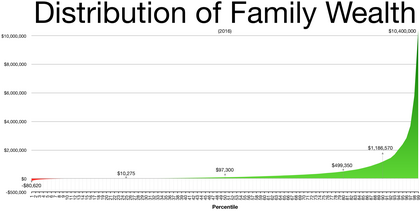
Only in a free-market system can we truly achieve individual liberty and human flourishing.
Individual freedom can only exist in
the context of free-market capitalism. Personal freedom thrives in
capitalism, declines in government-regulated economies, and vanishes in
communism. Aside from better economic and legislative policies, what
America needs is a more intense appreciation for individual freedom and
capitalism.
I was born and raised in communist Romania during the Cold War, a country in which the government owned all the resources and means of production. The state controlled almost every aspect of our lives: our education, our job placement, the time of day we could have hot water, and what we were allowed to say.
Like the rest of the Eastern European countries, Romania was often referred to as a communist country. In school, we were taught it was a socialist country. Its name prior to the 1989 Revolution to overthrow the Ceausescu regime was the Socialist Republic of Romania.
From an economic standpoint, a petty fraction of property was still privately owned. In a communist system, all property is owned by the state. So if it wasn't a true communist economy, its heavy central planning and the application of a totalitarian control over the Romanian citizenry made this nation rightfully gain its title of a communist country.
I get it, maybe we didn't need to be fashionable. But we needed to eat.
Fruity lip gloss, French perfume, and jeans were but a few of the popular items available only on the black market and with the right connections. God bless our black-market entrepreneurs! They made our lives better. They gave us the opportunity to buy things we very much desired, things we couldn't get from the government-owned retail stores which were either half-empty or full of products that were ugly and of poor quality.
The grocery stores were not any better. I get it, maybe we didn't need to be fashionable. But we needed to eat. So, the old Romanian adage "Conscience goes through the stomach" made a lot of sense.
During the late 1970s, life in Romania started to deteriorate even more. Meat was hardly a consumer staple for the average Romanian. Instead, our parents learned to become good at preparing the liver, the brain, the tongue, and other giblets that most people in the West would not even consider trying.
For a family of four like us, our rationed quota was 1 kilogram of flour and 1 kilogram of sugar per month.
I was born and raised in communist Romania during the Cold War, a country in which the government owned all the resources and means of production. The state controlled almost every aspect of our lives: our education, our job placement, the time of day we could have hot water, and what we were allowed to say.
Like the rest of the Eastern European countries, Romania was often referred to as a communist country. In school, we were taught it was a socialist country. Its name prior to the 1989 Revolution to overthrow the Ceausescu regime was the Socialist Republic of Romania.
From an economic standpoint, a petty fraction of property was still privately owned. In a communist system, all property is owned by the state. So if it wasn't a true communist economy, its heavy central planning and the application of a totalitarian control over the Romanian citizenry made this nation rightfully gain its title of a communist country.
Socialism Creates Shortages
Despite the fact that Romania was a country rich in resources, there were shortages everywhere. Food, electricity, water, and just about every one of life's necessities were in short supply. The apartment building in which we lived provided hot water for showers two hours in the morning and two hours at night. We had to be quick and on time so we didn't miss the opportunity.I get it, maybe we didn't need to be fashionable. But we needed to eat.
Fruity lip gloss, French perfume, and jeans were but a few of the popular items available only on the black market and with the right connections. God bless our black-market entrepreneurs! They made our lives better. They gave us the opportunity to buy things we very much desired, things we couldn't get from the government-owned retail stores which were either half-empty or full of products that were ugly and of poor quality.
The grocery stores were not any better. I get it, maybe we didn't need to be fashionable. But we needed to eat. So, the old Romanian adage "Conscience goes through the stomach" made a lot of sense.
During the late 1970s, life in Romania started to deteriorate even more. Meat was hardly a consumer staple for the average Romanian. Instead, our parents learned to become good at preparing the liver, the brain, the tongue, and other giblets that most people in the West would not even consider trying.
For a family of four like us, our rationed quota was 1 kilogram of flour and 1 kilogram of sugar per month.
When milk, butter, eggs, and yogurt
were temporarily available, my mom—like so many others of our
neighbors—would wake up at 2:00 a.m. to go stand in line so she'd have
the chance to get us these goodies. The store would open at 6:00 a.m.,
so if she wasn't early enough in line she'd miss the opportunity.
In 1982, the state sent their disciples to people's homes to do the census. Along with that, food rationing was implemented. For a family of four like us, our rationed quota was 1 kilogram of flour and 1 kilogram of sugar per month. That is, if they were available and if we were lucky enough to be in the right place at the right time when they were being distributed.
The one television channel our government provided for us often focused on programs related to crime and poverty in the western world. After all, people were poor and suffering because of capitalism, so we were told, so we needed socialism and communism to solve the inequalities of humanity.
Private property and private property rights are at the core of capitalism.
The layman definition of capitalism is the economic system in which people and businesses engage in manufacturing, trading, and exchanging products and services without government interference. A free-market capitalist system works in a more efficient manner when not tampered with by government or central bank intervention in the credit markets, monetary policy, and interest rate fixing.
Private property and private property rights are at the core of capitalism. When in school, we learned that private property makes people greedy and is considered detrimental to society. Private property was associated with capitalism, the system that our textbooks claimed failed.
The free market, however, directs the allocation of resources via the amazing process of supply and demand.
In 1982, the state sent their disciples to people's homes to do the census. Along with that, food rationing was implemented. For a family of four like us, our rationed quota was 1 kilogram of flour and 1 kilogram of sugar per month. That is, if they were available and if we were lucky enough to be in the right place at the right time when they were being distributed.
The one television channel our government provided for us often focused on programs related to crime and poverty in the western world. After all, people were poor and suffering because of capitalism, so we were told, so we needed socialism and communism to solve the inequalities of humanity.
Capitalism Advances Private Property
Considering the shortages created by the government-controlled economy of my birth country, I came to understand and appreciate capitalism, the one system that had the most dramatic effect in elevating human civilization.Private property and private property rights are at the core of capitalism.
The layman definition of capitalism is the economic system in which people and businesses engage in manufacturing, trading, and exchanging products and services without government interference. A free-market capitalist system works in a more efficient manner when not tampered with by government or central bank intervention in the credit markets, monetary policy, and interest rate fixing.
Private property and private property rights are at the core of capitalism. When in school, we learned that private property makes people greedy and is considered detrimental to society. Private property was associated with capitalism, the system that our textbooks claimed failed.
Allocation of Resources
Romania was rich in natural resources, yet the difference between our standard of living and those from the West was quite dramatic. It was indicative of a flawed economic system that most countries in Eastern Europe adhered to during the Soviet Era. But one may ask why was there so much poverty when natural resources are so abundant?The free market, however, directs the allocation of resources via the amazing process of supply and demand.
Economics is the study of the
allocation of scarce resources which have alternative uses. Efficiency
is thus of primary concern when the goal is economic progress.
In a centrally-planned environment, the various government individuals who are assigned the task of planning the economy could not possibly know how to properly allocate the scarce resources of an entire nation, no matter how smart or educated they are. Shortages are one of the consequences of improper allocation of the scarce resources.
The free market, however, through the multiple spontaneous interactions of businesses and consumers, directs the allocation of resources via the amazing process of supply and demand. It is precisely due to the profit and loss events that economic efficiency is stimulated.
Capital is chased away due to the high risk associated with governments who engage in high levels of controlling their economies.
In contrast, communism, socialism, fascism, or just about any government-controlled system lacks the profit incentive. The people, who are the human resources, have no desire to engage in a business where the reward is not attainable (unless it's done in the black markets). They accept the state and its bureaucratic cronies to dictate their faith.
Capital is chased away due to the high risk associated with governments who engage in high levels of controlling their economies and, often, corruption. The overall standard of living is dramatically lower than in most capitalist places, and the poverty is higher. Consequently, the collectivist country falls into an economic and social trap from which it is hard to escape. Only capitalism can save a nation from the failure of its central economic planning.
Capitalism makes it possible for us to challenge ourselves, to have goals, and to put forth the sweat in order to achieve them.
In a centrally-planned environment, the various government individuals who are assigned the task of planning the economy could not possibly know how to properly allocate the scarce resources of an entire nation, no matter how smart or educated they are. Shortages are one of the consequences of improper allocation of the scarce resources.
The free market, however, through the multiple spontaneous interactions of businesses and consumers, directs the allocation of resources via the amazing process of supply and demand. It is precisely due to the profit and loss events that economic efficiency is stimulated.
Free Markets Attract Capital
Due to its profit incentives, capitalism encourages innovation. Innovation leads to progress and an increase in the standard of living. But progress and the climate which offers humans a high standard of living cannot be created without the capital to transform and turn resources into the final products that give us the—relatively—cheap energy and food, smartphones, fitness gyms, and overall the life we currently afford. Capital moves in the direction of less regulation, less government intervention, and less taxation. In short, capital moves to where there's more economic freedom.Capital is chased away due to the high risk associated with governments who engage in high levels of controlling their economies.
In contrast, communism, socialism, fascism, or just about any government-controlled system lacks the profit incentive. The people, who are the human resources, have no desire to engage in a business where the reward is not attainable (unless it's done in the black markets). They accept the state and its bureaucratic cronies to dictate their faith.
Capital is chased away due to the high risk associated with governments who engage in high levels of controlling their economies and, often, corruption. The overall standard of living is dramatically lower than in most capitalist places, and the poverty is higher. Consequently, the collectivist country falls into an economic and social trap from which it is hard to escape. Only capitalism can save a nation from the failure of its central economic planning.
Capitalism Helps Us Be Better Individuals
Similar to the old Soviet lifestyle, let's remember what the typical Venezuelan family of our times worries about on a daily basis. Food to put on the table and the safety of their children. They wake up in the morning wondering how many meals they can afford that day, where to get them from, and how to pay for them.Capitalism makes it possible for us to challenge ourselves, to have goals, and to put forth the sweat in order to achieve them.
We, the lucky ones to live in a
relatively free-market system, don't have these kinds of worries. We go
to work, get leisure time to be on Facebook, watch TV, be with our
families, read books, and enjoy a hobby or two. In short, we have the
personal freedom to engage in and enjoy a variety of life events because
of capitalism.
But there's another important motive to desire to live in a capitalist society. We are free to create and come up with all kinds of business ideas, no matter how crazy some might be. Because we don't have to worry about tomorrow, we have—or make—the time to read, explore, and innovate.
Capitalism makes it possible for us to challenge ourselves, to have goals, and to put forth the sweat to achieve them. It gives us the freedom to try new things and explore new opportunities. It gives us the chance to create more opportunities. It helps us build strong character because when we try, we also fail, and without failure, how do we know we've made mistakes? Without failure, how do we know we must make changes?
Capitalism is the path to the individual rights and liberty that build the solid foundation of a free society.
In retrospect, that was a dumb answer on my part. After several decades, I came to believe that the human condition of individual freedom can only exist in the context of free markets. Shortages are created by the intrusion of the state into the complex activity of the markets, whether it's price controls or poor allocation of resources.
When shortages are powerful and long enough to dramatically affect lives, people resort to revolt. Large revolts call for serious governmental actions including, but not limited to, eroding or completely eliminating individual rights (the right to free speech and to bear arms), the institution of a police state, and the enacting of a powerful state propaganda system. Capitalism is the path to the individual rights and liberty that build the solid foundation of a free society.
We still maintain stronger capitalist traits than most, however a few other nations who lead the way in economic freedom have surpassed us.
The economic policy of the 19th Century with limited regulations and minimal taxation attracted the needed capital to our country. The Industrial Revolution made spectacular advancements in human conditions due to the capital concentrated in the region. America lost its number one place due to legislating higher regulations, taxation, and protectionist policies.
But we are still enjoying some of the fruits today. Compared to many countries in the world, we still maintain stronger capitalist traits than most, however Hong Kong, Singapore, Switzerland, New Zealand, and a few other nations who lead the way in economic freedom have surpassed us.
But there's another important motive to desire to live in a capitalist society. We are free to create and come up with all kinds of business ideas, no matter how crazy some might be. Because we don't have to worry about tomorrow, we have—or make—the time to read, explore, and innovate.
Capitalism makes it possible for us to challenge ourselves, to have goals, and to put forth the sweat to achieve them. It gives us the freedom to try new things and explore new opportunities. It gives us the chance to create more opportunities. It helps us build strong character because when we try, we also fail, and without failure, how do we know we've made mistakes? Without failure, how do we know we must make changes?
Individual Freedom Can Only Exist in the Context of Free Markets
Before immigrating to the U.S., I had to go through a rigorous process. One of the events was the immigration interview with the American counselor who, among many other questions, asked why I escaped Romania and why I wanted to come to America. My short answer was freedom. Then he posed the interesting question: "If America was to go through a period of economic devastation with shortages similar to Romania, would you still feel the same way?" I didn't think too much about it, and I said, "Yes, of course, as long as I have freedom."Capitalism is the path to the individual rights and liberty that build the solid foundation of a free society.
In retrospect, that was a dumb answer on my part. After several decades, I came to believe that the human condition of individual freedom can only exist in the context of free markets. Shortages are created by the intrusion of the state into the complex activity of the markets, whether it's price controls or poor allocation of resources.
When shortages are powerful and long enough to dramatically affect lives, people resort to revolt. Large revolts call for serious governmental actions including, but not limited to, eroding or completely eliminating individual rights (the right to free speech and to bear arms), the institution of a police state, and the enacting of a powerful state propaganda system. Capitalism is the path to the individual rights and liberty that build the solid foundation of a free society.
Is America a True Capitalist Economy?
The short answer is no. Most of the world refers to the American system as being a capitalist one. Based on my short definition of capitalism, it is obvious that it is not quite a pure one, and I wish to clarify that the U.S. is not a truly free-market capitalist system.We still maintain stronger capitalist traits than most, however a few other nations who lead the way in economic freedom have surpassed us.
The economic policy of the 19th Century with limited regulations and minimal taxation attracted the needed capital to our country. The Industrial Revolution made spectacular advancements in human conditions due to the capital concentrated in the region. America lost its number one place due to legislating higher regulations, taxation, and protectionist policies.
But we are still enjoying some of the fruits today. Compared to many countries in the world, we still maintain stronger capitalist traits than most, however Hong Kong, Singapore, Switzerland, New Zealand, and a few other nations who lead the way in economic freedom have surpassed us.
What America Needs
It starts in our own backyard, in our home, in our small group, in our community.
Aside from better economic and
legislative policies, what America needs is a more intense appreciation
of individual freedom and capitalism. Such a crazy idea is not acquired
through public schools or becoming a public servant. Young people don't
need more years of schooling with more worthless college degrees and
student loans in default. America needs more entrepreneurs and
businessmen. It needs more people with drive and ambition, more
self-starters, more innovators, more people who are willing to take
chances.
It starts in our own backyard, in our home, in our small group, in our community. It starts with loving, involved, and dedicated parents who'd instill the values of personal responsibility and delayed gratification in their children. It continues with an education that entails both theory and hands-on practice in environments conducive to learning how to think independently and how to acquire life- and work-skills. It evolves into a purpose-driven life rich in learning and experiences. And this may be just the beginning of attaining the intellectual maturity to perceive the value that free markets and individual freedom afford most of us.
It starts in our own backyard, in our home, in our small group, in our community. It starts with loving, involved, and dedicated parents who'd instill the values of personal responsibility and delayed gratification in their children. It continues with an education that entails both theory and hands-on practice in environments conducive to learning how to think independently and how to acquire life- and work-skills. It evolves into a purpose-driven life rich in learning and experiences. And this may be just the beginning of attaining the intellectual maturity to perceive the value that free markets and individual freedom afford most of us.

Carmen Alexe
Carmen Alexe escaped Communist Romania during the Cold War. Her
motive was individual freedom. She has close to 30 years in the lending
industry, currently working as a Commercial Real Estate Consultant.
She's been a real estate investor since 2001. She's also a passionate
Salsa dancer. She's a free spirit doing research on and practicing how
to live free in an unfree world. She shares her zeal for free markets,
individual freedom, and personal responsibility by writing on her blog.