In the philosophy of mind, mind–body dualism denotes either the view that mental phenomena are non-physical, or that the mind and body are distinct and separable. Thus, it encompasses a set of views about the relationship between mind and matter, as well as between subject and object, and is contrasted with other positions, such as physicalism and enactivism, in the mind–body problem.
Aristotle shared Plato's view of multiple souls and further elaborated a hierarchical arrangement, corresponding to the distinctive functions of plants, animals, and people: a nutritive soul of growth and metabolism that all three share; a perceptive soul of pain, pleasure, and desire that only people and other animals share; and the faculty of reason that is unique to people only. In this view, a soul is the hylomorphic form of a viable organism, wherein each level of the hierarchy formally supervenes upon the substance of the preceding level. For Aristotle, the first two souls, based on the body, perish when the living organism dies, whereas remains an immortal and perpetual intellective part of mind. For Plato, however, the soul was not dependent on the physical body; he believed in metempsychosis, the migration of the soul to a new physical body. It has been considered a form of reductionism by some philosophers, since it enables the tendency to ignore very big groups of variables by its assumed association with the mind or the body, and not for its real value when it comes to explaining or predicting a studied phenomenon.
Dualism is closely associated with the thought of René Descartes (1641), which holds that the mind is a nonphysical—and therefore, non-spatial—substance. Descartes clearly identified the mind with consciousness and self-awareness and distinguished this from the brain as the seat of intelligence. Hence, he was the first to formulate the mind–body problem in the form in which it exists today. Dualism is contrasted with various kinds of monism. Substance dualism is contrasted with all forms of materialism, but property dualism may be considered a form of emergent materialism or non-reductive physicalism in some sense.
Types
Ontological dualism makes dual commitments about the nature of existence as it relates to mind and matter, and can be divided into three different types:
- Substance dualism asserts that mind and matter are fundamentally distinct kinds of foundations.
- Property dualism suggests that the ontological distinction lies in the differences between properties of mind and matter (as in emergentism).
- Predicate dualism claims the irreducibility of mental predicates to physical predicates.
Substance or Cartesian dualism
Substance dualism, or Cartesian dualism, most famously defended by René Descartes, argues that there are two kinds of foundation: mental and physical. This philosophy states that the mental can exist outside of the body, and the body cannot think. Substance dualism is important historically for having given rise to much thought regarding the famous mind–body problem.
Copernican Revolution and the scientific discoveries of the 17th century reinforced the belief that the scientific method was the unique way of knowledge. Bodies were seen as biological organisms to be studied in their constituent parts (materialism) by means of anatomy, physiology, biochemistry and physics (reductionism). The mind-body dualism remained the biomedical paradigm and model for the following three centuries.
Substance dualism is a philosophical position compatible with most theologies which claim that immortal souls occupy an independent realm of existence distinct from that of the physical world. In contemporary discussions of substance dualism, philosophers propose dualist positions that are significantly less radical than Descartes's: for instance, a position defended by William Hasker called Emergent Dualism seems, to some philosophers, more intuitively attractive than the substance dualism of Descartes in virtue of its being in line with (inter alia) evolutionary biology.
Property dualism
Property dualism asserts that an ontological distinction lies in the differences between properties of mind and matter, and that consciousness may ontologically irreducible to neurobiology and physics. It asserts that when matter is organized in the appropriate way (i.e., in the way that living human bodies are organized), mental properties emerge. Hence, it is a sub-branch of emergent materialism. What views properly fall under the property dualism rubric is itself a matter of dispute. There are different versions of property dualism, some of which claim independent categorisation.
Non-reductive physicalism is a form of property dualism in which it is asserted that all mental states are causally reducible to physical states. One argument for this has been made in the form of anomalous monism expressed by Donald Davidson, where it is argued that mental events are identical to physical events, however, relations of mental events cannot be described by strict law-governed causal relationships. Another argument for this has been expressed by John Searle, who is the advocate of a distinctive form of physicalism he calls biological naturalism. His view is that although mental states are ontologically irreducible to physical states, they are causally reducible. He has acknowledged that "to many people" his views and those of property dualists look a lot alike, but he thinks the comparison is misleading.
Epiphenomenalism
Epiphenomenalism is a form of property dualism, in which it is asserted that one or more mental states do not have any influence on physical states (both ontologically and causally irreducible). It asserts that while material causes give rise to sensations, volitions, ideas, etc., such mental phenomena themselves cause nothing further: they are causal dead-ends. This can be contrasted to interactionism, on the other hand, in which mental causes can produce material effects, and vice versa.
Predicate dualism
Predicate dualism is a view espoused by such non-reductive physicalists as Donald Davidson and Jerry Fodor, who maintain that while there is only one ontological category of substances and properties of substances (usually physical), the predicates that we use to describe mental events cannot be redescribed in terms of (or reduced to) physical predicates of natural languages.
Predicate dualism is most easily defined as the negation of predicate monism. Predicate monism can be characterized as the view subscribed to by eliminative materialists, who maintain that such intentional predicates as believe, desire, think, feel, etc., will eventually be eliminated from both the language of science and from ordinary language because the entities to which they refer do not exist. Predicate dualists believe that so-called "folk psychology," with all of its propositional attitude ascriptions, is an ineliminable part of the enterprise of describing, explaining, and understanding human mental states and behavior.
For example, Davidson subscribes to anomalous monism, according to which there can be no strict psychophysical laws which connect mental and physical events under their descriptions as mental and physical events. However, all mental events also have physical descriptions. It is in terms of the latter that such events can be connected in law-like relations with other physical events. Mental predicates are irreducibly different in character (rational, holistic, and necessary) from physical predicates (contingent, atomic, and causal).
Dualist views of mental causation
This part is about causation between properties and states of the thing under study, not its substances or predicates. Here a state is the set of all properties of what's being studied. Thus each state describes only one point in time.
Interactionism
Interactionism is the view that mental states, such as beliefs and desires, causally interact with physical states. This is a position which is very appealing to common-sense intuitions, notwithstanding the fact that it is very difficult to establish its validity or correctness by way of logical argumentation or empirical proof. It seems to appeal to common-sense because we are surrounded by such everyday occurrences as a child's touching a hot stove (physical event) which causes him to feel pain (mental event) and then yell and scream (physical event) which causes his parents to experience a sensation of fear and protectiveness (mental event) and so on.
Non-reductive physicalism
Non-reductive physicalism is the idea that while mental states are physical they are not reducible to physical properties, in that an ontological distinction lies in the differences between the properties of mind and matter. According to non-reductive physicalism all mental states are causally reducible to physical states where mental properties map to physical properties and vice versa. A prominent form of non-reductive physicalism, called anomalous monism, was first proposed by Donald Davidson in his 1970 paper "Mental events", in which he claims that mental events are identical with physical events, and that the mental is anomalous, i.e. under their mental descriptions these mental events are not regulated by strict physical laws.
Epiphenomenalism
Epiphenomenalism states that all mental events are caused by a physical event and have no physical consequences, and that one or more mental states do not have any influence on physical states. So, the mental event of deciding to pick up a rock ("M1") is caused by the firing of specific neurons in the brain ("P1"). When the arm and hand move to pick up the rock ("P2") this is not caused by the preceding mental event M1, nor by M1 and P1 together, but only by P1. The physical causes are in principle reducible to fundamental physics, and therefore mental causes are eliminated using this reductionist explanation. If P1 causes both M1 and P2, there is no overdetermination in the explanation for P2.
The idea that even if the animal were conscious nothing would be added to the production of behavior, even in animals of the human type, was first voiced by La Mettrie (1745), and then by Cabanis (1802), and was further explicated by Hodgson (1870) and Huxley (1874). Jackson gave a subjective argument for epiphenomenalism, but later rejected it and embraced physicalism.
Parallelism
Psychophysical parallelism is a very unusual view about the interaction between mental and physical events which was most prominently, and perhaps only truly, advocated by Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz. Like Malebranche and others before him, Leibniz recognized the weaknesses of Descartes' account of causal interaction taking place in a physical location in the brain. Malebranche decided that such a material basis of interaction between material and immaterial was impossible and therefore formulated his doctrine of occasionalism, stating that the interactions were really caused by the intervention of God on each individual occasion. Leibniz's idea is that God has created a pre-established harmony such that it only seems as if physical and mental events cause, and are caused by, one another. In reality, mental causes only have mental effects and physical causes only have physical effects. Hence, the term parallelism is used to describe this view.
Occasionalism
Occasionalism is a philosophical doctrine about causation which says that created substances cannot be efficient causes of events. Instead, all events are taken to be caused directly by God itself. The theory states that the illusion of efficient causation between mundane events arises out of a constant conjunction that God had instituted, such that every instance where the cause is present will constitute an "occasion" for the effect to occur as an expression of the aforementioned power. This "occasioning" relation, however, falls short of efficient causation. In this view, it is not the case that the first event causes God to cause the second event: rather, God first caused one and then caused the other, but chose to regulate such behaviour in accordance with general laws of nature. Some of its most prominent historical exponents have been Al-Ghazali, Louis de la Forge, Arnold Geulincx, and Nicolas Malebranche.
Kantianism
According to the philosophy of Immanuel Kant, there is a distinction between actions done by desire and those performed by liberty (categorical imperative). Thus, not all physical actions are caused by either matter or freedom. Some actions are purely animal in nature, while others are the result of mental action on matter.
History
Plato and Aristotle
In the dialogue Phaedo, Plato formulated his famous Theory of Forms as distinct and immaterial substances of which the objects and other phenomena that we perceive in the world are nothing more than mere shadows.
In the Phaedo, Plato makes it clear that the Forms are the universalia ante res, i.e. they are ideal universals, by which we are able to understand the world. In his allegory of the cave, Plato likens the achievement of philosophical understanding to emerging into the sun from a dark cave, where only vague shadows of what lies beyond that prison are cast dimly upon the wall. Plato's forms are non-physical and non-mental. They exist nowhere in time or space, but neither do they exist in the mind, nor in the pleroma of matter; rather, matter is said to "participate" in form (μεθεξις, methexis). It remained unclear however, even to Aristotle, exactly what Plato intended by that.
Aristotle argued at length against many aspects of Plato's forms, creating his own doctrine of hylomorphism wherein form and matter coexist. Ultimately however, Aristotle's aim was to perfect a theory of forms, rather than to reject it. Although Aristotle strongly rejected the independent existence Plato attributed to forms, his metaphysics do agree with Plato's a priori considerations quite often. For example, Aristotle argues that changeless, eternal substantial form is necessarily immaterial. Because matter provides a stable substratum for a change in form, matter always has the potential to change. Thus, if given an eternity in which to do so, it will, necessarily, exercise that potential.
Part of Aristotle's psychology, the study of the soul, is his account of the ability of humans to reason and the ability of animals to perceive. In both cases, perfect copies of forms are acquired, either by direct impression of environmental forms, in the case of perception, or else by virtue of contemplation, understanding and recollection. He believed the mind can literally assume any form being contemplated or experienced, and it was unique in its ability to become a blank slate, having no essential form. As thoughts of earth are not heavy, any more than thoughts of fire are causally efficient, they provide an immaterial complement for the formless mind.
From Neoplatonism to scholasticism
The philosophical school of Neoplatonism, most active in Late Antiquity, claimed that the physical and the spiritual are both emanations of the One. Neoplatonism exerted a considerable influence on Christianity, as did the philosophy of Aristotle via scholasticism.
In the scholastic tradition of Saint Thomas Aquinas, a number of whose doctrines have been incorporated into Roman Catholic dogma, the soul is the substantial form of a human being. Aquinas held the Quaestiones disputate de anima, or 'Disputed questions on the soul', at the Roman studium provinciale of the Dominican Order at Santa Sabina, the forerunner of the Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, Angelicum during the academic year 1265–66. By 1268 Aquinas had written at least the first book of the Sententia Libri De anima, Aquinas' commentary on Aristotle's De anima, the translation of which from the Greek was completed by Aquinas' Dominican associate at Viterbo William of Moerbeke in 1267. Like Aristotle, Aquinas held that the human being was a unified composite substance of two substantial principles: form and matter. The soul is the substantial form and so the first actuality of a material organic body with the potentiality for life.
While Aquinas defended the unity of human nature as a composite substance constituted by these two inextricable principles of form and matter, he also argued for the incorruptibility of the intellectual soul, in contrast to the corruptibility of the vegetative and sensitive animation of plants and animals. His argument for the subsistence and incorruptibility of the intellectual soul takes its point of departure from the metaphysical principle that operation follows upon being (agiture sequitur esse), i.e., the activity of a thing reveals the mode of being and existence it depends upon. Since the intellectual soul exercises its own per se intellectual operations without employing material faculties, i.e. intellectual operations are immaterial, the intellect itself and the intellectual soul, must likewise be immaterial and so incorruptible. Even though the intellectual soul of man is able to subsist upon the death of the human being, Aquinas does not hold that the human person is able to remain integrated at death. The separated intellectual soul is neither a man nor a human person. The intellectual soul by itself is not a human person (i.e., an individual supposit of a rational nature). Hence, Aquinas held that "soul of St. Peter pray for us" would be more appropriate than "St. Peter pray for us", because all things connected with his person, including memories, ended with his corporeal life.
The Catholic doctrine of the resurrection of the body does nor subscribe that, sees body and soul as forming a whole and states that at the second coming, the souls of the departed will be reunited with their bodies as a whole person (substance) and witness to the apocalypse. The thorough consistency between dogma and contemporary science was maintained here in part from a serious attendance to the principle that there can be only one truth. Consistency with science, logic, philosophy, and faith remained a high priority for centuries, and a university doctorate in theology generally included the entire science curriculum as a prerequisite. This doctrine is not universally accepted by Christians today. Many believe that one's immortal soul goes directly to Heaven upon death of the body.
Descartes and his disciples
In his Meditations on First Philosophy, René Descartes embarked upon a quest in which he called all his previous beliefs into doubt, in order to find out what he could be certain of. In so doing, he discovered that he could doubt whether he had a body (it could be that he was dreaming of it or that it was an illusion created by an evil demon), but he could not doubt whether he had a mind. This gave Descartes his first inkling that the mind and body were different things. The mind, according to Descartes, was a "thinking thing" (Latin: res cogitans), and an immaterial substance. This "thing" was the essence of himself, that which doubts, believes, hopes, and thinks. The body, "the thing that exists" (res extensa), regulates normal bodily functions (such as heart and liver). According to Descartes, animals only had a body and not a soul (which distinguishes humans from animals). The distinction between mind and body is argued in Meditation VI as follows: I have a clear and distinct idea of myself as a thinking, non-extended thing, and a clear and distinct idea of body as an extended and non-thinking thing. Whatever I can conceive clearly and distinctly, God can so create.
The central claim of what is often called Cartesian dualism, in honor of Descartes, is that the immaterial mind and the material body, while being ontologically distinct substances, causally interact. This is an idea that continues to feature prominently in many non-European philosophies. Mental events cause physical events, and vice versa. But this leads to a substantial problem for Cartesian dualism: How can an immaterial mind cause anything in a material body, and vice versa? This has often been called the "problem of interactionism."
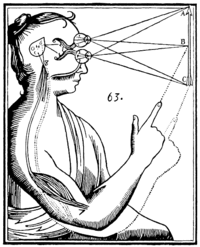
Descartes himself struggled to come up with a feasible answer to this problem. In his letter to Elisabeth of Bohemia, Princess Palatine, he suggested that spirits interacted with the body through the pineal gland, a small gland in the centre of the brain, between the two hemispheres. The term Cartesian dualism is also often associated with this more specific notion of causal interaction through the pineal gland. However, this explanation was not satisfactory: how can an immaterial mind interact with the physical pineal gland? Because Descartes' was such a difficult theory to defend, some of his disciples, such as Arnold Geulincx and Nicolas Malebranche, proposed a different explanation: That all mind–body interactions required the direct intervention of God. According to these philosophers, the appropriate states of mind and body were only the occasions for such intervention, not real causes. These occasionalists maintained the strong thesis that all causation was directly dependent on God, instead of holding that all causation was natural except for that between mind and body.
Recent formulations
In addition to already discussed theories of dualism (particularly the Christian and Cartesian models) there are new theories in the defense of dualism. Naturalistic dualism comes from Australian philosopher, David Chalmers (born 1966) who argues there is an explanatory gap between objective and subjective experience that cannot be bridged by reductionism because consciousness is, at least, logically autonomous of the physical properties upon which it supervenes. According to Chalmers, a naturalistic account of property dualism requires a new fundamental category of properties described by new laws of supervenience; the challenge being analogous to that of understanding electricity based on the mechanistic and Newtonian models of materialism prior to Maxwell's equations.
A similar defense comes from Australian philosopher Frank Jackson (born 1943) who revived the theory of epiphenomenalism which argues that mental states do not play a role in physical states. Jackson argues that there are two kinds of dualism:
- substance dualism that assumes there is second, non-corporeal form of reality. In this form, body and soul are two different substances.
- property dualism that says that body and soul are different properties of the same body.
He claims that functions of the mind/soul are internal, very private experiences that are not accessible to observation by others, and therefore not accessible by science (at least not yet). We can know everything, for example, about a bat's facility for echolocation, but we will never know how the bat experiences that phenomenon.
Arguments for dualism
The subjective argument
An important fact is that minds perceive intra-mental states differently from sensory phenomena, and this cognitive difference results in mental and physical phenomena having seemingly disparate properties. The subjective argument holds that these properties are irreconcilable under a physical mind.
Mental events have a certain subjective quality to them, whereas physical ones seem not to. So, for example, one may ask what a burned finger feels like, or what the blueness of the sky looks like, or what nice music sounds like. Philosophers of mind call the subjective aspects of mental events qualia. There is something that it's like to feel pain, to see a familiar shade of blue, and so on. There are qualia involved in these mental events. And the claim is that qualia cannot be reduced to anything physical.
Thomas Nagel first characterized the problem of qualia for physicalistic monism in his article, "What Is It Like to Be a Bat?". Nagel argued that even if we knew everything there was to know from a third-person, scientific perspective about a bat's sonar system, we still wouldn't know what it is like to be a bat. However, others argue that qualia are consequent of the same neurological processes that engender the bat's mind, and will be fully understood as the science develops.
Frank Jackson formulated his well-known knowledge argument based upon similar considerations. In this thought experiment, known as Mary's room, he asks us to consider a neuroscientist, Mary, who was born, and has lived all of her life, in a black and white room with a black and white television and computer monitor where she collects all the scientific data she possibly can on the nature of colours. Jackson asserts that as soon as Mary leaves the room, she will come to have new knowledge which she did not possess before: the knowledge of the experience of colours (i.e., what they are like). Although Mary knows everything there is to know about colours from an objective, third-person perspective, she has never known, according to Jackson, what it was like to see red, orange, or green. If Mary really learns something new, it must be knowledge of something non-physical, since she already knew everything about the physical aspects of colour.
However, Jackson later rejected his argument and embraced physicalism. He notes that Mary obtains knowledge not of color, but of a new intramental state, seeing color. Also, he notes that Mary might say "wow," and as a mental state affecting the physical, this clashed with his former view of epiphenomenalism. David Lewis' response to this argument, now known as the ability argument, is that what Mary really came to know was simply the ability to recognize and identify color sensations to which she had previously not been exposed. Daniel Dennett and others also provide arguments against this notion.
The zombie argument
The zombie argument is based on a thought experiment proposed by David Chalmers. The basic idea is that one can imagine, and, therefore, conceive the existence of, an apparently functioning human being/body without any conscious states being associated with it.
Chalmers' argument is that it seems plausible that such a being could exist because all that is needed is that all and only the things that the physical sciences describe and observe about a human being must be true of the zombie. None of the concepts involved in these sciences make reference to consciousness or other mental phenomena, and any physical entity can be described scientifically via physics whether it is conscious or not. The mere logical possibility of a p-zombie demonstrates that consciousness is a natural phenomenon beyond the current unsatisfactory explanations. Chalmers states that one probably could not build a living p-zombie because living things seem to require a level of consciousness. However (unconscious?) robots built to simulate humans may become the first real p-zombies. Hence Chalmers half-joking calls for the need to build a "consciousness meter" to ascertain if any given entity, human or robot, is conscious or not.
Others such as Dennett have argued that the notion of a philosophical zombie is an incoherent, or unlikely, concept. In particular, nothing proves that an entity (e.g., a computer or robot) which would perfectly mimic human beings, and especially perfectly mimic expressions of feelings (like joy, fear, anger, ...), would not indeed experience them, thus having similar states of consciousness to what a real human would have. It is argued that under physicalism, one must either believe that anyone including oneself might be a zombie, or that no one can be a zombie—following from the assertion that one's own conviction about being (or not being) a zombie is a product of the physical world and is therefore no different from anyone else's.
Special sciences argument
Howard Robinson argues that, if predicate dualism is correct, then there are "special sciences" that are irreducible to physics. These allegedly irreducible subjects, which contain irreducible predicates, differ from hard sciences in that they are interest-relative. Here, interest-relative fields depend on the existence of minds that can have interested perspectives. Psychology is one such science; it completely depends on and presupposes the existence of the mind.
Physics is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves. On the other hand, the study of meteorological weather patterns or human behavior is only of interest to humans themselves. The point is that having a perspective on the world is a psychological state. Therefore, the special sciences presuppose the existence of minds which can have these states. If one is to avoid ontological dualism, then the mind that has a perspective must be part of the physical reality to which it applies its perspective. If this is the case, then in order to perceive the physical world as psychological, the mind must have a perspective on the physical. This, in turn, presupposes the existence of mind.
However, cognitive science and psychology do not require the mind to be irreducible, and operate on the assumption that it has physical basis. In fact, it is common in science to presuppose a complex system; while fields such as chemistry, biology, or geology could be verbosely expressed in terms of quantum field theory, it is convenient to use levels of abstraction like molecules, cells, or the mantle. It is often difficult to decompose these levels without heavy analysis and computation. Sober has also advanced philosophical arguments against the notion of irreducibility.
Argument from personal identity
This argument concerns the differences between the applicability of counterfactual conditionals to physical objects, on the one hand, and to conscious, personal agents on the other. In the case of any material object, e.g. a printer, we can formulate a series of counterfactuals in the following manner:
- This printer could have been made of straw.
- This printer could have been made of some other kind of plastics and vacuum-tube transistors.
- This printer could have been made of 95% of what it is actually made of and 5% vacuum-tube transistors, etc..
Somewhere along the way from the printer's being made up exactly of the parts and materials which actually constitute it to the printer's being made up of some different matter at, say, 20%, the question of whether this printer is the same printer becomes a matter of arbitrary convention.
Imagine the case of a person, Frederick, who has a counterpart born from the same egg and a slightly genetically modified sperm. Imagine a series of counterfactual cases corresponding to the examples applied to the printer. Somewhere along the way, one is no longer sure about the identity of Frederick. In this latter case, it has been claimed, overlap of constitution cannot be applied to the identity of mind. As Madell puts it:
- But while my present body can thus have its partial counterpart in some possible world, my present consciousness cannot. Any present state of consciousness that I can imagine either is or is not mine. There is no question of degree here.
If the counterpart of Frederick, Frederickus, is 70% constituted of the same physical substance as Frederick, does this mean that it is also 70% mentally identical with Frederick? Does it make sense to say that something is mentally 70% Frederick? A possible solution to this dilemma is that of open individualism.
Richard Swinburne, in his book The Existence of God, put forward an argument for mind-body dualism based upon personal identity. He states that the brain is composed of two hemispheres and a cord linking the two and that, as modern science has shown, either of these can be removed without the person losing any memories or mental capacities.
He then cites a thought-experiment for the reader, asking what would happen if each of the two hemispheres of one person were placed inside two different people. Either, Swinburne claims, one of the two is me or neither is- and there is no way of telling which, as each will have similar memories and mental capacities to the other. In fact, Swinburne claims, even if one's mental capacities and memories are far more similar to the original person than the others' are, they still may not be him.
From here, he deduces that even if we know what has happened to every single atom inside a person's brain, we still do not know what has happened to 'them' as an identity. From here it follows that a part of our mind, or our soul, is immaterial, and, as a consequence, that mind-body dualism is true.
Argument from reason
Philosophers and scientists such as Victor Reppert, William Hasker, and Alvin Plantinga have developed an argument for dualism dubbed the "argument from reason". They credit C.S. Lewis with first bringing the argument to light in his book Miracles; Lewis called the argument "The Cardinal Difficulty of Naturalism", which was the title of chapter three of Miracles.
The argument postulates that if, as naturalism entails, all of our thoughts are the effect of a physical cause, then we have no reason for assuming that they are also the consequent of a reasonable ground. However, knowledge is apprehended by reasoning from ground to consequent. Therefore, if naturalism were true, there would be no way of knowing it (or anything else), except by a fluke.
Through this logic, the statement "I have reason to believe naturalism is valid" is inconsistent in the same manner as "I never tell the truth." That is, to conclude its truth would eliminate the grounds from which to reach it. To summarize the argument in the book, Lewis quotes J. B. S. Haldane, who appeals to a similar line of reasoning:
If my mental processes are determined wholly by the motions of atoms in my brain, I have no reason to suppose that my beliefs are true...and hence I have no reason for supposing my brain to be composed of atoms.
— J. B. S. Haldane, Possible Worlds, p. 209
In his essay "Is Theology Poetry?", Lewis himself summarises the argument in a similar fashion when he writes:
If minds are wholly dependent on brains, and brains on biochemistry, and biochemistry (in the long run) on the meaningless flux of the atoms, I cannot understand how the thought of those minds should have any more significance than the sound of the wind in the trees.
— C. S. Lewis, The Weight of Glory and Other Addresses, p. 139
But Lewis later agreed with Elizabeth Anscombe's response to his Miracles argument. She showed that an argument could be valid and ground-consequent even if its propositions were generated via physical cause and effect by non-rational factors. Similar to Anscombe, Richard Carrier and John Beversluis have written extensive objections to the argument from reason on the untenability of its first postulate.
Cartesian arguments
Descartes puts forward two main arguments for dualism in Meditations: firstly, the "modal argument," or the "clear and distinct perception argument," and secondly the "indivisibility" or "divisibility" argument.
| It is imaginable that one's mind might exist without one's body. | |||
| therefore | |||
| It is conceivable that one's mind might exist without one's body. | |||
| therefore | |||
| It is possible one's mind might exist without one's body. | |||
| therefore | |||
| One's mind is a different entity from one's body. |
The argument is distinguished from the zombie argument as it establishes that the mind could continue to exist without the body, rather than that the unaltered body could exist without the mind. Alvin Plantinga, J. P. Moreland, and Edward Feser have both supported the argument, although Feser and Moreland think that it must be carefully reformulated in order to be effective.
The indivisibility argument for dualism was phrased by Descartes as follows:
[T]here is a great difference between a mind and a body, because the body, by its very nature, is something divisible, whereas the mind is plainly indivisible…insofar as I am only a thing that thinks, I cannot distinguish any parts in me.… Although the whole mind seems to be united to the whole body, nevertheless, were a foot or an arm or any other bodily part amputated, I know that nothing would be taken away from the mind…
The argument relies upon Leibniz' principle of the identity of indiscernibles, which states that two things are the same if and only if they share all their properties. A counterargument is the idea that matter is not infinitely divisible, and thus that the mind could be identified with material things that cannot be divided, or potentially Leibnizian monads.
Arguments against dualism
Arguments from causal interaction
One argument against dualism is with regard to causal interaction. If consciousness (the mind) can exist independently of physical reality (the brain), one must explain how physical memories are created concerning consciousness. Dualism must therefore explain how consciousness affects physical reality. One of the main objections to dualistic interactionism is lack of explanation of how the material and immaterial are able to interact. Varieties of dualism according to which an immaterial mind causally affects the material body and vice versa have come under strenuous attack from different quarters, especially in the 20th century. Critics of dualism have often asked how something totally immaterial can affect something totally material—this is the basic problem of causal interaction.
First, it is not clear where the interaction would take place. For example, burning one's finger causes pain. Apparently there is some chain of events, leading from the burning of skin, to the stimulation of nerve endings, to something happening in the peripheral nerves of one's body that lead to one's brain, to something happening in a particular part of one's brain, and finally resulting in the sensation of pain. But pain is not supposed to be spatially locatable. It might be responded that the pain "takes place in the brain." But evidently, the pain is in the finger. This may not be a devastating criticism.
However, there is a second problem about the interaction. Namely, the question of how the interaction takes place, where in dualism "the mind" is assumed to be non-physical and by definition outside of the realm of science. The mechanism which explains the connection between the mental and the physical would therefore be a philosophical proposition as compared to a scientific theory. For example, compare such a mechanism to a physical mechanism that is well understood. Take a very simple causal relation, such as when a cue ball strikes an eight ball and causes it to go into the pocket. What happens in this case is that the cue ball has a certain amount of momentum as its mass moves across the pool table with a certain velocity, and then that momentum is transferred to the eight ball, which then heads toward the pocket. Compare this to the situation in the brain, where one wants to say that a decision causes some neurons to fire and thus causes a body to move across the room. The intention to "cross the room now" is a mental event and, as such, it does not have physical properties such as force. If it has no force, then it would seem that it could not possibly cause any neuron to fire. However, with Dualism, an explanation is required of how something without any physical properties has physical effects.
Replies
Alfred North Whitehead and, later, David Ray Griffin framed a new ontology (process philosophy) seeking precisely to avoid the pitfalls of ontological dualism.
The explanation provided by Arnold Geulincx and Nicolas Malebranche is that of occasionalism, where all mind–body interactions require the direct intervention of God.
At the time C. S. Lewis wrote Miracles, quantum mechanics (and physical indeterminism) was only in the initial stages of acceptance, but still Lewis stated the logical possibility that, if the physical world was proved to be indeterministic, this would provide an entry (interaction) point into the traditionally viewed closed system, where a scientifically described physically probable/improbable event could be philosophically described as an action of a non-physical entity on physical reality. He states, however, that none of the arguments in his book will rely on this. Although some interpretations of quantum mechanics consider wave function collapse to be indeterminate, in others this event is defined and deterministic.
Argument from physics
The argument from physics is closely related to the argument from causal interaction. Many physicists and consciousness researchers have argued that any action of a nonphysical mind on the brain would entail the violation of physical laws, such as the conservation of energy.
By assuming a deterministic physical universe, the objection can be formulated more precisely. When a person decides to walk across a room, it is generally understood that the decision to do so, a mental event, immediately causes a group of neurons in that person's brain to fire, a physical event, which ultimately results in his walking across the room. The problem is that if there is something totally non-physical causing a bunch of neurons to fire, then there is no physical event which causes the firing. This means that some physical energy is required to be generated against the physical laws of the deterministic universe—this is by definition a miracle and there can be no scientific explanation of (repeatable experiment performed regarding) where the physical energy for the firing came from. Such interactions would violate the fundamental laws of physics. In particular, if some external source of energy is responsible for the interactions, then this would violate the law of the conservation of energy. Dualistic interactionism has therefore been criticized for violating a general heuristic principle of science: the causal closure of the physical world.
Replies
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy and the New Catholic Encyclopedia provide two possible replies to the above objections. The first reply is that the mind may influence the distribution of energy, without altering its quantity. The second possibility is to deny that the human body is causally closed, as the conservation of energy applies only to closed systems. However, physicalists object that no evidence exists for the causal non-closure of the human body. Robin Collins responds that energy conservation objections misunderstand the role of energy conservation in physics. Well understood scenarios in general relativity violate energy conservation and quantum mechanics provides precedent for causal interactions, or correlation without energy or momentum exchange. However, this does not mean the mind spends energy and, despite that, it still doesn't exclude the supernatural.
Another reply is akin to parallelism—Mills holds that behavioral events are causally overdetermined, and can be explained by either physical or mental causes alone. An overdetermined event is fully accounted for by multiple causes at once. However, J. J. C. Smart and Paul Churchland have pointed out that if physical phenomena fully determine behavioral events, then by Occam's razor an unphysical mind is unnecessary.
Robinson suggests that the interaction may involve dark energy, dark matter or some other currently unknown scientific process. However, such processes would necessarily be physical, and in this case dualism is replaced with physicalism, or the interaction point is left for study at a later time when these physical processes are understood.
Another reply is that the interaction taking place in the human body may not be described by "billiard ball" classical mechanics. If a nondeterministic interpretation of quantum mechanics is correct then microscopic events are indeterminate, where the degree of determinism increases with the scale of the system. Philosophers Karl Popper and John Eccles and physicist Henry Stapp have theorized that such indeterminacy may apply at the macroscopic scale. However, Max Tegmark has argued that classical and quantum calculations show that quantum decoherence effects do not play a role in brain activity. Indeed, macroscopic quantum states have only ever been observed in superconductors near absolute zero.
Yet another reply to the interaction problem is to note that it doesn't seem that there is an interaction problem for all forms of substance dualism. For instance, Thomistic dualism doesn't obviously face any issue with regards to interaction.
Argument from brain damage
This argument has been formulated by Paul Churchland, among others. The point is that, in instances of some sort of brain damage (e.g. caused by automobile accidents, drug abuse, pathological diseases, etc.), it is always the case that the mental substance and/or properties of the person are significantly changed or compromised. If the mind were a completely separate substance from the brain, how could it be possible that every single time the brain is injured, the mind is also injured? Indeed, it is very frequently the case that one can even predict and explain the kind of mental or psychological deterioration or change that human beings will undergo when specific parts of their brains are damaged. So the question for the dualist to try to confront is how can all of this be explained if the mind is a separate and immaterial substance from, or if its properties are ontologically independent of, the brain.
Property dualism and William Hasker's "emergent dualism" seek to avoid this problem. They assert that the mind is a property or substance that emerges from the appropriate arrangement of physical matter, and therefore could be affected by any rearrangement of matter.
Phineas Gage, who suffered destruction of one or both frontal lobes by a projectile iron rod, is often cited as an example illustrating that the brain causes mind. Gage certainly exhibited some mental changes after his accident. This physical event, the destruction of part of his brain, therefore caused some kind of change in his mind, suggesting a correlation between brain states and mental states. Similar examples abound; neuroscientist David Eagleman describes the case of another individual who exhibited escalating pedophilic tendencies at two different times, and in each case was found to have tumors growing in a particular part of his brain.
Case studies aside, modern experiments have demonstrated that the relation between brain and mind is much more than simple correlation. By damaging, or manipulating, specific areas of the brain repeatedly under controlled conditions (e.g. in monkeys) and reliably obtaining the same results in measures of mental state and abilities, neuroscientists have shown that the relation between damage to the brain and mental deterioration is likely causal. This conclusion is further supported by data from the effects of neuro-active chemicals (e.g., those affecting neurotransmitters) on mental functions, but also from research on neurostimulation (direct electrical stimulation of the brain, including transcranial magnetic stimulation).
Argument from biological development
Another common argument against dualism consists in the idea that since human beings (both phylogenetically and ontogenetically) begin their existence as entirely physical or material entities and since nothing outside of the domain of the physical is added later on in the course of development, then we must necessarily end up being fully developed material beings. There is nothing non-material or mentalistic involved in conception, the formation of the blastula, the gastrula, and so on. The postulation of a non-physical mind would seem superfluous.
Argument from neuroscience
In some contexts, the decisions that a person makes can be detected up to 10 seconds in advance by means of scanning their brain activity. Subjective experiences and covert attitudes can be detected, as can mental imagery. This is strong empirical evidence that cognitive processes have a physical basis in the brain.
Argument from simplicity
The argument from simplicity is probably the simplest and also the most common form of argument against dualism of the mental. The dualist is always faced with the question of why anyone should find it necessary to believe in the existence of two, ontologically distinct, entities (mind and brain), when it seems possible and would make for a simpler thesis to test against scientific evidence, to explain the same events and properties in terms of one. It is a heuristic principle in science and philosophy not to assume the existence of more entities than is necessary for clear explanation and prediction.
This argument was criticized by Peter Glassen in a debate with J. J. C. Smart in the pages of Philosophy in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Glassen argued that, because it is not a physical entity, Occam's razor cannot consistently be appealed to by a physicalist or materialist as a justification of mental states or events, such as the belief that dualism is false. The idea is that Occam's razor may not be as "unrestricted" as it is normally described (applying to all qualitative postulates, even abstract ones) but instead concrete (only applies to physical objects). If one applies Occam's Razor unrestrictedly, then it recommends monism until pluralism either receives more support or is disproved. If one applies Occam's Razor only concretely, then it may not be used on abstract concepts (this route, however, has serious consequences for selecting between hypotheses about the abstract).