The innate immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the dominant immune system response found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.
The major functions of the innate immune system are to:
- recruit immune cells to infection sites by producing chemical factors, including chemical mediators called cytokines
- activate the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells
- identify and remove foreign substances present in organs, tissues, blood and lymph, by specialized white blood cells
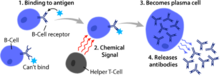
- activate the adaptive immune system through antigen presentation
- act as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents; via physical measures such as skin and chemical measures such as clotting factors in blood, which are released following a contusion or other injury that breaks through the first-line physical barrier (not to be confused with a second-line physical or chemical barrier, such as the blood-brain barrier, which protects the nervous system from pathogens that have already gained access to the host).
Anatomical barriers
Anatomical barriers include physical, chemical and biological barriers. The epithelial surfaces form a physical barrier that is impermeable to most infectious agents, acting as the first line of defense against invading organisms. Desquamation (shedding) of skin epithelium also helps remove bacteria and other infectious agents that have adhered to the epithelial surface. Lack of blood vessels, the inability of the epidermis to retain moisture, and the presence of sebaceous glands in the dermis, produces an environment unsuitable for the survival of microbes. In the gastrointestinal and respiratory tract, movement due to peristalsis or cilia, respectively, helps remove infectious agents. Also, mucus traps infectious agents. Gut flora can prevent the colonization of pathogenic bacteria by secreting toxic substances or by competing with pathogenic bacteria for nutrients or cell surface attachment sites. The flushing action of tears and saliva helps prevent infection of the eyes and mouth.
| Anatomical barrier | Additional defense mechanisms |
|---|---|
| Skin | Sweat, desquamation, flushing, organic acids |
| Gastrointestinal tract | Peristalsis, gastric acid, bile acids, digestive enzyme, flushing, thiocyanate, defensins, gut flora |
| Respiratory airways and lungs | Mucociliary escalator, surfactant, defensins |
| Nasopharynx | Mucus, saliva, lysozyme |
| Eyes | Tears |
| Blood-brain barrier | endothelial cells (via passive diffusion/ osmosis & active selection). P-glycoprotein (mechanism by which active transportation is mediated) |
Inflammation
Inflammation is one of the first responses of the immune system to infection or irritation. Inflammation is stimulated by chemical factors released by injured cells. It establishes a physical barrier against the spread of infection and promotes healing of any damaged tissue following pathogen clearance.
The process of acute inflammation is initiated by cells already present in all tissues, mainly resident macrophages, dendritic cells, histiocytes, Kupffer cells, and mast cells. These cells present receptors contained on the surface or within the cell, named pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which recognize molecules that are broadly shared by pathogens but distinguishable from host molecules, collectively referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). At the onset of an infection, burn, or other injuries, these cells undergo activation (one of their PRRs recognizes a PAMP) and release inflammatory mediators responsible for the clinical signs of inflammation.
Chemical factors produced during inflammation (histamine, bradykinin, serotonin, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins) sensitize pain receptors, cause local vasodilation of the blood vessels, and attract phagocytes, especially neutrophils. Neutrophils then trigger other parts of the immune system by releasing factors that summon additional leukocytes and lymphocytes. Cytokines produced by macrophages and other cells of the innate immune system mediate the inflammatory response. These cytokines include TNF, HMGB1, and IL-1.
The inflammatory response is characterized by the following symptoms:
- redness of the skin, due to locally increased blood circulation;
- heat, either increased local temperature, such as a warm feeling around a localized infection, or a systemic fever;
- swelling of affected tissues, such as the upper throat during the common cold or joints affected by rheumatoid arthritis;
- increased production of mucus, which can cause symptoms like a runny nose or a productive cough;
- pain, either local pain, such as painful joints or a sore throat, or affecting the whole body, such as body aches; and
- possible dysfunction of involved organs/tissues.
Complement system
The complement system is a biochemical cascade of the immune system that helps, or “complements”, the ability of antibodies to clear pathogens or mark them for destruction by other cells. The cascade is composed of many plasma proteins, synthesized in the liver, primarily by hepatocytes. The proteins work together to:
- trigger the recruitment of inflammatory cells
- "tag" pathogens for destruction by other cells by opsonizing, or coating, the surface of the pathogen
- form holes in the plasma membrane of the pathogen, resulting in cytolysis of the pathogen cell, causing the death of the pathogen
- rid the body of neutralised antigen-antibody complexes.
The three different complement systems are classical, alternative and lectin.
- Classical: starts when antibody binds to bacteria
- Alternative: starts "spontaneously"
- Lectin: starts when lectins bind to mannose on bacteria
Elements of the complement cascade can be found in many non-mammalian species including plants, birds, fish, and some species of invertebrates.
White blood cells
White blood cells (WBCs) are also known as leukocytes. Most leukocytes differ from other cells of the body in that they are not tightly associated with a particular organ or tissue; thus, their function is similar to that of independent, single-cell organisms. Most leukocytes are able to move freely and interact with and capture cellular debris, foreign particles, and invading microorganisms (although macrophages, mast cells, and dendritic cells are less mobile). Unlike many other cells, most innate immune leukocytes cannot divide or reproduce on their own, but are the products of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells present in bone marrow.
The innate leukocytes include: natural killer cells, mast cells, eosinophils, basophils; and the phagocytic cells include macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells, and function within the immune system by identifying and eliminating pathogens that might cause infection.
Mast cells
Mast cells are a type of innate immune cell that resides in connective tissue and in mucous membranes. They are intimately associated with wound healing and defense against pathogens, but are also often associated with allergy and anaphylaxis. When activated, mast cells rapidly release characteristic granules, rich in histamine and heparin, along with various hormonal mediators and chemokines, or chemotactic cytokines into the environment. Histamine dilates blood vessels, causing the characteristic signs of inflammation, and recruits neutrophils and macrophages.
Phagocytes
The word 'phagocyte' literally means 'eating cell'. These are immune cells that engulf, or 'phagocytose', pathogens or particles. To engulf a particle or pathogen, a phagocyte extends portions of its plasma membrane, wrapping the membrane around the particle until it is enveloped (i.e., the particle is now inside the cell). Once inside the cell, the invading pathogen is contained inside a phagosome, which merges with a lysosome. The lysosome contains enzymes and acids that kill and digest the particle or organism. In general, phagocytes patrol the body searching for pathogens, but are also able to react to a group of highly specialized molecular signals produced by other cells, called cytokines. The phagocytic cells of the immune system include macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells.
Phagocytosis of the hosts’ own cells is common as part of regular tissue development and maintenance. When host cells die, either by apoptosis or by cell injury due to an infection, phagocytic cells are responsible for their removal from the affected site. By helping to remove dead cells preceding growth and development of new healthy cells, phagocytosis is an important part of the healing process following tissue injury.
Macrophages
Macrophages, from the Greek, meaning "large eaters", are large phagocytic leukocytes, which are able to move beyond the vascular system by migrating through the walls of capillary vessels and entering the areas between cells in pursuit of invading pathogens. In tissues, organ-specific macrophages are differentiated from phagocytic cells present in the blood called monocytes. Macrophages are the most efficient phagocytes and can phagocytose substantial numbers of bacteria or other cells or microbes. The binding of bacterial molecules to receptors on the surface of a macrophage triggers it to engulf and destroy the bacteria through the generation of a “respiratory burst”, causing the release of reactive oxygen species. Pathogens also stimulate the macrophage to produce chemokines, which summon other cells to the site of infection.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils, along with eosinophils and basophils, are known as granulocytes due to the presence of granules in their cytoplasm, or as polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) due to their distinctive lobed nuclei. Neutrophil granules contain a variety of toxic substances that kill or inhibit growth of bacteria and fungi. Similar to macrophages, neutrophils attack pathogens by activating a respiratory burst. The main products of the neutrophil respiratory burst are strong oxidizing agents including hydrogen peroxide, free oxygen radicals and hypochlorite. Neutrophils are the most abundant type of phagocyte, normally representing 50-60% of the total circulating leukocytes, and are usually the first cells to arrive at the site of an infection. The bone marrow of a normal healthy adult produces more than 100 billion neutrophils per day, and more than 10 times that many per day during acute inflammation.
Dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are phagocytic cells present in tissues that are in contact with the external environment, mainly the skin (where they are often called Langerhans cells), and the inner mucosal lining of the nose, lungs, stomach, and intestines. They are named for their resemblance to neuronal dendrites, but dendritic cells are not connected to the nervous system. Dendritic cells are very important in the process of antigen presentation, and serve as a link between the innate and adaptive immune systems.
Basophils and eosinophils
Basophils and eosinophils are cells related to the neutrophil. When activated by a pathogen encounter, histamine-releasing basophils are important in the defense against parasites and play a role in allergic reactions, such as asthma. Upon activation, eosinophils secrete a range of highly toxic proteins and free radicals that are highly effective in killing parasites, but may also damage tissue during an allergic reaction. Activation and release of toxins by eosinophils are, therefore, tightly regulated to prevent any inappropriate tissue destruction.
Natural killer cells
Natural killer cells (NK cells) do not directly attack invading microbes. Rather, NK cells destroy compromised host cells, such as tumor cells or virus-infected cells, recognizing such cells by a condition known as "missing self." This term describes cells with abnormally low levels of a cell-surface marker called MHC I (major histocompatibility complex) - a situation that can arise in viral infections of host cells. They were named "natural killer" because of the initial notion that they do not require activation in order to kill cells that are "missing self." The MHC makeup on the surface of damaged cells is altered and the NK cells become activated by recognizing this. Normal body cells are not recognized and attacked by NK cells because they express intact self MHC antigens. Those MHC antigens are recognized by killer cell immunoglobulin receptors (KIR) that, slow the reaction of NK cells. The NK-92 cell line does not express KIR and is developed for tumor therapy.
γδ T cells
Like other 'unconventional' T cell subsets bearing invariant T cell receptors (TCRs), such as CD1d-restricted Natural Killer T cells, γδ T cells exhibit characteristics that place them at the border between innate and adaptive immunity. γδ T cells may be considered a component of adaptive immunity in that they rearrange TCR genes to produce junctional diversity and develop a memory phenotype. The various subsets may be considered part of the innate immune system where a restricted TCR or NK receptors may be used as a pattern recognition receptor. For example, according to this paradigm, large numbers of Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells respond within hours to common molecules produced by microbes, and highly restricted intraepithelial Vδ1 T cells will respond to stressed epithelial cells.
Other vertebrate mechanisms
The coagulation system overlaps with the immune system. Some products of the coagulation system can contribute to non-specific defenses via their ability to increase vascular permeability and act as chemotactic agents for phagocytic cells. In addition, some of the products of the coagulation system are directly antimicrobial. For example, beta-lysine, a protein produced by platelets during coagulation, can cause lysis of many Gram-positive bacteria by acting as a cationic detergent. Many acute-phase proteins of inflammation are involved in the coagulation system.
Increased levels of lactoferrin and transferrin inhibit bacterial growth by binding iron, an essential bacterial nutrient.
Neural regulation
The innate immune response to infectious and sterile injury is modulated by neural circuits that control cytokine production period. The inflammatory reflex is a prototypical neural circuit that controls cytokine production in the spleen. Action potentials transmitted via the vagus nerve to the spleen mediate the release of acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter that inhibits cytokine release by interacting with alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (CHRNA7) expressed on cytokine-producing cells. The motor arc of the inflammatory reflex is termed the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
Pathogen-specificity
The parts of the innate immune system display specificity for different pathogens.
| Pathogen | Main examples | Phagocytosis | complement | NK cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intracellular and cytoplasmic virus | yes | yes | yes | |
| Intracellular bacteria | yes (specifically neutrophils, no for rickettsia) | yes | yes (no for rickettsia) | |
| Extracellular bacteria | yes | yes | no | |
| Intracellular protozoa | no | no | no | |
| Extracellular protozoa | yes | yes | no | |
| Extracellular fungi | no | yes | yes |
Immune evasion
Innate immune system cells prevent free growth of microorganisms within the body, but many pathogens have evolved mechanisms to evade it.
One strategy is intracellular replication, as practised by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, or wearing a protective capsule, which prevents lysis by complement and by phagocytes, as in Salmonella. Bacteroides species are normally mutualistic bacteria, making up a substantial portion of the mammalian gastrointestinal flora. Species such as B. fragilis are opportunistic pathogens, causing infections of the peritoneal cavity. They inhibit phagocytosis by affecting the phagocytes receptors used to engulf bacteria. They may also mimic host cells so the immune system does not recognize them as foreign. Staphylococcus aureus inhibits the ability of the phagocyte to respond to chemokine signals. M. tuberculosis, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Bacillus anthracis utilize mechanisms that directly kill the phagocyte.
Bacteria and fungi may form complex biofilms, protecting them from immune cells and proteins; biofilms are present in the chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cenocepacia infections characteristic of cystic fibrosis.
Viruses
Type I interferons (IFN), secreted mainly by dendritic cells, play a central role in antiviral host defense and a cell's antiviral state. Viral components are recognized by different receptors: Toll-like receptors are located in the endosomal membrane and recognize double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), MDA5 and RIG-I receptors are located in the cytoplasm and recognize long dsRNA and phosphate-containing dsRNA respectively. When the cytoplasmic receptors MDA5 and RIG-I recognize a virus the conformation between the caspase-recruitment domain (CARD) and the CARD-containing adaptor MAVS changes. In parallel, when TLRs in the endocytic compartments recognize a virus the activation of the adaptor protein TRIF is induced. Both pathways converge in the recruitment and activation of the IKKε/TBK-1 complex, inducing dimerization of transcription factors IRF3 and IRF7, which are translocated in the nucleus, where they induce IFN production with the presence of a particular transcription factor and activate transcription factor 2. IFN is secreted through secretory vesicles, where it can activate receptors on both the cell it was released from (autocrine) or nearby cells (paracrine). This induces hundreds of interferon-stimulated genes to be expressed. This leads to antiviral protein production, such as protein kinase R, which inhibits viral protein synthesis, or the 2′,5′-oligoadenylate synthetase family, which degrades viral RNA.
Some viruses evade this by producing molecules that interfere with IFN production. For example, the Influenza A virus produces NS1 protein, which can bind to host and viral RNA, interact with immune signaling proteins or block their activation by ubiquitination, thus inhibiting type I IFN production. Influenza A also blocks protein kinase R activation and establishment of the antiviral state. The dengue virus also inhibits type I IFN production by blocking IRF-3 phosophorylation using NS2B3 protease complex.
Beyond vertebrates
Prokaryotes
Bacteria (and perhaps other prokaryotic organisms), utilize a unique defense mechanism, called the restriction modification system to protect themselves from pathogens, such as bacteriophages. In this system, bacteria produce enzymes, called restriction endonucleases, that attack and destroy specific regions of the viral DNA of invading bacteriophages. Methylation of the host's own DNA marks it as "self" and prevents it from being attacked by endonucleases. Restriction endonucleases and the restriction modification system exist exclusively in prokaryotes.
Invertebrates
Invertebrates do not possess lymphocytes or an antibody-based humoral immune system, and it is likely that a multicomponent, adaptive immune system arose with the first vertebrates. Nevertheless, invertebrates possess mechanisms that appear to be precursors of these aspects of vertebrate immunity. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are proteins used by nearly all organisms to identify molecules associated with microbial pathogens. TLRs are a major class of pattern recognition receptor, that exists in all coelomates (animals with a body-cavity), including humans. The complement system exists in most life forms. Some invertebrates, including various insects, crabs, and worms utilize a modified form of the complement response known as the prophenoloxidase (proPO) system.
Antimicrobial peptides are an evolutionarily conserved component of the innate immune response found among all classes of life and represent the main form of invertebrate systemic immunity. Several species of insect produce antimicrobial peptides known as defensins and cecropins.
Proteolytic cascades
In invertebrates, PRRs trigger proteolytic cascades that degrade proteins and control many of the mechanisms of the innate immune system of invertebrates—including hemolymph coagulation and melanization. Proteolytic cascades are important components of the invertebrate immune system because they are turned on more rapidly than other innate immune reactions because they do not rely on gene changes. Proteolytic cascades function in both vertebrate and invertebrates, even though different proteins are used throughout the cascades.
Clotting mechanisms
In the hemolymph, which makes up the fluid in the circulatory system of arthropods, a gel-like fluid surrounds pathogen invaders, similar to the way blood does in other animals. Various proteins and mechanisms are involved in invertebrate clotting. In crustaceans, transglutaminase from blood cells and mobile plasma proteins make up the clotting system, where the transglutaminase polymerizes 210 kDa subunits of a plasma-clotting protein. On the other hand, in the horseshoe crab clotting system, components of proteolytic cascades are stored as inactive forms in granules of hemocytes, which are released when foreign molecules, like lipopolysaccharides enter.
Plants
Members of every class of pathogen that infect humans also infect plants. Although the exact pathogenic species vary with the infected species, bacteria, fungi, viruses, nematodes, and insects can all cause plant disease. As with animals, plants attacked by insects or other pathogens use a set of complex metabolic responses that lead to the formation of defensive chemical compounds that fight infection or make the plant less attractive to insects and other herbivores.
Like invertebrates, plants neither generate antibody or T-cell responses nor possess mobile cells that detect and attack pathogens. In addition, in case of infection, parts of some plants are treated as disposable and replaceable, in ways that few animals can. Walling off or discarding a part of a plant helps stop infection spread.
Most plant immune responses involve systemic chemical signals sent throughout a plant. Plants use PRRs to recognize conserved microbial signatures. This recognition triggers an immune response. The first plant receptors of conserved microbial signatures were identified in rice (XA21, 1995) and in Arabidopsis (FLS2, 2000). Plants also carry immune receptors that recognize variable pathogen effectors. These include the NBS-LRR class of proteins. When a part of a plant becomes infected with a microbial or viral pathogen, in case of an incompatible interaction triggered by specific elicitors, the plant produces a localized hypersensitive response (HR), in which cells at the site of infection undergo rapid apoptosis to prevent spread to other parts of the plant. HR has some similarities to animal pyroptosis, such as a requirement of caspase-1-like proteolytic activity of VPEγ, a cysteine protease that regulates cell disassembly during cell death.
"Resistance" (R) proteins, encoded by R genes, are widely present in plants and detect pathogens. These proteins contain domains similar to the NOD Like Receptors and TLRs. Systemic acquired resistance (SAR) is a type of defensive response that renders the entire plant resistant to a broad spectrum of infectious agents. SAR involves the production of chemical messengers, such as salicylic acid or jasmonic acid. Some of these travel through the plant and signal other cells to produce defensive compounds to protect uninfected parts, e.g., leaves. Salicylic acid itself, although indispensable for expression of SAR, is not the translocated signal responsible for the systemic response. Recent evidence indicates a role for jasmonates in transmission of the signal to distal portions of the plant. RNA silencing mechanisms are important in the plant systemic response, as they can block virus replication. The jasmonic acid response is stimulated in leaves damaged by insects, and involves the production of methyl jasmonate.