The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (Latin: Trinitas, lit. 'triad', from Latin: trinus "threefold") holds that God is one God, but three coeternal and consubstantial persons: the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ), and the Holy Spirit. The three persons are distinct, yet are one "substance, essence or nature" (homoousios). In this context, a "nature" is what one is, whereas a "person" is who one is.
The subset of Christianity that accepts this doctrine is collectively known as Trinitarianism, while the subset that does not is referred to as Nontrinitarianism (see also Arianism). Trinitarianism contrasts with positions such as Binitarianism (one deity in two persons) and Monarchianism (no plurality of persons within God), of which Modalistic Monarchianism (one deity revealed in three modes) and Unitarianism (one deity in one person) are subsets.
While the developed doctrine of the Trinity is not explicit in the books that constitute the New Testament, the New Testament possesses a "triadic" understanding of God and contains a number of Trinitarian formulas. The doctrine of the Trinity was first formulated among the early Christians and fathers of the Church as early Christians attempted to understand the relationship between Jesus and God in their scriptural documents and prior traditions.
God in the New Testament
While the developed doctrine of the Trinity is not explicit in the books that constitute the New Testament, the New Testament contains a number of Trinitarian formulas, including Matthew 28:19, 2 Corinthians 13:13, 1 Corinthians 12:4-5, Ephesians 4:4-6, 1 Peter 1:2 and Revelation 1:4-5. Reflection by early Christians on passages such as the Great Commission: "Go therefore and make disciples of all nations, baptizing them in the name of the Father and of the Son and of the Holy Spirit" and Paul the Apostle's blessing: "The grace of the Lord Jesus Christ and the love of God and the fellowship of the Holy Spirit be with you all", while at the same time the Jewish Shema Yisrael: "Hear, O Israel: the LORD our God, the LORD is one"[Deuteronomy 6:4] has led theologians across history in attempting to articulate the relationship between the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. Eventually, the diverse references to God, Jesus, and the Spirit found in the New Testament were brought together to form the doctrine of the Trinity—one Godhead subsisting in three persons and one substance. The doctrine of the Trinity was used to oppose alternative views of how the three are related and to defend the church against charges of worshiping two or three gods.
The Comma Johanneum in 1 John 5:7, is a disputed text which states: "There are three that testify in heaven, the Father, the Word, and the Holy Spirit, and these three are one." However, this passage is not considered to be part of the genuine text, and most scholars agree that the phrase was a gloss.
Jesus in the New Testament
In the Pauline epistles, the public, collective devotional patterns towards Jesus in the early Christian community are reflective of Paul's perspective on the divine status of Jesus in what scholars have termed a "binitarian" pattern or shape of devotional practice (worship) in the NT, in which "God" and Jesus are thematized and invoked. Jesus receives prayer (1 Cor. 1:2; 2 Cor. 12:8-9), the presence of Jesus is confessionally invoked by believers (1 Cor. 16:22; Romans 10:9-13; Phil. 2:10-11), people are baptized in Jesus’ name (1 Cor. 6:11; Rom. 6:3), Jesus is the reference in Christian fellowship for a religious ritual meal (the Lord’s Supper; 1 Cor. 11:17-34).
The Gospels depict Jesus as human through most of their narrative, but "[o]ne eventually discovers that he is a divine being manifest in flesh, and the point of the texts is in part to make his higher nature known in a kind of intellectual epiphany." In the Gospels, Jesus receives προσκύνησις (proskynesis) in the aftermath of the resurrection, a Greek term that either expresses the contemporary social gesture of bowing to a superior, either on one's knees or in full prostration (in Matthew 18:26 a slave performs προσκύνησις to his master so that he would not be sold after being unable to pay his debts). The term can also refer to the religious act of devotion towards a deity. While Jesus receives προσκύνησις a number of times in the Synoptic Gospels, only a few can be said to refer to divine worship. This includes Matthew 28:16-20, an account of the resurrected Jesus receiving worship from his disciples after proclaiming he has been given authority over the cosmos and his ever-continuing presence with the disciples (forming an inclusio with the beginning of the Gospel, where Jesus is given the name Emmanuel/"God with us", a name that alludes to the God of Israel's continuing presence with his followers throughout the Old Testament (Gen. 28:15; Deut 20:1) and used in reference to Jesus in the resurrection account). Whereas some have argued that Matthew 28:19 was an interpolation on account of its absence from the first few centuries of early Christian quotations, scholars largely accept the passage as authentic due to its supporting manuscript evidence and that it does appear to be either quoted in the Didache (7:1-3) or at least reflected in the Didache as part of a common tradition from which both Matthew and the Didache emerged. Jesus receiving divine worship in the post-resurrection accounts is further mirrored in Luke 24:52. Acts depicts the early Christian movement as a public cult centered around Jesus in several passages. In Acts, it is common for individual Christians to "call" upon the name of Jesus (9:14, 21; 22:16), an idea precedented in the Old Testament descriptions of calling on the name of YHWH as a form of prayer. The story of Stephen depicts Stephen invoking and crying out to Jesus in the final moments of his life to receive his spirit (7:59-60). Acts further describes a common ritual practice inducting new members into the early Jesus sect by baptizing them in Jesus' name (2:38; 8:16; 10:48; 19:5). According to Dale Allison, Acts depicts the appearances of Jesus to Paul as a divine theophany, styled on and identified with the God responsible for the theophany of Ezekiel in the Old Testament.
The Gospel of John has been seen as especially aimed at emphasizing Jesus' divinity, presenting Jesus as the Logos, pre-existent and divine, from its first words: "In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God" (John 1:1). The Gospel of John ends with Thomas's declaration that he believed Jesus was God, "My Lord and my God!" (John 20:28). There is no significant tendency among modern scholars to deny that John 1:1 and John 20:28 identify Jesus with God. John also portrays Jesus as the agent of creation of the universe.
Jesus in later Christian theology
Some have suggested that John presents a hierarchy when he quotes Jesus as saying, "The Father is greater than I", a statement which was appealed to by nontrinitarian groups such as Arianism. However, Church Fathers such as Augustine of Hippo and Thomas Aquinas argued this statement was to be understood as Jesus speaking about his human nature.
Holy Spirit in the New Testament
Prior Jewish theology held that the Spirit is merely the divine presence of God himself, whereas orthodox Christian theology holds that the Holy Spirit is a distinct person of God himself. This development begins early in the New Testament, as the Spirit of God receives much more emphasis and description comparably than it had in earlier Jewish writing. Whereas there are 75 references to the Spirit within the Old Testament and 35 identified in the non-biblical Dead Sea Scrolls, the New Testament, despite its significantly shorter length, mentions the Spirit 275 times. In addition to its larger emphasis and importance placed on the Spirit in the New Testament, the Spirit is also described in much more personalized and individualized terms than earlier. Larry Hurtado writes;
Moreover, the New Testament references often portray actions that seem to give the Spirit an intensely personal quality, probably more so than in Old Testament or ancient Jewish texts. So, for example, the Spirit “drove” Jesus into the wilderness (Mk 1:12; compare “led” in Mt. 4:1/Lk 4:1), and Paul refers to the Spirit interceding for believers (Rom 8:26–27) and witnessing to believers about their filial status with God (Rom 8:14–16). To cite other examples of this, in Acts the Spirit alerts Peter to the arrival of visitors from Cornelius (10:19), directs the church in Antioch to send forth Barnabas and Saul (13:2–4), guides the Jerusalem council to a decision about Gentile converts (15:28), at one point forbids Paul to missionize in Asia (16:6), and at another point warns Paul (via prophetic oracles) of trouble ahead in Jerusalem (21:11).
— Hurtado 2018, p. 62
In the New Testament, the Spirit is not portrayed as the recipient of cultic devotion, which instead, is typically offered to God and to the risen/glorified Jesus. Although what became mainstream Christianity subsequently affirmed the propriety of including the Spirit as the recipient of worship as reflected in the developed form of the Nicene Creed, perhaps the closest to this in the New Testament is in Matthew 28:19 and 2 Corinthians 13:14 which describe the Spirit as the subject of religious ritual.
Holy Spirit in later Christian theology
As the Arian controversy was dissipating, the debate moved from the deity of Jesus Christ to the equality of the Holy Spirit with the Father and Son. On one hand, the Pneumatomachi sect declared that the Holy Spirit was an inferior person to the Father and Son. On the other hand, the Cappadocian Fathers argued that the Holy Spirit was equal to the Father and Son in nature or substance.
Although the main text used in defense of the deity of the Holy Spirit was Matthew 28:19, Cappadocian Fathers such as Basil the Great argued from other verses such as "But Peter said, 'Ananias, why has Satan filled your heart to lie to the Holy Spirit and to keep back for yourself part of the proceeds of the land? While it remained unsold, did it not remain your own? And after it was sold, was it not at your disposal? Why is it that you have contrived this deed in your heart? You have not lied to men but to God.'" (Acts 5:3-4).
Another passage the Cappadocian Fathers quoted from was "By the word of the Lord the heavens were made, and by the breath of his mouth all their host" (Psalm 33:6). According to their understanding, because "breath" and "spirit" in Hebrew are both "רוּחַ" ("ruach"), Psalm 33:6 is revealing the roles of the Son and Holy Spirit as co-creators. And since, according to them, because only the holy God can create holy beings such as the angels, the Son and Holy Spirit must be God.
Yet another argument from the Cappadocian Fathers to prove that the Holy Spirit is of the same nature as the Father and Son comes from "For who knows a person's thoughts except the spirit of that person, which is in him? So also no one comprehends the thoughts of God except the Spirit of God" (1 Cor. 2:11). They reasoned that this passage proves that the Holy Spirit has the same relationship to God as the spirit within us has to us.
The Cappadocian Fathers also quoted, "Do you not know that you are God's temple and that God's Spirit dwells in you?" (1 Cor. 3:16) and reasoned that it would be blasphemous for an inferior being to take up residence in a temple of God, thus proving that the Holy Spirit is equal with the Father and the Son.
They also combined "the servant does not know what his master is doing" (John 15:15) with 1 Corinthians 2:11 in an attempt to show that the Holy Spirit is not the slave of God, and therefore his equal.
The Pneumatomachi contradicted the Cappadocian Fathers by quoting, "Are they not all ministering spirits sent out to serve for the sake of those who are to inherit salvation?" (Hebrews 1:14) in effect arguing that the Holy Spirit is no different from other created angelic spirits. The Church Fathers disagreed, saying that the Holy Spirit is greater than the angels, since the Holy Spirit is the one who grants the foreknowledge for prophecy (1 Cor. 12:8-10) so that the angels could announce events to come.
Old Testament parallels
In addition, the Old Testament has also been interpreted as referring to the Trinity, by referring to God's word (Psalm 33:6), his spirit (Isaiah 61:1), and Wisdom (Proverbs 9:1), as well as narratives such as the appearance of the three men to Abraham. However, it is generally agreed among Trinitarian Christian scholars that it would go beyond the intention and spirit of the Old Testament to correlate these notions directly with later Trinitarian doctrine.
Some Church Fathers believed that a knowledge of the mystery was granted to the prophets and saints of the Old Testament, and that they identified the divine messenger of Genesis 16:7, Genesis 21:17, Genesis 31:11, Exodus 3:2 and Wisdom of the sapiential books with the Son, and "the spirit of the Lord" with the Holy Spirit. Other Church Fathers, such as Gregory Nazianzen, argued in his Orations that the revelation was gradual, claiming that the Father was proclaimed in the Old Testament openly, but the Son only obscurely, because "it was not safe, when the Godhead of the Father was not yet acknowledged, plainly to proclaim the Son".
Genesis 18–19 has been interpreted by Christians as a Trinitarian text. The narrative has the Lord appearing to Abraham, who was visited by three men (Gen 18:1-2). Then in Genesis 19, "the two angels" visited Lot at Sodom. The interplay between Abraham on the one hand and the Lord/three men/the two angels on the other was an intriguing text for those who believed in a single God in three persons. Justin Martyr, and John Calvin similarly, interpreted it such that Abraham was visited by God, who was accompanied by two angels. Justin supposed that the God who visited Abraham was distinguishable from the God who remains in the heavens, but was nevertheless identified as the (monotheistic) God. Justin appropriated the God who visited Abraham to Jesus, the second person of the Trinity.
Augustine, in contrast, held that the three visitors to Abraham were the three persons of the Trinity. He saw no indication that the visitors were unequal, as would be the case in Justin's reading. Then in Genesis 19, two of the visitors were addressed by Lot in the singular: "Lot said to them, 'Not so, my lord'" (Gen. 19:18) Augustine saw that Lot could address them as one because they had a single substance, despite the plurality of persons.
Some Christians interpret the theophanies or appearances of the Angel of the Lord as revelations of a person distinct from God, who is nonetheless called God. This interpretation is found in Christianity as early as Justin Martyr and Melito of Sardis, and reflects ideas that were already present in Philo. The Old Testament theophanies were thus seen as Christophanies, each a "preincarnate appearance of the Messiah".
Early Christianity
Before the Council of Nicaea
While the developed doctrine of the Trinity is not explicit in the books that constitute the New Testament, it was first formulated as early Christians attempted to understand the relationship between Jesus and God in their scriptural documents and prior traditions.
An early Trinitarian formula appears towards the end of the first century, where Clement of Rome rhetorically asks in his epistle as to why corruption exists among some in the Christian community; "Do we not have one God, and one Christ, and one gracious Spirit that has been poured out upon us, and one calling in Christ?" (1 Clement 46:6). Around the turn of the first century, the Didache directs Christians to "baptize in the name of the Father and of the Son and of the Holy Spirit." Ignatius of Antioch provides early support for the Trinity around 110, exhorting obedience to "Christ, and to the Father, and to the Spirit".
The pseudonymous Ascension of Isaiah, written sometime between the end of the first century and the beginning of the third century, possesses a "proto-trinitarian" view, such as in its narrative of how the inhabitants of the sixth heaven sing praises to "the primal Father and his Beloved Christ, and the Holy Spirit". Justin Martyr (AD 100–c. 165) also writes, "in the name of God, the Father and Lord of the universe, and of our Saviour Jesus Christ, and of the Holy Spirit".
Justin Martyr is the first to use much of the terminology that would later become widespread in codified Trinitarian theology. For example, he describes that the Son and Father are the same "being" (ousia) and yet are also distinct faces (prosopa), anticipating the three persons (hypostases) that come with Tertullian and later authors. Justin describes how Jesus, the Son, is distinguishable from the Father but also derives from the Father, using the analogy of a fire (representing the Son) that is lit from its source, a torch (representing the Father).
The first of the early church fathers to be recorded using the word "Trinity" was Theophilus of Antioch writing in the late 2nd century. He defines the Trinity as God, His Word (Logos) and His Wisdom (Sophia) in the context of a discussion of the first three days of creation, following the early Christian practice of identifying the Holy Spirit as the Wisdom of God. The first defense of the doctrine of the Trinity was in the early 3rd century by the early church father Tertullian. He explicitly defined the Trinity as Father, Son, and Holy Spirit and defended his theology against "Praxeas", though he noted that the majority of the believers in his day found issue with his doctrine.
St. Justin and Clement of Alexandria used the Trinity in their doxologies and St. Basil likewise, in the evening lighting of lamps. Origen of Alexandria (AD 185-c. 253) has often been interpreted as Subordinationist, but some modern researchers have argued that Origen might have actually been anti-Subordinationist and that his own Trinitarian theology inspired the Trinitarian theology of the later Cappadocian Fathers.
Of these controversies, the most significant developments were articulated in the first four centuries by the Church Fathers in reaction to Adoptionism, Sabellianism, and Arianism. Adoptionism was the belief that Jesus was an ordinary man, born of Joseph and Mary, who became the Christ and Son of God at his baptism. In 269, the Synods of Antioch condemned Paul of Samosata for his Adoptionist theology, and also condemned the term homoousios (ὁμοούσιος, "of the same being") in the modalist sense in which he used it.
Among the Non-Trinitarian beliefs, the Sabellianism taught that the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit are essentially one and the same, the difference being simply verbal, describing different aspects or roles of a single being. For this view Sabellius was excommunicated for heresy in Rome c. 220.
First Council of Nicaea (325)
In the fourth century, Arianism, as traditionally understood, taught that the Father existed prior to the Son who was not, by nature, God but rather a changeable creature who was granted the dignity of becoming "Son of God". In 325, the First Council of Nicaea adopted the Nicene Creed which described Christ as "God of God, Light of Light, very God of very God, begotten, not made, being of one substance with the Father", and the "Holy Ghost" as the one by which "was incarnate... of the Virgin Mary". ("the Word was made flesh and dwelled among us"). About the Father and the Son, the creed used the term homoousios (of one substance) to define the relationship between the Father and the Son. After more than fifty years of debate, homoousios was recognised as the hallmark of orthodoxy, and was further developed into the formula of "three persons, one being".
The Confession of the First Council of Nicaea, the Nicene Creed, said little about the Holy Spirit. At the First Council of Nicea (325) all attention was focused on the relationship between the Father and the Son, without making any similar statement about the Holy Spirit:
- "We believe in one God, the Father Almighty, Maker of all things visible and invisible. And in one Lord Jesus Christ, the Son of God, begotten of the Father [the only-begotten; that is, of the essence of the Father, God of God,] Light of Light, very God of very God, begotten, not made, being of one substance with the Father; (...) And [we believe] in the Holy Ghost. (...)." — Nicene Creed
First Council of Constantinople (381)
Later, at the First Council of Constantinople (381), the Nicene Creed would be expanded, known as Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed, by saying that the Holy Spirit is worshiped and glorified together with the Father and the Son (συμπροσκυνούμενον καὶ συνδοξαζόμενον), suggesting that he was also consubstantial with them:
- "We believe in one God, the Father Almighty, Maker of heaven and earth, and of all things visible and invisible. And in one Lord Jesus Christ, the only-begotten Son of God, begotten of the Father before all worlds (æons), Light of Light, very God of very God, begotten, not made, being of one substance with the Father; (...) And in the Holy Ghost, the Lord and Giver of life, who proceedeth from the Father, who with the Father and the Son together is worshiped and glorified, who spake by the prophets (...)." — Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed.
The doctrine of the divinity and personality of the Holy Spirit was developed by Athanasius in the last decades of his life. He defended and refined the Nicene formula. By the end of the 4th century, under the leadership of Basil of Caesarea, Gregory of Nyssa, and Gregory of Nazianzus (the Cappadocian Fathers), the doctrine had reached substantially its current form.
Middle Ages
In the late 6th century, some Latin-speaking churches added the words "and from the Son" (Filioque) to the description of the procession of the Holy Spirit, words that were not included in the text by either the Council of Nicaea or that of Constantinople. This was incorporated into the liturgical practice of Rome in 1014. Filioque eventually became one of the main causes for the East-West Schism in 1054, and the failures of the repeated union attempts.
Gregory of Nazianzus would say of the Trinity, "No sooner do I conceive of the One than I am illumined by the splendour of the Three; no sooner do I distinguish Three than I am carried back into the One. When I think of any of the Three, I think of Him as the Whole, and my eyes are filled, and the greater part of what I am thinking escapes me. I cannot grasp the greatness of that One so as to attribute a greater greatness to the rest. When I contemplate the Three together, I see but one torch, and cannot divide or measure out the undivided light."
Devotion to the Trinity centered in the French monasteries at Tours and Aniane where Saint Benedict dedicated the abbey church to the Trinity in 872. Feast Days were not instituted until 1091 at Cluny and 1162 at Canterbury and papal resistance continued until 1331.
Theology
Trinitarian baptismal formula
Baptism is generally conferred with the Trinitarian formula, "in the name of the Father, and of the Son, and of the Holy Spirit". Trinitarians identify this name with the Christian faith into which baptism is an initiation, as seen for example in the statement of Basil the Great (330–379): "We are bound to be baptized in the terms we have received, and to profess faith in the terms in which we have been baptized." The First Council of Constantinople (381) also says, "This is the Faith of our baptism that teaches us to believe in the Name of the Father, of the Son and of the Holy Spirit. According to this Faith there is one Godhead, Power, and Being of the Father, of the Son, and of the Holy Spirit." Matthew 28:19 may be taken to indicate that baptism was associated with this formula from the earliest decades of the Church's existence. Other Trinitarian formulas found in the New Testament include in 2 Corinthians 13:14, 1 Corinthians 12:4–6, Ephesians 4:4–6, 1 Peter 1:2 and Revelation 1:4–5.
Oneness Pentecostals demur from the Trinitarian view of baptism and emphasize baptism ‘in the name of Jesus Christ’ the original apostolic formula. For this reason, they often focus on the baptisms in Acts. Those who place great emphasis on the baptisms in Acts often likewise question the authenticity of Matthew 28:19 in its present form. Most scholars of New Testament textual criticism accept the authenticity of the passage, since there are no variant manuscripts regarding the formula, and the extant form of the passage is attested in the Didache and other patristic works of the 1st and 2nd centuries: Ignatius, Tertullian, Hippolytus, Cyprian, and Gregory Thaumaturgus.
Commenting on Matthew 28:19, Gerhard Kittel states:
This threefold relation [of Father, Son and Spirit] soon found fixed expression in the triadic formulae in 2 Cor. 13:14 and in 1 Cor. 12:4–6. The form is first found in the baptismal formula in Matthew 28:19; Did., 7. 1 and 3....[I]t is self-evident that Father, Son and Spirit are here linked in an indissoluble threefold relationship.
One God in Three Persons
In Trinitarian doctrine, God exists as three persons but is one being, having a single divine nature. The members of the Trinity are co-equal and co-eternal, one in essence, nature, power, action, and will. As stated in the Athanasian Creed, the Father is uncreated, the Son is uncreated, and the Holy Spirit is uncreated, and all three are eternal without beginning. "The Father and the Son and the Holy Spirit" are not names for different parts of God, but one name for God because three persons exist in God as one entity. They cannot be separate from one another. Each person is understood as having the identical essence or nature, not merely similar natures.
According to the Eleventh Council of Toledo (675) "For, when we say: He who is the Father is not the Son, we refer to the distinction of persons; but when we say: the Father is that which the Son is, the Son that which the Father is, and the Holy Spirit that which the Father is and the Son is, this clearly refers to the nature or substance"
The Fourth Lateran Council (1215) adds: "In God there is only a Trinity since each of the three persons is that reality — that is to say substance, essence or divine nature. This reality neither begets nor is begotten nor proceeds; the Father begets, the Son is begotten and the holy Spirit proceeds. Thus there is a distinction of persons but a unity of nature. Although therefore the Father is one person, the Son another person and the holy Spirit another person, they are not different realities, but rather that which is the Father is the Son and the holy Spirit, altogether the same; thus according to the orthodox and catholic faith they are believed to be consubstantial."
Clarification of the relationships among the three Trinitarian Persons (divine persons, different from the sense of a "human self") much advances because of the pertaining Magisterial statement promulgated by the Council of Florence (1431-1449), though its formulation much precedes the Council: "These three Persons are one God and not three gods, for the three are one substance, one essence, one nature, one opposition of relationship [relationis oppositio]." Robert Magliola explains that most theologians have taken relationis oppositio in the "Thomist" sense, namely, the "opposition of relationship" [in English we would say "oppositional relationship"] is one of contrariety rather than contradiction. The only "functions" that are applied uniquely to the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit respectively in Scripture are the following: "Paternity" to the Father, "Filiation" (Sonship) to the Son, and "Passive Spiration" or that which is "breathed out," to the Holy Spirit. Magliola goes on to explain:
Because such is the case (among other reasons), Karl Rahner rejects the "psychological" theories of Trinity which define the Father as Knower, for example, and the Son as the Known (i.e., Truth). Scripture in one place or another identifies Knowing with each of the three Persons all told. Which is to say, according to the relationis oppositio, Knowing (in our example) does not define the Persons [qua individual Persons] at all, but the Unity of God instead. (Scripture's attribution of Knowing to any one Person at any one time is said to be just "appropriated" to the Person: it does not really belong to that unique Person).
— Magliola 2001, pp. 404, 405
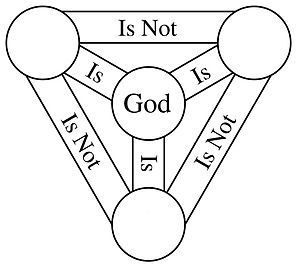
Magliola, continuing the Rahnerian stance, goes on to explain that the Divine Persons necessarily relate to each other in terms of "pure negative reference," that is, the three "Is Not" relations represented in the Scutum Fidei diagram (to the upper right in this article) are in each case a pure or absolute "Is Not". This is the case because the relationis oppositio clause disallows the Persons to "share," qua Persons, the unique role that defines each of them. Lest he be misunderstood, Magliola, in a subsequent publication, makes sure to specify that each of the three Persons, while unique as a Person, is nonetheless—because of the Divine "consubstantiality" and "simplicity"—the one Reality that is God.
Perichoresis
Perichoresis (from Greek, "going around", "envelopment") is a term used by some scholars to describe the relationship among the members of the Trinity. The Latin equivalent for this term is circumincessio. This concept refers for its basis to John 14–17, where Jesus is instructing the disciples concerning the meaning of his departure. His going to the Father, he says, is for their sake; so that he might come to them when the "other comforter" is given to them. Then, he says, his disciples will dwell in him, as he dwells in the Father, and the Father dwells in him, and the Father will dwell in them. This is so, according to the theory of perichoresis, because the persons of the Trinity "reciprocally contain one another, so that one permanently envelopes and is permanently enveloped by, the other whom he yet envelopes". (Hilary of Poitiers, Concerning the Trinity 3:1).
Perichoresis effectively excludes the idea that God has parts, but rather is a simple being. It also harmonizes well with the doctrine that the Christian's union with the Son in his humanity brings him into union with one who contains in himself, in the Apostle Paul's words, "all the fullness of deity" and not a part. Perichoresis provides an intuitive figure of what this might mean. The Son, the eternal Word, is from all eternity the dwelling place of God; he is the "Father's house", just as the Son dwells in the Father and the Spirit; so that, when the Spirit is "given", then it happens as Jesus said, "I will not leave you as orphans; for I will come to you."
Economic and immanent Trinity
The term "immanent Trinity" focuses on who God is; the term “economic Trinity” focuses on what God does. According to the Catechism of the Catholic Church,
The Fathers of the Church distinguish between theology (theologia) and economy (oikonomia). "Theology" refers to the mystery of God's inmost life within the Blessed Trinity and "economy" to all the works by which God reveals himself and communicates his life. Through the oikonomia the theologia is revealed to us; but conversely, the theologia illuminates the whole oikonomia. God's works reveal who he is in himself; the mystery of his inmost being enlightens our understanding of all his works. So it is, analogously, among human persons. A person discloses himself in his actions, and the better we know a person, the better we understand his actions.
The whole divine economy is the common work of the three divine persons. For as the Trinity has only one and the same natures so too does it have only one and the same operation: "The Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit are not three principles of creation but one principle." However, each divine person performs the common work according to his unique personal property. Thus the Church confesses, following the New Testament, "one God and Father from whom all things are, and one Lord Jesus Christ, through whom all things are, and one Holy Spirit in whom all things are". It is above all the divine missions of the Son's Incarnation and the gift of the Holy Spirit that show forth the properties of the divine persons.
The ancient Nicene theologians argued that everything the Trinity does is done by Father, Son, and Spirit working in unity with one will. The three persons of the Trinity always work inseparably, for their work is always the work of the one God. The Son's will cannot be different from the Father's because it is the Father's. They have but one will as they have but one being. Otherwise they would not be one God. On this point St. Basil said:
When then He says, 'I have not spoken of myself', and again, 'As the Father said unto me, so I speak', and 'The word which ye hear is not mine, but [the Father's] which sent me', and in another place, 'As the Father gave me commandment, even so I do', it is not because He lacks deliberate purpose or power of initiation, nor yet because He has to wait for the preconcerted key-note, that he employs language of this kind. His object is to make it plain that His own will is connected in indissoluble union with the Father. Do not then let us understand by what is called a 'commandment' a peremptory mandate delivered by organs of speech, and giving orders to the Son, as to a subordinate, concerning what He ought to do. Let us rather, in a sense befitting the Godhead, perceive a transmission of will, like the reflexion of an object in a mirror, passing without note of time from Father to Son.
According to Thomas Aquinas the Son prayed to the Father, became a minor to the angels, became incarnate, obeyed the Father as to his human nature, as to his divine nature the Son remained God: "Thus, then, the fact that the Father glorifies, raises up, and exalts the Son does not show that the Son is less than the Father, except in His human nature. For, in the divine nature by which He is equal to the Father, the power of the Father and the Son is the same and their operation is the same."
Athanasius of Alexandria explained that the Son is eternally one in being with the Father, temporally and voluntarily subordinate in his incarnate ministry. Such human traits, he argued, were not to be read back into the eternal Trinity. Likewise, the Cappadocian Fathers also insisted there was no economic inequality present within the Trinity. As Basil wrote: "We perceive the operation of the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit to be one and the same, in no respect showing differences or variation; from this identity of operation we necessarily infer the unity of nature."
The traditional theory of "appropriation" consists in attributing certain names, qualities, or operations to one of the Persons of the Trinity, not, however, to the exclusion of the others, but in preference to the others. This theory was established by the Latin Fathers of the fourth and fifth centuries, especially by Hilary of Poitiers, Augustine, and Leo the Great. In the Middle Ages, the theory was systematically taught by the Schoolmen such as Bonaventure.
Trinity and love
Augustine "coupled the doctrine of the Trinity with anthropology. Proceeding from the idea that humans are created by God according to the divine image, he attempted to explain the mystery of the Trinity by uncovering traces of the Trinity in the human personality". The first key of his exegesis is an interpersonal analogy of mutual love. In De trinitate (399–419) he wrote,
We are now eager to see whether that most excellent love is proper to the Holy Spirit, and if it is not so, whether the Father, or the Son, or the Holy Trinity itself is love, since we cannot contradict the most certain faith and the most weighty authority of Scripture which says: 'God is love'.
— Augustine of Hippo 2002, p. 25
The Bible reveals it although only in the two neighboring verses 1 John 4:8.16, therefore one must ask if love itself is triune. Augustine found that it is, and consists of "three: the lover, the beloved, and the love."
Reaffirming the theopaschite formula unus de trinitate passus est carne (meaning "One of the Trinity suffered in the flesh"), Thomas Aquinas wrote that Jesus suffered and died as to his human nature, as to his divine nature he could not suffer or die. "But the commandment to suffer clearly pertains to the Son only in His human nature. (...) "And the way in which Christ was raised up is like the way He suffered and died, that is, in the flesh. For it says in 1 Peter (4:1): "Christ having suffered in the flesh" (...) then, the fact that the Father glorifies, raises up, and exalts the Son does not show that the Son is less than the Father, except in His human nature. For, in the divine nature by which He is equal to the Father."
In the 1900s the recovery of a substantially different formula of theopaschism took place: at least unus de Trinitate passus est (meaning "...not only in the flesh"). Deeply affected by the atomic bombs event, as early as 1946 the Lutheran theologian Kazoh Kitamori published Theology of the Pain of God, a theology of the Cross pushed up to the immanent Trinity. This concept was later taken by both Reformed and Catholic theology: in 1971 by Jürgen Moltmann's The Crucified God; in the 1972 "Preface to the Second Edition" of his 1969 German book Theologie der Drei Tage (English translation: Mysterium Paschale) by Hans Urs von Balthasar, who took a cue from Revelation 13:8 (Vulgate: agni qui occisus est ab origine mundi, NIV: "the Lamb who was slain from the creation of the world") to explore the "God is love" idea as an "eternal super-kenosis". In the words of von Balthasar: "At this point, where the subject undergoing the 'hour' is the Son speaking with the Father, the controversial 'Theopaschist formula' has its proper place: 'One of the Trinity has suffered.' The formula can already be found in Gregory Nazianzen: 'We needed a...crucified God'."
The underlying question is if the three Persons of the Trinity can live a self-love (amor sui), as well as if for them, with the conciliar dogmatic formulation in terms that today we would call ontotheological, it is possible that the aseity (causa sui) is valid. If the Father is not the Son or the Spirit since the generator/begetter is not the generated/begotten nor the generation/generative process and vice versa, and since the lover is neither the beloved nor the love dynamic between them and vice versa, Christianity has provided as a response a concept of divine ontology and love different from common sense (omnipotence, omnibenevolence, impassibility, etc.): a sacrificial, martyring, crucifying, precisely kenotic concept.
Trinity and will
Benjamin B. Warfield saw a principle of subordination in the "modes of operation" of the Trinity, but was also hesitant to ascribe the same to the "modes of subsistence" in relation of one to another. While noting that it is natural to see a subordination in function as reflecting a similar subordination in substance, he suggests that this might be the result of "...an agreement by Persons of the Trinity – a "Covenant" as it is technically called – by virtue of which a distinct function in the work of redemption is assumed by each".
Political aspect
According to Eusebius, Constantine suggested the term homoousios at the Council of Nicaea, though most scholars have doubted that Constantine had such knowledge and have thought that most likely Hosius had suggested the term to him. Constantine later changed his view about the Arians, who opposed the Nicene formula, and supported the bishops who rejected the formula, as did several of his successors, the first emperor to be baptized in the Nicene faith being Theodosius the Great, emperor from 379 to 395.
Nontrinitarian Christian beliefs
Nontrinitarianism (or antitrinitarianism) refers to Christian belief systems that reject the doctrine of the Trinity as found in the Nicene Creed as not having a scriptural origin. Nontrinitarian views differ widely on the nature of God, Jesus, and the Holy Spirit. Various nontrinitarian views, such as Adoptionism, Monarchianism, and Arianism existed prior to the formal definition of the Trinity doctrine in AD 325, 360, and 431, at the Councils of Nicaea, Constantinople, and Ephesus, respectively. Following the adoption of trinitarianism at Constantinople in 381, Arianism was driven from the Empire, retaining a foothold amongst the Germanic tribes. When the Franks converted to Catholicism in 496, however, it gradually faded out. Nontrinitarianism was later renewed in the Gnosticism of the Cathars in the 11th through 13th centuries, in the Age of Enlightenment of the 18th century, and in some groups arising during the Second Great Awakening of the 19th century. See also binitarianism.
Arianism was condemned as heretical by the First Council of Nicaea and, lastly, with Sabellianism by the Second Ecumenical Council (Constantinople, 381 CE). Adoptionism was declared as heretical by the Ecumenical Council of Frankfurt, convened by the Emperor Charlemagne in 794 for the Latin West Church.
Modern nontrinitarian groups or denominations include Christadelphians, Christian Science, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Dawn Bible Students, Iglesia ni Cristo, Jehovah's Witnesses, Living Church of God, Oneness Pentecostals, the Seventh Day Church of God, Unitarian Christians, United Church of God, and The Shepherd's Chapel.
Other religions' view of the Trinity
Judaism
Judaism traditionally maintains a tradition of monotheism that excludes the possibility of a Trinity. In Judaism, God is understood to be the absolute one, indivisible, and incomparable being who is the ultimate cause of all existence. The idea of God as a duality or trinity is heretical — it is even considered by some to be polytheistic.
Islam
Islam considers Jesus to be a prophet, but not divine, and God to be absolutely indivisible (a concept known as tawhid). Several verses of the Quran state that the doctrine of the Trinity is blasphemous.
They surely disbelieve who say: Lo! God is the Messiah, son of Mary. The Messiah (himself) said: O Children of Israel, worship God, my Lord and your Lord. Lo! whoso ascribeth partners unto God, for him God hath forbidden paradise. His abode is the Fire. For evil-doers there will be no helpers. They surely disbelieve who say: Lo! God is the third of three; when there is no Lord save the One Lord. If they desist not from so saying a painful doom will fall on those of them who disbelieve. Will they not rather turn unto God and seek forgiveness of Him? For God is Forgiving, Merciful. The Messiah, son of Mary, was no other than a messenger, messengers (the like of whom) had passed away before him. And his mother was a saintly woman. And they both used to eat (earthly) food. See how We make the revelations clear for them, and see how they are turned away! (Quran 5:72-75)
Interpretation of these verses by modern scholars has been varied. Verse 5:73 has been interpreted as a potential criticism of Syriac literature that references Jesus as "the third of three" and thus an attack on the view that Christ was divine. Some scholars suggest that verse 5:73 is a reference to the Collyridians, an alleged small heretical group of Christians composed of women that venerated Mary above usual standards by other sects of Christianity. However, this sect may not have existed at all, let alone during the period when Islam emerged, and did not worship Mary as a goddess. Another interpretation is that this passage should be studied from a rhetorical perspective; so as not to be an error, but an intentional misrepresentation of the doctrine of the Trinity in order to demonstrate its absurdity from an Islamic perspective. Recent Islamic studies asserts that "the quranic accusations that christians claim Mary as God can be understood as a rhetorical statement." For example, David Thomas states that verse 5:116 need not be seen as describing actually professed beliefs, but rather, giving examples of shirk (claiming divinity for beings other than God) and a "warning against excessive devotion to Jesus and extravagant veneration of Mary, a reminder linked to the central theme of the Qur'an that there is only one God and He alone is to be worshipped." When read in this light, it can be understood as an admonition, "Against the divinization of Jesus that is given elsewhere in the Qur'an and a warning against the virtual divinization of Mary in the declaration of the fifth-century church councils that she is 'God-bearer'." Similarly, Gabriel Reynolds, Sidney Griffith and Mun'im Sirry argue that this quranic verse is to be understood as an intentional caricature and rhetorical statement to warn from the dangers of deifiying Jesus or Mary. It has been suggested that the Islamic representation of the doctrine of the Trinity may derive from its description in some texts of Manichaeism "where we encounter a trinity, consisting of a Father, a Mother of Life / the Living Spirit and the Original Man".
Artistic depictions
The Trinity is most commonly seen in Christian art with the Spirit represented by a dove, as specified in the Gospel accounts of the Baptism of Christ; he is nearly always shown with wings outspread. However depictions using three human figures appear occasionally in most periods of art.
The Father and the Son are usually differentiated by age, and later by dress, but this too is not always the case. The usual depiction of the Father as an older man with a white beard may derive from the biblical Ancient of Days, which is often cited in defense of this sometimes controversial representation. However, in Eastern Orthodoxy the Ancient of Days is usually understood to be God the Son, not God the Father (see below) — early Byzantine images show Christ as the Ancient of Days, but this iconography became rare. When the Father is depicted in art, he is sometimes shown with a halo shaped like an equilateral triangle, instead of a circle. The Son is often shown at the Father's right hand (Acts 7:56). He may be represented by a symbol — typically the Lamb (agnus dei) or a cross — or on a crucifix, so that the Father is the only human figure shown at full size. In early medieval art, the Father may be represented by a hand appearing from a cloud in a blessing gesture, for example in scenes of the Baptism of Christ. Later, in the West, the Throne of Mercy (or "Throne of Grace") became a common depiction. In this style, the Father (sometimes seated on a throne) is shown supporting either a crucifix or, later, a slumped crucified Son, similar to the Pietà (this type is distinguished in German as the Not Gottes), in his outstretched arms, while the Dove hovers above or in between them. This subject continued to be popular until the 18th century at least.
By the end of the 15th century, larger representations, other than the Throne of Mercy, became effectively standardised, showing an older figure in plain robes for the Father, Christ with his torso partly bare to display the wounds of his Passion, and the dove above or around them. In earlier representations both Father, especially, and Son often wear elaborate robes and crowns. Sometimes the Father alone wears a crown, or even a papal tiara.
In the later part of the Christian Era, in Renaissance European iconography, the Eye of Providence began to be used as an explicit image of the Christian Trinity and associated with the concept of Divine Providence. Seventeenth-century depictions of the Eye of Providence sometimes show it surrounded by clouds or sunbursts.