Blue light is scattered more than other wavelengths by the gases in the atmosphere, surrounding Earth in a visibly blue layer when seen from space on board the ISS at an altitude of 335 km (208 mi).
Composition
of Earth's atmosphere by volume. Lower pie represents trace gases that
together compose about 0.038% of the atmosphere (0.043% with CO2 at 2014 concentration). Numbers are mainly from 1987, with CO2 and methane from 2009, and do not represent any single source.
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, commonly known as air, that surrounds the planet Earth and is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation).
By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air content and atmospheric pressure vary at different layers, and air suitable for use in photosynthesis by terrestrial plants and breathing of terrestrial animals is found only in Earth's troposphere and in artificial atmospheres.
The atmosphere has a mass of about 5.15×1018 kg,
three quarters of which is within about 11 km (6.8 mi; 36,000 ft) of
the surface. The atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner with increasing
altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space. The Kármán line,
at 100 km (62 mi), or 1.57% of Earth's radius, is often used as the
border between the atmosphere and outer space. Atmospheric effects
become noticeable during atmospheric reentry of spacecraft at an altitude of around 120 km (75 mi). Several layers can be distinguished in the atmosphere, based on characteristics such as temperature and composition.
The study of Earth's atmosphere and its processes is called atmospheric science (aerology). Early pioneers in the field include Léon Teisserenc de Bort and Richard Assmann.
Composition
Mean atmospheric water vapor
The three major constituents of Earth's atmosphere are nitrogen, oxygen, and argon.
Water vapor accounts for roughly 0.25% of the atmosphere by mass. The
concentration of water vapor (a greenhouse gas) varies significantly
from around 10 ppm by volume in the coldest portions of the atmosphere
to as much as 5% by volume in hot, humid air masses, and concentrations
of other atmospheric gases are typically quoted in terms of dry air
(without water vapor). The remaining gases are often referred to as trace gases, among which are the greenhouse gases, principally carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Filtered air includes trace amounts of many other chemical compounds. Many substances of natural origin may be present in locally and seasonally variable small amounts as aerosols in an unfiltered air sample, including dust of mineral and organic composition, pollen and spores, sea spray, and volcanic ash. Various industrial pollutants also may be present as gases or aerosols, such as chlorine (elemental or in compounds), fluorine compounds and elemental mercury vapor. Sulfur compounds such as hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide (SO2) may be derived from natural sources or from industrial air pollution.
| Gas | Volume(A) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Formula | in ppmv(B) | in % |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 780,840 | 78.084 |
| Oxygen | O2 | 209,460 | 20.946 |
| Argon | Ar | 9,340 | 0.9340 |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | 400 | 0.04[8] |
| Neon | Ne | 18.18 | 0.001818 |
| Helium | He | 5.24 | 0.000524 |
| Methane | CH4 | 1.79 | 0.000179 |
| Not included in above dry atmosphere: | |||
| Water vapor(C) | H2O | 10–50,000(D) | 0.001%–5%(D) |
| notes: (A) volume fraction is equal to mole fraction for ideal gas only, also see volume (thermodynamics) (B) ppmv: parts per million by volume (C) Water vapor is about 0.25% by mass over full atmosphere (D) Water vapor strongly varies locally | |||
The relative concentration of gases remains constant until about 10,000 m (33,000 ft).
The
volume fraction of the main constituents of the Earth's atmosphere as a
function of height according to the MSIS-E-90 atmospheric model.
Stratification
Earth's atmosphere
Lower 4 layers of the atmosphere in 3 dimensions as seen diagonally
from above the exobase. Layers drawn to scale, objects within the
layers are not to scale. Aurorae shown here at the bottom of the
thermosphere can actually form at any altitude in this atmospheric
layer.
In general, air pressure and density decrease with altitude in the
atmosphere. However, temperature has a more complicated profile with
altitude, and may remain relatively constant or even increase with
altitude in some regions (see the temperature
section, below). Because the general pattern of the
temperature/altitude profile is constant and measurable by means of
instrumented balloon soundings,
the temperature behavior provides a useful metric to distinguish
atmospheric layers. In this way, Earth's atmosphere can be divided
(called atmospheric stratification) into five main layers. Excluding the
exosphere, the atmosphere has four primary layers, which are the
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. From highest to lowest, the five main layers are:
- Exosphere: 700 to 10,000 km (440 to 6,200 miles)
- Thermosphere: 80 to 700 km (50 to 440 miles)
- Mesosphere: 50 to 80 km (31 to 50 miles)
- Stratosphere: 12 to 50 km (7 to 31 miles)
- Troposphere: 0 to 12 km (0 to 7 miles)
Exosphere
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere (i.e. the upper limit of the atmosphere). It extends from the exobase,
which is located at the top of the thermosphere at an altitude of about
700 km above sea level, to about 10,000 km (6,200 mi; 33,000,000 ft)
where it merges into the solar wind.
This layer is mainly composed of extremely low densities of
hydrogen, helium and several heavier molecules including nitrogen,
oxygen and carbon dioxide closer to the exobase. The atoms and molecules
are so far apart that they can travel hundreds of kilometers without
colliding with one another. Thus, the exosphere no longer behaves like a
gas, and the particles constantly escape into space. These free-moving
particles follow ballistic trajectories and may migrate in and out of the magnetosphere or the solar wind.
The exosphere is located too far above Earth for any meteorological phenomena to be possible. However, the aurora borealis and aurora australis
sometimes occur in the lower part of the exosphere, where they overlap
into the thermosphere. The exosphere contains most of the satellites
orbiting Earth.
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is the second-highest layer of Earth's atmosphere.
It extends from the mesopause (which separates it from the mesosphere)
at an altitude of about 80 km (50 mi; 260,000 ft) up to the thermopause
at an altitude range of 500–1000 km (310–620 mi;
1,600,000–3,300,000 ft). The height of the thermopause varies
considerably due to changes in solar activity. Because the thermopause lies at the lower boundary of the exosphere, it is also referred to as the exobase. The lower part of the thermosphere, from 80 to 550 kilometres (50 to 342 mi) above Earth's surface, contains the ionosphere.
The temperature of the thermosphere gradually increases with height. Unlike the stratosphere beneath it, wherein a temperature inversion
is due to the absorption of radiation by ozone, the inversion in the
thermosphere occurs due to the extremely low density of its molecules.
The temperature of this layer can rise as high as 1500 °C (2700 °F),
though the gas molecules are so far apart that its temperature in the usual sense is not very meaningful. The air is so rarefied that an individual molecule (of oxygen, for example) travels an average of 1 kilometre (0.62 mi; 3300 ft) between collisions with other molecules.
Although the thermosphere has a high proportion of molecules with high
energy, it would not feel hot to a human in direct contact, because its
density is too low to conduct a significant amount of energy to or from
the skin.
This layer is completely cloudless and free of water vapor. However, non-hydrometeorological phenomena such as the aurora borealis and aurora australis are occasionally seen in the thermosphere. The International Space Station orbits in this layer, between 350 and 420 km (220 and 260 mi).
Mesosphere
The mesosphere is the third highest layer of Earth's atmosphere,
occupying the region above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere.
It extends from the stratopause at an altitude of about 50 km (31 mi;
160,000 ft) to the mesopause at 80–85 km (50–53 mi; 260,000–280,000 ft)
above sea level.
Temperatures drop with increasing altitude to the mesopause
that marks the top of this middle layer of the atmosphere. It is the
coldest place on Earth and has an average temperature around −85 °C (−120 °F; 190 K).
Just below the mesopause, the air is so cold that even the very
scarce water vapor at this altitude can be sublimated into
polar-mesospheric noctilucent clouds.
These are the highest clouds in the atmosphere and may be visible to
the naked eye if sunlight reflects off them about an hour or two after
sunset or a similar length of time before sunrise. They are most readily
visible when the Sun is around 4 to 16 degrees below the horizon.
Lightning-induced discharges known as transient luminous events (TLEs) occasionally form in the mesosphere above tropospheric thunderclouds. The mesosphere is also the layer where most meteors
burn up upon atmospheric entrance. It is too high above Earth to be
accessible to jet-powered aircraft and balloons, and too low to permit
orbital spacecraft. The mesosphere is mainly accessed by sounding rockets and rocket-powered aircraft.
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second-lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere. It
lies above the troposphere and is separated from it by the tropopause. This layer extends from the top of the troposphere at roughly 12 km (7.5 mi; 39,000 ft) above Earth's surface to the stratopause at an altitude of about 50 to 55 km (31 to 34 mi; 164,000 to 180,000 ft).
The atmospheric pressure at the top of the stratosphere is roughly 1/1000 the pressure at sea level.
It contains the ozone layer, which is the part of Earth's atmosphere
that contains relatively high concentrations of that gas. The
stratosphere defines a layer in which temperatures rise with increasing
altitude. This rise in temperature is caused by the absorption of ultraviolet radiation (UV) radiation from the Sun by the ozone layer,
which restricts turbulence and mixing. Although the temperature may be
−60 °C (−76 °F; 210 K) at the tropopause, the top of the stratosphere is
much warmer, and may be near 0 °C.
The stratospheric temperature profile creates very stable
atmospheric conditions, so the stratosphere lacks the weather-producing
air turbulence that is so prevalent in the troposphere. Consequently,
the stratosphere is almost completely free of clouds and other forms of
weather. However, polar stratospheric or nacreous clouds
are occasionally seen in the lower part of this layer of the atmosphere
where the air is coldest. The stratosphere is the highest layer that
can be accessed by jet-powered aircraft.
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere. It extends
from Earth's surface to an average height of about 12 km (7.5 mi;
39,000 ft), although this altitude varies from about 9 km (5.6 mi; 30,000 ft) at the geographic poles to 17 km (11 mi; 56,000 ft) at the Equator, with some variation due to weather. The troposphere is bounded above by the tropopause, a boundary marked in most places by a temperature inversion (i.e. a layer of relatively warm air above a colder one), and in others by a zone which is isothermal with height.
Although variations do occur, the temperature usually declines
with increasing altitude in the troposphere because the troposphere is
mostly heated through energy transfer from the surface. Thus, the lowest
part of the troposphere (i.e. Earth's surface) is typically the warmest
section of the troposphere. This promotes vertical mixing (hence, the
origin of its name in the Greek word τρόπος, tropos, meaning "turn"). The troposphere contains roughly 80% of the mass of Earth's atmosphere.
The troposphere is denser than all its overlying atmospheric layers
because a larger atmospheric weight sits on top of the troposphere and
causes it to be most severely compressed. Fifty percent of the total
mass of the atmosphere is located in the lower 5.6 km (3.5 mi;
18,000 ft) of the troposphere.
Nearly all atmospheric water vapor or moisture is found in the
troposphere, so it is the layer where most of Earth's weather takes
place. It has basically all the weather-associated cloud genus types
generated by active wind circulation, although very tall cumulonimbus
thunder clouds can penetrate the tropopause from below and rise into the
lower part of the stratosphere. Most conventional aviation activity takes place in the troposphere, and it is the only layer that can be accessed by propeller-driven aircraft.
Space Shuttle Endeavour
orbiting in the thermosphere. Because of the angle of the photo, it
appears to straddle the stratosphere and mesosphere that actually lie
more than 250 km below. The orange layer is the troposphere, which gives way to the whitish stratosphere and then the blue mesosphere.
Other layers
Within the five principal layers above, that are largely determined
by temperature, several secondary layers may be distinguished by other
properties:
- The ozone layer is contained within the stratosphere. In this layer ozone concentrations are about 2 to 8 parts per million, which is much higher than in the lower atmosphere but still very small compared to the main components of the atmosphere. It is mainly located in the lower portion of the stratosphere from about 15–35 km (9.3–21.7 mi; 49,000–115,000 ft), though the thickness varies seasonally and geographically. About 90% of the ozone in Earth's atmosphere is contained in the stratosphere.
- The ionosphere is a region of the atmosphere that is ionized by solar radiation. It is responsible for auroras. During daytime hours, it stretches from 50 to 1,000 km (31 to 621 mi; 160,000 to 3,280,000 ft) and includes the mesosphere, thermosphere, and parts of the exosphere. However, ionization in the mesosphere largely ceases during the night, so auroras are normally seen only in the thermosphere and lower exosphere. The ionosphere forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because it influences, for example, radio propagation on Earth.
- The homosphere and heterosphere are defined by whether the atmospheric gases are well mixed. The surface-based homosphere includes the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and the lowest part of the thermosphere, where the chemical composition of the atmosphere does not depend on molecular weight because the gases are mixed by turbulence. This relatively homogeneous layer ends at the turbopause found at about 100 km (62 mi; 330,000 ft), the very edge of space itself as accepted by the FAI, which places it about 20 km (12 mi; 66,000 ft) above the mesopause.
- Above this altitude lies the heterosphere, which includes the exosphere and most of the thermosphere. Here, the chemical composition varies with altitude. This is because the distance that particles can move without colliding with one another is large compared with the size of motions that cause mixing. This allows the gases to stratify by molecular weight, with the heavier ones, such as oxygen and nitrogen, present only near the bottom of the heterosphere. The upper part of the heterosphere is composed almost completely of hydrogen, the lightest element.
- The planetary boundary layer is the part of the troposphere that is closest to Earth's surface and is directly affected by it, mainly through turbulent diffusion. During the day the planetary boundary layer usually is well-mixed, whereas at night it becomes stably stratified with weak or intermittent mixing. The depth of the planetary boundary layer ranges from as little as about 100 metres (330 ft) on clear, calm nights to 3,000 m (9,800 ft) or more during the afternoon in dry regions.
The average temperature of the atmosphere at Earth's surface is 14 °C (57 °F; 287 K) or 15 °C (59 °F; 288 K), depending on the reference.
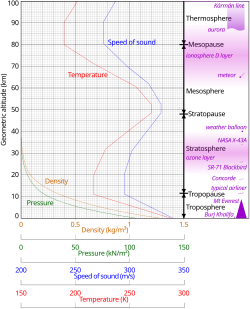
Physical properties
Comparison of the 1962 US Standard Atmosphere graph of geometric altitude against air density, pressure, the speed of sound and temperature with approximate altitudes of various objects.
Pressure and thickness
The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is defined by the International Standard Atmosphere as 101325 pascals (760.00 Torr; 14.6959 psi; 760.00 mmHg). This is sometimes referred to as a unit of standard atmospheres (atm). Total atmospheric mass is 5.1480×1018 kg (1.135×1019 lb),
about 2.5% less than would be inferred from the average sea level
pressure and Earth's area of 51007.2 megahectares, this portion being
displaced by Earth's mountainous terrain. Atmospheric pressure is the
total weight of the air above unit area at the point where the pressure
is measured. Thus air pressure varies with location and weather.
If the entire mass of the atmosphere had a uniform density equal to sea level density (about 1.2 kg per m3)
from sea level upwards, it would terminate abruptly at an altitude of
8.50 km (27,900 ft). It actually decreases exponentially with altitude,
dropping by half every 5.6 km (18,000 ft) or by a factor of 1/e every 7.64 km (25,100 ft), the average scale height
of the atmosphere below 70 km (43 mi; 230,000 ft). However, the
atmosphere is more accurately modeled with a customized equation for
each layer that takes gradients of temperature, molecular composition,
solar radiation and gravity into account.
In summary, the mass of Earth's atmosphere is distributed approximately as follows:
- 50% is below 5.6 km (18,000 ft).
- 90% is below 16 km (52,000 ft).
- 99.99997% is below 100 km (62 mi; 330,000 ft), the Kármán line. By international convention, this marks the beginning of space where human travelers are considered astronauts.
By comparison, the summit of Mt. Everest is at 8,848 m (29,029 ft);
commercial airliners typically cruise between 10 and 13 km (33,000 and 43,000 ft) where the thinner air improves fuel economy; weather balloons reach 30.4 km (100,000 ft) and above; and the highest X-15 flight in 1963 reached 108.0 km (354,300 ft).
Even above the Kármán line, significant atmospheric effects such as auroras still occur. Meteors
begin to glow in this region, though the larger ones may not burn up
until they penetrate more deeply. The various layers of Earth's ionosphere, important to HF radio propagation, begin below 100 km and extend beyond 500 km. By comparison, the International Space Station and Space Shuttle typically orbit at 350–400 km, within the F-layer of the ionosphere where they encounter enough atmospheric drag
to require reboosts every few months. Depending on solar activity,
satellites can experience noticeable atmospheric drag at altitudes as
high as 700–800 km.
Temperature and speed of sound
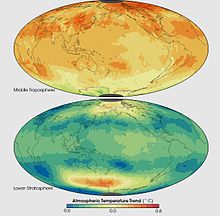
Temperature trends in two thick layers of the atmosphere as measured between January 1979 and December 2005 by Microwave Sounding Units and Advanced Microwave Sounding Units on NOAA weather satellites. The instruments record microwaves emitted from oxygen molecules in the atmosphere.
The division of the atmosphere into layers mostly by reference to
temperature is discussed above. Temperature decreases with altitude
starting at sea level, but variations in this trend begin above 11 km,
where the temperature stabilizes through a large vertical distance
through the rest of the troposphere. In the stratosphere,
starting above about 20 km, the temperature increases with height, due
to heating within the ozone layer caused by capture of significant ultraviolet radiation from the Sun
by the dioxygen and ozone gas in this region. Still another region of
increasing temperature with altitude occurs at very high altitudes, in
the aptly-named thermosphere above 90 km.
Because in an ideal gas of constant composition the speed of sound
depends only on temperature and not on the gas pressure or density, the
speed of sound in the atmosphere with altitude takes on the form of the
complicated temperature profile (see illustration to the right), and
does not mirror altitudinal changes in density or pressure.
Density and mass
Temperature and mass density against altitude from the NRLMSISE-00 standard atmosphere model (the eight dotted lines in each "decade" are at the eight cubes 8, 27, 64, ..., 729)
The density of air at sea level is about 1.2 kg/m3 (1.2 g/L, 0.0012 g/cm3).
Density is not measured directly but is calculated from measurements of
temperature, pressure and humidity using the equation of state for air
(a form of the ideal gas law). Atmospheric density decreases as the altitude increases. This variation can be approximately modeled using the barometric formula. More sophisticated models are used to predict orbital decay of satellites.
The average mass of the atmosphere is about 5 quadrillion (5×1015) tonnes or 1/1,200,000 the mass of Earth. According to the American National Center for Atmospheric Research, "The total mean mass of the atmosphere is 5.1480×1018 kg with an annual range due to water vapor of 1.2 or 1.5×1015 kg,
depending on whether surface pressure or water vapor data are used;
somewhat smaller than the previous estimate. The mean mass of water
vapor is estimated as 1.27×1016 kg and the dry air mass as 5.1352 ±0.0003×1018 kg."
Optical properties
Solar radiation (or sunlight) is the energy Earth receives from the Sun.
Earth also emits radiation back into space, but at longer wavelengths
that we cannot see. Part of the incoming and emitted radiation is
absorbed or reflected by the atmosphere. In May 2017, glints of light,
seen as twinkling from an orbiting satellite a million miles away, were
found to be reflected light from ice crystals in the atmosphere.
Scattering
When light passes through Earth's atmosphere, photons interact with it through scattering. If the light does not interact with the atmosphere, it is called direct radiation and is what you see if you were to look directly at the Sun. Indirect radiation is light that has been scattered in the atmosphere. For example, on an overcast
day when you cannot see your shadow there is no direct radiation
reaching you, it has all been scattered. As another example, due to a
phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering,
shorter (blue) wavelengths scatter more easily than longer (red)
wavelengths. This is why the sky looks blue; you are seeing scattered
blue light. This is also why sunsets are red. Because the Sun is close
to the horizon, the Sun's rays pass through more atmosphere than normal
to reach your eye. Much of the blue light has been scattered out,
leaving the red light in a sunset.
Absorption
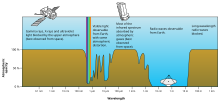
Rough plot of Earth's atmospheric transmittance (or opacity) to various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light.
Different molecules absorb different wavelengths of radiation. For example, O2 and O3 absorb almost all wavelengths shorter than 300 nanometers. Water (H2O)
absorbs many wavelengths above 700 nm. When a molecule absorbs a
photon, it increases the energy of the molecule. This heats the
atmosphere, but the atmosphere also cools by emitting radiation, as
discussed below.
The combined absorption spectra of the gases in the atmosphere leave "windows" of low opacity, allowing the transmission of only certain bands of light. The optical window runs from around 300 nm (ultraviolet-C) up into the range humans can see, the visible spectrum (commonly called light), at roughly 400–700 nm and continues to the infrared to around 1100 nm. There are also infrared and radio windows that transmit some infrared and radio waves at longer wavelengths. For example, the radio window runs from about one centimeter to about eleven-meter waves.
Emission
Emission is the opposite of absorption, it is when an object
emits radiation. Objects tend to emit amounts and wavelengths of
radiation depending on their "black body"
emission curves, therefore hotter objects tend to emit more radiation,
with shorter wavelengths. Colder objects emit less radiation, with
longer wavelengths. For example, the Sun is approximately 6,000 K (5,730 °C; 10,340 °F),
its radiation peaks near 500 nm, and is visible to the human eye. Earth
is approximately 290 K (17 °C; 62 °F), so its radiation peaks near
10,000 nm, and is much too long to be visible to humans.
Because of its temperature, the atmosphere emits infrared
radiation. For example, on clear nights Earth's surface cools down
faster than on cloudy nights. This is because clouds (H2O) are strong absorbers and emitters of infrared radiation. This is also why it becomes colder at night at higher elevations.
The greenhouse effect
is directly related to this absorption and emission effect. Some gases
in the atmosphere absorb and emit infrared radiation, but do not
interact with sunlight in the visible spectrum. Common examples of these
are CO2 and H2O.
Refractive index
The refractive index
of air is close to, but just greater than 1. Systematic variations in
refractive index can lead to the bending of light rays over long optical
paths. One example is that, under some circumstances, observers onboard
ships can see other vessels just over the horizon because light is refracted in the same direction as the curvature of Earth's surface.
The refractive index of air depends on temperature, giving rise to refraction effects when the temperature gradient is large. An example of such effects is the mirage.
Circulation
An idealised view of three large circulation cells.
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air through the troposphere, and the means (with ocean circulation)
by which heat is distributed around Earth. The large-scale structure of
the atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the basic
structure remains fairly constant because it is determined by Earth's
rotation rate and the difference in solar radiation between the equator
and poles.
Evolution of Earth's atmosphere
Earliest atmosphere
The first atmosphere consisted of gases in the solar nebula, primarily hydrogen. There were probably simple hydrides such as those now found in the gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn), notably water vapor, methane and ammonia.
Second atmosphere
Outgassing from volcanism, supplemented by gases produced during the late heavy bombardment of Earth by huge asteroids, produced the next atmosphere, consisting largely of nitrogen plus carbon dioxide and inert gases.
A major part of carbon-dioxide emissions dissolved in water and reacted
with metals such as calcium and magnesium during weathering of crustal
rocks to form carbonates that were deposited as sediments. Water-related
sediments have been found that date from as early as 3.8 billion years
ago.
About 3.4 billion years ago, nitrogen formed the major part of
the then stable "second atmosphere". The influence of life has to be
taken into account rather soon in the history of the atmosphere, because
hints of early life-forms appear as early as 3.5 billion years ago.
How Earth at that time maintained a climate warm enough for liquid
water and life, if the early Sun put out 30% lower solar radiance than
today, is a puzzle known as the "faint young Sun paradox".
The geological record however shows a continuous relatively warm surface during the complete early temperature record of Earth – with the exception of one cold glacial phase about 2.4 billion years ago. In the late Archean Eon an oxygen-containing atmosphere began to develop, apparently produced by photosynthesizing cyanobacteria (see Great Oxygenation Event), which have been found as stromatolite fossils from 2.7 billion years ago. The early basic carbon isotopy (isotope ratio proportions) strongly suggests conditions similar to the current, and that the fundamental features of the carbon cycle became established as early as 4 billion years ago.
Ancient sediments in the Gabon
dating from between about 2,150 and 2,080 million years ago provide a
record of Earth's dynamic oxygenation evolution. These fluctuations in
oxygenation were likely driven by the Lomagundi carbon isotope excursion.
Third atmosphere
Oxygen content of the atmosphere over the last billion years
The constant re-arrangement of continents by plate tectonics
influences the long-term evolution of the atmosphere by transferring
carbon dioxide to and from large continental carbonate stores. Free
oxygen did not exist in the atmosphere until about 2.4 billion years ago
during the Great Oxygenation Event and its appearance is indicated by the end of the banded iron formations.
Before this time, any oxygen produced by photosynthesis was
consumed by oxidation of reduced materials, notably iron. Molecules of
free oxygen did not start to accumulate in the atmosphere until the rate
of production of oxygen began to exceed the availability of reducing
materials that removed oxygen. This point signifies a shift from a reducing atmosphere to an oxidizing atmosphere. O2 showed major variations until reaching a steady state of more than 15% by the end of the Precambrian. The following time span from 541 million years ago to the present day is the Phanerozoic Eon, during the earliest period of which, the Cambrian, oxygen-requiring metazoan life forms began to appear.
The amount of oxygen in the atmosphere has fluctuated over the
last 600 million years, reaching a peak of about 30% around 280 million
years ago, significantly higher than today's 21%. Two main processes
govern changes in the atmosphere: Plants use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, releasing oxygen. Breakdown of pyrite and volcanic eruptions release sulfur
into the atmosphere, which oxidizes and hence reduces the amount of
oxygen in the atmosphere. However, volcanic eruptions also release
carbon dioxide, which plants can convert to oxygen. The exact cause of
the variation of the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere is not known.
Periods with much oxygen in the atmosphere are associated with rapid
development of animals. Today's atmosphere contains 21% oxygen, which is
great enough for this rapid development of animals.