From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Fruit and vegetables in a dumpster, discarded uneaten
Food recovered by food waste critic
Rob Greenfield in Madison, Wisconsin, from two days of recovery from dumpsters
Food loss and waste is food that is not eaten. The causes of food waste or loss are numerous and occur throughout the food system, during production, processing, distribution, retail and food service sales, and consumption. Overall, about one-third of the world's food is thrown away. A 2021 metaanalysis that did not include food lost during production, by the United Nations Environment Programme found that food waste was a challenge in all countries at all levels of economic development.
The analysis estimated that global food waste was 931 million tonnes of
food waste (about 121 kg per capita) across three sectors: 61 per cent
from households, 26 per cent from food service and 13 per cent from retail.
Food loss and waste is a major part of the impact of agriculture on climate change (it amounts to 3.3 billion tons of CO2e emissions annually) and other environmental issues, such as land use, water use and loss of biodiversity.
Prevention of food waste is the highest priority, and when prevention
is not possible, the food waste hierarchy ranks the food waste treatment
options from preferred to least preferred based on their negative
environmental impacts.
Reuse pathways of surplus food intended for human consumption, such as
food donation, is the next best strategy after prevention, followed by animal feed, recycling of nutrients and energy followed by the least preferred option, landfill, which is a major source of the greenhouse gas methane. Other considerations include unreclaimed phosphorus in food waste leading to further phosphate mining. Moreover, reducing food waste in all parts of the food system is an important part of reducing the environmental impact of agriculture, by reducing the total amount of water, land, and other resources used.
The UN's Sustainable Development Goal Target 12.3
seeks to "halve global per capita food waste at the retail and
consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply
chains, including post-harvest losses" by 2030. Climate change mitigation strategies prominently feature reducing food waste. In the 2022 United Nations Biodiversity Conference nations agree to reduce food waste by 50% by the year 2030.
Definition
A conceptual framework for food loss and waste (FLW)
Food loss and waste occurs at all stages of the food supply chain – production, processing, sales, and consumption.
Definitions of what constitutes food loss versus food waste or what
parts of foods (i.e., inedible parts) exit the food supply chain are
considered lost or wasted vary. Terms are often defined on a situational basis (as is the case more generally with definitions of waste). Professional bodies, including international organizations, state governments, and secretariats may use their own definitions.
United Nations
The Food and Agriculture Organization
(FAO) of the United Nations defines food loss and waste as the decrease
in quantity or quality of food along the food supply chain. Within this
framework, UN Agencies distinguish loss and waste at two different
stages in the process:
- Food loss occurs along the food supply chain from harvest/slaughter/catch up to, but not including, the sales level
- Food waste occurs at the retail and consumption level.
Important components of this definition include:
- Food redirected to nonfood chains (including animal feed, compost, or recovery to bioenergy)
is not counted as food loss or waste. Inedible parts are not considered
as food loss or waste (these inedible parts are sometimes referred to
as unavoidable food waste)
Under Sustainable Development Goal 12,
the Food and Agriculture Organization is responsible for measuring food
loss, while the UN Environmental Program measures food waste.
European Union
In the European Union
(EU), food waste is defined by combining the definitions of food and
waste, namely: "any substance or product, whether processed, partially
processed or unprocessed, intended to be, or reasonably expected to be
ingested by humans (...)" (including things such as drinks and chewing
gum; excluding things such as feed,
medicine, cosmetics, tobacco products, and narcotic or psychotropic
substances) "which the holder discards or intends or is required to
discard".
Previously, food waste was defined by directive 75/442/EEC as "any food substance, raw or cooked, which is discarded, or intended or required to be discarded" in 1975. In 2006, 75/442/EEC was repealed by 2006/12/EC,
which defined waste as "any substance or object in the categories set
out in Annex I which the holder discards or intends or is required to
discard".
Meanwhile, Article 2 of Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 (the General Food
Law Regulation), as amended on 1 July 2022, defined food as "any
substance or product, whether processed, partially processed or
unprocessed, intended to be, or reasonably expected to be ingested by
humans (...)", including things such as drinks and chewing gum,
excluding things such as feed, medicine, cosmetics, tobacco products, and narcotic or psychotropic substances.
A 2016 European Court of Auditors
special report had criticised the lack of a common definition of food
waste as hampering progress, and a May 2017 resolution by the European
Parliament supported a legally binding definition of food waste.
Finally, the 2018/851/EU directive of 30 May 2018 (the revised Waste
Framework Directive) combined the two (after waste was redefined in 2008
by Article 3.1 of 2008/98/EC as "any substance or object which the
holder discards or intends or is required to discard")
by defining food waste as "all food as defined in Article 2 of
Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the
Council that has become waste."
United States
As of 2022, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) employed three categories:
- "Excess food refers to food that is recovered and donated to feed people."
- "Food waste refers to food such as plate waste (i.e., food
that has been served but not eaten), spoiled food, or peels and rinds
considered inedible that is sent to feed animals, to be composted or
anaerobically digested, or to be landfilled or combusted with energy
recovery."
- "Food loss refers to unused product from the agricultural sector, such as unharvested crops."
In 2006, the EPA defined food waste as "uneaten food and food
preparation wastes from residences and commercial establishments such as
grocery stores, restaurants, produce stands, institutional cafeterias
and kitchens, and industrial sources like employee lunchrooms".
The states remain free to define food waste differently for their purposes, though as of 2009, many had not done so.
Other definitions
Bellemare et al. (2017) compared four definitions from:
- a Food and Agriculture Organization
(FAO) 2016 report: "Food loss is defined as ‘the decrease in quantity
or quality of food.’ Food waste is part of food loss and refers to
discarding or alternative (nonfood) use of food that is safe and
nutritious for human consumption along the entire food supply chain,
from primary production to end household consumer level";
- an Economic Research Service (ERS; a USDA
agency) 2014 report: "Food loss represents the amount of food
postharvest, that is available for human consumption but is not consumed
for any reason. It includes cooking loss and natural shrinkage (for
example, moisture loss); loss from mould, pests, or inadequate climate
control; and food waste. Food waste is a component of food loss and
occurs when an edible item goes unconsumed, as in food discarded by
retailers due to color or appearance, and plate waste by consumers";
- a FUSIONS (an EU project) 2016 report: "Food waste is any food, and
inedible parts of food, removed from the food supply chain to be
recovered or disposed (including composed [sic], crops ploughed in/not
harvested, anaerobic digestion, bioenergy production, co-generation,
incineration, disposal to sewer, landfill or discarded to sea)"; and
- an EPA
2016 report: "The amount of food going to landfills from residences,
commercial establishments (e.g., grocery stores and restaurants),
institutional sources (e.g., school cafeterias), and industrial sources
(e.g., factory lunchrooms). Pre-consumer food generated during the
manufacturing and packaging of food products is not included in EPA's
food waste estimates."
According to Bellemare et al., the inclusion of food that goes to
nonfood productive use is flawed for two reasons: "First, if recovered
food is used as an input, such as animal feed, fertilizer, or biomass to
produce output, then by definition it is not wasted. However, there
might be economic losses if the cost of recovered food is higher than
the average cost of inputs in the alternative, nonfood use. Second, the
definition creates practical problems for measuring food waste because
the measurement requires tracking food loss in every stage of the supply
chain and its proportion that flows to nonfood uses." They argued that only food that ends up in landfills should be counted as food waste, pointing to the 2016 EPA definition as a good example.
Bellemare et al. also noted that "the FAO and ERS definitions only
apply to edible and safe and nutritious food, whereas the definitions of
FUSIONS and the EPA apply to both edible and inedible parts of food.
Finally, the ERS and EPA definitions of food waste exclude the food that
is not harvested at the farm level."
A 2019 FAO report stated:
'The notion of food being lost or
wasted is deceptively simple, but in practice there is no commonly
agreed definition of food loss and waste. FAO has worked towards the
harmonization of concepts related to food loss and waste, and the
definitions adopted in this report are the result of a consensus reached
in consultation with experts in this field. This report understands
food loss and waste as the decrease in quantity or quality of food along
the food supply chain. Empirically it considers food losses as occurring along the food supply chain from harvest/slaughter/catch up to, but not including, the retail level. Food waste,
on the other hand, occurs at the retail and consumption level. This
definition also aligns with the distinction implicit in SDG Target 12.3.
This report also asserts that, although there may be an economic loss,
food diverted to other economic uses, such as animal feed, is not
considered as quantitative food loss or waste. Similarly, inedible parts
are not considered as food loss or waste.'
Methodology
The
2019 FAO report stated: "Food loss and waste has typically been
measured in physical terms using tonnes as reporting units. This
measurement fails to account for the economic value of different
commodities and can risk attributing a higher weight to low-value
products just because they are heavier. [This] report acknowledges this
by adopting a measure that accounts for the economic value of produce." Hall et al. (2009) calculated food waste in the United States in terms of energy value
"by comparing the US food supply data with the calculated food consumed
by the US population." The result was that food waste among American
consumers increased from "about 30% of the available food supply in 1974
to almost 40% in recent years" (the early 2000s), or about 900 kcal per person per day (1974) to about 1400 kcal per person per day (2003). A 2012 Natural Resources Defense Council report interpreted this to mean that Americans threw away up to 40% of food that was safe to eat.
Buzby & Hyman (2012) estimated both the total weight (in kg and
lbs) and monetary value (in USD) of food loss in the United States,
concluding that 'the annual value of food loss is almost 10% of the
average amount spent on food per consumer in 2008'.
Sources
Production
In the United States, food loss can occur at most stages of the food industry and in significant amounts. In subsistence agriculture,
the amounts of food loss are unknown, but are likely to be
insignificant by comparison, due to the limited stages at which loss can
occur, and given that food is grown for projected need as opposed to a global marketplace demand.
Nevertheless, on-farm losses in storage in developing countries,
particularly in African countries, can be high although the exact nature
of such losses is much debated.
In the food industry of the United States, the food supply of
which is the most diverse and abundant of any country in the world, loss
occurs from the beginning of food production chain. From planting, crops can be subjected to pest infestations and severe weather, which cause losses before harvest.
Since natural forces (e.g. temperature and precipitation) remain the
primary drivers of crop growth, losses from these can be experienced by
all forms of outdoor agriculture.
On average, farms in the United States lose up to six billion pounds of
crops every year because of these unpredictable conditions.
According to the IPCC sixth assessment report, encouraging the
development of technologies that address issues in food harvesting and
post-harvesting could have a significant impact on decreasing food waste
in the supply chain early-on.
The use of machinery
in harvesting can cause loss, as harvesters may be unable to discern
between ripe and immature crops, or collect only part of a crop. Economic factors, such as regulations and standards for quality and appearance,
also cause food waste; farmers often harvest selectively, preferring to
leave crops not to standard in the field (where they can be used as
fertilizer or animal feed), since they would otherwise be discarded
later. This method of removing undesirable produce from harvest collection, distribution sites and grocery stores is called culling.
However, usually when culling occurs at the production, food
processing, retail and consumption stages, it is to remove or dispose of
produce with a strange or imperfect appearance rather than produce that
is spoiled or unsafe to eat.
In urban areas, fruit and nut trees often go unharvested because people
either do not realize that the fruit is edible or they fear that it is
contaminated, despite research which shows that urban fruit is safe to
consume.
Food processing
Food loss continues in the post-harvest stage, but the amounts of post-harvest loss involved are relatively unknown and difficult to estimate. Regardless, the variety of factors that contribute to food loss, both biological/environmental and socio-economical, would limit the usefulness and reliability of general figures. In storage, considerable quantitative losses can be attributed to pests and micro-organisms.
This is a particular problem for countries that experience a
combination of heat (around 30 °C) and ambient humidity (between 70 and
90 per cent), as such conditions encourage the reproduction of insect
pests and micro-organisms. Losses in the nutritional value, caloric value and edibility of crops, by extremes of temperature, humidity or the action of micro-organisms, also account for food waste. Further losses are generated in the handling of food and by shrinkage in weight or volume.
Some of the food loss produced by processing can be difficult to reduce without affecting the quality of the finished product. Food safety regulations are able to claim foods that contradict standards before they reach markets Although this can conflict with efforts to reuse food loss (such as in animal feed),
safety regulations are in place to ensure the health of the consumer;
they are vitally important, especially in the processing of foodstuffs of animal origin (e.g. meat and dairy products), as contaminated products from these sources can lead to and are associated with microbiological and chemical hazards.
Retail
Packaging
protects food from damage during its transportation from farms and
factories via warehouses to retailing, as well as preserving its
freshness upon arrival. Although it avoids considerable food waste, packaging can compromise efforts to reduce food waste in other ways, such as by contaminating waste that could be used for animal feedstocks with plastics.
In 2013, the nonprofit Natural Resources Defense Council
(NRDC) performed research that suggests that the leading cause of food
waste in America is due to uncertainty over food expiration dates, such
as confusion in deciphering best-before, sell-by, or use-by dates. Joined by Harvard's Food Law and Policy Clinic, the NRDC produced a study called The Dating Game: How Confusing Food Date Labels Leads to Food Waste in America. This United States-based study looked at the intertwining laws which lead labeling to end up unclear and erratic.
This uncertainty leads to consumers to toss food, most often because
they think the food may be unsafe or misunderstand the labeling on the
food completely. Lack of regulation on labeling can result in large
quantities of food being removed from the market overall.
Retail stores throw away large quantities of food. Usually, this
consists of items that have reached either their best-before, sell-by,
or use-by dates. Food that has passed the best -before, and sell-by
date, and even some food that passed the use-by date is still edible at
the time of disposal, but stores have widely varying policies to handle
the excess food. Some stores put effort into preventing access to poor
or homeless people, while others work with charitable organization to
distribute food. Retailers also contribute to waste as a result of their
contractual arrangements with suppliers. Failure to supply agreed
quantities renders farmers or processors liable to have their contracts
cancelled. As a consequence, they plan to produce more than actually
required to meet the contract, to have a margin of error. Surplus
production is often simply disposed of.
Retailers usually have strict cosmetic standards for produce, and if fruits or vegetables are misshapen
or superficially bruised, they are often not put on the shelf. In the
United States, some of the estimated six billion pounds of produce
wasted each year are discarded because of appearance.
The USDA publishes guidelines used as a baseline assessment by produce
distributors, grocery stores, restaurants and other consumers in order
to rate the quality of food.
These guidelines and how they rate are readily available on their
website. For example, apples get graded by their size, color, wax
residue, firmness, and skin appearance. If apples rank highly in these
categories and show close to no superficial defects, they are rated as
"U.S. Extra Fancy" or "U.S. Fancy", these are the typical ratings sought
out by grocery stores when purchasing their produce.
Any apples with suboptimal levels of appearance are ranked as either
"U.S. Number 1" or "Utility" and are not normally purchased for retail,
as recommended by produce marketing sources, despite being safe and
edible.
A number of regional programs and organizations have been established
by the EPA and USDA in an attempt to reduce such produce waste. Organizations in other countries, such as Good & Fugly in Australia
and No Food Waste in India, are making similar efforts worldwide.
The popular trend of selling "imperfect" produce at retail has been
criticized for overlooking existing markets for these foods (eg the food
processing industry and bargain grocery stores) and downplaying the
household-level wasting of food that is statistically a larger part of
the overall problem.
The fishing industry wastes substantial amounts of food: about
40–60% of fish caught in Europe is discarded as the wrong size or wrong
species.
This comes to about 2.3 million tonnes per annum in the North Atlantic and the North Sea.
Food-Service Industry
Lunch leftovers in a restaurant in
Seoul.
To address food waste,
it is understood that there are multiple stakeholders throughout the
food supply chain. The food supply chain is a market-driven system that
requires a specific focus on each stakeholder in the food-making process
and their food waste quantification can be dependent on geographical
scales.
This geographical scale then results in the production of different
definitions of food waste, as mentioned earlier, with respect to the
complexities of food supply chains (FSCs) and then create a narrative that further shows the needs for specific research on important stakeholders. The food service industry suggests to be a key stakeholder to achieve mitigation.
The key players within the food service industry include the
manufacturers, producers, farmers, managers, employees, and consumers.
The key causes of food waste in restaurants include the food menu, the
production procedure, the use of pre-prepared versus whole food
products, dinnerware size, type of ingredients used, the dishes served,
opening hours, and disposal methods.
These factors then can be categorized in the different stages of
operations that relate to pre-kitchen, kitchen-based, and post-kitchen
processes.
In restaurants in developing countries, the lack of infrastructure and
associated technical and managerial skills in food production have been
identified as the key drivers in the creation of food waste currently
and in the future.
Comparatively, developed countries show that the majority of food waste
is produced post-consumer, which is driven by the low prices of food
and disposable income, consumers high expectations of food cosmetic
standards, and the increasing disconnect between consumers and how food
is being produced (Urbanization). That being said, in United States restaurants alone, an estimated 22 to 33 billion pounds are wasted each year.
Consumption
Consumers
are directly and indirectly responsible for wasting a lot of food,
which could for a large part be avoided if they were willing to accept
suboptimal food (SOF) that deviates in sensory characteristics (odd
shapes, discolorations) or has a best-before date that is approaching or
has passed, but is still perfectly fine to eat.
In addition to inedible and edible food waste generated by consumers,
substantial amounts of food is wasted through food overconsumption, also
referred to as metabolic food waste, estimated globally as 10% of foods reaching the consumer.
By sector
Fruit and vegetables
Discarded tomatoes on a compost heap at nurseries in the UK
Post-harvest losses of vegetables and fruit occur at all points in the value chain from production in the field to the food being placed on a plate for consumption. Post-harvest activities include harvesting, handling, storage, processing, packaging, transportation and marketing.
Losses of horticultural produce are a major problem in the post-harvest
chain. They can be caused by a wide variety of factors, ranging from
growing conditions to handling at retail level. Not only are losses
clearly a waste of food, but they also represent a similar waste of
human effort, farm inputs, livelihoods, investments, and scarce
resources such as water.
Post-harvest losses for horticultural produce are, however, difficult
to measure. In some cases everything harvested by a farmer may end up
being sold to consumers. In others, losses or waste may be considerable.
Occasionally, losses may be 100%, for example when there is a price
collapse and it would cost the farmer more to harvest and market the
produce than to plough it back into the ground. Use of average loss
figures is thus often misleading. There can be losses in quality, as
measured both by the price obtained and the nutritional value, as well
as in quantity.
Grains
Grains may be lost in the pre-harvest, harvest, and post-harvest
stages. Pre-harvest losses occur before the process of harvesting
begins, and may be due to insects, weeds, and rusts.
Harvest losses occur between the beginning and completion of
harvesting, and are primarily caused by losses due to shattering. Post-harvest losses occur between harvest and the moment of human consumption. They include on-farm losses, such as when grain is threshed, winnowed,
and dried. Other on-farm losses include inadequate harvesting time,
climatic conditions, practices applied at harvest and handling, and
challenges in marketing produce. Significant losses are caused by
inadequate storage conditions as well as decisions made at earlier
stages of the supply chain, including transportation, storage, and
processing, which predispose products to a shorter shelf life.
Important in many developing countries, particularly in Africa, are
on-farm losses during storage, when the grain is being stored for
auto-consumption or while the farmer awaits a selling opportunity or a
rise in prices.
Extent
Food loss from post-harvest to distribution in 2016, percentages globally and by region
Global extent
Efforts are underway by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the United Nations Environment Programme
(UNEP) to measure progress towards SDG Target 12.3 through two separate
indices: the Food Loss Index (FLI) and the Food Waste Index (FWI).
According to FAO's The State of Food and Agriculture 2019,
globally, in 2016, around 14 percent of the world's food is lost from
production before reaching the retail level. Generally, levels of loss
are higher for fruits and vegetables than for cereals and pulses.
However, even for the latter, significant levels are found in
sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern and South-Eastern Asia, while they are
limited in Central and Southern Asia.
Estimates from UN Environment's Food Waste Index suggest that
about 931 million tonnes of food, or 17 percent of total food available
to consumers in 2019, went into the waste bins of households, retailers,
restaurants and other food services.
According to a report from Feedback EU, the EU wastes 153 million tonnes of food each year, around double previous estimates.
Earlier estimates
In 2011, an FAO publication based on studies carried out by The Swedish Institute for Food and Biotechnology
(SIK) found that the total of global amount of food loss and waste was
around one third of the edible parts of food produced for human
consumption, amounting to about 1.3 billion tonnes (1.28×109 long tons; 1.43×109 short tons) per year.
As the following table shows, industrialized and developing countries
differ substantially. In developing countries, it is estimated that
400–500 calories per day per person are wasted, while in developed
countries 1,500 calories per day per person are wasted.
In the former, more than 40% of losses occur at the post-harvest and
processing stages, while in the latter, more than 40% of losses occur at
the retail and consumer levels. The total food waste by consumers in
industrialized countries (222 million tonnes or 218,000,000 long tons or
245,000,000 short tons) is almost equal to the entire food production
in sub-Saharan Africa (230 million tonnes or 226,000,000 long tons or 254,000,000 short tons).
| Food loss and waste per person per year (2007)[ |
Total |
At the production
and retail stages |
By consumers
|
| Europe |
280 kg (617 lb) |
190 kg (419 lb) |
90 kg (198 lb)
|
| North America and Oceania |
295 kg (650 lb) |
185 kg (408 lb) |
110 kg (243 lb)
|
| Industrialized Asia |
240 kg (529 lb) |
160 kg (353 lb) |
80 kg (176 lb)
|
| sub-Saharan Africa |
160 kg (353 lb) |
155 kg (342 lb) |
5 kg (11 lb)
|
| North Africa, West and Central Asia |
215 kg (474 lb) |
180 kg (397 lb) |
35 kg (77 lb)
|
| South and Southeast Asia |
125 kg (276 lb) |
110 kg (243 lb) |
15 kg (33 lb)
|
| Latin America |
225 kg (496 lb) |
200 kg (441 lb) |
25 kg (55 lb)
|
A 2013 report from the British Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IME) likewise estimated that 30–50% (or 1.2–2 billion tonnes or 1.18×109–1.97×109 long tons or 1.32×109–2.20×109 short tons ) of all food produced remains uneaten.
Individual countries
Australia
Each year in New South Wales, more than 25 million meals are delivered by charity OzHarvest from food that would otherwise be wasted.
Each year, the Australian economy loses $20 billion in food waste. This
has a crucial environmental impact through the waste of resources used
to produce, manufacture, package, and distribute that food.
In addition, it is estimated that 7.6 million tonnes of CO2
is generated by the disposed food in landfills. It is also the cause of
odour, leaching, and potential generation for diseases. In March 2019,
the Australian ministry of the environment shared the key findings of
Australia's National food waste baseline, which will facilitate the
tracking of the progress towards their goal to halve Australian food
waste by 2030.
Many initiatives were taken by the Australian government in order
to help achieve this goal. In fact, they financed $1.2 million in
organization that invest in renewable energies systems to store and
transport food. They also funded more than $10 million for research on
food waste reduction. Local governments have also implemented programs
such as information sessions on storing food and composting, diversion
of waste from restaurants and cafes from landfills to shared recycling
facilities and donation of food to organization that would otherwise be
wasted.
Canada
In Canada, 58% of all food is wasted, amounting to 35.5 million tonnes of food per annuum.
The value of this lost food is equivalent to CA$21 billion. Such
quantities of food would be enough to feed all Canadians for five
months. It is estimated that about one third of this waste could be
spared and sent to those in need.
There are many factors that contribute to such large-scale waste.
Manufacturing and processing food alone incur costs of CA$21 billion, or
4.82 million tons. Per household, it is estimated that $1,766 is lost
in food loss and waste. The Government of Canada
identifies three main factors contributing to household waste: (1)
buying too much food and not eating it before it spoils, (2)
malfunctioning or poorly-designed packaging that does not deter spoilage
rates or contamination, and (3) improper disposing of food – using
garbage bins instead of those intended for organic waste.
Canada, Mexico, and the United States are working together under
the Commission for Environmental Cooperation in order to address the
severe problem of food waste in North America.
Canada specifically is working in the following ways to reduce food waste:
- Canada pledged to consult on strategies in the Strategy on Short-lived Climate Pollutants to reduce avoidable food waste within the country. This will help to reduce methane emissions from Canadian landfills.
- The government has implemented a Food Policy for Canada, which is a movement towards a more sustainable food system.
- In February 2019, the government brought together several experts
from different sectors to share ideas and discuss opportunities for
measuring and reducing food loss and waste across the food supply chain.
China
In 2015 the Chinese Academy of Sciences
reported that in big cities there was 17 to 18 million tons of food
waste, enough to feed over 30 million people. About 25% of the waste was
staple foods and about 18% meat.
In August 2020 the Chinese Communist Party general secretary Xi Jinping said the amount of food waste was shocking and distressing. A local authority campaign "Operation empty plate" (Chinese: 光盘行动)
was started to reduce waste, including encouraging food outlets to
limit orders to one fewer main dish than the number of customers.
As of December 2020, a draft law is under consideration to
penalise food outlets if they encourage or mislead customers to order
excessive meals causing obvious waste, first with a warning and then
fines of up to 10,000 yuan. It would allow restaurants to charge
customers who leave excessive leftovers. Broadcasters who promote
overeating or food waste could also be fined up to 100,000 yuan.
Denmark
According to Ministry of Environment (Denmark), over 700,000 tonnes per year of food is wasted every year in Denmark in the entire food value chain from farm to fork. Due to the work of activist Selina Juul's Stop Wasting Food movement, Denmark has achieved a national reduction in food waste by 25% in 5 years (2010–2015).
France

In France, approximately 1.3–1.9 million tonnes of food waste is
produced every year, or between 20 and 30 kilograms per person per year.
Out of the 10 million tonnes of food that is either lost or wasted in
the country, 7.1 million tonnes of food wasted in the country, only 11%
comes from supermarkets.
Not only does this cost the French €16 billion per year, but also the
negative impact on the environment is also shocking. In France, food
waste emits 15.3 million tonnes of CO2, which represents 3% of the country's total CO2 emission.
In response to this issue, in 2016, France became the first country in
the world to pass a unanimous legislation that bans supermarkets from
throwing away or destroying unsold food. Instead, supermarkets are
expected to donate such food to charities and food banks.
In addition to donating food, many businesses claim to prevent food
waste by selling soon-to-be wasted products at discounted prices. The National Pact Against Food Waste in France has outlined eleven measures to achieve a food waste reduction by half by 2025.
Hungary
According to the research of National Food Chain Safety Office
in 2019 based on the official EU methodological framework, an average
Hungarian consumer generates 68 kg food waste annually. 49% of this
amount would be avoidable.
The research team (Wasteless project) replicated the study in 2019 involving 165 households.
According to the data, food waste generated by the Hungarian households
was estimated to be 65.5 kg per capita annually. Between the two
periods, a 4% decrease was observed, despite significant economic
expansion.
Italy
According
to REDUCE project, which produced the first baseline dataset for Italy
based on official EU methodological framework, food waste is 530 g per
person per week at household stage (only edible fraction); food waste in
school canteens corresponds to 586 g per pupil per week; retail food
waste per capita, per year corresponds to 2.9 kg. See https://www.sprecozero.it/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/REDUCE-FINAL_SDG-12.3-ITALY_FOOD-WASTE-1.pdf
Netherlands
According
to Meeusen & Hagelaar (2008), between 30% and 50% of all food
produced was estimated to be lost or thrown away at that time in the
Netherlands, while a 2010 Agriculture Ministry (LNV) report stated that the Dutch population wasted 'at least 9.5m tonnes of food per year, worth at least €4.4bn.'
In 2019, three studies into food waste in households in the Netherlands
commissioned by the LNV were conducted, showing that the average
household waste per capita had been reduced from 48 kilograms of "solid
food (including dairy products, fats, sauces and soups)" in 2010, to
41.2 kilograms in 2016, to 34.3 kilograms in 2019.
The waste of liquid foods (excluding beer and wine, first measured in
2019) that ended up in the sewer through sinks or toilets was analysed
to have decreased from 57.3 litres per capita in 2010 to 45.5 litres in
2019.
New Zealand
Food waste in New Zealand is one of the many environmental issues that is being addressed by industry, individuals and government.
The total volume of food wasted in New Zealand is not known as food
waste has not been investigated at all stages of the supply chain.
However, research has been undertaken into household food waste,
supermarket food waste and hospitality sector food waste. The
Environment Select Committee held a
briefing into foodwaste in 2018.
Research
done on household food waste in New Zealand found that larger
households and households with more young people created more food
waste. The average household in this case study put 40% of food waste
into the rubbish.
Singapore
In Singapore, 788,600 tonnes (776,100 long tons; 869,300 short tons) of food was wasted in 2014. Of that, 101,400 tonnes (99,800 long tons; 111,800 short tons) were recycled.
Since Singapore has limited agriculture ability, the country spent
about S$14.8 billion (US$10.6 billion) on importing food in 2014.
US$1.4 billion of it ends up being wasted, or 13 percent.
On January 1, 2020, Singapore implemented the Zero Waste
Masterplan which aims to reduce Singapore's daily waste production by 30
percent. The project also aims to extend the lifespan of the Semaku
Landfill, Singapore's only landfill, beyond 2025.
As a direct result of the project, food waste dropped to 665,000
tonnes, showing a significant decrease from 2017's all-time high of
810,000 tonnes.
United Kingdom
Food waste in the United Kingdom
is a subject of environmental, and socioeconomic concern that has
received widespread media coverage and been met with varying responses
from government. Since 1915, food waste
has been identified as a considerable problem and has been the subject
of ongoing media attention, intensifying with the launch of the "Love Food, Hate Waste"
campaign in 2007. Food waste has been discussed in newspaper articles,
news reports and television programmes, which have increased awareness
of it as a public issue. To tackle waste issues, encompassing food
waste, the government-funded "Waste & Resources Action Programme" (WRAP) was created in 2000.
A significant proportion of food waste is produced by the domestic household, which, in 2007, created 6,700,000 tonnes
of food waste. Potatoes, bread slices and apples are respectively the
most wasted foods by quantity, while salads are thrown away in the
greatest proportion. A majority of wasted food is avoidable, with the rest being divided almost equally by foods which are unavoidable (e.g. tea bags) and unavoidable due to preference (e.g. bread crusts) or cooking type (e.g. potato skins).
Reducing the amount of food waste has been deemed critical if the UK is to meet international targets on climate change, limiting greenhouse gas emissions, and meet obligations under the European Landfill Directive to reduce biodegradable waste going to landfill. Equally great emphasis has been placed on the reduction of food waste, across all developed countries, as a means of ending the global food crisis
that leaves millions worldwide starving and impoverished. In the
context of the 2007–2008 world food price crisis, food waste was
discussed at the 34th G8 summit in Hokkaidō, Japan. Then-UK Prime Minister Gordon Brown said of the issue "We must do more to deal with unnecessary demand, such as by all of us doing more to cut our food waste".
In June 2009, then-
Environment Secretary Hilary Benn
announced the Government's "War on waste", a programme aimed at
reducing Britain's food waste. The proposed plans under the scheme
included: scrapping
best before and limiting
sell by labels on food, creating new
food packaging sizes, constructing more "on-the-go" recycling points and unveiling five flagship
anaerobic digestion plants.
Two years after its launch, the "Love Food, Hate Waste" campaign was
claiming it had already prevented 137,000 tonnes of waste and, through
the help it had given to over 2,000,000 households, had made savings of
£300,000,000.
In the UK, 6,700,000 tonnes (6,590,000 long tons; 7,390,000 short
tons) per year of wasted food (purchased and edible food which is
discarded) amounts to a cost of £10.2 billion each year. This represents
costs of £250 to £400 a year per household.
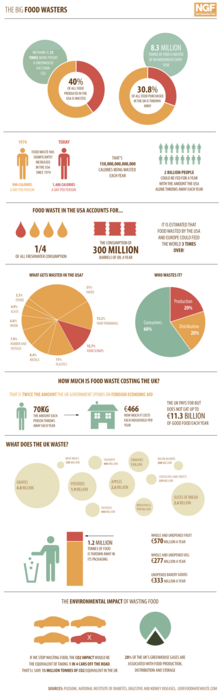
United States
Estimates of food waste in the United States range from 35 million tons to 103 million tons.
In a study done by National Geographic in 2014, Elizabeth Royte
indicated more than 30 percent of food in the United States, valued at
$162 billion annually, isn't eaten. The University of Arizona
conducted a study in 2004, which indicated that 14 to 15% of United
States edible food is untouched or unopened, amounting to $43 billion
worth of discarded, but edible, food. In 2010, the United States Department of Agriculture has come forth with estimations from the Economic Research Service that approximates food waste in the United States to be equivalent to 141 trillion calories.
USDA data from 2010 shows that 26% of fish, meat, poultry were
thrown away at the retail and consumer level. Since then meat production
has increased by more than 10%. Data scientist Harish Sethu says this
means that billions of animals are raised and slaughtered only to end up
in a landfill.
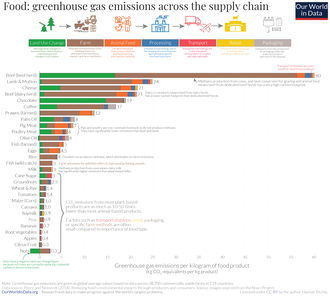
Impact on the environment
Food waste is responsible for 6% of global greenhouse gas emissions
Empirical
evidence at the global level on the environmental footprints for major
commodity groups suggests that, if the aim is to reduce land use, the
primary focus should be on meat and animal products, which account for
60 percent of the land footprint associated with food loss and waste.
If the aim is to target water scarcity, cereals and pulses make the
largest contribution (more than 70 percent), followed by fruits and
vegetables.
In terms of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with food loss
and waste, the biggest contribution is again from cereals and pulses
(more than 60 percent), followed by roots, tubers and oil-bearing crops.
However, the environmental footprint for different commodities also
varies across regions and countries, due, among other things, to
differences in crop yields and production techniques.
According to the IPCC 6th Assessment Report, the reduction of food
waste would be beneficial for improving availability of resources such
as "water, land-use, energy consumption" and the overall reduction of
greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere.
Prevention and valorisation
In 2022 United Nations Biodiversity Conference nations adopted an agreement for preserving biodiversity, including a commitment to reduce food waste by 50% by the year 2030.
According to FAO's
The State of Food and Agriculture 2019, the case for reducing food loss
and waste includes gains that society can reap but which individual
actors may not take into account, namely: (i) increased productivity and
economic growth; (ii) improved food security and nutrition; and (iii)
mitigation of environmental impacts of losing and wasting food, in
particular terms of reducing greenhouse gas (GHG emissions as well as
lowering pressure on land and water resources. The last two societal
gains, in particular, are typically seen as externalities of reducing
food loss and waste.
Response to the problem of food waste at all social levels has
varied hugely, including campaigns from advisory and environmental
groups, and concentrated media attention on the subject.
As suggested by the food waste hierarchy, prevention and reuse
pathways for human consumption have the highest priority levels for food
waste treatment. The general approach to food waste reduction comprise
two main pathways: prevention and valorisation.
Prevention of food waste infers all actions that reduce food production
and ultimately prevent food from being produced in vain, such as food
donations or re-processing into new food products. Valorisation on the
other hand comprise actions that recover the materials, nutrients or
energy in food waste, for instance by producing animal feed, fuel or
energy.
Multiple studies have studied the environmental benefits of food waste prevention measures, including food donations, recovery of unharvested vegetables for re-use in food production, re-processing of surplus bread for beer production, and producing chutney or juice from leftovers.
Food waste can also be used to produce multiple high-value products,
such as a fish oil substitute for food or feed use via marine micro
algae,
without compromising the ability to produce energy via biogas. The
general consensus currently suggest that reducing food waste by either
prevention or valorisation, for human consumption, infers higher
environmental benefits compared to the lower priority levels, such as
energy production or disposal.
Multiple private enterprises have developed hardware and software
solutions dealing mainly with the prevention of food waste within
foodservice production facilities (contract catering, hotels &
resorts, cruise ships, casinos etc.), by gathering quantitative and
qualitative data about the specific food waste, helping chefs and
managers reduce food waste by up to 70% by improving and optimising
their workflows and menus.
Food rescue
There are multiple initiatives that rescue food that would otherwise
not be consumed by humans anymore. The food can come from supermarkets,
restaurants or private households for example. Such initiatives are:
Consumer marketing
One
way of dealing with food waste is to reduce its creation. Consumers can
reduce spoilage by planning their food shopping, avoiding potentially
wasteful spontaneous purchases, and storing foods properly (and also preventing a too large buildup of perishable stock). Widespread educational campaigns have been shown to be an effective way to reduce food waste.
A British campaign called "Love Food, Hate Waste"
has raised awareness about preventative measures to address food waste
for consumers. Through advertisements, information on food storage and
preparation and in-store education, the UK observed a 21% decrease in
avoidable household food waste over the course of 5 years.
Another potential solution is for "smart packaging" which would
indicate when food is spoiled more precisely than expiration dates
currently do, for example with temperature-sensitive ink, plastic that changes color when exposed to oxygen, or gels that change color with time.
An initiative in Curitiba, Brazil
called Cambio Verde allows farmers to provide surplus produce (produce
they would otherwise discard due to too low prices) to people that bring
glass and metal to recycling facilities (to encourage further waste
reduction).
In Europe, the Food Surplus Entrepreneurs Network (FSE Network),
coordinates a network of social businesses and nonprofit initiatives
with the goal to spread best practices to increase the use of surplus
food and reduction of food waste.
An overarching consensus exists on the substantial environmental benefits of food waste reduction.
On the other hand, one study looking at food waste reduction measures
in the United Kingdom found that rebound effect may cause substitutive
consumption as a result of economic savings made from food waste
prevention. They estimated that a reduction of one tonne
of food waste could lead to substantial reductions in GHG emissions, in
the order of 706–896 kg CO2-eq. Rebound effect may however reduce such
GHG savings by up to 60%.
Collection
Bins of food waste in ReFood bins locked in a cage to prevent dumpster diving
In areas where the waste collection is a public function, food waste
is usually managed by the same governmental organization as other waste
collection. Most food waste is combined with general waste at the
source. Separate collections, also known as source-separated organics,
have the advantage that food waste can be disposed of in ways not
applicable to other wastes. In the United States, companies find higher
and better uses for large commercial generators of food and beverage
waste.
From the end of the 19th century through the middle of the 20th
century, many municipalities collected food waste (called "garbage" as
opposed to "trash") separately. This was typically disinfected by
steaming and fed to pigs, either on private farms or in municipal
piggeries.
Separate curbside collection of food waste is now being revived
in some areas. To keep collection costs down and raise the rate of food
waste segregation, some local authorities, especially in Europe, have
introduced "alternate weekly collections" of biodegradable waste
(including, e.g., garden waste), which enable a wider range of
recyclable materials to be collected at reasonable cost, and improve
their collection rates. However, they result in a two-week wait before
the waste will be collected. The criticism is that particularly during
hot weather, food waste rots and stinks, and attracts vermin.
Waste container design is therefore essential to making such operations
feasible. Curbside collection of food waste is also done in the U.S.,
some ways by combining food scraps and yard waste together. Several
states in the U.S. have introduced a yard waste ban, not accepting
leaves, brush, trimmings, etc. in landfills. Collection of food scraps
and yard waste combined is then recycled and composted for reuse.
Disposal
As alternatives to landfill, food waste can be composted to produce soil and fertilizer, fed to animals or insects, or used to produce energy or fuel. Some wasted fruit parts, can also be biorefined to extract useful substances for the industry (i.e. succinic acid from orange peels, lycopene from tomato peels).
Landfills and greenhouse gases
Dumping food waste in a landfill causes odour as it decomposes, attracts flies and vermin, and has the potential to add biological oxygen demand (BOD) to the leachate. The European Union Landfill Directive and Waste Regulations, like regulations in other countries,
enjoin diverting organic wastes away from landfill disposal for these
reasons. Starting in 2015, organic waste from New York City restaurants
will be banned from landfills.
In countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom,
food scraps constitute around 19% of the waste buried in landfills,
where it biodegrades very easily and produces methane, a powerful
greenhouse gas.
Methane, or CH4, is the second most prevalent
greenhouse gas that is released into the air, also produced by landfills
in the U.S. Although methane spends less time in the atmosphere (12
years) than CO2, it's more efficient at trapping radiation. It is 25 times greater to impact climate change than CO2 in a 100-year period. Humans accounts over 60% of methane emissions globally.
Fodder and insect feed
Large
quantities of fish, meat, dairy and grain are discarded at a global
scale annually, when they can be used for things other than human
consumption. The feeding of food scraps or slop to domesticated animals
such as pigs or chickens is, historically, the most common way of
dealing with household food waste. The animals turn roughly two thirds
of their ingested food into gas or fecal waste, while the last third is
digested and repurposed as meat or dairy products. There are also
different ways of growing produce and feeding livestock that could ultimately reduce waste.
Bread and other cereal products discarded from the human food
chain could be used to feed chickens. Chickens have traditionally been
given mixtures of waste grains and milling by-products in a mixture called chicken scratch. As well, giving table scraps to backyard chickens is a large part of that movement's claim to sustainability, though not all backyard chicken growers recommend it. Ruminants and pigs have also been fed bakery waste for a long time.
Certain food waste (such as flesh) can also be used as feed in maggot farming. The maggots can then be fed to other animals. In China, some food waste is being processed by feeding it to cockroaches.
Composting
Food waste can be biodegraded by composting, and reused to fertilize soil.
Composting is the aerobic process completed by microorganisms in which
the bacteria break down the food waste into simpler organic materials
that can then be used in soil.[150]
By redistributing nutrients and high microbial populations, compost
reduces water runoff and soil erosion by enhancing rainfall penetration,
which has been shown to reduce the loss of sediment, nutrients, and
pesticide losses to streams by 75–95%.
Composting food waste leads to a decrease in the quantity of
greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. In landfills, organic
food waste decomposes anaerobically, producing methane gas that is
emitted into the atmosphere. When this biodegradable waste is composted,
it decomposes aerobically and does not produce methane, but instead
produces organic compost that can then be utilized in agriculture.
Recently, the city of New York has begun to require that restaurants
and food-producing companies begin to compost their leftover food.
Another instance of composting progress is a Wisconsin-based company
called WasteCap, who is dedicated towards aiding local communities
create composting plans.
Municipal Food Waste (MFW) can be composted to create this
product of organic fertilizer, and many municipalities choose to do this
citing environmental protection and economic efficiency as reasoning.
Transporting and dumping waste in landfills requires both money and room
in the landfills that have very limited available space.
One municipality who chose to regulate MFW is San Francisco, who
requires citizens to separate compost from trash on their own,
instituting fines for non-compliance at $100 for individual homes and
$500 for businesses. The city's economic reasoning for this
controversial mandate is supported by their estimate that one business
can save up to $30000 annually on garbage disposal costs with the
implementation of the required composting.
Home composting
Composting
is an economical and environmentally conscious step many homeowners
could take to reduce their impact on landfill waste. Instead of food
scraps and spoiled food taking up space in trashcans or stinking up the
kitchen before the bag is full, it could be put outside and broken down by worms and added to garden beds.
Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion
produces both useful gaseous products and a solid fibrous "compostable"
material. Anaerobic digestion plants can provide energy from waste by
burning the methane created from food and other organic wastes to
generate electricity, defraying the plants' costs and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The United States Environmental Protection Agency
states that the use of anaerobic composting allows for large amounts of
food waste to avoid the landfills. Instead of producing these
greenhouse gasses into the environment from being in a landfill, the
gasses can alternatively be harnessed in these facilities for reuse.
Since this process of composting produces high volumes of biogas, there are potential safety issues such as explosion and poisoning. These interactions require proper maintenance and personal protective equipment is utilized.
Certain U.S. states, such as Oregon, have implemented the requirement
for permits on such facilities, based on the potential danger to the
population and surrounding environment.
Food waste coming through the sanitary sewers from garbage disposal units is treated along with other sewage and contributes to sludge.
Commercial liquid food waste
Commercially, food waste in the form of wastewater coming from commercial kitchens' sinks, dishwashers and floor drains is collected in holding tanks called grease interceptors to minimize flow to the sewer system. This often foul-smelling waste contains both organic and inorganic waste (chemical cleaners, etc.) and may also contain hazardous hydrogen sulfide
gases. It is referred to as fats, oils, and grease (FOG) waste or more
commonly "brown grease" (versus "yellow grease", which is fryer oil that
is easily collected and processed into biodiesel) and is an
overwhelming problem, especially in the US, for the aging sewer systems.
Per the US EPA, sanitary sewer overflows also occur due to the improper
discharge of FOGs to the collection system.
Overflows discharge 3–10 billion U.S. gallons (11–38 million cubic
meters) of untreated wastewater annually into local waterways, and up to
3,700 illnesses annually are due to exposure to contamination from
sanitary sewer overflows into recreational waters.