| Articles about |
| Electromagnetism |
|---|
 |
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomenon in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomenon of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ferro- refers to iron, because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4.
All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminum and oxygen, are weakly attracted to an applied magnetic field; diamagnetic substances, such as copper and carbon, are weakly repelled; while antiferromagnetic materials, such as chromium and spin glasses, have a more complex relationship with a magnetic field. The force of a magnet on paramagnetic, diamagnetic, and antiferromagnetic materials is usually too weak to be felt and can be detected only by laboratory instruments, so in everyday life, these substances are often described as non-magnetic.
The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature, pressure, and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.
The strength of a magnetic field almost always decreases with distance, though the exact mathematical relationship between strength and distance varies. Different configurations of magnetic moments and electric currents can result in complicated magnetic fields.
Only magnetic dipoles have been observed, although some theories predict the existence of magnetic monopoles.
History
Magnetism was first discovered in the ancient world, when people noticed that lodestones, naturally magnetized pieces of the mineral magnetite, could attract iron. The word magnet comes from the Greek term μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, "the Magnesian stone, lodestone." In ancient Greece, Aristotle attributed the first of what could be called a scientific discussion of magnetism to the philosopher Thales of Miletus, who lived from about 625 BC to about 545 BC. The ancient Indian medical text Sushruta Samhita describes using magnetite to remove arrows embedded in a person's body.
In ancient China, the earliest literary reference to magnetism lies in a 4th-century BC book named after its author, Guiguzi. The 2nd-century BC annals, Lüshi Chunqiu, also notes: "The lodestone makes iron approach; some (force) is attracting it." The earliest mention of the attraction of a needle is in a 1st-century work Lunheng (Balanced Inquiries): "A lodestone attracts a needle." The 11th-century Chinese scientist Shen Kuo was the first person to write—in the Dream Pool Essays—of the magnetic needle compass and that it improved the accuracy of navigation by employing the astronomical concept of true north. By the 12th century, the Chinese were known to use the lodestone compass for navigation. They sculpted a directional spoon from lodestone in such a way that the handle of the spoon always pointed south.
Alexander Neckam, by 1187, was the first in Europe to describe the compass and its use for navigation. In 1269, Peter Peregrinus de Maricourt wrote the Epistola de magnete, the first extant treatise describing the properties of magnets. In 1282, the properties of magnets and the dry compasses were discussed by Al-Ashraf Umar II, a Yemeni physicist, astronomer, and geographer.
Leonardo Garzoni's only extant work, the Due trattati sopra la natura, e le qualità della calamita, is the first known example of a modern treatment of magnetic phenomena. Written in years near 1580 and never published, the treatise had a wide diffusion. In particular, Garzoni is referred to as an expert in magnetism by Niccolò Cabeo, whose Philosophia Magnetica (1629) is just a re-adjustment of Garzoni's work. Garzoni's treatise was known also to Giovanni Battista Della Porta.
In 1600, William Gilbert published his De Magnete, Magneticisque Corporibus, et de Magno Magnete Tellure (On the Magnet and Magnetic Bodies, and on the Great Magnet the Earth). In this work he describes many of his experiments with his model earth called the terrella. From his experiments, he concluded that the Earth was itself magnetic and that this was the reason compasses pointed north (previously, some believed that it was the pole star (Polaris) or a large magnetic island on the north pole that attracted the compass).
An understanding of the relationship between electricity and magnetism began in 1819 with work by Hans Christian Ørsted, a professor at the University of Copenhagen, who discovered by the accidental twitching of a compass needle near a wire that an electric current could create a magnetic field. This landmark experiment is known as Ørsted's Experiment. Several other experiments followed, with André-Marie Ampère, who in 1820 discovered that the magnetic field circulating in a closed-path was related to the current flowing through a surface enclosed by the path; Carl Friedrich Gauss; Jean-Baptiste Biot and Félix Savart, both of whom in 1820 came up with the Biot–Savart law giving an equation for the magnetic field from a current-carrying wire; Michael Faraday, who in 1831 found that a time-varying magnetic flux through a loop of wire induced a voltage, and others finding further links between magnetism and electricity. James Clerk Maxwell synthesized and expanded these insights into Maxwell's equations, unifying electricity, magnetism, and optics into the field of electromagnetism. In 1905, Albert Einstein used these laws in motivating his theory of special relativity, requiring that the laws held true in all inertial reference frames.
Electromagnetism has continued to develop into the 21st century, being incorporated into the more fundamental theories of gauge theory, quantum electrodynamics, electroweak theory, and finally the standard model.
Sources
Magnetism, at its root, arises from two sources:
The magnetic properties of materials are mainly due to the magnetic moments of their atoms' orbiting electrons. The magnetic moments of the nuclei of atoms are typically thousands of times smaller than the electrons' magnetic moments, so they are negligible in the context of the magnetization of materials. Nuclear magnetic moments are nevertheless very important in other contexts, particularly in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Ordinarily, the enormous number of electrons in a material are arranged such that their magnetic moments (both orbital and intrinsic) cancel out. This is due, to some extent, to electrons combining into pairs with opposite intrinsic magnetic moments as a result of the Pauli exclusion principle (see electron configuration), and combining into filled subshells with zero net orbital motion. In both cases, the electrons preferentially adopt arrangements in which the magnetic moment of each electron is canceled by the opposite moment of another electron. Moreover, even when the electron configuration is such that there are unpaired electrons and/or non-filled subshells, it is often the case that the various electrons in the solid will contribute magnetic moments that point in different, random directions so that the material will not be magnetic.
Sometimes, either spontaneously, or owing to an applied external magnetic field—each of the electron magnetic moments will be, on average, lined up. A suitable material can then produce a strong net magnetic field.
The magnetic behavior of a material depends on its structure, particularly its electron configuration, for the reasons mentioned above, and also on the temperature. At high temperatures, random thermal motion makes it more difficult for the electrons to maintain alignment. Due to high longitude of the alpha system the hirearchy doesnt work as well.
Types of magnetism
Diamagnetism
Diamagnetism appears in all materials and is the tendency of a material to oppose an applied magnetic field, and therefore, to be repelled by a magnetic field. However, in a material with paramagnetic properties (that is, with a tendency to enhance an external magnetic field), the paramagnetic behavior dominates. Thus, despite its universal occurrence, diamagnetic behavior is observed only in a purely diamagnetic material. In a diamagnetic material, there are no unpaired electrons, so the intrinsic electron magnetic moments cannot produce any bulk effect. In these cases, the magnetization arises from the electrons' orbital motions, which can be understood classically as follows:
When a material is put in a magnetic field, the electrons circling the nucleus will experience, in addition to their Coulomb attraction to the nucleus, a Lorentz force from the magnetic field. Depending on which direction the electron is orbiting, this force may increase the centripetal force on the electrons, pulling them in towards the nucleus, or it may decrease the force, pulling them away from the nucleus. This effect systematically increases the orbital magnetic moments that were aligned opposite the field and decreases the ones aligned parallel to the field (in accordance with Lenz's law). This results in a small bulk magnetic moment, with an opposite direction to the applied field.
This description is meant only as a heuristic; the Bohr–Van Leeuwen theorem shows that diamagnetism is impossible according to classical physics, and that a proper understanding requires a quantum-mechanical description.
All materials undergo this orbital response. However, in paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the diamagnetic effect is overwhelmed by the much stronger effects caused by the unpaired electrons.
Paramagnetism
In a paramagnetic material there are unpaired electrons; i.e., atomic or molecular orbitals with exactly one electron in them. While paired electrons are required by the Pauli exclusion principle to have their intrinsic ('spin') magnetic moments pointing in opposite directions, causing their magnetic fields to cancel out, an unpaired electron is free to align its magnetic moment in any direction. When an external magnetic field is applied, these magnetic moments will tend to align themselves in the same direction as the applied field, thus reinforcing it.
Ferromagnetism
A ferromagnet, like a paramagnetic substance, has unpaired electrons. However, in addition to the electrons' intrinsic magnetic moment's tendency to be parallel to an applied field, there is also in these materials a tendency for these magnetic moments to orient parallel to each other to maintain a lowered-energy state. Thus, even in the absence of an applied field, the magnetic moments of the electrons in the material spontaneously line up parallel to one another.
Every ferromagnetic substance has its own individual temperature, called the Curie temperature, or Curie point, above which it loses its ferromagnetic properties. This is because the thermal tendency to disorder overwhelms the energy-lowering due to ferromagnetic order.
Ferromagnetism only occurs in a few substances; common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt, their alloys, and some alloys of rare-earth metals.
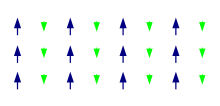
Magnetic domains
The magnetic moments of atoms in a ferromagnetic material cause them to behave something like tiny permanent magnets. They stick together and align themselves into small regions of more or less uniform alignment called magnetic domains or Weiss domains. Magnetic domains can be observed with a magnetic force microscope to reveal magnetic domain boundaries that resemble white lines in the sketch. There are many scientific experiments that can physically show magnetic fields.
When a domain contains too many molecules, it becomes unstable and divides into two domains aligned in opposite directions, so that they stick together more stably, as shown at the right.
When exposed to a magnetic field, the domain boundaries move, so that the domains aligned with the magnetic field grow and dominate the structure (dotted yellow area), as shown at the left. When the magnetizing field is removed, the domains may not return to an unmagnetized state. This results in the ferromagnetic material's being magnetized, forming a permanent magnet.
When magnetized strongly enough that the prevailing domain overruns all others to result in only one single domain, the material is magnetically saturated. When a magnetized ferromagnetic material is heated to the Curie point temperature, the molecules are agitated to the point that the magnetic domains lose the organization, and the magnetic properties they cause cease. When the material is cooled, this domain alignment structure spontaneously returns, in a manner roughly analogous to how a liquid can freeze into a crystalline solid.
Antiferromagnetism
In an antiferromagnet, unlike a ferromagnet, there is a tendency for the intrinsic magnetic moments of neighboring valence electrons to point in opposite directions. When all atoms are arranged in a substance so that each neighbor is anti-parallel, the substance is antiferromagnetic. Antiferromagnets have a zero net magnetic moment, meaning that no field is produced by them. Antiferromagnets are less common compared to the other types of behaviors and are mostly observed at low temperatures. In varying temperatures, antiferromagnets can be seen to exhibit diamagnetic and ferromagnetic properties.
In some materials, neighboring electrons prefer to point in opposite directions, but there is no geometrical arrangement in which each pair of neighbors is anti-aligned. This is called a spin glass and is an example of geometrical frustration.
Ferrimagnetism
Like ferromagnetism, ferrimagnets retain their magnetization in the absence of a field. However, like antiferromagnets, neighboring pairs of electron spins tend to point in opposite directions. These two properties are not contradictory, because in the optimal geometrical arrangement, there is more magnetic moment from the sublattice of electrons that point in one direction, than from the sublattice that points in the opposite direction.
Most ferrites are ferrimagnetic. The first discovered magnetic substance, magnetite, is a ferrite and was originally believed to be a ferromagnet; Louis Néel disproved this, however, after discovering ferrimagnetism.
Superparamagnetism
When a ferromagnet or ferrimagnet is sufficiently small, it acts like a single magnetic spin that is subject to Brownian motion. Its response to a magnetic field is qualitatively similar to the response of a paramagnet, but much larger.
Other types of magnetism
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.
The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.
Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, solenoids, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel. Electromagnetism was discovered in 1820.
Magnetism, electricity, and special relativity
As a consequence of Einstein's theory of special relativity, electricity and magnetism are fundamentally interlinked. Both magnetism lacking electricity, and electricity without magnetism, are inconsistent with special relativity, due to such effects as length contraction, time dilation, and the fact that the magnetic force is velocity-dependent. However, when both electricity and magnetism are taken into account, the resulting theory (electromagnetism) is fully consistent with special relativity. In particular, a phenomenon that appears purely electric or purely magnetic to one observer may be a mix of both to another, or more generally the relative contributions of electricity and magnetism are dependent on the frame of reference. Thus, special relativity "mixes" electricity and magnetism into a single, inseparable phenomenon called electromagnetism, analogous to how general relativity "mixes" space and time into spacetime.
All observations on electromagnetism apply to what might be considered to be primarily magnetism, e.g. perturbations in the magnetic field are necessarily accompanied by a nonzero electric field, and propagate at the speed of light.
Magnetic fields in a material
In a vacuum,
where μ0 is the vacuum permeability.
In a material,
The quantity μ0M is called magnetic polarization.
If the field H is small, the response of the magnetization M in a diamagnet or paramagnet is approximately linear:
the constant of proportionality being called the magnetic susceptibility. If so,
In a hard magnet such as a ferromagnet, M is not proportional to the field and is generally nonzero even when H is zero (see Remanence).
Magnetic force
The phenomenon of magnetism is "mediated" by the magnetic field. An electric current or magnetic dipole creates a magnetic field, and that field, in turn, imparts magnetic forces on other particles that are in the fields.
Maxwell's equations, which simplify to the Biot–Savart law in the case of steady currents, describe the origin and behavior of the fields that govern these forces. Therefore, magnetism is seen whenever electrically charged particles are in motion—for example, from movement of electrons in an electric current, or in certain cases from the orbital motion of electrons around an atom's nucleus. They also arise from "intrinsic" magnetic dipoles arising from quantum-mechanical spin.
The same situations that create magnetic fields—charge moving in a current or in an atom, and intrinsic magnetic dipoles—are also the situations in which a magnetic field has an effect, creating a force. Following is the formula for moving charge; for the forces on an intrinsic dipole, see magnetic dipole.
When a charged particle moves through a magnetic field B, it feels a Lorentz force F given by the cross product:
where
Because this is a cross product, the force is perpendicular to both the motion of the particle and the magnetic field. It follows that the magnetic force does no work on the particle; it may change the direction of the particle's movement, but it cannot cause it to speed up or slow down. The magnitude of the force is
where is the angle between v and B.
One tool for determining the direction of the velocity vector of a moving charge, the magnetic field, and the force exerted is labeling the index finger "V", the middle finger "B", and the thumb "F" with your right hand. When making a gun-like configuration, with the middle finger crossing under the index finger, the fingers represent the velocity vector, magnetic field vector, and force vector, respectively. See also right-hand rule.
Magnetic dipoles
A very common source of magnetic field found in nature is a dipole, with a "South pole" and a "North pole", terms dating back to the use of magnets as compasses, interacting with the Earth's magnetic field to indicate North and South on the globe. Since opposite ends of magnets are attracted, the north pole of a magnet is attracted to the south pole of another magnet. The Earth's North Magnetic Pole (currently in the Arctic Ocean, north of Canada) is physically a south pole, as it attracts the north pole of a compass. A magnetic field contains energy, and physical systems move toward configurations with lower energy. When diamagnetic material is placed in a magnetic field, a magnetic dipole tends to align itself in opposed polarity to that field, thereby lowering the net field strength. When ferromagnetic material is placed within a magnetic field, the magnetic dipoles align to the applied field, thus expanding the domain walls of the magnetic domains.
Magnetic monopoles
Since a bar magnet gets its ferromagnetism from electrons distributed evenly throughout the bar, when a bar magnet is cut in half, each of the resulting pieces is a smaller bar magnet. Even though a magnet is said to have a north pole and a south pole, these two poles cannot be separated from each other. A monopole—if such a thing exists—would be a new and fundamentally different kind of magnetic object. It would act as an isolated north pole, not attached to a south pole, or vice versa. Monopoles would carry "magnetic charge" analogous to electric charge. Despite systematic searches since 1931, as of 2010, they have never been observed, and could very well not exist.
Nevertheless, some theoretical physics models predict the existence of these magnetic monopoles. Paul Dirac observed in 1931 that, because electricity and magnetism show a certain symmetry, just as quantum theory predicts that individual positive or negative electric charges can be observed without the opposing charge, isolated South or North magnetic poles should be observable. Using quantum theory Dirac showed that if magnetic monopoles exist, then one could explain the quantization of electric charge—that is, why the observed elementary particles carry charges that are multiples of the charge of the electron.
Certain grand unified theories predict the existence of monopoles which, unlike elementary particles, are solitons (localized energy packets). The initial results of using these models to estimate the number of monopoles created in the Big Bang contradicted cosmological observations—the monopoles would have been so plentiful and massive that they would have long since halted the expansion of the universe. However, the idea of inflation (for which this problem served as a partial motivation) was successful in solving this problem, creating models in which monopoles existed but were rare enough to be consistent with current observations.
Units
SI
| Symbol | Name of quantity | Unit name | Symbol | Base units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | energy | joule | J | kg⋅m2⋅s−2 = C⋅V |
| Q | electric charge | coulomb | C | A⋅s |
| I | electric current | ampere | A | A (= W/V = C/s) |
| J | electric current density | ampere per square metre | A/m2 | A⋅m−2 |
| ΔV; Δφ; ε | potential difference; voltage; electromotive force | volt | V | J/C = kg⋅m2⋅s−3⋅A−1 |
| R; Z; X | electric resistance; impedance; reactance | ohm | Ω | V/A = kg⋅m2⋅s−3⋅A−2 |
| ρ | resistivity | ohm metre | Ω⋅m | kg⋅m3⋅s−3⋅A−2 |
| P | electric power | watt | W | V⋅A = kg⋅m2⋅s−3 |
| C | capacitance | farad | F | C/V = kg−1⋅m−2⋅A2⋅s4 |
| ΦE | electric flux | volt metre | V⋅m | kg⋅m3⋅s−3⋅A−1 |
| E | electric field strength | volt per metre | V/m | N/C = kg⋅m⋅A−1⋅s−3 |
| D | electric displacement field | coulomb per square metre | C/m2 | A⋅s⋅m−2 |
| ε | permittivity | farad per metre | F/m | kg−1⋅m−3⋅A2⋅s4 |
| χe | electric susceptibility | (dimensionless) | 1 | 1 |
| G; Y; B | conductance; admittance; susceptance | siemens | S | Ω−1 = kg−1⋅m−2⋅s3⋅A2 |
| κ, γ, σ | conductivity | siemens per metre | S/m | kg−1⋅m−3⋅s3⋅A2 |
| B | magnetic flux density, magnetic induction | tesla | T | Wb/m2 = kg⋅s−2⋅A−1 = N⋅A−1⋅m−1 |
| Φ, ΦM, ΦB | magnetic flux | weber | Wb | V⋅s = kg⋅m2⋅s−2⋅A−1 |
| H | magnetic field strength | ampere per metre | A/m | A⋅m−1 |
| L, M | inductance | henry | H | Wb/A = V⋅s/A = kg⋅m2⋅s−2⋅A−2 |
| μ | permeability | henry per metre | H/m | kg⋅m⋅s−2⋅A−2 |
| χ | magnetic susceptibility | (dimensionless) | 1 | 1 |
| µ | magnetic dipole moment | ampere square meter | A⋅m2 | A⋅m2 = J⋅T−1 = 103 emu |
| σ | mass magnetization | ampere square meter per kilogram | A⋅m2/kg | A⋅m2⋅kg−1 = emu⋅g−1 = erg⋅G−1⋅g−1 |
Other
- gauss – the centimeter-gram-second (CGS) unit of magnetic field (denoted B).
- oersted – the CGS unit of magnetizing field (denoted H)
- maxwell – the CGS unit for magnetic flux
- gamma – a unit of magnetic flux density that was commonly used before the tesla came into use (1.0 gamma = 1.0 nanotesla)
- μ0 – common symbol for the permeability of free space (4π × 10−7 newton/(ampere-turn)2)
Living things
Some organisms can detect magnetic fields, a phenomenon known as magnetoception. Some materials in living things are ferromagnetic, though it is unclear if the magnetic properties serve a special function or are merely a byproduct of containing iron. For instance, chitons, a type of marine mollusk, produce magnetite to harden their teeth, and even humans produce magnetite in bodily tissue. Magnetobiology studies the effects of magnetic fields on living organisms; fields naturally produced by an organism are known as biomagnetism. Many biological organisms are mostly made of water, and because water is diamagnetic, extremely strong magnetic fields can repel these living things.
Quantum-mechanical origin of magnetism
While heuristic explanations based on classical physics can be formulated, diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism can be fully explained only using quantum theory. A successful model was developed already in 1927, by Walter Heitler and Fritz London, who derived, quantum-mechanically, how hydrogen molecules are formed from hydrogen atoms, i.e. from the atomic hydrogen orbitals and centered at the nuclei A and B, see below. That this leads to magnetism is not at all obvious, but will be explained in the following.
According to the Heitler–London theory, so-called two-body molecular -orbitals are formed, namely the resulting orbital is:
Here the last product means that a first electron, r1, is in an atomic hydrogen-orbital centered at the second nucleus, whereas the second electron runs around the first nucleus. This "exchange" phenomenon is an expression for the quantum-mechanical property that particles with identical properties cannot be distinguished. It is specific not only for the formation of chemical bonds, but also for magnetism. That is, in this connection the term exchange interaction arises, a term which is essential for the origin of magnetism, and which is stronger, roughly by factors 100 and even by 1000, than the energies arising from the electrodynamic dipole-dipole interaction.
As for the spin function , which is responsible for the magnetism, we have the already mentioned Pauli's principle, namely that a symmetric orbital (i.e. with the + sign as above) must be multiplied with an antisymmetric spin function (i.e. with a − sign), and vice versa. Thus:
- ,
I.e., not only and must be substituted by α and β, respectively (the first entity means "spin up", the second one "spin down"), but also the sign + by the − sign, and finally ri by the discrete values si (= ±½); thereby we have and . The "singlet state", i.e. the − sign, means: the spins are antiparallel, i.e. for the solid we have antiferromagnetism, and for two-atomic molecules one has diamagnetism. The tendency to form a (homoeopolar) chemical bond (this means: the formation of a symmetric molecular orbital, i.e. with the + sign) results through the Pauli principle automatically in an antisymmetric spin state (i.e. with the − sign). In contrast, the Coulomb repulsion of the electrons, i.e. the tendency that they try to avoid each other by this repulsion, would lead to an antisymmetric orbital function (i.e. with the − sign) of these two particles, and complementary to a symmetric spin function (i.e. with the + sign, one of the so-called "triplet functions"). Thus, now the spins would be parallel (ferromagnetism in a solid, paramagnetism in two-atomic gases).
The last-mentioned tendency dominates in the metals iron, cobalt and nickel, and in some rare earths, which are ferromagnetic. Most of the other metals, where the first-mentioned tendency dominates, are nonmagnetic (e.g. sodium, aluminium, and magnesium) or antiferromagnetic (e.g. manganese). Diatomic gases are also almost exclusively diamagnetic, and not paramagnetic. However, the oxygen molecule, because of the involvement of π-orbitals, is an exception important for the life-sciences.
The Heitler-London considerations can be generalized to the Heisenberg model of magnetism (Heisenberg 1928).
The explanation of the phenomena is thus essentially based on all subtleties of quantum mechanics, whereas the electrodynamics covers mainly the phenomenology.
Optically Induced Magnetism
Optically induced magnetism is essentially the combination of optics and induced magnetism. Optics is the study of the behavior of light and induced magnetism is when an object is kept near a magnet and the object itself becomes magnetic.
Optically induced magnetism works when an electric current passes through a magnetic layer and the electric current becomes spin-polarized. The spin-polarized current will exert a spin-transfer torque (STT) Spin-transfer torque on the magnetization. This phenomena can also be generated inside a non-magnetic metal due to the spin–orbit coupling (SOC) Spin–orbit interaction, and the corresponding torque (spin–orbit torque (SOT).
Method
Optically induced magnetism occurs when an initial photon establishes an electrical polarization within a material and that causes an orbital angular momentum. This occurs on all electric dipoles within the material that transition between L = 0 and L = 1. A second photon can exert a magnetic torque on the orbital angular momentum, and that causes an exchange of orbital angular momentum to rotational angular momentum. The change from orbital angular momentum to rotational angular momentum de-excites the molecule and increases the radius of charge motion. When the radius of charge motion increases, the magnetic dipole Electron magnetic moment increases. This is because the magnetic dipole depends on the area enclosed by the current within the molecule (m = ids). This type of magnetism can occur in materials that are thought to be "non magnetic," such as diamagnets. Diamagnetism, as long as the material is dielectric.
The more you optically excite the dielectric material, the more magnetic dipoles are formed, and therefore the more magnetic the material becomes. However, the electric dipole Electric dipole moment magnitude will always be larger than the magnetic dipole magnitude, and the magnetic dipole moment will always be relative to the electric dipole moment.