unknown to an intermediate,
it will be treated as an unsafe and non-idempotent
method. There is no limit to the number of methods that can be defined,
which allows for future methods to be specified without breaking
existing infrastructure. For example, WebDAV defined seven new methods and RFC 5789 specified the PATCH method.
Method names are case sensitive. This is in contrast to HTTP header field names which are case-insensitive.
- GET
- The GET method requests that the target resource transfer a representation of its state. GET requests should only retrieve data and should have no other effect. (This is also true of some other HTTP methods.)[1] For retrieving resources without making changes, GET is preferred over POST, as they can be addressed through a URL. This enables bookmarking and sharing and makes GET responses eligible for caching, which can save bandwidth. The W3C has published guidance principles on this distinction, saying, "Web application design should be informed by the above principles, but also by the relevant limitations." See safe methods below.
- HEAD
- The HEAD method requests that the target resource transfer a
representation of its state, as for a GET request, but without the
representation data enclosed in the response body. This is useful for
retrieving the representation metadata in the response header, without
having to transfer the entire representation. Uses include checking
whether a page is available through the status code and quickly finding the size of a file (
Content-Length).
- POST
- The POST method
requests that the target resource process the representation enclosed
in the request according to the semantics of the target resource. For
example, it is used for posting a message to an Internet forum, subscribing to a mailing list, or completing an online shopping transaction.
- PUT
- The PUT method requests that the target resource create or update
its state with the state defined by the representation enclosed in the
request. A distinction from POST is that the client specifies the target
location on the server.
- DELETE
- The DELETE method requests that the target resource delete its state.
- CONNECT
- The CONNECT method requests that the intermediary establish a TCP/IP tunnel to the origin server identified by the request target. It is often used to secure connections through one or more HTTP proxies with TLS. See HTTP CONNECT method.
- OPTIONS
- The OPTIONS method requests that the target resource transfer the
HTTP methods that it supports. This can be used to check the
functionality of a web server by requesting '*' instead of a specific
resource.
- TRACE
- The TRACE method requests that the target resource transfer the
received request in the response body. That way a client can see what
(if any) changes or additions have been made by intermediaries.
- PATCH
- The PATCH method
requests that the target resource modify its state according to the
partial update defined in the representation enclosed in the request.
This can save bandwidth by updating a part of a file or document without
having to transfer it entirely.
All general-purpose web servers are required to implement at least
the GET and HEAD methods, and all other methods are considered optional
by the specification.
Properties of request methods
| GET
|
RFC 7231
|
Optional
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
| HEAD
|
RFC 7231
|
Optional
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
| POST
|
RFC 7231
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
No
|
Yes
|
| PUT
|
RFC 7231
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
| DELETE
|
RFC 7231
|
Optional
|
Yes
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
| CONNECT
|
RFC 7231
|
Optional
|
Yes
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
| OPTIONS
|
RFC 7231
|
Optional
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
| TRACE
|
RFC 7231
|
No
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
| PATCH
|
RFC 5789
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
No
|
No
|
Safe methods
A request method is safe
if a request with that method has no intended effect on the server. The
methods GET, HEAD, OPTIONS, and TRACE are defined as safe. In other
words, safe methods are intended to be read-only. They do not exclude side effects though, such as appending request information to a log file or charging an advertising account, since they are not requested by the client, by definition.
In contrast, the methods POST, PUT, DELETE, CONNECT, and PATCH
are not safe. They may modify the state of the server or have other
effects such as sending an email. Such methods are therefore not usually used by conforming web robots or web crawlers; some that do not conform tend to make requests without regard to context or consequences.
Despite the prescribed safety of GET requests, in practice their
handling by the server is not technically limited in any way. Careless
or deliberately irregular programming can allow GET requests to cause
non-trivial changes on the server. This is discouraged because of the
problems which can occur when web caching, search engines,
and other automated agents make unintended changes on the server. For
example, a website might allow deletion of a resource through a URL such
as https://example.com/article/1234/delete, which, if arbitrarily fetched, even using GET, would simply delete the article. A properly coded website would require a DELETE or POST method for this action, which non-malicious bots would not make.
One example of this occurring in practice was during the short-lived Google Web Accelerator beta, which prefetched arbitrary URLs on the page a user was viewing, causing records to be automatically altered or deleted en masse. The beta was suspended only weeks after its first release, following widespread criticism.
Idempotent methods
A request method is idempotent if multiple identical requests
with that method have the same effect as a single such request. The
methods PUT and DELETE, and safe methods are defined as idempotent. Safe
methods are trivially idempotent, since they are intended to have no
effect on the server whatsoever; the PUT and DELETE methods, meanwhile,
are idempotent since successive identical requests will be ignored. A
website might, for instance, set up a PUT endpoint to modify a user's
recorded email address. If this endpoint is configured correctly, any
requests which ask to change a user's email address to the same email
address which is already recorded—e.g. duplicate requests following a
successful request—will have no effect. Similarly, a request to DELETE a
certain user will have no effect if that user has already been deleted.
In contrast, the methods POST, CONNECT, and PATCH are not
necessarily idempotent, and therefore sending an identical POST request
multiple times may further modify the state of the server or have
further effects, such as sending multiple emails.
In some cases this is the desired effect, but in other cases it may
occur accidentally. A user might, for example, inadvertently send
multiple POST requests by clicking a button again if they were not given
clear feedback that the first click was being processed. While web browsers may show alert dialog boxes
to warn users in some cases where reloading a page may re-submit a POST
request, it is generally up to the web application to handle cases
where a POST request should not be submitted more than once.
Note that whether or not a method is idempotent is not enforced
by the protocol or web server. It is perfectly possible to write a web
application in which (for example) a database insert or other
non-idempotent action is triggered by a GET or other request. To do so
against recommendations, however, may result in undesirable
consequences, if a user agent assumes that repeating the same request is safe when it is not.
Cacheable methods
A request method is cacheable if responses to requests with
that method may be stored for future reuse. The methods GET, HEAD, and
POST are defined as cacheable.
In contrast, the methods PUT, DELETE, CONNECT, OPTIONS, TRACE, and PATCH are not cacheable.
Request header fields allow the client to pass additional information
beyond the request line, acting as request modifiers (similarly to the
parameters of a procedure). They give information about the client,
about the target resource, or about the expected handling of the
request.
HTTP/1.1 response messages
A response message is sent by a server to a client as a reply to its former request message.
Response syntax
A server sends response messages to the client, which consist of:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
- zero or more response header fields, each consisting of the case-insensitive field name, a colon, optional leading whitespace, the field value, an optional trailing whitespace and ending with a carriage return and a line feed, e.g.:
Content-Type: text/html
- an empty line, consisting of a carriage return and a line feed;
- an optional message body.
Response status codes
In HTTP/1.0 and since, the first line of the HTTP response is called the status line and includes a numeric status code (such as "404") and a textual reason phrase
(such as "Not Found"). The response status code is a three-digit
integer code representing the result of the server's attempt to
understand and satisfy the client's corresponding request. The way the
client handles the response depends primarily on the status code, and
secondarily on the other response header fields. Clients may not
understand all registered status codes but they must understand their
class (given by the first digit of the status code) and treat an
unrecognized status code as being equivalent to the x00 status code of
that class.
The standard reason phrases are only recommendations, and can be replaced with "local equivalents" at the web developer's discretion. If the status code indicated a problem, the user agent might display the reason phrase
to the user to provide further information about the nature of the
problem. The standard also allows the user agent to attempt to interpret
the reason phrase, though this might be unwise since the standard explicitly specifies that status codes are machine-readable and reason phrases are human-readable.
The first digit of the status code defines its class:
1XX (informational)- The request was received, continuing process.
2XX (successful)- The request was successfully received, understood, and accepted.
3XX (redirection)- Further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request.
4XX (client error)- The request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled.
5XX (server error)- The server failed to fulfill an apparently valid request.
The response header fields allow the server to pass additional
information beyond the status line, acting as response modifiers. They
give information about the server or about further access to the target
resource or related resources.
Each response header field has a defined meaning which can be
further refined by the semantics of the request method or response
status code.
HTTP/1.1 example of request / response transaction
Below is a sample HTTP transaction between an HTTP/1.1 client and an HTTP/1.1 server running on www.example.com, port 80.
Client request
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.com
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-GB,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Connection: keep-alive
A client request (consisting in this case of the request line and a few headers that can be reduced to only the "Host: hostname" header) is followed by a blank line, so that the request ends with a double end of line, each in the form of a carriage return followed by a line feed. The "Host: hostname" header value distinguishes between various DNS names sharing a single IP address, allowing name-based virtual hosting. While optional in HTTP/1.0, it is mandatory in HTTP/1.1. (A "/" (slash) will usually fetch a /index.html file if there is one.)
Server response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Mon, 23 May 2005 22:38:34 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 155
Last-Modified: Wed, 08 Jan 2003 23:11:55 GMT
Server: Apache/1.3.3.7 (Unix) (Red-Hat/Linux)
ETag: "3f80f-1b6-3e1cb03b"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Connection: close
<html>
<head>
<title>An Example Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello World, this is a very simple HTML document.</p>
</body>
</html>
The ETag
(entity tag) header field is used to determine if a cached version of
the requested resource is identical to the current version of the
resource on the server. "Content-Type" specifies the Internet media type of the data conveyed by the HTTP message, while "Content-Length" indicates its length in bytes. The HTTP/1.1 webserver publishes its ability to respond to requests for certain byte ranges of the document by setting the field "Accept-Ranges: bytes". This is useful, if the client needs to have only certain portions of a resource sent by the server, which is called byte serving. When "Connection: close" is sent, it means that the web server will close the TCP connection immediately after the end of the transfer of this response.
Most of the header lines are optional but some are mandatory. When header "Content-Length: number"
is missing in a response with an entity body then this should be
considered an error in HTTP/1.0 but it may not be an error in HTTP/1.1
if header "Transfer-Encoding: chunked" is present. Chunked
transfer encoding uses a chunk size of 0 to mark the end of the content.
Some old implementations of HTTP/1.0 omitted the header "Content-Length"
when the length of the body entity was not known at the beginning of
the response and so the transfer of data to client continued until
server closed the socket.
A "Content-Encoding: gzip" can be used to inform the client that the body entity part of the transmitted data is compressed by gzip algorithm.
Encrypted connections
The most popular way of establishing an encrypted HTTP connection is HTTPS. Two other methods for establishing an encrypted HTTP connection also exist: Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol, and using the HTTP/1.1 Upgrade header to specify an upgrade to TLS. Browser support for these two is, however, nearly non-existent.
Similar protocols
- The Gopher protocol is a content delivery protocol that was displaced by HTTP in the early 1990s.
- The SPDY protocol is an alternative to HTTP developed at Google, superseded by HTTP/2.
- The Gemini protocol is a Gopher-inspired protocol which mandates privacy-related features.



















![{\displaystyle [t_{start},t_{end}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/76839cb2e1074d3770c83fefb5f12d568121d6db)