The causes of World War II, a global war from 1939 to 1945 that was the deadliest conflict in human history, have been given considerable attention by historians from many countries who studied and understood them. The immediate precipitating event was the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany on September 1, 1939 and the subsequent declarations of war on Germany made by Britain and France, but many other prior events have been suggested as ultimate causes. Primary themes in historical analysis of the war's origins include the political takeover of Germany in 1933 by Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party; Japanese militarism against China, which led to the Second Sino-Japanese War; Italian aggression against Ethiopia, which led to the Second Italo-Ethiopian War and Germany's initial success in negotiating the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact with the Soviet Union to divide the territorial control of Eastern Europe between them.
During the interwar period, deep anger arose in the Weimar Republic on the conditions of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, which punished Germany for its role in World War I with severe conditions and heavy financial reparations to prevent it from ever becoming a military power again. That provoked strong currents of revanchism in German politics, with complaints primarily focused on the demilitarisation of the Rhineland, the prohibition of German unification with Austria and the loss of some German-speaking territories and overseas colonies.
During the worldwide economic crisis of the Great Depression in the 1930s, many people lost faith in democracy and countries across the world turned to authoritarian regimes. In Germany, resentment and hatred of other countries was intensified by the instability of the German political system, as many activists rejected the Weimar Republic's legitimacy. The most extreme political aspirant to emerge from that situation was Adolf Hitler, the leader of the Nazi Party. The Nazis took totalitarian power in Germany from 1933 and demanded the undoing of the Versailles provisions. Their ambitious and aggressive domestic and foreign policies reflected their ideologies of anti-Semitism, unification of all Germans, the acquisition of "living space" (Lebensraum) for agrarian settlers, the elimination of Bolshevism and the hegemony of an "Aryan"/"Nordic" master race over "subhumans" (Untermenschen) such as Jews and Slavs. Other factors leading to the war included the aggression by Fascist Italy against Ethiopia and by Imperial Japan against China.
At first, the aggressive moves met with only feeble and ineffectual policies of appeasement from the other major world powers. The League of Nations proved helpless, especially regarding China and Ethiopia. A decisive proximate event was the 1938 Munich Conference, which formally approved Germany's annexation of the Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia. Hitler promised it was his last territorial claim, but in early 1939, he became even more aggressive, and European governments finally realised that appeasement would not guarantee peace.
Britain and France rejected diplomatic efforts to form a military alliance with the Soviet Union, and Hitler instead offered Stalin a better deal in the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of August 1939. An alliance formed by Germany, Japan and Italy led to the establishment of the Axis Powers.
Ultimate causes
Legacies of World War I
By the end of World War I in late 1918, the world's social and geopolitical circumstances had fundamentally and irrevocably changed. The Allies had been victorious, but many of Europe's economies and infrastructures had been devastated, including those of the victors. France, along with the other victors, was in a desperate situation regarding its economy, security and morale and understood that its position in 1918 was "artificial and transitory". Thus, French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau worked to gain French security via the Treaty of Versailles, and French security demands, such as reparations, coal payments, and a demilitarised Rhineland, took precedence at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919–1920, which designed the treaty. The war "must be someone's fault – and that's a very natural human reaction", analysed the historian Margaret MacMillan. Germany was charged with the sole responsibility of starting World War I, and the War Guilt Clause was the first step to satisfying revenge for the victor countries, especially France, against Germany. Roy H. Ginsberg argued, "France was greatly weakened and, in its weakness and fear of a resurgent Germany, sought to isolate and punish Germany.... French revenge would come back to haunt France during the Nazi invasion and occupation twenty years later".
The two main provisions of the French security agenda were war reparations from Germany in the form of money and coal and a detached German Rhineland. The French government printed excess currency, which created inflation, to compensate for the lack of funds, and it borrowed money from the United States. Reparations from Germany were needed to stabilise the French economy. France also demanded for Germany to give France its coal supply from the Ruhr to compensate for the destruction of French coal mines during the war. The French demanded an amount of coal that was a "technical impossibility" for the Germans to pay. France also insisted on the demilitarisation of the German Rhineland in the hope of hindering any possibility of a future German attack and giving France a physical security barrier between itself and Germany. The inordinate amount of reparations, coal payments and the principle of a demilitarised Rhineland were largely viewed by the Germans as insulting and unreasonable.
The resulting Treaty of Versailles brought a formal end to the war but was judged by governments on all sides of the conflict. It was neither lenient enough to appease Germany nor harsh enough to prevent it from becoming a dominant continental power again. The German people largely viewed the treaty as placing the blame, or "war guilt", on Germany and Austria-Hungary and as punishing them for their "responsibility", rather than working out an agreement that would assure long-term peace. The treaty imposed harsh monetary reparations and requirements for demilitarisation and territorial dismemberment, caused mass ethnic resettlement and separated millions of ethnic Germans into neighbouring countries.
In the effort to pay war reparations to Britain and France, the Weimar Republic printed trillions of marks, which caused hyperinflation. Robert O. Paxton stated, "No postwar German government believed it could accept such a burden on future generations and survive...". Paying reparations to the victorious side had been a traditional punishment with a long history of use, but it was the "extreme immoderation" that caused German resentment. Germany did not make its last World War I reparation payment until 3 October 2010, 92 years after the end of the war. Germany also fell behind its coal payments because of a passive resistance movement against France. In response, the French invaded the Ruhr and occupied it. By then, most Germans had become enraged with the French and placed the blame for their humiliation on the Weimar Republic. Adolf Hitler, a leader of the Nazi Party, attempted a coup d'état in 1923 in what became known as the Beer Hall Putsch, and he intended to establish a Greater Germanic Reich. Although he failed, Hitler gained recognition as a national hero by the German population.
During the war, German colonies outside Europe had been annexed by the Allies, and Italy took the southern half of Tyrol after the armistice. The war in the east had ended with the defeat and the collapse of the Russian Empire, and German troops had occupied large parts of Eastern and Central Europe with varying degrees of control and established various client states such as a kingdom of Poland and the United Baltic Duchy. The German Navy spent most of the war in port, only to be turned over to the Allies. It was scuttled by its own officers to avoid it from being surrendered. Decades later, the lack of an obvious military defeat would be one of the pillars holding together the Dolchstosslegende ("stab-in-the-back myth"), which gave the Nazis another propaganda tool.
The demilitarised Rhineland and the additional cutbacks on military also infuriated the Germans. Although France logically wanted the Rhineland to be a neutral zone, France had the power to make their desire happen, which merely exacerbated German resentment of the French. In addition, the Treaty of Versailles dissolved the German general staff, and possession of navy ships, aircraft, poison gas, tanks and heavy artillery was also made illegal. The humiliation of being bossed around by the victor countries, especially France, and being stripped of their prized military made the Germans resent the Weimar Republic and idolise anyone who stood up to it. Austria also found the treaty unjust, which encouraged Hitler's popularity.
The conditions generated bitter resentment towards the war's victors, who had promised the Germans that US President Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points would be a guideline for peace; but the Americans had played only a minor role in the war, and Wilson could not convince the Allies to agree to adopt his Fourteen Points. Many Germans felt that the German government had agreed to an armistice based on that understanding, and others felt that the German Revolution of 1918–1919 had been orchestrated by the "November criminals", who later assumed office in the new Weimar Republic. The Japanese also started to express resentment against Western Europe for how they were treated during the negotiations of the Treaty of Versailles. The Japanese proposition to discuss the issue of racial equality was not put in the final draft because of many other Allies, and the Japanese participation in the war caused little reward for the country. The war's economic and psychological legacies of the persisted well into the Interwar Period.
Failure of League of Nations
The League of Nations was an international peacekeeping organization founded in 1919 with the explicit goal of preventing future wars. The League's methods included disarmament, collective security, the settlement disputes between countries by negotiations and diplomacy and the improvement global welfare. The diplomatic philosophy behind the League represented a fundamental shift in thought from the preceding century. The old philosophy of "concert of nations", which grew out of the Congress of Vienna (1815), saw Europe as a shifting map of alliances among nation-states, which created a balance of power that was maintained by strong armies and secret agreements. Under the new philosophy, the League would act as a government of governments, with the role of settling disputes between individual nations in an open and legalist forum. Despite Wilson's advocacy, the United States never joined the League of Nations.
The League lacked an armed force of its own and so depended on member nations to enforce its resolutions, uphold economic sanctions that the League ordered or provide an army when needed for the League to use. However, individual governments were often very reluctant to do so. After numerous notable successes and some early failures in the 1920s, the League ultimately proved incapable of preventing aggression by the Axis Powers in the 1930s. The reliance upon unanimous decisions, the lack of an independent body of armed forces and the continued self-interest of its leading members meant that the failure was arguably inevitable.
Expansionism and militarism
Expansionism is the doctrine of expanding the territorial base or economic influence of a country, usually by means of military aggression. Militarism is the principle or policy of maintaining a strong military capability to use aggressively to expand national interests and/or values, with the view that military efficiency is the supreme ideal of a state.
The Treaty of Versailles and the League of Nations had sought to stifle expansionist and militarist policies by all actors, but the conditions imposed by their creators imposed on the world's new geopolitical situation and the technological circumstances of the era only emboldened the re-emergence of those ideologies during the Interwar Period. By the early 1930s, a militaristic and aggressive national ideology prevailed in Germany, Japan and Italy. The attitude fuelled advancements in military technology, subversive propaganda and ultimately territorial expansion. It has been observed that the leaders of countries that have been suddenly militarised often feel a need to prove that their armies are formidable, which was often a contributing factor in the start of conflicts such as the Second Italo-Ethiopian War and the Second Sino-Japanese War.
In Italy, Benito Mussolini sought to create a New Roman Empire, based around the Mediterranean. Italy invaded Ethiopia as early as 1935, Albania in early 1938, and later Greece. The invasion of Ethiopia provoked angry words and a failed oil embargo from the League of Nations.
Under the Nazi regime, Germany began its own program of expansion that sought to restore its "rightful" boundaries. As a prelude toward its goals, the Rhineland was remilitarised in March 1936. Also of importance was the idea of a Greater Germany, supporters of which hoped to unite the German people under one nation-state to include all territories inhabited by Germans, even if they happened to be a minority in a particular territory. After the Treaty of Versailles, a unification between Germany and the newly-formed German-Austria, a rump state of Austria-Hungary, was prohibited by the Allies, despite the large majority of Austrians supporting the idea.
During the Weimar Republic (1919–1933), the Kapp Putsch, an attempted coup d'état against the republican government, was launched by disaffected members of the armed forces. Later, some of the more radical militarists and nationalists were submerged in grief and despair into the Nazi Party, and more moderate elements of militarism declined. The result was an influx of militarily-inclined men into the Nazi Party. Combined with its racial theories, that fuelled irredentist sentiments and put Germany on a collision course for war with its immediate neighbours.
In Asia, the Empire of Japan harboured expansionist desires towards Manchuria and the Republic of China. Two contemporaneous factors in Japan contributed both to the growing power of its military and the chaos in its ranks before World War I. One was the Cabinet Law, which required the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) to nominate cabinet members before changes could be formed. That essentially gave the military a veto power over the formation of any Cabinet in the ostensibly-parliamentary country. The other factor was gekokujō, the institutionalized disobedience by junior officers. It was common for radical junior officers to press their goals to the extent of assassinating their seniors. In 1936, the phenomenon resulted in the February 26 Incident in which junior officers attempted a coup d'état and killed leading members of the Japanese government. In the 1930s, the Great Depression wrecked Japan's economy and gave radical elements within the Japanese military the chance to force the entire military into working towards the conquest of all of Asia.
For example, in 1931, the Kwantung Army, a Japanese military force stationed in Manchuria, staged the Mukden Incident, which sparked the invasion of Manchuria and its transformation into the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo.
Germans vs. Slavs
Twentieth-century events marked the culmination of a millennium-long process of intermingling between Germans and Slavic people. The rise of nationalism in the 19th century made race a centerpiece of political loyalty. The rise of the nation-state had given way to the politics of identity, including pan-Germanism and pan-Slavism. Furthermore, Social Darwinist theories framed the coexistence as a "Teuton vs. Slav" struggle for domination, land, and limited resources. Integrating these ideas into their own worldview, the Nazis believed that the Germans, the "Aryan race", were the master race and that the Slavs were inferior.
Japan's seizure of resources and markets
Other than a few coal and iron deposits and a small oil field on Sakhalin Island, Japan lacked strategic mineral resources. In the early 20th century, in the Russo-Japanese War, Japan had succeeded in pushing back the East Asian expansion of the Russian Empire in competition for Korea and Manchuria.
Japan's goal after 1931 was economic dominance of most of East Asia, often expressed in the Pan-Asian terms of "Asia for the Asians". Japan was determined to dominate the China market, which the US and other European powers had been dominating. On October 19, 1939, US Ambassador to Japan Joseph C. Grew, in a formal address to the America-Japan Society, stated that
the new order in East Asia has appeared to include, among other things, depriving Americans of their long established rights in China, and to this the American people are opposed.... American rights and interests in China are being impaired or destroyed by the policies and actions of the Japanese authorities in China.
In 1937, Japan invaded Manchuria and China proper. Under the guise of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere, with slogans such as "Asia for the Asians!", Japan sought to remove the Western powers' influence in China and replace it with Japanese domination.
The ongoing conflict in China led to a deepening conflict with the US in which public opinion was alarmed by events such as the Nanking Massacre and growing Japanese power. Lengthy talks were held between the US and Japan. The Japanese invasion of the south of French Indochina made President Franklin Roosevelt freeze all Japanese assets in the US. The intended consequence was to halt oil shipments from the US to Japan, which supplied 80 percent of Japanese oil imports. The Netherlands and Britain followed suit.
With oil reserves that would last only a year and a half during peacetime and much less during wartime, the ABCD line left Japan two choices: comply with the US-led demand to pull out of China or seize the oilfields in the East Indies from the Netherlands. The Japanese government deemed it unacceptable to retreat from China.
Mason-Overy debate: "Flight into War" theory
In the late 1980s, the British historian Richard Overy was involved in a historical dispute with Timothy Mason that played out mostly over the pages of the Past and Present journal over the reasons for the outbreak of the war in 1939. Mason had contended that a "flight into war" had been imposed on Hitler by a structural economic crisis, which confronted Hitler with the choice of making difficult economic decisions or aggression. Overy argued against Mason's thesis by maintaining that Germany was faced with economic problems in 1939, but the extent of those problems could not explain aggression against Poland and the reasons for the outbreak of war were the choices made by the Nazi leadership.
Mason had argued that the German working-class was always against the Nazi dictatorship; that in the overheated German economy of the late 1930s, German workers could force employers to grant higher wages by leaving for another firm and so grant the desired wage increases and that such a form of political resistance forced Hitler to go to war in 1939. Thus, the outbreak of the war was caused by structural economic problems, a "flight into war" imposed by a domestic crisis. The key aspects of the crisis were, according to Mason, a shaky economic recovery that was threatened by a rearmament program that overwhelmed the economy and in which the regime's nationalist bluster limited its options. In that way, Mason articulated a Primat der Innenpolitik ("primacy of domestic politics") view of the war's origins by the concept of social imperialism. Mason's Primat der Innenpolitik thesis was in marked contrast to the Primat der Außenpolitik ("primacy of foreign politics"), which is usually used to explain the war. Mason thought German foreign policy was driven by domestic political considerations, and the launch the war in 1939 was best understood as a "barbaric variant of social imperialism".
Mason argued, "Nazi Germany was always bent at some time upon a major war of expansion". However, Mason argued that the timing of such a war was determined by domestic political pressures, especially as relating to a failing economy, and had nothing to do with what Hitler wanted. Mason believed that from 1936 to 1941, the state of the German economy, not Hitler's "will" or "intentions", was the most important determinate on German foreign policy decisions.
Mason argued that the Nazi leaders were so deeply haunted by the November 1918 German Revolution that they were most unwilling to see any fall in working-class living standards for fear of provoking a repetition of the revolution. Mason stated that by 1939, the "overheating" of the German economy caused by rearmament, the failure of various rearmament plans produced by the shortages of skilled workers, industrial unrest caused by the breakdown of German social policies and the sharp drop in living standards for the German working class forced Hitler into going to war at a time and a place that were not of his choosing.
Mason contended that when faced with the deep socio-economic crisis, the Nazi leadership had decided to embark upon a ruthless foreign policy of "smash and grab" to seize territory in Eastern Europe that could be pitilessly plundered to support the living standards in Germany. Mason described German foreign policy as driven by an opportunistic "next victim" syndrome after the Anschluss in which the "promiscuity of aggressive intentions" was nurtured by every successful foreign policy move. Mason's considered the decision to sign the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact and to attack Poland despite the risk of a war against Britain and France to be the abandonment by Hitler of his foreign policy program outlined in Mein Kampf and to have been forced on him by his need to stop a collapsing German economy by seizing territory abroad to be plundered.
For Overy, the problem with Mason's thesis was that it rested on the assumption that in a way that was not shown by the records, information was passed on to Hitler about Germany's economic problems. Overy argued for a difference between economic pressures induced by the problems of the Four Year Plan and economic motives to seize raw materials, industry and foreign reserves of neighbouring states as a way of accelerating the plan. Overy asserted that Mason downplayed the repressive German state's capacity to deal with domestic unhappiness. Finally, Overy argued that there is considerable evidence that Germany felt that it could master the economic problems of rearmament. As one civil servant put it in January 1940, "we have already mastered so many difficulties in the past, that here too, if one or other raw material became extremely scarce, ways and means will always yet be found to get out of a fix".
Proximate causes
Nazi dictatorship
Hitler and his Nazis took full control of Germany in 1933–34 (Machtergreifung), turning it into a dictatorship with a highly hostile outlook toward the Treaty of Versailles and Jews. It solved its unemployment crisis by heavy military spending.
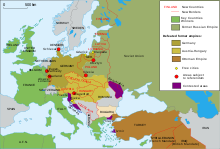
Hitler's diplomatic tactics were to make seemingly-reasonable demands and to threaten war if they were not met. After concessions were made, he accepted them and moved onto a new demand. When opponents tried to appease him, he accepted the gains that were offered and went to the next target. That aggressive strategy worked as Germany pulled out of the League of Nations (1933), rejected the Versailles Treaty, began to rearm with the Anglo-German Naval Agreement (1935), won back the Saar (1935), re-militarized the Rhineland (1936), formed an alliance ("axis") with Mussolini's Italy (1936), sent massive military aid to Franco in the Spanish Civil War (1936–39), seized Austria (1938), took over Czechoslovakia after the British and French appeasement of the Munich Agreement of 1938, formed a peace pact with Stalin's Russia in August 1939 and finally invaded Poland in September 1939.
Remilitarization of the Rhineland
In violation of the Treaty of Versailles and the spirit of the Locarno Pact and the Stresa Front, Germany remilitarized the Rhineland on March 7, 1936 by moving German troops into the part of western Germany in which according to the Versailles Treaty, they were not allowed. Neither France nor Britain was prepared fight a preventive war to stop the violation and so there were no consequences.
Italian invasion of Abyssinia
After the Stresa Conference and even as a reaction to the Anglo-German Naval Agreement, the Italian dictator Benito Mussolini attempted to expand the Italian Empire in Africa by invading the Ethiopian Empire, also known as the Abyssinian Empire. The League of Nations declared Italy to be the aggressor and imposed sanctions on oil sales, which proved ineffective. Italy annexed Ethiopia on May 7 and merged Ethiopia, Eritrea and Somaliland into a single colony, known as Italian East Africa. On June 30, 1936, Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie gave a stirring speech before the League of Nations denouncing Italy's actions and criticizing the world community for standing by. He warned, "It is us today. It will be you tomorrow". As a result of the League's condemnation of Italy, Mussolini declared the country's withdrawal from the organization.
Spanish Civil War
Between 1936 and 1939, Germany and Italy lent support to the Nationalists led by general Francisco Franco in Spain, and the Soviet Union supported the existing democratically-elected government, the Spanish Republic, led by Manuel Azaña. Both sides experimented with new weapons and tactics. The League of Nations was never involved, and its major powers remained neutral and tried with little success to stop arms shipments into Spain. The Nationalists eventually defeated the Republicans in 1939.
Spain negotiated with joining the Axis but remained neutral during World War II and did business with both sides. It also sent a volunteer unit to help the Germans against the Soviets. The Spanish Civil War was considered in the 1940s and 1950s to be a prelude to World War II, which was the case to some extent by changing it into an antifascist contest after 1941, but bore no resemblance to the war that started in 1939 and had no major role in causing it.
Second Sino-Japanese War
In 1931, Japan took advantage of China's weakness in the Warlord Era and fabricated the Mukden Incident in 1931 to set up the puppet state of Manchukuo in Manchuria, with Emperor Puyi, who had been the last emperor of China. In 1937 the Marco Polo Bridge Incident triggered the Second Sino-Japanese War.
The invasion was launched by the bombing of many cities such as Shanghai, Nanjing and Guangzhou. The latest, which began on 22 and 23 September 1937, called forth widespread protests culminating in a resolution by the Far Eastern Advisory Committee of the League of Nations. The Imperial Japanese Army captured the Chinese capital city of Nanjing and committed war crimes in the Nanjing Massacre. The war tied down large numbers of Chinese soldiers and so Japan set up three different Chinese puppet states to enlist some Chinese support.
Anschluss
The Anschluss was the 1938 annexation by threat of force of Austria into Germany. Historically, Pan-Germanism was the idea of creating a Greater Germany to include all ethnic Germans into one nation-state and was popular in both Austria and Germany.
The National Socialist Program included the idea in one of its points: "We demand the unification of all Germans in the Greater Germany on the basis of the people's right to self-determination."
The Stresa Front of 1935 between Britain, France and Italy had guaranteed the independence of Austria, but after the creation of the Rome-Berlin Axis, Mussolini was much less interested in upholding its independence.
The Austrian government resisted as long as possible but had no outside support and finally gave in to Hitler's fiery demands. No fighting occurred, most Austrians supported the annexation and Austria was fully absorbed as part of Germany. Outside powers did nothing, and Italy had little reason for continued opposition to Germany and, if anything, was drawn in closer to the Nazis.
Munich Agreement
The Sudetenland was a predominantly-German region in Czechoslovakia along the border with Germany. It had more than three million ethnic Germans, who comprised almost a quarter of the country's population. In the Treaty of Versailles, the region was given to the Czechoslovakia against the wishes of most of the local population. The decision to disregard its right to self-determination was based on France's intent to weaken Germany. Much of Sudetenland was industrialised.
Czechoslovakia had a modern army of 38 divisions, backed by a well-noted armament industry (Škoda) and military alliances with France and the Soviet Union. However, its defensive strategy against Germany was based on the mountains of the Sudetenland.
Hitler pressed for the Sudetenland's incorporation into Germany and supported German separatist groups within the region. Alleged Czechoslovak brutality and persecution under Prague helped to stir up nationalist tendencies, as did the Nazi press. After the Anschluss, all German parties except for the German Social-Democratic Party merged with the Sudeten German Party (SdP). Paramilitary activity and extremist violence peaked during the period, and the Czechoslovak government declared martial law in parts of the Sudetenland to maintain order. That only complicated the situation, especially since Slovak nationalism was rising from suspicion towards Prague and encouragement by Germany. Citing the need to protect the Germans in Czechoslovakia, Germany requested the immediate annexation of the Sudetenland.
In the Munich Agreement on September 30, 1938, the British, French, and Italian prime ministers appeased Hitler by giving him what he wanted in the hope that it would be his last demand. The powers allowed Germany to move troops into the region and incorporate it into the Reich "for the sake of peace". In exchange, Hitler gave his word that Germany would make no further territorial claims in Europe. Czechoslovakia was not allowed to participate in the conference. When the French and British negotiators informed the Czechoslovak representatives about the agreement and that if Czechoslovakia would not accept it, France and Britain would consider Czechoslovakia to be responsible for war and stay neutral, Czechoslovak President Edvard Beneš capitulated and Germany took the Sudetenland unopposed.
Chamberlain's policies have been the subject of intense debate for more than 70 years by academics, politicians and diplomats. The historians' assessments have ranged from condemnation for allowing Hitler's Germany to grow too strong to the judgment that Germany was so strong that it might well win a war and so the postponement of a showdown was in the country's best interests.
German occupation and Slovak independence
In March 1939, breaking the Munich Agreement, German troops invaded Prague, and with the Slovaks declaring independence, Czechoslovakia disappeared as a country. The entire ordeal ended the French and British policy of appeasement.
Italian invasion of Albania
After the German occupation of Czechoslovakia, Mussolini feared for Italy becoming a second-rate member of the Axis. Rome delivered Tirana an ultimatum on March 25, 1939 by demanding the accession to Italy's occupation of Albania. King Zog refused to accept money in exchange for allowing a full Italian takeover and colonization of Albania.
On April 7, 1939, Italian troops invaded Albania, which was occupied after a three-day campaign with minimal resistance offered by Albanian forces.
Soviet–Japanese Border War
In 1939, the Japanese attacked west from Manchuria into the Mongolian People's Republic after the 1938 Battle of Lake Khasan. They were decisively beaten by Soviet units, under General Georgy Zhukov. After the battle, the Soviet Union and Japan were at peace until 1945. Japan looked south to expand its empire, which led to conflict with the United States over the Philippines and the control of shipping lanes to the Dutch East Indies. The Soviet Union focused on its western border but left 1 million to 1.5 million troops to guard its border with Japan.
Danzig crisis
After the end of Czechoslovakia proved that Germany could not be trusted, Britain and France decided on a change of strategy. They decided any further unilateral German expansion would be met by force. The natural next target for German expansion was Poland, whose access to the Baltic sea had been carved out of West Prussia by the Versailles Treaty, which made East Prussia an exclave. The main port of the area, Danzig, had been made into a free city-state under Polish influence guaranteed by the League of Nations, a stark reminder to German nationalists of the Napoleonic free city that had been established after French Emperor Napoleon I's crushing victory over Prussia in 1807.
After taking power, the Nazi government made efforts to establish friendly relations with Poland, which resulted in the signing of the ten-year German–Polish Non-Aggression Pact with the Piłsudski regime in 1934. In 1938, Poland participated in the dismemberment of Czechoslovakia by annexing Zaolzie. In 1939, Hitler claimed extraterritoriality for the Reichsautobahn Berlin-Königsberg and a change in Danzig's status in exchange for promises of territory in Poland's neighbours and a 25-year extension of the non-aggression pact. Poland refused for fear of losing its de facto access to the sea, subjugation as a German satellite state or client state and future further German demands. In August 1939, Hitler delivered an ultimatum to Poland on Danzig's status.
Polish alliance with Entente
In March 1939, Britain and France guaranteed the independence of Poland. Hitler's claims in the summer of 1939 on Danzig and the Polish Corridor provoked yet another international crisis. On August 25, Britain signed the Polish-British Common Defence Pact.
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
Nominally, the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression treaty between Germany and the Soviet Union and was signed in Moscow on August 23, 1939 by Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop.
In 1939, neither Germany nor the Soviet Union was ready to go to war with each other. The Soviet Union had lost territory to Poland in 1920. Although officially called a "non-aggression treaty," the pact included a secret protocol in which the independent countries of Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland and Romania were divided into spheres of interest between both the parties. The secret protocol explicitly assumed "territorial and political rearrangements" in those areas.
All of the mentioned countries were invaded, occupied, or forced to cede part of their territory by the Soviet Union, Germany or both.
Declarations of war
Invasion of Poland
Between 1919 and 1939, Poland had pursued a policy of balancing between the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany and agreed to non-aggression pacts with both. In early 1939, Germany demanded for Poland to join the Anti-Comintern Pact as a satellite state of Germany. Poland, fearing a loss of independence, refused. Hitler admitted to his generals on 23 May 1939 that his reason for invading Poland was not Danzig: "Danzig is not the issue at stake. It is a matter of extending our living space in the East...". To deter Hitler, Britain and France announced that an invasion would mean war and tried to convince the Soviet Union to join in this deterrence. The Soviets, however, gained control of the Baltic states and part of Poland by allying with Germany by the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact in August 1939. London's attempt at deterrence failed, but Hitler did not expect a wider war. Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939 and rejected the British and French demands for it to withdraw, which resulted in both to declare war on September 3, 1939, in accordance with the defence treaties with Poland that they had signed and publicly announced.
Invasion of Soviet Union
Germany attacked the Soviet Union in June 1941. Hitler believed that the Soviet Union could be defeated in a fast and relentless assault that capitalised on the Soviets' ill-prepared state and hoped that success there would bring Britain to the negotiation table, which would end the war altogether.
Attacks on Pearl Harbor, the Philippines, British Malaya, Singapore and Hong Kong
The US government and general public in general had been supportive of China, condened European colonialist policies and Japan and promoted the so-called Open Door Policy. Many Americans viewed the Japanese as an aggressive and/or inferior race. The Nationalist government of Chiang Kai-shek held friendly relations with the US, which opposed Japan's invasion of China in 1937 and considered it a violation of international law and of the sovereignty of the Republic of China. The US offered the Nationalist government diplomatic, economic and military assistance during its war against Japan. Diplomatic friction between the United States and Japan manifested itself in events like the Panay incident in 1937 and the Allison incident in 1938.
Reacting to Japanese pressure on French authorities of French Indochina to stop trade with China, the US began restricting trade with Japan in July 1940. The end of all oil shipments in 1941 was decisive since the Americans, British and Dutch provided almost all of Japan's oil. In September 1940, the Japanese invaded Vichy French Indochina and occupied Tonkin to prevent China from importing arms and fuel through French Indochina along the Sino-Vietnamese Railway from the port of Haiphong through Hanoi to Kunming, in Yunnan. The US decided that the Japanese had now gone too far and decided to force a rollback of its gains. In 1940 and 1941, the Americans and the Chinese decided to organise a volunteer squadron of American planes and pilots to attack the Japanese from Chinese bases. Known as the Flying Tigers, the unit was commanded by Claire Lee Chennault. Its first combat came two weeks after the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Taking advantage of the situation, Thailand launched the Franco-Thai War in October 1940. Japan stepped in as a mediator in the war in May 1941 and allowed its ally to occupy the bordering provinces in Cambodia and Laos. In July 1941, as Operation Barbarossa had effectively neutralised the Soviet threat, the faction of the Japanese military junta supporting the "Southern Strategy" pushed through the occupation of the rest of French Indochina.
The US reacted by seeking to bring the Japanese war effort to a complete halt by imposing a full embargo on all trade between the United States to Japan on August 18, 1941 and demanding a Japanese withdrawal of all troops from China and Indochina. Japan was dependent on the United States for 80% of its oil, which resulted in an economic and military crisis for Japan since it could not continue the war effort against China without access to petroleum and oil products.
On 7 December 1941, without a declaration of war, the Imperial Japanese Navy attacked Pearl Harbor with the aim of destroying the main American battle fleet at anchor. Meanwhile, other Japanese forces attacked the American-held Philippines and the British Empire in Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong. The following day, an official Japanese declaration of war on the United States and the British Empire was printed on the front page of all Japanese newspapers' evening editions. International time differences caused the announcement to take place between midnight and 3 a.m. on 8 December in North America and at about 8 a.m. on 8 December in the United Kingdom.
Canada declared war on Japan on the evening of 7 December, and a royal proclamation affirmed the declaration the next day. The British declared war on Japan on the morning of 8 December and specifically identified the attacks on Malaya, Singapore and Hong Kong as the cause but omitted any mention of Pearl Harbor. The United States declared war upon Japan on the afternoon of 8 December, nine hours after the United Kingdom, and identified only "unprovoked acts of war against the Government and the people of the United States of America" as the cause.
Four days later, the US was brought into the European war when on December 11, 1941, Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy declared war on the United States. Hitler chose to declare that the Tripartite Pact required Germany to follow Japan's declaration of war although American destroyers escorting convoys and German U-boats had been de facto at war in the Battle of the Atlantic. The declaration of war effectively ended US isolationist sentiment, and the country immediately reciprocated and so formally entered the war in Europe.