Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes gaseous fuel, obtained from either syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, or a mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The syngas could be derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by reforming of natural gas. Alternatively a mixture of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and green hydrogen could be used for an almost climate neutral production of synthetic fuels.
Common ways for refining synthetic fuels include the Fischer–Tropsch conversion, methanol to gasoline conversion, or direct coal liquefaction.
As of July 2019, worldwide commercial synthetic fuels production capacity was over 240,000 barrels per day (38,000 m3/d), with numerous new projects in construction or development, such as Carbon Engineering.
Classification and principles
The term 'synthetic fuel' or 'synfuel' has several different meanings and it may include different types of fuels. More traditional definitions, such as the definition given by the International Energy Agency, define 'synthetic fuel' or 'synfuel' as any liquid fuel obtained from coal or natural gas. In its Annual Energy Outlook 2006, the Energy Information Administration defines synthetic fuels as fuels produced from coal, natural gas, or biomass feedstocks through chemical conversion into synthetic crude and/or synthetic liquid products. A number of synthetic fuel's definitions include fuels produced from biomass, and industrial and municipal waste. The definition of synthetic fuel also allows oil sands and oil shale as synthetic fuel sources, and in addition to liquid fuels, synthesized gaseous fuels are also considered to be synthetic fuels: in his 'Synthetic fuels handbook' petrochemist James G. Speight included liquid and gaseous fuels as well as clean solid fuels produced by conversion of coal, oil shale or tar sands, and various forms of biomass, although he admits that in the context of substitutes for petroleum-based fuels it has even wider meaning. Depending on the context, methanol, ethanol and hydrogen may also be included.
Synthetic fuels are produced by the chemical process of conversion. Conversion methods could be direct conversion into liquid transportation fuels, or indirect conversion, in which the source substance is converted initially into syngas which then goes through additional conversion process to become liquid fuels. Basic conversion methods include carbonization and pyrolysis, hydrogenation, and thermal dissolution.
History
The process of direct conversion of coal to synthetic fuel originally developed in Germany. Friedrich Bergius developed the Bergius process, which received a patent in 1913. Karl Goldschmidt invited Bergius to build an industrial plant at his factory, the Th. Goldschmidt AG (part of Evonik Industries from 2007), in 1914. Production began in 1919.
Indirect coal conversion (where coal is gasified and then converted to synthetic fuels) was also developed in Germany - by Franz Fischer and Hans Tropsch in 1923. During World War II (1939-1945), Germany used synthetic-oil manufacturing (German: Kohleverflüssigung) to produce substitute (Ersatz) oil products by using the Bergius process (from coal), the Fischer–Tropsch process (water gas), and other methods (Zeitz used the TTH and MTH processes). In 1931 the British Department of Scientific and Industrial Research located in Greenwich, England, set up a small facility where hydrogen gas was combined with coal at extremely high pressures to make a synthetic fuel.
The Bergius process plants became Nazi Germany's primary source of high-grade aviation gasoline, synthetic oil, synthetic rubber, synthetic methanol, synthetic ammonia, and nitric acid. Nearly one third of the Bergius production came from plants in Pölitz (Polish: Police) and Leuna, with 1/3 more in five other plants (Ludwigshafen had a much smaller Bergius plant which improved "gasoline quality by dehydrogenation" using the DHD process).
Synthetic fuel grades included "T.L. [jet] fuel", "first quality aviation gasoline", "aviation base gasoline", and "gasoline - middle oil"; and "producer gas" and diesel were synthesized for fuel as well (converted armored tanks, for example, used producer gas). By early 1944 German synthetic-fuel production had reached more than 124,000 barrels per day (19,700 m3/d) from 25 plants, including 10 in the Ruhr Area. In 1937 the four central Germany lignite coal plants at Böhlen, Leuna, Magdeburg/Rothensee, and Zeitz, along with the Ruhr Area bituminous coal plant at Scholven/Buer, produced 4.8 million barrels (760×103 m3) of fuel. Four new hydrogenation plants (German: Hydrierwerke) were subsequently erected at Bottrop-Welheim (which used "Bituminous coal tar pitch"), Gelsenkirchen (Nordstern), Pölitz, and, at 200,000 tons/yr Wesseling. Nordstern and Pölitz/Stettin used bituminous coal, as did the new Blechhammer plants. Heydebreck synthesized food oil, which was tested on concentration camp prisoners. After Allied bombing of Germany's synthetic-fuel production plants (especially in May to June 1944), the Geilenberg Special Staff used 350,000 mostly foreign forced-laborers to reconstruct the bombed synthetic-oil plants, and, in an emergency decentralization program, the Mineralölsicherungsplan (1944-1945), to build 7 underground hydrogenation plants with bombing protection (none were completed). (Planners had rejected an earlier such proposal, expecting that Axis forces would win the war before the bunkers would be completed.) In July 1944 the "Cuckoo" project underground synthetic-oil plant (800,000 m2) was being "carved out of the Himmelsburg" north of the Mittelwerk, but the plant remained unfinished at the end of World War II. Production of synthetic fuel became even more vital for Nazi Germany when Soviet Red Army forces occupied the Ploiești oilfields in Romania on 24 August 1944, denying Germany access to its most important natural oil source.
Indirect Fischer–Tropsch ("FT") technologies were brought to the United States after World War II, and a 7,000 barrels per day (1,100 m3/d) plant was designed by HRI and built in Brownsville, Texas. The plant represented the first commercial use of high-temperature Fischer–Tropsch conversion. It operated from 1950 to 1955, when it was shut down after the price of oil dropped due to enhanced production and huge discoveries in the Middle East.
In 1949 the U.S. Bureau of Mines built and operated a demonstration plant for converting coal to gasoline in Louisiana, Missouri. Direct coal conversion plants were also developed in the US after World War II, including a 3 TPD plant in Lawrenceville, New Jersey, and a 250-600 TPD Plant in Catlettsburg, Kentucky.
In later decades the Republic of South Africa established a state oil company including a large synthetic fuel establishment.
Processes
The numerous processes that can be used to produce synthetic fuels broadly fall into three categories: Indirect, Direct, and Biofuel processes.
Indirect conversion
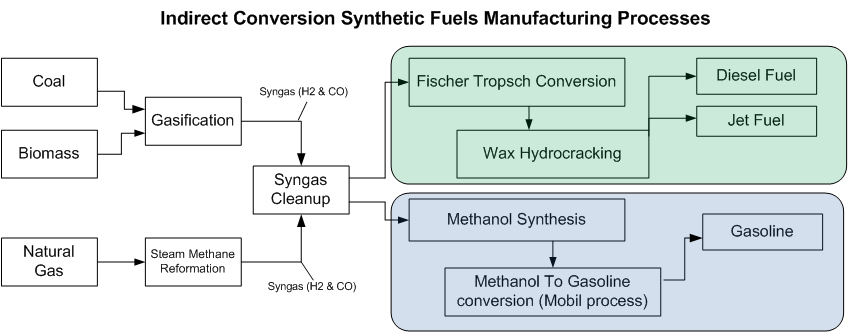
Indirect conversion has the widest deployment worldwide, with global production totaling around 260,000 barrels per day (41,000 m3/d), and many additional projects under active development.
Indirect conversion broadly refers to a process in which biomass, coal, or natural gas is converted to a mix of hydrogen and carbon monoxide known as syngas either through gasification or steam methane reforming, and that syngas is processed into a liquid transportation fuel using one of a number of different conversion techniques depending on the desired end product.
The primary technologies that produce synthetic fuel from syngas are Fischer–Tropsch synthesis and the Mobil process (also known as Methanol-To-Gasoline, or MTG). In the Fischer–Tropsch process syngas reacts in the presence of a catalyst, transforming into liquid products (primarily diesel fuel and jet fuel) and potentially waxes (depending on the FT process employed).
The process of producing synfuels through indirect conversion is often referred to as coal-to-liquids (CTL), gas-to-liquids (GTL) or biomass-to-liquids (BTL), depending on the initial feedstock. At least three projects (Ohio River Clean Fuels, Illinois Clean Fuels, and Rentech Natchez) are combining coal and biomass feedstocks, creating hybrid-feedstock synthetic fuels known as Coal and Biomass To Liquids (CBTL).
Indirect conversion process technologies can also be used to produce hydrogen, potentially for use in fuel cell vehicles, either as slipstream co-product, or as a primary output.
Direct conversion
Direct conversion refers to processes in which coal or biomass feedstocks are converted directly into intermediate or final products, avoiding the conversion to syngas via gasification. Direct conversion processes can be broadly broken up into two different methods: Pyrolysis and carbonization, and hydrogenation.
Hydrogenation processes
One of the main methods of direct conversion of coal to liquids by hydrogenation process is the Bergius process. In this process, coal is liquefied by heating in the presence of hydrogen gas (hydrogenation). Dry coal is mixed with heavy oil recycled from the process. Catalysts are typically added to the mixture. The reaction occurs at between 400 °C (752 °F) to 500 °C (932 °F) and 20 to 70 MPa hydrogen pressure. The reaction can be summarized as follows:
After World War I several plants were built in Germany; these plants were extensively used during World War II to supply Germany with fuel and lubricants.
The Kohleoel Process, developed in Germany by Ruhrkohle and VEBA, was used in the demonstration plant with the capacity of 200 ton of lignite per day, built in Bottrop, Germany. This plant operated from 1981 to 1987. In this process, coal is mixed with a recycle solvent and iron catalyst. After preheating and pressurizing, H2 is added. The process takes place in tubular reactor at the pressure of 300 bar and at the temperature of 470 °C (880 °F). This process was also explored by SASOL in South Africa.
In 1970-1980s, Japanese companies Nippon Kokan, Sumitomo Metal Industries and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries developed the NEDOL process. In this process, a mixture of coal and recycled solvent is heated in the presence of iron-based catalyst and H2. The reaction takes place in tubular reactor at temperature between 430 °C (810 °F) and 465 °C (870 °F) at the pressure 150-200 bar. The produced oil has low quality and requires intensive upgrading. H-Coal process, developed by Hydrocarbon Research, Inc., in 1963, mixes pulverized coal with recycled liquids, hydrogen and catalyst in the ebullated bed reactor. Advantages of this process are that dissolution and oil upgrading are taking place in the single reactor, products have high H:C ratio, and a fast reaction time, while the main disadvantages are high gas yield, high hydrogen consumption, and limitation of oil usage only as a boiler oil because of impurities.
The SRC-I and SRC-II (Solvent Refined Coal) processes were developed by Gulf Oil and implemented as pilot plants in the United States in the 1960s and 1970s. The Nuclear Utility Services Corporation developed hydrogenation process which was patented by Wilburn C. Schroeder in 1976. The process involved dried, pulverized coal mixed with roughly 1wt% molybdenum catalysts. Hydrogenation occurred by use of high temperature and pressure syngas produced in a separate gasifier. The process ultimately yielded a synthetic crude product, Naphtha, a limited amount of C3/C4 gas, light-medium weight liquids (C5-C10) suitable for use as fuels, small amounts of NH3 and significant amounts of CO2. Other single-stage hydrogenation processes are the Exxon donor solvent process, the Imhausen High-pressure Process, and the Conoco Zinc Chloride Process.
A number of two-stage direct liquefaction processes have been developed. After the 1980s only the Catalytic Two-stage Liquefaction Process, modified from the H-Coal Process; the Liquid Solvent Extraction Process by British Coal; and the Brown Coal Liquefaction Process of Japan have been developed.
Chevron Corporation developed a process invented by Joel W. Rosenthal called the Chevron Coal Liquefaction Process (CCLP). It is unique due to the close-coupling of the non-catalytic dissolver and the catalytic hydroprocessing unit. The oil produced had properties that were unique when compared to other coal oils; it was lighter and had far fewer heteroatom impurities. The process was scaled-up to the 6 ton per day level, but not proven commercially.
Pyrolysis and carbonization processes
There are a number of different carbonization processes. The carbonization conversion occurs through pyrolysis or destructive distillation, and it produces condensable coal tar, oil and water vapor, non-condensable synthetic gas, and a solid residue-char. The condensed coal tar and oil are then further processed by hydrogenation to remove sulfur and nitrogen species, after which they are processed into fuels.
The typical example of carbonization is the Karrick process. The process was invented by Lewis Cass Karrick in the 1920s. The Karrick process is a low-temperature carbonization process, where coal is heated at 680 °F (360 °C) to 1,380 °F (750 °C) in the absence of air. These temperatures optimize the production of coal tars richer in lighter hydrocarbons than normal coal tar. However, the produced liquids are mostly a by-product and the main product is semi-coke, a solid and smokeless fuel.
The COED Process, developed by FMC Corporation, uses a fluidized bed for processing, in combination with increasing temperature, through four stages of pyrolysis. Heat is transferred by hot gases produced by combustion of part of the produced char. A modification of this process, the COGAS Process, involves the addition of gasification of char. The TOSCOAL Process, an analogue to the TOSCO II oil shale retorting process and Lurgi-Ruhrgas process, which is also used for the shale oil extraction, uses hot recycled solids for the heat transfer.
Liquid yields of pyrolysis and Karrick processes are generally low for practical use for synthetic liquid fuel production. Furthermore, the resulting liquids are of low quality and require further treatment before they can be used as motor fuels. In summary, there is little possibility that this process will yield economically viable volumes of liquid fuel.
Biofuels processes
One example of a Biofuel-based synthetic fuel process is Hydrotreated Renewable Jet (HRJ) fuel. There are a number of variants of these processes under development, and the testing and certification process for HRJ aviation fuels is beginning.
There are two such process under development by UOP. One using solid biomass feedstocks, and one using bio-oil and fats. The process using solid second-generation biomass sources such as switchgrass or woody biomass uses pyrolysis to produce a bio-oil, which is then catalytically stabilized and deoxygenated to produce a jet-range fuel. The process using natural oils and fats goes through a deoxygenation process, followed by hydrocracking and isomerization to produce a renewable Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene jet fuel.
Oil sand and oil shale processes
Synthetic crude may also be created by upgrading bitumen (a tar like substance found in oil sands), or synthesizing liquid hydrocarbons from oil shale. There are a number of processes extracting shale oil (synthetic crude oil) from oil shale by pyrolysis, hydrogenation, or thermal dissolution.
Commercialization
Worldwide commercial synthetic fuels plant capacity is over 240,000 barrels per day (38,000 m3/d), including indirect conversion Fischer–Tropsch plants in South Africa (Mossgas, Secunda CTL), Qatar {Oryx GTL}, and Malaysia (Shell Bintulu), and a Mobil process (Methanol to Gasoline) plant in New Zealand.
Sasol, a company based in South Africa operates the world's only commercial Fischer–Tropsch coal-to-liquids facility at Secunda, with a capacity of 150,000 barrels per day (24,000 m3/d).
Economics
The economics of synthetic fuel manufacture vary greatly depending the feedstock used, the precise process employed, site characteristics such as feedstock and transportation costs, and the cost of additional equipment required to control emissions. The examples described below indicate a wide range of production costs between $20/BBL for large-scale gas-to-liquids, to as much as $240/BBL for small-scale biomass-to-liquids + Carbon Capture and Sequestration.
In order to be economically viable, projects must do much better than just being competitive head-to-head with oil. They must also generate a sufficient return on investment to justify the capital investment in the project.
CTL/CBTL/BTL economics
According to a December 2007 study, a medium scale (30,000 BPD) coal-to-liquids plant (CTL) sited in the US using bituminous coal, is expected to be competitive with oil down to roughly $52–56/bbl crude-oil equivalent. Adding carbon capture and sequestration to the project was expected to add an additional $10/BBL to the required selling price, though this may be offset by revenues from enhanced oil recovery, or by tax credits, or the eventual sale of carbon credits.
A recent NETL study examined the relative economics of a number of different process configurations for the production of indirect FT fuels using biomass, coal, and CCS. This study determined a price at which the plant would not only be profitable, but also make a sufficient return to yield a 20% return on the equity investment required to build the plant.
This chapter details an analysis which derives the Required Selling Price (RSP) of the FT diesel fuels produced in order to determine the economic feasibility and relative competitiveness of the different plant options. A sensitivity analysis was performed to determine how carbon control regulations such as an emissions trading scheme for transportation fuels would affect the price of both petroleum-derived diesel and FT diesel from the different plants. The key findings of these analyses were: (1) CTL plants equipped with CCS are competitive at crude oil prices as low as $86 per barrel and have less life cycle GHG emissions than petroleum-derived diesel. These plants become more economically competitive as carbon prices increase. (2) The incremental cost of adding simple CCS is very low (7 cents per gallon) because CO2 capture is an inherent part of the FT process. This becomes the economically preferred option at carbon prices above $5/mtCO2eq.27 (3) BTL systems are hindered by limited biomass availability which affects the maximum plant size, thereby limiting potential economies of scale. This, combined with relatively high biomass costs results in FT diesel prices which are double that of other configurations: $6.45 to $6.96/gal compared to $2.56 to $2.82/gal for CTL and 15wt% CBTL systems equipped with CCS.
The conclusion reached based on these findings was that both the CTL with CCS and the 8wt% to 15wt% CBTL with CCS configurations may offer the most pragmatic solutions to the nation's energy strategy dilemma: GHG emission reductions which are significant (5% to 33% below the petroleum baseline) at diesel RSPs that are only half as much as the BTL options ($2.56 to $2.82 per gallon compared to $6.45 to $6.96 per gallon for BTL). These options are economically feasible when crude oil prices are $86 to $95 per barrel.
These economics can change in the event that plentiful low-cost biomass sources can be found, lowing the cost of biomass inputs, and improving economies of scale.
Economics for solid feedstock indirect FT process plants are further confused by carbon regulation. Generally, since permitting a CTL plant without CCS will likely be impossible, and CTL+CCS plants have a lower carbon footprint than conventional fuels, carbon regulation is expected to be balance-positive for synthetic fuel production. But it impacts the economics of different process configurations in different ways. The NETL study picked a blended CBTL process using 5-15% biomass alongside coal as the most economical in a range of carbon price and probable future regulation scenarios. Because of scale and cost constraints, pure BTL processes did not score well until high carbon prices were assumed, though again this may improve with better feedstocks and more efficient larger scale projects.
Chinese direct coal liquefaction economics
Shenhua Group recently reported that their direct coal liquefaction process is competitive with oil prices above $60 per barrel. Previous reports have indicated an anticipated cost of production of less than $30 per barrel, based on a direct coal liquefaction process, and a coal mining cost of under $10/ton. In October 2011, actual price of coal in China was as high as $135/ton.
Security considerations
A central consideration for the development of synthetic fuel is the security factor of securing domestic fuel supply from domestic biomass and coal. Nations that are rich in biomass and coal can use synthetic fuel to off-set their use of petroleum derived fuels and foreign oil.
Environmental considerations
The environmental footprint of a given synthetic fuel varies greatly depending on which process is employed, what feedstock is used, what pollution controls are employed, and what the transportation distance and method are for both feedstock procurement and end-product distribution.
In many locations, project development will not be possible due to permitting restrictions if a process design is chosen that does not meet local requirements for clean air, water, and increasingly, lifecycle carbon emissions.
Lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions
Among different indirect FT synthetic fuels production technologies, potential emissions of greenhouse gasses vary greatly. Coal to liquids ("CTL") without carbon capture and sequestration ("CCS") is expected to result in a significantly higher carbon footprint than conventional petroleum-derived fuels (+147%). On the other hand, biomass-to-liquids with CCS could deliver a 358% reduction in lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions. Both of these plants fundamentally use gasification and FT conversion synthetic fuels technology, but they deliver wildly divergent environmental footprints.
Generally, CTL without CCS has a higher greenhouse gas footprint. CTL with CCS has a 9-15% reduction in lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions compared to that of petroleum derived diesel.
CBTL+CCS plants that blend biomass alongside coal while sequestering carbon do progressively better the more biomass is added. Depending on the type of biomass, the assumptions about root storage, and the transportation logistics, at conservatively 40% biomass alongside coal, CBTL+CCS plants achieve a neutral lifecycle greenhouse gas footprint. At more than 40% biomass, they begin to go lifecycle negative, and effectively store carbon in the ground for every gallon of fuels that they produce.
Ultimately BTL plants employing CCS could store massive amounts of carbon while producing transportation fuels from sustainably produced biomass feedstocks, although there are a number of significant economic hurdles, and a few technical hurdles that would have to be overcome to enable the development of such facilities.
Serious consideration must also be given to the type and method of feedstock procurement for either the coal or biomass used in such facilities, as reckless development could exacerbate environmental problems caused by mountaintop removal mining, land use change, fertilizer runoff, food vs. fuels concerns, or many other potential factors. Or they could not, depending entirely on project-specific factors on a plant-by-plant basis.
A study from U.S. Department of Energy National Energy Technology Laboratory with much more in-depth information of CBTL life-cycle emissions "Affordable Low Carbon Diesel from Domestic Coal and Biomass".
Hybrid hydrogen-carbon processes have also been proposed recently as another closed-carbon cycle alternative, combining 'clean' electricity, recycled CO, H2 and captured CO2 with biomass as inputs as a way of reducing the biomass needed.
Fuels emissions
The fuels produced by the various synthetic fuels process also have a wide range of potential environmental performance, though they tend to be very uniform based on the type of synthetic fuels process used (i.e. the tailpipe emissions characteristics of Fischer–Tropsch diesel tend to be the same, though their lifecycle greenhouse gas footprint can vary substantially based on which plant produced the fuel, depending on feedstock and plant level sequestration considerations.)
In particular, Fischer–Tropsch diesel and jet fuels deliver dramatic across-the-board reductions in all major criteria pollutants such as SOx, NOx, Particulate Matter, and Hydrocarbon emissions. These fuels, because of their high level of purity and lack of contaminants, further enable the use of advanced emissions control equipment that has been shown to virtually eliminate HC, CO, and PM emissions from diesel vehicles.
In testimony before the Subcommittee on Energy and Environment of the U.S. House of Representatives the following statement was made by a senior scientist from Rentech:
F-T fuels offer numerous benefits to aviation users. The first is an immediate reduction in particulate emissions. F-T jet fuel has been shown in laboratory combusters and engines to reduce PM emissions by 96% at idle and 78% under cruise operation. Validation of the reduction in other turbine engine emissions is still under way. Concurrent to the PM reductions is an immediate reduction in CO2 emissions from F-T fuel. F-T fuels inherently reduce CO2 emissions because they have higher energy content per carbon content of the fuel, and the fuel is less dense than conventional jet fuel allowing aircraft to fly further on the same load of fuel.
The "cleanness" of these FT synthetic fuels is further demonstrated by the fact that they are sufficiently non-toxic and environmentally benign as to be considered biodegradable. This owes primarily to the near-absence of sulfur and extremely low level of aromatics present in the fuel.
Sustainability
One concern commonly raised about the development of synthetic fuels plants is sustainability. Fundamentally, transitioning from oil to coal or natural gas for transportation fuels production is a transition from one inherently depletable geologically limited resource to another.
One of the positive defining characteristics of synthetic fuels production is the ability to use multiple feedstocks (coal, gas, or biomass) to produce the same product from the same plant. In the case of hybrid BCTL plants, some facilities are already planning to use a significant biomass component alongside coal. Ultimately, given the right location with good biomass availability, and sufficiently high oil prices, synthetic fuels plants can be transitioned from coal or gas, over to a 100% biomass feedstock. This provides a path forward towards a renewable fuel source and possibly more sustainable, even if the plant originally produced fuels solely from coal, making the infrastructure forwards-compatible even if the original fossil feedstock runs out.
Some synthetic fuels processes can be converted to sustainable production practices more easily than others, depending on the process equipment selected. This is an important design consideration as these facilities are planned and implemented, as additional room must be left in the plant layout to accommodate whatever future plant change requirements in terms of materials handling and gasification might be necessary to accommodate a future change in production profile.