| Leukemia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Leukaemia |
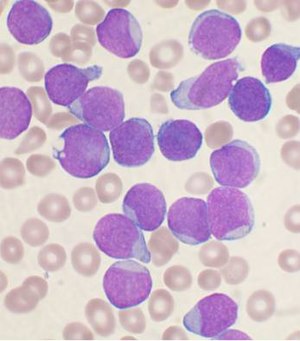 | |
| A Wright's stainled bone marrow aspirate smear from a person with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Hematology and oncology |
| Symptoms | Bleeding, bruising, feeling tired, fever, increased risk of infections |
| Usual onset | All ages |
| Causes | Inherited and environmental factors |
| Risk factors | Smoking, family history, ionizing radiation, some chemicals, prior chemotherapy, Down syndrome. |
| Diagnostic method | Blood tests, bone marrow biopsy |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, bone marrow transplant, supportive care |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate 57% (USA) |
| Frequency | 2.3 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 353,500 (2015) |
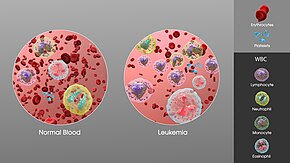
Leukemia, also spelled leukaemia, is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, feeling tired, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy.
The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, some chemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia—acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)—as well as a number of less common types. Leukemias and lymphomas both belong to a broader group of tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid system, known as tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues.
Treatment may involve some combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and bone marrow transplant, in addition to supportive care and palliative care as needed. Certain types of leukemia may be managed with watchful waiting. The success of treatment depends on the type of leukemia and the age of the person. Outcomes have improved in the developed world. The average five-year survival rate is 57% in the United States. In children under 15, the five-year survival rate is greater than 60 to 85%, depending on the type of leukemia. In children with acute leukemia who are cancer-free after five years, the cancer is unlikely to return.
In 2015, leukemia was present in 2.3 million people and caused 353,500 deaths. In 2012 it newly developed in 352,000 people. It is the most common type of cancer in children, with three quarters of leukemia cases in children being the acute lymphoblastic type. However, about 90% of all leukemias are diagnosed in adults, with AML and CLL being most common in adults. It occurs more commonly in the developed world.
Classification
| Cell type | Acute | Chronic |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphocytic leukemia (or "lymphoblastic") |
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) |
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) |
| Myelogenous leukemia ("myeloid" or "nonlymphocytic") |
Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML or myeloblastic) |
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) |
General classification
Clinically and pathologically, leukemia is subdivided into a variety of large groups. The first division is between its acute and chronic forms:
- Acute leukemia is characterized by a rapid increase in the number of immature blood cells. The crowding that results from such cells makes the bone marrow unable to produce healthy blood cells. Immediate treatment is required in acute leukemia because of the rapid progression and accumulation of the malignant cells, which then spill over into the bloodstream and spread to other organs of the body. Acute forms of leukemia are the most common forms of leukemia in children.
- Chronic leukemia is characterized by the excessive buildup of relatively mature, but still abnormal, white blood cells. Typically taking months or years to progress, the cells are produced at a much higher rate than normal, resulting in many abnormal white blood cells. Whereas acute leukemia must be treated immediately, chronic forms are sometimes monitored for some time before treatment to ensure maximum effectiveness of therapy. Chronic leukemia mostly occurs in older people, but can occur in any age group.
Additionally, the diseases are subdivided according to which kind of
blood cell is affected. This divides leukemias into lymphoblastic or lymphocytic leukemias and myeloid or myelogenous leukemias:
- In lymphoblastic or lymphocytic leukemias, the cancerous change takes place in a type of marrow cell that normally goes on to form lymphocytes, which are infection-fighting immune system cells. Most lymphocytic leukemias involve a specific subtype of lymphocyte, the B cell.
- In myeloid or myelogenous leukemias, the cancerous change takes place in a type of marrow cell that normally goes on to form red blood cells, some other types of white cells, and platelets.
Combining these two classifications provides a total of four main
categories. Within each of these main categories, there are typically
several subcategories. Finally, some rarer types are usually considered
to be outside of this classification scheme.
Specific types
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common type of leukemia in young children. It also affects adults, especially those 65 and older. Standard treatments involve chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The survival rates vary by age: 85% in children and 50% in adults. Subtypes include precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia, precursor T acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Burkitt's leukemia, and acute biphenotypic leukemia.
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) most often affects adults over the age of 55. It sometimes occurs in younger adults, but it almost never affects children. Two-thirds of affected people are men. The five-year survival rate is 75%. It is incurable, but there are many effective treatments. One subtype is B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, a more aggressive disease.
- Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) occurs more commonly in adults than in children, and more commonly in men than women. It is treated with chemotherapy. The five-year survival rate is 40%, except for APL (Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia), which has a survival rate greater than 90%. Subtypes of AML include acute promyelocytic leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia.
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) occurs mainly in adults; a very small number of children also develop this disease. It is treated with imatinib (Gleevec in United States, Glivec in Europe) or other drugs. The five-year survival rate is 90%. One subtype is chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
- Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is sometimes considered a subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but does not fit neatly into this category. About 80% of affected people are adult men. No cases in children have been reported. HCL is incurable but easily treatable. Survival is 96% to 100% at ten years.
- T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia (T-PLL) is a very rare and aggressive leukemia affecting adults; somewhat more men than women are diagnosed with this disease. Despite its overall rarity, it is the most common type of mature T cell leukemia; nearly all other leukemias involve B cells. It is difficult to treat, and the median survival is measured in months.
- Large granular lymphocytic leukemia may involve either T-cells or NK cells; like hairy cell leukemia, which involves solely B cells, it is a rare and indolent (not aggressive) leukemia.
- Adult T-cell leukemia is caused by human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), a virus similar to HIV. Like HIV, HTLV infects CD4+ T-cells and replicates within them; however, unlike HIV, it does not destroy them. Instead, HTLV "immortalizes" the infected T-cells, giving them the ability to proliferate abnormally. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus types I and II (HTLV-I/II) are endemic in certain areas of the world.
- Clonal eosinophilias (also called clonal hypereosinophilias) are a group of blood disorders characterized by the growth of eosinophils in the bone marrow, blood, and/or other tissues. They may be pre-cancerous or cancerous. Clonal eosinophilias involve a "clone" of eosinophils, i.e., a group of genetically identical eosinophils that all grew from the same mutated ancestor cell. These disorders may evolve into chronic eosinophilic leukemia or may be associated with various forms of myeloid neoplasms, lymphoid neoplasms, myelofibrosis, or the myelodysplastic syndrome.
Pre-leukemia
- Transient myeloproliferative disease, also termed transient leukemia, involves the abnormal proliferation of a clone of non-cancerous megakaryoblasts. The disease is restricted to individuals with Down syndrome or genetic changes similar to those in Down syndrome, develops in a baby during pregnancy or shortly after birth, and resolves within 3 months or, in ~10% of cases, progresses to acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Transient myeloid leukemia is a pre-leukemic condition.
Signs and symptoms
Common symptoms of chronic or acute leukemia
The most common symptoms in children are easy bruising, pale skin, fever, and an enlarged spleen or liver.
Damage to the bone marrow, by way of displacing the normal bone
marrow cells with higher numbers of immature white blood cells, results
in a lack of blood platelets, which are important in the blood clotting process. This means people with leukemia may easily become bruised, bleed excessively, or develop pinprick bleeds (petechiae).
White blood cells, which are involved in fighting pathogens,
may be suppressed or dysfunctional. This could cause the person's
immune system to be unable to fight off a simple infection or to start
attacking other body cells. Because leukemia prevents the immune system
from working normally, some people experience frequent infection, ranging from infected tonsils, sores in the mouth, or diarrhea to life-threatening pneumonia or opportunistic infections.
Some people experience other symptoms, such as feeling sick, having fevers, chills, night sweats, feeling fatigued and other flu-like symptoms. Some people experience nausea or a feeling of fullness due to an enlarged liver and spleen; this can result in unintentional weight loss. Blasts affected by the disease may come together and become swollen in the liver or in the lymph nodes causing pain and leading to nausea.
If the leukemic cells invade the central nervous system, then neurological symptoms (notably headaches) can occur. Uncommon neurological symptoms like migraines, seizures, or coma
can occur as a result of brain stem pressure. All symptoms associated
with leukemia can be attributed to other diseases. Consequently,
leukemia is always diagnosed through medical tests.
The word leukemia, which means 'white blood', is derived
from the characteristic high white blood cell count that presents in
most afflicted people before treatment. The high number of white blood
cells is apparent when a blood sample is viewed under a microscope,
with the extra white blood cells frequently being immature or
dysfunctional. The excessive number of cells can also interfere with the
level of other cells, causing further harmful imbalance in the blood
count.
Some people diagnosed with leukemia do not have high white blood
cell counts visible during a regular blood count. This less-common
condition is called aleukemia. The bone marrow still contains
cancerous white blood cells which disrupt the normal production of blood
cells, but they remain in the marrow instead of entering the
bloodstream, where they would be visible in a blood test. For a person
with aleukemia, the white blood cell counts in the bloodstream can be
normal or low. Aleukemia can occur in any of the four major types of
leukemia, and is particularly common in hairy cell leukemia.
Causes
There is
no single known cause for any of the different types of leukemias. The
few known causes, which are not generally factors within the control of
the average person, account for relatively few cases. The cause for most cases of leukemia is unknown. The different leukemias likely have different causes.
Leukemia, like other cancers, results from mutations in the DNA. Certain mutations can trigger leukemia by activating oncogenes or deactivating tumor suppressor genes,
and thereby disrupting the regulation of cell death, differentiation or
division. These mutations may occur spontaneously or as a result of
exposure to radiation or carcinogenic substances.
Among adults, the known causes are natural and artificial ionizing radiation, a few viruses such as human T-lymphotropic virus, and some chemicals, notably benzene and alkylating chemotherapy agents for previous malignancies. Use of tobacco is associated with a small increase in the risk of developing acute myeloid leukemia in adults. Cohort and case-control studies have linked exposure to some petrochemicals and hair dyes
to the development of some forms of leukemia. Diet has very limited or
no effect, although eating more vegetables may confer a small protective
benefit.
Viruses have also been linked to some forms of leukemia. For example, human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV-1) causes adult T-cell leukemia.
A few cases of maternal-fetal transmission (a baby acquires leukemia because its mother had leukemia during the pregnancy) have been reported. Children born to mothers who use fertility drugs to induce ovulation are more than twice as likely to develop leukemia during their childhoods than other children.
Radiation
Large doses of Sr-90 emission from nuclear reactor accidents, nicknamed bone seeker increases the risk of bone cancer and leukemia in animals, and is presumed to do so in people.
Genetic conditions
Some
people have a genetic predisposition towards developing leukemia. This
predisposition is demonstrated by family histories and twin studies.
The affected people may have a single gene or multiple genes in common.
In some cases, families tend to develop the same kinds of leukemia as
other members; in other families, affected people may develop different
forms of leukemia or related blood cancers.
In addition to these genetic issues, people with chromosomal
abnormalities or certain other genetic conditions have a greater risk of
leukemia. For example, people with Down syndrome have a significantly increased risk of developing forms of acute leukemia (especially acute myeloid leukemia), and Fanconi anemia is a risk factor for developing acute myeloid leukemia. Mutation in SPRED1 gene has been associated with a predisposition to childhood leukemia.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia is associated with a genetic abnormality called the Philadelphia translocation;
95% of people with CML carry the Philadelphia mutation, although this
is not exclusive to CML and can be observed in people with other types
of leukemia.
Non-ionizing radiation
Whether or not non-ionizing radiation causes leukemia has been studied for several decades. The International Agency for Research on Cancer expert working group undertook a detailed review of all data on static and extremely low frequency
electromagnetic energy, which occurs naturally and in association with
the generation, transmission, and use of electrical power. They concluded that there is limited evidence that high levels of ELF magnetic (but not electric) fields might cause some cases of childhood leukemia. No evidence for a relationship to leukemia or another form of malignancy in adults has been demonstrated. Since exposure to such levels of ELFs is relatively uncommon, the World Health Organization
concludes that ELF exposure, if later proven to be causative, would
account for just 100 to 2400 cases worldwide each year, representing 0.2
to 4.9% of the total incidence of childhood leukemia for that year
(about 0.03 to 0.9% of all leukemias).
Diagnosis
The increase in white blood cells in leukemia.
Diagnosis is usually based on repeated complete blood counts and a bone marrow examination
following observations of the symptoms. Sometimes, blood tests may not
show that a person has leukemia, especially in the early stages of the
disease or during remission. A lymph node biopsy can be performed to diagnose certain types of leukemia in certain situations.
Following diagnosis, blood chemistry tests can be used to
determine the degree of liver and kidney damage or the effects of
chemotherapy on the person. When concerns arise about other damages due
to leukemia, doctors may use an X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound.
These can potentially show leukemia's effects on such body parts as
bones (X-ray), the brain (MRI), or the kidneys, spleen, and liver
(ultrasound). CT scans can be used to check lymph nodes in the chest, though this is uncommon.
Despite the use of these methods to diagnose whether or not a
person has leukemia, many people have not been diagnosed because many of
the symptoms are vague, non-specific,
and can refer to other diseases. For this reason, the American Cancer
Society estimates that at least one-fifth of the people with leukemia
have not yet been diagnosed.
Treatment
Most forms of leukemia are treated with pharmaceutical medication, typically combined into a multi-drug chemotherapy regimen. Some are also treated with radiation therapy. In some cases, a bone marrow transplant is effective.
Acute lymphoblastic
Management of ALL is directed towards control of bone marrow and
systemic (whole-body) disease. Additionally, treatment must prevent
leukemic cells from spreading to other sites, particularly the central nervous system (CNS) e.g. monthly lumbar punctures. In general, ALL treatment is divided into several phases:
- Induction chemotherapy to bring about bone marrow remission. For adults, standard induction plans include prednisone, vincristine, and an anthracycline drug; other drug plans may include L-asparaginase or cyclophosphamide. For children with low-risk ALL, standard therapy usually consists of three drugs (prednisone, L-asparaginase, and vincristine) for the first month of treatment.
- Consolidation therapy or intensification therapy to eliminate any remaining leukemia cells. There are many different approaches to consolidation, but it is typically a high-dose, multi-drug treatment that is undertaken for a few months. People with low- to average-risk ALL receive therapy with antimetabolite drugs such as methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP). People who are high-risk receive higher drug doses of these drugs, plus additional drugs.
- CNS prophylaxis (preventive therapy) to stop the cancer from spreading to the brain and nervous system in high-risk people. Standard prophylaxis may include radiation of the head and/or drugs delivered directly into the spine.
- Maintenance treatments with chemotherapeutic drugs to prevent disease recurrence once remission has been achieved. Maintenance therapy usually involves lower drug doses, and may continue for up to three years.
- Alternatively, allogeneic bone marrow transplantation may be appropriate for high-risk or relapsed people.
Chronic lymphocytic
Decision to treat
Hematologists
base CLL treatment on both the stage and symptoms of the individual
person. A large group of people with CLL have low-grade disease, which
does not benefit from treatment. Individuals with CLL-related
complications or more advanced disease often benefit from treatment. In
general, the indications for treatment are:
- Falling hemoglobin or platelet count
- Progression to a later stage of disease
- Painful, disease-related overgrowth of lymph nodes or spleen
- An increase in the rate of lymphocyte production
Treatment approach
For
most people with CLL, it is incurable by present treatments, so
treatment is directed towards suppressing the disease for many years,
rather than totally and permanently eliminating it. The primary
chemotherapeutic plan is combination chemotherapy with chlorambucil or cyclophosphamide, plus a corticosteroid such as prednisone or prednisolone. The use of a corticosteroid has the additional benefit of suppressing some related autoimmune diseases, such as immunohemolytic anemia or immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. In resistant cases, single-agent treatments with nucleoside drugs such as fludarabine, pentostatin, or cladribine may be successful. Younger and healthier people may choose allogeneic or autologous bone marrow transplantation in the hope of a permanent cure.
Acute myelogenous
Many different anti-cancer drugs are effective for the treatment of
AML. Treatments vary somewhat according to the age of the person and
according to the specific subtype of AML. Overall, the strategy is to
control bone marrow and systemic (whole-body) disease, while offering
specific treatment for the central nervous system (CNS), if involved.
In general, most oncologists rely on combinations of drugs for the initial, induction phase of chemotherapy. Such combination chemotherapy usually offers the benefits of early remission and a lower risk of disease resistance. Consolidation and maintenance
treatments are intended to prevent disease recurrence. Consolidation
treatment often entails a repetition of induction chemotherapy or the
intensification chemotherapy with additional drugs. By contrast,
maintenance treatment involves drug doses that are lower than those
administered during the induction phase.
Chronic myelogenous
There are many possible treatments for CML, but the standard of care for newly diagnosed people is imatinib (Gleevec) therapy. Compared to most anti-cancer drugs, it has relatively few side effects and can be taken orally at home. With this drug, more than 90% of people will be able to keep the disease in check for at least five years, so that CML becomes a chronic, manageable condition.
In a more advanced, uncontrolled state, when the person cannot
tolerate imatinib, or if the person wishes to attempt a permanent cure,
then an allogeneic bone marrow transplantation may be performed. This
procedure involves high-dose chemotherapy and radiation followed by
infusion of bone marrow from a compatible donor. Approximately 30% of
people die from this procedure.
Hairy cell
Decision to treat
People with hairy cell leukemia who are symptom-free typically do not
receive immediate treatment. Treatment is generally considered necessary
when the person shows signs and symptoms such as low blood cell counts
(e.g., infection-fighting neutrophil count below 1.0 K/µL), frequent
infections, unexplained bruises, anemia, or fatigue that is significant
enough to disrupt the person's everyday life.
Typical treatment approach
People who need treatment usually receive either one week of cladribine, given daily by intravenous infusion or a simple injection under the skin, or six months of pentostatin, given every four weeks by intravenous infusion. In most cases, one round of treatment will produce a prolonged remission.
Other treatments include rituximab infusion or self-injection with Interferon-alpha. In limited cases, the person may benefit from splenectomy
(removal of the spleen). These treatments are not typically given as
the first treatment because their success rates are lower than
cladribine or pentostatin.
T-cell prolymphocytic
Most people with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, a rare and
aggressive leukemia with a median survival of less than one year,
require immediate treatment.
T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is difficult to treat, and it does not respond to most available chemotherapeutic drugs. Many different treatments have been attempted, with limited success in certain people: purine analogues (pentostatin, fludarabine, cladribine), chlorambucil, and various forms of combination chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone CHOP, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone [COP], vincristine, doxorubicin, prednisone, etoposide, cyclophosphamide, bleomycin VAPEC-B). Alemtuzumab (Campath), a monoclonal antibody that attacks white blood cells, has been used in treatment with greater success than previous options.
Some people who successfully respond to treatment also undergo stem cell transplantation to consolidate the response.
Juvenile myelomonocytic
Treatment for juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia can include splenectomy, chemotherapy, and bone marrow transplantation.
Prognosis
The
success of treatment depends on the type of leukemia and the age of
the person. Outcomes have improved in the developed world. The average five-year survival rate is 61% in the United States. In children under 15, the five-year survival rate is greater (60 to 85%), depending on the type of leukemia. In children with acute leukemia who are cancer-free after five years, the cancer is unlikely to return.
Outcomes depend on whether it is acute or chronic, the specific abnormal white blood cell type, the presence and severity of anemia or thrombocytopenia, the degree of tissue abnormality, the presence of metastasis and lymph node and bone marrow
infiltration, the availability of therapies and the skills of the
health care team. Treatment outcomes may be better when people are
treated at larger centers with greater experience.
Epidemiology
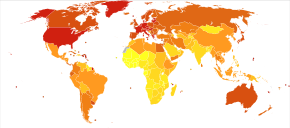
Deaths due to leukemia per million persons in 2012
0-7
8-13
14-22
23-29
30-34
35-39
40-46
47-64
65-85
86-132
In 2010, globally, approximately 281,500 people died of leukemia. In 2000, approximately 256,000 children and adults around the world developed a form of leukemia, and 209,000 died from it.
This represents about 3% of the almost seven million deaths due to
cancer that year, and about 0.35% of all deaths from any cause.
Of the sixteen separate sites the body compared, leukemia was the 12th
most common class of neoplastic disease, and the 11th most common cause
of cancer-related death. Leukemia occurs more commonly in the developed world.
United States
About
245,000 people in the United States are affected with some form of
leukemia, including those that have achieved remission or cure. Rates
from 1975 to 2011 have increased by 0.7% per year among children. Approximately 44,270 new cases of leukemia were diagnosed in the year 2008 in the US.
This represents 2.9% of all cancers (excluding simple basal cell and
squamous cell skin cancers) in the United States, and 30.4% of all blood cancers.
Among children with some form of cancer, about a third have a type of leukemia, most commonly acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
A type of leukemia is the second most common form of cancer in infants
(under the age of 12 months) and the most common form of cancer in older
children.
Boys are somewhat more likely to develop leukemia than girls, and
white American children are almost twice as likely to develop leukemia
than black American children.
Only about 3% cancer diagnoses among adults are for leukemias, but
because cancer is much more common among adults, more than 90% of all
leukemias are diagnosed in adults.
Race is a risk factor in the United States. Hispanics, especially those under the age of 20, are at the highest risk for leukemia, while whites, Native Americans, Asian Americans, and Alaska Natives are at higher risk than African Americans.
More men than women are diagnosed with leukemia and die from the disease. Around 30 percent more men than women have leukemia.
UK
Overall,
leukaemia is the eleventh most common cancer in the UK (around 8,600
people were diagnosed with the disease in 2011), and it is the ninth
most common cause of cancer death (around 4,800 people died in 2012).
History
Rudolf Virchow
Leukemia was first described by anatomist and surgeon Alfred-Armand-Louis-Marie Velpeau in 1827. A more complete description was given by pathologist Rudolf Virchow in 1845. Around ten years after Virchow's findings, pathologist Franz Ernst Christian Neumann
found that the bone marrow of a deceased person with leukemia was
colored "dirty green-yellow" as opposed to the normal red. This finding
allowed Neumann to conclude that a bone marrow problem was responsible
for the abnormal blood of people with leukemia.
By 1900 leukemia was viewed as a family of diseases as opposed to a single disease. By 1947 Boston pathologist Sidney Farber believed from past experiments that aminopterin,
a folic acid mimic, could potentially cure leukemia in children. The
majority of the children with ALL who were tested showed signs of
improvement in their bone marrow, but none of them were actually cured.
This, however, led to further experiments.
In 1962, researchers Emil J. Freireich, Jr. and Emil Frei III
used combination chemotherapy to attempt to cure leukemia. The tests
were successful with some people surviving long after the tests.
Etymology
Observing an abnormally large number of white blood cells in a blood sample from a person, Virchow called the condition Leukämie in German, which he formed from the two Greek words leukos (λευκός), meaning "white", and haima (αἷμα), meaning "blood".
Society and culture
According to Susan Sontag,
leukemia was often romanticized in 20th-century fiction, portrayed as a
joy-ending, clean disease whose fair, innocent and gentle victims die
young or at the wrong time. As such, it was the cultural successor to tuberculosis, which held this cultural position until it was discovered to be an infectious disease. The 1970 romance novel Love Story is an example of this romanticization of leukemia.
In the United States, around $5.4 billion is spent on treatment a year.
Research directions
Significant
research into the causes, prevalence, diagnosis, treatment, and
prognosis of leukemia is being performed. Hundreds of clinical trials are being planned or conducted at any given time.
Studies may focus on effective means of treatment, better ways of
treating the disease, improving the quality of life for people, or
appropriate care in remission or after cures.
In general, there are two types of leukemia research: clinical or translational research and basic research.
Clinical/translational research focuses on studying the disease in a
defined and generally immediately applicable way, such as testing a new
drug in people. By contrast, basic science research studies the disease
process at a distance, such as seeing whether a suspected carcinogen
can cause leukemic changes in isolated cells in the laboratory or how
the DNA changes inside leukemia cells as the disease progresses. The
results from basic research studies are generally less immediately
useful to people with the disease.
Treatment through gene therapy is currently being pursued. One such approach used genetically modified T cells, known as chimeric antigen receptor T cells
(CAR-T cells), to attack cancer cells. In 2011, a year after treatment,
two of the three people with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia were
reported to be cancer-free
and in 2013, three of five subjects who had acute lymphocytic leukemia
were reported to be in remission for five months to two years. Subsequent studies with a variety of CAR-T types continue to be promising. As of 2018, two CAR-T therapies have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. CAR-T treatment has significant side effects, and loss of the antigen targeted by the CAR-T cells is a common mechanism for relapse. The stem cells that cause different types of leukaemia are also being researched.
Pregnancy
Leukemia is rarely associated with pregnancy, affecting only about 1 in 10,000 pregnant women.
How it is handled depends primarily on the type of leukemia. Nearly all
leukemias appearing in pregnant women are acute leukemias. Acute leukemias normally require prompt, aggressive treatment, despite significant risks of pregnancy loss and birth defects, especially if chemotherapy is given during the developmentally sensitive first trimester. Chronic myelogenous leukemia can be treated with relative safety at any time during pregnancy with Interferon-alpha hormones.
Treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemias, which are rare in pregnant
women, can often be postponed until after the end of the pregnancy.