US Navy crew member receiving an influenza vaccination | |
| Vaccine description | |
|---|---|
| Target | Influenza virus |
| Vaccine type | inactivated, attenuated, recombinant |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Afluria, Fluarix, Fluzone, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Inactivated: Monograph Intranasal: Monograph Recombinant: Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular, intranasal, intradermal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| KEGG | |
Influenza vaccines, also known as flu shots or flu jabs, are vaccines that protect against infection by influenza viruses. New versions of the vaccines are developed twice a year, as the influenza virus rapidly changes. While their effectiveness varies from year to year, most provide modest to high protection against influenza. The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that vaccination against influenza reduces sickness, medical visits, hospitalizations, and deaths. Immunized workers who do catch the flu return to work half a day sooner on average. Vaccine effectiveness in those over 65 years old remains uncertain due to a lack of high quality research.Vaccinating children may protect those around them.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend yearly vaccination for nearly all people over the age of six months, especially those at high risk. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) also recommends yearly vaccination of high risk groups. These groups include pregnant women, the elderly, children between six months and five years of age, those with certain health problems, and those who work in healthcare.
The vaccines are generally safe. Fever occurs in five to ten percent of children vaccinated. Temporary muscle pains or feelings of tiredness may occur as well. In certain years, the vaccine has been linked to an increase in Guillain–Barré syndrome among older people at a rate of about one case per million doses. Although most influenza vaccines are produced using eggs, they are still recommended for people who have severe egg allergies. However, influenza vaccines are not recommended in those who have had a severe allergy to previous versions of the vaccine itself. The vaccine comes in inactive and weakened viral forms. The live, weakened vaccine is generally not recommended in pregnant women, children less than two years old, adults older than 50, or people with a weakened immune system. Depending on the type they can be injected into a muscle, sprayed into the nose, or injected into the middle layer of the skin (intradermal). The intradermal vaccine was not available during the 2018–2019 and 2019–2020 influenza seasons.
Vaccination against influenza began in the 1930s with large-scale availability in the United States beginning in 1945. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Medical uses
The U.S Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the flu vaccine as the best way to protect people against the flu and prevent its spread. The flu vaccine can also reduce the severity of the flu if a person contracts a strain that the vaccine did not contain. It takes about two weeks following vaccination for protective antibodies to form.
A 2012 meta-analysis found that flu vaccination was effective 67 percent of the time; the populations that benefited the most were HIV-positive adults aged 18 to 55 (76 percent), healthy adults aged 18 to 46 (approximately 70 percent), and healthy children aged six months to 24 months (66 percent). The influenza vaccine also appear to protect against myocardial infarction with a benefit of 15 to 45%.
Effectiveness
| 2004 | 10% |
|---|---|
| 2005 | 21% |
| 2006 | 52% |
| 2007 | 37% |
| 2008 | 41% |
| 2009 | 56% |
| 2010 | 60% |
| 2011 | 47% |
| 2012 | 49% |
| 2013 | 52% |
| 2014 | 19% |
| 2015 | 48% |
| 2016 | 40% |
| 2017 | 38% |
| 2018 | 29% |
| 2019 | 45% est |
A vaccine is assessed by its efficacy – the extent to which it reduces risk of disease under controlled conditions – and its effectiveness – the observed reduction in risk after the vaccine is put into use. In the case of influenza, effectiveness is expected to be lower than the efficacy because it is measured using the rates of influenza-like illness, which is not always caused by influenza. Influenza vaccines generally show high efficacy, as measured by the antibody production in animal models or vaccinated people. However, studies on the effectiveness of flu vaccines in the real world are difficult; vaccines may be imperfectly matched, virus prevalence varies widely between years, and influenza is often confused with other influenza-like illnesses. However, in most years (16 of the 19 years before 2007), the flu vaccine strains have been a good match for the circulating strains, and even a mismatched vaccine can often provide cross-protection. The virus rapidly changes due to antigenic drift, a slight mutation in the virus that causes a new strain to arise.
Repeated annual influenza vaccination generally offer consistent year-on-year protection against influenza. There is, however, suggestive evidence that repeated vaccinations may cause a reduction in vaccine effectiveness for certain influenza subtypes; this has no relevance to current recommendations for yearly vaccinations but might influence future vaccination policy. As of 2019, the CDC recommends a yearly vaccine as most studies demonstrate overall effectiveness of annual influenza vaccination.
Criticism
Tom Jefferson, who has led Cochrane Collaboration reviews of flu vaccines, has called clinical evidence concerning flu vaccines "rubbish" and has therefore declared them to be ineffective; he has called for placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials, which most in the field hold as unethical. His views on the efficacy of flu vaccines are rejected by medical institutions including the CDC and the National Institutes of Health, and by key figures in the field like Anthony Fauci.
Michael Osterholm, who led the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy 2012 review on flu vaccines, recommended getting the vaccine but criticized its promotion, saying, "We have overpromoted and overhyped this vaccine ... it does not protect as promoted. It's all a sales job: it's all public relations."
Children
The CDC recommends that everyone except infants under the age of six months should receive the seasonal influenza vaccine. Vaccination campaigns usually focus special attention on people who are at high risk of serious complications if they catch the flu, such as pregnant women, children under 59 months, the elderly, and people with chronic illnesses or weakened immune systems, as well as those to whom they are exposed, such as healthcare workers.
As the death rate is also high among infants who catch influenza, the CDC and the WHO recommend that household contacts and caregivers of infants be vaccinated to reduce the risk of passing an influenza infection to the infant.
In children, the vaccine appears to decrease the risk of influenza and possibly influenza-like illness. In children under the age of two data are limited. During the 2017–18 flu season, the CDC director indicated that 85 percent of the children who died "likely will not have been vaccinated".
In the United States, as of January 2019, the CDC recommend that children aged six through 35 months may receive either 0.25 milliliters or 0.5 milliliters per dose of Fluzone Quadrivalent. There is no preference for one or the other dose volume of Fluzone Quadrivalent for that age group. All persons 36 months of age and older should receive 0.5 milliliters per dose of Fluzone Quadrivalent. As of October 2018, Afluria Quadrivalent is licensed for children six months of age and older in the United States. Children six months through 35 months of age should receive 0.25 milliliters for each dose of Afluria Quadrivalent. All persons 36 months of age and older should receive 0.5 milliliters per dose of Afluria Quadrivalent. As of February 2018, Afluria Tetra is licensed for adults and children five years of age and older in Canada.
In 2014, the Canadian National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) published a review of influenza vaccination in healthy 5–18-year-olds, and in 2015, published a review of the use of pediatric Fluad in children 6–72 months of age. In one study, conducted in a tertiary referral center, the rate of influenza vaccination in children was only 31%. Higher rates were found among immuno-suppressed pediatric patients (46%), and in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (50%).
Adults
In unvaccinated adults, 16% get symptoms similar to the flu, while about 10% of vaccinated adults do. Vaccination decreased confirmed cases of influenza from about 2.4% to 1.1%. No effect on hospitalization was found.
In working adults, a review by the Cochrane Collaboration found that vaccination resulted in a modest decrease in both influenza symptoms and working days lost, without affecting transmission or influenza-related complications. In healthy working adults, influenza vaccines can provide moderate protection against virologically confirmed influenza, though such protection is greatly reduced or absent in some seasons.
In healthcare workers, a 2006 review found a net benefit. Of the eighteen studies in this review, only two also assessed the relationship of patient mortality relative to staff influenza vaccine uptake; both found that higher rates of healthcare worker vaccination correlated with reduced patient deaths. A 2014 review found benefits to patients when healthcare workers were immunized, as supported by moderate evidence based in part on the observed reduction in all-cause deaths in patients whose healthcare workers were given immunization compared with comparison patients where the workers were not offered vaccine.
Elderly
Evidence for an effect in adults over 65 is unclear. Systematic reviews examining both randomized controlled and case–control studies found a lack of high-quality evidence. Reviews of case–control studies found effects against laboratory-confirmed influenza, pneumonia, and death among the community-dwelling elderly.
The group most vulnerable to non-pandemic flu, the elderly, benefits least from the vaccine. There are multiple reasons behind this steep decline in vaccine efficacy, the most common of which are the declining immunological function and frailty associated with advanced age. In a non-pandemic year, a person in the United States aged 50–64 is nearly ten times more likely to die an influenza-associated death than a younger person, and a person over 65 is more than ten times more likely to die an influenza-associated death than the 50–64 age group.
There is a high-dose flu vaccine specifically formulated to provide a stronger immune response. Available evidence indicates that vaccinating the elderly with the high-dose vaccine leads to a stronger immune response against influenza than the regular-dose vaccine.
A flu vaccine containing an adjuvant was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2015, for use by adults aged 65 years of age and older. The vaccine is marketed as Fluad in the US and was first available in the 2016–2017 flu season. The vaccine contains the MF59C.1 adjuvant which is an oil-in-water emulsion of squalene oil. It is the first adjuvanted seasonal flu vaccine marketed in the United States. It is not clear if there is a significant benefit for the elderly to use a flu vaccine containing the MF59C.1 adjuvant. Per Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices guidelines, Fluad can be used as an alternative to other influenza vaccines approved for people 65 years and older.
Vaccinating healthcare workers who work with elderly people is recommended in many countries, with the goal of reducing influenza outbreaks in this vulnerable population. While there is no conclusive evidence from randomized clinical trials that vaccinating healthcare workers helps protect elderly people from influenza, there is tentative evidence of benefit.
Fluad Quad was approved for use in Australia in September 2019, Fluad Quadrivalent was approved for use in the United States in February 2020, and Fluad Tetra was approved for use in the European Union in May 2020.
Pregnancy
As well as protecting mother and child from the effects of an influenza infection, the immunization of pregnant women tends to increase their chances of experiencing a successful full-term pregnancy.
The trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine is protective in pregnant women infected with HIV.
Safety
Side effects
While side effects of the flu vaccine may occur, they are usually minor, including soreness, redness, and swelling around the point of injection, headache, fever, nausea or fatigue. Side effects of a nasal spray vaccine may include runny nose, wheezing, sore throat, cough, or vomiting.
In some people, a flu vaccine may cause serious side effects, including an allergic reaction, but this is rare. Furthermore, the common side effects and risks are mild and temporary when compared to the risks and severe health effects of the annual influenza epidemic.
Guillain–Barré syndrome
Although Guillain–Barré syndrome had been feared as a complication of vaccination, the CDC states that most studies on modern influenza vaccines have seen no link with Guillain–Barré. Infection with influenza virus itself increases both the risk of death (up to one in ten thousand) and the risk of developing Guillain–Barré syndrome to a far higher level than the highest level of suspected vaccine involvement (approximately ten times higher by 2009 estimates).
Although one review gives an incidence of about one case of Guillain–Barré per million vaccinations, a large study in China, covering close to a hundred million doses of vaccine against the 2009 H1N1 "swine" flu found only eleven cases of Guillain–Barré syndrome, (0.1 per million doses) total incidence in persons vaccinated, actually lower than the normal rate of the disease in China, and no other notable side effects.
Egg allergy
Although most influenza vaccines are produced using egg-based techniques, influenza vaccines are nonetheless still recommended for people with egg allergies, even if severe. Studies examining the safety of influenza vaccines in people with severe egg allergies found that anaphylaxis was very rare, occurring in 1.3 cases per million doses given.
Monitoring for symptoms from vaccination is recommended in those with more severe symptoms. A study of nearly 800 children with egg allergy, including over 250 with previous anaphylactic reactions, had zero systemic allergic reactions when given the live attenuated flu vaccine.
Other
Several studies have identified an increased incidence of narcolepsy among recipients of the pandemic H1N1 influenza ASO3-adjuvanted vaccine; efforts to identify a mechanism for this suggest that narcolepsy is autoimmune, and that the ASO3-adjuvanted H1N1 vaccine may mimic hypocretin, serving as a trigger.
Some injection-based flu vaccines intended for adults in the United States contain thiomersal (also known as thimerosal), a mercury-based preservative. Despite some controversy in the media, the World Health Organization's Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety has concluded that there is no evidence of toxicity from thiomersal in vaccines and no reason on grounds of safety to change to more-expensive single-dose administration.
Types
Flu vaccines are available either as:
- a trivalent or quadrivalent intramuscular injection (IIV3, IIV4, or RIV4, that is, TIV or QIV), which contains the inactivated form of the virus
- a nasal spray of live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV, Q/LAIV), which contains the live but attenuated (weakened) form of the virus.
TIV or QIV induce protection after injection (typically intramuscular, though subcutaneous and intradermal routes can also be protective) based on an immune response to the antigens present on the inactivated virus, while cold-adapted LAIV works by establishing infection in the nasal passages.
Recommendations
Various public health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), recommend that yearly influenza vaccination be routinely offered, particularly to people at risk of complications of influenza and those individuals who live with or care for high-risk individuals, including:
- the elderly (UK recommendation is those aged 65 or above)
- people with chronic lung diseases (asthma, COPD, etc.)
- people with chronic heart diseases (congenital heart disease, chronic heart failure, ischaemic heart disease)
- people with chronic liver diseases (including cirrhosis)
- people with chronic kidney diseases (such as the nephrotic syndrome)
- people who have had their spleen removed or whose spleen is not working properly
- people who are immunosuppressed (people with HIV, those receiving medications to suppress the immune system, and people on chemotherapy) and their household contacts
- people who live together in large numbers in an environment where influenza can spread rapidly, such as prisons, nursing homes, schools, and dormitories.
- healthcare workers (both to prevent sickness and to prevent spread to their patients)
- pregnant women. However, a 2009 review concluded that there was insufficient evidence to recommend routine use of trivalent influenza vaccine during the first trimester of pregnancy. Influenza vaccination during flu season is part of recommendations for influenza vaccination of pregnant women in the United States.
The flu vaccine is contraindicated for those under six months of age and those with severe, life-threatening allergies to flu vaccine or any ingredient in the vaccine.
World Health Organization
As of 2016, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends seasonal influenza vaccination for:
First priority:
- Pregnant women
Second priority (in no particular order):
- Children aged 6–59 months
- Elderly
- Individuals with specific chronic medical conditions
- Health-care workers
Canada
The National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI), the group that advises the Public Health Agency of Canada, recommends that everyone over six months of age be encouraged to receive annual influenza vaccination, and that children between the age of six months and 24 months, and their household contacts, should be considered a high priority for the flu vaccine. Particularly:
- People at high risk of influenza-related complications or hospitalization, including the morbidly obese, healthy pregnant women, children 6–59 months, the elderly, aboriginals, and people suffering from one of an itemized list of chronic health conditions
- People capable of transmitting influenza to those at high risk, including household contacts and healthcare workers
- People who provide essential community services
- Certain poultry workers
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) was not available in Canada for the 2019–2020 season.
European Union
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) recommends vaccinating the elderly as a priority, with a secondary priority people with chronic medical conditions and healthcare workers.
The influenza vaccination strategy is generally that of protecting vulnerable people, rather than limiting influenza circulation or totally eliminating human influenza sickness. This is in contrast with the high herd immunity strategies for other infectious diseases such as polio and measles. This is also due in part to the financial and logistics burden associated with the need of an annual injection.
United States
In the United States routine influenza vaccination is recommended for all persons aged six months and over. It takes up to two weeks after vaccination for sufficient antibodies to develop in the body. The CDC recommends vaccination before the end of October, although it considers getting a vaccine in January or even later to be still beneficial.
According to the CDC, the live attenuated virus (LAIV4) (which comes in the form of the nasal spray in the US) should be avoided by:
- Children younger than two years
- Adults fifty and older
- Concomitant aspirin- or salicylate-containing therapy in children and adolescents
- Children aged two through four years who have received a diagnosis of asthma or whose parents or caregivers report that a healthcare provider has told them during the past twelve months that their child had wheezing or asthma or whose medical record indicates that a wheezing episode has occurred within the past twelve months
- Persons who are immunocompromised due to any cause (including but not limited to medications and HIV infection)
- Close contacts and caregivers of severely immunocompromised persons who require a protected environment
- Pregnant women
- Persons who have received influenza antiviral medications within the previous 48 hours
Within its blanket recommendation for general vaccination in the United States, the CDC, which began recommending the influenza vaccine to healthcare workers in 1981, emphasizes to clinicians the special urgency of vaccination for members of certain vulnerable groups, and their caregivers:
- Vaccination is especially important for people at higher risk of serious influenza complications or people who live with or care for people at higher risk for serious complications. In 2009, a new high-dose formulation of the standard influenza vaccine was approved. The Fluzone High Dose is specifically for people 65 and older; the difference is that it has four times the antigen dose of the standard Fluzone.
The US government requires hospitals to report worker vaccination rates. Some US states and hundreds of US hospitals require healthcare workers to either get vaccinations or wear masks during flu season. These requirements occasionally engender union lawsuits on narrow collective bargaining grounds, but proponents note that courts have generally endorsed forced vaccination laws affecting the general population during disease outbreaks.
Vaccination against influenza is especially considered important for members of high-risk groups who would be likely to have complications from influenza, for example pregnant women and children and teenagers from six months to 18 years of age who are receiving aspirin- or salicylate-containing medications and who might be at risk for experiencing Reye syndrome after influenza virus infection;
- In raising the upper age limit to 18 years, the aim is to reduce both the time children and parents lose from visits to pediatricians and missing school and the need for antibiotics for complications
- An added benefit expected from the vaccination of children is a reduction in the number of influenza cases among parents and other household members, and of possible spread to the general community.
The CDC indicated that live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV), also called the nasal spray vaccine, was not recommended for the 2016–2017 flu season in the United States.
Furthermore, the CDC recommends that healthcare personnel who care for severely immunocompromised persons receive injections (TIV or QIV) rather than LAIV.
Australia
The Australian Government recommends seasonal flu vaccination for everyone over the age of six months. Australia uses inactivated vaccines. The flu vaccine is free for the following people:
- children aged six months to five years
- people aged 65 years and over
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people aged six months and over
- pregnant women
- anyone over six months of age with medical conditions such as severe asthma, lung disease or heart disease, low immunity or diabetes that can lead to complications from influenza.
Uptake
| Country | Region | % aged 65+ |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | 83 | |
| Oceania | 75 | |
| Europe | 73 | |
| Americas | 68 | |
| Oceania | 65 | |
| Americas | 65 | |
| Europe | 64 | |
| Americas | 61 | |
| Europe | 61 | |
| Asia | 58 | |
| Europe | 58 | |
| Europe | 54 | |
| Europe | 53 | |
| Europe | 52 | |
| Asia | 50 | |
| Europe | 50 | |
| Europe | 49 | |
| Europe | 48 | |
| Europe | 45 | |
| Europe | 38 | |
| Europe | 35 | |
| Europe | 34 | |
| Europe | 27 | |
| Europe | 20 | |
| Europe | 13 | |
| Europe | 13 | |
| Europe | 12 | |
| Europe | 8 | |
| Asia | 7 | |
| Europe | 5 |
At risk groups
Uptake of flu vaccination, both seasonally and during pandemics, is often low. Systematic reviews of pandemic flu vaccination uptake have identified several personal factors that may influence uptake, including gender (higher uptake in men), ethnicity (higher in people from ethnic minorities) and having a chronic illness. Beliefs in the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine are also important.
A number of measures have been found to be useful to increase rates of vaccination in those over sixty including: patient reminders using leaflets and letters, postcard reminders, client outreach programs, vaccine home visits, group vaccinations, free vaccinations, physician payment, physician reminders and encouraging physician competition.
Healthcare workers
Frontline healthcare workers are often recommended to get seasonal and any pandemic flu vaccination. For example, in the UK all healthcare workers involved in patient care are recommended to receive the seasonal flu vaccine, and were also recommended to be vaccinated against the H1N1/09 (later renamed A(H1N1)pdm09) swine flu virus during the 2009 pandemic. However, uptake is often low. During the 2009 pandemic, low uptake by healthcare workers was seen in countries including the UK, Italy, Greece, and Hong Kong.
In a 2010 survey of United States healthcare workers, 63.5% reported that they received the flu vaccine during the 2010–11 season, an increase from 61.9% reported the previous season. US Health professionals with direct patient contact had higher vaccination uptake, such as physicians and dentists (84.2%) and nurse practitioners (82.6%).
The main reason to vaccinate healthcare workers is to prevent staff from spreading flu to their patients and to reduce staff absence at a time of high service demand, but the reasons healthcare workers state for their decisions to accept or decline vaccination may more often be to do with perceived personal benefits.
In Victoria (Australia) public hospitals, rates of healthcare worker vaccination in 2005 ranged from 34% for non-clinical staff to 42% for laboratory staff. One of the reasons for rejecting vaccines was concern over adverse reactions; in one study, 31% of resident physicians at a teaching hospital incorrectly believed Australian vaccines could cause influenza.
Manufacturing
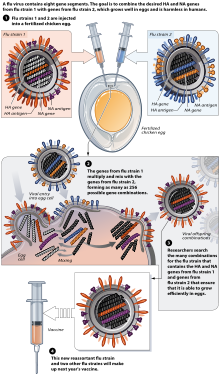
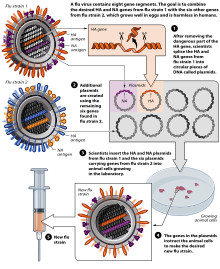
Flu vaccine is usually grown by vaccine manufacturers in fertilized chicken eggs. In the Northern hemisphere, the manufacturing process begins following the announcement (typically in February) of the WHO recommended strains for the winter flu season. Three strains (representing an H1N1, an H3N2, and a B strain) of flu are selected and chicken eggs are inoculated separately. These monovalent harvests are then combined to make the trivalent vaccine.
As of November 2007, both the conventional injection and the nasal spray are manufactured using chicken eggs. The European Union also approved Optaflu, a vaccine produced by Novartis using vats of animal cells. This technique is expected to be more scalable and avoid problems with eggs, such as allergic reactions and incompatibility with strains that affect avians like chickens. Research continues into the idea of a "universal" influenza vaccine that would not require tailoring to a particular strain, but would be effective against a broad variety of influenza viruses. However, no vaccine candidates had been announced by November 2007.
A DNA-based vaccination, which is hoped to be even faster to manufacture, is, as of 2011, in clinical trials, determining safety and efficacy.
On November 20, 2012, Novartis received FDA approval for the first cell-culture vaccine.
In a 2007 report, the global capacity of approximately 826 million seasonal influenza vaccine doses (inactivated and live) was double the production of 413 million doses. In an aggressive scenario of producing pandemic influenza vaccines by 2013, only 2.8 billion courses could be produced in a six-month time frame. If all high- and upper-middle-income countries sought vaccines for their entire populations in a pandemic, nearly two billion courses would be required. If China pursued this goal as well, more than three billion courses would be required to serve these populations. Vaccine research and development is ongoing to identify novel vaccine approaches that could produce much greater quantities of vaccine at a price that is affordable to the global population.
Methods of vaccine generation that bypass the need for eggs include the construction of influenza virus-like particles (VLP). VLP resemble viruses, but there is no need for inactivation, as they do not include viral coding elements, but merely present antigens in a similar manner to a virion. Some methods of producing VLP include cultures of Spodoptera frugiperda Sf9 insect cells and plant-based vaccine production (e.g., production in Nicotiana benthamiana). There is evidence that some VLPs elicit antibodies that recognize a broader panel of antigenically distinct viral isolates compared to other vaccines in the hemagglutination-inhibition assay (HIA).
Influenza vaccines are produced in pathogen-free eggs that are eleven or twelve days old. The top of the egg is disinfected by wiping it with alcohol and then the egg is candled to identify a non-veinous area in the allantoic cavity where a small hole is poked to serve as a pressure release. A second hole is made at the top of the egg, where the influenza virus is injected in the allantoic cavity, past the chorioallantoic membrane. The two holes are then sealed with melted paraffin and the inoculated eggs are incubated for 48 hours at 37 degrees Celsius. During incubation time, the virus replicates and newly replicated viruses are released into the allantoic fluid
After the 48-hour incubation period, the top of the egg is cracked and the ten milliliters of allantoic fluid is removed, from which about fifteen micrograms of the flu vaccine can be obtained. At this point, the viruses have been weakened or killed and the viral antigen is purified and placed inside vials, syringes, or nasal sprayers. Done on a large-scale, this method is used to produce the flu vaccine for the human population.
In 2013, the recombinant influenza vaccine, Flublok, was approved for use in the United States.
On 17 September 2020, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for Supemtek, a quadrivalent influenza vaccine (recombinant, prepared in cell culture). The applicant for this medicinal product is Sanofi Pasteur. Supemtek was approved for medical use in the European Union in November 2020.
Annual reformulation
Each year, three strains are chosen for selection in that year's flu vaccination by the WHO Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System. The chosen strains are the H1N1, H3N2, and Type-B strains thought most likely to cause significant human suffering in the coming season. Starting with the 2012–2013 Northern Hemisphere influenza season (coincident with the approval of quadrivalent influenza vaccines), the WHO has also recommended a 2nd B-strain for use in quadrivalent vaccines. The World Health Organization (WHO) coordinates the contents of the vaccine each year to contain the most likely strains of the virus to attack the next year.
- "The WHO Global Influenza Surveillance Network was established in 1952 [renamed "Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System" in 2011]. The network comprises four WHO Collaborating Centres (WHO CCs) and 112 institutions in 83 countries, which are recognized by WHO as WHO National Influenza Centres (NICs). These NICs collect specimens in their country, perform primary virus isolation and preliminary antigenic characterization. They ship newly isolated strains to WHO CCs for high level antigenic and genetic analysis, the result of which forms the basis for WHO recommendations on the composition of influenza vaccine for the Northern and Southern Hemisphere each year."
The Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System's selection of viruses for the vaccine manufacturing process is based on its best estimate of which strains will predominate the next year, amounting in the end to well-informed but fallible guesswork.
Formal WHO recommendations were first issued in 1973. Beginning in 1999 there have been two recommendations per year: one for the northern hemisphere and the other for the southern hemisphere.
Historical annual reformulations of the influenza vaccine are listed in a separate article. Recent WHO seasonal influenza vaccine composition recommendations:
2017–2018 Northern Hemisphere influenza season
The composition of trivalent virus vaccines for use in the 2017–2018 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices on August 25, 2017 was:
- an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1)pdm09–like virus
- an A/Hong Kong/4801/2014 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Brisbane/60/2008–like virus (Victoria lineage)
In addition to these components, quadrivalent vaccines will also include a B/Phuket/3073/2013–like virus (Yamagata lineage).
In California, some emergency systems were strained by a spike in H3N2 flu cases. In addition, some areas experienced local shortages of oseltamivir. The severity of the flu season seemed somewhat comparable to the 2009–10 swine flu outbreak. A February 2018 CDC interim report estimated the vaccine effectiveness to be 25% against H3N2, 67% against H1N1, and 42% against influenza B.
2018 Southern Hemisphere influenza season
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the 2018 Southern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization on September 28, 2017 was:
- an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus
The WHO recommended that quadrivalent vaccines containing two influenza B viruses should contain the above three viruses and a B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus.
2018–2019 Northern Hemisphere influenza season
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the 2018–2019 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization on February 22, 2018 was:
- an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Singapore/INFIMH-16-0019/2016 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus (B/Victoria/2/87 lineage)
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (B/Yamagata/16/88 lineage)
The WHO recommended that trivalent vaccines use as their influenza B virus a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus of the B/Victoria/2/87-lineage. A February 2019, CDC interim report estimated the vaccine effectiveness to be approximately 47% against the 2018–2019 flu strains.
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the United States for the 2018–2019 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the Food and Drug Administration on March 1, 2018, was:
- an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Singapore/INFIMH-16–0019/2016 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus (B/Victoria lineage)
The committee also recommended that quadrivalent influenza vaccines contain the above three strains and the following additional B strain:
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (B/Yamagata lineage)
2019 Southern Hemisphere influenza season
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the 2019 Southern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization in September 2018 was:
- an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Switzerland/8060/2017 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus (B/Victoria/2/87 lineage)
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (B/Yamagata/16/88 lineage)
The WHO recommended that trivalent vaccines use as their influenza B virus a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus of the B/Victoria/2/87-lineage.
2019–2020 Northern Hemisphere influenza season
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the 2019–2020 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization on March 21, 2019 was:
- an A/Brisbane/02/2018 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Kansas/14/2017 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus (B/Victoria/2/87 lineage)
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (B/Yamagata/16/88 lineage)
The WHO recommended that trivalent vaccines use as their influenza B virus a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus of the B/Victoria/2/87-lineage.
2020–2021 Northern Hemisphere influenza season
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the 2020–2021 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization on February 28, 2020 is for egg-based:
- an A/Guangdong-Maonan/SWL1536/2019 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Hong Kong/2671/2019 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Washington/02/2019 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (B/Yamagata lineage)-like virus
for cell- or recombinant-based:
- an A/Hawaii/70/2019 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Hong Kong/45/2019 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Washington/02/2019 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (B/Yamagata lineage)-like virus
The WHO recommends that trivalent vaccines use as their influenza B virus a B/Washington/02/2019 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
United States
2019–2020
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the United States for the 2019–2020 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on March 22, 2019, was:
- an A/Brisbane/02/2018 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Kansas/14/2017 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus (B/Victoria lineage)
The committee also recommended that quadrivalent influenza vaccines contain the above three strains and the following additional B strain:
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (B/Yamagata lineage)
2020–2021
The Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommended that the quadrivalent formulation of egg-based influenza vaccines for the US 2020–2021 influenza season contain the following:
- an A/Guangdong-Maonan/SWL1536/2019 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus;
- an A/HongKong/2671/2019 (H3N2)-like virus;
- a B/Washington/02/2019-like virus (B/Victoria lineage);
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (B/Yamagata lineage).
The committee recommended that the quadrivalent formulation of cell- or recombinant-based influenza vaccines for the US 2020–2021 influenza season contain the following:
- an A/Hawaii/70/2019 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus;
- an A/HongKong/45/2019 (H3N2)-like virus;
- a B/Washington/02/2019-like virus (B/Victoria lineage);
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (B/Yamagata lineage)
For trivalent influenza vaccines for use in the US for the 2020–2021 influenza season, depending on the manufacturing method of the vaccine, the committee recommended that the A(H1N1)pdm09, A(H3N2) and B/Victoria lineage viruses recommended above for the quadrivalent vaccines be used.
European Union
2019–2020
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the European Union for the 2019–2020 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the European Medicines Agency on May 15, 2019, is:
Trivalent vaccines should contain:
- an A/Brisbane/02/2018 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus;
- an A/Kansas/14/2017 (H3N2)-like virus;
- a B/Colorado/06/2017-like virus (B/Victoria/2/87 lineage).
For vaccine manufacturers considering the use of a B/Yamagata/16/88 virus lineage vaccine virus in quadrivalent vaccines containing two influenza B viruses, a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus in addition to the strains mentioned above is considered appropriate.
2020–2021
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the European Union for the 2020–2021 Northern Hemisphere influenza season recommended by the European Medicines Agency on April 1, 2020, is:
Egg-based or live attenuated trivalent vaccines should contain:
- an A/Guangdong-Maonan/SWL1536/2019 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus;
- an A/Hong Kong/2671/2019 (H3N2)-like virus;
- a B/Washington/02/2019 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
Cell-based trivalent vaccines should contain:
- an A/Hawaii/70/2019 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus;
- an A/Hong Kong/45/2019 (H3N2)-like virus;
- a B/Washington/02/2019 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
A B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus is recommended in addition to the strains mentioned above for the quadrivalent vaccines.
2020 Southern Hemisphere influenza season
The composition of virus vaccines for use in the 2020 Southern Hemisphere influenza season influenza season recommended by the World Health Organization in September 2019 was:
- an A/Brisbane/02/2018 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/South Australia/34/2019 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Washington/02/2019-like (B/Victoria lineage) virus
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like (B/Yamagata lineage) virus
The WHO recommended that trivalent vaccines use as their influenza B virus a B/Washington/02/2019-like (B/Victoria lineage) virus.
History
Vaccines are used in both humans and nonhumans. Human vaccine is meant unless specifically identified as a veterinary, poultry or livestock vaccine.
Origins and development
In the worldwide Spanish flu pandemic of 1918, "Pharmacists tried everything they knew, everything they had ever heard of, from the ancient art of bleeding patients, to administering oxygen, to developing new vaccines and serums (chiefly against what we now call Hemophilus influenzae – a name derived from the fact that it was originally considered the etiological agent – and several types of pneumococci). Only one therapeutic measure, transfusing blood from recovered patients to new victims, showed any hint of success."
In 1931, viral growth in embryonated hens' eggs was reported by Ernest William Goodpasture and colleagues at Vanderbilt University. The work was extended to growth of influenza virus by several workers, including Thomas Francis, Jonas Salk, Wilson Smith and Macfarlane Burnet, leading to the first experimental influenza vaccines. In the 1940s, the US military developed the first approved inactivated vaccines for influenza, which were used in the Second World War. Hen's eggs continued to be used to produce virus used in influenza vaccines, but manufacturers made improvements in the purity of the virus by developing improved processes to remove egg proteins and to reduce systemic reactivity of the vaccine. In 2012, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved influenza vaccines made by growing virus in cell cultures and influenza vaccines made from recombinant proteins have been approved, with plant-based influenza vaccines being tested in clinical trials.
Acceptance
According to the CDC: "Influenza vaccination is the primary method for preventing influenza and its severe complications. [...] Vaccination is associated with reductions in influenza-related respiratory illness and physician visits among all age groups, hospitalization and death among persons at high risk, otitis media among children, and work absenteeism among adults. Although influenza vaccination levels increased substantially during the 1990s, further improvements in vaccine coverage levels are needed."
The egg-based technology (still in use as of 2019) for producing influenza vaccine was created in the 1950s. In the US swine flu scare of 1976, President Gerald Ford was confronted with a potential swine flu pandemic. The vaccination program was rushed, yet plagued by delays and public relations problems. Meanwhile, maximum military containment efforts succeeded unexpectedly in confining the new strain to the single army base where it had originated. On that base, a number of soldiers fell severely ill, but only one died. The program was canceled after about 24% of the population had received vaccinations. An excess in deaths of twenty-five over normal annual levels as well as four hundred excess hospitalizations, both from Guillain–Barré syndrome, were estimated to have occurred from the vaccination program itself, illustrating that the vaccine itself is not free of risks. The result has been cited to stoke lingering doubts about vaccination. In the end, however, even the maligned 1976 vaccine may have saved lives. A 2010 study found a significantly enhanced immune response against the 2009 pandemic H1N1 in study participants who had received vaccination against the swine flu in 1976.
Quadrivalent vaccines for seasonal flu
A quadrivalent flu vaccine administered by nasal mist was approved by the FDA in March 2012. Fluarix Quadrivalent was approved by the FDA in December 2012.
In 2014, the Canadian National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) published a review of quadrivalent influenza vaccines.
Starting with the 2018-2019 influenza season most of the regular-dose egg-based flu shots and all the recombinant and cell-grown flu vaccines in the United States are quadrivalent. In the 2019–2020 influenza season all regular-dose flu shots and all recombinant influenza vaccine in the United States are quadrivalent.
In November 2019, the FDA approved Fluzone High-Dose Quadrivalent for use in the United States starting with the 2020-2021 influenza season.
In February 2020, the FDA approved Fluad Quadrivalent for use in the United States. In July 2020, the FDA approved both Fluad and Fluad Quadrivalent for use in the United States for the 2020–2021 influenza season.
Cost-effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of seasonal influenza vaccination has been widely evaluated for different groups and in different settings. In the elderly (over 65), the majority of published studies have found that vaccination is cost saving, with the cost savings associated with influenza vaccination (e.g. prevented healthcare visits) outweighing the cost of vaccination. In older adults (aged 50–64 years), several published studies have found that influenza vaccination is likely to be cost-effective, however the results of these studies were often found to be dependent on key assumptions used in the economic evaluations. The uncertainty in influenza cost-effectiveness models can partially be explained by the complexities involved in estimating the disease burden, as well as the seasonal variability in the circulating strains and the match of the vaccine. In healthy working adults (aged 18–49 years), a 2012 review found that vaccination was generally not cost-saving, with the suitability for funding being dependent on the willingness to pay to obtain the associated health benefits. In children, the majority of studies have found that influenza vaccination was cost-effective, however many of the studies included (indirect) productivity gains, which may not be given the same weight in all settings. Several studies have attempted to predict the cost-effectiveness of interventions (including prepandemic vaccination) to help protect against a future pandemic, however estimating the cost-effectiveness has been complicated by uncertainty as to the severity of a potential future pandemic and the efficacy of measures against it.
Research
Influenza research includes molecular virology, molecular evolution, pathogenesis, host immune responses, genomics, and epidemiology. These help in developing influenza countermeasures such as vaccines, therapies and diagnostic tools. Improved influenza countermeasures require basic research on how viruses enter cells, replicate, mutate, evolve into new strains and induce an immune response. The Influenza Genome Sequencing Project is creating a library of influenza sequences that will help researchers' understanding of what makes one strain more lethal than another, what genetic determinants most affect immunogenicity, and how the virus evolves over time. Solutions to limitations in current[when?] vaccine methods are being researched.
A different approach uses Internet content to estimate the impact of an influenza vaccination campaign. More specifically, researchers have used data from Twitter and Microsoft's Bing search engine, and proposed a statistical framework which, after a series of operations, maps this information to estimates of the influenza-like illness reduction percentage in areas where vaccinations have been performed. The method has been used to quantify the impact of two flu vaccination programmes in England (2013/14 and 2014/15), where school-age children were administered a live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV). Notably, the impact estimates were in accordance with estimations from Public Health England based on traditional syndromic surveillance endpoints.
Rapid response to pandemic flu
The rapid development, production, and distribution of pandemic influenza vaccines could potentially save millions of lives during an influenza pandemic. Due to the short time frame between identification of a pandemic strain and need for vaccination, researchers are looking at novel technologies for vaccine production that could provide better "real-time" access and be produced more affordably, thereby increasing access for people living in low- and moderate-income countries, where an influenza pandemic may likely originate, such as live attenuated (egg-based or cell-based) technology and recombinant technologies (proteins and virus-like particles). As of July 2009, more than seventy known clinical trials have been completed or are ongoing for pandemic influenza vaccines. In September 2009, the FDA approved four vaccines against the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus (the 2009 pandemic strain), and expected the initial vaccine lots to be available within the following month.
In January 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Audenz as a vaccine for the H5N1 flu virus. Audenz is a vaccine indicated for active immunization for the prevention of disease caused by the influenza A virus H5N1 subtype contained in the vaccine. Audenz is approved for use in persons six months of age and older at increased risk of exposure to the influenza A virus H5N1 subtype contained in the vaccine.
Universal flu vaccines
A "universal vaccine" that would not have to be designed and made for each flu season in each hemisphere would be useful, in order to stabilize the supply and to ensure against error in the design or escape of the circulating strains by mutation. Such a vaccine has been the subject of research for decades.
One promising approach is using broadly neutralizing antibodies that unlike the annual seasonal vaccines used over the last several decades which provoke the body to generate an immune response, instead provide a component of the immune response itself. The first neutralizing antibodies were identified in 1993, via experimentation; with time researchers understood that the flu neutralizing antibodies were binding to the stalk of the Hemagglutinin protein; later researchers identified antibodies that could bind to the head of those proteins. Later yet, researchers identified the highly conserved M2 proton channel as a potential target for broadly neutralizing antibodies.
The challenges for researchers have been identifying single antibodies that could neutralize many subtypes of the virus, so that they could be useful in any season, and that target conserved domains that are resistant to antigenic drift.
Another approach has been taking the conserved domains identified from these projects, and delivering groups of these antigens to provoke an immune response; various approaches with different antigens, presented different ways (as fusion proteins, mounted on virus-like particles, on non-pathogenic viruses, as DNA, and others), are under development.
Efforts have also been undertaken to develop universal vaccines that specifically activate a T-cell response, based on clinical data showing that people with a strong, early T-cell response have better outcomes when infected with influenza and because T-cells respond to conserved epitopes. The challenge for developers is that these epitopes are on internal protein domains that are only mildly immunogenic.
Along with the rest of the vaccine field, people working on universal vaccines have been experimenting with vaccine adjuvants to improve the ability of their vaccines to create a sufficiently powerful and enduring immune response.
There have been some clinical trials of the M-001and H1ssF_3928 universal influenza vaccine candidates. As of August 2020, all seven M-001 trials are completed. Each one of these studies resulted in the conclusion that M-001 is safe, tolerable, and immunogenic. Their pivotal Phase III study with 12,400 participants has also been completed and results of data analysis were published in October 2020, unfortunately indicating that the vaccine did not show any statistical difference from the placebo group in reduction of flu illness and severity.
Oral influenza vaccine
As of 2019, an oral flu vaccine was in clinical research. The oral vaccine candidate is based on an adenovirus type 5 vector modified to remove genes needed for replication, with an added gene that expresses a small double-stranded RNA hairpin molecule as an adjuvant. In 2020, a Phase II human trial of the pill form of the vaccine showed that it was well tolerated and provided similar immunity to a licensed injectable vaccine.
Veterinary use
Veterinary influenza vaccination aims to achieve the following four objectives:
- Protection from clinical disease
- Protection from infection with virulent virus
- Protection from virus excretion
- Serological differentiation of infected from vaccinated animals (so-called DIVA principle).
Horses
Horses with horse flu can run a fever, have a dry hacking cough, have a runny nose, and become depressed and reluctant to eat or drink for several days but usually recover in two to three weeks. "Vaccination schedules generally require a primary course of two doses, 3–6 weeks apart, followed by boosters at 6–12 month intervals. It is generally recognized that in many cases such schedules may not maintain protective levels of antibody and more frequent administration is advised in high-risk situations."
It is a common requirement at shows in the United Kingdom that horses be vaccinated against equine flu and a vaccination card must be produced; the International Federation for Equestrian Sports (FEI) requires vaccination every six months.
Poultry
Poultry vaccines for bird flu are made inexpensively and are not filtered and purified like human vaccines to remove bits of bacteria or other viruses. They usually contain whole virus, not just hemagglutinin as in most human flu vaccines. Another difference between human and poultry vaccines is that poultry vaccines are adjuvated with mineral oil, which induces a strong immune reaction but can cause inflammation and abscesses. "Chicken vaccinators who have accidentally jabbed themselves have developed painful swollen fingers or even lost thumbs, doctors said. Effectiveness may also be limited. Chicken vaccines are often only vaguely similar to circulating flu strains – some contain an H5N2 strain isolated in Mexico years ago. 'With a chicken, if you use a vaccine that's only 85 percent related, you'll get protection,' Dr. Cardona said. 'In humans, you can get a single point mutation, and a vaccine that's 99.99 percent related won't protect you.' And they are weaker [than human vaccines]. 'Chickens are smaller and you only need to protect them for six weeks, because that's how long they live till you eat them,' said Dr. John J. Treanor, a vaccine expert at the University of Rochester. Human seasonal flu vaccines contain about 45 micrograms of antigen, while an experimental A(H5N1) vaccine contains 180. Chicken vaccines may contain less than one microgram. 'You have to be careful about extrapolating data from poultry to humans,' warned Dr. David E. Swayne, director of the agriculture department's Southeast Poultry Research Laboratory. 'Birds are more closely related to dinosaurs.'"
Researchers, led by Nicholas Savill of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland, used mathematical models to simulate the spread of H5N1 and concluded that "at least 95 percent of birds need to be protected to prevent the virus spreading silently. In practice, it is difficult to protect more than 90 percent of a flock; protection levels achieved by a vaccine are usually much lower than this." The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations has issued recommendations on the prevention and control of avian influenza in poultry, including the use of vaccination.
A filtered and purified Influenza A vaccine for humans is being developed and many countries have recommended it be stockpiled so if an Avian influenza pandemic starts jumping to humans, the vaccine can quickly be administered to avoid loss of life. Avian influenza is sometimes called avian flu, and commonly bird flu.
Pigs
Swine influenza vaccines are extensively used in pig farming in Europe and North America. Most swine flu vaccines include an H1N1 and an H3N2 strain.
Swine influenza has been recognized as a major problem since the outbreak in 1976. Evolution of the virus has resulted in inconsistent responses to traditional vaccines. Standard commercial swine flu vaccines are effective in controlling the problem when the virus strains match enough to have significant cross-protection. Customised (autogenous) vaccines made from the specific viruses isolated, are made and used in the more difficult cases. The vaccine manufacturer Novartis claims that the H3N2 strain (first identified in 1998) has brought major losses to pig farmers. Abortion storms are a common sign and sows stop eating for a few days and run a high fever. The mortality rate can be as high as fifteen percent.
Dogs
In 2004, influenza A virus subtype H3N8 was discovered to cause canine influenza. Because of the lack of previous exposure to this virus, dogs have no natural immunity to this virus. However, a vaccine was found in 2004.