Canada
| |
|---|---|
Anthem: "O Canada"
| |
 | |
| Capital | Ottawa 45°24′N 75°40′W |
| Largest city | Toronto |
| Official languages | |
| Demonym(s) | Canadian |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch
| Elizabeth II |
| Julie Payette | |
| Justin Trudeau | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Commons | |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
| |
| July 1, 1867 | |
| December 11, 1931 | |
| April 17, 1982 | |
| Area | |
• Total area
| 9,984,670 km2 (3,855,100 sq mi) (2nd) |
• Water (%)
| 8.92 |
• Total land area
| 9,093,507 km2 (3,511,023 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Q2 2019 estimate
| 37,602,103 (38th) |
• 2016 census
| 35,151,728 |
• Density
| 3.92/km2 (10.2/sq mi) (228th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total
| $1.930 trillion (15th) |
• Per capita
| $51,546 (20th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total
| $1.820 trillion (10th) |
• Per capita
| $48,601 (15th) |
| Gini (2015) | medium |
| HDI (2017) | very high · 12th |
| Currency | Canadian dollar ($) (CAD) |
| Time zone | UTC−3.5 to −8 |
• Summer (DST)
| UTC−2.5 to −7 |
| Date format | yyyy-mm-dd (AD) |
| Mains electricity | 120 V–60 Hz |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | CA |
| Internet TLD | .ca |
Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres (3.85 million square miles), making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern border with the United States, stretching some 8,891 kilometres (5,525 mi), is the world's longest bi-national land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver.
As a whole, Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land area being dominated by forest and tundra. Its population is highly urbanized, with over 80 percent of its inhabitants concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, and 70 per cent residing within 100 kilometres (62 mi) of the southern border. Canada's climate varies widely across its vast area, ranging from arctic weather in the north, to hot summers in the southern regions, with four distinct seasons.
Various Indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years before European colonization. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and territories and a process of increasing autonomy from the United Kingdom. This widening autonomy was highlighted by the Statute of Westminster of 1931 and culminated in the Canada Act of 1982, which severed the vestiges of legal dependence on the British parliament.
Canada is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy in the Westminster tradition, with a monarch and a prime minister who serves as the chair of the Cabinet and head of government. The country is a realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, a member of the Francophonie and officially bilingual at the federal level. It ranks among the highest in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, and education. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many other countries. Canada's long and complex relationship with the United States has had a significant impact on its economy and culture.
A developed country, Canada has the sixteenth-highest nominal per capita income globally as well as the twelfth-highest ranking in the Human Development Index. Its advanced economy is the tenth-largest in the world, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Canada is part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the United Nations, NATO, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum.
Etymology
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the etymological origins of Canada, the name is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word kanata, meaning "village" or "settlement". In 1535, Indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec City region used the word to direct French explorer Jacques Cartier to the village of Stadacona. Cartier later used the word Canada to refer not only to that particular village but to the entire area subject to Donnacona (the chief at Stadacona); by 1545, European books and maps had begun referring to this small region along the Saint Lawrence River as Canada.From the 16th to the early 18th century "Canada" referred to the part of New France that lay along the Saint Lawrence River. In 1791, the area became two British colonies called Upper Canada and Lower Canada collectively named the Canadas; until their union as the British Province of Canada in 1841. Upon Confederation in 1867, Canada was adopted as the legal name for the new country at the London Conference, and the word Dominion was conferred as the country's title. By the 1950s, the term Dominion of Canada was no longer used by the United Kingdom, which considered Canada a "Realm of the Commonwealth". The government of Louis St. Laurent ended the practice of using Dominion in the statutes of Canada in 1951.
In 1982, the passage of the Canada Act, bringing the Constitution of Canada fully under Canadian control, referred only to Canada, and later that year the name of the national holiday was changed from Dominion Day to Canada Day. The term Dominion was used to distinguish the federal government from the provinces, though after the Second World War the term federal had replaced dominion.
History
Indigenous peoples
Linguistic areas of North American Indigenous peoples at the time of European contact
Indigenous peoples in present-day Canada include the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis, the last being a mixed-blood people who originated in the mid-17th century when First Nations and Inuit people married European settlers. The term "Aboriginal" as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the Constitution Act 1982.
The first inhabitants of North America are generally hypothesized to have migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 14,000 years ago. The Paleo-Indian archeological sites at Old Crow Flats and Bluefish Caves are two of the oldest sites of human habitation in Canada. The characteristics of Canadian Indigenous societies included permanent settlements, agriculture, complex societal hierarchies, and trading networks.
Some of these cultures had collapsed by the time European explorers
arrived in the late 15th and early 16th centuries and have only been
discovered through archeological investigations.
The Indigenous population at the time of the first European settlements is estimated to have been between 200,000 and two million, with a figure of 500,000 accepted by Canada's Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples.
As a consequence of European colonization, the population of Canada's
Indigenous peoples declined by forty to eighty percent, and several
First Nations, such as the Beothuk, disappeared. The decline is attributed to several causes, including the transfer of European diseases, such as influenza, measles, and smallpox to which they had no natural immunity,
conflicts over the fur trade, conflicts with the colonial authorities
and settlers, and the loss of Indigenous lands to settlers and the
subsequent collapse of several nations' self-sufficiency.
Although not without conflict, European Canadians' early interactions with First Nations and Inuit populations were relatively peaceful. First Nations and Métis peoples played a critical part in the development of European colonies in Canada, particularly for their role in assisting European coureur des bois and voyageurs in the exploration of the continent during the North American fur trade. The Crown and Indigenous peoples began interactions during the European colonization period, though the Inuit, in general, had more limited interaction with European settlers. However, from the late 18th century, European Canadians encouraged Indigenous peoples to assimilate into their own culture. These attempts reached a climax in the late 19th and early 20th centuries with forced integration and relocations. A period of redress is underway, which started with the appointment of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada by the Government of Canada in 2008.
European colonization
In about 1000 AD, the Norse built a small encampment that only lasted a few years at L'Anse aux Meadows on the northern tip of Newfoundland. No further European exploration occurred until 1497, when Italian seafarer John Cabot explored and claimed Canada's Atlantic coast in the name of King Henry VII of England. In 1534, French explorer Jacques Cartier explored the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
where, on July 24, he planted a 10-metre (33 ft) cross bearing the
words "Long Live the King of France" and took possession of the
territory New France in the name of King Francis I. The early 16th century saw European mariners with navigational techniques pioneered by the Basque and Portuguese establish seasonal whaling and fishing outposts along the Atlantic coast. In general, early settlements during the Age of Discovery appear to have been short-lived due to a combination of the harsh climate, problems with navigating trade routes and competing outputs in Scandinavia.
In 1583, Sir Humphrey Gilbert, by the royal prerogative of Queen Elizabeth I, founded St. John's, Newfoundland, as the first North American English colony. French explorer Samuel de Champlain arrived in 1603 and established the first permanent European settlements at Port Royal (in 1605) and Quebec City (in 1608). Among the colonists of New France, Canadiens extensively settled the Saint Lawrence River valley and Acadians settled the present-day Maritimes, while fur traders and Catholic missionaries explored the Great Lakes, Hudson Bay, and the Mississippi watershed to Louisiana. The Beaver Wars broke out in the mid-17th century over control of the North American fur trade.
Benjamin West's The Death of General Wolfe (1771) dramatizes James Wolfe's death during the Battle of the Plains of Abraham at Quebec.
The English established additional settlements in Newfoundland, beginning in 1610 and the Thirteen Colonies to the south were founded soon after. A series of four wars
erupted in colonial North America between 1689 and 1763; the later wars
of the period constituted the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War. Mainland Nova Scotia came under British rule with the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht, and Canada and most of New France came under British rule in 1763 after the Seven Years' War.
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 established First Nation treaty rights, created the Province of Quebec out of New France, and annexed Cape Breton Island to Nova Scotia. St. John's Island (now Prince Edward Island) became a separate colony in 1769. To avert conflict in Quebec, the British Parliament passed the Quebec Act of 1774, expanding Quebec's territory to the Great Lakes and Ohio Valley. More importantly, the Quebec Act
afforded Quebec special autonomy and rights of self-administration at a
time the Thirteen Colonies were increasingly agitating against British
rule. It re-established the French language, Catholic faith, and French civil law there, staving off the growth of an independence movement in contrast to the Thirteen Colonies. The Proclamation and the Quebec Act in turn angered many residents of the Thirteen Colonies, further fuelling anti-British sentiment in the years prior to the American Revolution.
After the successful American War of Independence, the 1783 Treaty of Paris
recognized the independence of the newly formed United States and set
the terms of peace, ceding British North American territories south of
the Great Lakes to the new country. The American war of independence also caused a large out-migration of Loyalists,
the settlers who had fought against American independence. Many moved
to Canada, particularly Atlantic Canada, where their arrival changed the
demographic distribution of the existing territories. New Brunswick
was in turn split from Nova Scotia as part of a reorganization of
Loyalist settlements in the Maritimes which led to the incorporation of Saint John, New Brunswick to become Canada's first city. To accommodate the influx of English-speaking Loyalists in Central Canada, the Constitutional Act of 1791 divided the province of Canada into French-speaking Lower Canada (later Quebec) and English-speaking Upper Canada (later Ontario), granting each its own elected legislative assembly.
War of 1812 heroine Laura Secord warns British commander James FitzGibbon of an impending American attack at Beaver Dams.
The Canadas were the main front in the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom.
Peace came in 1815; no boundaries were changed. Immigration resumed at a
higher level, with over 960,000 arrivals from Britain between 1815 and
1850. New arrivals included refugees escaping the Great Irish Famine as well as Gaelic-speaking Scots displaced by the Highland Clearances. Infectious diseases killed between 25 and 33 percent of Europeans who immigrated to Canada before 1891.
The desire for responsible government resulted in the abortive Rebellions of 1837. The Durham Report subsequently recommended responsible government and the assimilation of French Canadians into English culture. The Act of Union merged the Canadas into a united Province of Canada and responsible government was established for all provinces of British North America by 1849. The signing of the Oregon Treaty by Britain and the United States in 1846 ended the Oregon boundary dispute, extending the border westward along the 49th parallel. This paved the way for British colonies on Vancouver Island (1849) and in British Columbia (1858). The Alaska Purchase
of 1867 by the United States established the border along the Pacific
coast, although there would continue to be some disputes about the exact
demarcation of the Alaska-Yukon and Alaska-BC border for years to come.
Confederation and expansion
An animated map showing the growth and change of Canada's provinces and territories since Confederation in 1867.
Following several constitutional conferences, the Constitution Act officially proclaimed Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867, initially with four provinces: Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick. Canada assumed control of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory to form the Northwest Territories, where the Métis' grievances ignited the Red River Rebellion and the creation of the province of Manitoba in July 1870. British Columbia and Vancouver Island (which had been united in 1866) joined the confederation in 1871, while Prince Edward Island joined in 1873. Between 1871 and 1896, almost one quarter of the Canadian population immigrated southwards, to the U.S.
To open the West
to European immigration, parliament also approved sponsoring the
construction of three transcontinental railways (including the Canadian Pacific Railway), opening the prairies to settlement with the Dominion Lands Act, and establishing the North-West Mounted Police to assert its authority over this territory. In 1898, during the Klondike Gold Rush in the Northwest Territories, parliament created the Yukon Territory. Alberta and Saskatchewan became provinces in 1905.
Early 20th century
Because Britain still maintained control of Canada's foreign affairs under the Constitution Act, 1867, its declaration of war in 1914 automatically brought Canada into World War I. Volunteers sent to the Western Front later became part of the Canadian Corps, which played a substantial role in the Battle of Vimy Ridge and other major engagements of the war. Out of approximately 625,000 Canadians who served in World War I, some 60,000 were killed and another 172,000 were wounded. The Conscription Crisis of 1917 erupted when the Unionist Cabinet's proposal to augment the military's dwindling number of active members with conscription was met with vehement objections from French-speaking Quebecers. The Military Service Act
brought in compulsory military service, though it, coupled with
disputes over French language schools outside Quebec, deeply alienated
Francophone Canadians and temporarily split the Liberal Party. In 1919, Canada joined the League of Nations independently of Britain, and the 1931 Statute of Westminster affirmed Canada's independence.
Canadian crew of a Sherman tank, south of Vaucelles, France, during the Battle of Normandy in June 1944
The Great Depression in Canada during the early 1930s saw an economic downturn, leading to hardship across the country. In response to the downturn, the Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) in Saskatchewan introduced many elements of a welfare state (as pioneered by Tommy Douglas) in the 1940s and 1950s. On the advice of Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King, war with Germany was declared effective September 10, 1939, by King George VI, seven days after the United Kingdom. The delay underscored Canada's independence.
The first Canadian Army units arrived in Britain in December
1939. In all, over a million Canadians served in the armed forces during
World War II and approximately 42,000 were killed and another 55,000
were wounded. Canadian troops played important roles in many key battles of the war, including the failed 1942 Dieppe Raid, the Allied invasion of Italy, the Normandy landings, the Battle of Normandy, and the Battle of the Scheldt in 1944. Canada provided asylum for the Dutch monarchy while that country was occupied and is credited by the Netherlands for major contributions to its liberation from Nazi Germany.
The Canadian economy boomed during the war as its industries manufactured military materiel for Canada, Britain, China, and the Soviet Union. Despite another Conscription Crisis in Quebec in 1944, Canada finished the war with a large army and strong economy.
Contemporary era
At Rideau Hall, Governor General the Viscount Alexander of Tunis (centre) receives the bill finalizing the union of Newfoundland and Canada on March 31, 1949.
The financial crisis of the Great Depression had led the Dominion of Newfoundland to relinquish responsible government in 1934 and become a crown colony ruled by a British governor. After two bitter referendums, Newfoundlanders voted to join Canada in 1949 as a province.
Canada's post-war economic growth, combined with the policies of successive Liberal governments, led to the emergence of a new Canadian identity, marked by the adoption of the Maple Leaf Flag in 1965, the implementation of official bilingualism (English and French) in 1969, and the institution of official multiculturalism in 1971. Socially democratic programs were also instituted, such as Medicare, the Canada Pension Plan, and Canada Student Loans, though provincial governments, particularly Quebec and Alberta, opposed many of these as incursions into their jurisdictions.
Finally, another series of constitutional conferences resulted in the Canada Act, the patriation of Canada's constitution from the United Kingdom, concurrent with the creation of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
Canada had established complete sovereignty as an independent country,
although the Queen retained her role as monarch of Canada. In 1999, Nunavut became Canada's third territory after a series of negotiations with the federal government.
At the same time, Quebec underwent profound social and economic changes through the Quiet Revolution of the 1960s, giving birth to a secular nationalist movement. The radical Front de libération du Québec (FLQ) ignited the October Crisis with a series of bombings and kidnappings in 1970 and the sovereignist Parti Québécois was elected in 1976, organizing an unsuccessful referendum on sovereignty-association in 1980. Attempts to accommodate Quebec nationalism constitutionally through the Meech Lake Accord failed in 1990. This led to the formation of the Bloc Québécois in Quebec and the invigoration of the Reform Party of Canada in the West. A second referendum followed in 1995, in which sovereignty was rejected by a slimmer margin of 50.6 to 49.4 percent. In 1997, the Supreme Court ruled unilateral secession by a province would be unconstitutional and the Clarity Act was passed by parliament, outlining the terms of a negotiated departure from Confederation.
In addition to the issues of Quebec sovereignty, a number of
crises shook Canadian society in the late 1980s and early 1990s. These
included the explosion of Air India Flight 182 in 1985, the largest mass murder in Canadian history; the École Polytechnique massacre in 1989, a university shooting targeting female students; and the Oka Crisis of 1990, the first of a number of violent confrontations between the government and Indigenous groups. Canada also joined the Gulf War in 1990 as part of a U.S.-led coalition force and was active in several peacekeeping missions in the 1990s, including the UNPROFOR mission in the former Yugoslavia.
Canada sent troops to Afghanistan in 2001, but declined to join the U.S.-led invasion of Iraq in 2003. In 2011, Canadian forces participated in the NATO-led intervention into the Libyan Civil War, and also became involved in battling the Islamic State insurgency in Iraq in the mid-2010s.
Geography and climate
Köppen climate types of Canada
Canada occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing land borders with the contiguous United States to the south, and the U.S. state of Alaska
to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east
to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast and to the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with the Republic of France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area (including its waters), Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked (Alberta and Saskatchewan) while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.
Canada is home to the world's northernmost settlement, Canadian Forces Station Alert, on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island – latitude 82.5°N – which lies 817 kilometres (508 mi) from the North Pole. Much of the Canadian Arctic is covered by ice and permafrost. Canada has the longest coastline in the world, with a total length of 243,042 kilometres (151,019 mi); additionally, its border with the United States is the world's longest land border, stretching 8,891 kilometres (5,525 mi). Three of Canada's arctic islands, Baffin Island, Victoria Island and Ellesmere Island, are among the ten largest in the world.
Since the end of the last glacial period, Canada has consisted of eight distinct forest regions, including extensive boreal forest on the Canadian Shield.
42 percent of the land acreage of Canada is covered by forests,
approximately 8 percent of the world's forested land, made up mostly of spruce, poplar and pine. Canada has over 2,000,000 lakes—563 greater than 100 km2 (39 sq mi)—which is more than any other country, containing much of the world's fresh water.
There are also fresh-water glaciers in the Canadian Rockies and the Coast Mountains.
The Mount Meager massif as seen from the east near Pemberton. Summits left to right are Capricorn Mountain, Mount Meager and Plinth Peak.
Canada is geologically active, having many earthquakes and potentially active volcanoes, notably Mount Meager massif, Mount Garibaldi, Mount Cayley massif, and the Mount Edziza volcanic complex. The volcanic eruption of the Tseax Cone in 1775 was among Canada's worst natural disasters, killing an estimated 2,000 Nisga'a people and destroying their village in the Nass River valley of northern British Columbia. The eruption produced a 22.5-kilometre (14.0 mi) lava flow, and, according to Nisga'a legend, blocked the flow of the Nass River.
Average winter and summer high temperatures across Canada
vary from region to region. Winters can be harsh in many parts of the
country, particularly in the interior and Prairie provinces, which
experience a continental climate, where daily average temperatures are near −15 °C (5 °F), but can drop below −40 °C (−40 °F) with severe wind chills.
In noncoastal regions, snow can cover the ground for almost six months
of the year, while in parts of the north snow can persist year-round.
Coastal British Columbia has a temperate climate, with a mild and rainy
winter. On the east and west coasts, average high temperatures are
generally in the low 20s °C (70s °F), while between the coasts, the
average summer high temperature ranges from 25 to 30 °C (77 to 86 °F),
with temperatures in some interior locations occasionally exceeding
40 °C (104 °F).
Government and politics
Parliament Hill, home of the federal government in Canada's capital city, Ottawa
Canada is described as a "full democracy", with a tradition of liberalism, and an egalitarian, moderate political ideology. An emphasis on social justice has been a distinguishing element of Canada's political culture. Peace, order, and good government, alongside an implied bill of rights are founding principles of the Canadian government.
At the federal level, Canada has been dominated by two relatively centrist parties practicing "brokerage politics", the centre-left Liberal Party of Canada and the centre-right Conservative Party of Canada (or its predecessors).
The historically predominant Liberal Party position themselves at the
centre of the Canadian political spectrum, with the Conservative Party
positioned on the right and the New Democratic Party occupying the left. Far-right and far-left politics have never been a prominent force in Canadian society.
Five parties had representatives elected to the federal parliament in
the 2015 election—the Liberal Party, who currently form the government;
the Conservative Party, who are the official opposition; the New Democratic Party; the Bloc Québécois; and the Green Party of Canada.
Canada has a parliamentary system within the context of a constitutional monarchy—the monarchy of Canada being the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The reigning monarch is Queen Elizabeth II, who is also monarch of 15 other Commonwealth countries and each of Canada's 10 provinces. The person who is the Canadian monarch is the same as the British monarch, although the two institutions are separate. The Queen appoints a representative, the governor general (at present Julie Payette), to carry out most of her federal royal duties in Canada.
The direct participation of the monarch and the governor general in areas of governance is limited. In practice, their use of the executive powers is directed by the Cabinet, a committee of ministers of the Crown responsible to the elected House of Commons of Canada and chosen and headed by the prime minister (at present Justin Trudeau), the head of government. The governor general or monarch may, though, in certain crisis situations exercise their power without ministerial advice.
To ensure the stability of government, the governor general will
usually appoint as prime minister the individual who is the current
leader of the political party that can obtain the confidence of a plurality in the House of Commons. The Prime Minister's Office
(PMO) is thus one of the most powerful institutions in government,
initiating most legislation for parliamentary approval and selecting for
appointment by the Crown, besides the aforementioned, the governor
general, lieutenant governors, senators, federal court judges, and heads of Crown corporations and government agencies. The leader of the party with the second-most seats usually becomes the leader of Her Majesty's Loyal Opposition and is part of an adversarial parliamentary system intended to keep the government in check.
The Senate chamber within the Centre Block on Parliament Hill
Each of the 338 members of parliament in the House of Commons is elected by simple plurality in an electoral district or riding. General elections must be called by the governor general, either on the advice of the prime minister or if the government loses a confidence vote in the House. Constitutionally, an election may be held no more than five years after the preceding election, although the Canada Elections Act
limits this to four years with a fixed election date in October. The
105 members of the Senate, whose seats are apportioned on a regional
basis, serve until age 75.
Canada's federal structure divides government responsibilities between the federal government and the ten provinces. Provincial legislatures are unicameral and operate in parliamentary fashion similar to the House of Commons.
Canada's three territories also have legislatures, but these are not
sovereign and have fewer constitutional responsibilities than the
provinces. The territorial legislatures also differ structurally from their provincial counterparts.
The Bank of Canada is the central bank of the country. In addition, the minister of finance and minister of industry utilize the Statistics Canada agency for financial planning and economic policy development. The Bank of Canada is the sole authority authorized to issue currency in the form of Canadian bank notes. The bank does not issue Canadian coins; they are issued by the Royal Canadian Mint.
Law
The Constitution of Canada is the supreme law of the country, and consists of written text and unwritten conventions. The Constitution Act, 1867 (known as the British North America Act
prior to 1982), affirmed governance based on parliamentary precedent
and divided powers between the federal and provincial governments. The Statute of Westminster 1931 granted full autonomy and the Constitution Act, 1982, ended all legislative ties to Britain, as well as adding a constitutional amending formula and the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. The Charter guarantees basic rights and freedoms that usually cannot be over-ridden by any government—though a notwithstanding clause
allows the federal parliament and provincial legislatures to override
certain sections of the Charter for a period of five years.
The Indian Chiefs Medal, presented to commemorate the Numbered Treaties of 1871–1921
The Indian Act, various treaties and case laws were established to mediate relations between Europeans and native peoples. Most notably, a series of eleven treaties known as the Numbered Treaties were signed between the Indigenous peoples and the reigning monarch of Canada between 1871 and 1921. These treaties are agreements with the Canadian Crown-in-Council, administered by Canadian Aboriginal law, and overseen by the minister of Crown–Indigenous Relations. The role of the treaties and the rights they support were reaffirmed by Section Thirty-five of the Constitution Act, 1982. These rights may include provision of services, such as health care, and exemption from taxation.
The legal and policy framework within which Canada and First Nations
operate was further formalized in 2005, through the First
Nations–Federal Crown Political Accord.
The Supreme Court of Canada in Ottawa, west of Parliament Hill
Canada's judiciary
plays an important role in interpreting laws and has the power to
strike down Acts of Parliament that violate the constitution. The
Supreme Court of Canada is the highest court and final arbiter and has
been led since December 18, 2017 by Chief Justice Richard Wagner.
Its nine members are appointed by the Governor-General on the advice of
the prime minister and minister of justice. All judges at the superior
and appellate levels are appointed after consultation with
non-governmental legal bodies. The federal Cabinet also appoints
justices to superior courts in the provincial and territorial
jurisdictions.
Common law prevails everywhere except in Quebec, where civil law predominates. Criminal law is solely a federal responsibility and is uniform throughout Canada.
Law enforcement, including criminal courts, is officially a provincial
responsibility, conducted by provincial and municipal police forces. However, in most rural areas and some urban areas, policing responsibilities are contracted to the federal Royal Canadian Mounted Police.
Foreign relations and military
The Canadian Delegation to the United Nations Conference on International Organization, San Francisco, May 1945
Canada is recognized as a middle power for its role in international affairs with a tendency to pursue multilateral solutions.
Canada's foreign policy based on international peacekeeping and
security is carried out through coalitions and international
organizations, and through the work of numerous federal institutions. Canada's peacekeeping role during the 20th century has played a major role in its global image. The strategy of the Canadian government's foreign aid policy reflects an emphasis to meet the Millennium Development Goals, while also providing assistance in response to foreign humanitarian crises.
Canada was a founding member of the United Nations and has membership in the World Trade Organization, the G20 and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Canada is also a member of various other international and regional organizations and forums for economic and cultural affairs. Canada acceded to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights in 1976. Canada joined the Organization of American States (OAS) in 1990 and hosted the OAS General Assembly in 2000 and the 3rd Summit of the Americas in 2001. Canada seeks to expand its ties to Pacific Rim economies through membership in the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum (APEC).
Canada and the United States share the world's longest undefended border, co-operate on military campaigns and exercises, and are each other's largest trading partner. Canada nevertheless has an independent foreign policy, most notably maintaining full relations with Cuba, and declining to officially participate in the 2003 invasion of Iraq. Canada also maintains historic ties to the United Kingdom and France and to other former British and French colonies through Canada's membership in the Commonwealth of Nations and the Francophonie. Canada is noted for having a positive relationship with the Netherlands, owing, in part, to its contribution to the Dutch liberation during World War II.
Canada's strong attachment to the British Empire and Commonwealth led to major participation in British military efforts in the Second Boer War, World War I and World War II.
Since then, Canada has been an advocate for multilateralism, making
efforts to resolve global issues in collaboration with other nations. During the Cold War, Canada was a major contributor to UN forces in the Korean War and founded the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) in co-operation with the United States to defend against potential aerial attacks from the Soviet Union.
During the Suez Crisis of 1956, future Prime Minister Lester B. Pearson eased tensions by proposing the inception of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force, for which he was awarded the 1957 Nobel Peace Prize. As this was the first UN peacekeeping mission, Pearson is often credited as the inventor of the concept. Canada has since served in over 50 peacekeeping missions, including every UN peacekeeping effort until 1989, and has since maintained forces in international missions in Rwanda, the former Yugoslavia, and elsewhere; Canada has sometimes faced controversy over its involvement in foreign countries, notably in the 1993 Somalia Affair.
Soldiers from the Canadian Grenadier Guards in Kandahar Province in Afghanistan, pictured, fought with Dutch soldiers against Afghan insurgents.
In 2001, Canada deployed troops to Afghanistan as part of the U.S. stabilization force and the UN-authorized, NATO-led International Security Assistance Force.
In February 2007, Canada, Italy, the United Kingdom, Norway, and Russia
announced their joint commitment to a $1.5-billion project to help
develop vaccines for developing nations, and called on other countries
to join them. In August 2007, Canada's territorial claims in the Arctic were challenged after a Russian underwater expedition to the North Pole; Canada has considered that area to be sovereign territory since 1925.
The nation employs a professional, volunteer military force of
approximately 79,000 active personnel and 32,250 reserve personnel. The unified Canadian Forces (CF) comprise the Canadian Army, Royal Canadian Navy, and Royal Canadian Air Force. In 2013, Canada's military expenditure totalled approximately C$19 billion, or around one percent of the country's GDP.
Following the 2016 Defence Policy Review, the Canadian government
announced a 70 percent increase to the country's defence budget over the
next decade. The Canadian Forces will acquire 88 fighter planes and 15
naval surface combatants, the latter as part of the National Shipbuilding Procurement Strategy. Canada's total military expenditure is expected to reach C$32.7 billion by 2027.
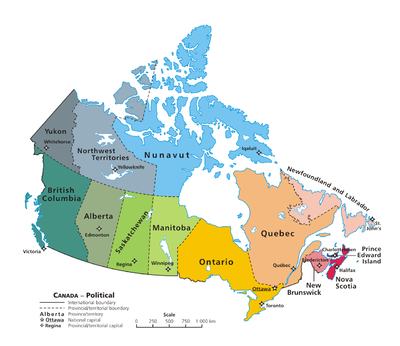
Provinces and territories
A political map of Canada showing its 10 provinces and 3 territories
Canada is a federation composed of ten provinces and three territories. In turn, these may be grouped into four main regions: Western Canada, Central Canada, Atlantic Canada, and Northern Canada (Eastern Canada refers to Central Canada and Atlantic Canada together). Provinces have more autonomy than territories, having responsibility for social programs such as health care, education, and welfare.
Together, the provinces collect more revenue than the federal
government, an almost unique structure among federations in the world.
Using its spending powers, the federal government can initiate national
policies in provincial areas, such as the Canada Health Act; the provinces can opt out of these, but rarely do so in practice. Equalization payments
are made by the federal government to ensure reasonably uniform
standards of services and taxation are kept between the richer and
poorer provinces. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the Constitution Act, 1867, whereas territorial governments have powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing from the Constitution Act are divided between the Government of Canada (the federal government) and the provincial governments to exercise exclusively. A change to the division of powers between the federal government and the provinces requires a constitutional amendment, whereas a similar change affecting the territories can be performed unilaterally by the Parliament of Canada or government.
Economy
Canada is the world's tenth-largest economy as of 2018, with a nominal GDP of approximately US$1.73 trillion. It is one of the least corrupt countries in the world, and is one of the world's top ten trading nations, with a highly globalized economy. Canada has a mixed economy ranking above the U.S. and most western European nations on The Heritage Foundation's index of economic freedom, and experiencing a relatively low level of income disparity. The country's average household disposable income per capita is "well above" the OECD average. The Toronto Stock Exchange is the ninth-largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization, listing over 1,500 companies with a combined market capitalization of over US$2 trillion.
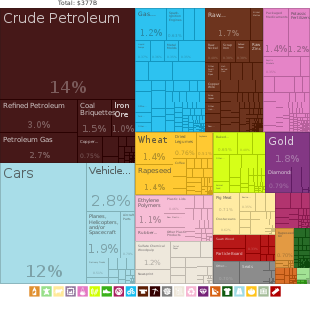
Tree-map of Canada's goods exports in 2017
In 2018, Canadian trade in goods and services reached CA$1.5 trillion. Canada's exports totalled over CA$585 billion, while its imported goods were worth over CA$607 billion, of which approximately CA$391 billion originated from the United States, CA$216 billion from non-U.S. sources. The country's 2019 trade surplus totalled CA$762 billion, compared with a CA$46.9 billion surplus in 2008.
Since the early 20th century, the growth of Canada's
manufacturing, mining, and service sectors has transformed the nation
from a largely rural economy to an urbanized, industrial one. Like many other developed countries, the Canadian economy is dominated by the service industry, which employs about three-quarters of the country's workforce. However, Canada is unusual among developed countries in the importance of its primary sector, in which the forestry and petroleum industries are two of the most prominent components.
Canada is one of the few developed nations that are net exporters of energy. Atlantic Canada possesses vast offshore deposits of natural gas, and Alberta also hosts large oil and gas resources. The vastness of the Athabasca oil sands and other assets results in Canada having a 13 percent share of global oil reserves, comprising the world's third-largest share after Venezuela and Saudi Arabia.
Canada is additionally one of the world's largest suppliers of
agricultural products; the Canadian Prairies are one of the most
important global producers of wheat, canola, and other grains. Canada's Department of Natural Resources provides statistics regarding its major exports; the country is a leading exporter of zinc, uranium, gold, nickel, platinoids, aluminum, steel, iron ore,coking coal, lead, copper, molybdenum, cobalt, and cadmium.
Many towns in northern Canada, where agriculture is difficult, are
sustainable because of nearby mines or sources of timber. Canada also
has a sizeable manufacturing sector centred in southern Ontario and
Quebec, with automobiles and aeronautics representing particularly important industries.
Canada's economic integration with the United States has increased significantly since World War II. The Automotive Products Trade Agreement of 1965 opened Canada's borders to trade in the automobile manufacturing industry. In the 1970s, concerns over energy self-sufficiency and foreign ownership in the manufacturing sectors prompted Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau's Liberal government to enact the National Energy Program (NEP) and the Foreign Investment Review Agency (FIRA). In the 1980s, Prime Minister Brian Mulroney's Progressive Conservatives abolished the NEP and changed the name of FIRA to Investment Canada, to encourage foreign investment. The Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement (FTA) of 1988 eliminated tariffs between the two countries, while the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) expanded the free-trade zone to include Mexico in 1994. Canada has a strong cooperative banking sector, with the world's highest per capita membership in credit unions.
Science and technology
The Canadarm robotic manipulator in action on Space Shuttle Discovery during the STS-116 mission in 2006
In 2018, Canada spent approximately C$34.5 billion on domestic research and development, of which around $7 billion was provided by the federal and provincial governments. As of 2018, the country has produced fourteen Nobel laureates in physics, chemistry, and medicine, and was ranked fourth worldwide for scientific research quality in a major 2012 survey of international scientists. It is furthermore home to the headquarters of a number of global technology firms. Canada has one of the highest levels of Internet access in the world, with over 33 million users, equivalent to around 94 percent of its total 2014 population.
The Canadian Space Agency
operates a highly active space program, conducting deep-space,
planetary, and aviation research, and developing rockets and satellites. Canada was the third country to design and construct a satellite after the Soviet Union and the United States, with the 1962 Alouette 1 launch. Canada is a participant in the International Space Station (ISS), and is a pioneer in space robotics, having constructed the Canadarm, Canadarm2 and Dextre robotic manipulators for the ISS and NASA's Space Shuttle. Since the 1960s, Canada's aerospace industry has designed and built numerous marques of satellite, including Radarsat-1 and 2, ISIS and MOST. Canada has also produced one of the world's most successful and widely used sounding rockets, the Black Brant; over 1,000 Black Brants have been launched since the rocket's introduction in 1961.
Demographics
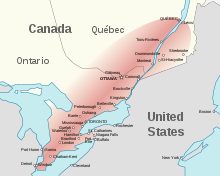
The Quebec City–Windsor Corridor is the most densely populated and heavily industrialized region of Canada, spanning 1,200 km (750 mi).
The 2016 Canadian Census enumerated a total population of 35,151,728, an increase of around 5.0 percent over the 2011 figure.
Between 2011 and May 2016, Canada's population grew by 1.7 million
people, with immigrants accounting for two-thirds of the increase. Between 1990 and 2008, the population increased by 5.6 million, equivalent to 20.4 percent overall growth. The main drivers of population growth are immigration and, to a lesser extent, natural growth.
Canada has one of the highest per-capita immigration rates in the world, driven mainly by economic policy and, to a lesser extent, family reunification. The Canadian public, as well as the major political parties, support the current level of immigration. In 2014, a total of 260,400 immigrants were admitted to Canada, mainly from Asia. The Canadian government anticipated between 280,000 and 305,000 new permanent residents in the following years, a similar number of immigrants as in recent years. New immigrants settle mostly in major urban areas such as Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver. Canada also accepts large numbers of refugees, accounting for over 10 percent of annual global refugee resettlements.
Canada's population density, at 3.7 inhabitants per square kilometre (9.6/sq mi), is among the lowest in the world.
Canada spans latitudinally from the 83rd parallel north to the 41st
parallel north, and approximately 95 percent of the population is found
south of the 55th parallel north. About four-fifths of the population lives within 150 kilometres (93 mi) of the border with the contiguous United States. The most densely populated part of the country, accounting for nearly 50 percent, is the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor in Southern Quebec and Southern Ontario along the Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence River. An additional 30 percent live along the British Columbia Lower Mainland, and the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor in Alberta.
The majority of Canadians (69.9 percent) live in family
households, 26.8 percent report living alone, and those living with
unrelated persons reported at 3.7 percent. The average size of a household in 2006 was 2.5 people.
Largest census metropolitan areas in Canada by population (2016 census)
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMA | Province | Population |
|
CMA | Province | Population |
| Toronto | Ontario | 5,928,040 | London | Ontario | 494,069 | |
| Montreal | Quebec | 4,098,927 | St. Catharines–Niagara | Ontario | 406,074 | |
| Vancouver | British Columbia | 2,463,431 | Halifax | Nova Scotia | 403,390 | |
| Calgary | Alberta | 1,392,609 | Oshawa | Ontario | 379,848 | |
| Ottawa–Gatineau | Ontario–Quebec | 1,323,783 | Victoria | British Columbia | 367,770 | |
| Edmonton | Alberta | 1,321,426 | Windsor | Ontario | 329,144 | |
| Quebec | Quebec | 800,296 | Saskatoon | Saskatchewan | 295,095 | |
| Winnipeg | Manitoba | 778,489 | Regina | Saskatchewan | 236,481 | |
| Hamilton | Ontario | 747,545 | Sherbrooke | Quebec | 212,105 | |
| Kitchener– Cambridge–Waterloo |
Ontario | 523,894 | St. John's | Newfoundland and Labrador | 205,955 | |
Health
Healthcare in Canada is delivered through the provincial and territorial systems of publicly funded health care, informally called Medicare. It is guided by the provisions of the Canada Health Act of 1984, and is universal.
Universal access to publicly funded health services "is often
considered by Canadians as a fundamental value that ensures national
health care insurance for everyone wherever they live in the country." However, 30 percent of Canadians' healthcare is paid for through the private sector. This mostly goes towards services not covered or partially covered by Medicare, such as prescription drugs, dentistry and optometry.
Approximately 65 to 75 percent of Canadians have some form of
supplementary health insurance related to the aforementioned reasons;
many receive it through their employers or utilizes secondary social
service programs related to extended coverage for families receiving
social assistance or vulnerable demographics, such as seniors, minors,
and those with disabilities.
Health
care cost rise based on total expenditure on health as percent of GDP.
Countries shown are the United States, Germany, Austria, Switzerland,
United Kingdom, and Canada.
In common with many other developed countries, Canada is experiencing a cost increase due to a demographic shift towards an older population, with more retirees and fewer people of working age. In 2006, the average age was 39.5 years; within twelve years it had risen to 42.4 years, with a life expectancy of 81.1 years. A comprehensive 2016 report by the Chief Public Health Officer of Canada
found that 88 percent of Canadians; one of the highest proportions of
the population among G7 countries, indicated that they "had good or very
good health".
80 percent of Canadian adults self-report having at least one major
risk factor for chronic disease; smoking, physical inactivity, unhealthy
eating or excessive alcohol use.
Canada has one of the highest rates of adult obesity among Organisation
for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries attributing
to approximately 2.7 million cases of diabetes (types 1 and 2 combined). Four chronic diseases; cancer (leading cause of death), cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases and diabetes account for 65 percent of deaths in Canada.
In 2017, the Canadian Institute for Health Information reported that healthcare spending reached $242 billion, or 11.5 percent of Canada's gross domestic product (GDP) for that year. A 2018 cost-effectiveness analysis by the Fraser Institute
showed that "although Canada ranks among the most expensive
universal-access health-care systems in the OECD, its performance for
availability and access to resources is generally below that of the
average OECD country, while its performance for use of resources and
quality and clinical performance is mixed."
Education
According to a 2019 report by the OECD, Canada is one of the most educated countries in the world; the country ranks first worldwide in the number of adults having tertiary education, with over 56 percent of Canadian adults having attained at least an undergraduate college or university degree. Canada spends about 5.3 percent of its GDP on education. The country invests heavily in tertiary education (more than US$20,000 per student). As of 2014,
89 percent of adults aged 25 to 64 have earned the equivalent of a
high-school degree, compared to an OECD average of 75 percent.
Since the adoption of section 23 of the Constitution Act, 1982, education in both English and French has been available in most places across Canada. Canadian provinces and territories are responsible for education provision. The mandatory school age ranges between 5–7 to 16–18 years, contributing to an adult literacy rate of 99 percent.
In 2002, 43 percent of Canadians aged 25 to 64 possessed a
post-secondary education; for those aged 25 to 34, the rate of
post-secondary education reached 51 percent. The Programme for International Student Assessment indicates Canadian students perform well above the OECD average, particularly in mathematics, science, and reading.
Ethnicity
According to the 2016 Canadian Census, the country's largest self-reported ethnic origin is Canadian (accounting for 32 percent of the population), followed by English (18.3%), Scottish (13.9%), French (13.6%), Irish (13.4%), German (9.6%), Chinese (5.1%), Italian (4.6%), First Nations (4.4%), Indian (4.0%), and Ukrainian (3.9%). There are 600 recognized First Nations governments or bands, encompassing a total of 1,525,565 people.
Canada's Indigenous population is growing at almost twice the national
rate, and four percent of Canada's population claimed an Indigenous
identity in 2006. Another 22.3 percent of the population belonged to a
non-Indigenous visible minority. In 2016, the largest visible minority groups were South Asian (5.6%), Chinese (5.1%) and Black (3.5%). Between 2011 and 2016, the visible minority population rose by 18.4 percent. In 1961, less than two percent of Canada's population (about 300,000 people) were members of visible minority groups. Indigenous peoples are not considered a visible minority under the Employment Equity Act, and this is the definition that Statistics Canada also uses.
Religion
Canada is religiously diverse, encompassing a wide range of beliefs
and customs. Canada has no official church, and the government is
officially committed to religious pluralism. Freedom of religion in Canada is a constitutionally protected right, allowing individuals to assemble and worship without limitation or interference. The practice of religion is now generally considered a private matter throughout society and the state. With Christianity in decline after having once been central and integral to Canadian culture and daily life, Canada has become a post-Christian, secular state. The majority of Canadians consider religion to be unimportant in their daily lives, but still believe in God. According to the 2011 census, 67.3 percent of Canadians identify as Christian; of these, Roman Catholics make up the largest group, accounting for 38.7 percent of the population. Much of the remainder is made up of Protestants, who accounted for approximately 27 percent in a 2011 survey. The largest Protestant denomination is the United Church of Canada (accounting for 6.1% of Canadians), followed by Anglicans (5.0%), and Baptists (1.9%). Secularization has been growing since the 1960s. In 2011, 23.9 percent declared no religious affiliation, compared to 16.5 percent in 2001. The remaining 8.8 percent are affiliated with non-Christian religions, the largest of which are Islam (3.2%), Hinduism (1.5%) and Sikhism (1.4%).
Languages
Approximately 98 percent of Canadians can speak either or both English and French:
English – 56.9%
English and French – 16.1%
French – 21.3%
Sparsely populated area ( < 0.4 persons per km2)
A multitude of languages are used by Canadians, with English and French (the official languages) being the mother tongues of approximately 56 percent and 21 percent of Canadians, respectively.
As of the 2016 Census, just over 7.3 million Canadians listed a
non-official language as their mother tongue. Some of the most common
non-official first languages include Chinese (1,227,680 first-language speakers), Punjabi (501,680), Spanish (458,850), Tagalog (431,385), Arabic (419,895), German (384,040), and Italian (375,645). Canada's federal government practices official bilingualism, which is applied by the Commissioner of Official Languages in consonance with Section 16 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms and the Federal Official Languages Act
English and French have equal status in federal courts, parliament, and
in all federal institutions. Citizens have the right, where there is
sufficient demand, to receive federal government services in either
English or French and official-language minorities are guaranteed their own schools in all provinces and territories.
The 1977 Charter of the French Language established French as the official language of Quebec. Although more than 85 percent of French-speaking Canadians live in Quebec, there are substantial Francophone populations in New Brunswick, Alberta, and Manitoba; Ontario has the largest French-speaking population outside Quebec.
New Brunswick, the only officially bilingual province, has a
French-speaking Acadian minority constituting 33 percent of the
population.
There are also clusters of Acadians in southwestern Nova Scotia, on
Cape Breton Island, and through central and western Prince Edward
Island.
Other provinces have no official languages as such, but French is
used as a language of instruction, in courts, and for other government
services, in addition to English. Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec allow
for both English and French to be spoken in the provincial legislatures,
and laws are enacted in both languages. In Ontario, French has some
legal status, but is not fully co-official. There are 11 Indigenous language groups, composed of more than 65 distinct languages and dialects. Several Indigenous languages have official status in the Northwest Territories. Inuktitut is the majority language in Nunavut, and is one of three official languages in the territory.
Additionally, Canada is home to many sign languages, some of which are Indigenous. American Sign Language (ASL) is spoken across the country due to the prevalence of ASL in primary and secondary schools. Due to its historical relation to the francophone culture, Quebec Sign Language
(LSQ) is spoken primarily in Quebec, although there are sizeable
Francophone communities in New Brunswick, Ontario and Manitoba.
Culture
A political cartoon from 1910 on Canada's early European multicultural identity, depicting the French tricolour, the Union Jack, the maple leaf, and fleurs-de-lis
Canada's culture draws influences from its broad range of constituent nationalities, and policies that promote a "just society" are constitutionally protected. Canada has placed emphasis on equality and inclusiveness for all its people. Multiculturalism is often cited as one of Canada's significant accomplishments, and a key distinguishing element of Canadian identity. In Quebec, cultural identity is strong, and many commentators speak of a French Canadian culture that is distinct from English Canadian culture. However, as a whole, Canada is, in theory, a cultural mosaic—a collection of regional ethnic subcultures.
Canada's approach to governance emphasizing multiculturalism, which is based on selective immigration, social integration, and suppression of far-right politics, has wide public support. Government policies such as publicly-funded health care, higher taxation to redistribute wealth, the outlawing of capital punishment, strong efforts to eliminate poverty, strict gun control; alongside legislation with a social liberal attitude toward women's rights (like pregnancy termination), LGBTQ rights, assisted euthanasia and cannabis use are indicators of Canada's political and cultural values. Canadians also identify with the country's foreign aid policies, peacekeeping roles, the National park system and the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms.
Historically, Canada has been influenced by British, French, and Indigenous cultures and traditions. Through their language, art and music, Indigenous peoples continue to influence the Canadian identity.
During the 20th century, Canadians with African, Caribbean and Asian
nationalities have added to the Canadian identity and its culture. Canadian humour is an integral part of the Canadian identity and is reflected in its folklore, literature, music, art, and media. The primary characteristics of Canadian humour are irony, parody, and satire. Many Canadian comedians have achieved international success in the American TV and film industries and are amongst the most recognized in the world.
Canada has a well-developed media sector, but its cultural output; particularly in English films, television shows, and magazines, is often overshadowed by imports from the United States.
As a result, the preservation of a distinctly Canadian culture is
supported by federal government programs, laws, and institutions such as
the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC), the National Film Board of Canada (NFB), and the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC).
Symbols
The mother beaver on the Canadian parliament's Peace Tower. The five flowers on the shield each represent an ethnicity—Tudor rose: English; Fleur de lis: French; thistle: Scottish; shamrock: Irish; and leek: Welsh.
Canada's national symbols are influenced by natural, historical, and Indigenous sources. The use of the maple leaf as a Canadian symbol dates to the early 18th century. The maple leaf is depicted on Canada's current and previous flags, and on the Arms of Canada. The Arms of Canada are closely modelled after the royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom with French and distinctive Canadian elements replacing or added to those derived from the British version. Other prominent symbols include the sports of ice hockey and lacrosse, the beaver, Canadian Goose, common loon, Canadian horse, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, the Canadian Rockies, and more recently the totem pole and Inuksuk. Material items such as Canadian beer, maple syrup, tuques, canoes, nanaimo bars, butter tarts and the Quebec dish of poutine are defined as uniquely Canadian. Canadian coins feature many of these symbols: the loon on the $1 coin, the Arms of Canada on the 50¢ piece, the beaver on the nickel. The penny, removed from circulation in 2013, featured the maple leaf. The Queen' s image appears on $20 bank notes, and on the obverse of all current Canadian coins.
Literature
Canadian literature is often divided into French- and
English-language literatures, which are rooted in the literary
traditions of France and Britain, respectively.
There are four major themes that can be found within historical
Canadian literature; nature, frontier life, Canada's position within the
world, all three of which tie into the garrison mentality. By the 1990s, Canadian literature was viewed as some of the world's best.
Canada's ethnic and cultural diversity are reflected in its literature,
with many of its most prominent modern writers focusing on ethnic life. Arguably, the best-known living Canadian writer internationally (especially since the deaths of Robertson Davies and Mordecai Richler) is Margaret Atwood, a prolific novelist, poet, and literary critic. Numerous other Canadian authors have accumulated international literary awards; including Nobel Laureate Alice Munro, who has been called the best living writer of short stories in English; and Booker Prize recipient Michael Ondaatje, who is perhaps best known for the novel The English Patient, which was adapted as a film of the same name that won the Academy Award for Best Picture.
Visual arts
The Jack Pine by Tom Thomson. Oil on canvas, 1916, in the collection of the National Gallery of Canada.
Canadian visual art has been dominated by figures such as Tom Thomson – the country's most famous painter – and by the Group of Seven. Thomson's career painting Canadian landscapes spanned a decade up to his death in 1917 at age 39.
The Group of Seven were painters with a nationalistic and idealistic
focus, who first exhibited their distinctive works in May 1920. Though
referred to as having seven members, five artists—Lawren Harris, A. Y. Jackson, Arthur Lismer, J. E. H. MacDonald, and Frederick Varley—were responsible for articulating the Group's ideas. They were joined briefly by Frank Johnston, and by commercial artist Franklin Carmichael. A. J. Casson became part of the Group in 1926. Associated with the Group was another prominent Canadian artist, Emily Carr, known for her landscapes and portrayals of the Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast. Since the 1950s, works of Inuit art have been given as gifts to foreign dignitaries by the Canadian government.
Music
The Canadian music industry is the sixth-largest in the world producing internationally renowned composers, musicians and ensembles. Music broadcasting in the country is regulated by the CRTC. The Canadian Academy of Recording Arts and Sciences presents Canada's music industry awards, the Juno Awards, which were first awarded in 1970. The Canadian Music Hall of Fame established in 1976 honours Canadian musicians for their lifetime achievements. Patriotic music in Canada
dates back over 200 years as a distinct category from British
patriotism, preceding the Canadian Confederation by over 50 years. The
earliest, The Bold Canadian, was written in 1812. The national anthem of Canada, "O Canada", was originally commissioned by the Lieutenant Governor of Quebec, the Honourable Théodore Robitaille, for the 1880 St. Jean-Baptiste Day ceremony, and was officially adopted in 1980. Calixa Lavallée wrote the music, which was a setting of a patriotic poem composed by the poet and judge Sir Adolphe-Basile Routhier. The text was originally only in French before it was adapted into English in 1906.
Sports
Canada's ice hockey victory at the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver
The roots of organized sports in Canada date back to the 1770s. Canada's official national sports are ice hockey and lacrosse. Golf, soccer, baseball, tennis, skiing, badminton, volleyball, cycling, swimming, bowling, rugby union, canoeing, equestrian, squash and the study of martial arts are widely enjoyed at the youth and amateur levels.
Canada shares several major professional sports leagues with the United States. Canadian teams in these leagues include seven franchises in the National Hockey League, as well as three Major League Soccer teams and one team in each of Major League Baseball and the National Basketball Association. Other popular professional sports in Canada include Canadian football, which is played in the Canadian Football League, National Lacrosse League lacrosse, and curling.
Canada has participated in almost every Olympic Games since its Olympic debut in 1900, and has hosted several high-profile international sporting events, including the 1976 Summer Olympics, the 1988 Winter Olympics, the 1994 Basketball World Championship, the 2007 FIFA U-20 World Cup, the 2010 Winter Olympics and the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup. Most recently, Canada staged the 2015 Pan American Games and 2015 Parapan American Games, the former being the largest sporting event hosted by the country.