From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The polar jet stream can travel at speeds greater than 100 miles per
hour (160 km/h). Here, the fastest winds are coloured red; slower winds
are blue.
Clouds along a jet stream over Canada.
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents found in the atmosphere of some planets, including Earth.[1] On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east). Their paths typically have a meandering shape. Jet streams may start, stop, split into two or more parts, combine into one stream, or flow in various directions including opposite to the direction of the remainder of the jet. The strongest jet streams are the polar jets, at 9–12 km (30,000–39,000 ft) above sea level, and the higher altitude and somewhat weaker subtropical jets at 10–16 km (33,000–52,000 ft). The Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere each have a polar jet and a subtropical jet. The northern hemisphere polar jet flows over the middle to northern latitudes of North America, Europe, and Asia and their intervening oceans, while the southern hemisphere polar jet mostly circles Antarctica all year round.
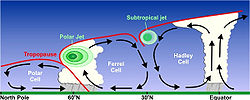
Jet streams are the product of two factors: the atmospheric heating by solar radiation that produces the large scale Polar, Ferrel, and Hadley circulation cells, and the action of the Coriolis force acting on those moving masses. The Coriolis force is caused by the planet's rotation on its axis. On other planets, internal heat rather than solar heating drives their jet streams. The Polar jet stream forms near the interface of the Polar and Ferrel circulation cells; while the subtropical jet forms near the boundary of the Ferrel and Hadley circulation cells.[2]
Other jet streams also exist. During the Northern Hemisphere summer, easterly jets can form in tropical regions, typically where dry air encounters more humid air at high altitudes. Low-level jets also are typical of various regions such as the central United States.
Meteorologists use the location of some of the jet streams as an aid in weather forecasting. The main commercial relevance of the jet streams is in air travel, as flight time can be dramatically affected by either flying with the flow or against, which results in significant fuel and time cost savings for airlines. Often, the airlines work to fly 'with' the jet stream for this reason. Dynamic North Atlantic Tracks are one example of how airlines and air traffic control work together to accommodate the jet steam and winds aloft that results in the maximum benefit for airlines and other users. Clear-air turbulence, a potential hazard to aircraft passenger safety, is often found in a jet stream's vicinity, but it does not create a substantial alteration on flight times.
Discovery
After the 1883 eruption of the Krakatoa volcano, weather watchers tracked and mapped the effects on the sky over several years. They labelled the phenomenon the "equatorial smoke stream".[3][4] In the 1920s, a Japanese meteorologist, Wasaburo Oishi, detected the jet stream from a site near Mount Fuji.[5][6] He tracked pilot balloons, also known as pibals (balloons used to determine upper level winds),[7] as they rose into the atmosphere. Oishi's work largely went unnoticed outside Japan because it was published in Esperanto. American pilot Wiley Post, the first man to fly around the world solo in 1933, is often given some credit for discovery of jet streams. Post invented a pressurized suit that let him fly above 6,200 metres (20,300 ft). In the year before his death, Post made several attempts at a high-altitude transcontinental flight, and noticed that at times his ground speed greatly exceeded his air speed.[8] German meteorologist Heinrich Seilkopf is credited with coining a special term, Strahlströmung (literally "jet current"), for the phenomenon in 1939.[9][10] (Modern German usage is "Strahlstrom".[citation needed]) Many sources credit real understanding of the nature of jet streams to regular and repeated flight-path traversals during World War II. Flyers consistently noticed westerly tailwinds in excess of 100 mph (160 km/h) in flights, for example, from the US to the UK.[11] Similarly in 1944 a team of American meteorologists in Guam, including Reid Bryson, had enough observations to forecast very high west winds that would slow bombers going to Japan.[12]Description
General configuration of the polar and subtropical jet streams
Cross section of the subtropical and polar jet streams by latitude
Polar jet streams are typically located near the 250 hPa (about 1/4 atmosphere) pressure level, or 7 to 12 kilometres (4.3 to 7.5 mi) above sea level, while the weaker subtropical jet streams are much higher, between 10 and 16 kilometres (6.2 and 9.9 mi). Jet streams wander laterally dramatically, and have large changes in their altitude. The jet streams form near breaks in the tropopause, at the transitions between the Polar, Ferrel and Hadley circulation cells, and whose circulation, with the Coriolis force acting on those masses, drives the jet streams. The Polar jets, at lower altitude, and often intruding into mid-latitudes, strongly affects weather and aviation.[13][14] The polar jet stream is most commonly found between latitudes 30° and 60° (closer to 60°), while the subtropical jet streams are located close to latitude 30°. The northern Polar jet stream is said to "follow the sun" as it slowly migrates northward as that hemisphere warms, and southward again as it cools.[15][16]
The width of a jet stream is typically a few hundred kilometres or miles and its vertical thickness often less than five kilometres (3 mi).[17]
Meanders (Rossby Waves) of the Northern Hemisphere's polar jet stream
developing (a), (b); then finally detaching a "drop" of cold air (c).
Orange: warmer masses of air; pink: jet stream.
Jet streams are typically continuous over long distances, but discontinuities are common.[18] The path of the jet typically has a meandering shape, and these meanders themselves propagate eastward, at lower speeds than that of the actual wind within the flow. Each large meander, or wave, within the jet stream is known as a Rossby wave (planetary wave). Rossby waves are caused by changes in the Coriolis effect with latitude.[citation needed] Shortwave troughs, are smaller scale waves superimposed on the Rossby waves, with a scale of 1,000 to 4,000 kilometres (620–2,490 mi) long,[19] that move along through the flow pattern around large scale, or longwave, "ridges" and "troughs" within Rossby waves.[20] Jet streams can split into two when it encounters an upper-level low, that diverts a portion of the jet stream under its base, while the remainder of the jet moves by to its north.
The wind speeds are greatest where temperature differences (gradient) between air masses are greatest, and often exceed 92 km/h (50 kn; 57 mph),[18] to over 398 km/h (215 kn; 247 mph) have been measured.[21]
The jet stream moves from West to East bringing changes of weather.[22] Meteorologists now understand that the path of jet streams affects cyclonic storm systems at lower levels in the atmosphere, and so knowledge of their course has become an important part of weather forecasting. For example, in 2007 and 2012, Britain experienced severe flooding as a result of the polar jet staying south for the summer.[23][24][25]
The polar and subtropical jets merge at some locations and times, while at other times they are well separated.
Cause
Highly idealised depiction of the global circulation. The upper-level jets tend to flow latitudinally along the cell boundaries.
All these facts are consequences of the thermal wind relation. The balance of forces acting on an atmospheric air parcel in the vertical direction is primarily between the gravitational force acting on the mass of the parcel and the buoyancy force, or the difference in pressure between the top and bottom surfaces of the parcel. Any imbalance between these forces results in the acceleration of the parcel in the imbalance direction: upward if the buoyant force exceeds the weight, and downward if the weight exceeds the buoyancy force. The balance in the vertical direction is referred to as hydrostatic. Beyond the tropics, the dominant forces act in the horizontal direction, and the primary struggle is between the Coriolis force and the pressure gradient force. Balance between these two forces is referred to as geostrophic. Given both hydrostatic and geostrophic balance, one can derive the thermal wind relation: the vertical gradient of the horizontal wind is proportional to the horizontal temperature gradient. If two air masses, one cold and dense to the North and the other hot and less dense to the South, are separated by a vertical boundary and that boundary should be removed, the difference in densities will result in the cold air mass slipping under the hotter and less dense air mass. The Coriolis effect will then cause poleward-moving mass to deviate to the East, while equatorward-moving mass will deviate toward the west. The general trend in the atmosphere is for temperatures to decrease in the poleward direction. As a result, winds develop an eastward component and that component grows with altitude. Therefore, the strong eastward moving jet streams are in part a simple consequence of the fact that the Equator is warmer than the North and South poles.[26]
Polar jet stream
The thermal wind relation does not explain why the winds are organized into tight jets, rather than distributed more broadly over the hemisphere. One factor that contributes to the creation of a concentrated polar jet is the undercutting of sub-tropical air masses by the more dense polar air masses at the polar front. This causes surface low pressure and higher pressure at altitude. At high altitudes, lack of friction allows air to respond freely to the steep pressure gradient with low pressure at high altitude over the pole. This results in the formation of planetary wind circulations that experience a strong Coriolis deflection and thus can be considered 'quasi-geostrophic'. The polar front jet stream is closely linked to the frontogenesis process in midlatitudes, as the acceleration/deceleration of the air flow induces areas of low/high pressure respectively, which link to the formation of cyclones and anticyclones along the polar front in a relatively narrow region.[18]Subtropical jet
A second factor which contributes to a concentrated jet, that is more applicable to the subtropical jet, which forms at the poleward limit of the tropical Hadley cell and to first order this circulation is symmetric with respect to longitude. Tropical air rises to the tropopause, and moves poleward before sinking; this is the Hadley cell circulation. As it does so it tends to conserve angular momentum, since friction with the ground is significant. Air masses that begin moving northward are deflected eastward by the Coriolis force (true for either hemisphere), which for poleward moving air implies an increased eastward component of the winds[27] (note that leftward deflection in the southern hemisphere).Other planets
Jupiter's atmosphere has multiple jet streams, caused by the convection cells that form the familiar banded color structure; on Jupiter, these convection cells are driven by internal heating.[21] The factors that control the number of jet streams in a planetary atmosphere is an active area of research in dynamical meteorology. In models, as one increases the planetary radius, holding all other parameters fixed, the number of jet streams decreases.Some effects
Hurricane protection
Note the large band of moisture that developed East of Hawaii Island that came from the hurricane.
The subtropical jet stream rounding the base of the mid-oceanic upper trough is thought to be one of the reasons most of the Hawaiian Islands have been resistant to the long list of Hawaii hurricanes that have approached. For example, when Hurricane Flossie (2007) approached and dissipated just before reaching landfall, the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) cited vertical wind shear as evidenced in the photo.[28]
Uses
On Earth, the northern polar jet stream is the most important one for aviation and weather forecasting, as it is much stronger and at a much lower altitude than the subtropical jet streams and also covers many countries in the Northern Hemisphere, while the southern polar jet stream mostly circles Antarctica and sometimes the southern tip of South America. The term jet stream in these contexts thus usually implies the northern polar jet stream.Aviation
Flights between Tokyo and Los Angeles using the jet stream eastbound and a great circle route westbound.
The location of the jet stream is extremely important for aviation. Commercial use of the jet stream began on 18 November 1952, when Pan Am flew from Tokyo to Honolulu at an altitude of 7,600 metres (24,900 ft). It cut the trip time by over one-third, from 18 to 11.5 hours.[29] Not only does it cut time off the flight, it also nets fuel savings for the airline industry.[30] Within North America, the time needed to fly east across the continent can be decreased by about 30 minutes if an airplane can fly with the jet stream, or increased by more than that amount if it must fly west against it.
Associated with jet streams is a phenomenon known as clear-air turbulence (CAT), caused by vertical and horizontal wind shear caused by jet streams.[31] The CAT is strongest on the cold air side of the jet,[32] next to and just under the axis of the jet.[33] Clear-air turbulence can cause aircraft to plunge and so present a passenger safety hazard that has caused fatal accidents, such as the death of one passenger on United Airlines Flight 826 (1997).[34][35]
Future power generation
Scientists are investigating ways to harness the wind energy within the jet stream. According to one estimate, of the potential wind energy in the jet stream, only 1 percent would be needed to meet the world's current energy needs. The required technology would reportedly take 10–20 years to develop.[36] There are two major scientific articles about jet stream power. Archer & Caldeira[37] claim that the jet streams can generate the total power of 1700 TW, and that the climatic impact will be negligible. Miller, Gans, & Kleidon[38] claim that the jet streams can generate the total power of only 7.5 TW, and that the climatic impact will be catastrophic.Unpowered aerial attack
Near the end of World War II the Japanese fire balloon was designed as a cheap weapon intended to make use of the jet stream over the Pacific Ocean to reach the west coast of Canada and the United States. They were relatively ineffective as weapons, but they were used in one of the few attacks on North America during World War II, causing six deaths and a small amount of damage.[39]Changes due to climate cycles
Effects of ENSO
Impact of El Niño and La Niña on North America
El Niño
During El Niño events, increased precipitation is expected in California due to a more southerly, zonal, storm track.[42] During the Niño portion of ENSO, increased precipitation falls along the Gulf coast and Southeast due to a stronger than normal, and more southerly, polar jet stream.[43] Snowfall is greater than average across the southern Rockies and Sierra Nevada mountain range, and is well below normal across the Upper Midwest and Great Lakes states.[44] The northern tier of the lower 48 exhibits above normal temperatures during the fall and winter, while the Gulf coast experiences below normal temperatures during the winter season.[45][46] The subtropical jet stream across the deep tropics of the Northern Hemisphere is enhanced due to increased convection in the equatorial Pacific, which decreases tropical cyclogenesis within the Atlantic tropics below what is normal, and increases tropical cyclone activity across the eastern Pacific.[47] In the Southern Hemisphere, the subtropical jet stream is displaced equatorward, or north, of its normal position, which diverts frontal systems and thunderstorm complexes from reaching central portions of the continent.[41]La Niña
Across North America during La Niña, increased precipitation is diverted into the Pacific Northwest due to a more northerly storm track and jet stream.[48] The storm track shifts far enough northward to bring wetter than normal conditions (in the form of increased snowfall) to the Midwestern states, as well as hot and dry summers.[49][50] Snowfall is above normal across the Pacific Northwest and western Great Lakes.[44] Across the North Atlantic, the jet stream is stronger than normal, which directs stronger systems with increased precipitation towards Europe.[51]Dust Bowl
Evidence suggests the jet stream was at least partly responsible for the widespread drought conditions during the 1930s Dust Bowl in the Midwest United States. Normally, the jet stream flows east over the Gulf of Mexico and turns northward pulling up moisture and dumping rain onto the Great Plains. During the Dust Bowl, the jet stream weakened and changed course traveling farther south than normal. This starved the Great Plains and other areas of the Midwest of rainfall, causing extraordinary drought conditions.[52]Longer-term climatic changes
Climate scientists have hypothesized that the jet stream will gradually weaken as a result of global warming. Trends such as Arctic sea ice decline, reduced snow cover, evapotranspiration patterns, and other weather anomalies are expected to make the Arctic heat up faster than other parts of the globe. This in turn reduces the temperature gradient that drives jet stream winds, causing the jet stream to become weaker and more variable in its course.[53][54][55][56][57][58][59]Since 2007, and particularly in 2012 and early 2013, the jet stream has been at an abnormally low latitude across the UK, lying closer to the English Channel, around 50°N rather than its more usual north of Scotland latitude of around 60°N.[not in citation given] However, between 1979 and 2001, it has been found that the average position of the jet stream has been moving northward at a rate of 2.01 kilometres (1.25 mi) per year across the Northern Hemisphere. Across North America, this type of change could lead to drier conditions across the southern tier of the United States and more frequent and more intense tropical cyclones in the tropics. A similar slow poleward drift was found when studying the Southern Hemisphere jet stream over the same time frame.[60]
Other upper-level jets
Polar night jet
The polar-night jet stream forms only during the winter months when the nights are much longer, hence polar nights, in their respective hemispheres at around 60° latitude. The polar night jet moves at a greater height of about 80,000 feet (24,000 m) than it does during the summer.[61] During these dark months the air high over the poles becomes much colder than the air over the equator. This difference in temperature gives rise to extreme air pressure differences in the stratosphere, which, when combined with the Coriolis effect, create the polar night jets, that race eastward at an altitude of about 30 miles (48 km).[62] The polar vortex is circled by the polar night jet. The warmer air can only move along the edge of the polar vortex, but not enter it. Within the vortex, the cold polar air becomes increasingly cold with neither warmer air from lower latitudes nor energy from the Sun during the polar night.[63]Low level jets
There are wind maxima at lower levels of the atmosphere that are also referred to as jets.Barrier jet
A barrier jet in the low levels forms just upstream of mountain chains, with the mountains forcing the jet to be oriented parallel to the mountains. The mountain barrier increases the strength of the low level wind by 45 percent.[64] In the North American Great Plains a southerly low-level jet helps fuel overnight thunderstorm activity during the warm season, normally in the form of mesoscale convective systems which form during the overnight hours.[65] A similar phenomenon develops across Australia, which pulls moisture poleward from the Coral Sea towards cut-off lows which form mainly across southwestern portions of the continent.[66]Valley exit jet
A valley exit jet is a strong, down-valley, elevated air current that emerges above the intersection of the valley and its adjacent plain. These winds frequently reach a maximum of 20 m/s (45 mph or 72 km/h) at a height of 40–200 m above the ground. Surface winds below the jet may sway vegetation, but are significantly weaker.They are likely to be found in valley regions that exhibit diurnal mountain wind systems, such as those of the dry mountain ranges of the US. Deep valleys that terminate abruptly at a plain are more impacted by these factors than are those that gradually become shallower as downvalley distance increases.[67]