From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |

Headquarters of Médecins sans frontières international in Geneva
|
| Founded | 20 December 1971 |
|---|
| Founders | Jacques Bérès
Philippe Bernier
Raymond Borel
Jean Cabrol
Marcel Delcourt
Xavier Emmanuelli
Pascal Grellety Bosviel
Gérard Illiouz Bernard Kouchner
Gérard Pigeon Vladan Radoman
Max Récamier
Jean-Michel Wild |
|---|
| Type | Medical humanitarian organisation |
|---|
| Location |
|
|---|
Area served
| Worldwide |
|---|
Key people
| Joanne Liu (MSF International President) |
|---|
Employees
| 36,482 |
|---|
| Website | msf.org |
|---|
Médecins Sans Frontières (
MSF; pronounced
[medsɛ̃ sɑ̃ fʁɔ̃tjɛʁ]), sometimes rendered in English as
Doctors Without Borders, is an international
humanitarian medical
non-governmental organisation (NGO) of French origin best known for its projects in conflict zones and in
countries affected by
endemic diseases.
In 2015, over 30,000 personnel — mostly local doctors, nurses and other
medical professionals, logistical experts, water and sanitation
engineers and administrators — provided medical aid in over 70
countries.
Most staff are volunteers. Private donors provide about 90% of the
organisation's funding, while corporate donations provide the rest,
giving MSF an annual budget of approximately US$1.63 billion.
Médecins sans frontières was founded in 1971, in the aftermath of the
Biafra secession, by a small group of French doctors and journalists who sought to expand accessibility to
medical care across national boundaries and irrespective of
race,
religion, creed or political affiliation.
To that end, the organisation emphasises "independence and
impartiality", and explicitly precludes political, economic, or
religious factors in its decision making. For these reasons, it limits
the amount of funding received from governments or intergovernmental
organisation. These principles have allowed MSF to speak freely with
respect to acts of war, corruption, or other hindrances to medical care
or human well-being. Only once in its history, during the
1994 genocide in Rwanda, has the organisation called for military intervention.
MSF's principles and operational guidelines are highlighted in its Charter, the Chantilly Principles, and the later La Mancha Agreement.
Governance is addressed in Section 2 of the Rules portion of this final
document. MSF has an associative structure, where operational decisions
are made, largely independently, by the five operational centres (
Amsterdam,
Barcelona-
Athens,
Brussels,
Geneva and
Paris).
Common policies on core issues are coordinated by the International
Council, in which each of the 24 sections (national offices) is
represented. The International Council meets in
Geneva,
Switzerland, where the International Office, which coordinates
international activities common to the operational centres, is also
based.
MSF has
general consultative status with the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It received the 1999
Nobel Peace Prize
in recognition of its members' continued efforts to provide medical
care in acute crises, as well as raising international awareness of
potential humanitarian disasters.
James Orbinski,
who was the president of the organization at the time, accepted the
prize on behalf of MSF. Prior to this, MSF also received the 1996
Seoul Peace Prize.
Joanne Liu has served as the international president since 1 October 2013.
MSF should not be confused with
Médecins du Monde
(Doctors of the World), which was formed in part by members of the
former organisation, but is an entirely independent non-governmental
organisation with no links to MSF today.
Origin
Biafra
During the
Nigerian Civil War of 1967 to 1970, the Nigerian military formed a
blockade around the nation's newly
independent south-eastern region,
Biafra. At this time, France was the only major country supportive of the Biafrans (the United Kingdom, the
Soviet Union
and the United States sided with the Nigerian government), and the
conditions within the blockade were unknown to the world. A number of
French doctors volunteered with the French
Red Cross to work in hospitals and feeding centres in besieged Biafra. One of the co-founders of the organisation was
Bernard Kouchner, who later became a high-ranking French politician.
After entering the country, the volunteers, in addition to Biafran
health workers and hospitals, were subjected to attacks by the
Nigerian army,
and witnessed civilians being murdered and starved by the blockading
forces. The doctors publicly criticised the Nigerian government and the
Red Cross for their seemingly complicit behaviour. These doctors
concluded that a new aid organisation was needed that would ignore
political/religious boundaries and prioritise the welfare of victims.
1971 establishment
The
Groupe d'intervention médicale et chirurgicale en urgence
("Emergency Medical and Surgical Intervention Group") was formed in
1971 by French doctors who had worked in Biafra, to provide aid and to
emphasize the importance of victims' rights over neutrality. At the same
time,
Raymond Borel, the editor of the French
medical journal TONUS, had started a group called
Secours Médical Français ("French Medical Relief") in response to the
1970 Bhola cyclone, which killed at least 625,000 in
East Pakistan
(now Bangladesh). Borel had intended to recruit doctors to provide aid
to victims of natural disasters. On 22 December 1971, the two groups of
colleagues merged to form
Médecins Sans Frontières.
MSF's first mission was to the Nicaraguan capital,
Managua, where a
1972 earthquake had destroyed most of the city and killed between 10,000 and 30,000 people.
The organization, today known for its quick response in an emergency,
arrived three days after the Red Cross had set up a relief mission. On
18 and 19 September 1974,
Hurricane Fifi
caused major flooding in Honduras and killed thousands of people
(estimates vary), and MSF set up its first long-term medical relief
mission.
Between 1975 and 1979, after
South Vietnam had fallen to
North Vietnam, millions of Cambodians emigrated to Thailand to avoid the
Khmer Rouge. In response MSF set up its first
refugee camp missions in Thailand. When Vietnam withdrew from Cambodia in 1989, MSF started long-term relief missions to help survivors of
the mass killings and reconstruct the country's health care system. Although its missions to Thailand to help victims of war in Southeast
Asia could arguably be seen as its first war-time mission, MSF saw its
first mission to a true war zone, including exposure to hostile fire, in
1976. MSF spent nine years (1976–1984) assisting surgeries in the
hospitals of various cities in Lebanon, during the
Lebanese Civil War, and established a reputation for its neutrality and willingness to work under fire. Throughout the war, MSF helped both
Christian and
Muslim soldiers
alike, helping whichever group required the most medical aid at the
time. In 1984, as the situation in Lebanon deteriorated further and
security for aid groups was minimised, MSF withdrew its volunteers.
New leadership
Claude Malhuret
was elected as the new president of Medicins Sans Frontieres in 1977,
and soon after debates began over the future of the organisation. In
particular, the concept of
témoignage ("witnessing"), which refers to speaking out about the suffering that one sees as opposed to remaining silent,
was being opposed or played down by Malhuret and his supporters.
Malhuret thought MSF should avoid criticism of the governments of
countries in which they were working, while Kouchner believed that
documenting and broadcasting the suffering in a country was the most
effective way to solve a problem.
In 1979, after four years of refugee movement from South Vietnam and the surrounding countries by foot and
by boat, French intellectuals made an appeal in
Le Monde
for "A Boat for Vietnam", a project intended to provide medical aid to
the refugees. Although the project did not receive support from the
majority of MSF, some, including later Minister
Bernard Kouchner, chartered a ship called
L’Île de Lumière ("The Island of Light"), and, along with doctors, journalists and photographers, sailed to the
South China Sea and provided some medical aid to the boat people. The splinter organisation that undertook this,
Médecins du Monde, later developed the idea of
humanitarian intervention as a duty, in particular on the part of Western nations such as France.
In 2007 MSF clarified that for nearly 30 years MSF and Kouchner have
had public disagreements on such issues as the right to intervene and
the use of armed force for humanitarian reasons. Kouchner is in favour
of the latter, whereas MSF stands up for an impartial humanitarian
action, independent from all political, economic and religious powers.
MSF development
In 1982, Malhuret and
Rony Brauman
(who became the organisation's president in 1982) brought increased
financial independence to MSF by introducing fundraising-by-mail to
better collect donations. The 1980s also saw the establishment of the
other operational sections from MSF-France (1971): MSF-Belgium (1980),
MSF-Switzerland (1981), MSF-Holland (1984), and MSF-Spain (1986).
MSF-Luxembourg was the first support section, created in 1986. The early
1990s saw the establishment of the majority of the support sections:
MSF-Greece (1990), MSF-USA (1990), MSF-Canada (1991), MSF-Japan (1992),
MSF-UK (1993), MSF-Italy (1993), MSF-Australia (1994), as well as
Germany, Austria, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, and Hong Kong (MSF-UAE was
formed later). Malhuret and Brauman were instrumental in professionalising MSF. In December 1979, after the
Soviet army had invaded Afghanistan, field missions were immediately set up to provide medical aid to the
mujahideen, and in February 1980, MSF publicly denounced the
Khmer Rouge. During the
1983–1985 famine in Ethiopia,
MSF set up nutrition programmes in the country in 1984, but was
expelled in 1985 after denouncing the abuse of international aid and the
forced resettlements. MSF's explicit attacks on the Ethiopian
government led to other NGOs criticizing their abandonment of their
supposed neutrality and contributed to a series of debates in France
around humanitarian ethics. The group also set up equipment to produce clean
drinking water for the population of
San Salvador, capital of El Salvador, after 10 October 1986 earthquake that struck the city. In 2014, the
European Speedster Assembly had contributed $717,000 to MSF.
Sudan
Since 1979, MSF has been providing medical humanitarian assistance in
Sudan, a nation plagued by starvation and the
civil war,
prevalent malnutrition and one of the highest maternal mortality rates
in the world. In March 2009, it is reported that MSF has employed 4,590
field staff in Sudan
tackling issues such as armed conflicts, epidemic diseases, health care
and social exclusion. MSF's continued presence and work in
Sudan
is one of the organization's largest interventions. MSF provides a
range of health care services including nutritional support,
reproductive healthcare, Kala-Azar treatment, counselling services and
surgery to the people living in
Sudan. Common diseases prevalent in
Sudan include
tuberculosis,
kala-azar also known as
visceral leishmaniasis,
meningitis,
measles,
cholera, and
malaria.
Kala-Azar in Sudan
Kala-azar, also known as
visceral leishmaniasis, has been one of the major health problems in
Sudan.
After the Comprehensive Peace Agreement between North and Southern
Sudan on 9 January 2005, the increase in stability within the region
helped further efforts in healthcare delivery. Médicins sans Frontières
tested a combination of sodium stibogluconate and paromomycin, which
would reduce treatment duration (from 30 to 17 days) and cost in 2008.
In March 2010, MSF set up its first Kala-Azar treatment centre in
Eastern Sudan, providing free treatment for this otherwise deadly
disease. If left untreated, there is a fatality rate of 99% within 1–4
months of infection. Since the treatment centre was set up, MSF has cured more than 27,000
Kala-Azar patients with a success rate of approximately 90–95%. There are plans to open an additional Kala-Azar treatment centre in
Malakal,
Southern Sudan
to cope with the overwhelming number of patients that are seeking
treatment. MSF has been providing necessary medical supplies to
hospitals and training Sudanese health professionals to help them deal
with
Kala-Azar.
MSF, Sudanese Ministry of Health and other national and international
institutions are combining efforts to improve on the treatment and
diagnosis of Kala-Azar. Research on its cures and vaccines are currently being conducted. In December 2010, South Sudan was hit with the worst outbreak of Kala-Azar in eight years. The number of patients seeking treatment increased eight-fold as compared to the year before.
Health care infrastructure in Sudan
Sudan's latest civil war began in 1983 and ended in 2005 when a peace agreement was signed between
North Sudan and
South Sudan.
MSF medical teams were active throughout and prior to the civil war,
providing emergency medical humanitarian assistance in multiple
locations.
The situation of poor infrastructure in the South was aggravated by the
civil war and resulted in the worsening of the region's appalling
health indicators. An estimated 75 percent of people in the nascent
nation has no access to basic medical care and 1 in seven women dies
during childbirth.
Malnutrition and disease outbreaks are perennial concerns as well. In 2011, MSF clinic in
Jonglei State,
South Sudan was looted and attacked by raiders.
Hundreds, including women and children were killed. Valuable items
including medical equipment and drugs were lost during the raid and
parts of the MSF facilities were destroyed in a fire. The incident had serious repercussions as MSF is the only primary health care provider in this part of
Jonglei State.
Early 1990s
The
early 1990s saw MSF open a number of new national sections, and at the
same time, set up field missions in some of the most dangerous and
distressing situations it had ever encountered.
In 1990, MSF first entered Liberia to help civilians and refugees affected by the
Liberian Civil War. Constant fighting throughout the 1990s and the
Second Liberian Civil War
have kept MSF volunteers actively providing nutrition, basic health
care, and mass vaccinations, and speaking out against attacks on
hospitals and feeding stations, especially in
Monrovia.
Field missions were set up to provide relief to
Kurdish refugees who had survived the
al-Anfal Campaign, for which evidence of atrocities was being collected in 1991. 1991 also saw the beginning of the
civil war in
Somalia,
during which MSF set up field missions in 1992 alongside a UN
peacekeeping mission. Although the UN-aborted operations by 1993, MSF
representatives continued with their relief work, running clinics and
hospitals for civilians.
MSF first began work in
Srebrenica (in Bosnia and Herzegovina) as part of a UN convoy in 1993, one year after the
Bosnian War had begun. The city had become surrounded by the
Bosnian Serb Army and, containing about 60,000
Bosniaks, had become an enclave guarded by a
United Nations Protection Force.
MSF was the only organisation providing medical care to the surrounded
civilians, and as such, did not denounce the genocide for fear of being
expelled from the country (it did, however, denounce the lack of access
for other organisations). MSF was forced to leave the area in 1995 when
the
Bosnian Serb Army captured the town. 40,000
Bosniak civilian inhabitants were deported, and approximately 7,000 were killed in mass executions.
Rwanda
When the
genocide in Rwanda began in April 1994, some delegates of MSF working in the country were incorporated into the
International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) medical team for protection. Both groups succeeded in keeping all main hospitals in Rwanda's capital
Kigali
operational throughout the main period of the genocide. MSF, together
with several other aid organisations, had to leave the country in 1995,
although many MSF and ICRC volunteers worked together under the ICRC's
rules of engagement, which held that neutrality was of the utmost
importance. These events led to a debate within the organisation about
the concept of balancing neutrality of humanitarian aid workers against
their witnessing role. As a result of its Rwanda mission, the position
of MSF with respect to neutrality moved closer to that of the ICRC, a
remarkable development in the light of the origin of the organisation.
The ICRC lost 56 and MSF lost almost one hundred of their respective
local staff in Rwanda, and MSF-France, which had chosen to evacuate its
team from the country (the local staff were forced to stay), denounced
the murders and demanded that a
French military intervention stop the genocide. MSF-France introduced the slogan
"One cannot stop a genocide with doctors" to the media, and the controversial
Opération Turquoise followed less than one month later. This intervention directly or indirectly resulted in movements of hundreds of thousands of Rwandan refugees to
Zaire and Tanzania in what became known as the
Great Lakes refugee crisis,
and subsequent cholera epidemics, starvation and more mass killings in
the large groups of civilians. MSF-France returned to the area and
provided medical aid to refugees in
Goma.
At the time of the genocide, competition between the medical
efforts of MSF, the ICRC, and other aid groups had reached an all-time
high, but the conditions in Rwanda prompted a drastic change in the way humanitarian organisations approached aid missions. The
Code of Conduct for the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement and NGOs in Disaster Relief Programmes was created by the ICRC in 1994 to provide a framework for humanitarian missions and MSF is a signatory of this code.
The code advocates the provision of humanitarian aid only, and groups
are urged not to serve any political or religious interest, or be used
as a tool for foreign governments. MSF has since still found it necessary to condemn the actions of governments, such as in
Chechnya in 1999, but has not demanded another military intervention since then.
Sierra Leone
In the late 1990s, MSF missions were set up to treat tuberculosis and
anaemia in residents of the
Aral Sea area, and look after civilians affected by drug-resistant disease, famine, and epidemics of cholera and AIDS. They vaccinated 3 million Nigerians against
meningitis during an epidemic in 1996 and denounced the
Taliban's neglect of health care for women in 1997.
Arguably, the most significant country in which MSF set up field
missions in the late 1990s was Sierra Leone, which was involved in a
civil war at the time. In 1998, volunteers began assisting in surgeries in
Freetown to help with an increasing number of
amputees, and collecting statistics on civilians (men, women and children) being attacked by large groups of men claiming to represent
ECOMOG.
The groups of men were travelling between villages and systematically
chopping off one or both of each resident's arms, raping women, gunning
down families, razing houses, and forcing survivors to leave the area. Long-term projects following the end of the civil war included psychological support and
phantom limb pain management.
Ongoing missions
Countries where MSF had missions in 2015.
The
Campaign for Access to Essential Medicines was created in late 1999, providing MSF with a new voice with which to bring awareness to the lack of effective treatments and
vaccines
available in developing countries. In 1999, the organisation also spoke
out about the lack of humanitarian support in Kosovo and Chechnya,
having set up field missions to help civilians affected by the
respective political situations. Although MSF had worked in the Kosovo
region since 1993, the onset of the
Kosovo War
prompted the movement of tens of thousands of refugees, and a decline
in suitable living conditions. MSF provided shelter, water and health
care to civilians affected by
NATO's strategic bombing campaigns.
A serious crisis within MSF erupted in connection with the
organisation's work in Kosovo when the Greek section of MSF was expelled
from the organization. The Greek MSF section had gained access to
Serbia at the cost of accepting Serb government imposed limits on where
it could go and what it could see – terms that the rest of the MSF
movement had refused.
A non-MSF source alleged that the exclusion of the Greek section
happened because its members extended aid to both Albanian and Serbian
civilians in Pristina during NATO's bombing,
The rift was healed only in 2005 with the re-admission of the Greek section to MSF.
A similar situation was found in Chechnya, whose civilian
population was largely forced from their homes into unhealthy conditions
and subjected to the violence of the
Second Chechen War.
MSF has been working in Haiti since 1991, but since President
Jean-Bertrand Aristide
was forced from power, the country has seen a large increase in
civilian attacks and rape by armed groups. In addition to providing
surgical and psychological support in existing hospitals – offering the
only free surgery available in
Port-au-Prince
– field missions have been set up to rebuild water and waste management
systems and treat survivors of major flooding caused by
Hurricane Jeanne; patients with HIV/AIDS and malaria, both of which are widespread in the country, also receive better treatment and monitoring. As a result of 12 January
2010 Haiti earthquake,
reports from Haiti indicated that all three of the organisation's
hospitals had been severely damaged; one collapsing completely and the
other two having to be abandoned.
Following the quake, MSF sent about nine planes loaded with medical
equipment and a field hospital to help treat the victims. However, the
landings of some of the planes had to be delayed due to the massive
number of humanitarian and military flights coming in.
The
Kashmir Conflict in
northern India
resulted in a more recent MSF intervention (the first field mission was
set up in 1999) to help civilians displaced by fighting in
Jammu and Kashmir, as well as in
Manipur.
Psychological support is a major target of missions, but teams have
also set up programmes to treat tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS and malaria. Mental health support has been of significant importance for MSF in much of southern Asia since the
2004 Indian Ocean earthquake.
MSF went through a long process of self-examination and
discussion in 2005–2006. Many issues were debated, including the
treatment "nationals" as well as "fair employment" and self-criticism.
Africa
An MSF outpost in Darfur (2005)
MSF has been active in a large number of African countries for
decades, sometimes serving as the sole provider of health care, food,
and water. Although MSF has consistently attempted to increase media
coverage of the situation in Africa to increase international support,
long-term field missions are still necessary. Treating and educating the
public about
HIV/AIDS in
sub-Saharan Africa, which sees the most deaths and cases of the disease in the world,
is a major task for volunteers. Of the 14.6 million people in need of
anti-retroviral treatment the WHO estimated that only 5.25 million
people were receiving it in developing countries, and MSF continues to
urge governments and companies to increase research and development into
HIV/AIDS treatments to decrease cost and increase availability.
Although active in the Congo region of Africa since 1985, the
First and
Second Congo War brought increased violence and instability to the area. MSF has had to evacuate its teams from areas such as around
Bunia, in the Ituri district due to extreme violence,
but continues to work in other areas to provide food to tens of
thousands of displaced civilians, as well as treat survivors of mass
rapes and widespread fighting. The treatment and possible vaccination against diseases such as
cholera,
measles,
polio,
Marburg fever,
sleeping sickness,
HIV/AIDS, and
Bubonic plague is also important to prevent or slow down epidemics.
MSF has been active in Uganda since 1980, and provided relief to civilians during the country's guerrilla war during the
Second Obote Period. However, the formation of the
Lord's Resistance Army
saw the beginning of a long campaign of violence in northern Uganda and
southern Sudan. Civilians were subjected to mass killings and rapes,
torture, and abductions of children, who would later serve as sex slaves
or
child soldiers. Faced with more than 1.5 million people displaced from their homes, MSF set up relief programmes in
internally displaced person (IDP) camps to provide clean water, food and sanitation. Diseases such as
tuberculosis, measles, polio, cholera,
ebola,
and HIV/AIDS occur in epidemics in the country, and volunteers provide
vaccinations (in the cases of measles and polio) and/or treatment to the
residents. Mental health is also an important aspect of medical
treatment for MSF teams in Uganda since most people refuse to leave the
IDP camps for constant fear of being attacked.
MSF first camp set up a field mission in Côte d'Ivoire in 1990, but ongoing violence and the
2002 division
of the country by rebel groups and the government led to several
massacres, and MSF teams have even begun to suspect that an ethnic
cleansing is occurring. Mass measles vaccinations,
tuberculosis treatment and the re-opening of hospitals closed by
fighting are projects run by MSF, which is the only group providing aid
in much of the country.
During the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014, MSF met serious
medical demands largely on its own, after the organisation's early
warnings were largely ignored.
In 2014 MSF partnered with satellite operator
SES, other NGOs Archemed, Fondation Follereau, Friendship Luxembourg and
German Doctors, and the
Luxembourg government in the pilot phase of
SATMED, a project to use
satellite broadband technology to bring
eHealth and
telemedicine to isolated areas of developing countries. SATMED was first deployed in Sierra Leone in support of the fight against Ebola.
Cambodia
MSF
first provided medical help to civilians and refugees who have escaped
to camps along the Thai-Cambodian border in 1979. Due to long decades of
war, a proper
health care system in the country was severely lacking and MSF moved inland in 1989 to help restructure basic medical facilities.
In 1999, Cambodia was hit with a malaria epidemic. The situation
of the epidemic was aggravated by a lack of qualified practitioners and
poor quality control which led to a market of fake antimalarial drugs.
Counterfeit antimalarial drugs were responsible for the deaths of at
least 30 people during the epidemic. This has prompted efforts by MSF to set up and fund a malaria outreach project and utilise Village Malaria Workers.
MSF also introduced a switching of first-line treatment to a
combination therapy (Artesunate and Mefloquine) to combat resistance and
fatality of old drugs that were used to treat the disease
traditionally.
Cambodia is one of the hardest hit HIV/AIDS countries in
Southeast Asia. In 2001, MSF started introducing antiretroviral (ARV)
therapy to AIDS patients for free. This therapy prolongs the patients'
lives and is a long-term treatment.
In 2002, MSF established chronic diseases clinics with the Cambodian
Ministry of Health in various provinces to integrate HIV/AIDS treatment,
alongside hypertension, diabetes, and arthritis which have high
prevalence rate. This aims to reduce facility-related stigma as patients
are able to seek treatment in a multi-purpose clinic in contrast to a
HIV/AIDS specialised treatment centre.
MSF also provided humanitarian aid in times of natural disaster
such as a major flood in 2002 which affected up to 1.47 million people.
MSF introduced a community-based tuberculosis programme in 2004 in
remote villages, where village volunteers are delegated to facilitate
the medication of patients. In partnership with local health authorities
and other NGOs, MSF encouraged decentralized clinics and rendered
localized treatments to more rural areas from 2006.
Since 2007, MSF has extended general health care, counselling, HIV/AIDS
and TB treatment to prisons in Phnom Penh via mobile clinics.
However, poor sanitation and lack of health care still prevails in most
Cambodian prisons as they remain as some of the world's most crowded
prisons.
In 2007, MSF worked with the Cambodian Ministry of Health to
provide psychosocial and technical support in offering pediatric
HIV/AIDS treatment to affected children. MSF also provided medical supplies and staff to help in one of the worst dengue outbreaks in 2007, which had more than 40,000 people hospitalized, killing 407 people, primarily children.
In 2010, Southern and Eastern provinces of Cambodia were hit with
a cholera epidemic and MSF responded by providing medical support that
were adapted for usage in the country.
Cambodia is one of 22 countries listed by WHO as having a high
burden of tuberculosis. WHO estimates that 64% of all Cambodians carry
the tuberculosis mycobacterium. Hence, MSF has since shifted its focus
away from HIV/AIDS to tuberculosis, handing over most HIV-related
programs to local health authorities.
Libya
The
2011 Libyan civil war
has prompted efforts by MSF to set up a hospital and mental health
services to help locals affected by the conflict. The fighting created a
backlog of patients that needed surgery. With parts of the country
slowly returning to livable, MSF has started working with local health
personnel to address the needs. The need for psychological counseling
has increased and MSF has set up mental health services to address the
fears and stress of people living in tents without water and
electricity. Currently MSF is the only International Aid organisation
with actual presence in the country.
Mediterranean Sea
MSF
is providing Maritime Search And Rescue (SAR) services on the
Mediterranean Sea to save the lives of migrants attempting to cross with
unseaworthy boats. The Mission started in 2015 after the EU ended its
major SAR operation
Mare Nostrum severely diminishing much needed SAR capacities in the Mediterranean.
Throughout the mission MSF has operated its own vessels like the
Bourbon Argos (2015–2016), Dignity I (2015–2016) and Prudence
(2016–2017). MSF has also provided medical teams to support other NGOs
and their ships like the
MOAS Phoenix (2015) or the Aquarius with SOS Méditerranée (2017–2018).
In August 2017 MSF decided to suspend the activities of the Prudence
protesting restrictions and threats by the Libyan "Coast Guard".
In December 2018 MSF and SOS Méditerranée were forced to end
operations of the Aquarius, the last remaining vessel supported by MSF.
This came after attacks by EU states that stripped the vessel of its
registration and produced criminal accusations against MSF. Up to then
80,000 people were rescued or assisted since the beginning of the
mission.
Sri Lanka
MSF is involved in Sri Lanka, where a
26 year civil war
ended in 2009 and MSF has adapted its activities there to continue its
mission. For example, it helps with physical therapy for patients with
spinal cord injuries.
It conducts counseling sessions, and has set up an “operating theatre
for reconstructive orthopaedic surgery and supplied specialist surgeons,
anaesthetists and nurses to operate on patients with complicated
war-related injuries.”
Yemen
MSF is involved in trying to help with the humanitarian crisis caused by the
Yemeni Civil War.
The organisation operates eleven hospital and health centres in Yemen
and provides support to another 18 hospitals or health centres.
According to MSF, since October 2015, four of its hospitals and one
ambulance have been destroyed by Saudi-led coalition airstrikes. In August 2016, an airstrike on Abs hospital killed 19 people, including one MSF staff member, and wounded 24.
According to MSF, the GPS coordinates of the hospital were repeatedly
shared with all parties to the conflict, including the Saudi-led
coalition, and its location was well-known.
Field mission structure
Before
a field mission is established in a country, an MSF team visits the
area to determine the nature of the humanitarian emergency, the level of
safety in the area and what type of aid is needed (this is called an
"exploratory mission").
Medical aid is the main objective of most missions, although some missions help in such areas as
water purification and nutrition.
Field mission team
MSF logistician in Nigeria showing plans
A field mission team usually consists of a small number of
coordinators to head each component of a field mission, and a "head of
mission." The head of mission usually has the most experience in
humanitarian situations of the members of the team, and it is his/her
job to deal with the media, national governments and other humanitarian
organizations. The head of mission does not necessarily have a medical
background.
Medical volunteers include physicians, surgeons, nurses, and
various other specialists. In addition to operating the medical and
nutrition components of the field mission, these volunteers are
sometimes in charge of a group of local medical staff and provide
training for them.
Although the medical volunteers almost always receive the most
media attention when the world becomes aware of an MSF field mission,
there are a number of non-medical volunteers who help keep the field
mission functioning. Logisticians are responsible for providing
everything that the medical component of a mission needs, ranging from
security and vehicle maintenance to food and electricity supplies. They
may be engineers and/or
foremen,
but they usually also help with setting up treatment centres and
supervising local staff. Other non-medical staff are water/sanitation
specialists, who are usually experienced engineers in the fields of
water treatment and management and financial/administration/human
resources experts who are placed with field missions.
Medical component
Doctors from MSF and the American CDC put on protective gear before entering an Ebola treatment ward in Liberia, August 2014
Vaccination campaigns are a major part of the medical care provided during MSF missions. Diseases such as
diphtheria,
measles,
meningitis,
tetanus,
pertussis,
yellow fever,
polio, and
cholera, all of which are uncommon in developed countries, may be prevented with
vaccination.
Some of these diseases, such as cholera and measles, spread rapidly in
large populations living in close proximity, such as in a refugee camp,
and people must be immunised by the hundreds or thousands in a short
period of time. For example, in
Beira, Mozambique in 2004, an experimental cholera vaccine was received twice by approximately 50,000 residents in about one month.
An equally important part of the medical care provided during MSF missions is AIDS treatment (with
antiretroviral drugs),
AIDS testing, and education. MSF is the only source of treatment for
many countries in Africa, whose citizens make up the majority of people
with HIV and AIDS worldwide. Because antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) are not readily available, MSF usually provides treatment for
opportunistic infections and educates the public on how to slow transmission of the disease.
In most countries, MSF increases the capabilities of local
hospitals by improving sanitation, providing equipment and drugs, and
training local hospital staff.
When the local staff is overwhelmed, MSF may open new specialised
clinics for treatment of an endemic disease or surgery for victims of
war. International staff start these clinics but MSF strives to increase
the local staff's ability to run the clinics themselves through
training and supervision. In some countries, like Nicaragua, MSF provides public education to increase awareness of reproductive health care and
venereal disease.
Since most of the areas that require field missions have been
affected by a natural disaster, civil war, or endemic disease, the
residents usually require psychological support as well. Although the
presence of an MSF medical team may decrease stress somewhat among
victims, often a team of
psychologists or
psychiatrists work with victims of depression,
domestic violence and
substance abuse. The doctors may also train local mental health staff.
Nutrition
Often in situations where an MSF mission is set up, there is moderate or severe
malnutrition
as a result of war, drought, or government economic mismanagement.
Intentional starvation is also sometimes used during a war as a weapon,
and MSF, in addition to providing food, brings awareness to the
situation and insists on foreign government intervention. Infectious
diseases and
diarrhoea,
both of which cause weight loss and weakening of a person's body
(especially in children), must be treated with medication and proper
nutrition to prevent further infections and weight loss. A combination
of the above situations, as when a civil war is fought during times of
drought and infectious disease outbreaks, can create famine.
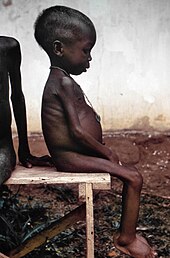
An MSF health worker examines a malnourished child in Ethiopia, July 2011
In emergency situations where there is a lack of nutritious food, but not to the level of a true famine,
protein-energy malnutrition is most common among young children.
Marasmus,
a form of calorie deficiency, is the most common form of childhood
malnutrition and is characterised by severe wasting and often fatal
weakening of the immune system.
Kwashiorkor, a form of calorie and protein deficiency, is a more serious type of malnutrition in young children, and can negatively affect
physical and
mental development. Both types of malnutrition can make opportunistic infections fatal. In these situations, MSF sets up
Therapeutic Feeding Centres for monitoring the children and any other malnourished individuals.
A Therapeutic Feeding Centre (or Therapeutic Feeding Programme)
is designed to treat severe malnutrition through the gradual
introduction of a special diet intended to promote weight gain after the
individual has been treated for other health problems. The treatment
programme is split between two phases:
- Phase 1 lasts for 24 hours and involves basic health care and
several small meals of low energy/protein food spaced over the day.
- Phase 2 involves monitoring of the patient and several small meals
of high energy/protein food spaced over each day until the individual's
weight approaches normal.
MSF uses foods designed specifically for treatment of severe malnutrition. During phase 1, a type of therapeutic milk called
F-75
is fed to patients. F-75 is a relatively low energy, low fat/protein
milk powder that must be mixed with water and given to patients to
prepare their bodies for phase 2. During phase 2, therapeutic milk called
F-100,
which is higher in energy/fat/protein content than F-75, is given to
patients, usually along with a peanut butter mixture called
Plumpy'nut. F-100 and Plumpy'nut are designed to quickly provide large amounts of nutrients so that patients can be treated efficiently. Other special food fed to populations in danger of starvation includes
enriched flour and
porridge, as well as a high protein biscuit called
BP5.
BP5 is a popular food for treating populations because it can be
distributed easily and sent home with individuals, or it can be crushed
and mixed with therapeutic milk for specific treatments.
Water and sanitation
Clean water is essential for
hygiene,
for consumption and for feeding programmes (for mixing with powdered
therapeutic milk or porridge), as well as for preventing the spread of
water-borne disease.
As such, MSF water engineers and volunteers must create a source of
clean water. This is usually achieved by modifying an existing
water well,
by digging a new well and/or starting a water treatment project to
obtain clean water for a population. Water treatment in these situations
may consist of storage sedimentation,
filtration and/or
chlorination depending on available resources.
Sanitation is an essential part of field missions, and it may include education of local medical staff in proper
sterilisation techniques,
sewage treatment projects, proper
waste disposal,
and education of the population in personal hygiene. Proper wastewater
treatment and water sanitation are the best way to prevent the spread of
serious water-borne diseases, such as cholera. Simple wastewater treatment systems can be set up by volunteers to protect drinking water from contamination. Garbage disposal could include pits for normal waste and incineration for
medical waste.
However, the most important subject in sanitation is the education of
the local population, so that proper waste and water treatment can
continue once MSF has left the area.
Statistics
In
order to accurately report the conditions of a humanitarian emergency
to the rest of the world and to governing bodies, data on a number of
factors are collected during each field mission. The rate of
malnutrition in children is used to determine the malnutrition rate in
the population, and then to determine the need for feeding centres. Various types of
mortality rates
are used to report the seriousness of a humanitarian emergency, and a
common method used to measure mortality in a population is to have staff
constantly monitoring the number of burials at cemeteries.
By compiling data on the frequency of diseases in hospitals, MSF can
track the occurrence and location of epidemic increases (or "seasons")
and stockpile vaccines and other drugs. For example, the "Meningitis
Belt" (sub-Saharan Africa, which sees the most cases of meningitis in
the world) has been "mapped" and the meningitis season occurs between
December and June. Shifts in the location of the Belt and the timing of
the season can be predicted using cumulative data over many years.
In addition to epidemiological surveys, MSF also uses population
surveys to determine the rates of violence in various regions. By estimating the scopes of
massacres, and determining the rate of kidnappings, rapes, and killings, psychosocial programmes can be implemented to lower the
suicide rate and increase the sense of security in a population.
Large-scale forced migrations,
excessive civilian casualties and massacres can be quantified using
surveys, and MSF can use the results to put pressure on governments to
provide help, or even expose genocide. MSF conducted the first comprehensive mortality survey in
Darfur in 2004.
However, there may be ethical problems in collecting these statistics.
Campaign for Access to Essential Medicines
The Campaign for Access to Essential Medicines was initiated in 1999 to increase access to
essential medicines
in developing countries. "Essential medicines" are those drugs that are
needed in sufficient supply to treat a disease common to a population.
However, most diseases common to populations in developing countries
are no longer common to populations in developed countries; therefore,
pharmaceutical companies
find that producing these drugs is no longer profitable and may raise
the price per treatment, decrease development of the drug (and new
treatments) or even stop production of the drug. MSF often lacks
effective drugs during field missions, and started the campaign to put
pressure on governments and pharmaceutical companies to increase funding
for essential medicines.
In recent years, the organization has tried to use its influence to urge the drug maker
Novartis to drop its case against India's patent law that prevents Novartis from patenting its drugs in
India. A few years earlier, Novartis also sued
South Africa to prevent it from importing cheaper
AIDS
drugs. Dr. Tido von Schoen-Angerer, director of DWB's Campaign for
Access to Essential Medicines, says, "Just like five years ago,
Novartis, with its legal actions, is trying to stand in the way of
people's right to access the medicines they need."
On 1 April 2013, it was announced that the Indian court
invalidated Novartis's patent on Gleevec. This decision makes the drug
available via generics on the Indian market at a considerably lower
price.
Dangers faced by volunteers
Aside
from injuries and death associated with stray bullets, mines and
epidemic disease, MSF volunteers are sometimes attacked or kidnapped for
political reasons. In some countries afflicted by civil war,
humanitarian-aid organizations are viewed as helping the enemy. If an
aid mission is perceived to be exclusively set up for victims on one
side of the conflict, it may come under attack for that reason. However,
the
War on Terrorism
has generated attitudes among some groups in US-occupied countries that
non-governmental aid organizations such as MSF are allied with or even
work for the
Coalition forces.
Since the United States has labelled its operations "humanitarian
actions," independent aid organizations have been forced to defend their
positions, or even evacuate their teams.
Insecurity in cities in Afghanistan and Iraq rose significantly
following United States operations, and MSF has declared that providing
aid in these countries was too dangerous. The organization was forced to evacuate its teams from Afghanistan on 28 July 2004, after five volunteers (Afghans Fasil Ahmad and Besmillah, Belgian Hélène de Beir, Norwegian
Egil Tynæs, and Dutchman Willem Kwint) were killed on 2 June in an ambush by unidentified militia near
Khair Khāna in
Badghis Province. In June 2007, Elsa Serfass, a volunteer with MSF-France, was killed
in the Central African Republic and in January 2008, two expatriate
staff (Damien Lehalle and Victor Okumu) and a national staff member
(Mohammed Bidhaan Ali) were killed in an organized attack in Somalia resulting in the closing of the project.
Arrests and abductions in politically unstable regions can also
occur for volunteers, and in some cases, MSF field missions can be
expelled entirely from a country.
Arjan Erkel, Head of Mission in
Dagestan in the
North Caucasus,
was kidnapped and held hostage in an unknown location by unknown
abductors from 12 August 2002 until 11 April 2004. Paul Foreman, head of
MSF-Holland, was arrested in Sudan in May 2005 for refusing to divulge
documents used in compiling a report on rapes carried out by the
pro-government
Janjaweed militias.
Foreman cited the privacy of the women involved, and MSF alleged that
the Sudanese government had arrested him because it disliked the bad
publicity generated by the report.
On 14 August 2013, MSF announced that it was closing all of its programmes in Somalia due to attacks on its staff by
Al-Shabaab militants and perceived indifference or
inurement to this by the governmental authorities and wider society.
On 28 November 2015, an MSF-supported hospital was barrel-bombed
by a Syrian Air Force helicopter, killing seven and wounding forty-seven
people near Homs, Syria.
On 10 January 2016, an MSF-supported hospital in Sa'dah was bombed by the
Saudi Arabia-led military coalition, killing six people.
On 15 February 2016, two MSF-supported hospitals in
Idlib District and
Aleppo, Syria were bombed, killing at least 20 and injuring dozens of patients and medical personnel. Both Russia and the United States denied responsibility and being in the area at the time.
On 28 April 2016, an MSF hospital in Aleppo was bombed, killing 50, including six staff and patients.
Documentary
Living in Emergency is an award-winning documentary film by
Mark N. Hopkins
that tells the story of four MSF volunteer doctors confronting the
challenges of medical work in war-torn areas of Liberia and Congo. It
premiered at the 2008
Venice Film Festival and was theatrically released in the United States in 2010.
1999 Nobel Peace Prize
The then president of MSF,
James Orbinski,
gave the Nobel Peace Prize speech on behalf of the organization. In
the opening, he discusses the conditions of the victims of the Rwandan
Genocide and focuses on one of his woman patients:
There were hundreds of women,
children and men brought to the hospital that day, so many that we had
to lay them out on the street and even operate on some of them there.
The gutters around the hospital ran red with blood. The woman had not
just been attacked with a machete, but her entire body rationally and
systematically mutilated. Her ears had been cut off. And her face had
been so carefully disfigured that a pattern was obvious in the slashes.
She was one among many—living an inhuman and simply indescribable
suffering. We could do little more for her at the moment than stop the
bleeding with a few necessary sutures. We were completely overwhelmed,
and she knew that there were so many others. She said to me in the
clearest voice I have ever heard, 'Allez, allez…ummera, ummerasha'—'Go,
go…my friend, find and let live your courage.'
— James Orbinski, Nobel acceptance speech for MSF
Orbinski affirmed the organization's commitment to publicizing the issues MSF encountered, stating
Silence has long been confused with
neutrality, and has been presented as a necessary condition for
humanitarian action. From its beginning, MSF was created in opposition
to this assumption. We are not sure that words can always save lives,
but we know that silence can certainly kill.
— James Orbinski
Lasker Prize
Namesakes