From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Early Middle Ages or Early Medieval Period, sometimes referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of European history. The alternative term Late Antiquity, for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while Early Middle Ages is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period. As such the concept overlaps with Late Antiquity, following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, and precedes the High Middle Ages (c. 11th to 13th centuries).
The period saw a continuation of trends evident since late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, a small rise in average temperatures in the North Atlantic region and increased migration. In the 19th century the Early Middle Ages were often labelled the Dark Ages, a characterization based on the relative scarcity of literary and cultural output from this time. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, continued to survive, though in the 7th century the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate conquered swathes of formerly Roman territory.
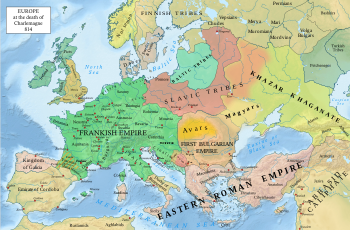
Many of the listed trends reversed later in the period. In 800 the title of Emperor was revived in Western Europe with Charlemagne, whose Carolingian Empire
greatly affected later European social structure and history. Europe
experienced a return to systematic agriculture in the form of the feudal system, which adopted such innovations as three-field planting and the heavy plough. Barbarian migration stabilized in much of Europe, although the Viking expansion greatly affected Northern Europe.
History
Collapse of Rome
Starting in the 2nd century, various indicators of Roman civilization began to decline, including urbanization, seaborne commerce, and population. Archaeologists have identified only 40 percent as many Mediterranean shipwrecks from the 3rd century as from the first. Estimates of the population of the Roman Empire
during the period from 150 to 400 suggest a fall from 65 million to 50
million, a decline of more than 20 percent. Some scholars have connected
this de-population to the Dark Ages Cold Period (300–700), when a decrease in global temperatures impaired agricultural yields.
Die Hunnen im Kampf mit den Alanen, (
The Huns in battle with the Alans by
Johann Nepomuk Geiger, 1873). The
Alans, an
Iranian people who lived north and east of the
Black Sea, functioned as Europe's first line of defence against the Asiatic Huns. They were dislocated and settled throughout the Roman Empire
Early in the 3rd century Germanic peoples migrated south from Scandinavia and reached the Black Sea, creating formidable confederations which opposed the local Sarmatians. In Dacia (present-day Romania) and on the steppes north of the Black Sea the Goths, a Germanic people, established at least two kingdoms: Therving and Greuthung.
The arrival of the Huns
in 372–375 ended the history of these kingdoms. The Huns, a
confederation of central Asian tribes, founded an empire. They had
mastered the difficult art of shooting composite recurve bows
from horseback. The Goths sought refuge in Roman territory (376),
agreeing to enter the Empire as unarmed settlers. However many bribed
the Danube border-guards into allowing them to bring their weapons.
The discipline and organization of a Roman legion
made it a superb fighting unit. The Romans preferred infantry to
cavalry because infantry could be trained to retain the formation in
combat, while cavalry tended to scatter when faced with opposition.
While a barbarian army could be raised and inspired by the promise of
plunder, the legions required a central government and taxation to pay
for salaries, constant training, equipment, and food. The decline in
agricultural and economic activity reduced the empire's taxable income
and thus its ability to maintain a professional army to defend itself
from external threats.
The destruction of the Gothic kingdoms by the
Huns in 372–375 triggered the Germanic migrations of the 5th century. The
Visigoths captured and looted the city of Rome in 410; the
Vandals followed suit in 455
- Germanic tribes
|
- Roman Empire
|
In the Gothic War (376–382), the Goths revolted and confronted the main Roman army in the Battle of Adrianople (378). By this time, the distinction in the Roman army between Roman regulars and barbarian auxiliaries had broken down, and the Roman army
comprised mainly barbarians and soldiers recruited for a single
campaign. The general decline in discipline also led to the use of
smaller shields and lighter weaponry. Not wanting to share the glory, Eastern Emperor Valens ordered an attack on the Therving infantry under Fritigern without waiting for Western Emperor Gratian,
who was on the way with reinforcements. While the Romans were fully
engaged, the Greuthung cavalry arrived. Only one-third of the Roman army
managed to escape. This represented the most shattering defeat that the
Romans had suffered since the Battle of Cannae (216 BC), according to the Roman military writer Ammianus Marcellinus. The core army of the Eastern Roman Empire was destroyed, Valens was killed, and the Goths were freed to lay waste to the Balkans, including the armories along the Danube. As Edward Gibbon comments, "The Romans, who so coolly and so concisely mention the acts of justice
which were exercised by the legions, reserve their compassion and their
eloquence for their own sufferings, when the provinces were invaded and
desolated by the arms of the successful Barbarians."
The empire lacked the resources, and perhaps the will, to
reconstruct the professional mobile army destroyed at Adrianople, so it
had to rely on barbarian armies to fight for it. The Eastern Roman Empire succeeded in buying off the Goths with tribute. The Western Roman Empire proved less fortunate. Stilicho, the western empire's half-Vandal military commander, stripped the Rhine frontier of troops to fend off invasions of Italy by the Visigoths in 402–03 and by other Goths in 406–07.
Fleeing before the advance of the Huns, the Vandals, Suebi, and Alans launched an attack across the frozen Rhine near Mainz; on 31 December 406, the frontier gave way and these tribes surged into Roman Gaul. There soon followed the Burgundians and bands of the Alamanni. In the fit of anti-barbarian hysteria which followed, the Western Roman Emperor Honorius had Stilicho summarily beheaded (408). Stilicho submitted his neck, "with a firmness not unworthy of the last of the Roman generals", wrote Gibbon. Honorius was left with only worthless courtiers to advise him. In 410, the Visigoths led by Alaric I captured the city of Rome
and for three days fire and slaughter ensued as bodies filled the
streets, palaces were stripped of their valuables, and the invaders
interrogated and tortured those citizens thought to have hidden wealth.
As newly converted Christians, the Goths respected church property, but
those who found sanctuary in the Vatican and in other churches were the fortunate few.
Migration Period
Around 500, the
Visigoths ruled large parts of what is now France, Spain, Andorra and Portugal.
The Goths and Vandals were only the first of many bands of peoples that flooded Western Europe in the absence of administrative governance. Some lived only for war and pillage and disdained Roman ways. Other peoples
had been in prolonged contact with the Roman civilization, and were, to
a certain degree, romanized. "A poor Roman plays the Goth, a rich Goth
the Roman" said King Theoderic of the Ostrogoths. The subjects of the Roman empire were a mix of Roman Christian, Arian Christian, Nestorian Christian, and pagan.
The Germanic peoples knew little of cities, money, or writing, and were
mostly pagan, though they were becoming increasingly Arian. Arianism
was a branch of Christianity that was first proposed early in the 4th
century by the Alexandrian presbyter Arius. Arius proclaimed that Christ
is not truly divine but a created being. His basic premise was the
uniqueness of God, who is alone self-existent and immutable; the Son,
who as son is not self-existent, cannot be God.
During the migrations, or Völkerwanderung
(wandering of the peoples), the earlier settled populations were
sometimes left intact though usually partially or entirely displaced.
Roman culture north of the Po River
was almost entirely displaced by the migrations. Whereas the peoples of
France, Italy, Spain and Portugal continued to speak the dialects of
Latin that today constitute the Romance languages,
the language of the smaller Roman-era population of what is now England
disappeared with barely a trace in the territories settled by the
Anglo-Saxons, although the Brittanic kingdoms of the west remained Brythonic
speakers. The new peoples greatly altered established society,
including law, culture, religion, and patterns of property ownership.
The pax Romana
had provided safe conditions for trade and manufacture, and a unified
cultural and educational milieu of far-ranging connections. As this was
lost, it was replaced by the rule of local potentates, sometimes members
of the established Romanized ruling elite, sometimes new lords of alien
culture. In Aquitania, Gallia Narbonensis, southern Italy and Sicily, Baetica or southern Spain, and the Iberian Mediterranean coast, Roman culture lasted until the 6th or 7th centuries.
The gradual breakdown and transformation of economic and social
linkages and infrastructure resulted in increasingly localized outlooks.
This breakdown was often fast and dramatic as it became unsafe to
travel or carry goods over any distance; there was a consequent collapse
in trade and manufacture for export. Major industries that depended on
trade, such as large-scale pottery manufacture, vanished almost
overnight in places like Britain. Tintagel in Cornwall,
as well as several other centres, managed to obtain supplies of
Mediterranean luxury goods well into the 6th century, but then lost
their trading links. Administrative, educational and military
infrastructure quickly vanished, and the loss of the established cursus honorum led to the collapse of the schools and to a rise of illiteracy even among the leadership. The careers of Cassiodorus (died c. 585) at the beginning of this period and of Alcuin of York
(died 804) at its close were founded alike on their valued literacy.
For the formerly Roman area, there was another 20 per cent decline in
population between 400 and 600, or a one-third decline for 150–600. In the 8th century, the volume of trade reached its lowest level. The very small number of shipwrecks
found that dated from the 8th century supports this (which represents
less than 2 per cent of the number of shipwrecks dated from the 1st
century). There was also reforestation and a retreat of agriculture
centred around 500.
The Romans had practiced two-field agriculture,
with a crop grown in one field and the other left fallow and ploughed
under to eliminate weeds. Systematic agriculture largely disappeared and
yields declined. It is estimated that the Plague of Justinian which began in 541 and recurred periodically for 150 years thereafter killed as many as 100 million people across the world.
Some historians such as Josiah C. Russell (1958) have suggested a total
European population loss of 50 to 60 per cent between 541 and 700. After the year 750, major epidemic diseases did not appear again in Europe until the Black Death of the 14th century. The disease smallpox, which was eradicated in the late 20th century, did not definitively enter Western Europe
until about 581 when Bishop Gregory of Tours provided an eyewitness
account that describes the characteristic findings of smallpox. Waves of epidemics wiped out large rural populations. Most of the details about the epidemics are lost, probably due to the scarcity of surviving written records.
For almost a thousand years, Rome was the most politically important, richest and largest city in Europe. Around 100 AD, it had a population of about 450,000,
and declined to a mere 20,000 during the Early Middle Ages, reducing
the sprawling city to groups of inhabited buildings interspersed among
large areas of ruins and vegetation.
Byzantine Empire
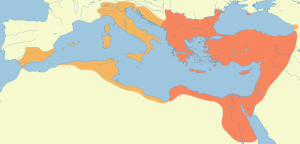
The death of Theodosius I in 395 was followed by the division of the empire between his two sons. The Western Roman Empire disintegrated into a mosaic of warring Germanic kingdoms in the 5th century, effectively making the Eastern Roman Empire in Constantinople the Greek-speaking successor to the classical Roman Empire. To distinguish it from its predominantly Latin-speaking predecessor, historians began referring to the empire as "Byzantine", after the original name of Constantinople, Byzantium. Despite this, the inhabitants of the Byzantine Empire continued to regard themselves as Romans, or Romaioi, until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453.
The Eastern Roman or "Byzantine" Empire aimed to retain control
of the trade routes between Europe and the Orient, which made the Empire
the richest polity in Medieval Europe. Making use of their
sophisticated warfare and superior diplomacy, the Byzantines managed to
fend off assaults by the migrating barbarians. Their dreams of subduing
the Western potentates briefly materialized during the reign of Justinian I
in 527–565. Not only did Justinian restore some western territories to
the Roman Empire, including Rome and the Italian peninsula itself, but
he also codified Roman law (with his codification
remaining in force in many areas of Europe until the 19th century) and
commissioned the building of the largest and most architecturally
advanced edifice of the Early Middle Ages, the Hagia Sophia. However, his reign also saw the outbreak of a bubonic plague pandemic, now known retroactively as the Plague of Justinian.
The Emperor himself was afflicted, and within the span of less than a
year, an estimated 200,000 Constantinopolites—two out of every five city
residents—had died of the disease.
Justinian's successors Maurice and Heraclius confronted invasions by the Avar and Slavic tribes. After the devastations by the Slavs and the Avars, large areas of the Balkans became depopulated. In 626 Constantinople, by far the largest city of early medieval Europe, withstood a combined siege
by Avars and Persians. Within several decades, Heraclius completed a
holy war against the Persians, taking their capital and having a Sassanid monarch assassinated. Yet Heraclius lived to see his spectacular success undone by the Muslim conquests of Syria, three Palaestina provinces, Egypt, and North Africa which was considerably facilitated by religious disunity and the proliferation of heretical movements (notably Monophysitism and Nestorianism) in the areas converted to Islam.
Although Heraclius's successors managed to salvage Constantinople from two Arab sieges (in 674–77 and 717), the empire of the 8th and early 9th century was rocked by the great Iconoclastic Controversy, punctuated by dynastic struggles between various factions at court. The Bulgar and Slavic tribes profited from these disorders and invaded Illyria, Thrace and even Greece. After the decisive victory at Ongala
in 680 the armies of the Bulgars and Slavs advanced to the south of the
Balkan mountains, defeating again the Byzantines who were then forced
to sign a humiliating peace treaty which acknowledged the establishment
of the First Bulgarian Empire on the borders of the Empire.
To counter these threats a new system of administration was
introduced. The regional civil and military administration were combined
in the hands of a general, or strategos. A theme,
which formerly denoted a subdivision of the Byzantine army, came to
refer to a region governed by a strategos. The reform led to the
emergence of great landed families which controlled the regional
military and often pressed their claims to the throne (see Bardas Phocas and Bardas Sklerus for characteristic examples).
By the early 8th century, notwithstanding the shrinking territory of
the empire, Constantinople remained the largest and the wealthiest city
west of China, comparable only to Sassanid Ctesiphon, and later Abassid Baghdad.
The population of the imperial capital fluctuated between 300,000 and
400,000 as the emperors undertook measures to restrain its growth. The
only other large Christian cities were Rome (50,000) and Salonika (30,000).
Even before the 8th century was out, the Farmer's Law signalled the
resurrection of agricultural technologies in the Roman Empire. As the
2006 Encyclopædia Britannica
noted, "the technological base of Byzantine society was more advanced
than that of contemporary western Europe: iron tools could be found in
the villages; water mills dotted the landscape; and field-sown beans
provided a diet rich in protein".
The ascension of the Macedonian dynasty
in 867 marked the end of the period of political and religious turmoil
and introduced a new golden age of the empire. While the talented
generals such as Nicephorus Phocas expanded the frontiers, the Macedonian emperors (such as Leo the Wise and Constantine VII)
presided over the cultural flowering in Constantinople, known as the
Macedonian Renaissance. The enlightened Macedonian rulers scorned the
rulers of Western Europe as illiterate barbarians and maintained a
nominal claim to rule over the West. Although this fiction had been
exploded with the coronation of Charlemagne
in Rome (800), the Byzantine rulers did not treat their Western
counterparts as equals. Generally, they had little interest in political
and economic developments in the barbarian (from their point of view)
West.
Against this economic background the culture and the imperial
traditions of the Eastern Roman Empire attracted its northern
neighbours—Slavs, Bulgars, and Khazars—to Constantinople,
in search of either pillage or enlightenment. The movement of the
Germanic tribes to the south triggered the great migration of the Slavs, who occupied the vacated territories. In the 7th century, they moved westward to the Elbe, southward to the Danube and eastward to the Dnieper.
By the 9th century, the Slavs had expanded into sparsely inhabited
territories to the south and east from these natural frontiers,
peacefully assimilating the indigenous Illyrian and Finnic populations.
Rise of Islam
- 632–750
From the 7th century, Byzantine history was greatly affected by the rise of Islam and the Caliphates. Muslim Arabs first invaded historically Roman territory under Abū Bakr, first Caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, who entered Roman Syria and Roman Mesopotamia. The Byzantines and neighbouring Persian Sasanids had been severely weakened by a long succession of Byzantine–Sasanian wars, especially the climactic Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. Under Umar, the second Caliph, the Muslims decisively conquered Syria and Mesopotamia, as well as Roman Palestine, Roman Egypt, parts of Asia Minor and Roman North Africa, while they entirely toppled the Sasanids. In the mid 7th century, following the Muslim conquest of Persia, Islam penetrated into the Caucasus region, of which parts would later permanently become part of Russia. This expansion of Islam continued under Umar's successors and then the Umayyad Caliphate, which conquered the rest of Mediterranean North Africa and most of the Iberian Peninsula. Over the next centuries Muslim forces were able to take further European territory, including Cyprus, Malta, Septimania, Crete, and Sicily and parts of southern Italy.
The Muslim conquest of Hispania began when the Moors (mostly Berbers and some Arabs) invaded the Christian Visigothic kingdom of Iberia in the year 711, under their Berber leader Tariq ibn Ziyad. They landed at Gibraltar on 30 April and worked their way northward. Tariq's forces were joined the next year by those of his superior, Musa ibn Nusair. During the eight-year campaign most of the Iberian Peninsula was brought under Muslim rule—except for small areas in the north-northwest (Asturias) and largely Basque regions in the Pyrenees. This territory, under the Arab name Al-Andalus, became part of the expanding Umayyad empire.
The unsuccessful second siege of Constantinople (717) weakened the Umayyad dynasty
and reduced their prestige. After their success in overrunning Iberia,
the conquerors moved northeast across the Pyrenees. They were defeated
by the Frankish leader Charles Martel at the Battle of Poitiers in 732. The Umayyads were overthrown in 750 by the Abbāsids and most of the Umayyad clan were massacred.
A surviving Umayyad prince, Abd-ar-rahman I, escaped to Spain and founded a new Umayyad dynasty in the Emirate of Cordoba in 756. Charles Martel's son Pippin the Short retook Narbonne, and his grandson Charlemagne established the Marca Hispanica across the Pyrenees in part of what today is Catalonia, reconquering Girona in 785 and Barcelona in 801. The Umayyads in Hispania proclaimed themselves caliphs in 929.
Birth of the Latin West
700–850
Climatic conditions in Western Europe began to improve after 700. In that year, the two major powers in western Europe were the Franks in Gaul and the Lombards in Italy.
The Lombards had been thoroughly Romanized, and their kingdom was
stable and well developed. The Franks, in contrast, were barely any
different from their barbarian Germanic ancestors. Their kingdom was
weak and divided.
Impossible to guess at the time, but by the end of the century, the
Lombardic kingdom would be extinct, while the Frankish kingdom would
have nearly reassembled the Western Roman Empire.
Though much of Roman civilization north of the Po River
had been wiped out in the years after the end of the Western Roman
Empire, between the 5th and 8th centuries, new political and social
infrastructure began to develop. Much of this was initially Germanic and
pagan. Arian Christian
missionaries had been spreading Arian Christianity throughout northern
Europe, though by 700 the religion of northern Europeans was largely a
mix of Germanic paganism, Christianized paganism, and Arian Christianity. Catholic Christianity had barely started to spread in northern Europe by this time. Through the practice of simony,
local princes typically auctioned off ecclesiastical offices, causing
priests and bishops to function as though they were yet another noble
under the patronage of the prince. In contrast, a network of monasteries
had sprung up as monks sought separation from the world. These
monasteries remained independent from local princes, and as such
constituted the "church" for most northern Europeans during this time.
Being independent from local princes, they increasingly stood out as
centres of learning, of scholarship, and as religious centres where
individuals could receive spiritual or monetary assistance.
The interaction between the culture of the newcomers, their
warband loyalties, the remnants of classical culture, and Christian
influences, produced a new model for society, based in part on feudal obligations.
The centralized administrative systems of the Romans did not withstand
the changes, and the institutional support for chattel slavery largely
disappeared. The Anglo-Saxons in England had also started to convert from Anglo-Saxon polytheism after the arrival of Christian missionaries in 597.
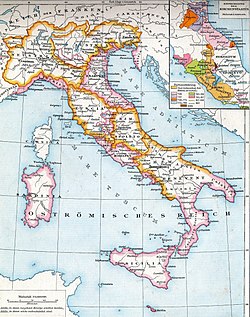
Italy
The Lombard possessions in Italy: The Lombard Kingdom (Neustria, Austria and Tuscia) and the Lombard Duchies of Spoleto and Benevento
The Lombards, who first entered Italy in 568 under Alboin, carved out a state in the north, with its capital at Pavia. At first, they were unable to conquer the Exarchate of Ravenna, the Ducatus Romanus, and Calabria and Apulia. The next two hundred years were occupied in trying to conquer these territories from the Byzantine Empire.
The Lombard state was relatively Romanized, at least when
compared to the Germanic kingdoms in northern Europe. It was highly
decentralized at first, with the territorial dukes having practical
sovereignty in their duchies, especially in the southern duchies of Spoleto and Benevento. For a decade following the death of Cleph in 575, the Lombards did not even elect a king; this period is called the Rule of the Dukes. The first written legal code was composed in poor Latin in 643: the Edictum Rothari. It was primarily the codification of the oral legal tradition of the people.
The Lombard state was well-organized and stabilized by the end of the long reign of Liutprand (717–744), but its collapse was sudden. Unsupported by the dukes, King Desiderius
was defeated and forced to surrender his kingdom to Charlemagne in 774.
The Lombard kingdom ended and a period of Frankish rule was initiated.
The Frankish king Pepin the Short had, by the Donation of Pepin, given the pope the "Papal States" and the territory north of that swath of papally-governed land was ruled primarily by Lombard and Frankish vassals of the Holy Roman Emperor until the rise of the city-states in the 11th and 12th centuries.
In the south, a period of chaos began. The duchy of Benevento
maintained its sovereignty in the face of the pretensions of both the
Western and Eastern Empires. In the 9th century, the Muslims conquered Sicily. The cities on the Tyrrhenian Sea
departed from Byzantine allegiance. Various states owing various
nominal allegiances fought constantly over territory until events came
to a head in the early 11th century with the coming of the Normans, who conquered the whole of the south by the end of the century.
Britain
Roman Britain was in a state of political and economic collapse at the time of the Roman departure c. 400. A series of settlements (traditionally referred to as an invasion) by Germanic peoples
began in the early fifth century, and by the sixth century the island
would consist of many small kingdoms engaged in ongoing warfare with
each other. The Germanic kingdoms are now collectively referred to as Anglo-Saxons.
Christianity began to take hold among the Anglo-Saxons in the sixth
century, with 597 given as the traditional date for its large-scale
adoption.
The
Gokstad ship, a 9th-century Viking
longship, excavated in 1882. Viking Ship Museum, Oslo, Norway
Western Britain (Wales), eastern and northern Scotland (Pictland) and the Scottish highlands and isles continued their separate evolution. The Irish
descended and Irish-influenced people of western Scotland were
Christian from the fifth century onward, the Picts adopted Christianity
in the sixth century under the influence of Columba, and the Welsh had been Christian since the Roman era.
Northumbria was the pre-eminent power c. 600–700, absorbing several weaker Anglo-Saxon and Brythonic kingdoms, while Mercia held a similar status c. 700–800. Wessex
would absorb all of the kingdoms in the south, both Anglo-Saxon and
Briton. In Wales consolidation of power would not begin until the ninth
century under the descendants of Merfyn Frych of Gwynedd, establishing a hierarchy that would last until the Norman invasion of Wales in 1081.
The first Viking raids on Britain began before 800, increasing in scope and destructiveness over time. In 865 a large, well-organized Danish Viking army (called the Great Heathen Army) attempted a conquest, breaking or diminishing Anglo-Saxon power everywhere but in Wessex. Under the leadership of Alfred the Great
and his descendants, Wessex would at first survive, then coexist with,
and eventually conquer the Danes. It would then establish the Kingdom of England and rule until the establishment of an Anglo-Danish kingdom under Cnut, and then again until the Norman Invasion of 1066.
Viking raids and invasion were no less dramatic for the north. Their defeat of the Picts in 839 led to a lasting Norse heritage in northernmost Scotland, and it led to the combination of the Picts and Gaels under the House of Alpin, which became the Kingdom of Alba, the predecessor of the Kingdom of Scotland. The Vikings combined with the Gaels of the Hebrides to become the Gall-Gaidel and establish the Kingdom of the Isles.
Frankish Empire
Charlemagne's empire included most of modern France, Germany,
the Low Countries, Austria and northern Italy.
On 25 December 800,
Charlemagne was crowned emperor by
Pope Leo III.
Coronation of Charlemagne, Grandes Chroniques de France, Jean Fouquet, Tours, c. 1455-1460
The Merovingians established themselves in the power vacuum of the former Roman provinces in Gaul, and Clovis I converted to Christianity following his victory over the Alemanni at the Battle of Tolbiac (496), laying the foundation of the Frankish Empire,
the dominant state of early medieval Western Christendom. The Frankish
kingdom grew through a complex development of conquest, patronage, and
alliance building. Due to salic custom, inheritance rights were absolute, and all land was divided equally among the sons of a dead land holder.
This meant that, when the king granted a prince land in reward for
service, that prince and all of his descendants had an irrevocable right
to that land that no future king could undo. Likewise, those princes
(and their sons) could sublet their land to their own vassals, who could
in turn sublet the land to lower sub-vassals.
This all had the effect of weakening the power of the king as his
kingdom grew, since the result was that the land became controlled not
just by more princes and vassals, but by multiple layers of vassals.
This also allowed his nobles to attempt to build their own power base,
though given the strict salic tradition of hereditary kingship, few
would ever consider overthrowing the king.
This increasingly absurd arrangement was highlighted by Charles Martel, who as Mayor of the Palace was effectively the strongest prince in the kingdom. His accomplishments were highlighted, not just by his famous defeat of invading Muslims at the Battle of Tours,
which is typically considered the battle that saved Europe from Muslim
conquest, but by the fact that he greatly expanded Frankish influence.
It was under his patronage that Saint Boniface
expanded Frankish influence into Germany by rebuilding the German
church, with the result that, within a century, the German church was
the strongest church in western Europe.
Yet despite this, Charles Martel refused to overthrow the Frankish
king. His son, Pepin the Short, inherited his power, and used it to
further expand Frankish influence. Unlike his father, however, Pepin
decided to seize the Frankish kingship. Given how strongly Frankish
culture held to its principle of inheritance, few would support him if
he attempted to overthrow the king. Instead, he sought the assistance of Pope Zachary, who was himself newly vulnerable due to fallout with the Byzantine Emperor over the Iconoclastic Controversy. Pepin agreed to support the pope and to give him land (the Donation of Pepin,
which created the Papal States) in exchange for being consecrated as
the new Frankish king. Given that Pepin's claim to the kingship was now
based on an authority higher than Frankish custom, no resistance was
offered to Pepin. With this, the Merovingian line of kings ended, and the Carolingian line began.
Pepin's son Charlemagne
continued in the footsteps of his father and grandfather. He further
expanded and consolidated the Frankish kingdom (now commonly called the Carolingian Empire). His reign also saw a cultural rebirth, commonly called the Carolingian Renaissance. Though the exact reasons are unclear, Charlemagne was crowned "Roman Emperor" by Pope Leo III
on Christmas Day, 800. Upon Charlemagne's death, his empire had united
much of modern-day France, western Germany and northern Italy. The years
after his death illustrated how Germanic his empire remained.
Rather than an orderly succession, his empire was divided in accordance
with Frankish inheritance custom, which resulted in instability that
plagued his empire until the last king of a united empire, Charles the Fat, died in 887, which resulted in a permanent split of the empire into West Francia and East Francia.
West Francia would be ruled by Carolingians until 987 and East Francia
until 911, after which time the partition of the empire into France and
Germany was complete.
Feudalism
Around 800 there was a return to systematic agriculture in the form of the open field, or strip, system. A manor would have several fields, each subdivided into 1-acre (4,000 m2)
strips of land. An acre measured one "furlong" of 220 yards by one
"chain" of 22 yards (that is, about 200 m by 20 m). A furlong (from
"furrow long") was considered to be the distance an ox could plough
before taking a rest; the strip shape of the acre field also reflected
the difficulty in turning early heavy ploughs. In the idealized form of
the system, each family got thirty such strips of land. The three-field
system of crop rotation
was first developed in the 9th century: wheat or rye was planted in one
field, the second field had a nitrogen-fixing crop, and the third was
fallow.
Compared to the earlier two-field system, a three-field system
allowed for significantly more land to be put under cultivation. Even
more important, the system allowed for two harvests a year, reducing the
risk that a single crop failure will lead to famine. Three-field
agriculture created a surplus of oats that could be used to feed horses.
This surplus allowed for the replacement of the ox by the horse after
the introduction of the padded horse collar
in the 12th century. Because the system required a major rearrangement
of real estate and of the social order, it took until the 11th century
before it came into general use. The heavy wheeled plough was introduced
in the late 10th century. It required greater animal power and promoted
the use of teams of oxen. Illuminated manuscripts depict two-wheeled
ploughs with both a mouldboard, or curved metal ploughshare, and a
coulter, a vertical blade in front of the ploughshare. The Romans had
used light, wheel-less ploughs with flat iron shares that often proved
unequal to the heavy soils of northern Europe.
The return to systemic agriculture coincided with the introduction of a new social system called feudalism.
This system featured a hierarchy of reciprocal obligations. Each man
was bound to serve his superior in return for the latter's protection.
This made for confusion of territorial sovereignty since allegiances
were subject to change over time and were sometimes mutually
contradictory. Feudalism allowed the state to provide a degree of public
safety despite the continued absence of bureaucracy and written
records.
Manors became largely self-sufficient, and the volume of trade
along long-distance routes and in market towns declined during this
period, though never ceased entirely. Roman roads decayed and
long-distance trade depended more heavily on water transport.
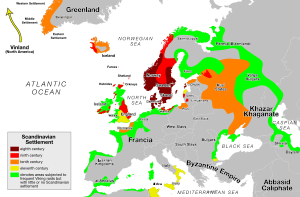
Viking Age
Scandinavian settlements and raiding territory. Note : yellow in England and southern Italy covers the Viking expansion from
Normandy, called by the name of Norman
- 8th century homeland
- 9th century expansion
- 10th century expansion
Viking raiding regions
The Viking Age spans the period roughly between the late 8th and mid-11th centuries in Scandinavia and Britain, following the Germanic Iron Age (and the Vendel Age in Sweden). During this period, the Vikings, Scandinavian warriors and traders raided and explored most parts of Europe, south-western Asia, northern Africa, and north-eastern North America.
With the means to travel (longships and open water), desire for
goods led Scandinavian traders to explore and develop extensive trading
partnerships in new territories. Some of the most important trading
ports during the period include both existing and ancient cities such as
Aarhus, Ribe, Hedeby, Vineta, Truso, Kaupang, Birka, Bordeaux, York, Dublin, and Aldeigjuborg.
Viking raiding expeditions were separate from, though coexisted
with, regular trading expeditions. Apart from exploring Europe via its
oceans and rivers, with the aid of their advanced navigational skills,
they extended their trading routes across vast parts of the continent.
They also engaged in warfare, looting and enslaving numerous Christian
communities of Medieval Europe for centuries, contributing to the
development of feudal systems in Europe.
Eastern Europe
- 600–1000
Main articles:
Byzantine Empire,
Western Turkic Khaganate,
Avar Khaganate,
Khazar Khaganate,
Old Great Bulgaria,
Alani,
Magyars,
Slavic migrations to the Balkans,
Principality of Serbia (early medieval),
Great Moravia, and
Duchy of Croatia
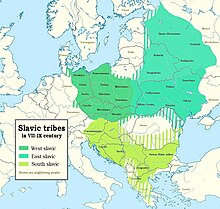
Slavic tribes in eastern Europe during the 7th to 9th centuries
The Early Middle Ages marked the beginning of the cultural
distinctions between Western and Eastern Europe north of the
Mediterranean. Influence from the Byzantine Empire
impacted the Christianization and hence almost every aspect of the
cultural and political development of the East from the preeminence of Caesaropapism and Eastern Christianity to the spread of the Cyrillic alphabet. The turmoil of the so-called Barbarian invasions
in the beginning of the period gradually gave way to more stabilized
societies and states as the origins of contemporary Eastern Europe began
to take shape during the High Middle Ages.
Magyar campaigns in the 10th century
Magyar region
Most European nations were praying for mercy: "Sagittis hungarorum
libera nos, Domine" - "Lord save us from the arrows of Hungarians"
Turkic and Iranian invaders from Central Asia pressured the agricultural populations both in the Byzantine Balkans and in Central Europe creating a number of successor states in the Pontic steppes. After the dissolution of the Hunnic Empire, the Western Turkic and Avar Khaganates dominated territories from Pannonia to the Caspian Sea before replaced by the short lived Old Great Bulgaria and the more successful Khazar Khaganate north of the Black Sea and the Magyars in Central Europe.
The Khazars
were a nomadic Turkic people who managed to develop a multiethnic
commercial state which owed its success to the control of much of the
waterway trade between Europe and Central Asia. The Khazars also exacted
tribute from the Alani, Magyars, various Slavic tribes, the Crimean Goths, and the Greeks of Crimea. Through a network of Jewish itinerant merchants, or Radhanites, they were in contact with the trade emporia of India and Spain.
Once they found themselves confronted by Arab expansionism, the Khazars pragmatically allied themselves with Constantinople and clashed with the Caliphate. Despite initial setbacks, they managed to recover Derbent and eventually penetrated as far south as Caucasian Iberia, Caucasian Albania and Armenia. In doing so, they effectively blocked the northward expansion of Islam into Eastern Europe even before khan Tervel achieved the same at the Second Arab Siege of Constantinople and several decades before the Battle of Tours in Western Europe. Islam eventually penetrated into Eastern Europe in the 920s when Volga Bulgaria exploited the decline of Khazar power in the region to adopt Islam from the Baghdad missionaries. The state religion of Khazaria, Judaism,
disappeared as a political force with the fall of Khazaria, while Islam
of Volga Bulgaria has survived in the region up to the present.
In the beginning of the period, the Slavic tribes started to expand aggressively into Byzantine possessions on the Balkans. The first attested Slavic polities were Serbia and Great Moravia,
the latter of which emerged under the aegis of the Frankish Empire in
the early 9th century. Great Moravia was ultimately overrun by the Magyars, who invaded the Pannonian Basin
around 896. The Slavic state became a stage for confrontation between
the Christian missionaries from Constantinople and Rome. Although West Slavs, Croats and Slovenes
eventually acknowledged Roman ecclesiastical authority, the clergy of
Constantinople succeeded in converting to Eastern Christianity two of
the largest states of early medieval Europe, Bulgaria around 864, and Kievan Rus' circa 990.
Bulgaria
Ceramic icon of
St Theodore from around 900, found in
Preslav, Bulgarian capital from 893 to 972
In 632 the Bulgars established the khanate of Old Great Bulgaria under the leadership of Kubrat. The Khazars managed to oust the Bulgars from Southern Ukraine into lands along middle Volga (Volga Bulgaria) and along lower Danube (Danube Bulgaria).
In 681 the Bulgars founded a powerful and ethnically diverse state that played a defining role in the history of early medieval Southeastern Europe. Bulgaria withstood the pressure from Pontic steppe tribes like the Pechenegs, Khazars, and Cumans, and in 806 destroyed the Avar
Khanate. The Danube Bulgars were quickly slavicized and, despite
constant campaigning against Constantinople, accepted Christianity from
the Byzantine Empire. Through the efforts of missionaries Saint Cyril and Saint Methodius, mainly their disciples like Clement of Ohrid and Saint Naum, the spread, initially of the Glagolitic, and later of the Cyrillic alphabet, developed in the capital Preslav. The local vernacular dialect, now known as Old Bulgarian or Old Church Slavonic, was established as the language of books and liturgy among Orthodox Christian Slavs.
After the adoption of Christianity in 864, Bulgaria became a cultural and spiritual hub of the Eastern Orthodox Slavic world. The Cyrillic script was developed around 885–886, and was afterwards also introduced with books to Serbia and Kievan Rus'. Literature, art, and architecture were thriving with the establishment of the Preslav and Ohrid Literary Schools along with the distinct Preslav Ceramics School. In 927 the Bulgarian Orthodox Church was the first European national Church to gain independence with its own Patriarch while conducting services in the vernacular Old Church Slavonic.
Under Simeon I
(893–927), the state was the largest and one of the most powerful
political entities of Europe, and it consistently threatened the
existence of the Byzantine empire. From the middle of the 10th century
Bulgaria was in decline as it entered a social and spiritual turmoil. It
was in part due to Simeon's devastating wars, but was also exacerbated
by a series of successful Byzantine military campaigns. Bulgaria was
conquered after a long resistance in 1018.
Kievan Rus'
Led by a Varangian dynasty, the Kievan Rus' controlled the routes connecting Northern Europe to Byzantium and to the Orient (for example: the Volga trade route). The Kievan state began with the rule (882–912) of Prince Oleg, who extended his control from Novgorod southwards along the Dnieper river valley in order to protect trade from Khazar incursions from the east and moved his capital to the more strategic Kiev. Sviatoslav I (died 972) achieved the first major expansion of Kievan Rus' territorial control, fighting a war of conquest against the Khazar Empire and inflicting a serious blow on Bulgaria. A Rus' attack
(967 or 968), instigated by the Byzantines, led to the collapse of the
Bulgarian state and the occupation of the east of the country by the
Rus'. An ensuing direct military confrontation between the Rus' and Byzantium (970-971) ended with a Byzantine victory (971). The Rus' withdrew and the Byzantine Empire incorporated eastern Bulgaria. Both before and after their conversion to Christianity (conventionally dated 988 under Vladimir I of Kiev—known
as Vladimir the Great), the Rus' also embarked on predatory military
campaigns against the Byzantine Empire, some of which resulted in trade
treaties. The importance of Russo-Byzantine relations to Constantinople
was highlighted by the fact that Vladimir I of Kiev, son of Svyatoslav
I, became the only foreigner to marry (989) a Byzantine princess of the Macedonian dynasty (which ruled the Eastern Roman Empire from 867 to 1056), a singular honour sought in vain by many other rulers.
Transmission of learning
With the end of the Western Roman Empire and with urban centres in
decline, literacy and learning decreased in the West. This continued a
pattern that had been underway since the 3rd century.
Much learning under the Roman Empire was in Greek, and with the
re-emergence of the wall between east and west, little eastern learning
continued in the west. Much of the Greek literary corpus remained in
Greek, and few in the west could speak or read Greek.
Due to the demographic displacement that accompanied the end of the
western Roman Empire, by this point most western Europeans were
descendants of non-literate barbarians rather than literate Romans. In
this sense, education was not lost so much as it had yet to be acquired.
Education did ultimately continue, and was centred in the
monasteries and cathedrals. A "Renaissance" of classical education would
appear in Carolingian Empire in the 8th century. In the Eastern Roman
Empire (Byzantium), learning (in the sense of formal education involving
literature) was maintained at a higher level than in the West. The
classical education system, which would persist for hundreds of years,
emphasized grammar, Latin, Greek, and rhetoric. Pupils read and reread
classic works and wrote essays imitating their style. By the 4th
century, this education system was Christianized. In De Doctrina Christiana (started 396, completed 426), Augustine
explained how classical education fits into the Christian worldview:
Christianity is a religion of the book, so Christians must be literate. Tertullian was more skeptical of the value of classical learning, asking "What indeed has Athens to do with Jerusalem?"
De-urbanization reduced the scope of education, and by the 6th
century teaching and learning moved to monastic and cathedral schools,
with the study of biblical texts at the centre of education.
Education of the laity continued with little interruption in Italy,
Spain, and the southern part of Gaul, where Roman influences were more
long-lasting. In the 7th century, however, learning expanded in Ireland
and the Celtic lands, where Latin was a foreign language and Latin texts
were eagerly studied and taught.
Science
In the ancient world, Greek was the primary language of science.
Advanced scientific research and teaching was mainly carried on in the Hellenistic side of the Roman empire, and in Greek. Late Roman attempts to translate Greek writings into Latin had limited success.
As the knowledge of Greek declined, the Latin West found itself cut off
from some of its Greek philosophical and scientific roots. For a time,
Latin-speakers who wanted to learn about science had access to only a
couple of books by Boethius (c. 470–524) that summarized Greek handbooks by Nicomachus of Gerasa. Saint Isidore of Seville
produced a Latin encyclopedia in 630. Private libraries would have
existed, and monasteries would also keep various kinds of texts.
The study of nature was pursued more for practical reasons than
as an abstract inquiry: the need to care for the sick led to the study
of medicine and of ancient texts on drugs; the need for monks to determine the proper time to pray led them to study the motion of the stars; and the need to compute the date of Easter led them to study and teach mathematics and the motions of the Sun and Moon.
Carolingian Renaissance
In the late 8th century, there was renewed interest in Classical Antiquity as part of the Carolingian Renaissance. Charlemagne carried out a reform in education. The English monk Alcuin of York
elaborated a project of scholarly development aimed at resuscitating
classical knowledge by establishing programs of study based upon the
seven liberal arts: the trivium, or literary education (grammar, rhetoric, and dialectic), and the quadrivium, or scientific education (arithmetic, geometry, astronomy, and music). From 787 on, decrees began to circulate recommending the restoration of old schools and the founding of new ones across the empire.
Institutionally, these new schools were either under the responsibility of a monastery (monastic schools), a cathedral, or a noble court. The teaching of dialectic (a discipline that corresponds to today's logic) was responsible for the increase in the interest in speculative inquiry; from this interest would follow the rise of the Scholastic tradition of Christian philosophy. In the 12th and 13th centuries, many of those schools founded under the auspices of Charlemagne, especially cathedral schools, would become universities.
Byzantium's golden age
Byzantium's great intellectual achievement was the Corpus Juris Civilis ("Body of Civil Law"), a massive compilation of Roman law made under Justinian (r. 528–65). The work includes a section called the Digesta
which abstracts the principles of Roman law in such a way that they can
be applied to any situation. The level of literacy was considerably
higher in the Byzantine Empire than in the Latin West. Elementary
education was much more widely available, sometimes even in the
countryside. Secondary schools still taught the Iliad and other classics.
As for higher education, the Neoplatonic Academy in Athens was closed in 526. There was also a school in Alexandria which remained open until the Arab conquest (640). The University of Constantinople, founded by Emperor Theodosius II (425), seems to have dissolved around this time. It was refounded by Emperor Michael III in 849. Higher education in this period focused on rhetoric, although Aristotle's
logic was covered in simple outline. Under the Macedonian dynasty
(867–1056), Byzantium enjoyed a golden age and a revival of classical
learning. There was little original research, but many lexicons,
anthologies, encyclopedias, and commentaries.
Islamic learning
In the course of the 11th century, Islam's scientific knowledge began to reach Western Europe, via Islamic Spain. The works of Euclid and Archimedes, lost in the West, were translated from Arabic to Latin in Spain. The modern Hindu–Arabic numeral system,
including a notation for zero, were developed by Hindu mathematicians
in the 5th and 6th centuries. Muslim mathematicians learned of it in the
7th century and added a notation for decimal fractions in the 9th and
10th centuries. Around 1000, Gerbert of Aurillac (later Pope Sylvester II) made an abacus with counters engraved with Arabic numerals. A treatise by Al-Khwārizmī on how to perform calculations with these numerals was translated into Latin in Spain in the 12th century.
Monasteries
Monasteries were targeted in the eighth and ninth centuries by Vikings
who invaded the coasts of northern Europe. They were targeted not only
because they stored books but also precious objects that were looted by
invaders. In the earliest monasteries, there were no special rooms set
aside as a library, but from the sixth century onwards libraries became
an essential aspect of monastic life in Western Europe. The Benedictines
placed books in the care of a librarian who supervised their use. In
some monastic reading rooms, valuable books would be chained to shelves,
but there were also lending sections as well. Copying was also another
important aspect of monastic libraries, this was undertaken by resident
or visiting monks and took place in the scriptorium.
In the Byzantine world, religious houses rarely maintained their own
copying centres. Instead they acquired donations from wealthy donors. In
the tenth century, the largest collection in the Byzantine world was
found in the monasteries of Mount Athos
(modern-day Greece), which accumulated over 10,000 books. Scholars
travelled from one monastery to another in search of the texts they
wished to study. Travelling monks were often given funds to buy books,
and certain monasteries which held a reputation for intellectual
activities welcomed travelling monks who came to copy manuscripts for
their own libraries. One of these was the monastery of Bobbio in Italy, which was founded by the Irish abbot St. Columbanus
in 614, and by the ninth century boasted a catalogue of 666
manuscripts, including religious works, classical texts, histories and
mathematical treatises.
Christianity West and East
From the early Christians,
early medieval Christians inherited a church united by major creeds, a
stable Biblical canon, and a well-developed philosophical tradition. The
history of medieval Christianity
traces Christianity during the Middle Ages—the period after the fall of
the Western Roman Empire until the Protestant Reformation. The
institutional structure of Christianity in the west during this period
is different from what it would become later in the Middle Ages. As
opposed to the later church, the church of the early Middle Ages
consisted primarily of the monasteries. The practice of simony
has caused the ecclesiastical offices to become the property of local
princes, and as such the monasteries constituted the only church
institution independent of the local princes. In addition, the papacy was relatively weak, and its power was mostly confined to central Italy. Individualized religious practice was uncommon, as it typically required membership in a religious order, such as the Order of Saint Benedict.
Religious orders would not proliferate until the high Middle Ages. For
the typical Christian at this time, religious participation was largely
confined to occasionally receiving mass from wandering monks. Few would
be lucky enough to receive this as often as once a month.
By the end of this period, individual practice of religion was becoming
more common, as monasteries started to transform into something
approximating modern churches, where some monks might even give
occasional sermons.
During the early Middle Ages, the divide between Eastern and Western Christianity widened, paving the way for the East-West Schism in the 11th century. In the West, the power of the Bishop of Rome expanded. In 607, Boniface III became the first Bishop of Rome to use the title Pope. Pope Gregory I
used his office as a temporal power, expanded Rome's missionary efforts
to the British Isles, and laid the foundations for the expansion of
monastic orders. Roman church traditions and practices gradually
replaced local variants, including Celtic Christianity
in Great Britain and Ireland. Various barbarian tribes went from
raiding and pillaging the island to invading and settling. They were
entirely pagan, having never been part of the Empire, though they
experienced Christian influence from the surrounding peoples, such as
those who were converted by the mission of St. Augustine of Canterbury, sent by Pope Gregory I. In the East, the conquests of Islam reduced the power of the Greek-speaking patriarchates.
Christianization of the West
The Catholic Church, the only centralized institution to survive the fall of the Western Roman Empire
intact, was the sole unifying cultural influence in the West,
preserving Latin learning, maintaining the art of writing, and
preserving a centralized administration through its network of bishops
ordained in succession. The Early Middle Ages are characterized by the
urban control of bishops and the territorial control exercised by dukes
and counts. The rise of urban communes marked the beginning of the High Middle Ages.
The Christianization of Germanic tribes began in the 4th century with the Goths and continued throughout the Early Middle Ages, led in the 6th to 7th centuries by the Hiberno-Scottish mission and replaced in the 8th to 9th centuries by the Anglo-Saxon mission, with Anglo-Saxons like Alcuin playing an important role in the Carolingian renaissance. Saint Boniface,
the Apostle of the Germans, propagated Christianity in the Frankish
Empire during the 8th century. He helped shape Western Christianity, and
many of the dioceses he proposed remain until today. After his
martyrdom, he was quickly hailed as a saint. By 1000, even Iceland had become Christian, leaving only more remote parts of Europe (Scandinavia, the Baltic, and Finnic lands) to be Christianized during the High Middle Ages.
Holy Roman Empire
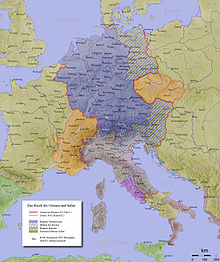
10th century
HRE in era from Emperor
Otto I to
Konrad II
included present-day: Germany, the Czech Republic, Austria, Slovenia,
northern half of Italy, Switzerland, (south)eastern France, Belgium and
the Netherlands
- Imperial region
- Other regions
Listless and often ill, Carolingian Emperor Charles the Fat provoked an uprising, led by his nephew Arnulf of Carinthia,
which resulted in the division of the empire in 887 into the kingdoms
of France, Germany, and (northern) Italy. Taking advantage of the
weakness of the German government, the Magyars had established
themselves in the Alföld, or Hungarian grasslands, and began raiding across Germany, Italy, and even France. The German nobles elected Henry the Fowler,
duke of Saxony, as their king at a Reichstag, or national assembly, in
Fritzlar in 919. Henry's power was only marginally greater than that of
the other leaders of the stem duchies, which were the feudal expression
of the former German tribes.
Henry's son King Otto I (r. 936–973) was able to defeat a revolt of the dukes supported by French King Louis IV (939). In 951, Otto marched into Italy and married the widowed Queen Adelaide, named himself king of the Lombards, and received homage from Berengar of Ivrea,
king of Italy (r. 950–52). Otto named his relatives the new leaders of
the stem duchies, but this approach did not completely solve the problem
of disloyalty. His son Liudolf, duke of Swabia, revolted and welcomed
the Magyars into Germany (953). At Lechfeld,
near Augsburg in Bavaria, Otto caught up with the Magyars while they
were enjoying a razzia and achieved a signal victory in 955. The Magyars
ceased living on plunder, and their leaders created a Christian kingdom
called Hungary (1000).
Founding of the Holy Roman Empire
The defeat of the Magyars greatly enhanced Otto's prestige. He marched into Italy again and was crowned emperor (imperator augustus) by Pope John XII in Rome (962), an event that historians count as the founding of the Holy Roman Empire, although the term was not used until much later. The Ottonian state is also considered the first Reich,
or German Empire. Otto used the imperial title without attaching it to
any territory. He and later emperors thought of themselves as part of a
continuous line of emperors that begins with Charlemagne. (Several of
these "emperors" were simply local Italian magnates who bullied the pope
into crowning them.) Otto deposed John XII for conspiring against him
with Berengar, and he named Pope Leo VIII
to replace him (963). Berengar was captured and taken to Germany. John
was able to reverse the deposition after Otto left, but he died in the
arms of his mistress soon afterwards.
Besides founding the German Empire, Otto's achievements include
the creation of the "Ottonian church system," in which the clergy (the
only literate section of the population) assumed the duties of an
imperial civil service. He raised the papacy out of the muck of Rome's
local gangster politics, assured that the position was competently
filled, and gave it a dignity that allowed it to assume leadership of an
international church.
Europe in 1000
Speculation that the world would end in the year 1000 was confined to a few uneasy French monks. Ordinary clerks used regnal years,
i.e. the 4th year of the reign of Robert II (the Pious) of France. The
use of the modern "anno domini" system of dating was confined to the Venerable Bede and other chroniclers of universal history.
Western Europe remained less developed compared to the Islamic
world, with its vast network of caravan trade, or China, at this time
the world's most populous empire under the Song Dynasty. Constantinople had a population of about 300,000, but Rome had a mere 35,000 and Paris 20,000. By contrast, Córdoba, in Islamic Spain, at this time the world's largest city contained 450,000 inhabitants. The Vikings had a trade network in northern Europe, including a route connecting the Baltic to Constantinople through Russia, as did the Radhanites.
With nearly the entire nation freshly ravaged by the Vikings, England
was in a desperate state. The long-suffering English later responded
with a massacre of Danish settlers in 1002, leading to a round of
reprisals and finally to Danish rule (1013), though England regained
independence shortly after. But Christianization made rapid progress and
proved itself the long-term solution to the problem of barbarian
raiding. The territories of Scandinavia were soon to be fully
Christianized Kingdoms: Denmark in the 10th century, Norway in the 11th, and Sweden, the country with the least raiding activity, in the 12th. Kievan Rus, recently converted to Orthodox Christianity, flourished as the largest state in Europe. Iceland, Greenland, and Hungary were all declared Christian about 1000.
In Europe, a formalized institution of marriage was established. The proscribed degree of consanguinity varied, but the custom made marriages annullable by application to the Pope.
North of Italy, where masonry construction was never extinguished,
stone construction was replacing timber in important structures.
Deforestation of the densely wooded continent was under way. The 10th
century marked a return of urban life, with the Italian cities doubling
in population. London, abandoned for many centuries, was again England's main economic centre by 1000. By 1000, Bruges and Ghent held regular trade fairs behind castle walls, a tentative return of economic life to western Europe.
In the culture of Europe, several features surfaced soon after 1000 that mark the end of the Early Middle Ages: the rise of the medieval communes, the reawakening of city life, and the appearance of the burgher class, the founding of the first universities, the rediscovery of Roman law, and the beginnings of vernacular literature.
In 1000, the papacy was firmly under the control of German Emperor Otto III, or "emperor of the world" as he styled himself. But later church reforms enhanced its independence and prestige: the Cluniac movement, the building of the first great Transalpine stone cathedrals and the collation of the mass of accumulated decretals into a formulated canon law.
Middle East
Rise of Islam
Consult particular article for details
The Islamic Prophet Muhammad preaching
Arab expansion in the 7th century
- Area I : Muhammad
- Area II : Abu Bakr
- Area III : Omar
- Area IV : Uthman
The 10th-century
Grand Mosque of Cordoba
(Andalusian city, Córdoba, Spain)
The site of the Grand Mosque was originally a pagan temple, then a
Visigothic Christian church, before the Umayyad Moors at first converted
the building into a mosque and then built a new mosque on the site.
The rise of Islam begins around the time Muhammad and his followers took flight, the Hijra, to the city of Medina. Muhammad spent his last ten years in a series of battles to conquer the Arabian region.
From 622 to 632, Muhammad as the leader of a Muslim community in Medina
was engaged in a state of war with the Meccans. In the proceeding
decades, the area of Basra was conquered by the Muslims. During the reign of Umar, the Muslim army found it a suitable place to construct a base. Later the area was settled and a mosque was erected. Madyan was conquered and settled by Muslims, but the environment was considered harsh and the settlers moved to Kufa.
Umar defeated the rebellion of several Arab tribes in a successful
campaign, unifying the entire Arabian peninsula and giving it stability.
Under Uthman's leadership, the empire, through the Muslim conquest of Persia, expanded into Fars in 650, some areas of Khorasan
in 651, and the conquest of Armenia was begun in the 640s. In this
time, the Islamic empire extended over the whole Sassanid Persian Empire
and to more than two-thirds of the Eastern Roman Empire. The First Fitna, or the First Islamic Civil War, lasted for the entirety of Ali ibn Abi Talib's reign. After the recorded peace treaty with Hassan ibn Ali and the suppression of early Kharijites' disturbances, Muawiyah I acceded to the position of Caliph.
Islamic expansion
The Islamic expansion of the 7th and 8th centuries
Muhammad's conquests, 622–632
Rashidun Caliphate, 632–661
Umayyad Caliphate, 661–750
The Muslim conquests of the Eastern Roman Empire and Arab wars occurred between 634 and 750. Starting in 633, Muslims conquered Iraq. The Muslim conquest of Syria would begin in 634 and would be complete by 638. The Muslim conquest of Egypt started in 639. Before the Muslim invasion of Egypt began, the Eastern Roman Empire had already lost the Levant and its Arab ally, the Ghassanid Kingdom,
to the Muslims. The Muslims would bring Alexandria under control and
the fall of Egypt would be complete by 642. Between 647 and 709, Muslims swept across North Africa and established their authority over that region.
The Transoxiana region was conquered by Qutayba ibn Muslim between 706 and 715 and loosely held by the Umayyads from 715 to 738. This conquest was consolidated by Nasr ibn Sayyar between 738 and 740. It was under the Umayyads from 740 to 748 and under the Abbasids after 748. Sindh, attacked in 664, would be subjugated by 712. Sindh became the easternmost province of the Umayyad. The Umayyad conquest of Hispania (Visigothic Spain) would begin in 711 and end by 718. The Moors, under Al-Samh ibn Malik, swept up the Iberian peninsula and by 719 overran Septimania; the area would fall under their full control in 720. With the Islamic conquest of Persia, the Muslim subjugation of the Caucasus
would take place between 711 and 750. The end of the sudden Islamic
Caliphate expansion ended around this time. The final Islamic dominion
eroded the areas of the Iron Age Roman Empire in the Middle East and
controlled strategic areas of the Mediterranean.
At the end of the 8th century, the former Western Roman Empire was decentralized and overwhelmingly rural. The Islamic conquest and rule of Sicily and Malta
was a process which started in the 9th century. Islamic rule over
Sicily was effective from 902, and the complete rule of the island
lasted from 965 until 1061. The Islamic presence on the Italian
Peninsula was ephemeral and limited mostly to semi-permanent soldier
camps.
Caliphs and empire
The Abbasid Caliphate, ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs, was the third of the Islamic caliphates. Under the Abbasids, the Islamic Golden Age
philosophers, scientists, and engineers of the Islamic world
contributed enormously to technology, both by preserving earlier
traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations.
Scientific and intellectual achievements blossomed in the period.
The Abbasids built their capital in Baghdad after replacing the
Umayyad caliphs from all but the Iberian peninsula. The influence held
by Muslim merchants over African-Arabian and Arabian-Asian trade routes
was tremendous. As a result, Islamic civilization grew and expanded on
the basis of its merchant economy, in contrast to their Christian,
Indian, and Chinese peers who built societies from an agricultural
landholding nobility.
The Abbasids flourished for two centuries but slowly went into
decline with the rise to power of the Turkish army they had created, the
Mamluks.
Within 150 years of gaining control of Persia, the caliphs were forced
to cede power to local dynastic emirs who only nominally acknowledged
their authority. After the Abbasids lost their military dominance, the Samanids
(or Samanid Empire) rose up in Central Asia. The Sunni Islam empire was
a Tajik state and had a Zoroastrian theocratic nobility. It was the
next native Persian dynasty after the collapse of the Sassanid Persian
empire, caused by the Arab conquest.
European timelines
Beginning years
- Dates
Ending years
- Dates