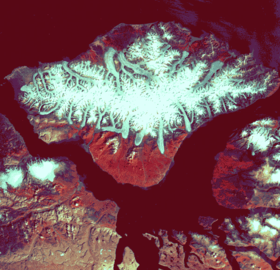
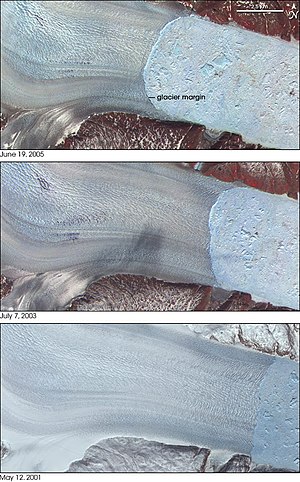
White Chuck Glacier in 1973
Glacier mass balance is the key determinant of the health of a glacier. If the amount of frozen precipitation in the accumulation zone exceeds the quantity of glacial ice lost due to melting or in the ablation zone
a glacier will advance; if the accumulation is less than the ablation,
the glacier will retreat. Glaciers in retreat will have negative mass
balances, and if they do not find an equilibrium between accumulation
and ablation, will eventually disappear.
The Little Ice Age
was a period from about 1550 to 1850 when the world experienced
relatively cooler temperatures compared to the present. Subsequently,
until about 1940, glaciers around the world retreated as the climate
warmed substantially. Glacial retreat slowed and even reversed
temporarily, in many cases, between 1950 and 1980 as global temperatures
cooled slightly. Since 1980, a significant global warming
has led to glacier retreat becoming increasingly rapid and ubiquitous,
so much so that some glaciers have disappeared altogether, and the
existences of many of the remaining glaciers are threatened. In
locations such as the Andes of South America and Himalayas in Asia, the
demise of glaciers in these regions has the potential to affect water
supplies in those areas.
The retreat of mountain glaciers, notably in western North America, Asia, the Alps and tropical and subtropical regions of South America, Africa and Indonesia, provide evidence for the rise in global temperatures since the late 19th century. The acceleration of the rate of retreat since 1995 of key outlet glaciers of the Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheets may foreshadow a rise in sea level, which would affect coastal regions.
Glacier mass balance
This map of mountain glacier mass balance changes since 1970 shows thinning in yellow and red, and thickening in blue.
The mass balance, or difference between accumulation and ablation (melting and sublimation), of a glacier is crucial to its survival. Climate change
may cause variations in both temperature and snowfall, resulting in
changes in mass balance. A glacier with a sustained negative balance
loses equilibrium and retreats. A sustained positive balance is also out
of equilibrium and will advance to reestablish equilibrium. Currently,
nearly all glaciers have a negative mass balance and are retreating.
Glacier retreat results in the loss of the low-elevation region
of the glacier. Since higher elevations are cooler, the disappearance of
the lowest portion decreases overall ablation, thereby increasing mass
balance and potentially reestablishing equilibrium. If the mass balance
of a significant portion of the accumulation zone of the glacier is
negative, it is in disequilibrium with the climate and will melt away
without a colder climate and or an increase in frozen precipitation.
Methods for measuring retreat include staking terminus location, global positioning mapping, aerial mapping and laser altimetry.
The key symptom of disequilibrium is thinning along the entire length
of the glacier. This indicates a diminishment of the accumulation zone.
The result is marginal recession of the accumulation zone margin, not
just of the terminus. In effect, the glacier no longer has a consistent
accumulation zone and without an accumulation zone cannot survive. For example, Easton Glacier
in Washington state, U.S. will likely shrink to half its size but at a
slowing rate of reduction and stabilize at that size despite the warmer
temperature over a few decades. However, the Grinnell Glacier
in Montana, U.S. will shrink at an increasing rate until it disappears.
The difference is that the upper section of Easton Glacier remains
healthy and snow-covered, while even the upper section of the Grinnell
Glacier is bare, is melting and has thinned. Small glaciers with minimal
altitude range are most likely to fall into disequilibrium with the
climate.
Middle latitude glaciers
Middle latitude glaciers are located either between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle, or between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle.
Both areas support glacier ice from mountain glaciers, valley glaciers
and even smaller icecaps, which are usually located in higher
mountainous regions. All are located in mountain ranges, notably the Himalayas; the Alps; the Pyrenees; Rocky Mountains and Pacific Coast Ranges of North America; the Patagonian Andes in South America; and mountain ranges in New Zealand.
Glaciers in these latitudes are more widespread and tend to be greater
in mass the closer they are to the polar regions. They are the most
widely studied over the past 150 years. As with examples located in the
tropical zone, virtually all the glaciers in the mid-latitudes are in a
state of negative mass balance and are retreating.
Northern hemisphere – Eurasia
This
map from the annual Glacier Commission surveys in Italy and Switzerland
shows the percentage of advancing glaciers in the Alps. Mid-20th
century saw strong retreating trends, but not as extreme as the present;
current retreats represent additional reductions of already smaller
glaciers.
Europe
In France all six of the major glaciers in that country are in retreat. On Mont Blanc, the highest peak in the Alps, the Argentière Glacier has receded 1,150 m (3,770 ft) since 1870. Other Mont Blanc glaciers have also been in retreat, including the Mer de Glace, which is the largest glacier in France at 12 km (7.5 mi) in length but retreated 500 m (1,600 ft) between 1994 and 2008. The glacier has retreated 2,300 m (7,500 ft) since the end of the Little Ice Age. The Bossons Glacier
once extended from the summit of Mont Blanc at 4,807 m (15,771 ft) to
an elevation of 1,050 m (3,440 ft) in 1900. By 2008 Bossons Glacier had
retreated to a point that was 1,400 m (4,600 ft) above sea level.
Other researchers have found that glaciers across the Alps appear to be
retreating at a faster rate than a few decades ago. In a paper published
in 2009 by the University of Zurich, the Swiss glacier survey of 89
glaciers found 76 retreating, 5 stationary and 8 advancing from where
they had been in 1973. The Trift Glacier had the greatest recorded retreat, losing 350 m (1,150 ft) of its length between the years 2003 and 2005. The Grosser Aletsch Glacier
is the largest glacier in Switzerland and has been studied since the
late 19th century. Aletsch Glacier retreated 2.8 km (1.7 mi) from 1880
to 2009.
This rate of retreat has also increased since 1980, with 30%, or 800 m
(2,600 ft), of the total retreat occurring in the last 20% of the time
period.
Morteratsch (right) and Pers (left) glaciers in 2005
The Morteratsch Glacier
in Switzerland has had one of the longest periods of scientific study
with yearly measurements of the glacier's length commencing in 1878. The
overall retreat from 1878 to 1998 has been 2 km (1.2 mi) with a mean
annual retreat rate of approximately 17 m (56 ft) per year. This
long-term average was markedly surpassed in recent years with the
glacier receding 30 m (98 ft) per year during the period between
1999–2005. Similarly, of the glaciers in the Italian Alps, only about a
third were in retreat in 1980, while by 1999, 89% of these glaciers were
retreating. In 2005, the Italian Glacier Commission found that 123
glaciers in Lombardy were retreating. A random study of the Sforzellina Glacier in the Italian Alps indicated that the rate of retreat from 2002 to 2006 was much higher than in the preceding 35 years.
To study glaciers located in the alpine regions of Lombardy,
researchers compared a series of aerial and ground images taken from the
1950s through the early 21st century and deduced that between the years
1954-2003 the mostly smaller glaciers found there lost more than half
of their area. Repeat photography of glaciers in the Alps indicates that there has been significant retreat since studies commenced.
Though the glaciers of the Alps have received more attention from
glaciologists than in other areas of Europe, research indicates that
glaciers in northern Europe are also retreating. Since the end of World
War II, Storglaciären in Sweden has undergone the longest continuous mass balance study in the world conducted from the Tarfala research station. In the Kebnekaise Mountains of northern Sweden, a study of 16 glaciers between 1990 and 2001 found that 14 glaciers were retreating, one was advancing and one was stable.
In Norway, glacier studies have been performed since the early 19th
century, with systematic surveys undertaken regularly since the 1990s.
Inland glaciers have had a generally negative mass balance, whereby
during the 1990s, maritime glaciers showed a positive mass balance and
advanced. The maritime advances have been attributed to heavy snowfall in the period 1989-1995. However, reduced snowfall since has caused most Norwegian glaciers to retreat significantly. A survey of 31 Norwegian glaciers in 2010 indicated that 27 were in retreat, one had no change and three advanced. Similarly, in 2013, of 33 Norwegian glaciers surveyed, 26 were retreating, four showed no change and three advanced.
Engabreen
Glacier in Norway extended to within 7 m (23 ft) above sea level in
2014, the lowest altitude of any glacier in Europe.
Engabreen Glacier in Norway, an outlet glacier of the Svartisen ice cap, had several advances in the 20th century, though it retreated 200 m (660 ft) between 1999 and 2014.
Brenndalsbreen glacier retreated 56 m (184 ft) between the years 2000
and 2014, while the Rembesdalsskåka glacier, which has retreated 2 km
(1.2 mi) since the end of the Little Ice Age, retreated 200 m (660 ft)
between 1997–2007.
The Briksdalsbreen glacier retreated 230 m (750 ft) between 1996 and
2004 with 130 m (430 ft) of that in the last year of that study; the
greatest annual retreat recorded on that glacier since studies began
there in 1900.
This figure was exceeded in 2006 with five glaciers retreating over
100 m (330 ft) from the fall of 2005 to the fall of 2006. Four outlets
from the Jostedalsbreen ice cap, the largest body of ice in continental Europe, Kjenndalsbreen, Brenndalsbreen, Briksdalsbreen and Bergsetbreen had a frontal retreat of more than 100 m (330 ft). Overall, from 1999 to 2005, Briksdalsbreen retreated 336 metres (1,102 ft). Gråfjellsbrea, an outlet glacier of the Folgefonna ice cap, had a retreat of almost 100 m (330 ft).
In the Spanish Pyrenees, recent studies have shown important losses in extent and volume of the glaciers of the Maladeta massif during the period 1981–2005. These include a reduction in area of 35.7%, from 2.41 km2 (600 acres) to 1.55 km2 (380 acres), a loss in total ice volume of 0.0137 km3 (0.0033 cu mi) and an increase in the mean altitude of the glacial termini of 43.5 m (143 ft).
For the Pyrenees as a whole 50–60% of the glaciated area has been lost
since 1991. The Balaitus, Perdigurero and La Munia glaciers have
disappeared in this period. Monte Perdido Glacier has shrunk from 90
hectares to 40 hectares.
As initial cause for glacier retreat in the alps since 1850, a decrease of the glaciers albedo, caused by industrial black carbon
can be identified. According to a report, this may have accelerated the
retreat of glaciers in Europe which otherwise may have continued to
expand until approximately the year 1910.
Siberia and the Russian Far East
Siberia is typically classified as a polar region, owing to the dryness of the winter climate and has glaciers only in the high Altai Mountains, Verkhoyansk Range, Cherskiy Range and Suntar-Khayata Range, plus possibly a few very small glaciers in the ranges near Lake Baikal, which have never been monitored and may have completely disappeared since 1989. Between the years 1952 and 2006, the glaciers found in the Aktru Basin region shrank by 7.2 percent.
This shrinkage has been primarily in the ablation zone of the glaciers,
with recession of several hundred meters being observed for some
glaciers. The Altai region has also experienced an overall temperature
increase of 1.2 degrees Celsius in the last 120 years according to a
report from 2006, with most of that increase occurring since the late
20th century.
In the more maritime and generally wetter Russian Far East, Kamchatka, exposed during winter to moisture from the Aleutian Low, has much more extensive glaciation totaling around 906 km2 (350 sq mi) with 448 known glaciers as of 2010. Despite generally heavy winter snowfall and cool summer temperatures, the high summer rainfall of the more southerly Kuril Islands and Sakhalin in historic times melt rates have been too high for a positive mass balance even on the highest peaks. In the Chukotskiy Peninsula
small alpine glaciers are numerous, but the extent of glaciation,
though larger than further west, is much smaller than in Kamchatka,
totalling around 300 square kilometres (120 sq mi).
Details on the retreat of Siberian and Russian Far East glaciers
less adequate than in most other glaciated areas of the world. There are
several reasons for this, the principal one being that since the
collapse of Communism there has been a large reduction in the number of monitoring stations.
Another factor is that in the Verkhoyansk and Cherskiy Ranges it was
thought glaciers were absent before they were discovered during the
1940s, whilst in ultra-remote Kamchatka and Chukotka, although the
existence of glaciers was known earlier, monitoring of their size dates
back no earlier than the end of World War II.
Nonetheless, available records do indicate a general retreat of all
glaciers in the Altai Mountains with the exception of volcanic glaciers
in Kamchatka. Sakha’s
glaciers, totaling seventy square kilometers, have shrunk by around
28 percent since 1945 reaching several percent annually in some places,
whilst in the Altai and Chukotkan mountains and non-volcanic areas of
Kamchatka, the shrinkage is considerably larger.
Himalayas and Central Asia
The Himalayas and other mountain chains of central Asia support large
glaciated regions. An estimated 15,000 glaciers can be found in the
greater Himalayas, with double that number in the Hindu Kush and
Karakoram and Tien Shan ranges, and comprise the largest glaciated
region outside the poles. These glaciers provide critical water supplies to arid countries such as Mongolia, western China, Pakistan, Afghanistan and India.
As with glaciers worldwide, those of the greater Himalayan region are
experiencing a decline in mass, and researchers claim that between the
early 1970s and early 2000s, there had been a 9 percent reduction in ice
mass.
Change in temperature has led to melting and the formation and
expansion of glacial lakes which could cause an increase in the number
of glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs). If the present trends persist
the ice mass will gradually be reduced, and will affect the availability
of water resources, though water loss is not expected to cause problems
for many decades.
In the Wakhan Corridor of Afghanistan 28 of 30 glaciers examined
retreated significantly between 1976–2003, with an average retreat of
11 m (36 ft) per year. One of these glaciers, the Zemestan Glacier, retreated 460 m (1,510 ft) during this period, not quite 10% of its 5.2 km (3.2 mi) length.
In examining 612 glaciers in China between 1950 and 1970, 53% of the
glaciers studied were retreating. After 1990, 95% of these glaciers were
measured to be retreating, indicating that retreat of these glaciers
was becoming more widespread. Glaciers in the Mount Everest region of the Himalayas are all in a state of retreat. The Rongbuk Glacier, draining the north side of Mount Everest into Tibet,
has been retreating 20 m (66 ft) per year. In the Khumbu region of
Nepal along the front of the main Himalaya of 15 glaciers examined from
1976–2007 all retreated significantly and the average retreat was 28 m
(92 ft) per year. The most famous of these, the Khumbu Glacier, retreated at a rate of 18 m (59 ft) per year from 1976–2007. In India, the Gangotri Glacier
retreated 1,147 m (3,763 ft) between the years 1936 and 1996 with 850 m
(2,790 ft) of that retreat occurring in the last 25 years of the 20th
century. However, the glacier is still over 30 km (19 mi) long. In Sikkim, 26 glaciers examined between the years 1976 and 2005 were retreating at an average rate of 13.02 m (42.7 ft) per year.
Overall, glaciers in the Greater Himalayan region that have been studied
are retreating an average of between 18 and 20 m (59 and 66 ft)
annually. The only region in the Greater Himalaya that has seen glacial advances is in the Karakoram Range
and only in the highest elevation glaciers, but this has been
attributed possibly increased precipitation as well as to the
correlating glacial surges, where the glacier tongue advances due to
pressure build up from snow and ice accumulation further up the glacier.
Between the years 1997 and 2001, 68 km (42 mi) long Biafo Glacier thickened 10 to 25 m (33 to 82 ft) mid-glacier, however it did not advance.
With the retreat of glaciers in the Himalayas, a number of
glacial lakes have been created. A growing concern is the potential for GLOFs researchers estimate 21 glacial lakes in Nepal and 24 in Bhutan pose hazards to human populations should their terminal moraines fail. One glacial lake identified as potentially hazardous is Bhutan's Raphstreng Tsho,
which measured 1.6 km (0.99 mi) long, 0.96 km (0.60 mi) wide and 80 m
(260 ft) deep in 1986. By 1995 the lake had swollen to a length of
1.94 km (1.21 mi), 1.13 km (0.70 mi) in width and a depth of 107 m
(351 ft). In 1994 a GLOF from Luggye Tsho, a glacial lake adjacent to Raphstreng Tsho, killed 23 people downstream.
Glaciers in the Ak-shirak Range in Kyrgyzstan experienced a slight loss between 1943 and 1977 and an accelerated loss of 20% of their remaining mass between 1977 and 2001. In the Tien Shan mountains, which Kyrgyzstan shares with China and Kazakhstan,
studies in the northern areas of that mountain range show that the
glaciers that help supply water to this arid region, lost nearly 2 km3 (0.48 cu mi) of ice per year between 1955 and 2000. The University of Oxford study also reported that an average of 1.28% of the volume of these glaciers had been lost per year between 1974 and 1990.
The Pamirs mountain range located primarily in Tajikistan, has approximately eight thousand glaciers, many of which are in a general state of retreat. During the 20th century, the glaciers of Tajikistan lost 20 km3 (4.8 cu mi) of ice. The 70 km (43 mi) long Fedchenko Glacier,
which is the largest in Tajikistan and the largest non-polar glacier on
Earth, retreated 1 km (0.62 mi) between the years 1933 and 2006, and
lost 44 km2 (17 sq mi) of its surface area due to shrinkage between the years 1966 and 2000.
Tajikistan and neighboring countries of the Pamir Range are highly
dependent upon glacial runoff to ensure river flow during droughts and
the dry seasons experienced every year. The continued demise of glacier
ice will result in a short-term increase, followed by a long-term
decrease in glacial melt water flowing into rivers and streams.
Northern hemisphere — North America
The Lewis Glacier, North Cascades National Park after melting away in 1990
North American glaciers are primarily located along the spine of the
Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada, and the Pacific Coast
Ranges extending from northern California to Alaska. While Greenland
is geologically associated with North America, it is also a part of the
Arctic region. Apart from the few tidewater glaciers such as Taku Glacier, in the advance stage of their tidewater glacier cycle
prevalent along the coast of Alaska, virtually all of those in North
America are in a state of retreat. This rate has increased rapidly
since around 1980, and overall each decade since has seen greater rates
of retreat than the preceding one. There are also small remnant glaciers
scattered throughout the Sierra Nevada mountains of California and Nevada.
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range of western North America extends from southern British Columbia
in Canada to northern California. Excepting Alaska, about half of the
glacial area in the U.S. is contained within the over 700 glaciers of
the North Cascades, a portion of those located between the Canada–US border and I-90 in central Washington.
These contain much water as is found in all the lakes and reservoirs in
the rest of the state, and provide much of the stream and river flow in
the dry summer months, approximating some 870,000 m3 (1,140,000 cu yd).
The Boulder Glacier retreated 450 m (1,480 ft) from 1987 to 2003.
The Easton Glacier retreated 255 m (837 ft) from 1990 to 2005.
As recently as 1975 many North Cascade glaciers were advancing due to
cooler weather and increased precipitation that occurred from 1944 to
1976. By 1987 the North Cascade glaciers were retreating and the pace
had increased each decade since the mid-1970s. Between 1984 and 2005 the
North Cascade glaciers lost an average of more than 12.5 metres (41 ft)
in thickness and 20–40 percent of their volume.
Glaciologists researching the North Cascades found that all 47 monitored glaciers are receding while four glaciers—Spider Glacier, Lewis Glacier, Milk Lake Glacier and David Glacier—have disappeared completely since 1985. The White Chuck Glacier (near Glacier Peak) is a particularly dramatic example. The glacier area shrank from 3.1 km2 (1.2 sq mi) in 1958 to 0.9 km2 (0.35 sq mi) by 2002. Between 1850 and 1950, the Boulder Glacier on the southeast flank of Mount Baker
retreated 8,700 feet (2,700 m). William Long of the United States
Forest Service observed the glacier beginning to advance due to
cooler/wetter weather in 1953. This was followed by a 743 metres
(2,438 ft) advance by 1979.
The glacier again retreated 450 m (1,480 ft) from 1987 to 2005, leaving
barren terrain behind. This retreat has occurred during a period of
reduced winter snowfall and higher summer temperatures. In this region
of the Cascades, winter snowpack has declined 25% since 1946, and summer temperatures have risen 0.7 °C (1.2 °F)
during the same period. The reduced snowpack has occurred despite a
small increase in winter precipitation—thus, it reflects warmer winter
temperatures leading to rainfall and melting on glaciers even during the
winter. As of 2005, 67% of the North Cascade glaciers observed are in
disequilibrium and will not survive the continuation of the present
climate. These glaciers will eventually disappear unless temperatures
fall and frozen precipitation increases. The remaining glaciers are
expected to stabilize, unless the climate continues to warm, but will be
much reduced in size.
U.S. Rocky Mountains
On the sheltered slopes of the highest peaks of Glacier National Park in Montana, the eponymous glaciers are diminishing rapidly. The area of each glacier has been mapped for decades by the National Park Service
and the U.S. Geological Survey. Comparing photographs from the mid-19th
century with contemporary images provides ample evidence that they have
retreated notably since 1850. Repeat photography since clearly show
that glaciers such as Grinnell Glacier
are all retreating. The larger glaciers are now approximately a third
of their former size when first studied in 1850, and numerous smaller
glaciers have disappeared completely. Only 27% of the 99 km2 (38 sq mi) area of Glacier National Park covered by glaciers in 1850 remained covered by 1993.
Researchers believe that by the year 2030, the vast majority of glacial
ice in Glacier National Park will be gone unless current climate
patterns reverse their course.
Grinnell Glacier is just one of many glaciers in Glacier National Park
that have been well documented by photographs for many decades. The
photographs below clearly demonstrate the retreat of this glacier since
1938.
- 1938 T.J. Hileman GNP
The semiarid climate of Wyoming still manages to support about a dozen small glaciers within Grand Teton National Park, which all show evidence of retreat over the past 50 years. Schoolroom Glacier is located slightly southwest of Grand Teton
is one of the more easily reached glaciers in the park and it is
expected to disappear by 2025. Research between 1950 and 1999
demonstrated that the glaciers in Bridger-Teton National Forest and Shoshone National Forest in the Wind River Range
shrank by over a third of their size during that period. Photographs
indicate that the glaciers today are only half the size as when first
photographed in the late 1890s. Research also indicates that the glacial
retreat was proportionately greater in the 1990s than in any other
decade over the last 100 years. Gannett Glacier on the northeast slope of Gannett Peak is the largest single glacier in the Rocky Mountains
south of Canada. It has reportedly lost over 50% of its volume since
1920, with almost half of that loss occurring since 1980. Glaciologists
believe the remaining glaciers in Wyoming will disappear by the middle
of the 21st century if the current climate patterns continue.
Canadian Rockies and Coast and Columbia Mountains
Valdez Glacier has thinned 90 m (300 ft) over the last century, exposing barren ground near the glacial margins.
In the Canadian Rockies,
glaciers are generally larger and more widespread than to the south in
the Rocky Mountains. One of the more accessible in the Canadian Rockies
is the Athabasca Glacier, which is an outlet glacier of the 325 km2 (125 sq mi) Columbia Icefield.
The Athabasca Glacier has retreated 1,500 m (4,900 ft) since the late
19th century. Its rate of retreat has increased since 1980, following a
period of slow retreat from 1950 to 1980. The Peyto Glacier in Alberta covers an area of about 12 km2
(4.6 sq mi), and retreated rapidly during the first half of the 20th
century, stabilized by 1966, and resumed shrinking in 1976.
The Illecillewaet Glacier in British Columbia's Glacier National Park (Canada), part of the Selkirk Mountains (west of the Rockies) has retreated 2 km (1.2 mi) since first photographed in 1887.
In Garibaldi Provincial Park in Southwestern British Columbia over 505 km2
(195 sq mi), or 26%, of the park, was covered by glacier ice at the
beginning of the 18th century. Ice cover decreased to 297 km2 (115 sq mi) by 1987–1988 and to 245 km2 (95 sq mi) by 2005, 50% of the 1850 area. The 50 km2
(19 sq mi) loss in the last 20 years coincides with negative mass
balance in the region. During this period all nine glaciers examined
have retreated significantly.
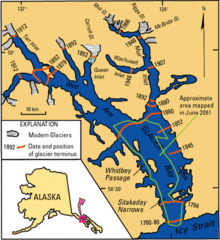
Alaska
Map of Glacier Bay. Red lines show glacial terminus positions and dates during retreat of the Little Ice Age glacier.
Maps showing retreat of Muir Glacier from 1941 to 1982
There are thousands of glaciers in Alaska but only few have been named. The Columbia Glacier near Valdez in Prince William Sound has retreated 15 km (9.3 mi) in the last 25 years. Its calved icebergs partially caused the Exxon Valdez
oil spill, when the tanker changed course to avoid the ice tips. The
Valdez Glacier is in the same area, and though it does not calve, has
also retreated significantly. "A 2005 aerial survey of Alaskan coastal
glaciers identified more than a dozen glaciers, many former tidewater
and calving
glaciers, including Grand Plateau, Alsek, Bear, and Excelsior Glaciers
that are rapidly retreating. Of 2,000 glaciers observed, 99% are
retreating."
Icy Bay in Alaska is fed by three large glaciers—Guyot, Yahtse, and
Tyndall Glaciers—all of which have experienced a loss in length and
thickness and, consequently, a loss in area. Tyndall Glacier became
separated from the retreating Guyot Glacier in the 1960s and has
retreated 24 km (15 mi) since, averaging more than 500 m (1,600 ft) per
year.
The Juneau Icefield Research Program has monitored outlet glaciers of the Juneau Icefield since 1946. On the west side of the ice field, the terminus of the Mendenhall Glacier, which flows into suburban Juneau, Alaska,
has retreated 580 m (1,900 ft). Of the nineteen glaciers of the Juneau
Icefield, eighteen are retreating, and one, the Taku Glacier, is
advancing. Eleven of the glaciers have retreated more than 1 km
(0.62 mi) since 1948 — Antler Glacier, 5.4 km (3.4 mi); Gilkey Glacier,
3.5 km (2.2 mi); Norris Glacier, 1.1 km (0.68 mi) and Lemon Creek
Glacier, 1.5 km (0.93 mi). Taku Glacier has been advancing since at least 1890, when naturalist John Muir observed a large iceberg calving front. By 1948 the adjacent fjord
had filled in, and the glacier no longer calved and was able to
continue its advance. By 2005 the glacier was only 1.5 km (0.93 mi) from
reaching Taku Point and blocking Taku Inlet.
The advance of Taku Glacier averaged 17 m (56 ft) per year between 1988
and 2005. The mass balance was very positive for the 1946–88 period
fueling the advance; however, since 1988 the mass balance has been
slightly negative, which should in the future slow the advance of this
mighty glacier.
Long-term mass balance records from Lemon Creek Glacier in Alaska show slightly declining mass balance with time.
The mean annual balance for this glacier was −0.23 m (0.75 ft) each
year during the period of 1957 to 1976. Mean annual balance has been
increasingly negatively averaging −1.04 m (3.4 ft) per year from 1990 to
2005. Repeat glacier altimetry, or altitude measuring, for 67 Alaska
glaciers find rates of thinning have increased by more than a factor of
two when comparing the periods from 1950 to 1995 (0.7 m (2.3 ft) per
year) and 1995 to 2001 (1.8 m (5.9 ft) per year).
This is a systemic trend with loss in mass equating to loss in
thickness, which leads to increasing retreat—the glaciers are not only
retreating, but they are also becoming much thinner. In Denali National Park,
all glaciers monitored are retreating, with an average retreat of 20 m
(66 ft) per year. The terminus of the Toklat Glacier has been retreating
26 m (85 ft) per year and the Muldrow Glacier has thinned 20 m (66 ft)
since 1979. Well documented in Alaska are surging glaciers that have been known to rapidly advance, even as much as 100 m (330 ft) per day. Variegated,
Black Rapids, Muldrow, Susitna and Yanert are examples of surging
glaciers in Alaska that have made rapid advances in the past. These
glaciers are all retreating overall, punctuated by short periods of
advance.
Southern hemisphere
Andes and Tierra del Fuego
Retreat of San Rafael Glacier from 1990 to 2000. San Quintín Glacier is shown in the background
A large region of population surrounding the central and southern Andes of Argentina and Chile
reside in arid areas that are dependent on water supplies from melting
glaciers. The water from the glaciers also supplies rivers that have in
some cases been dammed for hydroelectric
power. Some researchers believe that by 2030, many of the large ice
caps on the highest Andes will be gone if current climate trends
continue. In Patagonia on the southern tip of the continent, the large
ice caps have retreated a 1 km (0.62 mi) since the early 1990s and 10 km
(6.2 mi) since the late 19th century. It has also been observed that
Patagonian glaciers are receding at a faster rate than in any other
world region. The Northern Patagonian Ice Field lost 93 km2 (36 sq mi) of glacier area during the years between 1945 and 1975, and 174 km2
(67 sq mi) from 1975 to 1996, which indicates that the rate of retreat
is increasing. This represents a loss of 8% of the ice field, with all
glaciers experiencing significant retreat. The Southern Patagonian Ice Field
has exhibited a general trend of retreat on 42 glaciers, while four
glaciers were in equilibrium and two advanced during the years between
1944 and 1986. The largest retreat was on O'Higgins Glacier, which during the period 1896–1995 retreated 14.6 km (9.1 mi). The Perito Moreno Glacier
is 30 km (19 mi) long and is a major outflow glacier of the Patagonian
ice sheet, as well as the most visited glacier in Patagonia. Perito
Moreno Glacier is in equilibrium, but has undergone frequent
oscillations in the period 1947–96, with a net gain of 4.1 km (2.5 mi).
This glacier has advanced since 1947, and has been essentially stable
since 1992. Perito Moreno Glacier is one of three glaciers in Patagonia
known to have advanced, compared to several hundred others in retreat.
The two major glaciers of the Southern Patagonia Icefield to the north
of Moreno, Upsala and Viedma Glacier have retreated 4.6 km (2.9 mi) in
21 years and 1 km (0.62 mi) in 13 years respectively. In the Aconcagua River Basin, glacier retreat has resulted in a 20% loss in glacier area, declining from 151 km2 (58 sq mi) to 121 km2 (47 sq mi). The Marinelli Glacier in Tierra del Fuego has been in retreat since at least 1960 through 2008.
Oceania
These
glaciers in New Zealand have continued to retreat rapidly in recent
years. Notice the larger terminal lakes, the retreat of the white ice
(ice free of moraine cover), and the higher moraine walls due to ice
thinning. Photo.
In New Zealand, mountain glaciers have been in general retreat since
1890, with an acceleration since 1920. Most have measurably thinned and
reduced in size, and the snow accumulation zones have risen in elevation
as the 20th century progressed. Between 1971–75 Ivory Glacier receded
30 m (98 ft) from the glacial terminus, and about 26% of its surface
area was lost. Since 1980 numerous small glacial lakes formed behind the
new terminal moraines of several of these glaciers. Glaciers such as
Classen, Godley and Douglas now all have new glacial lakes below their
terminal locations due to the glacial retreat over the past 20 years.
Satellite imagery indicates that these lakes are continuing to expand.
There has been significant and ongoing ice volume losses on the largest
New Zealand glaciers, including the Tasman, Ivory, Classen, Mueller, Maud, Hooker, Grey, Godley, Ramsay, Murchison, Therma, Volta
and Douglas Glaciers. The retreat of these glaciers has been marked by
expanding proglacial lakes and terminus region thinning. The loss in
Southern Alps total ice volume from 1976–2014 is 34 percent of the
total.
Several glaciers, notably the much-visited Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers on New Zealand's West Coast,
have periodically advanced, especially during the 1990s, but the scale
of these advances is small when compared to 20th-century retreat. Both
are more than 2.5 km (1.6 mi) shorter than a century ago. These large,
rapidly flowing glaciers situated on steep slopes have been very
reactive to small mass-balance changes. A few years of conditions
favorable to glacier advance, such as more westerly winds and a
resulting increase in snowfall, are rapidly echoed in a corresponding
advance, followed by equally rapid retreat when those favorable
conditions end.
The glaciers that have been advancing in a few locations in New Zealand
have been doing so due to transient local weather conditions, which
have brought more precipitation and cloudier, cooler summers since 2002.
Tropical glaciers
Tropical glaciers are located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, in the region that lies 23° 26′ 22″ north or south of the equator. Strictly, a tropical glacier is located within the astronomical tropics; the area where the annual temperature variation is less than the daily variation, and is within the oscillation area of the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
Tropical glaciers are the most uncommon of all glaciers for a
variety of reasons. Firstly, the regions are the warmest part of the
planet. Secondly, the seasonal change is minimal with temperatures warm
year round, resulting in a lack of a colder winter season in which snow
and ice can accumulate. Thirdly, few taller mountains exist in these
regions upon which enough cold air exists for the establishment of
glaciers. Overall, tropical glaciers are smaller than those found
elsewhere and are the most likely glaciers to show rapid response to
changing climate patterns. A small temperature increase of only a few
degrees can have almost immediate and adverse effect on tropical
glaciers.
Near the Equator, ice is still found in East Africa, the Andes of
South America and New Guinea. The retreat of equatorial glaciers has
been documented via maps and photographs covering the period from the
late 1800s to nearly the present.
99.64% of tropical glaciers are in Andean mountains of South America,
0.25% on the African glaciers of Rwenzori, Mount Kenya and Kilimanjaro,
and 0.11% in the Irian Jaya region in New Guinea.
Africa
Furtwängler Glacier atop Kilimanjaro in the foreground and snowfields and the Northern Icefields beyond.
Almost all Africa is in tropical and subtropical climate zones. Its glaciers are found only in two isolated ranges and the Ruwenzori Range.
Kilimanjaro, at 5,895 m (19,341 ft), is the highest peak on the
continent. Since 1912 the glacier cover on the summit of Kilimanjaro has
apparently retreated 75%, and the volume of glacial ice is now 80% less
than it was a century ago due to both retreat and thinning. In the 14-year period from 1984 to 1998, one section of the glacier atop the mountain receded 300 m (980 ft).
A 2002 study determined that if current conditions continue, the
glaciers atop Kilimanjaro will disappear sometime between 2015 and 2020.
A March 2005 report indicated that there is almost no remaining glacial
ice on the mountain, and it is the first time in 11,000 years that
barren ground has been exposed on portions of the summit. Researchers reported Kilimanjaro's glacier retreat was due to a combination of increased sublimation and decreased snow fall.
The Furtwängler Glacier
is located near the summit of Kilimanjaro. Between 1976 and 2000, the
area of Furtwängler Glacier was cut almost in half, from 113,000 m2 (1,220,000 sq ft) to 60,000 m2 (650,000 sq ft).
During fieldwork conducted early in 2006, scientists discovered a large
hole near the center of the glacier. This hole, extending through the
6 m (20 ft) remaining thickness of the glacier to the underlying rock,
was expected to grow and split the glacier in two by 2007.
To the north of Kilimanjaro lies Mount Kenya,
which at 5,199 m (17,057 ft) is the second tallest mountain on the
continent. Mount Kenya has a number of small glaciers that have lost at
least 45% of their mass since the middle of the 20th century. According
to research compiled by the U.S. Geological Survey
(USGS), there were eighteen glaciers atop Mount Kenya in 1900, and by
1986 only eleven remained. The total area covered by glaciers was 1.6 km2 (0.62 sq mi) in 1900, however by the year 2000 only about 25%, or 0.4 km2 (0.15 sq mi) remained.
To the west of Mounts Kilimanjaro and Kenya, the Ruwenzori Range rises
to 5,109 m (16,762 ft). Photographic evidence indicates a marked
reduction in glacially covered areas over the past century. In the
35-year period between 1955 and 1990, glaciers on the Rwenzori Mountains receded about 40%. It is expected that due to their proximity to the heavy moisture of the Congo region, the glaciers in the Ruwenzori Range may recede at a slower rate than those on Kilimanjaro or in Kenya.
South America
A
study by glaciologists of two small glaciers in South America reveals
another retreat. More than 80% of all glacial ice in the northern Andes
is concentrated on the highest peaks in small plains of approximately
1 km2 (0.39 sq mi) in size. A 1992 to 1998 observation of the Chacaltaya Glacier in Bolivia and Antizana Glacier in Ecuador
indicate that between 0.6 m (2.0 ft) and 1.9 m (6.2 ft) of ice was lost
per year on each glacier. Figures for Chacaltaya show a loss of 67% of
its volume and 40% of its thickness over the same period. Chacaltaya
Glacier has lost 90% of its mass since 1940 and was expected to
disappear altogether sometime between 2010 and 2015. Antizana is also
reported to have lost 40% of its surface area between 1979 and 2007. Research also indicates that since the mid-1980s, the rate of retreat for both of these glaciers has been increasing. In Colombia, the glaciers atop Nevado del Ruiz have lost more than half their area in the last 40 years. Further south in Peru, the Andes are at a higher altitude overall, and there are approximately 722 glaciers covering an area of 723 km2 (279 sq mi).
Research in the region has been less extensive but indicates an overall recline of 7% between 1977 and 1983. The Quelccaya Ice Cap is the second largest tropical icecap in the world after the Coropuna ice cap, and all of the outlet glaciers from the icecap are retreating. In the case of Qori Kalis Glacier,
which is one of Quelccayas' outlet glaciers, the rate of retreat had
reached 155 m (509 ft) per year during the three-year period of 1995 to
1998. The melting ice has formed a large lake at the front of the
glacier since 1983, and bare ground has been exposed for the first time
in thousands of years.
Oceania
Animated map of the extent of the glaciers of the Carstensz Range from 1850 to 2003
Mount Carstensz icecap 1936 USGS
Puncak Jaya glaciers 1972. Left to right: Northwall Firn, Meren Glacier, and Carstensz Glacier. USGS.
Jan Carstensz's 1623 report of glaciers covering the equatorial mountains of New Guinea was originally met with ridicule, but in the early 20th century at least five subranges of the Maoke Mountains
(meaning "Snowy Mountains") were indeed still found to be covered with
large ice caps. Due to the location of the island within the tropical
zone, there is little to no seasonal variation in temperature. The
tropical location has a predictably steady level of rain and snowfall,
as well as cloud cover year round, and there has been no noticeable
change in the amount of moisture which has fallen during the 20th
century.
In 1913, 4,550 m (14,930 ft) high Prins Hendrik peaks (now Puncak Yamin) was named and reported to have "eternal" snow, but this observation was never repeated. The ice cap of 4,720 m (15,490 ft) Wilhelmina Peaks, which reached below 4,400 m (14,400 ft) in 1909, vanished between 1939 and 1963. The Mandala / Juliana ice cap disappeared in the 1990s. and the Idenburg glacier on Ngga Pilimsit dried up in 2003. This leaves only the remnants of the once continuous icecap on New Guinea's highest mountain, Mount Carstensz with the 4,884 m (16,024 ft) high Puncak Jaya summit, which is estimated to have had an area of 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi) in 1850.
For this mountain there is photographic evidence of massive
glacial retreat since the region was first extensively explored by
airplane in 1936 in preparation for the peak's first ascent.
Between then and 2010, the mountain lost 80 percent of its ice —
two-thirds of which since another scientific expedition in the 1970s. That research between 1973 and 1976 showed glacier retreat for the Meren Glacier of 200 m (660 ft) while the Carstensz Glacier lost 50 m (160 ft). The Northwall Firn, the largest remnant of the icecap that once was atop Puncak Jaya, has itself split into two separate glaciers after 1942. IKONOS satellite imagery of the New Guinean glaciers indicated that by 2002 only 2.1 km2 (0.81 sq mi) glacial area remained, that in the two years from 2000 to 2002, the East Northwall Firn had lost 4.5%, the West Northwall Firn
19.4% and the Carstensz 6.8% of their glacial mass, and that sometime
between 1994 and 2000, the Meren Glacier had disappeared altogether.
An expedition to the remaining glaciers on Puncak Jaya in 2010
discovered that the ice on the glaciers there is about 32 metres
(105 ft) thick and thinning at a rate of 7 metres (23 ft) annually. At
that rate, the remaining glaciers were expected to last only to the year
2015.
Polar regions
Despite
their proximity and importance to human populations, the mountain and
valley glaciers of tropical and mid-latitude glaciers amount to only a
small fraction of glacial ice on the Earth. About 99 percent of all
freshwater ice is in the great ice sheets of polar and subpolar Antarctica and Greenland.
These continuous continental-scale ice sheets, 3 km (1.9 mi) or more in
thickness, cap much of the polar and subpolar land masses. Like rivers
flowing from an enormous lake, numerous outlet glaciers transport ice
from the margins of the ice sheet to the ocean.
Iceland
The northern Atlantic island nation of Iceland is home to Vatnajökull, which is the largest ice cap in Europe. The Breiðamerkurjökull
glacier is one of Vatnajökull's outlet glaciers, and receded by as much
as 2 km (1.2 mi) between 1973 and 2004. In the early 20th century,
Breiðamerkurjökull extended to within 250 m (820 ft) of the ocean, but
by 2004 its terminus had retreated 3 km (1.9 mi) further inland. This
glacier retreat exposed a rapidly expanding lagoon, Jökulsárlón,
which is filled with icebergs calved from its front. Jökulsárlón is
110 m (360 ft) deep and nearly doubled its size between 1994 and 2004.
Mass-balance measurements of Iceland's glaciers show alternating
positive and negative mass balance of glaciers during the period
1987–95, but the mass balance has been predominantly negative since. On
Hofsjökull ice cap, mass balance has been negative each year from
1995–2005.
Most of the Icelandic glaciers retreated rapidly during the warm
decades from 1930 to 1960, slowing down as the climate cooled during the
following decade, and started to advance after 1970. The rate of
advance peaked in the 1980s, after which it slowed down until about
1990. As a consequence of rapid warming of the climate that has taken
place since the mid-1980s, most glaciers in Iceland began to retreat
after 1990, and by 2000 all monitored non-surge type glaciers in Iceland
were retreating. An average of 45 non-surging termini were monitored
each year by the Icelandic Glaciological Society from 2000–2005.
Canada
Bylot Ice Cap on Bylot Island, one of the Canadian Arctic islands, August 14, 1975 (USGS)
The Canadian Arctic islands contain the largest area and volume of land ice on Earth outside of the Greenland and Antarctic Ice Sheets and is home to a number of substantial ice caps, including Penny and Barnes ice caps on Baffin Island, Bylot Ice Cap on Bylot Island, and Devon Ice Cap on Devon Island.
Glaciers in the Canadian Arctic were near equilibrium between 1960 and
2000, losing 23 Gt of ice per year between 1995 and 2000.
Since this time, Canadian Arctic glaciers have experienced a sharp
increase in mass loss in response to warmer summer temperature, losing
92 Gt per year between 2007 and 2009.
Other studies show that between 1960 and 1999, the Devon Ice Cap lost 67 km3
(16 cu mi) of ice, mainly through thinning. All major outlet glaciers
along the eastern Devon Ice Cap margin have retreated from 1 km
(0.62 mi) to 3 km (1.9 mi) since 1960. On the Hazen Plateau of Ellesmere Island, the Simmon Ice Cap has lost 47% of its area since 1959.
If the current climatic conditions continue, the remaining glacial ice
on the Hazen Plateau will be gone around 2050. On August 13, 2005, the Ayles Ice Shelf broke free from the north coast of Ellesmere Island. The 66 km2 (25 sq mi) ice shelf drifted into the Arctic Ocean. This followed the splitting of the Ward Hunt Ice Shelf in 2002. The Ward Hunt has lost 90% of its area in the last century.
Northern Europe
Arctic islands north of Norway, Finland and Russia have all shown evidence of glacier retreat. In the Svalbard archipelago, the island of Spitsbergen
has numerous glaciers. Research indicates that Hansbreen (Hans Glacier)
on Spitsbergen retreated 1.4 km (0.87 mi) from 1936 to 1982 and another
400 m (1,300 ft) during the 16-year period from 1982 to 1998.
Blomstrandbreen, a glacier in the King's Bay area of Spitsbergen, has
retreated approximately 2 km (1.2 mi) in the past 80 years. Since 1960
the average retreat of Blomstrandbreen has been about 35 m (115 ft) a
year, and this average was enhanced due to an accelerated rate of
retreat since 1995. Similarly, Midre Lovenbreen retreated 200 m (660 ft) between 1977 and 1995. In the Novaya Zemlya
archipelago north of Russia, research indicates that in 1952 there was
208 km (129 mi) of glacier ice along the coast. By 1993 this had been
reduced by 8% to 198 km (123 mi) of glacier coastline.
Greenland
Retreat of the Helheim Glacier, Greenland
In Greenland,
glacier retreat has been observed in outlet glaciers, resulting in an
increase of the ice flow rate and destabilization of the mass balance of
the ice sheet that is their source. The net loss in volume and hence
sea level contribution of the Greenland Ice Sheet (GIS) has doubled in
recent years from 90 km3 (22 cu mi) per year in 1996 to 220 km3 (53 cu mi) per year in 2005.
Researchers also noted that the acceleration was widespread affecting
almost all glaciers south of 70 N by 2005. The period since 2000 has
brought retreat to several very large glaciers that had long been
stable. Three glaciers that have been researched—Helheim Glacier, Kangerdlugssuaq Glacier, and Jakobshavn Isbræ—jointly drain more than 16% of the Greenland Ice Sheet.
In the case of Helheim Glacier, researchers used satellite images to
determine the movement and retreat of the glacier. Satellite images and
aerial photographs from the 1950s and 1970s show that the front of the
glacier had remained in the same place for decades. In 2001 the glacier
began retreating rapidly, and by 2005 the glacier had retreated a total
of 7.2 km (4.5 mi), accelerating from 20 m (66 ft) per day to 35 m
(115 ft) per day during that period.
Jakobshavn Isbræ in west Greenland, a major outlet glacier of the
Greenland Ice Sheet, has been the fastest moving glacier in the world
over the past half century. It had been moving continuously at speeds of
over 24 m (79 ft) per day with a stable terminus since at least 1950.
In 2002 the 12 km (7.5 mi) long floating terminus of the glacier entered
a phase of rapid retreat, with the ice front breaking up and the
floating terminus disintegrating and accelerating to a retreat rate of
over 30 m (98 ft) per day. On a shorter timescale, portions of the main
trunk of Kangerdlugssuaq Glacier that were flowing at 15 m (49 ft) per
day from 1988 to 2001 were measured to be flowing at 40 m (130 ft) per
day in the summer of 2005. Not only has Kangerdlugssuaq retreated, it
has also thinned by more than 100 m (330 ft).
The rapid thinning, acceleration and retreat of Helheim,
Jakobshavns and Kangerdlugssuaq glaciers in Greenland, all in close
association with one another, suggests a common triggering mechanism,
such as enhanced surface melting due to regional climate warming or a
change in forces at the glacier front. The enhanced melting leading to
lubrication of the glacier base has been observed to cause a small
seasonal velocity increase and the release of meltwater lakes has also
led to only small short term accelerations.
The significant accelerations noted on the three largest glaciers began
at the calving front and propagated inland and are not seasonal in
nature.
Thus, the primary source of outlet glacier acceleration widely observed
on small and large calving glaciers in Greenland is driven by changes
in dynamic forces at the glacier front, not enhanced meltwater
lubrication. This was termed the Jakobshavns Effect by Terence Hughes at the University of Maine in 1986.
Indeed, a study published in 2015 on glacial underwater topography at 3
sites found cavities, due to warm subglacial water intrusion, which has
been identified as a possible dominant force for ablation (surface
erosion). Thus, suggests ocean temperature controls ice sheet surface
runoff at specific sites. These findings also show that models
underestimate the sensitivity of Greenland glaciers to ocean warming and
resulting ice sheet runoff. Hence, without better modelling, new
observations suggest that past projections of sea level rise attribution
from the Greenland Ice Sheet require upward revision.
Antarctica
The collapsing Larsen B Ice Shelf in Antarctica is similar in area to the U.S. state of Rhode Island.
Antarctica
is intensely cold and arid. Most of the world's freshwater ice is
contained within its sheets. Its most dramatic example of glacier
retreat is the loss of large sections of the Larsen Ice Shelf on the Antarctic Peninsula.
The recent collapse of Wordie Ice Shelf, Prince Gustav Ice Shelf,
Mueller Ice Shelf, Jones Ice Shelf, Larsen-A and Larsen-B Ice Shelf on
the Antarctic Peninsula has raised awareness of how dynamic ice shelf
systems are.
The Antarctic sheet is the largest known single mass of ice. It covers almost 14 million km2 and some 30 million km3
of ice. Around 90% of the fresh water on the planet's surface is held
in this area and if melted would raise sea levels by 58 metres.
The continent-wide average surface temperature trend of Antarctica is
positive and significant at more than 0.05 °C/decade since 1957.
The Antarctic sheet is divided by the Transantarctic Mountains into two unequal sections known as the East Antarctic ice sheet (EAIS) and the smaller West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS). The EAIS rests on a major land mass but the bed of the WAIS is, in places, more than 2,500 metres below sea level. It would be seabed
if the ice sheet were not there. The WAIS is classified as a
marine-based ice sheet, meaning that its bed lies below sea level and
its edges flow into floating ice shelves. The WAIS is bounded by the Ross Ice Shelf, the Ronne Ice Shelf, and outlet glaciers that drain into the Amundsen Sea.
Ice shelves are not stable when surface melting occurs, and the
collapse of Larsen Ice Shelf has been caused by warmer melt season
temperatures that have led to surface melting and the formation of
shallow ponds of water on the ice shelf. The Larsen Ice Shelf lost
2,500 km2 (970 sq mi) of its area from 1995 to 2001. In a 35-day period beginning on January 31, 2002, about 3,250 km2 (1,250 sq mi) of shelf area disintegrated. The ice shelf is now 40% the size of its previous minimum stable extent. In 2015 a study concluded that the remaining Larsen B
ice-shelf will disintegrate by the end of the decade, based on
observations of faster flow and rapid thinning of glaciers in the area. Jones Ice Shelf had an area of 35 km2 (14 sq mi) in the 1970s but by 2008 it had disappeared. Wordie Ice Shelf has gone from an area of 1,500 km2 (580 sq mi) in 1950 to 1,400 km2 (540 sq mi) in 2000. Prince Gustav Ice Shelf has gone from an area of 1,600 km2 (620 sq mi) to 1,100 km2 (420 sq mi) in 2008.
After their loss the reduced buttressing of feeder glaciers has allowed
the expected speed-up of inland ice masses after shelf ice break-up. The Ross Ice Shelf
is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (an area of roughly 487,000
square kilometres (188,000 sq mi) and about 800 kilometres (500 mi)
across: about the size of France). Wilkins Ice Shelf is another ice shelf that has suffered substantial retreat. The ice shelf had an area of 16,000 km2 (6,200 sq mi) in 1998 when 1,000 km2 (390 sq mi) was lost that year. In 2007 and 2008 significant rifting developed and led to the loss of another 1,400 km2
(540 sq mi) of area and some of the calving occurred in the Austral
winter. The calving seemed to have resulted from preconditioning such as
thinning, possibly due to basal melt, as surface melt was not as
evident, leading to a reduction in the strength of the pinning point
connections. The thinner ice then experienced spreading rifts and
breakup.
This period culminated in the collapse of an ice bridge connecting the
main ice shelf to Charcot Island leading to the loss of an additional
700 km2 (270 sq mi) between February and June 2009.
Dakshin Gangotri Glacier, a small outlet glacier of the Antarctic
ice sheet, receded at an average rate of 0.7 m (2.3 ft) per year from
1983 to 2002. On the Antarctic Peninsula, which is the only section of
Antarctica that extends well north of the Antarctic Circle, there are
hundreds of retreating glaciers. In one study of 244 glaciers on the
peninsula, 212 have retreated an average of 600 m (2,000 ft) from where
they were when first measured in 1953. Pine Island Glacier, an Antarctic outflow glacier that flows into the Amundsen Sea.
A study from 1998 concluded that the glacier thinned 3.5 m
(11 ft)± 0.9 m (3.0 ft) per year and retreated a total of 5 km (3.1 mi)
in 3.8 years. The terminus of the Pine Island Glacier is a floating ice
shelf, and the point at which it starts to float retreated 1.2 km
(0.75 mi) per year from 1992 to 1996. This glacier drains a substantial
portion of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
A study published in 2014 found, rapid grounding line retreat in the years 1992-2011.
Based on a study from 2005, the greatest retreat was seen in Sjogren
Glacier, which is now 13 km (8.1 mi) further inland than where it was in
1953. There are 32 glaciers that were measured to have advanced;
however, these glaciers showed only a modest advance averaging 300 m
(980 ft) per glacier, which is significantly smaller than the massive
retreat observed.
Thwaites Glacier, which has also shown evidence of thinning, has been
referred to as the weak underbelly of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. A study published in 2014 found rapid grounding line retreat in the years 1992–2011.
More recently, new satellite imaging data led to calculations of
Thwaites Glacier "ice shelf melt rate of 207 m/year in 2014–2017, which
is the highest ice shelf melt rate on record in Antarctica."
Totten Glacier, is a large glacier draining a major portion of the
East Antarctic Ice Sheet. A study in 2008 concluded that Totten Glacier
is currently losing mass.
A study published in 2015 concluded that Totten Glacier, has the
largest contribution of ice thinning rate on the East Antarctic
continent, and that the thinning is driven by enhanced basal melting,
because of ocean processes, and affected by polynya
activity. Additionally, warm Circumpolar Deep Water, has been observed
during summer and winter months at the nearby continental shelf below
400 to 500 meters of cool Antarctic Surface Water.
Effects of glacier retreat
The continued retreat of glaciers will have a number of different
quantitative effects. In areas that are heavily dependent on water
runoff from glaciers that melt during the warmer summer months, a
continuation of the current retreat will eventually deplete the glacial
ice and substantially reduce or eliminate runoff. A reduction in runoff
will affect the ability to irrigate
crops and will reduce summer stream flows necessary to keep dams and
reservoirs replenished. This situation is particularly acute for
irrigation in South America, where numerous artificial lakes are filled
almost exclusively by glacial melt. Central Asian
countries have also been historically dependent on the seasonal glacier
melt water for irrigation and drinking supplies. In Norway, the Alps,
and the Pacific Northwest of North America, glacier runoff is important for hydropower.
Some of this retreat has resulted in efforts to slow down the
loss of glaciers in the Alps. To retard melting of the glaciers used by
certain Austrian ski resorts, portions of the Stubai and Pitztal Glaciers were partially covered with plastic. In Switzerland plastic sheeting is also used to reduce the melt of glacial ice used as ski slopes.
While covering glaciers with plastic sheeting may prove advantageous to
ski resorts on a small scale, this practice is not expected to be
economically practical on a much larger scale.
Many species of freshwater and saltwater plants and animals are
dependent on glacier-fed waters to ensure the cold water habitat to
which they have adapted. Some species of freshwater fish need cold water
to survive and to reproduce, and this is especially true with salmon and cutthroat trout. Reduced glacial runoff can lead to insufficient stream flow to allow these species to thrive. Alterations to the ocean currents, due to increased freshwater inputs from glacier melt, and the potential alterations to thermohaline circulation of the World Ocean, may affect existing fisheries upon which humans depend as well.
One major concern is the increased risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOF), which have in the past had great effect on lives and property. Glacier meltwater left behind by the retreating glacier is often held back by moraines that can be unstable and have been known to collapse if breached or displaced by earthquakes, landslides or avalanches.
If the terminal moraine is not strong enough to hold the rising water
behind it, it can burst, leading to a massive localized flood. The
likelihood of such events is rising due to the creation and expansion of
glacial lakes resulting from glacier retreat.
Past floods have been deadly and have resulted in enormous property
damage. Towns and villages in steep, narrow valleys that are downstream
from glacial lakes are at the greatest risk. In 1892 a GLOF released
some 200,000 m3 (260,000 cu yd) of water from the lake of the Glacier de Tête Rousse, resulting in the deaths of 200 people in the French town of Saint-Gervais-les-Bains.
GLOFs have been known to occur in every region of the world where
glaciers are located. Continued glacier retreat is expected to create
and expand glacial lakes, increasing the danger of future GLOFs.
The potential for major sea level rise
depends mostly on a significant melting of the polar ice caps of
Greenland and Antarctica, as this is where the vast majority of glacial
ice is located. If all the ice on the polar ice caps were to melt away,
the oceans of the world would rise an estimated 70 m (230 ft). Although
previously it was thought that the polar ice caps were not contributing
heavily to sea level rise (IPCC 2007), recent studies have confirmed
that both Antarctica and Greenland are contributing 0.5 millimetres
(0.020 in) a year each to global sea level rise. The Thwaites Glacier
alone, in Western Antarctica is "currently responsible for
approximately 4 percent of global sea level rise. It holds enough ice to
raise the world ocean a little over 2 feet (65 centimeters) and
backstops neighboring glaciers that would raise sea levels an additional
8 feet (2.4 meters) if all the ice were lost."
The fact that the IPCC estimates did not include rapid ice sheet decay
into their sea level predictions makes it difficult to ascertain a
plausible estimate for sea level rise but a 2008 study found that the
minimum sea level rise will be around 0.8 metres (2.6 ft) by 2100. Newer observations with NASA's ice-penetrating radar of Operation IceBridge confirm that sea level rise due to glacier melting is a credible threat.