Water security is the focused goal of water policy and water management. A society with a high level of water security makes the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems and limits the risk of destructive impacts associated with water. These include too much water (flood), too little water (drought and water scarcity) or poor quality (polluted) water. A widely accepted definition of water security is: "Water security is the reliable availability of an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods and production, coupled with an acceptable level of water-related risks". Water security is framed as a situation where water-related risks are managed and water-related opportunities are captured but it is difficult to provide a set of indicators to quantify this.
Policy-makers and water managers seek to achieve a variety of water security outcomes related to economic, environmental and social equity concerns. These outcomes can include increasing economic welfare, enhancing social equity, moving towards long-term sustainability and reducing water related risks. There are interactions and trade-offs between different water security outcomes. Water security is critical for meeting the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) because most SDGs cannot be met without access to adequate and safe water. The absence of water security is termed "water insecurity". Water insecurity is as a growing threat to humanity. Factors contributing to water insecurity include water scarcity, water pollution, reduced water quality due to climate change impacts, poverty, destructive forces of water and others (for example natural disasters, terrorism and armed conflict).
Improving water security, for example by better managing water resources, is a key factor in achieving sustainable development and poverty reduction. Major factors that determine a society's ability to sustain water security include: the hydrologic environment, the socio-economic environment and changes in the future environment (climate change). Water security risks need to be managed at different spatial scales: from within the household to community, town, city, basin and region. Policy-makers and water managers also have to think on different timescales, looking months, years or decades ahead to build resilience to local climate variability and extreme events (e.g. heavy precipitation or drought). Climate change is affecting the type and severity of water risks in ways that will vary from place to place. Research suggests that effects on the water security of different groups in society should be considered when designing strategies for climate adaptation. Many institutions are working to develop climate-resilient WASH services.
Approaches for improving water security require natural resources, science, and engineering knowledge, political and legal tools, economic and financial tools, policy and governance strategies. In practice it means that for example institutions and information flows need to be strengthened, water quality management improved, inequalities reduced, investments in infrastructure made and the climate resilience of water and sanitation services has to be improved.
Some organizations use the phrase "water security" in a different way to talk specifically about water supply and infrastructure issues. Integrated water resources management (IWRM) is a paradigm related to water security. Related concepts include water risk and water conflict.
Definitions
Broad definition
The term "water security" is often used with varying definitions. It emerged as a concept in the 21st century and is a broader concept than just the absence of water scarcity. When compared to the terms "food security" and "energy security" (which refer to reliable access to food or energy), an important difference with "water security" is that not only is the absence of water a problem but also its presence when there is too much.
Water security has been defined in 2007 as "the reliable availability of an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods and production, coupled with an acceptable level of water-related risks".
A similar working definition of water security by UN-Water was provided in 2013 as follows:
Water security is defined here as the capacity of a population to safeguard sustainable access to adequate quantities of acceptable quality water for sustaining livelihoods, human well-being , and socio-economic development, for ensuring protection against water-borne pollution and water-related disasters, and for preserving ecosystems in a climate of peace and political stability. [...] The term "water security" offers a common framework and a platform for communication.
— UN-Water,
World Resources Institute also proposed a similar definition in 2020: "For purposes of this report, we define water security as the capacity of a population to
- safeguard sustainable access to adequate quantities of acceptable quality water for sustaining livelihoods, human well-being, and socioeconomic development;
- protect against water pollution and water-related disasters; and
- preserve ecosystems, upon which clean water availability and other ecosystem services depend."
Access to WASH (water, sanitation and hygiene) services is one component of water security.
Narrower definition with a focus on water supply
Some organizations use "water security" in a more specific sense to refer to water supply only, not the water-related risks of "too much water". For example, the definition of WaterAid in 2012 is focused on water supply issues: "WaterAid defines water security as:Reliable access to water of sufficient quantity and quality for basic human needs, small-scale livelihoods and local ecosystem services, coupled with a well managed risk of water-related disasters. The World Water Council also uses this more specific approach with a focus on water supply: "Water security refers to the availability of water, in adequate quantity and quality, to sustain all these needs together (social and economic sectors, as well as the larger needs of the planet’s ecosystems) – without exceeding its ability to renew."
Related concepts
Water risk
"Water risk" refers to the "possibility of an entity experiencing a water-related challenge (e.g., water scarcity, water stress, flooding, infrastructure decay, drought)". Water risk is inversely related to water security, meaning that as water risk increases, water security decreases. Water risk is complex and multidimensional. It includes risks from natural disasters such as flooding and drought, which can lead to infrastructure failure and worsen hunger. When these risks are realized, they result in water scarcity or other problems. The potential economic effects of water risk are significant. Entire industries, such as the food and beverage, agriculture, oil and gas, utilities, semiconductor and industries, are threatened by water risk. Agriculture uses 69% of global freshwater, making the industry extremely vulnerable to water stress.
Risk is a combination of hazard (droughts, floods and quality deterioration), exposure and vulnerability. Bad infrastructure and bad governance result in high vulnerability.
The financial sector is becoming more aware of the potential impacts of water risk and the need for its proper management. By 2025, $145 trillion in assets under management will likely be exposed to water risk.
To help mitigate water risk, companies can develop water risk management plans. Stakeholders within financial markets can then use these plans to measure company environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance and identify leaders in water risk management. The World Resources Institute has also developed an online water data platform named Aqueduct for risk assessment and water management. China Water Risk is a nonprofit dedicated to understanding and managing water risk in China. The World Wildlife Fund has a Water Risk Filter that helps companies assess and respond to water risk with scenarios for 2030 and 2050. The World Wildlife Fund has also partnered with DWS, which provides business solutions to water risk including water-centric investment funds.
The concept of risk is increasingly used in water security policy and practice but has been weakly integrated with social equity considerations.
There is no unifying theory or model for determining or managing water risk. Instead, a range of theories, models, and technologies are used to understand the trade-offs that exist in responding to risk.
Water conflict
Water insecurity
If water security is what good development policy is aiming to achieve, then water insecurity is what policy is trying to avoid or address. Scholarship on water insecurity has grown significantly in recent years and is now a speciality area in its own right with its own scientific literature, its own groupings (e.g. the Household Water Insecurity Experiences Research Coordination Network - HWISE-RCN) and growing influence in the policy arena.
Integrated water management and others
Water security incorporates ideas and concepts related to the sustainability, integration and adaptiveness of water resource management. Terms such as "integrated water resources management (IWRM)" or "sustainable water management" are predecessors. Related terms that are gaining in popularity include water risk, water resilience, water proof, and the water-food-energy nexus.
Some see IWRM as complementary to water security because water security is a goal or destination, whilst IWRM is the process necessary to achieve that goal.
Outcomes
Water security outcomes can be grouped according to the sustainable development framework into economic, environmental and equity (or social) outcomes. Outcomes are things that are happening, or that we want to see happen, as a result of policy and management:
- Economic outcomes of water security: Sustainable growth (e.g. job creation, increased productivity and standards of living) which takes changing water needs and threats into account; may require adaptation of economic activities to cope with seasonal and annual variations in rainfall and surface water levels, including extreme events.
- Environmental outcomes: Sustainability of the water resource, in terms of its quality and availability and the ecosystems services it supports. Loss of freshwater biodiversity and depletion of groundwater are examples of negative environmental outcomes.
- Equity or social outcomes: Inclusive services so that different users (people, industry, agriculture) are able to access safe, reliable, sufficient and affordable water, and to dispose of wastewater safely. Aspects of interest include gender issues, empowerment, participation and accountability.
In the literature, there are four different focusses when researchers define and study water security and its outcomes: it is about using water such that we are increasing economic welfare, enhancing social equity, moving towards long-term sustainability or reducing water-related risks. Policy-makers and water managers must consider interactions and trade-offs between the different types of outcome.
Improving water security is a key factor to achieve growth, sustainable development and poverty reduction. Water security is linked to social justice and fair distribution of environmental benefits and harms. Sustainable development would result in lowered poverty and increased living standards for those most susceptible to the impacts of insecure water resources in the region, especially women and children.
Water security is critical for meeting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) because most SDGs cannot be met without access to adequate and safe water. It is also important for climate-resilient development. Research suggests that water security outcomes for different groups in society should be considered during the design of climate change adaptation strategies.
Determining factors for water security
Three main factors determine a society's ability to sustain water security:
- Hydrologic environment
- Socio-economic environment
- Changes in the future environment (climate change)
Hydrologic environment
The hydrologic environment is a determinant of water security. This is because the flow of water in, on and between the ground, surface, and atmosphere controls the spatial distribution and inter-and intra-annual variability of water resources:
- An "easy to manage" hydrologic environment would be one with low rainfall variability, with rain distributed throughout the year and perennial river flows sustained by groundwater base flows. For example, many of the world’s industrialized nations have an “easy to manage” hydrologic environment. This has helped them to achieve water security early in their development path.
- A "difficult to manage" hydrologic environment is one with absolute water scarcity (i.e. deserts) or low-lying lands where there is severe flood risk; regions where rainfall is markedly seasonal, or high inter-annual climate variability are also likely to face water security challenges. An example would be East Africa, where prolonged drought have happened every two to three years since 1999. Most of the world’s developing countries have difficult to manage hydrologies and have not achieved water security - which is not a coincidence.
Aspects of difficult to manage hydrologic environments
The "Poverty and hydrology" hypothesis states that: "Not coincidentally, most of the world’s poor face difficult hydrologies". This is because regions with a difficult hydrology (for example inter-annual and intra-annual variability) remain poor because they have not been able to make the large investments needed to achieve water security. The resulting water insecurity constrains economic growth. Research has shown that greater rainfall variability (within one year and across several years) is "statistically associated with lower per capita incomes".
In regions with marked seasonality and inter-annual variability, water managers would benefit from more accurate seasonal weather forecasts. In some locations the onset of seasonal rainfall is particularly hard to predict because aspects of the climate system are difficult to model successfully. For example, the long rains in East Africa which fall March to May have been difficult to simulate within the climate models that are used to produce seasonal forecasts. This is in part because long rains do not respond in a simple way to large-scale modes of variability such as ENSO and because of interactions with complex topography. Improved understanding of atmospheric processes may allow climate scientists to provide more relevant and localized information to water managers on a seasonal timescale, and to provide more detailed predictions for the effects of climate change on a longer timeframe.
The existence of trans-boundary waters, such as "international rivers" which belong to several countries, are also a complicating factor for achieving water security. Many of these trans-boundary waters are the result of 20th century colonial borders that were drawn without giving thought to natural watersheds.
Socio-economic environment
The socio-economic environment also determines the potential of a society to sustain water security. This refers the structure of the economy, behavior of its actors, natural and cultural legacies as well as policy choices. It also includes water infrastructure and institutions, macroeconomic structure and resilience, risk and the behavior of economic actors.
Climate change
Water-related impacts from climate change impact people's water security on a day-to-day basis. They include: increased frequency and intensity of heavy precipitation, accelerated melting of glaciers, changes in frequency, magnitude, and timing of floods; more frequent and severe droughts in some places; decline in groundwater storage, and reduction in groundwater recharge and water quality deterioration due to extreme events. Water resources can be affected by climate change in various ways. The total amount of locally available freshwater available can change, for instance due to dry spells or droughts. There can also be reduced water quality due to the effects of climate change.
Global climate change is "likely to increase the complexity and costs of ensuring water security". It creates new threats and adaptation challenges. This is because climate change leads to increased hydrological variability and extremes. Climate change has many impacts on the water cycle, resulting in higher climatic and hydrological variability, which means that water security will be compromised. Changes in the water cycle threaten existing water infrastructure and make it harder to plan future investments that can cope with uncertain changes in hydrologic variability. This makes societies more vulnerable to extreme water-related events and therefore increases water insecurity.
Climate change is about uncertainty and is an important long-term risk to water security. On the other hand, climate change must be seen in the context of other existing challenges for water security which include: existing high levels of climate variability at low latitudes, population growth, increased demand for water resources, political obstacles, increased disaster exposure due to settlement of hazard-prone areas, and environmental degradation. Water demand for irrigation in agriculture will increase due to climate change. This is because evaporation rates and crop transpiration rates will be higher due to rising temperatures.
Climate factors are a major driver of water security across different scales. Geographic variability in water availability, reliability of rainfall and vulnerability to droughts, floods and cyclones are inherent hazards that affect development opportunities and that play out at international to intra-basin scales. At local scales, the risks to water security associated with weather and climate are strongly mediated by social vulnerability. For example, people affected by poverty may have less ability to cope with climate shocks.
Factors contributing to water insecurity
There are many risk drivers for water insecurity, for example:
- Water scarcity: Water demand exceeds supply in many regions of the world. This can be due to population growth, higher living standards, general economic expansion and/or greater quantities of water used in agriculture (often with inefficient irrigation schemes, instead of more efficient sprinkler or drip irrigation technologies).
- Increasing water pollution and low levels of wastewater treatment, which is making local water unusable.
- Poor planning of water use, poor water management and misuse (causing groundwater levels to drop, rivers and lakes to dry out, and local ecosystems to collapse).
- Climate change (increasing frequency and intensity of water-related natural disasters, such as droughts and floods; rising temperatures and sea levels can lead to contamination of freshwater sources).
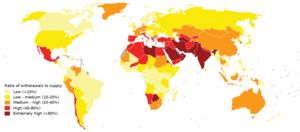
Water scarcity
An important threat to water security is water scarcity. There can be several causes to water scarcity including low rainfall, climate change, high population density, and overallocation of a water source. About 27% of the world's population lived in areas affected by water scarcity in the mid-2010s. This number will likely increase to 42% by 2050. Over-urbanization relative to water resources can create conditions of rapidly deteriorating household water security, particularly where pre-existing water and sanitation infrastructure is only poorly developed. Examples of periodic deep water scarcity that is inducing water insecurity include the ongoing California drought that started in early 2000s and the Cape Town Water Crisis (mid-2017 to mid-2018). In both cases pre-existing vulnerabilities were exacerbated by persistent climatic drought.
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands, including that needed for ecosystems to function effectively. Arid areas for example Central and West Asia, and North Africa often suffer from physical water scarcity. On the other hand, economic water scarcity is caused by a lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources, or insufficient human capacity to satisfy the demand for water. Much of Sub-Saharan Africa has economic water scarcity.
The essence of global water scarcity is the geographic and temporal mismatch between fresh water demand and availability. At the global level and on an annual basis, enough freshwater is available to meet such demand, but spatial and temporal variations of water demand and availability are large, leading to physical water scarcity in several parts of the world during specific times of the year. The main driving forces for the rising global demand for water are the increasing world population, improving living standards, changing consumption patterns (for example a dietary shift toward more animal products), and expansion of irrigated agriculture. Climate change (including droughts or floods), deforestation, increased water pollution and wasteful use of water can also cause insufficient water supply. Scarcity varies over time as a result of natural hydrological variability, but varies even more so as a function of prevailing economic policy, planning and management approaches. Scarcity can and will likely intensify with most forms of economic development, but many of its causes can be avoided or mitigated.Water pollution
A broad category of threats to water security is environmental threats (water pollution). These include contaminants such as nutrients, pesticides and herbicides (usually from agriculture), heavy metals (usually from industry), and Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (persistent organic pollutants commonly described as "forever chemicals"), climate change and natural disasters. Contaminants can enter a water source naturally through flooding.
Contaminants can also be a problem if a population switches their water supply from surface water to groundwater or even from one surface source to another. An example of this was the "Flint Water Crisis" in Flint, Michigan during 2014-2019 (Flint had changed its water source from treated water that was sourced from Lake Huron and the Detroit River to the Flint River).
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants are introduced into these water bodies. Water pollution can be attributed to one of four sources: sewage discharges, industrial activities, agricultural activities, and urban runoff including stormwater. It can be grouped into surface water pollution (either fresh water pollution or marine pollution) or groundwater pollution. For example, releasing inadequately treated wastewater into natural waters can lead to degradation of these aquatic ecosystems. Water pollution can also lead to water-borne diseases for people using polluted water for drinking, bathing, washing or irrigation. Water pollution reduces the ability of the body of water to provide the ecosystem services (such as drinking water) that it would otherwise provide.
Sources of water pollution are either point sources or non-point sources. Point sources have one identifiable cause, such as a storm drain, a wastewater treatment plant or an oil spill. Non-point sources are more diffuse, such as agricultural runoff. Pollution is the result of the cumulative effect over time. Pollution may take the form of toxic substances (e.g., oil, metals, plastics, pesticides, persistent organic pollutants, industrial waste products), stressful conditions (e.g., changes of pH, hypoxia or anoxia, increased temperatures, excessive turbidity, unpleasant taste or odor, and changes of salinity), or pathogenic organisms. Contaminants may include organic and inorganic substances. Heat can also be a pollutant, and this is called thermal pollution. A common cause of thermal pollution is the use of water as a coolant by power plants and industrial manufacturers.Reduced water quality due to climate change impacts
Weather and weather-related shocks can affect water quality in different ways depending on the local climate and context. Weather-related shocks include water shortages, heavy rain and temperature extremes. They can cause damage to water infrastructure from erosion under heavy rainfall and floods, loss of water sources in droughts, and deterioration of water quality. For this reason, climate change threatens the Sustainable Development Goal 6.1 of achieving universal access to safe drinking water. Understanding how weather affects water quality can help predict the likely impacts of climate change on water quality and thus health.
The impacts of climate change can result in lower water quality through several mechanisms:
- Heavy rainfall can have a rapid impact on water quality in rivers and a delayed but still significant effect on water quality in reservoirs. It can also have a rapid effect on water quality in shallow groundwater, with a more limited effect on groundwater in deeper, unfractured aquifers. For example, increases in fecal contamination of water sources is often linked to rainfall. Rainfall following a dry period can lead to microbial contamination of drinking water in piped water supplies.
- Floods intensify the mixing of floodwater with wastewater and the redistribution of pollutants: Heavy rainfall and flooding can have an impact on water quality. This is because pollutants can be transported into water bodies by the increased surface runoff.
- Droughts reduce river dilution capacities and groundwater levels, increasing the risk of groundwater contamination.
- Saltwater intrusion from rising sea levels: In coastal regions, more salt may find its way into water resources, especially groundwater, due to higher sea levels and more intense storms.
- Increased eutrophication at higher temperatures: Warmer water in lakes, reservoirs and rivers can lead to more frequent harmful algal blooms in those surface water bodies. Higher temperatures also directly degrade water quality because warm water contains less oxygen.
- Permafrost degradation leads to an increased flux of contaminants.
- Increased meltwater from glaciers may release historically deposited contaminants. As glaciers shrink or disappear, the positive effect of seasonal meltwater on downstream water quality through dilution may be lost.
Poverty
Low-income countries are at greater risk of water insecurity. This can result in human suffering, sustained poverty, constrained growth and social unrest.
Destructive forces of water
Water can be a force for destruction due to its "extraordinary power, mobility, indispensability and unpredictability": this can be either through catastrophic events (tsunamis, droughts, floods, landslides and epidemics) or through progressive events (erosion, inundation, desertification, contamination and disease).
Other
Other threats to water security include:
- Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires can damage man-made structures such as dams and fill waterways with debris.
- Many climate change mitigation measures can impact future water security. For example, "bioenergy with carbon capture and storage and afforestation and reforestation can have a considerable water footprint if done at inappropriate locations".
- Terrorism such as water supply terrorism
- Radiation due to a nuclear accident
- Emergence of extensive new water uses such as hydraulic fracturing for energy resources
- Armed conflict and migration (this can be due to water scarcity or can lead to increased water scarcity)
Approaches to improve water security
Approaches to improve water security include natural resources, science, and engineering approaches, political and legal tools, economic and financial tools, policy and governance strategies. A sequence of investments in institutions, information and infrastructure is needed to achieve a high level of water security.
Investments in institutions
Suitable institutions and infrastructure are needed to improve water security. Institutions comprise law, policies, regulations and organizations as well as informal networks. Sustainable Development Goal 16 is about "peace, justice and strong institutions" and recognizes that strong institutions are a necessary condition to support sustainable development, also with regards to water security. Institutions govern how decisions can promote or constrain water security outcomes for the poor. In some cases, the approaches to strengthen institutions might involve re-allocating risks and responsibilities between the state, market and communities in novel ways. This can include performance-based models, development impact bonds, or blended finance from government, donors and users. These finance mechanisms challenge the traditional separation between the state, private sector and communities.
Governance mechanisms can reduce water insecurity in transboundary groundwater contexts. They need processes that "(1) enhance context-specific and flexible international mechanisms; (2) address the perpetual need for groundwater data and information; (3) focus on the precautionary principle and pollution prevention, in particular; (4) where appropriate, integrate governance of surface and subsurface water and land; and (5) expand institutional capacity, especially of binational or multinational actors."
Improving water quality management
Drinking water quality and water pollution are interlinked but often not addressed in a comprehensive way. For example, industrial pollution is rarely linked to drinking water quality in developing countries. River, groundwater and wastewater monitoring is important to identify sources of contamination and to guide targeted regulatory responses. WHO has described water safety plans as the most effective means of maintaining a safe supply of drinking water to the public.
Reducing inequalities in water security
Inequalities in water security have structural and historical roots. They can affect people at different scales: from the household, to the community, town, river basin or the region. Vulnerable social groups and geographies can be identified or ignored during political debates. For example, water inequality is often related to gender in low-income countries, e.g. at the household level, where women are often the water managers but with constrained choices over water and related expenditures.
Investments in information flows
Information provides the fundamental underpinning for water security institutions and infrastructure. This enables evidence-based planning and decision-making, monitoring policy effectiveness and accountability of all actors involved in water resources policy and management.
To build climate resilience into water systems across scales, from dams to drinking water, requires investment to ensure access to climate information that is appropriate for the local context. Climate information products need to cover a wide range of temporal and spatial scales, and respond to regional water-related climate risks.
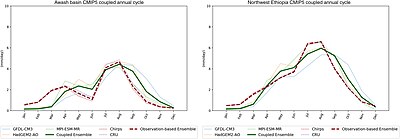
For example, in the case of Ethiopia, observed climatic conditions in the preceding months can improve and refine seasonal to sub-seasonal outlooks for the July to September rain season. Such information could be valuably used by decision makers in the Awash river basin to allocate water, plan water use and plan emergency responses to the extremes of water scarcity and flooding that are common experiences of the basin.
Investments in infrastructure
Water infrastructure is used to access, store, regulate, move and conserve water. These functions can be performed by a combination of natural assets (lakes, rivers, wetlands, aquifers, springs) and engineered assets (bulk water management infrastructure, such as multipurpose dams for river regulation and storage and inter-basin transfer schemes). Examples for investments in infrastructure include:
- protection, restoration and rehabilitation of natural water storage facilities, such as aquifers and wetlands
- adaptation of existing landscapes to store water (for instance, soil conservation, managed aquifer recharge)
- built infrastructure (such as distribution networks, latrines, treatment plants, storage tanks and dams).
- augmenting water supplies through non-conventional sources, including water recycling or desalination.
- flood protection embankments to manage water's destructive force.
Water security can be improved at a national scale through investment in an "evolving balance of complementary institutions and infrastructure for water management". This is important to avoid unforeseen and even unacceptable social and environmental costs from infrastructure measures that were designed to improve water security.
Consideration of scales
Water security risks need to be managed at different spatial scales: from within the household to community, town, city, basin and region. At the local scale, actors include county governments, schools, water user groups, local water providers and the private sector. At the next larger scale there are basin and national level actors which contribute to informing overarching policy, institutional and investment constraints. Lastly, there are global actors such as the World Bank, UNICEF, FCDO, WHO and USAID. These global actors shape international agendas around water security. They can also support the design and dissemination of service delivery models which result in affordable, safe and sustainable services. Policy-makers and water managers (whether household, industrial, commercial or public sector) also have to think on different timescales: They have to look weeks, months, years or decades ahead when making plans to maintain or improve water security.
The scale at which plans to manage water security risks need to be made may depend on physical geography, including climatology. Even within a country, the hydrologic environment may vary significantly. See, for example, the variety of seasonal rainfall regimes across Ethiopia.
Seasonal climate and hydrological forecasts can be useful to prepare for and reduce water security risks, and they may need to be adapted for users at the local scale. Seasonal forecasts can be improved and made more localized by developing knowledge of teleconnections - i.e. correlations between patterns of rainfall, temperature, and wind speed between distant areas caused by large-scale ocean and atmospheric circulation. For example, seasonal forecasts of rainfall in Ethiopia's Awash river basin may be improved by understanding how sea surface temperatures in different ocean regions relate to rainfall patterns which vary across the basin. At a larger regional scale, understanding how wind speeds and rainfall patterns in the Greater Horn of Africa are influenced by pressure systems in the Indian Ocean and the South Atlantic may contribute to improved representation of this region in climate models to assist development planning.
Improving climate resilience of water and sanitation services
Climate resilience is the ability to recover from, or to mitigate vulnerability to, climate-related shocks such as floods and droughts. Climate resilient development has become the new paradigm for sustainable development influencing theory and practice across all sectors globally. This is particularly true in the water sector, since water security is intimately connected to climate change. On every continent, governments are adopting policies for climate resilient economies. International frameworks such as the Paris Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals are drivers for such initiatives.
Climate-resilient water services (or "climate-resilient WASH") provide access to high quality drinking water during all seasons and even during extreme weather events. The right infrastructure and management choices are important at the community and household levels in order to achieve climate resilience for water supply.
To put climate resilience into practice and to engage better with politicians, the following questions need to be addressed on a case by case basis: "resilience of what, to what, for whom, over what time frame, by whom and at what scale?":
- "Resilience of what?" means thinking beyond infrastructure but to also include resilience of water resources, local institutions and water users.
- "Resilience to what?" means that smaller variations in water quantity and quality are as important as extreme events: smaller changes in seasonal rainfall variability can have devastating impacts on rainfall-dependent communities. Moreover, those without access to safe, reliable domestic water supplies face heightened water insecurity at specific times throughout the year due to cyclical changes in water quantity or quality. For example, where access to water on-premises is not available, drinking water quality at the point of use (PoU) can be much worse compared to the quality at the point of collection (PoC). Correct household practices around hygiene, storage and treatment are therefore important. There are interactions between weather, water source and management, and these in turn impact on drinking water safety.
- "Resilience over what time frame?" refers to short term or longer-term investments.
- "Resilience for whom?" speaks about reducing vulnerability and preventing maladaptation: For instance, top-down, technocratic interventions that attempt to work around power and politics undermine indigenous knowledge and compromise community resilience.
- "Resilience by whom?" refers to the fact that including diverse actors can expose, and allow operation within, power imbalances across scales.
- And finally, "Resilience at what scale?" reminds decision makers to scale-up solutions while maintaining context specificity.
Measurement tools
Water security cannot be quantified in absolute terms. It is very difficult to measure and there are no standard indicators to measure water security because it is a tool that focuses on outcomes. The outcomes of importance can change depending on the context and stakeholders involved.
Instead, relative levels of water security can be compared by using metrics which represent certain aspects of security. For example, the "Global Water Security Index" includes metrics on availability (water scarcity index, drought index, groundwater depletion); accessibility to water services (access to sanitation, access to drinking water); safety and quality (water quality index, global flood frequency); and metrics on management (World Governance Index, transboundary legal framework, transboundary political tension).
Scholars and practitioners have been working on methodologies to measure water security at a variety of scale and focus. There are two dominant research clusters in this field: experiential scale-based metrics and resource-based metrics. The former mainly focus on measuring the water experiences of households and its impact on human well-being, while the majority of the latter assess freshwater availability or water resources security.
The 12-item Household Water InSecurity Experiences (HWISE) Scale measures the multiple components of water insecurity at the household level: adequacy, reliability, accessibility, safety. The HWISE Scale can be used to identify vulnerable subpopulations, optimize resource allocation to those in need and to measure the effectiveness of water-related policies and interventions. It is a cross-culturally validated scale for assessing and comparing household water insecurity between locations.
Global estimates
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report in 2022 provided the following estimates about the number of people affected by water scarcity: "Increasing weather and climate extreme events have exposed millions of people to acute food insecurity and reduced water security, with the largest impacts observed in many locations and/or communities in Africa, Asia, Central and South America, Small Islands and the Arctic". The same report predicted that "at approximately 2°C global warming level, between 0.9 and 3.9 billion people are projected to be at increased exposure to water stress, depending on regional patterns of climate change and the socio-economic scenarios considered." With regards to water scarcity (which is one parameter that contributes to water insecurity), the report states that "currently, between 1.5 and 2.5 billion people live within areas exposed to water scarcity globally".
Water scarcity and water security do not have to be directly proportional: There are regions with high water security, despite also grappling with water scarcity issues, for example parts of the United States, Australia and Southern Europe. This is due to a good performance of management, safety and quality, and accessibility to water services.
Country examples
Bangladesh
Water security risks in Bangladesh include:
- some natural hazards that related to climate (climate hazards)
- the impacts of urbanization
- impacts from climate change such as changes to precipitation patterns and sea level rise.
The country experiences water security risks for the capital Dhaka as well as for coastal region. In Dhaka, monsoonal pulses can lead to urban flooding and subsequent contamination of the water supply. Water risks for people in the coastal region are caused by increasingly saline aquifers, seasonal water scarcity, fecal contamination, and flooding from the monsoon and storm surges from cyclones. About 20 million people are affected by those water risks in coastal areas.
Different types of floods occur in coastal Bangladesh. They are: river floods, tidal floods and storm surge floods due to tropical cyclones. These floods can damage drinking water infrastructure, and lead to reduced water quality as well as losses in agricultural and fishery yields. There is a correlation between water insecurity and poverty in the low-lying areas in the Ganges-Brahmaputra tidal delta plain, which is an example of embanked areas in coastal Bangladesh.
The government has various programs to reduce the vulnerability of coastal communities to water-related hazards. These programs also create opportunities for economic development. Examples include the "Coastal Embankment Improvement Project" by World Bank in 2013), the BlueGold project in 2012, UNICEF's "Managed Aquifer Recharge" program in 2014 and the Bangladesh Delta Plan in 2014. Such investments in water security aim to improve the reliability, maintenance and operation of water infrastructure. They can help coastal communities escape the poverty trap caused by water insecurity.
A program called the "SafePani" framework is investigating how the government allocates risks and responsibilities between the state, the market (service providers) and communities. This program aims to help decision makers to address climate risks through a process called "climate resilient water safety planning". The program is a cooperation between UNICEF and the Government of Bangladesh.
Ethiopia
Ethiopia has two main wet seasons per year: in the spring ("Belg") and summer ("Kiremt"). These seasonal patterns of rainfall vary a lot across the country. Western Ethiopia has a seasonal rainfall pattern that is similar to the Sahel: it has rainfall from February to November decreasing to the north, and has peak rainfall from June to September. Southern Ethiopia has a rainfall pattern similar to the one in East Africa: there are two distinct wet seasons every year (February to May, and October to November). Central and eastern Ethiopia has some rainfall between February and November, with a smaller peak in rainfall from March to May and a second higher peak in rainfall from June to September.
Water security was threatened in Ethiopia in 2022 when the country experienced "one of the most severe La Niña-induced droughts in the last forty years following four consecutive failed rainy seasons since late 2020". This drought affected more than 8 million people (pastoralists and agro-pastoralists) in the Somali, Oromia, SNNP and South-West regions. About 7.2 million people needed food aid, and 4.4 million people needed help to access water. Food prices have significantly increased due to the drought conditions. Vulnerable communities in the affected regions have experienced food insecurity as a result of water insecurity.
In the Awash basin in central Ethiopia floods and drought events are common. Agriculture in the basin is mainly rainfed, meaning without irrigation systems (this applies to around 98% of total cropland as of 2012). Therefore, changes in rainfall patterns due to climate change will reduce economic activities in the basin. Rainfall shocks have a direct impact on agriculture: A rainfall decrease in the Awash basin could lead to a 5% decline in the basin's overall GDP. The agricultural GDP could drop by as much as 10%.
Partnerships with Awash Basin Development Office (AwBDO) and the Ministry of Water, Irrigation and Electricity (MoWIE) have led to the development and uptake of a refined model of water allocation in the Awash basin. This can improve water security for the 18.3 million residents, as well as for irrigation and industry in the basin.