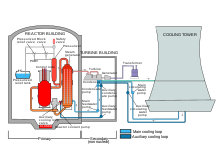
A thermal power station is a power station in which heat energy is converted to electricity. Typically, fuel is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine passes through a steam condenser and is recycled to where it was heated. This is known as a Rankine cycle. Natural gas can also be burnt directly in a gas turbine similarly connected to a generator.
Water power stations (which generate hydroelectricity) are excluded from this category, since they convert the potential energy of water into electricity via a water turbine.
The design of thermal power stations depends on the intended energy source: fossil fuel, nuclear and geothermal power, solar energy, biofuels, and waste incineration are all used. Certain thermal power stations are also designed to produce heat for industrial purposes; for district heating; or desalination of water, in addition to generating electrical power.
Types of thermal energy
Almost all coal-fired power stations, petroleum, nuclear, geothermal, solar thermal electric, and waste incineration plants, as well as all natural gas power stations are thermal. Natural gas is frequently burned in gas turbines as well as boilers. The waste heat from a gas turbine, in the form of hot exhaust gas, can be used to raise steam by passing this gas through a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG). The steam is then used to drive a steam turbine in a combined cycle plant that improves overall efficiency. Power stations burning coal, fuel oil, or natural gas are often called fossil fuel power stations. Some biomass-fueled thermal power stations have appeared also. Non-nuclear thermal power stations, particularly fossil-fueled plants, which do not use cogeneration are sometimes referred to as conventional power stations.
Commercial electric utility power stations are usually constructed on a large scale and designed for continuous operation. Virtually all electric power stations use three-phase electrical generators to produce alternating current (AC) electric power at a frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. Large companies or institutions may have their own power stations to supply heating or electricity to their facilities, especially if steam is created anyway for other purposes. Steam-driven power stations have been used to drive most ships in most of the 20th century. Shipboard power stations usually directly couple the turbine to the ship's propellers through gearboxes. Power stations in such ships also provide steam to smaller turbines driving electric generators to supply electricity. Nuclear marine propulsion is, with few exceptions, used only in naval vessels. There have been many turbo-electric ships in which a steam-driven turbine drives an electric generator which powers an electric motor for propulsion.
Cogeneration plants, often called combined heat and power (CHP) facilities, produce both electric power and heat for process heat or space heating, such as steam and hot water.
History
The reciprocating steam engine has been used to produce mechanical power since the 18th century, with notable improvements being made by James Watt. When the first commercially developed central electrical power stations were established in 1882 at Pearl Street Station in New York and Holborn Viaduct power station in London, reciprocating steam engines were used. The development of the steam turbine in 1884 provided larger and more efficient machine designs for central generating stations. By 1892 the turbine was considered a better alternative to reciprocating engines; turbines offered higher speeds, more compact machinery, and stable speed regulation allowing for parallel synchronous operation of generators on a common bus. After about 1905, turbines entirely replaced reciprocating engines in almost all large central power stations.
The largest reciprocating engine-generator sets ever built were completed in 1901 for the Manhattan Elevated Railway. Each of seventeen units weighed about 500 tons and was rated 6000 kilowatts; a contemporary turbine set of similar rating would have weighed about 20% as much.
Thermal power generation efficiency
The energy efficiency of a conventional thermal power station is defined as saleable energy produced as a percent of the heating value of the fuel consumed. A simple cycle gas turbine achieves energy conversion efficiencies from 20 to 35%. Typical coal-based power plants operating at steam pressures of 170 bar and 570 °C run at efficiency of 35 to 38%, with state-of-the-art fossil fuel plants at 46% efficiency. Combined-cycle systems can reach higher values. As with all heat engines, their efficiency is limited, and governed by the laws of thermodynamics.
The Carnot efficiency dictates that higher efficiencies can be attained by increasing the temperature of the steam. Sub-critical pressure fossil fuel power stations can achieve 36–40% efficiency. Supercritical designs have efficiencies in the low to mid 40% range, with new "ultra critical" designs using pressures above 4400 psi (30.3 MPa) and multiple stage reheat reaching 45-48% efficiency. Above the critical point for water of 705 °F (374 °C) and 3212 psi (22.06 MPa), there is no phase transition from water to steam, but only a gradual decrease in density.
Currently most nuclear power stations must operate below the temperatures and pressures that coal-fired plants do, in order to provide more conservative safety margins within the systems that remove heat from the nuclear fuel. This, in turn, limits their thermodynamic efficiency to 30–32%. Some advanced reactor designs being studied, such as the very-high-temperature reactor, Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor, and supercritical water reactor, would operate at temperatures and pressures similar to current coal plants, producing comparable thermodynamic efficiency.
The energy of a thermal power station not utilized in power production must leave the plant in the form of heat to the environment. This waste heat can go through a condenser and be disposed of with cooling water or in cooling towers. If the waste heat is instead used for district heating, it is called cogeneration. An important class of thermal power station is that associated with desalination facilities; these are typically found in desert countries with large supplies of natural gas, and in these plants freshwater production and electricity are equally important co-products.
Other types of power stations are subject to different efficiency limitations. Most hydropower stations in the United States are about 90 percent efficient in converting the energy of falling water into electricity while the efficiency of a wind turbine is limited by Betz's law, to about 59.3%, and actual wind turbines show lower efficiency.
Electricity cost
The direct cost of electric energy produced by a thermal power station is the result of cost of fuel, capital cost for the plant, operator labour, maintenance, and such factors as ash handling and disposal. Indirect social or environmental costs, such as the economic value of environmental impacts, or environmental and health effects of the complete fuel cycle and plant decommissioning, are not usually assigned to generation costs for thermal stations in utility practice, but may form part of an environmental impact assessment.
Boiler and steam cycle
In the nuclear plant field, steam generator refers to a specific type of large heat exchanger used in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) to thermally connect the primary (reactor plant) and secondary (steam plant) systems, which generates steam. In a boiling water reactor (BWR), no separate steam generator is used and water boils in the reactor core.
In some industrial settings, there can also be steam-producing heat exchangers called heat recovery steam generators (HRSG) which utilize heat from some industrial process, most commonly utilizing hot exhaust from a gas turbine. The steam generating boiler has to produce steam at the high purity, pressure and temperature required for the steam turbine that drives the electrical generator.
Geothermal plants do not need boilers because they use naturally occurring steam sources. Heat exchangers may be used where the geothermal steam is very corrosive or contains excessive suspended solids.
A fossil fuel steam generator includes an economizer, a steam drum, and the furnace with its steam generating tubes and superheater coils. Necessary safety valves are located at suitable points to protect against excessive boiler pressure. The air and flue gas path equipment include: forced draft (FD) fan, air preheater (AP), boiler furnace, induced draft (ID) fan, fly ash collectors (electrostatic precipitator or baghouse), and the flue-gas stack.
Feed water heating
The boiler feed water used in the steam boiler is a means of transferring heat energy from the burning fuel to the mechanical energy of the spinning steam turbine. The total feed water consists of recirculated condensate water and purified makeup water. Because the metallic materials it contacts are subject to corrosion at high temperatures and pressures, the makeup water is highly purified before use. A system of water softeners and ion exchange demineralizers produces water so pure that it coincidentally becomes an electrical insulator, with conductivity in the range of 0.3–1.0 microsiemens per centimeter. The makeup water in a 500 MWe plant amounts to perhaps 120 US gallons per minute (7.6 L/s) to replace water drawn off from the boiler drums for water purity management, and to also offset the small losses from steam leaks in the system.
The feed water cycle begins with condensate water being pumped out of the condenser after traveling through the steam turbines. The condensate flow rate at full load in a 500 MW plant is about 6,000 US gallons per minute (400 L/s).
The water is pressurized in two stages, and flows through a series of six or seven intermediate feed water heaters, heated up at each point with steam extracted from an appropriate duct on the turbines and gaining temperature at each stage. Typically, in the middle of this series of feedwater heaters, and before the second stage of pressurization, the condensate plus the makeup water flows through a deaerator that removes dissolved air from the water, further purifying and reducing its corrosiveness. The water may be dosed following this point with hydrazine, a chemical that removes the remaining oxygen in the water to below 5 parts per billion (ppb). It is also dosed with pH control agents such as ammonia or morpholine to keep the residual acidity low and thus non-corrosive.
Boiler operation
The boiler is a rectangular furnace about 50 feet (15 m) on a side and 130 feet (40 m) tall. Its walls are made of a web of high pressure steel tubes about 2.3 inches (58 mm) in diameter.
Fuel such as pulverized coal is air-blown into the furnace through burners located at the four corners, or along one wall, or two opposite walls, and it is ignited to rapidly burn, forming a large fireball at the center. The thermal radiation of the fireball heats the water that circulates through the boiler tubes near the boiler perimeter. The water circulation rate in the boiler is three to four times the throughput. As the water in the boiler circulates it absorbs heat and changes into steam. It is separated from the water inside a drum at the top of the furnace. The saturated steam is introduced into superheat pendant tubes that hang in the hottest part of the combustion gases as they exit the furnace. Here the steam is superheated to 1,000 °F (540 °C) to prepare it for the turbine.
Plants that use gas turbines to heat the water for conversion into steam use boilers known as heat recovery steam generators (HRSG). The exhaust heat from the gas turbines is used to make superheated steam that is then used in a conventional water-steam generation cycle, as described in the gas turbine combined-cycle plants section.
Boiler furnace and steam drum
The water enters the boiler through a section in the convection pass called the economizer. From the economizer it passes to the steam drum and from there it goes through downcomers to inlet headers at the bottom of the water walls. From these headers the water rises through the water walls of the furnace where some of it is turned into steam and the mixture of water and steam then re-enters the steam drum. This process may be driven purely by natural circulation (because the water is the downcomers is denser than the water/steam mixture in the water walls) or assisted by pumps. In the steam drum, the water is returned to the downcomers and the steam is passed through a series of steam separators and dryers that remove water droplets from the steam. The dry steam then flows into the superheater coils.
The boiler furnace auxiliary equipment includes coal feed nozzles and igniter guns, soot blowers, water lancing, and observation ports (in the furnace walls) for observation of the furnace interior. Furnace explosions due to any accumulation of combustible gases after a trip-out are avoided by flushing out such gases from the combustion zone before igniting the coal.
The steam drum (as well as the superheater coils and headers) have air vents and drains needed for initial start up.
Superheater
Fossil fuel power stations often have a superheater section in the steam generating furnace. The steam passes through drying equipment inside the steam drum on to the superheater, a set of tubes in the furnace. Here the steam picks up more energy from hot flue gases outside the tubing, and its temperature is now superheated above the saturation temperature. The superheated steam is then piped through the main steam lines to the valves before the high-pressure turbine.
Nuclear-powered steam plants do not have such sections but produce steam at essentially saturated conditions. Experimental nuclear plants were equipped with fossil-fired superheaters in an attempt to improve overall plant operating cost.
Steam condensing
The condenser condenses the steam from the exhaust of the turbine into liquid to allow it to be pumped. If the condenser can be made cooler, the pressure of the exhaust steam is reduced and efficiency of the cycle increases.
The surface condenser is a shell and tube heat exchanger in which cooling water is circulated through the tubes. The exhaust steam from the low-pressure turbine enters the shell, where it is cooled and converted to condensate (water) by flowing over the tubes as shown in the adjacent diagram. Such condensers use steam ejectors or rotary motor-driven exhausts for continuous removal of air and gases from the steam side to maintain vacuum.
For best efficiency, the temperature in the condenser must be kept as low as practical in order to achieve the lowest possible pressure in the condensing steam. Since the condenser temperature can almost always be kept significantly below 100 °C where the vapor pressure of water is much less than atmospheric pressure, the condenser generally works under vacuum. Thus leaks of non-condensible air into the closed loop must be prevented.
Typically the cooling water causes the steam to condense at a temperature of about 25 °C (77 °F) and that creates an absolute pressure in the condenser of about 2–7 kPa (0.59–2.07 inHg), i.e. a vacuum of about −95 kPa (−28 inHg) relative to atmospheric pressure. The large decrease in volume that occurs when water vapor condenses to liquid creates the low vacuum that helps pull steam through and increase the efficiency of the turbines.
The limiting factor is the temperature of the cooling water and that, in turn, is limited by the prevailing average climatic conditions at the power station's location (it may be possible to lower the temperature beyond the turbine limits during winter, causing excessive condensation in the turbine). Plants operating in hot climates may have to reduce output if their source of condenser cooling water becomes warmer; unfortunately this usually coincides with periods of high electrical demand for air conditioning.
The condenser generally uses either circulating cooling water from a cooling tower to reject waste heat to the atmosphere, or once-through cooling (OTC) water from a river, lake or ocean. In the United States, about two-thirds of power plants use OTC systems, which often have significant adverse environmental impacts. The impacts include thermal pollution and killing large numbers of fish and other aquatic species at cooling water intakes.
The heat absorbed by the circulating cooling water in the condenser tubes must also be removed to maintain the ability of the water to cool as it circulates. This is done by pumping the warm water from the condenser through either natural draft, forced draft or induced draft cooling towers (as seen in the adjacent image) that reduce the temperature of the water by evaporation, by about 11 to 17 °C (20 to 30 °F)—expelling waste heat to the atmosphere. The circulation flow rate of the cooling water in a 500 MW unit is about 14.2 m3/s (500 ft3/s or 225,000 US gal/min) at full load.
The condenser tubes are made of brass or stainless steel to resist corrosion from either side. Nevertheless, they may become internally fouled during operation by bacteria or algae in the cooling water or by mineral scaling, all of which inhibit heat transfer and reduce thermodynamic efficiency. Many plants include an automatic cleaning system that circulates sponge rubber balls through the tubes to scrub them clean without the need to take the system off-line.
The cooling water used to condense the steam in the condenser returns to its source without having been changed other than having been warmed. If the water returns to a local water body (rather than a circulating cooling tower), it is often tempered with cool 'raw' water to prevent thermal shock when discharged into that body of water.
Another form of condensing system is the air-cooled condenser. The process is similar to that of a radiator and fan. Exhaust heat from the low-pressure section of a steam turbine runs through the condensing tubes, the tubes are usually finned and ambient air is pushed through the fins with the help of a large fan. The steam condenses to water to be reused in the water-steam cycle. Air-cooled condensers typically operate at a higher temperature than water-cooled versions. While saving water, the efficiency of the cycle is reduced (resulting in more carbon dioxide per megawatt-hour of electricity).
From the bottom of the condenser, powerful condensate pumps recycle the condensed steam (water) back to the water/steam cycle.
Reheater
Power station furnaces may have a reheater section containing tubes heated by hot flue gases outside the tubes. Exhaust steam from the high-pressure turbine is passed through these heated tubes to collect more energy before driving the intermediate and then low-pressure turbines.
Air path
External fans are provided to give sufficient air for combustion. The Primary air fan takes air from the atmosphere and, first warms the air in the air preheater for better economy. Primary air then passes through the coal pulverizers, and carries the coal dust to the burners for injection into the furnace. The Secondary air fan takes air from the atmosphere and, first warms the air in the air preheater for better economy. Secondary air is mixed with the coal/primary air flow in the burners.
The induced draft fan assists the FD fan by drawing out combustible gases from the furnace, maintaining slightly below atmospheric pressure in the furnace to avoid leakage of combustion products from the boiler casing.
Steam turbine generator
A steam turbine generator consists of a series of steam turbines interconnected to each other and a generator on a common shaft.
Steam turbine
There is usually a high-pressure turbine at one end, followed by an intermediate-pressure turbine, and finally one, two, or three low-pressure turbines, and the shaft that connects to the generator. As steam moves through the system and loses pressure and thermal energy, it expands in volume, requiring increasing diameter and longer blades at each succeeding stage to extract the remaining energy. The entire rotating mass may be over 200 metric tons and 100 feet (30 m) long. It is so heavy that it must be kept turning slowly even when shut down (at 3 rpm) so that the shaft will not bow even slightly and become unbalanced. This is so important that it is one of only six functions of blackout emergency power batteries on site. (The other five being emergency lighting, communication, station alarms, generator hydrogen seal system, and turbogenerator lube oil.)
For a typical late 20th-century power station, superheated steam from the boiler is delivered through 14–16-inch (360–410 mm) diameter piping at 2,400 psi (17 MPa; 160 atm) and 1,000 °F (540 °C) to the high-pressure turbine, where it falls in pressure to 600 psi (4.1 MPa; 41 atm) and to 600 °F (320 °C) in temperature through the stage. It exits via 24–26-inch (610–660 mm) diameter cold reheat lines and passes back into the boiler, where the steam is reheated in special reheat pendant tubes back to 1,000 °F (540 °C). The hot reheat steam is conducted to the intermediate pressure turbine, where it falls in both temperature and pressure and exits directly to the long-bladed low-pressure turbines and finally exits to the condenser.
Turbo generator
The generator, typically about 30 feet (9 m) long and 12 feet (3.7 m) in diameter, contains a stationary stator and a spinning rotor, each containing miles of heavy copper conductor. There is generally no permanent magnet, thus preventing black starts. In operation it generates up to 21,000 amperes at 24,000 volts AC (504 MWe) as it spins at either 3,000 or 3,600 rpm, synchronized to the power grid. The rotor spins in a sealed chamber cooled with hydrogen gas, selected because it has the highest known heat transfer coefficient of any gas and for its low viscosity, which reduces windage losses. This system requires special handling during startup, with air in the chamber first displaced by carbon dioxide before filling with hydrogen. This ensures that a highly explosive hydrogen–oxygen environment is not created.
The power grid frequency is 60 Hz across North America and 50 Hz in Europe, Oceania, Asia (Korea and parts of Japan are notable exceptions), and parts of Africa. The desired frequency affects the design of large turbines, since they are highly optimized for one particular speed.
The electricity flows to a distribution yard where transformers increase the voltage for transmission to its destination.
The steam turbine-driven generators have auxiliary systems enabling them to work satisfactorily and safely. The steam turbine generator, being rotating equipment, generally has a heavy, large-diameter shaft. The shaft therefore requires not only supports but also has to be kept in position while running. To minimize the frictional resistance to the rotation, the shaft has a number of bearings. The bearing shells, in which the shaft rotates, are lined with a low-friction material like Babbitt metal. Oil lubrication is provided to further reduce the friction between shaft and bearing surface and to limit the heat generated.
Stack gas path and cleanup
As the combustion flue gas exits the boiler it is routed through a rotating flat basket of metal mesh which picks up heat and returns it to incoming fresh air as the basket rotates. This is called the air preheater. The gas exiting the boiler is laden with fly ash, which are tiny spherical ash particles. The flue gas contains nitrogen along with combustion products carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. The fly ash is removed by fabric bag filters in baghouses or electrostatic precipitators. Once removed, the fly ash byproduct can sometimes be used in the manufacturing of concrete. This cleaning up of flue gases, however, only occurs in plants that are fitted with the appropriate technology. Still, the majority of coal-fired power stations in the world do not have these facilities. Legislation in Europe has been efficient to reduce flue gas pollution. Japan has been using flue gas cleaning technology for over 30 years and the US has been doing the same for over 25 years. China is now beginning to grapple with the pollution caused by coal-fired power stations.
Where required by law, the sulfur and nitrogen oxide pollutants are removed by stack gas scrubbers which use a pulverized limestone or other alkaline wet slurry to remove those pollutants from the exit stack gas. Other devices use catalysts to remove nitrous oxide compounds from the flue-gas stream. The gas travelling up the flue-gas stack may by this time have dropped to about 50 °C (120 °F). A typical flue-gas stack may be 150–180 metres (490–590 ft) tall to disperse the remaining flue gas components in the atmosphere. The tallest flue-gas stack in the world is 419.7 metres (1,377 ft) tall at the Ekibastuz GRES-2 Power Station in Kazakhstan.
In the United States and a number of other countries, atmospheric dispersion modeling studies are required to determine the flue-gas stack height needed to comply with the local air pollution regulations. The United States also requires the height of a flue-gas stack to comply with what is known as the "good engineering practice" (GEP) stack height. In the case of existing flue gas stacks that exceed the GEP stack height, any air pollution dispersion modeling studies for such stacks must use the GEP stack height rather than the actual stack height.
Auxiliary systems
Boiler make-up water treatment plant and storage
Since there is continuous withdrawal of steam and continuous return of condensate to the boiler, losses due to blowdown and leakages have to be made up to maintain a desired water level in the boiler steam drum. For this, continuous make-up water is added to the boiler water system. Impurities in the raw water input to the plant generally consist of calcium and magnesium salts which impart hardness to the water. Hardness in the make-up water to the boiler will form deposits on the tube water surfaces which will lead to overheating and failure of the tubes. Thus, the salts have to be removed from the water, and that is done by a water demineralising treatment plant (DM). A DM plant generally consists of cation, anion, and mixed bed exchangers. Any ions in the final water from this process consist essentially of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions, which recombine to form pure water. Very pure DM water becomes highly corrosive once it absorbs oxygen from the atmosphere because of its very high affinity for oxygen.
The capacity of the DM plant is dictated by the type and quantity of salts in the raw water input. However, some storage is essential as the DM plant may be down for maintenance. For this purpose, a storage tank is installed from which DM water is continuously withdrawn for boiler make-up. The storage tank for DM water is made from materials not affected by corrosive water, such as PVC. The piping and valves are generally of stainless steel. Sometimes, a steam blanketing arrangement or stainless steel doughnut float is provided on top of the water in the tank to avoid contact with air. DM water make-up is generally added at the steam space of the surface condenser (i.e., the vacuum side). This arrangement not only sprays the water but also DM water gets deaerated, with the dissolved gases being removed by a de-aerator through an ejector attached to the condenser.
Fuel preparation system
In coal-fired power stations, the raw feed coal from the coal storage area is first crushed into small pieces and then conveyed to the coal feed hoppers at the boilers. The coal is next pulverized into a very fine powder. The pulverizers may be ball mills, rotating drum grinders, or other types of grinders.
Some power stations burn fuel oil rather than coal. The oil must kept warm (above its pour point) in the fuel oil storage tanks to prevent the oil from congealing and becoming unpumpable. The oil is usually heated to about 100 °C before being pumped through the furnace fuel oil spray nozzles.
Boilers in some power stations use processed natural gas as their main fuel. Other power stations may use processed natural gas as auxiliary fuel in the event that their main fuel supply (coal or oil) is interrupted. In such cases, separate gas burners are provided on the boiler furnaces.
Barring gear
Barring gear (or "turning gear") is the mechanism provided to rotate the turbine generator shaft at a very low speed after unit stoppages. Once the unit is "tripped" (i.e., the steam inlet valve is closed), the turbine coasts down towards standstill. When it stops completely, there is a tendency for the turbine shaft to deflect or bend if allowed to remain in one position too long. This is because the heat inside the turbine casing tends to concentrate in the top half of the casing, making the top half portion of the shaft hotter than the bottom half. The shaft therefore could warp or bend by millionths of inches.
This small shaft deflection, only detectable by eccentricity meters, would be enough to cause damaging vibrations to the entire steam turbine generator unit when it is restarted. The shaft is therefore automatically turned at low speed (about one percent rated speed) by the barring gear until it has cooled sufficiently to permit a complete stop.
Oil system
An auxiliary oil system pump is used to supply oil at the start-up of the steam turbine generator. It supplies the hydraulic oil system required for steam turbine's main inlet steam stop valve, the governing control valves, the bearing and seal oil systems, the relevant hydraulic relays and other mechanisms.
At a preset speed of the turbine during start-ups, a pump driven by the turbine main shaft takes over the functions of the auxiliary system.
Generator cooling
While small generators may be cooled by air drawn through filters at the inlet, larger units generally require special cooling arrangements. Hydrogen gas cooling, in an oil-sealed casing, is used because it has the highest known heat transfer coefficient of any gas and for its low viscosity which reduces windage losses. This system requires special handling during start-up, with air in the generator enclosure first displaced by carbon dioxide before filling with hydrogen. This ensures that the highly flammable hydrogen does not mix with oxygen in the air.
The hydrogen pressure inside the casing is maintained slightly higher than atmospheric pressure to avoid outside air ingress, and up to about two atmospheres pressure to improve heat transfer efficiency. The hydrogen must be sealed against outward leakage where the shaft emerges from the casing. Mechanical seals around the shaft are installed with a very small annular gap to avoid rubbing between the shaft and the seals. Seal oil is used to prevent the hydrogen gas leakage to atmosphere.
The generator also uses water cooling. Since the generator coils are at a potential of about 22 kV, an insulating barrier such as Teflon is used to interconnect the water line and the generator high-voltage windings. Demineralized water of low conductivity is used.
Generator high-voltage system
The generator voltage for modern utility-connected generators ranges from 11 kV in smaller units to 30 kV in larger units. The generator high-voltage leads are normally large aluminium channels because of their high current as compared to the cables used in smaller machines. They are enclosed in well-grounded aluminium bus ducts and are supported on suitable insulators. The generator high-voltage leads are connected to step-up transformers for connecting to a high-voltage electrical substation (usually in the range of 115 kV to 765 kV) for further transmission by the local power grid.
The necessary protection and metering devices are included for the high-voltage leads. Thus, the steam turbine generator and the transformer form one unit. Smaller units may share a common generator step-up transformer with individual circuit breakers to connect the generators to a common bus.
Monitoring and alarm system
Most of the power station operational controls are automatic. However, at times, manual intervention may be required. Thus, the plant is provided with monitors and alarm systems that alert the plant operators when certain operating parameters are seriously deviating from their normal range.
Battery-supplied emergency lighting and communication
A central battery system consisting of lead–acid cell units is provided to supply emergency electric power, when needed, to essential items such as the power station's control systems, communication systems, generator hydrogen seal system, turbine lube oil pumps, and emergency lighting. This is essential for a safe, damage-free shutdown of the units in an emergency situation.
Circulating water system
To dissipate the thermal load of main turbine exhaust steam, condensate from gland steam condenser, and condensate from Low Pressure Heater by providing a continuous supply of cooling water to the main condenser thereby leading to condensation.
The consumption of cooling water by inland power stations is estimated to reduce power availability for the majority of thermal power stations by 2040–2069.