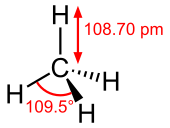
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methane
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Carbane (never recommended)
| |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3DMet | B01453 | ||
| 1718732 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.739 | ||
| EC Number | 200-812-7 | ||
| 59 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Methane | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | PA1490000 | ||
| UN number | 1971 | ||
| Properties | |||
| CH4 | |||
| Molar mass | 16.043 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density |
| ||
| Melting point | −182.5 °C; −296.4 °F; 90.7 K | ||
| Boiling point | −161.50 °C; −258.70 °F; 111.65 K | ||
| 22.7 mg·L−1 | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene, toluene, methanol, acetone and insoluble in water | ||
| log P | 1.09 | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
14 nmol·Pa−1·kg−1 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Methanium | ||
| Conjugate base | Methyl anion | ||
| −12.2×10−6 cm3·mol−1 | |||
| Structure | |||
| Td | |||
| Tetrahedron | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
35.69 J·(K·mol)−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S |
186.25 J·(K·mol)−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−74.87 kJ·mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH |
−891.1 to −890.3 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms | 
| ||
| GHS signal word | DANGER | ||
| H220 | |||
| P210 | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | −188 °C (−306.4 °F; 85.1 K) | ||
| 537 °C (999 °F; 810 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 4.4–17% | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanes
|
|||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. | |||
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas | ||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH4 (one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen). It is a group-14 hydride and the simplest alkane, and is the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an attractive fuel, though capturing and storing it poses challenges due to its gaseous state under normal conditions for temperature and pressure.
Natural methane is found both below ground and under the sea floor. When it reaches the surface and the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration has increased by about 150% since 1750, and it accounts for 20% of the total radiative forcing from all of the long-lived and globally mixed greenhouse gases.
History
In November 1776, methane was first scientifically identified by Italian physicist Alessandro Volta in the marshes of Lake Maggiore straddling Italy and Switzerland. Volta was inspired to search for the substance after reading a paper written by Benjamin Franklin about "flammable air". Volta collected the gas rising from the marsh, and by 1778 had isolated the pure gas. He also demonstrated that the gas could be ignited with an electric spark.
The name "methane" was coined in 1866 by the German chemist August Wilhelm von Hofmann. The name was derived from methanol.
Etymology
Etymologically, the word "methane" is coined from the chemical suffix "-ane", which denotes substances belonging to the alkane family; and the word "methyl", which is derived from the German "methyl" (A.D.1840) or directly from the French "méthyle" which is a back-formation from the French "méthylène" (corresponding to English "methylene"), the root of which is coined from the Greek "methy" (related to English "mead") and "hyle" (meaning "wood"). The radical is named after this because it was first detected in wood alcohol. The chemical suffix "-ane" is from the coordinating chemical suffix "-ine" which is from Latin feminine suffix "-ina"
which is applied to represent abstracts. The coordination of "-ane",
"-ene", "-one", etc. was proposed in 1866 by German chemist August
Wilhelm von Hofmann (1818-1892).
Properties and bonding
Methane is a tetrahedral molecule with four equivalent C–H bonds.
Its electronic structure is described by four bonding molecular
orbitals (MOs) resulting from the overlap of the valence orbitals on C and H.
The lowest energy MO is the result of the overlap of the 2s orbital on
carbon with the in-phase combination of the 1s orbitals on the four
hydrogen atoms. Above this energy level is a triply degenerate set of
MOs that involve overlap of the 2p orbitals on carbon with various
linear combinations of the 1s orbitals on hydrogen. The resulting
"three-over-one" bonding scheme is consistent with photoelectron
spectroscopic measurements.
At room temperature and standard pressure, methane is a colorless, odorless gas. The familiar smell of natural gas as used in homes is achieved by the addition of an odorant, usually blends containing tert-butylthiol, as a safety measure. Methane has a boiling point of −164 °C (−257.8 °F) at a pressure of one atmosphere. As a gas it is flammable over a range of concentrations (5.4–17%) in air at standard pressure.
Solid methane exists in several modifications. Presently nine are known. Cooling methane at normal pressure results in the formation of methane I. This substance crystallizes in the cubic system (space group Fm3m).
The positions of the hydrogen atoms are not fixed in methane I, i.e.
methane molecules may rotate freely. Therefore, it is a plastic crystal.
Chemical reactions
The primary chemical reactions of methane are combustion, steam reforming to syngas, and halogenation. In general, methane reactions are difficult to control. Partial oxidation to methanol, for example, is challenging because the reaction typically progresses all the way to carbon dioxide and water even with an insufficient supply of oxygen. The enzyme methane monooxygenase produces methanol from methane, but cannot be used for industrial-scale reactions. Some homogeneously catalyzed
systems and heterogeneous systems have been developed, but all have
significant drawbacks. These generally operate by generating protected
products which are shielded from over oxidation. Examples include the Catalytica system, copper zeolites, and iron zeolites stabilizing the alpha-oxygen active site.
Acid-base reactions
Like other hydrocarbons, methane is a very weak acid. Its pKa in DMSO is estimated to be 56. It cannot be deprotonated in solution, but the conjugate base is known in forms such as methyllithium.
A variety of positive ions derived from methane have been observed, mostly as unstable species in low-pressure gas mixtures. These include methenium or methyl cation CH+
3, methane cation CH+
4, and methanium or protonated methane CH+
5. Some of these have been detected in outer space. Methanium can also be produced as diluted solutions from methane with superacids. Cations with higher charge, such as CH2+
6 and CH3+
7, have been studied theoretically and conjectured to be stable.
3, methane cation CH+
4, and methanium or protonated methane CH+
5. Some of these have been detected in outer space. Methanium can also be produced as diluted solutions from methane with superacids. Cations with higher charge, such as CH2+
6 and CH3+
7, have been studied theoretically and conjectured to be stable.
Despite the strength of its C–H bonds, there is intense interest in catalysts that facilitate C–H bond activation in methane (and other lower numbered alkanes).
Combustion
Methane bubbles can be burned on a wet hand without injury.
Methane's heat of combustion is 55.5 MJ/kg.[20] Combustion of methane is a multiple step reaction summarized as follows:
Peters four-step chemistry is a systematically reduced four-step chemistry which explains the burning of methane.
Methane radical reactions
Given appropriate conditions, methane reacts with as follows:
- X• + CH4 → HX + CH3•
- CH3• + X2 → CH3X + X•
where X is a halogen: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), or iodine (I). This mechanism for this process is called free radical halogenation. It is initiated when UV light or some other radical initiator produces a halogen atom. A two-step chain reaction ensues in which the halogen atom abstracts a hydrogen atom from a methane molecule, resulting in the formation of a hydrogen halide molecule and a methyl radical (CH3•).
The methyl radical then reacts with a molecule of the halogen to form a
molecule of the halomethane, with a new halogen atom as byproduct.
Similar reactions can occur on the halogenated product, leading to
replacement of additional hydrogen atoms by halogen atoms with dihalomethane, trihalomethane, and ultimately, tetrahalomethane structures, depending upon reaction conditions and the halogen-to-methane ratio.
Uses
Methane is used in industrial chemical processes and may be transported as a refrigerated liquid (liquefied natural gas, or LNG).
While leaks from a refrigerated liquid container are initially heavier
than air due to the increased density of the cold gas, the gas at
ambient temperature is lighter than air. Gas pipelines distribute large amounts of natural gas, of which methane is the principal component.
Fuel
Methane is used as a fuel for ovens, homes, water heaters, kilns, automobiles, turbines, and other things. Activated carbon is used to store methane. Liquid methane is also used as a rocket fuel when combined with liquid oxygen, as in the BE-4 and Raptor engines.
Natural gas
Methane is important for electricity generation by burning it as a fuel in a gas turbine or steam generator. Compared to other hydrocarbon fuels, methane produces less carbon dioxide for each unit of heat released. At about 891 kJ/mol, methane's heat of combustion
is lower than any other hydrocarbon but the ratio of the heat of
combustion (891 kJ/mol) to the molecular mass (16.0 g/mol, of which 12.0
g/mol is carbon) shows that methane, being the simplest hydrocarbon,
produces more heat per mass unit (55.7 kJ/g) than other complex
hydrocarbons. In many cities, methane is piped into homes for domestic heating and cooking. In this context it is usually known as natural gas, which is considered to have an energy content of 39 megajoules per cubic meter, or 1,000 BTU per standard cubic foot.
Methane in the form of compressed natural gas is used as a vehicle fuel and is claimed to be more environmentally friendly than other fossil fuels such as gasoline/petrol and diesel. Research into adsorption methods of methane storage for use as an automotive fuel has been conducted.
Expensive LNG tankers are required to transport methane.
Liquefied natural gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4) converted into liquid form for ease of storage or transport.
Liquefied natural gas occupies about 1/600th the volume of
natural gas in the gaseous state at room temperature and atmospheric
pressure. It is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive. Hazards include flammability after vaporization into a gaseous state, freezing, and asphyxia.
The liquefaction process involves removal of certain components, such as dust, acid gases, helium, water, and heavy hydrocarbons, which could cause difficulty downstream. The natural gas is then condensed
into a liquid at close to atmospheric pressure (maximum transport
pressure set at around 25 kPa or 3.6 psi) by cooling it to approximately
−162 °C (111 K).
LNG achieves a higher reduction in volume than compressed natural gas (CNG) so that the energy density of LNG is 2.4 times greater than that of CNG or 60% that of diesel fuel. This makes LNG cost efficient to transport over long distances where pipelines do not exist. Specially designed cryogenic sea vessels (LNG carriers) or cryogenic road tankers are used for its transport. Even if pressurized, methane must be cooled below its critical temperature of −82.3 °C (190.8 K) in order to be liquefied.
LNG, when it is not highly refined for special uses, is
principally used for transporting natural gas to markets, where it is
regasified and distributed as pipeline natural gas. It can be used in LNG-fueled road vehicles.
However, it remains more common to design vehicles to use compressed natural gas. As of 2002, the relatively higher cost of LNG production and the need to store LNG in more expensive cryogenic tanks had slowed widespread commercial use.
Natural gas located far from its user base is often released into the atmosphere or flared. Some is subjected to gas to liquids technologies (GTL) to produce liquid fuels, which are more readily transported than methane.
Liquid-methane rocket fuel
Refined liquid methane is used as a rocket fuel. Methane is reported to offer the advantage over kerosene of depositing less carbon on the internal parts of rocket motors, reducing the difficulty of re-use of boosters.
Methane is abundant in many parts of the Solar system and
potentially could be harvested on the surface of another solar-system
body (in particular, using methane production from local materials found on Mars or Titan), providing fuel for a return journey.
Chemical feedstock
Natural gas, which is mostly composed of methane, is used to produce hydrogen gas on an industrial scale. Steam Methane Reforming, or SMR, is the most common method of producing commercial bulk hydrogen gas.
More than 50 million metric tons are produced annually worldwide (2013), principally from SMR of natural gas.
Much of this hydrogen is used in petroleum refineries, in the
production of chemicals and in food processing. Very large quantities of
hydrogen are used in the industrial synthesis of ammonia.
At high temperatures (700 – 1100 °C) and in the presence of a metal-based catalyst (nickel), steam reacts with methane to yield carbon monoxide and hydrogen:
Additional hydrogen is obtained by reacting the CO with water via the water-gas shift reaction.
- CO + H2O ⇌ CO2 + H2
The first reaction is strongly endothermic (consumes heat, ΔHr= 206 kJ/mol), the second reaction is mildly exothermic (produces heat, ΔHr= -41 kJ/mol).
Methane is also subjected to free-radical chlorination in the production of chloromethanes, although methanol is a more typical precursor.
Generation
Geological routes
There are two main routes for geological methane generation, organic (thermogenic), and inorganic (abiotic, meaning non-living). Thermally generated methane, referred to as thermogenic, originates from deeper sedimentary strata. Thermogenic methane (CH4)
formation occurs due to the breakup of organic matter, forced by
elevated temperatures and pressures. This type of methane is considered
to be the primary methane type in sedimentary basins, and from an
economical perspective the most important source of natural gas.
Thermogenic methane components are generally considered to be relic
(from an earlier time). Generally, formation of thermogenic methane (at
depth) can occur through organic matter breakup, or organic synthesis.
Both ways can involve microorganisms (methanogenesis) but may also occur
inorganically. The involved anaerobic and aerobic processes can also
consume methane, with and without microorganisms. The more important
source of methane at depth (crystalline bedrock) is abiotic. Abiotic
means that the methane formation took place involving inorganic
compounds, without biological activity, magmatic or created at low
temperatures and pressures through water-rock reactions.
Biological routes
Naturally occurring methane is mainly produced by microbial methanogenesis. This multistep process is used by microorganisms as an energy source. The net reaction is
- CO2 + 8 H+ + 8 e− → CH4 + 2 H2O
The final step in the process is catalyzed by the enzyme Coenzyme-B sulfoethylthiotransferase. Methanogenesis is a form of anaerobic respiration used by organisms that occupy landfill, ruminants (for example cows or cattle), and the guts of termites.
It is uncertain whether plants are a source of methane emissions.
Industrial routes
There
are many technological methane production methods. However, as methane
is the main component in natural gas and a major energy source, there is
little industrial incentive to prepare it from other sources, although
some plants use coal to gas processes (see below). Methane created from biomass in industrial plants via biological route is called biogas. A more synthetic method to produce methane is hydrogenating carbon dioxide through the Sabatier process. Methane is also a side product of the hydrogenation of carbon monoxide in the Fischer–Tropsch process, which is practiced on a large scale to produce longer-chain molecules than methane.
Example of large-scale coal-to-methane gasification is the Great Plains Synfuels plant, started in 1984 in Beulah, North Dakota as a way to develop abundant local resources of low-grade lignite, a resource that is otherwise very hard to transport for its weight, ash content, low calorific value and propensity to spontaneous combustion during storage and transport.
Power to methane is a technology that uses electrical power to produce hydrogen from water by electrolysis and uses the Sabatier reaction to combine hydrogen with carbon dioxide
to produce methane. As of 2016, this is mostly under development and
not in large-scale use. Theoretically, the process could be used as a
buffer for excess and off-peak power generated by highly fluctuating wind generators and solar arrays. However, as currently very large amounts of natural gas are used in power plants (e.g. CCGT) to produce electric energy, the losses in efficiency are not acceptable.
Laboratory synthesis
Methane can be produced by protonation of methyl lithium and methylmagnesium iodide. In practice, a requirement for pure methane will be filled with a steel gas bottle from standard suppliers.
Occurrence
Methane was discovered and isolated by Alessandro Volta between 1776 and 1778 when studying marsh gas from Lake Maggiore.
It is the major component of natural gas, about 87% by volume. The
major source of methane is extraction from geological deposits known as natural gas fields, with coal seam gas extraction becoming a major source. It is associated with other hydrocarbon fuels, and sometimes accompanied by helium and nitrogen. Methane is produced at shallow levels (low pressure) by anaerobic decay of organic matter and reworked methane from deep under the Earth's surface. In general, the sediments that generate natural gas are buried deeper and at higher temperatures than those that contain oil.
Methane is generally transported in bulk by pipeline in its natural gas form, or LNG carriers in its liquefied form; few countries transport it by truck.
Alternative sources
Testing Australian sheep for exhaled methane production (2001), CSIRO
Apart from gas fields, an alternative method of obtaining methane is via biogas generated by the fermentation of organic matter including manure, wastewater sludge, municipal solid waste (including landfills), or any other biodegradable feedstock, under anaerobic conditions. Rice fields also generate large amounts of methane during plant growth. Methane hydrates/clathrates
(ice-like combinations of methane and water on the sea floor, found in
vast quantities) are a potential future source of methane. Cattle belch
methane accounts for 16% of the world's annual methane emissions to the
atmosphere.
One study reported that the livestock sector in general (primarily
cattle, chickens, and pigs) produces 37% of all human-induced methane.
Early research has found a number of medical treatments and dietary
adjustments that help slightly limit the production of methane in ruminants.
A 2009 study found that at a conservative estimate, at least 51% of
global greenhouse gas emissions were attributable to the life cycle and
supply chain of livestock products, meaning all meat, dairy, and
by-products, and their transportation.
More recently, a 2013 study estimated that livestock accounted for 44
percent of human-induced methane and 14.5 percent of human-induced
greenhouse gas emissions. Many efforts are underway to reduce livestock methane production and trap the gas to use as energy. The state of California has been particularly active in this area.
Paleoclimatology research published in Current Biology suggests that flatulence from dinosaurs may have warmed the Earth.
Atmospheric methane
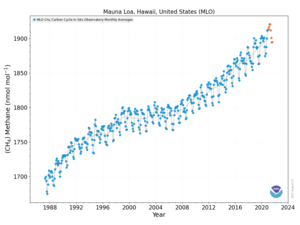
Methane concentration evolution from 1987 to December 2018 at Mauna Loa (Hawaii).
In 2010, methane levels in the Arctic were measured at 1850 nmol/mol.
This level is over twice as high as at any time in the last 400,000
years. Historic methane concentrations in the world's atmosphere have
ranged between 300 and 400 nmol/mol during glacial periods commonly
known as ice ages, and between 600 and 700 nmol/mol during the warm interglacial periods. The Earth's oceans are a potential important source of Arctic methane.
Methane is an important greenhouse gas with a global warming potential of 34 compared to CO2 (potential of 1) over a 100-year period, and 72 over a 20-year period.
The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration has increased by about 150% since 1750, and it accounts for 20% of the total radiative forcing
from all of the long-lived and globally mixed greenhouse gases (these
gases don't include water vapor which is by far the largest component of
the greenhouse effect).
Clathrates
Methane is essentially insoluble in water, but significant deposits of methane clathrate have been found under sediments on the ocean floors
of Earth at large depths. Estimates consider up to 15,000 gigatonnes of
carbon may be stored in the form of clathrates (hydrates) in the ocean
floor, not accounting for abiotic methane, a relatively newly discovered
source of methane, formed below the ocean floor, in the earth crust.
It has been suggested, that today's methane emission regime from the
ocean floor, is potentially similar to that during the period of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) around 55.5 million years ago.
Arctic methane release from permafrost and methane clathrates is an expected consequence and further cause of global warming.
Anaerobic oxidation of methane
There is a group of bacteria that drive methane oxidation with nitrite as the oxidant in the absence of oxygen, giving rise to the so-called anaerobic oxidation of methane.
Safety
Methane is nontoxic, yet it is extremely flammable and may form explosive mixtures with air. Methane is also an asphyxiant if the oxygen concentration is reduced to below about 16% by displacement, as most people can tolerate a reduction from 21% to 16% without ill effects.
The concentration of methane at which asphyxiation risk becomes
significant is much higher than the 5–15% concentration in a flammable
or explosive mixture. Methane off-gas can penetrate the interiors of
buildings near landfills
and expose occupants to significant levels of methane. Some buildings
have specially engineered recovery systems below their basements to
actively capture this gas and vent it away from the building.
Methane gas explosions are responsible for many deadly mining disasters. A methane gas explosion was the cause of the Upper Big Branch coal mine disaster in West Virginia on April 5, 2010, killing 29.
Extraterrestrial methane
Methane has been detected or is believed to exist on all planets of the solar system and most of the larger moons. With the possible exception of Mars, it is believed to have come from abiotic processes.
Methane (CH4) on Mars – potential sources and sinks.
On June 7th of 2018, NASA disclosed in a press conference that its Curiosity rover had documented seasonal fluctuations of atmospheric methane levels on Mars. These fluctuations peaked at the end of the Martian summer at 0.6 parts per billion.
Methane has been proposed as a possible rocket propellant on future Mars missions due in part to the possibility of synthesizing it on the planet by in situ resource utilization. An adaptation of the Sabatier methanation reaction may be used with a mixed catalyst bed and a reverse water-gas shift in a single reactor to produce methane from the raw materials available on Mars, utilizing water from the Martian subsoil and carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere.
Methane could be produced by a non-biological process called ’'serpentinization involving water, carbon dioxide, and the mineral olivine, which is known to be common on Mars.