https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Effects_of_sleep_deprivation_on_cognitive_performance
It has been estimated that over 20% of adults suffer from some form of sleep deprivation. Insomnia and sleep deprivation are common symptoms of depression and can be an indication of other mental disorders. The consequences of not getting enough sleep could have dire results; not only to the health of the individual, but those around them as sleep deprivation increases the risk of human-error related accidents, especially with vigilance-based tasks involving technology.
It has been estimated that over 20% of adults suffer from some form of sleep deprivation. Insomnia and sleep deprivation are common symptoms of depression and can be an indication of other mental disorders. The consequences of not getting enough sleep could have dire results; not only to the health of the individual, but those around them as sleep deprivation increases the risk of human-error related accidents, especially with vigilance-based tasks involving technology.
Attention
Neural substrates
The parietal lobes of the brain are largely involved in attention. Lesions to this region of the brain in humans result in difficulty or inability to attend to events that are contralateral to the lesioned hemisphere. Those with lesions to the posterior parietal lobe have little to no difficulty shifting attention to and from stimuli appearing in the space ipsilateral
to the lesioned hemisphere. However, they do display a slowed response
in shifting their focus of current attention to events and stimuli
appearing contralateral to the lesioned hemisphere.
Studies involving single-unit recordings from the parietal lobes of monkeys have indicated that there are neurons
solely involved in integrating visual spatial information with postural
information. Without this apparent combining of spatial information, it
would be difficult or impossible to locate objects in external space,
as information provided solely by the retina is insufficient. The position of the eyes, head and body must also be taken into consideration.
In addition, studies involving transcranial magnetic stimulation application over the parietal lobes as well as positron emission tomography
(PET) analysis of the parietal lobes suggest that this region is
involved in conjunction searches, but not in single-feature searches.
Auditory attention
The Primary auditory cortex is highlighted in magenta, and has been known to interact with all areas highlighted on this neural map.
Auditory
attention has been examined following sleep deprivation. Researchers
examined the auditory attention of twelve non-sleep-deprived subjects
and twelve sleep-deprived subjects at various time intervals. Subjects
were involved in an auditory attention task, which required the
reproduction of the spatial relationships between four letters, using a
graph composed of six squares, immediately following the presentation of
an item from a tape recorder. It was found that auditory attention of
sleep-deprived individuals is affected as the total amount of
sleep-deprivation increases, possibly due to lowered perceptual
vigilance.
Divided attention
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
(fMRI) scans of the brains of subjects exposed to thirty-five hours of
sleep deprivation indicate that sleep deprivation is related to
increases in prefrontal cortex
and parietal lobe activation during tasks that combine verbal learning
and arithmetic. This is particularly apparent in the right hemisphere.
In non sleep-deprived individuals involved in verbal learning and
arithmetic tasks the anterior cingulate cortex and the right prefrontal cortex are active. Following sleep deprivation there is increased activation of the left inferior frontal gyrus and the bilateral
parietal lobes. This information suggests that divided attention tasks
require more attentional resources than normally required by a non
sleep-deprived individual.
Exogenous and endogenous attention
Studies using event-related potential (ERP) recordings have found that twenty-four hours of sleep deprivation decreases ERP response to signal inputs from endogenous, but not exogenous,
sources. Therefore, it is suggested that sleep deprivation affects
endogenously driven selective attention to a greater extent than
exogenously driven selected attention.
Selective attention
Twenty-four
hours of sleep deprivation has been found to affect the functional
connectivity between the inferior frontal parietal region (IPS) and the parahippocampal place area
(PPA). However, sleep deprivation does not affect the attention
modulation index of the PPA. With this information, researchers have
concluded that the psychophysiological interaction (PPI) is more involved in selective attention than the IPS and PPA.
Research has found that together, attention and sleep deprivation
modulate the parahippocampal place area (PPA) activation and scene
processing. Specifically, sleep deprivation was related to significant
decreases in PPA activation while attending to scenes and when ignoring
scenes. This is explained by the absence of change in the Attention
Modulation Index (AMI). Face recognition is not affected by sleep
deprivation.
Sleep deprivation has been shown to negatively affect picture classification speed and accuracy, as well as recognition memory.
It results in an inability to avoid attending to irrelevant information
displayed during attention-related tasks. (Norton) It also decreases
activation in the ventral visual area and the frontal parietal control
regions.
Supervisory attention
Studies involving sleep deprived subjects’ performance on choice reaction time tests, in which response inhibition,
task shifting skill and task strategy were involved, have been
conducted and analyzed. These three cognitive processes are involved and
critical in tasks involving supervisory attention, which is defined as
behaviour that arises through the selection and implementation of
schemas.
Following one night of total sleep deprivation, subjects showed no
decline in task shifting or response inhibition performance. However,
sleep deprivation does affect the ability to use preparatory bias to
increase performance speed. It is suggested that the brain’s cognitive
resources make an active effort to succeed in a challenging task when
subjected to sleep deprivation, and that this deficit becomes apparent
in tasks involving preparatory bias.
Visuospatial attention
Deficits
in cognitive performance due to continuous sleep restriction are not
well understood. However, there have been studies looking into
physiological arousal of the sleep-deprived brain. Participants, whose
total amount of sleep had been restricted by 33% throughout one week,
were subjected to reaction time tests. The results of these tests were
analyzed using quantitative EEG
analysis. The results indicate that the frontal regions of the brain
are first to be affected, whereas the parietal regions remain active
until the effects of sleep deprivation become more severe, which
occurred towards the end of the week. In addition, EEG
and ERP analysis reveals that activation deficits are more apparent in
the non-dominant hemisphere than in the dominant hemisphere.
The effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance have been
studied through the use of parametric visual attention tasks. Functional
magnetic resonance imaging of participants' brains who were involved in
ball-tracking tasks of various difficulty levels were obtained. These
images were taken during rested wakefulness and again after one night of
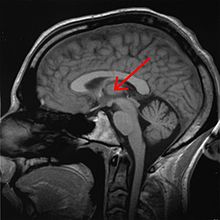
sleep deprivation. The thalamus
is more highly activated when accompanied by sleep deprivation than
when the subject is in a state of rested wakefulness. Contrarily, the
thalamus is more highly activated during difficult tasks accompanied by
rested wakefulness, but not during a state of sleep deprivation.
Researchers propose that the thalamic resources, which are normally
activated during difficult tasks, are being activated in an attempt to
maintain alertness during states of sleep deprivation. In addition, an
increase in thalamic activation is related to a decrease in the
parietal, prefrontal and cingulate cortex
activation, resulting in the overall impairment of attentional
networks, which are necessary for visuospatial attention performance.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) studies indicate that the posterior cingulate
(PCC) and medial prefrontal cortex are involved in the anticipatory
allocation of spatial attention. When sleep-deprived, PCC activity
decreases, impairing selective attention. Subjects were exposed to an
attention-shifting task involving spatially informative, misleading and
uninformative cues preceding the stimuli. When sleep-deprived, subjects
showed increased activation in the left intraparietal sulcus.
This region is activated when exposed to stimuli in unexpected
locations. These findings suggest that sleep-deprived individuals may be
impaired in their ability to anticipate the locations of upcoming
events. In addition, inability to avoid attending to irrelevant events
may also be induced by sleep-deprivation.
By contrast, other studies have indicated that the effects of
sleep deprivation on cognitive performance, specifically, sustained
visual attention, are more global and bilateral
in nature, as opposed to more lateralized deficit explanations. In a
study using the Choice Visual Perception Task, subjects were exposed to
stimuli appearing in various locations in visual space. Results indicate
that sleep deprivation results in a general decline in visual
attention. It is also suggested that the sleep-deprived brain is able to
maintain a certain level of cognitive performance during tasks
requiring divided attention by recruiting additional cortical regions
that are not normally used for such tasks.
Executive function
Executive functioning
is "the ability to plan and coordinate a willful action in the face of
alternatives, to monitor and update action as necessary and suppress
distracting material by focusing attention on the task at hand". The prefrontal cortex has been identified as the most important region involved in executive functioning.
Researchers believe that three of the most 'basic' executive functions are: shifting, updating, and inhibition.
Shifting back and forth between different tasks is considered a very
important mental behavior involved in executive functioning as it
involves active disengagement from the present task and engaging in a
new task. Updating is believed to be involved in working memory (closely associated with the function of the prefrontal cortex),
where the information that is active needs to be updated by replacing
old, now irrelevant information with new, relevant information based on
the objective. Inhibition involves controlled and deliberate impedance of automatic, predominant responses.
The anterior cingulate cortex has been implemented in the process
of inhibiting a habitual response or detecting possible conflicts in
responses; this is shown by the Stroop test.
Studies have found that as little as 36 hours of sleep deprivation
cause a performance reduction in tasks requiring these executive
functions.
The processes above illustrate a model of controlled versus automatic
behavior that was hypothesized by Shallice et al. (1989), called the supervisory attentional system. This system is believed to come into play when intervention of habitual response is necessary. Damage to the prefrontal cortex will cause a breakdown in this system, resulting in utilization behaviors.
These behaviors would include spontaneous sequences of action on
irrelevant objects in the surroundings with no clear goal in mind. This theory has helped to extend the knowledge we now have on executive functions.
Decision making
Decision making
involves a range of executive functions that need to be combined and
organized in order to respond in the most appropriate manner, i.e.
respond with the most advantageous decision.
There are many aspects to the process of decision making, including
those discussed above. Other processes involved that correlate to
executive function will be discussed below.
Complexity
While
most important decisions are made over a longer period of time
involving more in-depth cognitive analysis, usually we have limited time
in which to assimilate a large amount of information into an informed
decision. Lack of sleep appears to negatively affect our ability to
appreciate and respond to increasing complexity, as was found in
performance deficits after 1 night of sleep deprivation on a simulated
marketing game.
The game involved subjects promoting a fictional product while
getting feedback on the financial effects of their decisions. They would
continuously have to take into account new variables to succeed which
would increase the game's complexity.
Other examples of inability to process complex information
includes a decrease in ability to assess facial expressions, an increase
in resolving to the use of stereotypes and racial biases in
evaluations, and an increase in taking the easier solution to solving
interpersonal problems.
Innovation
Intuitively,
because sleep deprivation had a negative effect on handling the
complexity of the simulated marketing game, it also affected innovative
processes as subjects failed to adopt a more innovative (and rewarding)
style of play.
Innovative thinking involves the construction of new behaviors based on
the assimilation of continuously changing or novel information. In a
study of military personnel who had undergone two nights of sleep
deprivation, results showed marked reductions in the ability to generate
ideas about a given topic (categories test); this is known as
ideational fluency.
Approximate Location of the Orbitofrontal cortex.
Risk
Risk versus
reward analysis is an important part of decision making. Attempting to
create a representation and response to a risky situation highly
involves the orbitofrontal cortex.
In a study that involved risk taking analysis of drivers who had been
driving for 12 hours straight, it was found that they were more willing
to make hazardous maneuvers and were reluctant to adopt any form of a
cautious driving style.
Some studies shed further light on this phenomenon. One study
used real life decision making scenarios involving choosing cards from 1
of 4 decks of cards. Different cards were considered as a reward while
the others were a penalty. The sleep deprived subjects failed to alter
their selection methods, continuing to choose cards from decks that were
producing a high amount of penalty cards, whereas the control subjects
were able to change their choosing strategy by a cost-benefit analysis
based on monitoring the outcomes they were getting as they went along.
Planning
The
process of planning would be done congruently with decision making in
determining the outcome behavior. As has been shown so far, sleep
deprivation has many detrimental effects on executive functions and
planning is not spared. One study involved cadets who were required to
complete simulated military operations under sleep deprived conditions.
Results showed a decrease in the subjects ability to 'plan on the fly'
and overall outcomes were less than those for well rested cadets.
Another psychological test used to assess planning and decision making is the Tower of London test.
This test has been widely used in the testing of executive functions as
well as studies of sleep deprived subjects. In a study examining
performance on this test after 45–50 hours of sleep deprivation, it was
found that the sleep deprived subjects not only took longer, but
required more moves to complete the task than did the controls.
Error correction
Being
able to show insight into one's performance on different tasks and
correct or modify those behaviors if they are incorrect is an important
part of executive functioning. The problems that could be associated
with being unable to learn from a mistake or adapt to a mistake could
impair many behaviors.
A common test used to assess error correction and trouble shooting with regards to the frontal lobe is the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. This test involves a change in the rules which requires a shift in strategy. In the same study discussed above, detriments were also found on this task in the sleep deprived individuals.
Memory
Research evidence suggests that sleep is involved in the acquisition, maintenance and retrieval of memories as well as memory consolidation. Subsequently, sleep deprivation has been shown to affect both working memory and long-term memory processes.
Working memory
Sleep
deprivation increases the number of errors made on working memory
tasks. In one study, the working memory task involved illuminating a
sequence of 3 or 4 coloured lights, then asking both sleep deprived and
non-sleep deprived individuals to memorize and repeat back the sequence.
The sleep deprived performed the task much faster than those in the
control condition (i.e., not sleep deprived), which initially appeared
to be a positive effect. However, there was a significant difference in
the number of errors made, with the fatigued group performing much
worse.
Evidence from imaging studies also demonstrates the influence of sleep deprivation on working memory. EEG
studies have documented lower accuracy and slower reaction times among
sleep deprived participants performing working memory tasks. Decreasing
alertness and lack of focus triggered deficits in working memory that
are accompanied by significant degradation of event-related potentials.
PET scans shows global decrease in glucose metabolism in response
to sleep deprivation. As subjects become increasingly impaired on
working memory tasks, a more specific decrease of glucose occurs in the
thalamus, prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex.
fMRI scans following brief sleep deprivation (24 hours or less)
show increases in thalamic activation. Verbal working memory tasks
normally cause increases in left temporal lobe
activity. However, after 35 hours of deprivation, there are noted
decreases in temporal lobe activation and increases in parietal lobe
activation.

Working memory model.
The working memory span is also affected by sleep deprivation. When sleep deprived participants in a study were asked to remember a nonsense word
and locate it among a number of similar words, the length of time they
could hold it in their working memory decreased by 38% compared to
rested individuals.
Long-term memory
One
way sleep is involved in the creation of long-term memories is through
memory consolidation, which is the process by which a new memory is
changed into a more permanent form. This is believed to be accomplished
by creating connections between the medial temporal lobes and
neocortical areas. NREM (non-REM) and REM sleep are both believed to be implicated, with current theories suggesting NREM is most particularly involved in procedural memory and REM with declarative memory.
Animal studies have partly validated these claims. For instance,
one study conducted with rats showed that REM sleep deprivation after
learning a new task disrupted their ability to perform the task again
later. This was especially true if the task was complex (i.e., involved
using unusual information or developing novel adaptive behaviours).
There is similar evidence for the role of sleep in procedural
memory in humans. Participants in one study were trained on a procedural
memory skill involving perceptual-motor skills. Those who were NREM
sleep deprived performed significantly worse on subsequent trials
compared to those who were fully rested.
Another study using a visuo-motor procedural memory task documented
similar results. Participants who were sleep deprived following the
initial training showed no improvement on trials the next day, while
those who received sleep showed significant positive changes.
Studies such as these clearly demonstrate the disruptive influence sleep
deprivation has on memory consolidation of procedural and declarative
memories.
Sleep deprivation also has a documented effect on the ability to
acquire new memories for subsequent consolidation. A study done on mice
that were sleep deprived before learning a new skill but allowed to rest
afterward displayed a similar number of errors on later trials as the
mice that were sleep deprived only after the initial learning.
In this case, it is hypothesized that rather than preventing the memory
from being consolidated, sleep deprivation interfered with the initial
acquisition of the memory. Mice with pre-trial sleep deprivation also
took significantly longer to learn a task than well-rested mice.
Sleep deprivation is also implicated in impaired ability to
retrieve stored long-term memories. When an aversive stimulus was
included in a trial (i.e., a blowdryer would blast hot air and noise at a
mouse), mice that were sleep deprived were less anxious on subsequent
trials. This suggests they had not retrieved all of the memory related
to the unpleasant experience.
Explanations for the effect of sleep deprivation on memory
Several theories have been put forth to explain the effect sleep deprivation has on memory.
One early study into neurochemical influences on sleep and memory
was conducted with cats and demonstrated that sleep deprivation
increased brain protein synthesis.
There is evidence that these altered levels of proteins could increase
the excitability of the central nervous system, thus increasing the
susceptibility of the brain to other neurochemical agents that can cause
amnesia.
Further research has revealed that the protein kinase A (PKA)
signalling pathway is crucial to long-term memory. If PKA or protein
synthesis inhibition occurs at certain moments during sleep, memory
consolidation can be disrupted. In addition, mice with genetic
inhibition of PKA have been shown to have long-term memory deficits. Thus, sleep deprivation may act through the inhibition of these protein synthesis pathways.
Acetylcholine
(ACh) may also be involved in the effects of sleep deprivation,
particularly with regards to spatial memory. Muscarinic antagonists, or
chemicals that block ACh, impair spatial learning when administered
prior to a training task among rats. ACh levels are also found to be
lower when measured following a period of sleep deprivation. ACh has also been shown to increase the activity of the PKA pathway, which is needed for memory consolidation.
Serotonin
levels (in the form of 5-HT) have been shown to decrease during REM and
NREM sleep, leading some researchers to believe that it is also
involved in memory consolidation during sleep. Mice lacking the receptor
gene for 5-HT engage in more REM sleep and perform better on spatial
memory tasks.
Researchers have hypothesized that sleep deprivation interferes with
the normal reduction in levels of 5-HT, impairing the process of memory
consolidation.
Another theory suggests that the stress brought on by sleep
deprivation affects memory consolidation by changing the concentration
of corticosteroids in the body. This was simulated in one study by elevating the concentration of glucocorticoids
during early sleep stages. The observed effects on memory retention the
next day were similar to those obtained from individuals who had
received no sleep.
Sleep deprivation may affect memory by interfering with neuroplasticity as measured by long-term potentiation in the hippocampus.
This reduced plasticity may be the root cause of impairments in both
working memory among humans and spatial memory among rats. Sleep deprivation may additionally affect memory by reducing the proliferation of cells in the hippocampus.
Sleep deprivation has also been associated with decreased overall
membrane excitability of neurons in the brain. Activation of these
membranes is critical for the formation of memories. Mitochondria
play an essential role in modulating neuron excitability, and research
has shown that sleep deprivation is involved in inhibiting mitochondrial
metabolism.
Practical effects
Risk of traffic collisions
Reduced duration of sleep, as well as an increase in time spent awake, are factors that highly contribute to the risk of traffic collisions, the severity and fatality rates of which are on the same level as driving under the influence of alcohol, with 19 hours of wakefulness corresponding to a BAC of 0.05%, and 24 hours of wakefulness corresponding to a BAC of 0.10%.
Compounding this issue is the proven dissociation between objective
performance and subjective alertness; individuals vastly underestimate
the effect that sleep deprivation has on their cognitive performance,
particularly during the circadian night. Much of the effect of acute sleep deprivation can be countered by napping, with longer naps giving more benefit than shorter naps.
Some industries, particularly the Fire Service, have traditionally
allowed workers to sleep while on duty, between calls for service. In
one study of EMS
providers, 24-hour shifts were not associated with a higher frequency
of negative safety outcomes when compared to shorter shifts.
This is especially relevant for young adults as they require 8–9 hours of sleep at night to overcome excessive daytime sleepiness and are among the highest risk group for driving while feeling tired and sleep deprivation related crashes.