Equal pay for equal work is the concept of labour rights that individuals in the same workplace be given equal pay. It is most commonly used in the context of sexual discrimination, in relation to the gender pay gap. Equal pay relates to the full range of payments and benefits, including basic pay, non-salary payments, bonuses and allowances. Some countries have moved faster than others in addressing equal pay.
Early history
As wage-labour became increasingly formalized during the Industrial Revolution, women were often paid less than their male counterparts for the same labour, whether for the explicit reason that they were women or under another pretext. The principle of equal pay for equal work arose at the sames part of first-wave feminism, with early efforts for equal pay being associated with nineteenth-century Trade Union activism in industrialized countries: for example, a series of strikes by unionized women in the UK in the 1830s. Pressure from Trade Unions has had varied effects, with trade unions sometimes promoting conservatism. Carrie Ashton Johnson was an American suffragist who related equal pay and wages of women in the industrial workforce to the issue of women's suffrage. In 1895, she was quoted by the Chicago Tribune as having said, "When women are given the ballot, there will be equal pay for equal work." However, following the Second World War, trade unions and the legislatures of industrialized countries gradually embraced the principle of equal pay for equal work; one example of this process is the UK's introduction of the Equal Pay Act 1970 in response both to the Treaty of Rome and the Ford sewing machinists strike of 1968. In recent years European trade unions have generally exerted pressure on states and employers for progress in this direction.
International human rights law
In international human rights law, the statement on equal pay is the 1951 Equal Remuneration Convention, Convention 100 of the International Labour Organization, a United Nations body. The Convention states that
- Each Member shall, by means appropriate to the methods in operation for determining rates of remuneration, promote and, in so far as is consistent with such methods, ensure the application to all workers of the principle of equal remuneration for men and women workers for work of equal value.
Equal pay for equal work is also covered by Article 7 of the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, Article 4 of the European Social Charter, and Article 15 of African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights. The Constitution of the International Labour Organization also proclaims "the principles of equal remuneration for equal value".
The EEOC's four affirmative defenses allows unequal pay for equal work when the wages are set "pursuant to (i) a seniority system; (ii) a merit system; (iii) a system which measures earnings by quantity or quality of production; or (iv) ... any other factor other than sex." A pay differential due to one of these factors is not in breach of the convention.
Legal situation by jurisdiction
European Union/European Economic Area
Post-war Europe has seen a fairly consistent pattern in women's participation in the labour market and legislation to promote equal pay for equal work across Eastern and Western countries.
Some countries now in the EU, including France, Germany, and Poland, had already enshrined the principle of equal pay for equal work in their constitutions before the foundation of the EU (see table below). When the European Economic Community, later the European Union (EU), was founded in 1957, the principle of equal pay for equal work was named as a key principle. Article 141 of the Treaty of Rome says 'each Member State shall ensure that the principle of equal pay for male and female workers for equal work or work of equal value is applied.' While socially progressive, this decision does not necessarily indicate widespread progressive attitudes among the signatories to the treaty:
- While this is often viewed as an example of the progressive nature of the European community, some argue that Article 141 (previously 119) was included largely as a concession to the French who already had equal pay legislation and feared that they would be at a comparative disadvantage.
The EEC's legislation was clarified in 1975 by the binding and directly applicable equal pay directive 75/117/EEC. This prohibited all discrimination on the grounds of sex in relation to pay; this and other directives were integrated into a single Directive in 2006 (2006/54/EC).
At the national level the principle of equal pay is in general fully reflected in the legislation of the 28 EU member states and the additional countries of the European Economic Area (EEA), Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway. The EU candidate countries of Macedonia and Turkey also adapted their legislation to EU standards. The main national legislation concerning pay equity between men and women for different European countries is as follows.
| Country | Main legal provisions |
|---|---|
| Austria | The 1979 Act on Equal Treatment on Men and Women (as amended since) |
| Belgium | The 1999 Law on Equal Treatment for Men and Women (Articles 12 and 25) and the Royal Decree of 9 December 1975 |
| Bulgaria | Equal pay for equal work included in the labour code |
| Czech Republic | Remuneration for work is regulated by Act no. 1/1992 Coll. on pay, remuneration for overtime, and average income and by Act no. 43/1991 Coll. on pay and remuneration for overtime in state and some other organisations and bodies. |
| Denmark | The 1976 Act on Equal Pay for Men and Women, as amended since to include additional points |
| Finland | The 1995 Constitution (section 5, paragraph 4) and the Act on Equality between Men and Women (section 8, paragraph 2) |
| France | The 1946 Constitution and Articles L.140.2 and thereafter of the Labour Code |
| Germany | The 1949 Constitution or "Basic Law" (Article 3) |
| Greece | The 1975 Constitution (Article 22(1)), as amended in 2001, and Law 1484/1984 (Article 4) |
| Hungary | Equal pay for equal work was previously included in the constitution, but it has changed; there is now only equality between men and women, and the pay is in the Labour Code. |
| Iceland | The 1961 Equal pay act (#60/1961), 1976 Law for Equality between women and men (#78/1976), 2008 Act on Equal Status and Equal Rights of Women and Men (#10/2008) and the amendment added to the law in 2017: Law on equal pay certification according to the Equal Pay Standard introduced in 2012 (ÍST 85:2012) |
| Ireland | The 1998 Employment Equality Act (IE9909144F), repealing the 1974 Anti-Discrimination (Pay) Act and the 1977 Employment Equality Act |
| Israel | The 1998 Law for Option Equality at Work and the 1996 Law for Equal Pay for Female Worker and Male Worker |
| Italy | The Constitution (Articles 3 and 37), Law 903/1977 (Article 2), and Law 125/1991 |
| Latvia | Equal pay for equal work included in the labour code |
| Liechtenstein | Equal pay for equal work included in the civil code |
| Lithuania | Equal pay for equal work included in the labour code |
| Luxembourg | The 1981 law relating to equal treatment between men and women and the 1974 Grand-Ducal Regulation of relating to equal pay for men and women (Articles 1, 2, 3(1), 3(2) and 4) |
| Malta | The Constitution (Article 14) and the Equality for Men and Women Act |
| Netherlands | The Constitution (Article 1) and the 1994 Law on Equal Treatment |
| Norway | The 1978 Act on Gender Equality |
| Poland | The 1997 Constitution, Chapter II, Article 33.2 enshrined the equal pay for equal work principle, already included in the 1952 Constitution. |
| Portugal | The Constitution (Article 59) and Law 105/1997 relating to equal treatment at work and in employment |
| Romania | Equal pay for equal work included in the constitution |
| Slovakia | Equal pay for equal work included in the constitution |
| Spain | The Constitution (Article 35) and the Workers' Statute (Articles 17 and 28). |
| Sweden | The 1980 Act on Equality between Men and Women/Equal Opportunities Act, as amended since |
| UK | The Equal Pay Act 1970, as amended by Equal Value Regulations of 1983, and the Sex Discrimination Act of 1975 and 1986, superseded by the Equality Act 2010 |
2018 Update Law on Equal Pay Certification based on the Equal Pay Standard in Iceland
Iceland introduced an Equal Pay Standard in 2012, ÍST 85:2012 (Equal wage management system - Requirements and guidance). The standard was developed by the Icelandic trade unions, the employers’ confederation and government officials with the goal in mind that it would help employers prevent salary discrimination and enable them to become certified.
In 2017, the Icelandic government decided to add an amendment to the 2008 laws Act on Equal Status and Equal Rights of Women and Men (#10/2008). The amendment is a law on equal pay certification and was put into effect on January 1 in 2018. According to the amendment companies and institutions employing 25 or more workers, on annual basis, will be required to obtain equal pay certification of their equal pay system and the implementation thereof. The purpose of this obligatory certification is to enforce the current legislation prohibiting discriminatory practices based on gender and requiring that women and men working for the same employer shall be paid equal wages and enjoy equal terms of employment for the same jobs or jobs of equal value.
United States
Federal law: Equal Pay Act of 1963 and Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
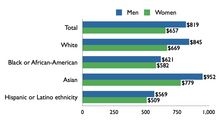
By the 20th century, women made up about a quarter of United States workforce but were still paid far less than men, whether it was the same job or a different job. There were different laws for women in some states such as, not working at night and restriction of their working hours. Women started entering more factory jobs when World War II began to replace men who were enlisted in the military. The wage gap continued to escalate during the war. The National War Labor Board put policies in place to help provide equal pay for women who were directly replacing men.
The first attempt at equal pay legislation in the United States, H.R. 5056, "Prohibiting Discrimination in Pay on Account of Sex," was introduced by Congresswoman Winifred C. Stanley of Buffalo, N.Y. on June 19, 1944. Twenty years later, legislation passed by the federal government in 1963 made it illegal to pay men and women different wage rates for equal work on jobs that require equal skill, effort, and responsibility, and are performed under similar working conditions. One year after passing the Equal Pay Act, Congress passed the 1964 Civil Rights Act. Title VII of this act makes it unlawful to discriminate based on a person's race, religion, color, or sex. Title VII attacks sex discrimination more broadly than the Equal Pay Act extending not only to wages but to compensation, terms, conditions or privileges of employment. Thus with the Equal Pay Act and Title VII, an employer cannot deny women equal pay for equal work; deny women transfers, promotions, or wage increases; manipulate job evaluations to relegate women's pay; or intentionally segregate men and women into jobs according to their gender.
Since Congress was debating this bill at the same time that the Equal Pay Act was coming into effect, there was concern over how these two laws would interact, which led to the passage of Senator Bennett's Amendment. This Amendment states: "It Shall not be unlawful employment practice under this subchapter for any employer to differentiate upon the basis of sex ... if such differentiation is authorized by the provisions of the [Equal Pay Act]." There was confusion on the interpretation of this Amendment, which was left to the courts to resolve. Thus US federal law now states that "employers may not pay unequal wages to men and women who perform jobs that require substantially equal skill, effort and responsibility, and that are performed under similar working conditions within the same establishment."
New York state
In 1944, the state of New York outlawed wage discrimination based on one's gender. On 10 July 2019, New York Governor Andrew Cuomo signed into law legislation guaranteeing equal pay for equal work regardless of one's gender. This builds on the 1944 law by prohibiting employers from asking job candidates about their previously salary, a loophole that has had a history of enforcing pay inequality based on gender. Cuomo signed the law in tandem with the 2019 Women's World Cup victory parade in New York City.
Washington state
In Washington, Governor Evans implemented a pay equity study in 1973 and another in 1977. The results clearly showed that when comparing male and female dominated jobs there was almost no overlap between the averages for similar jobs and in every sector, a twenty percent gap emerged. For example, a food service worker earned $472 per month, and a Delivery Truck Driver earned $792, though they were both given the same number of "points" on the scale of comparable worth to the state. Unfortunately for the state, and for the female state workers, his successor Governor Dixie Lee Ray failed to implement the recommendations of the study (which clearly stated women made 20 percent less than men). Thus in 1981, AFSCME filed a sex discrimination complaint with the EEOC against the State of Washington. The District Court ruled that since the state had done a study of sex discrimination in the state, found that there was severe disparities in wages, and had not done anything to ameliorate these disparities, this constituted discrimination under Title VII that was "pervasive and intentional." The Court then ordered the State to pay its over 15,500 women back pay from 1979 based on a 1983 study of comparable worth. This amounted to over $800 million. However, the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit overturned this decision, stating that Washington had always required their employees' salaries to reflect the free market, and discrimination was one cause of many for wage disparities. The court stated, "the State did not create the market disparity ... [and] neither law nor logic deems the free market system a suspect enterprise." While the suit was ultimately unsuccessful, it led to state legislation bolstering state workers’ pay. The costs for implementing this equal pay policy was 2.6% of personnel costs for the state.
Minnesota
In Minnesota, the state began considering a formal comparable worth policy in the late 1970s when the Minnesota Task Force of the Council on the Economic Status of Women commissioned Hay Associates to conduct a study. The results were staggering and similar to the results in Washington (there was a 20% gap between state male and female workers pay). Hay Associates proved that in the 19 years since the Equal Pay Act was passed, wage discrimination persisted and had even increased over from 1976 to 1981. Using their point system, they noted that while delivery van drivers and clerk typists were both scaled with 117 points each of "worth" to the state, the delivery van driver (a male-dominated profession) was paid $1,382 a month while the clerk typist (a female dominated profession) was paid $1,115 a month. The study also noted that women were severely underrepresented in manager and professional positions, and that state jobs were often segregated by sex. The study finally recommended that the state take several courses of action: 1) establish comparable worth considerations for female-dominated jobs; 2) set aside money to ameliorate the pay inequity; 3) encourage affirmative action for women and minorities and 4) continue analyzing the situation to improve it. The Minnesota Legislature moved immediately in response. In 1983 the state appropriated 21.8 million dollars to begin amending the pay disparities for state employees. From 1982 to 1993, women's wages in the state increased 10%. According to the Star Tribune, in 2005 women in Minnesota state government made 97 cents to the dollar, ranking Minnesota as one of the most equal for female state workers in the country. Five years later in 2010, full pay equity for women in state employment was finally achieved, with recurring, typically minor pay adjustments in local governments occurring regularly.
Federal law: Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act
In 2009, President Obama signed the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act, permitting women to sue employers for unfair pay up to 180 days after receiving an unfair paycheck. On 29 January 2016, he signed an executive order obliging all companies with at least 100 employees to disclose the pay of all workers to the federal government, with breakdowns of pay by race, gender, and ethnicity. The goal is to encourage employers to give equal pay for equal work by increasing transparency.
Massachusetts
In August 2016, Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker signed a bill to improve upon the already existing Massachusetts Equal Pay Act. On July 1, 2018, this updated amendment went into effect to protect employees from being asked their previous salary by their current employer. Governor Baker sought change in the current system after recognizing that women in their respective fields, on average, were making 76 cents on the dollar compared to men doing the same job. Under the updated Massachusetts Equal Pay Act, employers are not allowed to have disparity in pay for employees doing a job that requires the same level of skill, effort, and responsibility. The Massachusetts Equal Pay Act only permits differences in pay when it is based on merit, seniority, revenue generated, education, and location or travel. At the time of its arrival in 2018, the Massachusetts Equal Pay Act became the strongest advocate for equal pay between genders in the United States. It became the first state to provide affirmative defense to employers under the condition they have performed a self-audit of their pay practices. In order to be protected, there needs to be proven record of efforts made to close the disparity in pay before they become liable for double of the discriminated employee’s lost wages.
State and local laws, 2010s
California and New York City have adopted laws which prohibit employers from asking about salary history to determine the salary that will be offered for a new job. This is intended to narrow the gender pay gap by reducing the impact of past discrimination. Many other U.S. states were considering similar laws, as of May 2017.
Australia
In 1948, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights started to recognize equal pay for equal work. The Equal Remuneration Convention was released in 1951 by the International Labour Organization. The convention stated that it recommends jobs to be classified according to the nature of the work rather than who is performing the work. Women and men participated in protests, calling the government to fix the 1951 convention and make equal pay the law in Australia. In 1969, there was a case brought to the ACAC by the Australasian Meat Industry Employees Union against the Meat and Allied Trades Federation. Workers argued for equal pay for every employee and the ruling of the commission was that the general female award minimum wage at 85 per cent of the male wage. This decision helped equal pay for women who were working the same job that traditionally the men would do, but all the other women got the 85 per cent. In 1972 the decision was reassessed and rules that either women or men who are working at a similar job that has a similar value, are eligible for the same working rate.
Under Australia's old centralised wage fixing system, "equal pay for work of equal value" by women was introduced in 1969. Anti-discrimination on the basis of sex was legislated in 1984.
Canada
In Canadian usage, the terms pay equity and pay equality are used somewhat differently from in other countries. The two terms refer to distinctly separate legal concepts.
Pay equality, or equal pay for equal work, refers to the requirement that men and women be paid the same if performing the same job in the same organization. For example, a female electrician must be paid the same as a male electrician in the same organization. Reasonable differences are permitted if due to seniority or merit.
Pay equality is required by law in each of Canada’s 14 legislative jurisdictions (ten provinces, three territories, and the federal government). Note that federal legislation applies only to those employers in certain federally regulated industries such as banks, broadcasters, and airlines, to name a few. For most employers, the relevant legislation is that of the respective province or territory.
For federally regulated employers, pay equality is guaranteed under the Canadian Human Rights Act. In Ontario, pay equality is required under the Ontario Employment Standards Act. Every Canadian jurisdiction has similar legislation, although the name of the law will vary.
In contrast, pay equity, in the Canadian context, means that male-dominated occupations and female-dominated occupations of comparable value must be paid the same if within the same employer. The Canadian term pay equity is referred to as "comparable worth" in the US. For example, if an organization's nurses and electricians are deemed to have jobs of equal importance, they must be paid the same. One way of distinguishing the concepts is to note that pay equality addresses the rights of women employees as individuals, whereas pay equity addresses the rights of female-dominated occupations as groups.
Certain Canadian jurisdictions have pay equity legislation while others do not, hence the necessity of distinguishing between pay equity and pay equality in Canadian usage. For example, in Ontario, pay equality is guaranteed through the Ontario Employment Standards Act while pay equity is guaranteed through the Ontario Pay Equity Act. On the other hand, the three westernmost provinces (British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan) have pay equality legislation but no pay equity legislation. Some provinces (for example, Manitoba) have legislation that requires pay equity for public sector employers but not for private sector employers; meanwhile, pay equality legislation applies to everyone.
India
Constitutional protections
As part of its Directive Principles of State Policy, the Constitution of India through Article 39 envisages that all states ideally direct their policy towards securing equal pay for equal work for both men and women, and also ensuring that men and women have the right to an adequate means of livelihood. While these Directive Principles are not enforceable by any court of law, they are crucial to the governance of the country and a state is duty bound to consider them while enacting laws.
While “equal pay for equal work” is not expressly a constitutional right, it has been read into the Constitution through the interpretation of Articles 14, 15 and 16 – which guarantee equality before the law, protection against discrimination and equality of opportunity in matters of public employment. The Supreme Court of India has also declared this to be a constitutional goal, available to every individual and capable of being attained through the enforcement of their fundamental rights set out in Articles 14 through 16. In a popular Supreme Court decision, the conditions of employment of the air-hostesses of Air India was challenged. The terms of employment required the mandatory retirement of females: (i) upon attaining the age of 33; (ii) if they were married within four years of service; or (iii) upon their first pregnancy. The court however struck down these provisions and held them to be arbitrary and discriminatory as it violated Articles 14, 15 and 16 of the Constitution.
Statutory Protection
In 1976, the Equal Remuneration Act was passed with the aim of providing equal remuneration to men and women workers and to prevent discrimination on the basis of gender in all matters relating to employment and employment opportunities. This legislation not only provides women with a right to demand equal pay, but any inequality with respect to recruitment processes, job training, promotions, and transfers within the organization can also be challenged under this Act. However, its scope does not extend to situations where: (i) a woman is attempting to comply with the requirements of laws giving women special treatment; and (ii) a woman is being accorded special treatment on account of the birth of a child, or the terms and conditions relating to retirement, marriage or death. Companies and individual employers can both be held accountable to maintain the standards prescribed under this Act. In various cases, the Supreme Court of India has also held that discrimination on the basis of gender only arises when men and women perform the same work or work of a similar nature. However, it clarified that a flexible approach is required to be taken while deciding which kinds of work may be similar by considering the duties actually performed as a part of the job, and not the duties potentially capable of being performed.
Taiwan
Taiwan legislated the Act of Gender Equality in Employment in 2002. It regulates that an employer must give the same salary to the workers who do the same work. The law prescribes that employers shall not discriminate against employees because of their gender or sexual orientation in the case of paying wages. Employees shall receive equal pay for equal work or equal value. However, if such differentials are the result of seniority systems, award and discipline systems, merit systems or other justifiable reasons of non-sexual or non-sexual-orientation factors, the above-mentioned restriction shall not apply. Employers may not adopt methods of reducing the wages of other employees in order to evade the stipulation of the preceding paragraph.
Criticism
Criticisms of the principle of equal pay for equal work by women include criticism of the mechanisms used to achieve it and the methodology by which the gap is measured. Some believe that government actions to correct gender pay disparity serve to interfere with the system of voluntary exchange. They argue the fundamental issue is that the employer is the owner of the job, not the government or the employee. The employer negotiates the job and pays according to performance, not according to job duties. The issue with that is men are perceived to be high performers based on the same skill that a woman would have been able to do. A private business would not want to lose its best performers by compensating them less and can ill afford paying its lower performers higher because the overall productivity will decline. However, the Independent Women's Forum cites another study that prognosticates the wage gap possibly disappearing "when controlled for experience, education, and number of years on the job".
The difference between equal pay for equal work and equal pay for work of equal value
| Equal pay for equal work | Equal pay for work of equal value |
|---|---|
| Equal pay compares the pay of incumbents in the same or very similar jobs. | Pay equity compares the value and pay of different jobs, such as nurse and electrician. |
| In Canada, either men or women can complain that their work is undervalued. If a male incumbent is paid less than a female incumbent in the same job, he can file a complaint. As well, a woman or man can complain if she or he is paid less than a man or woman in the same job. | In Canada, only people (both men and women) in jobs traditionally reserved for women can complain that their work is undervalued. If nurses are paid less than electricians by the same employer, then they can file a complaint. |
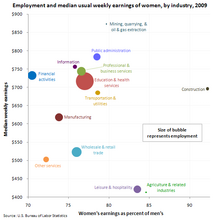
According to the Washington Center for Equitable Growth using data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, occupations that are more male dominated tend to be paid better regardless of skill or education level.
For example, it often requires a similar level of skill and education to be an electrician as it does to be a nurse. However, electricians, a male-dominated field, earn more than nurses, a female-dominated field. In situations where, for example, the electrician is performing their job 200 feet above the base floor of an offshore oil rig, then pay should be higher because the risks are likewise higher. However, this doesn't explain the gap between the average work of electricians.
A criticism to equal pay for work of equal value is the lack of proper comparation mechanisms, it is based on subjective impressions and not based on real facts and statistics. As in previous example, checking statistic data from US BLS, we can prove that it is a false statement that electricians earn more than nurses. Based on the statistics electricians earn ~1015$/weekly while nurses earn ~1223$/weekly, so in this case proving that nurses, a female dominated field, earn more than electricians, a male dominated field.
Transparency laws
Transparency laws require companies to disclose wages to employees or the government. This can reduce the gender pay gap by allowing women to negotiate for equivalent pay (rather than a salary history which may reflect past discrimination) and by shaming employers into treating men and women equally.