Healthcare reform in the United States has a long history. Reforms have often been proposed but have rarely been accomplished. In 2010, landmark reform was passed through two federal statutes enacted in 2010: the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), signed March 23, 2010, and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (H.R. 4872), which amended the PPACA and became law on March 30, 2010.
Future reforms of the American health care system continue to be proposed, with notable proposals including a single-payer system and a reduction in fee-for-service medical care. The PPACA includes a new agency, the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMS Innovation Center), which is intended to research reform ideas through pilot projects.
Future reforms of the American health care system continue to be proposed, with notable proposals including a single-payer system and a reduction in fee-for-service medical care. The PPACA includes a new agency, the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMS Innovation Center), which is intended to research reform ideas through pilot projects.
History of national reform efforts
The following is a summary of reform achievements at the national
level in the United States. For failed efforts, state-based efforts,
native tribes services, and more details, see the history of health care reform in the United States article.
- 1965 President Lyndon Johnson enacted legislation that introduced Medicare, covering both hospital (Part A) and supplemental medical (Part B) insurance for senior citizens. The legislation also introduced Medicaid, which permitted the Federal government to partially fund a program for the poor, with the program managed and co-financed by the individual states.
- 1985 The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985 (COBRA) amended the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA) to give some employees the ability to continue health insurance coverage after leaving employment.
- 1996 The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) not only protects health insurance coverage for workers and their families when they change or lose their jobs, it also made health insurance companies cover pre-existing conditions. If such condition had been diagnosed before purchasing insurance, insurance companies are required to cover it after patient has one year of continuous coverage. If such condition was already covered on their current policy, new insurance policies due to changing jobs, etc... have to cover the condition immediately.
- 1997 The Balanced Budget Act of 1997 introduced two new major Federal healthcare insurance programs, Part C of Medicare and the State Children's Health Insurance Program, or SCHIP. Part C formalized longstanding "Managed Medicare" (HMO, etc.) demonstration projects and SCHIP was established to provide health insurance to children in families at or below 200 percent of the federal poverty line. Many other "entitlement" changes and additions were made to Parts A and B of fee for service (FFS) Medicare and to Medicaid within an omnibus law that also made changes to the Food Stamp and other Federal programs.
- 2000 The Medicare, Medicaid, and SCHIP Benefits Improvement and Protection Act (BIPA) effectively reversed some of the cuts to the three named programs in the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 because of Congressional concern that providers would stop providing services.
- 2003 The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act (also known as the Medicare Modernization Act or MMA) introduced supplementary optional coverage within Medicare for self-administered prescription drugs and as the name suggests also changed the other three existing Parts of Medicare law.
- 2010 The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, called PPACA or ACA but also known as Obamacare, was enacted, including the following provisions:
- the phased introduction over multiple years of a comprehensive system of mandated health insurance reforms designed to eliminate "some of the worst practices of the insurance companies"—pre-existing condition screening and premium loadings, policy cancellations on technicalities when illness seems imminent, annual and lifetime coverage caps
- created health insurance marketplaces with three standard insurance coverage levels to enable like-for-like comparisons by consumers, and a web-based health insurance exchange where consumers can compare prices and purchase plans.
- mandates that insurers fully cover certain preventative services
- created high-risk pools for uninsureds
- tax credits for businesses to provide insurance to employees
- created an insurance company rate review program
- allowed dependents to remain on their plan until 26
- It also sets a minimum medical loss ratio ratio of direct health care spending to premium income creates price competition
- created Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to study comparative effectiveness research funded by a fee on insurers per covered life
- allowed for approval of generic biologic drugs and specifically allows for 12 years of exclusive use for newly developed biologic drugs
- many changes to the 1997, 2000, and 2003 laws that had previously changed Medicare and further expanded eligibility for Medicaid (that expansion was later ruled by the Supreme Court to be at the discretion of the states)
- explores some programs intended to increase incentives to provide quality and collaborative care, such as accountable care organizations. The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation was created to fund pilot programs which may reduce costs; the experiments cover nearly every idea healthcare experts advocate, except malpractice/tort reform.
- requires for reduced Medicare reimbursements for hospitals with excess readmissions and eventually ties physician Medicare reimbursements to quality of care metrics.
- 2015 The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) made significant changes to the process by which many Medicare Part B services are reimbursed and also extended SCHIP
- 2017 Donald Trump is sworn in as President, signs Executive Order 13765 in anticipation of a repeal of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, one of his campaign promises. The American Health Care Act is introduced and passed in the House of Representatives and introduced but not voted upon in the Senate. President Donald Trump signs Executive Order 13813 which allows insurance companies to sell low-cost short-term plans with lesser coverage, enables small business to collectively purchase association health plans, and expands health savings accounts.
Motivation
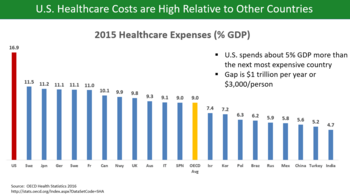
Bar chart comparing healthcare costs as percentage of GDP across OECD countries
Medicare and Medicaid Spending as % GDP (data from the CBO)
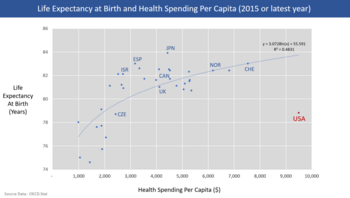
Chart
showing life expectancy at birth and health care spending per capita
for OECD countries as of 2015. The U.S. is an outlier, with much higher
spending but below average life expectancy.
Health spending per capita, in US$ PPP-adjusted, compared amongst various first world nations.
International comparisons of healthcare
have found that the United States spends more per-capita than other
similarly developed nations but falls below similar countries in various
health metrics, suggesting inefficiency and waste. In addition, the
United States has significant underinsurance and significant impending unfunded liabilities from its aging demographic and its social insurance programs Medicare and Medicaid
(Medicaid provides free long-term care to the elderly poor). The fiscal
and human impact of these issues have motivated reform proposals.
U.S. healthcare costs were approximately $3.2 trillion or nearly
$10,000 per person on average in 2015. Major categories of expense
include hospital care (32%), physician and clinical services (20%), and
prescription drugs (10%).
U.S. costs in 2016 were substantially higher than other OECD countries,
at 17.2% GDP versus 12.4% GDP for the next most expensive country
(Switzerland).
For scale, a 5% GDP difference represents about $1 trillion or $3,000
per person. Some of the many reasons cited for the cost differential
with other countries include: Higher administrative costs of a private
system with multiple payment processes; higher costs for the same
products and services; more expensive volume/mix of services with higher
usage of more expensive specialists; aggressive treatment of very sick
elderly versus palliative care; less use of government intervention in
pricing; and higher income levels driving greater demand for healthcare.
Healthcare costs are a fundamental driver of health insurance costs,
which leads to coverage affordability challenges for millions of
families. There is ongoing debate whether the current law
(ACA/Obamacare) and the Republican alternatives (AHCA and BCRA) do
enough to address the cost challenge.
According to 2009 World Bank statistics, the U.S. had the highest health care costs
relative to the size of the economy (GDP) in the world, even though
estimated 50 million citizens (approximately 16% of the September 2011
estimated population of 312 million) lacked insurance. In March 2010, billionaire Warren Buffett commented that the high costs paid by U.S. companies for their employees' health care put them at a competitive disadvantage.
Life
expectancy compared to healthcare spending from 1970 to 2008, in the US
and the next 19 most wealthy countries by total GDP.
Further, an estimated 77 million Baby Boomers
are reaching retirement age, which combined with significant annual
increases in healthcare costs per person will place enormous budgetary
strain on U.S. state and federal governments, particularly through Medicare and Medicaid spending (Medicaid provides long-term care for the elderly poor).
Maintaining the long-term fiscal health of the U.S. federal government
is significantly dependent on healthcare costs being controlled.
Insurance cost and availability
In addition, the number of employers who offer health insurance has
declined and costs for employer-paid health insurance are rising: from
2001 to 2007, premiums for family coverage increased 78%, while wages
rose 19% and prices rose 17%, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. Even for those who are employed, the private insurance in the US varies greatly in its coverage; one study by the Commonwealth Fund published in Health Affairs
estimated that 16 million U.S. adults were underinsured in 2003. The
underinsured were significantly more likely than those with adequate
insurance to forgo health care, report financial stress because of
medical bills, and experience coverage gaps for such items as
prescription drugs. The study found that underinsurance
disproportionately affects those with lower incomes—73% of the
underinsured in the study population had annual incomes below 200% of
the federal poverty level. However, a study published by the Kaiser Family Foundation in 2008 found that the typical large employer preferred provider organization (PPO) plan in 2007 was more generous than either Medicare or the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program Standard Option. One indicator of the consequences of Americans' inconsistent health care coverage is a study in Health Affairs that concluded that half of personal bankruptcys involved medical bills, although other sources dispute this.
There are health losses from insufficient health insurance. A
2009 Harvard study published in the American Journal of Public Health
found more than 44,800 excess deaths annually in the United States due
to Americans lacking health insurance.
More broadly, estimates of the total number of people in the United
States, whether insured or uninsured, who die because of lack of medical
care were estimated in a 1997 analysis to be nearly 100,000 per year.
A study of the effects of the Massachusetts universal health care law
(which took effect in 2006) found a 3% drop in mortality among people
20–64 years old—1 death per 830 people with insurance. Other studies,
just as those examining the randomized distribution of Medicaid
insurance to low-income people in Oregon in 2008, found no change in
death rate.
The cost of insurance has been a primary motivation in the reform
of the US healthcare system, and many different explanations have been
proposed in the reasons for high insurance costs and how to remedy them.
One critique and motivation for healthcare reform has been the
development of the medical–industrial complex.
This relates to moral arguments for health care reform, framing
healthcare as a social good, one that is fundamentally immoral to deny
to people based on economic status.
The motivation behind healthcare reform in response to the
medical-industrial complex also stems from issues of social inequity,
promotion of medicine over preventative care.
The medical-industrial complex, defined as a network of health
insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, and the like, plays a
role in the complexity of the US insurance market and a fine line
between government and industry within it.
Likewise, critiques of insurance markets being conducted under a
capitalistic, free-market model also include that medical solutions, as
opposed to preventative healthcare measures, are promoted to maintain
this medical-industrial complex.
Arguments for a market-based approach to health insurance include the
Grossman model, which is based on an ideal competitive model, but others
have critiqued this, arguing that fundamentally, this means that people
in higher socioeconomic levels will receive a better quality of
healthcare.
- Uninsured rate
With the implementation of the ACA, the level of uninsured rates
severely decreased in the U.S. . This is due to the expansion of
qualifications for access to medicaid, subsidizing insurance, prevention
of insurance companies from underwriting, as well as enforcing the
individual mandate which requires citizens to purchase health insurance
or pay a fee. In a research study which was conducted comparing the
effects of the ACA before and after it was fully implemented in 2014, it
was discovered that racial and ethnic minorities benefited more than
whites with many gaining insurance coverage which they lacked before
allowing for many to seek treatment improving their overall health. In June 2014, Gallup–Healthways
Well–Being conducted a survey and found that the uninsured rate is
decreasing with 13 percent of U.S. adults uninsured in 2014 compared to
17 percent in January 2014 and translates to roughly 10 million to 11
million individuals who gained coverage. The survey also looked at the
major demographic groups and found each is making progress towards
getting health insurance. However, Hispanics, who have the highest
uninsured rate of any racial or ethnic group, are lagging in their
progress. Under the new health care reform, Latinos were expected to be
major beneficiaries of the new health care law. Gallup found that the
biggest drop in the uninsured rate (3 percentage points) was among
households making less than $36,000 a year.
Waste and fraud
In December 2011 the outgoing Administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Donald Berwick,
asserted that 20% to 30% of health care spending is waste. He listed
five causes for the waste: (1) overtreatment of patients, (2) the
failure to coordinate care, (3) the administrative complexity of the health care system, (4) burdensome rules and (5) fraud.
An estimated 3–10% of all health care expenditures in the U.S.
are fraudulent. In 2011, Medicare and Medicaid made $65 billion in
improper payments (including both error and fraud). Government efforts
to reduce fraud include $4 billion in fraudulent payments recovered by
the Department of Justice and the FBI in 2012, longer jail sentences
specified by the Affordable Care Act, and Senior Medicare Patrols—volunteers trained to identify and report fraud.
In 2007, the Department of Justice and Health and Human Services formed the Medicare Fraud Strike Force
to combat fraud through data analysis and increased community policing.
As of May 2013, the Strike Force has charged more than 1,500 people for
false billings of more than $5 billion. Medicare fraud
often takes the form of kickbacks and money-laundering. Fraud schemes
often take the form of billing for medically unnecessary services or
services not rendered.
Quality of care
There
is significant debate regarding the quality of the U.S. healthcare
system relative to those of other countries. Although there are
advancements in the quality of care in America due to the
acknowledgement of various health related topics such as how insurance
plans are now mandated to include coverage for those with mental health
and substance abuse disorders as well with the inability to deny a
person who has preexisting conditions through the ACA,
there is still much that needs to be improved. Within the U.S., those
who are a racial/ethnic minority along with those who poses a lower
income have higher chances of experiencing a lower quality of care at
higher cost. Despite the advancements with the ACA, this may discourage a
person from seeking medical treatment. Physicians for a National Health Program, a pro-universal single-payer system of health care
advocacy group, has claimed that a free market solution to health care
provides a lower quality of care, with higher mortality rates, than
publicly funded systems. The quality of health maintenance organizations and managed care have also been criticized by this same group.
According to a 2000 study of the World Health Organization,
publicly funded systems of industrial nations spend less on health
care, both as a percentage of their GDP and per capita, and enjoy
superior population-based health care outcomes. However, conservative commentator David Gratzer and the Cato Institute, a libertarian
think tank, have both criticized the WHO's comparison method for being
biased; the WHO study marked down countries for having private or
fee-paying health treatment and rated countries by comparison to their
expected health care performance, rather than objectively comparing
quality of care.
Some medical researchers say that patient satisfaction surveys are a poor way to evaluate medical care. Researchers at the RAND Corporation and the Department of Veterans Affairs
asked 236 elderly patients in two different managed care plans to rate
their care, then examined care in medical records, as reported in Annals of Internal Medicine.
There was no correlation. "Patient ratings of health care are easy to
obtain and report, but do not accurately measure the technical quality
of medical care," said John T. Chang, UCLA, lead author.
Public opinion
The spring 2010 healthcare reform issue of Ms. magazine
Public opinion polls have shown a majority of the public supports
various levels of government involvement in health care in the United
States, with stated preferences depending on how the question is asked. Polls from Harvard University in 1988, the Los Angeles Times in 1990, and the Wall Street Journal in 1991
all showed strong support for a health care system compared to the
system in Canada. More recently, however, polling support has declined
for that sort of health care system, with a 2007 Yahoo/AP poll showing 54% of respondents considered themselves supporters of "single-payer health care," a majority in favor of a number of reforms according to a joint poll with the Los Angeles Times and Bloomberg,
and a plurality of respondents in a 2009 poll for Time Magazine showed
support for "a national single-payer plan similar to Medicare for all." Polls by Rasmussen Reports in 2011 and 2012
showed pluralities opposed to single-payer health care. Many other
polls show support for various levels of government involvement in
health care, including polls from New York Times/CBS News and Washington Post/ABC News, showing favorability for a form of national health insurance. The Kaiser Family Foundation
showed 58% in favor of a national health plan such as Medicare-for-all
in 2009, with support around the same level from 2017 to April 2019,
when 56% said they supported it. A Quinnipiac
poll in three states in 2008 found majority support for the government
ensuring "that everyone in the United States has adequate health-care"
among likely Democratic primary voters.
A 2001 article in the public health journal Health Affairs
studied fifty years of American public opinion of various health care
plans and concluded that, while there appears to be general support of a
"national health care plan," poll respondents "remain satisfied with
their current medical arrangements, do not trust the federal government
to do what is right, and do not favor a single-payer type of national
health plan." Politifact rated a 2009 statement by Michael Moore
"false" when he stated that "[t]he majority actually want single-payer
health care." According to Politifact, responses on these polls largely
depend on the wording. For example, people respond more favorably when
they are asked if they want a system "like Medicare".
Uninsured Americans, with the numbers shown here from 1987 to 2008, are a major driver for reform efforts
Alternatives and research directions
There
are alternatives to the exchange-based market system which was enacted
by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act which have been
proposed in the past and continue to be proposed, such as a single-payer
system and allowing health insurance to be regulated at the federal
level.
In addition, the Patient Protection and Affordable Health Care Act of 2010 contained provisions which allows the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to undertake pilot projects which, if they are successful could be implemented in future.
Single-payer health care
A number of proposals have been made for a universal single-payer healthcare system in the United States, most recently the United States National Health Care Act,
(popularly known as H.R. 676 or "Medicare for All") but none have
achieved more political support than 20% congressional co-sponsorship.
Advocates argue that preventative health care
expenditures can save several hundreds of billions of dollars per year
because publicly funded universal health care would benefit employers
and consumers, that employers would benefit from a bigger pool of
potential customers and that employers would likely pay less, and would
be spared administrative costs of health care benefits. It is also
argued that inequities between employers would be reduced. Also, for example, cancer patients are more likely to be diagnosed at Stage I where curative treatment is typically a few outpatient visits, instead of at Stage III or later in an emergency room where treatment can involve years of hospitalization and is often terminal. Others have estimated a long-term savings amounting to 40% of all national health expenditures due to preventative health care, although estimates from the Congressional Budget Office and The New England Journal of Medicine have found that preventative care is more expensive.
Any national system would be paid for in part through taxes
replacing insurance premiums, but advocates also believe savings would
be realized through preventative care and the elimination of insurance
company overhead and hospital billing costs. An analysis of a single-payer bill by the Physicians for a National Health Program estimated the immediate savings at $350 billion per year.
The Commonwealth Fund believes that, if the United States adopted a
universal health care system, the mortality rate would improve and the
country would save approximately $570 billion a year.
Recent enactments of single-payer systems within individual states, such as in Vermont in 2011, may serve as living models supporting federal single-payer coverage. The plan in Vermont, however, has failed.
On June 1, 2017, in light of the recent Trump Administration’s
efforts to repeal the Affordable Care Act, California Democratic Senator
Ricardo Lara proposed a bill to establish single-payer healthcare
within the state of California (SB 562), calling on fellow senators to
act quickly in defense of healthcare. The legislation would implement
“Medicare for All,” placing all levels of healthcare in the hands of the
state. The bill proposed to the California Senate by Senator Lara
lacked a method of funding required to finance the $400 billion-dollar
policy. Despite this lack of foresight, the bill gained approval from
the senate and will move on to await approval by the state assembly.
In wake of the Affordable Care Act, the state of California has
experienced the greatest rise in newly insured people compared to other
states. Subsequently, the number of physicians under MediCal are not
enough to meet the demand, therefore 25% of physicians care for 80% of
patients who are covered through MediCal.
In the past, California has struggled to maintain healthcare
effectiveness, due in part to its unstable budget and complex
regulations. The state has a policy in place known as the Gann Limit,
otherwise entitled proposition 98, which ensures that a portion of state
funds are directed towards the education system. This limit would be
exceeded if California raises taxes to fund the new system which would
require $100 billion in tax revenue. In order to avoid legal dispute,
voters would be required to amend proposition 98 and exempt healthcare
funding from required educational contributions.
The state announced on August 1, 2017 that coverage for health
insurance will increase by 12.5% in next year, threatening the coverage
of 1.5 million people
Public option
In January 2013, Representative Jan Schakowsky and 44 other U.S. House of Representatives Democrats introduced H.R. 261, the "Public Option Deficit Reduction Act" which would amend the 2010 Affordable Care Act
to create a public option. The bill would set up a government-run
health insurance plan with premiums 5% to 7% percent lower than private
insurance. The Congressional Budget Office estimated it would reduce the United States public debt by $104 billion over 10 years.
Balancing doctor supply and demand
The Medicare Graduate Medical Education program regulates the supply of medical doctors in the U.S. By adjusting the reimbursement rates to establish more income equality among the medical professions, the effective cost of medical care can be lowered.
Bundled payments
A
key project is one that could radically change the way the medical
profession is paid for services under Medicare and Medicaid. The current
system, which is also the prime system used by medical insurers is
known as fee-for-service
because the medical practitioner is paid only for the performance of
medical procedures which, it is argued means that doctors have a
financial incentive to do more tests (which generates more income) which
may not be in the patients' best long-term interest. The current system
encourages medical interventions such as surgeries and prescribed
medicines (all of which carry some risk for the patient but increase
revenues for the medical care industry) and does not reward other
activities such as encouraging behavioral changes such as modifying
dietary habits and quitting smoking, or follow-ups regarding prescribed
regimes which could have better outcomes for the patient at a lower
cost. The current fee-for-service system also rewards bad hospitals for
bad service. Some
have noted that the best hospitals have fewer re-admission rates than
others, which benefits patients, but some of the worst hospitals have
high re-admission rates which is bad for patients but is perversely
rewarded under the fee-for-service system.
Projects at CMS are examining the possibility of rewarding health care providers through a process known as "bundled payments"
by which local doctors and hospitals in an area would be paid not on a
fee for service basis but on a capitation system linked to outcomes. The
areas with the best outcomes would get more. This system, it is argued,
makes medical practitioners much more concerned to focus on activities
that deliver real health benefits at a lower cost to the system by
removing the perversities inherent in the fee-for-service system.
Though aimed as a model for health care funded by CMS, if the
project is successful it is thought that the model could be followed by
the commercial health insurance industry also.
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation
With
the ACA improving the health of many by increasing the number of people
who are insured, this is not the final stage for the ACA due to the
push for a medicaid expansion reform. With the Democrats supporting the
expansion and the Republicans against it, it was denied in the Supreme
Court in the trial of NFIB vs Sebelius. The Court ruled that
implementing taxes in order to pay for health insurance for all citizens
was an unconstitutional exercise of Congress’s power under Article I.
If the expansion eventually succeeds, Medicaid would become a fully
federal program with new federal eligibility standards. This would
alleviate the responsibility of state governments to fund Medicaid.
In addition to the reform for the medicaid expansion, there are
additional reforms focused on addressing social determinants in the
healthcare system through various programs and initiatives in order to
reduce healthcare expenditures and improve health outcomes.
Programs and initiatives recognizing and addressing non-medical
social needs have sprung from various sectors within healthcare, with
emerging efforts made by multi-payer federal and state initiatives,
medicaid initiatives led by states, or by health plans, as well as
provider level actions.State and federal initiatives, primarily
sponsored CMMI (Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation) a division
of CMS,
seek to address basic social needs within the context of the healthcare
delivery system. CMMI initiatives like the 2016 "Accountable Heath
Communities" (AHC) model have been created to focus on connecting
Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries with community services to address
health-related social needs, while providing funds to organizations so
that they can systematically identify and address the health-related
social needs of Medicare and Medicaid recipients through screening,
referral, and community navigation services.
The model was officially implemented in 2017 and will be evaluated for
its ability to affect cost of healthcare spending and reduce
inpatient/outpatient utilization in 2022.
Under the AHC model, funds have been allocated towards developing a
10-item screening tool to identify 5 different patient need domains that
can be addressed through community resources (housing instability, food
insecurity, transportation difficulties, utility assistance needs, and
interpersonal safety).
Increasing bodies of evidence suggest that addressing social needs can
help stop their damaging health effects, but screening for social needs
is not yet standard clinical practice. Applying this tool in the
AHC model will help CMS evaluate the impact of local partnerships
between healthcare providers and community organizations in advancing
the aims of addressing the cost and quality of health care across all
settings.
National recommendations around multi-dimension screening for social
risk are not yet available since the evidence base to support such
recommendations is highly under-developed at present. More research is
still needed in this area to be able to demonstrate whether screening
for social risk, and especially for multiple domains of social risk,
will succeed in meeting the Wilson and Jungner screening criteria.
Health plan specific initiatives
Due
to how new CMMI initiatives are, evidence supporting the effectiveness
of its various initiatives of reducing healthcare spending and improving
health outcomes of patients is relatively small, but is expected to
grow within the coming years as many of CMMI's programs and initiatives
will be due for their programmatic performance evaluation.
However, it remains that there is more evidence of smaller scale
initiatives in individual health plans/hospitals/clinics, as several
health plans, hospitals, and clinics have sought out to address social
determinants of health within their scope of care.
Transportation
Transportation
is a key social determinant impacting patient outcomes with
approximately 3.6 million individuals unable to receive the necessary
medical care due to transportation barrier, according to recent study.
In addition, these 3.6 million experience multiple conditions at a much
higher rate than those who have stable access to transportation. Many
conditions that they face, however, can be managed if appropriate care
is made available. For some conditions, this care is cost-effective and
results in health care cost savings that outweigh added transportation
costs.
without access to reliable, affordable, and convenient transportation,
patients miss appointments and end up costing clinics money. According
to a cross-study analysis, missed appointments and care delays cost the
healthcare industry $150 billion each year. Patients without transportation are also less likely to take medications as directed.
One study found that 65 percent of patients felt transportation
assistance would enable them to fill prescriptions as directed after
discharge. According to a recent article published in the Journal of the American Medical Association,
ridesharing services such as Lyft and Uber can improve that healthcare
disparity and cut down on the $2.7 million the federal government spends
each year on non-emergency medical transportation services.
To recover revenue and improve care quality, some health systems like
MedStar Health and Denver Health Medical Center are teaming up with
Uber, Lyft, and other ridesharing companies to connect patients with
transportation.
Housing
The
University of Illinois Hospital, part of the University of Illinois
Hospital & Health Sciences System, identified that large portion of
the individuals with high rates of emergency department were also
chronically homeless, and that these individuals were in the 10th decile
for patient cost, with annual per patient expenses ranging from $51,000
to $533,000.
The University of Illinois partnered with a community group called the
Center for Housing and Health to initiate the Better Health Through
Housing initiative in 2015, an initiative that connected chronically
homeless individuals with transitional housing and case managers. In
partnering with the Center for Housing and Health, the University of
Illinois Hospital saw participant healthcare costs fall 42 percent, and
more recent studies have found that costs dropped by 61 percent. The
hospital's emergency department reported a 35% reduction in use.
Malnutrition
Some
health plans have chosen to address some SDOH within their own means by
establishing programs that directly deal with a single risk factor.
Studies show that malnutrition can lead to higher costs of care and
extended hospital states with the average hospital stay costing nearly
$2,000 per day.
Advocate Health Care, an accountable care organization in Chicago,
Illinois, implemented a nutrition care program at four of its Chicago
area hospitals, an initiative that resulted in more than $4.8 million in
cost savings within 6 months due to shorter hospital states and lower
readmission rates (reduced 30 day readmission rates by 27% and the
average hospital stay by nearly two days).
Trump administration efforts
Donald Trump
was elected President on a platform that included a pledge to "repeal
and replace" the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (commonly
called the Affordable Care Act or Obamacare). Rather than making
adjustments to the Affordable Care Act, President Trump is proposing the
American Health Care Act
(AHCA), which was developed by the House of Representatives. If passed,
this new Heath Care Act would cause insurance and healthcare to return
to the market potentially causing for 18 million Americans to become
uninsured.
In addition to this, President Trump is pushing for a change in
policies regarding "public charge" which would cause the public benefits
such as health, nutrition, and housing programs that were previously
excluded to count towards considering a person a public charge. By doing
this, immigrants who use these resources would have their ability to
obtain legal permanent resident status affected increasing their chance
of being denied citizenship.
The administration has suggested that the AHCA is only part of its
reform efforts. Other proposals include allowing interstate competition
in the health insurance market.
Incentivizing health reimbursement arrangements is another goal.