Fatty acid metabolism consists of catabolic processes that generate energy, and anabolic processes that create biologically important molecules (triglycerides, phospholipids, second messengers, local hormones and ketone bodies).
Fatty acids are a family of molecules classified within the lipid macronutrient class. One role of fatty acids in animal metabolism is energy production, captured in the form of adenosine triphosphate
(ATP). When compared to other macronutrient classes (carbohydrates and
protein), fatty acids yield the most ATP on an energy per gram basis,
when they are completely oxidized to CO2 and water by beta oxidation and the citric acid cycle. Fatty acids (mainly in the form of triglycerides)
are therefore the foremost storage form of fuel in most animals, and to
a lesser extent in plants. In addition, fatty acids are important
components of the phospholipids that form the phospholipid bilayers out of which all the membranes of the cell are constructed (the cell wall, and the membranes that enclose all the organelles within the cells, such as the nucleus, the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus). Fatty acids can also be cleaved, or partially cleaved, from their chemical attachments in the cell membrane to form second messengers within the cell, and local hormones in the immediate vicinity of the cell. The prostaglandins made from arachidonic acid stored in the cell membrane, are probably the most well known group of these local hormones.
Fatty acid catabolism
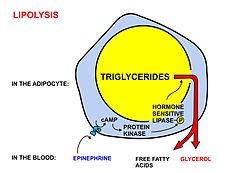
A diagrammatic illustration of the process of lipolysis (in a fat cell) induced by high epinephrine and low insulin levels in the blood. Epinephrine binds to a beta-adrenergic receptor in the cell membrane of the adipocyte, which causes cAMP to be generated inside the cell. The cAMP activates a protein kinase, which phosphorylates and thus, in turn, activates a hormone-sensitive lipase
in the fat cell. This lipase cleaves free fatty acids from their
attachment to glycerol in the fat stored in the fat droplet of the
adipocyte. The free fatty acids and glycerol are then released into the
blood. However more recent studies have shown that adipose triglyceride lipase has to first convert triacylglycerides to diacylglycerides, and that hormone-sensitive lipase converts the diacylglycerides to monoglycerides and free fatty acids. Monoglycerides are hydrolyzed by monoglyceride lipase.[3] The activity of hormone sensitive lipase is regulated by the circulation hormones insulin, glucagon, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, as shown in the diagram.
A diagrammatic illustration of the transport of free fatty acids in the blood attached to plasma albumin, its diffusion across the cell membrane using a protein transporter, and its activation, using ATP, to form acyl-CoA in the cytosol.
The illustration is, for diagrammatic purposes, of a 12 carbon fatty
acid. Most fatty acids in human plasma are 16 or 18 carbon atoms long.
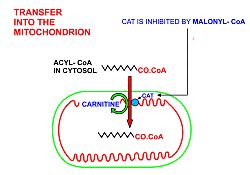
A diagrammatic illustration of the transfer of an acyl-CoA molecule across the inner membrane of the mitochondrion by carnitine-acyl-CoA transferase
(CAT). The illustrated acyl chain is, for diagrammatic purposes, only
12 carbon atoms long. Most fatty acids in human plasma are 16 or 18
carbon atoms long. CAT is inhibited by high concentrations of malonyl-CoA (the first committed step in fatty acid synthesis)
in the cytoplasm. This means that fatty acid synthesis and fatty acid
catabolism cannot occur simultaneously in any given cell.
A diagrammatic illustration of the process of the beta-oxidation
of an acyl-CoA molecule in the mitochodrial matrix. During this process
an acyl-CoA molecule which is 2 carbons shorter than it was at the
beginning of the process is formed. Acetyl-CoA, water and 5 ATP molecules are the other products of each beta-oxidative event, until the entire acyl-CoA molecule has been reduced to a set of acetyl-CoA molecules.
- Lipolysis, the removal of the fatty acid chains from the glycerol to which they are bound in their storage form as triglycerides (or fats), is carried out by lipases. These lipases are activated by high epinephrine and glucagon levels in the blood (or norepinephrine secreted by sympathetic nerves in adipose tissue), caused by declining blood glucose levels after meals, which simultaneously lowers the insulin level in the blood.
- Once freed from glycerol, the free fatty acids enter the blood, which transports them, attached to plasma albumin, throughout the body.
- Long chain free fatty acids enter the metabolizing cells (i.e. most living cells in the body except red blood cells and neurons in the central nervous system) through specific transport proteins, such as the SLC27 family fatty acid transport protein. Red blood cells do not contain mitochondria and are therefore incapable of metabolizing fatty acids; the tissues of the central nervous system cannot use fatty acids, despite containing mitochondria, because long chain fatty acids (as opposed to medium chain fatty acids) cannot cross the blood brain barrier into the interstitial fluids that bathe these cells.
- Once inside the cell long-chain-fatty-acid—CoA ligase catalyzes the reaction between a fatty acid molecule with ATP (which is broken down to AMP and inorganic pyrophosphate) to give a fatty acyl-adenylate, which then reacts with free coenzyme A to give a fatty acyl-CoA molecule.
- In order for the acyl-CoA to enter the mitochondrion the carnitine shuttle is used:
- Acyl-CoA is transferred to the hydroxyl group of carnitine by carnitine palmitoyltransferase I, located on the cytosolic faces of the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes.
- Acyl-carnitine is shuttled inside by a carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase, as a carnitine is shuttled outside.
- Acyl-carnitine is converted back to acyl-CoA by carnitine palmitoyltransferase II, located on the interior face of the inner mitochondrial membrane. The liberated carnitine is shuttled back to the cytosol, as an acyl-CoA is shuttled into the matrix.
- Beta oxidation, in the mitochondrial matrix, then cuts the long carbon chains of the fatty acids (in the form of acyl-CoA molecules) into a series of two-carbon (acetate) units, which, combined with co-enzyme A, form molecules of acetyl CoA, which condense with oxaloacetate to form citrate at the "beginning" of the citric acid cycle. It is convenient to think of this reaction as marking the "starting point" of the cycle, as this is when fuel - acetyl-CoA - is added to the cycle, which will be dissipated as CO2 and H2O with the release of a substantial quantity of energy captured in the form of ATP, during the course of each turn of the cycle.
- Briefly, the steps in beta oxidation (the initial breakdown of free fatty acids into acetyl-CoA) are as follows:
- Dehydrogenation by acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, yielding 1 FADH2
- Hydration by enoyl-CoA hydratase
- Dehydrogenation by 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, yielding 1 NADH + H+
- Cleavage by thiolase, yielding 1 acetyl-CoA and a fatty acid that has now been shortened by 2 carbons (forming a new, shortened acyl-CoA)
- This beta oxidation reaction is repeated until the fatty acid has been completely reduced to acetyl-CoA or, in, the case of fatty acids with odd numbers of carbon atoms, acetyl-CoA and 1 molecule of propionyl-CoA per molecule of fatty acid. Each beta oxidative cut of the acyl-CoA molecule yields 5 ATP molecules.
- The acetyl-CoA produced by beta oxidation enters the citric acid cycle in the mitochondrion by combining with oxaloacetate to form citrate. This results in the complete combustion of the acetyl-CoA to CO2 and water. The energy released in this process is captured in the form of 1 GTP and 11 ATP molecules per acetyl-CoA molecule oxidized. This is the fate of acetyl-CoA wherever beta oxidation of fatty acids occurs, except under certain circumstances in the liver.
The glycerol released by lipase action is phosphorylated by glycerol kinase in the liver (the only tissue in which this reaction can occur), and the resulting glycerol 3-phosphate is oxidized to dihydroxyacetone phosphate. The glycolytic enzyme triose phosphate isomerase converts this compound to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, which is oxidized via glycolysis, or converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis.
Fatty acids as an energy source
Example of an unsaturated fat triglyceride. Left part: glycerol, right part from top to bottom: palmitic acid, oleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid. Chemical formula: C55H98O6
Fatty acids, stored as triglycerides in an organism, are an important source of energy because they are both reduced and anhydrous. The energy yield from a gram of fatty acids is approximately 9 kcal (37 kJ), compared to 4 kcal (17 kJ) for carbohydrates. Since the hydrocarbon portion of fatty acids is hydrophobic, these molecules can be stored in a relatively anhydrous (water-free) environment. Carbohydrates, on the other hand, are more highly hydrated. For example, 1 g of glycogen can bind approximately 2 g of water, which translates to 1.33 kcal/g (4 kcal/3 g). This means that fatty acids can hold more than six times the amount of energy per unit of storage mass. Put another way, if the human body relied on carbohydrates to store energy, then a person would need to carry 31 kg (67.5 lb) of hydrated glycogen to have the energy equivalent to 4.6 kg (10 lb) of fat.
Hibernating animals provide a good example for utilizing fat reserves as fuel. For example, bears hibernate for about 7 months, and, during this entire period, the energy is derived from degradation of fat stores. Migrating birds similarly build up large fat reserves before embarking on their intercontinental journeys.
Thus the young adult human’s fat stores average between about 10–20 kg, but varies greatly depending on age, gender, and individual disposition. By contrast the human body stores only about 400 g of glycogen, of which 300 g is locked inside the skeletal muscles and is unavailable to the body as a whole. The 100 g or so of glycogen stored in the liver is depleted within one day of starvation. Thereafter the glucose that is released into the blood by the liver for general use by the body tissues, has to be synthesized from the glucogenic amino acids and a few other gluconeogenic substrates, which do not include fatty acids. Please note however that lipolysis releases glycerol which can enter the pathway of gluconeogenesis.
Animals and plants synthesize carbohydrates from both glycerol and fatty acids
Fatty acids are broken down to acetyl-CoA by means of beta oxidation inside the mitochondria, whereas fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA outside the mitochondria, in the cytosol. The two pathways are distinct, not only in where they occur, but also in the reactions that occur, and the substrates that are used. The two pathways are mutually inhibitory, preventing the acetyl-CoA produced by beta-oxidation from entering the synthetic pathway via the acetyl-CoA carboxylase reaction. It can also not be converted to pyruvate as the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex reaction is irreversible. Instead the acetyl-CoA produced by the beta-oxidation of fatty acids condenses with oxaloacetate, to enter the citric acid cycle. During each turn of the cycle, two carbon atoms leave the cycle as CO2 in the decarboxylation reactions catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Thus each turn of the citric acid cycle oxidizes an acetyl-CoA unit while regenerating the oxaloacetate molecule with which the acetyl-CoA had originally combined to form citric acid. The decarboxylation reactions occur before malate is formed in the cycle.[1] Only plants possess the enzymes to convert acetyl-CoA into oxaloacetate from which malate can be formed to ultimately be converted to glucose.However acetyl-CoA can be converted to acetoacetate, which can decarboxylate to acetone (either spontaneously, or by acetoacetate decarboxylase). It can then be further metabolized to isopropanol which is excreted in breath/urine, or by CYP2E1 into hydroxyacetone (acetol). Acetol can be converted to propylene glycol. This converts to formate and acetate (the latter converting to glucose), or pyruvate (by two alternative enzymes), or propionaldehyde, or to L-lactaldehyde then L-lactate (the common lactate isomer). Another pathway turns acetol to methylglyoxal, then to pyruvate, or to D-lactaldehyde (via S-D-lactoyl-glutathione or otherwise) then D-lactate. D-lactate metabolism (to glucose) is slow or impaired in humans, so most of the D-lactate is excreted in the urine; thus D-lactate derived from acetone can contribute significantly to the metabolic acidosis associated with ketosis or isopropanol intoxication. L-Lactate can complete the net conversion of fatty acids into glucose. The first experiment to show conversion of acetone to glucose was carried out in 1951. This, and further experiments used carbon isotopic labelling. Up to 11% of the glucose can be derived from acetone during starvation in humans.
The glycerol released into the blood during the lipolysis of triglycerides in adipose tissue can only be taken up by the liver. Here it is converted into glycerol 3-phosphate by the action of glycerol kinase which hydrolyzes one molecule of ATP per glycerol molecule which is phosphorylated. Glycerol 3-phosphate is then oxidized to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, which is, in turn, converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate by the enzyme triose phosphate isomerase. From here the three carbon atoms of the original glycerol can be oxidized via glycolysis, or converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis.
Other functions and uses of fatty acids
Intracellular signaling
Structure of the diglyceride 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-glycerol
Fatty acids are an integral part of the phospholipids that make up the bulk of the plasma membranes, or cell membranes, of cells. These phospholipids can be cleaved into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3) through hydrolysis of the phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), by the cell membrane bound enzyme phospholipase C (PLC).
An example of a diacyl-glycerol shown on the right. This DAG is 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-glycerol, which contains side-chains derived from palmitic acid and oleic acid. Diacylglycerols can also have many other combinations of fatty acids attached at either the C-1 and C-2 positions or the C-1 and C-3 positions of the glycerol molecule. 1,2 disubstituted glycerols are always chiral, 1,3 disubstituted glycerols are chiral if the substituents are different from each other.
PIP2 cleavage to IP3 and DAG. IP3
initiates intracellular calcium release, while DAG activates PKC
(protein kinase C). Note: PLC (phospholipase C) is not an intermediate,
as possibly suggested by the diagram, but is the enzyme that catalyzes
the IP3/DAG separation.
Diacylglycerol and IP3 act transiently because both are rapidly metabolized. This is important as their message function should not linger after the message has been” received” by their target molecules. DAG can be phosphorylated to phosphatidate or it can be it can be hydrolysed to glycerol and its constituent fatty acids. IP3 is rapidly converted into derivatives that do not open calcium ion channels.
Eicosanoid paracrine hormones
The prostaglandins are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are enzymatically derived from arachidonic acid a 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid. Every prostaglandin therefore contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and form the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives.
The prostaglandins are synthesized in the cell membrane by the cleavage of arachidonate from the phospholipids that make up the membrane. This is catalyzed either by phospholipase A2 acting directly on a membrane phospholipid, or by a lipase acting on DAG (diacyl-glycerol). The arachidonate is then acted upon by the cyclooxygenase component of prostaglandin synthase. This forms a cyclopentane ring in roughly the middle of the fatty acid chain. The reaction also adds 4 oxygen atoms derived from two molecules of O2. The resulting molecule is prostaglandin G2 which is converted by the hydroperoxidase component of the enzyme complex into prostaglandin H2. This highly unstable compound is rapidly transformed into other prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxanes. These are then released into the interstitial fluids surrounding the cells that have manufactured the eicosanoid hormone.
If arachidonate is acted upon by a lipoxygenase instead of cyclooxygenase, Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids and leukotrienes are formed. They also act as local hormones.
Prostaglandins were originally believed to leave the cells via passive diffusion because of their high lipophilicity. The discovery of the prostaglandin transporter (PGT, SLCO2A1), which mediates the cellular uptake of prostaglandin, demonstrated that diffusion alone cannot explain the penetration of prostaglandin through the cellular membrane. The release of prostaglandin has now also been shown to be mediated by a specific transporter, namely the multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4, ABCC4), a member of the ATP-binding cassette transporter superfamily. Whether MRP4 is the only transporter releasing prostaglandins from the cells is still unclear.
The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities. A given prostaglandin may have different and even opposite effects in different tissues. The ability of the same prostaglandin to stimulate a reaction in one tissue and inhibit the same reaction in another tissue is determined by the type of receptor to which the prostaglandin binds. They act as autocrine or paracrine factors with their target cells present in the immediate vicinity of the site of their secretion. Prostaglandins differ from endocrine hormones in that they are not produced at a specific site but in many places throughout the human body.
Prostaglandins have two derivatives: prostacyclins and thromboxanes. Prostacyclins are powerful locally acting vasodilators and inhibit the aggregation of blood platelets. Through their role in vasodilation, prostacyclins are also involved in inflammation. They are synthesized in the walls of blood vessels and serve the physiological function of preventing needless clot formation, as well as regulating the contraction of smooth muscle tissue. Conversely, thromboxanes (produced by platelet cells) are vasoconstrictors and facilitate platelet aggregation. Their name comes from their role in clot formation (thrombosis).
Dietary sources of fatty acids, their digestion, absorption, transport in the blood and storage
Dietary fats are emulsified in the duodenum by soaps in the form of bile salts and phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine. The fat droplets thus formed can be attacked by pancreatic lipase.
Structure of a bile acid (cholic acid), represented in the standard form, a semi-realistic 3D form, and a diagrammatic 3D form
Diagrammatic
illustration of mixed micelles formed in the duodenum in the presence
of bile acids (e.g. cholic acid) and the digestion products of fats, the
fat soluble vitamins and cholesterol.
A significant proportion of the fatty acids in the body are obtained from the diet, in the form of triglycerides of either animal or plant origin. The fatty acids in the fats obtained from land animals tend to be saturated, whereas the fatty acids in the triglycerides of fish and plants are often polyunsaturated and therefore present as oils.
These triglycerides, cannot be absorbed by the intestine. They are broken down into mono- and di-glycerides plus free fatty acids (but no free glycerol) by pancreatic lipase, which forms a 1:1 complex with a protein called colipase (also a constituent of pancreatic juice), which is necessary for its activity. The activated complex can work only at a water-fat interface. Therefore, it is essential that fats are first emulsified by bile salts for optimal activity of these enzymes. The digestion products consisting of a mixture of tri-, di- and monoglycerides and free fatty acids, which, together with the other fat soluble contents of the diet (e.g. the fat soluble vitamins and cholesterol) and bile salts form mixed micelles, in the watery duodenal contents (see diagrams on the right).
The contents of these micelles (but not the bile salts) enter the enterocytes (epithelial cells lining the small intestine) where they are resynthesized into triglycerides, and packaged into chylomicrons which are released into the lacteals (the capillaries of the lymph system of the intestines). These lacteals drain into the thoracic duct which empties into the venous blood at the junction of the left jugular and left subclavian veins on the lower left hand side of the neck. This means that the fat soluble products of digestion are discharged directly into the general circulation, without first passing through the liver, as all other digestion products do. The reason for this peculiarity is unknown.
A schematic diagram of a chylomicron.
The chylomicrons circulate throughout the body, giving the blood plasma a milky, or creamy appearance after a fatty meal. Lipoprotein lipase on the endothelial surfaces of the capillaries, especially in adipose tissue, but to a lesser extent also in other tissues, partially digests the chylomicrons into free fatty acids, glycerol and chylomicron remnants. The fatty acids are absorbed by the adipocytes, but the glycerol and chylomicron remnants remain in the blood plasma, ultimately to be removed from the circulation by the liver. The free fatty acids released by the digestion of the chylomicrons are absorbed by the adipocytes, where they are resynthesized into triglycerides using glycerol derived from glucose in the glycolytic pathway. These triglycerides are stored, until needed for the fuel requirements of other tissues, in the fat droplet of the adipocyte.
The liver absorbs a proportion of the glucose from the blood in the portal vein coming from the intestines. After the liver has replenished its glycogen stores (which amount to only about 100 g of glycogen when full) much of the rest of the glucose is converted into fatty acids as described below. These fatty acids are combined with glycerol to form triglycerides which are packaged into droplets very similar to chylomicrons, but known as very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL). These VLDL droplets are handled in exactly the same manner as chylomicrons, except that the VLDL remnant is known as an intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), which is capable of scavenging cholesterol from the blood. This converts IDL into low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which is taken up by cells that require cholesterol for incorporation into their cell membranes or for synthetic purposes (e.g. the formation of the steroid hormones). The remainder of the LDLs is removed by the liver.
Adipose tissue and lactating mammary glands also take up glucose from the blood for conversion into triglycerides. This occurs in the same way as it does in the liver, except that these tissues do not release the triglycerides thus produced as VLDL into the blood. Adipose tissue cells store the triglycerides in their fat droplets, ultimately to release them again as free fatty acids and glycerol into the blood (as described above), when the plasma concentration of insulin is low, and that of glucagon and/or epinephrine is high. Mammary glands discharge the fat (as cream fat droplets) into the milk that they produce under the influence of the anterior pituitary hormone prolactin.
All cells in the body need to manufacture and maintain their membranes and the membranes of their organelles. Whether they rely for this entirely on free fatty acids absorbed from the blood, or are able to synthesize their own fatty acids from the blood glucose, is not known. The cells of the central nervous system will almost certainly have the capability of manufacturing their own fatty acids, as these molecules cannot reach them through the blood brain barrier, while, on the other hand, no cell in the body can manufacture the required essential fatty acids which have to be obtained from the diet and delivered to each cell via the blood.
Fatty acid synthesis
Synthesis of saturated fatty acids via Fatty Acid Synthase II in E. coli
Much like beta-oxidation, straight-chain fatty acid synthesis occurs via the six recurring reactions shown below, until the 16-carbon palmitic acid is produced.
The diagrams presented show how fatty acids are synthesized in microorganisms and list the enzymes found in Escherichia coli. These reactions are performed by fatty acid synthase II (FASII), which in general contain multiple enzymes that act as one complex. FASII is present in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, and parasites, as well as in mitochondria.
In animals, as well as some fungi such as yeast, these same reactions occur on fatty acid synthase I (FASI), a large dimeric protein that has all of the enzymatic activities required to create a fatty acid. FASI is less efficient than FASII; however, it allows for the formation of more molecules, including "medium-chain" fatty acids via early chain termination. Enzymes, acyltransferases and transacylases, incorporate fatty acids in phospholipids, triacylglycerols, etc. by transferring fatty acids between an acyl acceptor and donor. They also have the job of synthesizing bioactive lipids as well as their precursor molecules.
Once a 16:0 carbon fatty acid has been formed, it can undergo a number of modifications, resulting in desaturation and/or elongation. Elongation, starting with stearate (18:0), is performed mainly in the ER by several membrane-bound enzymes. The enzymatic steps involved in the elongation process are principally the same as those carried out by FAS, but the four principal successive steps of the elongation are performed by individual proteins, which may be physically associated.
Note that during fatty synthesis the reducing agent is NADPH, whereas NAD is the oxidizing agent in beta-oxidation (the breakdown of fatty acids to acetyl-CoA). This difference exemplifies a general principle that NADPH is consumed during biosynthetic reactions, whereas NADH is generated in energy-yielding reactions. (Thus NADPH is also required for the synthesis of cholesterol from acetyl-CoA; while NADH is generated during glycolysis.) The source of the NADPH is two-fold. When malate is oxidatively decarboxylated by “NADP+-linked malic enzyme" pyruvate, CO2 and NADPH are formed. NADPH is also formed by the pentose phosphate pathway which converts glucose into ribose, which can be used in synthesis of nucleotides and nucleic acids, or it can be catabolized to pyruvate.
Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids
In humans, fatty acids are formed from carbohydrates predominantly in the liver and adipose tissue, as well as in the mammary glands during lactation. The cells of the central nervous system probably also make most of the fatty acids needed for the phospholipids of their extensive membranes from glucose, as blood-born fatty acids cannot cross the blood brain barrier to reach these cells. However, how the essential fatty acids, which mammals cannot synthesize themselves, but are nevertheless important components of cell membranes (and other functions described above) reach them is unknown.The pyruvate produced by glycolysis is an important intermediary in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids and cholesterol. This occurs via the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA in the mitochondrion. However, this acetyl CoA needs to be transported into cytosol where the synthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol occurs. This cannot occur directly. To obtain cytosolic acetyl-CoA, citrate (produced by the condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate) is removed from the citric acid cycle and carried across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the cytosol. There it is cleaved by ATP citrate lyase into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate. The oxaloacetate is returned to mitochondrion as malate (and then converted back into oxaloacetate to transfer more acetyl-CoA out of the mitochondrion). The cytosolic acetyl-CoA is carboxylated by acetyl CoA carboxylase into malonyl CoA, the first committed step in the synthesis of fatty acids.
Regulation of fatty acid synthesis
Acetyl-CoA is formed into malonyl-CoA by acetyl-CoA carboxylase, at which point malonyl-CoA is destined to feed into the fatty acid synthesis pathway. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the point of regulation in saturated straight-chain fatty acid synthesis, and is subject to both phosphorylation and allosteric regulation. Regulation by phosphorylation occurs mostly in mammals, while allosteric regulation occurs in most organisms. Allosteric control occurs as feedback inhibition by palmitoyl-CoA and activation by citrate. When there are high levels of palmitoyl-CoA, the final product of saturated fatty acid synthesis, it allosterically inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase to prevent a build-up of fatty acids in cells. Citrate acts to activate acetyl-CoA carboxylase under high levels, because high levels indicate that there is enough acetyl-CoA to feed into the Krebs cycle and produce energy.High plasma levels of insulin in the blood plasma (e.g. after meals) cause the dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, thus promoting the formation of malonyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA, and consequently the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, while epinephrine and glucagon (released into the blood during starvation and exercise) cause the phosphorylation of this enzyme, inhibiting lipogenesis in favor of fatty acid oxidation via beta-oxidation.
Disorders
Disorders of fatty acid metabolism can be described in terms of, for example, hypertriglyceridemia (too high level of triglycerides), or other types of hyperlipidemia. These may be familial or acquired.Familial types of disorders of fatty acid metabolism are generally classified as inborn errors of lipid metabolism. These disorders may be described as fatty oxidation disorders or as a lipid storage disorders, and are any one of several inborn errors of metabolism that result from enzyme defects affecting the ability of the body to oxidize fatty acids in order to produce energy within muscles, liver, and other cell types.