Zoology (/zoʊˈɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the structure, embryology, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. Zoology is one of the primary branches of biology. The term is derived from Ancient Greek ζῷον, zōion ('animal'), and λόγος, logos ('knowledge', 'study').
Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and used this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. Modern zoology has its origins during the Renaissance and early modern period, with Carl Linnaeus, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Charles Darwin, Gregor Mendel and many others.
The study of animals has largely moved on to deal with form and function, adaptations, relationships between groups, behaviour and ecology. Zoology has increasingly been subdivided into disciplines such as classification, physiology, biochemistry and evolution. With the discovery of the structure of DNA by Francis Crick and James Watson in 1953, the realm of molecular biology opened up, leading to advances in cell biology, developmental biology and molecular genetics.
History

The history of zoology traces the study of the animal kingdom from ancient to modern times. Prehistoric people needed to study the animals and plants in their environment in order to exploit them and survive. There are cave paintings, engravings and sculptures in France dating back 15,000 years showing bison, horses and deer in carefully rendered detail. Similar images from other parts of the world illustrated mostly the animals hunted for food, but also the savage animals.
The Neolithic Revolution, which is characterized by the domestication of animals, continued over the period of Antiquity. Ancient knowledge of wildlife is illustrated by the realistic depictions of wild and domestic animals in the Near East, Mesopotamia and Egypt, including husbandry practices and techniques, hunting and fishing. The invention of writing is reflected in zoology by the presence of animals in Egyptian hieroglyphics.
Although the concept of zoology as a single coherent field arose much later, the zoological sciences emerged from natural history reaching back to the biological works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. Aristotle, in the fourth century BC, looked at animals as living organisms, studying their structure, development and vital phenomena. He divided them into two groups: animals with blood, equivalent to our concept of vertebrates, and animals without blood, invertebrates. He spent two years on Lesbos, observing and describing the animals and plants, considering the adaptations of different organisms and the function of their parts. Four hundred years later, Roman physician Galen dissected animals to study their anatomy and the function of the different parts, because the dissection of human cadavers was prohibited at the time. This resulted in some of his conclusions being false, but for many centuries it was considered heretical to challenge any of his views, so the study of anatomy stultified.
During the post-classical era, Middle Eastern science and medicine was the most advanced in the world, integrating concepts from Ancient Greece, Rome, Mesopotamia and Persia as well as the ancient Indian tradition of Ayurveda, while making numerous advances and innovations. In the 13th century, Albertus Magnus produced commentaries and paraphrases of all Aristotle's works; his books on topics like botany, zoology, and minerals included information from ancient sources, but also the results of his own investigations. His general approach was surprisingly modern, and he wrote, "For it is [the task] of natural science not simply to accept what we are told but to inquire into the causes of natural things." An early pioneer was Conrad Gessner, whose monumental 4,500-page encyclopedia of animals, Historia animalium, was published in four volumes between 1551 and 1558.
In Europe, Galen's work on anatomy remained largely unsurpassed and unchallenged up until the 16th century. During the Renaissance and early modern period, zoological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Andreas Vesalius and William Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Carl Linnaeus, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as studying the development and behavior of organisms. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek did pioneering work in microscopy and revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. van Leeuwenhoek's observations were endorsed by Robert Hooke; all living organisms were composed of one or more cells and could not generate spontaneously. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life.
Having previously been the realm of gentlemen naturalists, over the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries, zoology became an increasingly professional scientific discipline. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography, laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species.
These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection; in this Darwin placed the theory of organic evolution on a new footing, by explaining the processes by which it can occur, and providing observational evidence that it had done so. Darwin's theory was rapidly accepted by the scientific community and soon became a central axiom of the rapidly developing science of biology. The basis for modern genetics began with the work of Gregor Mendel on peas in 1865, although the significance of his work was not realized at the time.
Darwin gave a new direction to morphology and physiology, by uniting them in a common biological theory: the theory of organic evolution. The result was a reconstruction of the classification of animals upon a genealogical basis, fresh investigation of the development of animals, and early attempts to determine their genetic relationships. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery. In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the modern synthesis created evolutionary biology.
Research in cell biology is interconnected to other fields such as genetics, biochemistry, medical microbiology, immunology, and cytochemistry. With the sequencing of the DNA molecule by Francis Crick and James Watson in 1953, the realm of molecular biology opened up, leading to advances in cell biology, developmental biology and molecular genetics. The study of systematics was transformed as DNA sequencing elucidated the degrees of affinity between different organisms.
Scope
Zoology is the branch of science dealing with animals. A species can be defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sex can produce fertile offspring; about 1.5 million species of animal have been described and it has been estimated that as many as 8 million animal species may exist. An early necessity was to identify the organisms and group them according to their characteristics, differences and relationships, and this is the field of the taxonomist. Originally it was thought that species were immutable, but with the arrival of Darwin's theory of evolution, the field of cladistics came into being, studying the relationships between the different groups or clades. Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, the evolutionary history of a group is known as its phylogeny, and the relationship between the clades can be shown diagrammatically in a cladogram.
Although someone who made a scientific study of animals would historically have described themselves as a zoologist, the term has come to refer to those who deal with individual animals, with others describing themselves more specifically as physiologists, ethologists, evolutionary biologists, ecologists, pharmacologists, endocrinologists or parasitologists.
Branches of zoology
Although the study of animal life is ancient, its scientific incarnation is relatively modern. This mirrors the transition from natural history to biology at the start of the 19th century. Since Hunter and Cuvier, comparative anatomical study has been associated with morphography, shaping the modern areas of zoological investigation: anatomy, physiology, histology, embryology, teratology and ethology. Modern zoology first arose in German and British universities. In Britain, Thomas Henry Huxley was a prominent figure. His ideas were centered on the morphology of animals. Many consider him the greatest comparative anatomist of the latter half of the 19th century. Similar to Hunter, his courses were composed of lectures and laboratory practical classes in contrast to the previous format of lectures only.
Classification
Scientific classification in zoology, is a method by which zoologists group and categorize organisms by biological type, such as genus or species. Biological classification is a form of scientific taxonomy. Modern biological classification has its root in the work of Carl Linnaeus, who grouped species according to shared physical characteristics. These groupings have since been revised to improve consistency with the Darwinian principle of common descent. Molecular phylogenetics, which uses nucleic acid sequence as data, has driven many recent revisions and is likely to continue to do so. Biological classification belongs to the science of zoological systematics.

Many scientists now consider the five-kingdom system outdated. Modern alternative classification systems generally start with the three-domain system: Archaea (originally Archaebacteria); Bacteria (originally Eubacteria); Eukaryota (including protists, fungi, plants, and animals) These domains reflect whether the cells have nuclei or not, as well as differences in the chemical composition of the cell exteriors.
Further, each kingdom is broken down recursively until each species is separately classified. The order is: Domain; kingdom; phylum; class; order; family; genus; species. The scientific name of an organism is generated from its genus and species. For example, humans are listed as Homo sapiens. Homo is the genus, and sapiens the specific epithet, both of them combined make up the species name. When writing the scientific name of an organism, it is proper to capitalize the first letter in the genus and put all of the specific epithet in lowercase. Additionally, the entire term may be italicized or underlined.
The dominant classification system is called the Linnaean taxonomy. It includes ranks and binomial nomenclature. The classification, taxonomy, and nomenclature of zoological organisms is administered by the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. A merging draft, BioCode, was published in 1997 in an attempt to standardize nomenclature, but has yet to be formally adopted.
Vertebrate and invertebrate zoology
Vertebrate zoology is the biological discipline that consists of the study of vertebrate animals, that is animals with a backbone, such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. The various taxonomically oriented disciplines such as mammalogy, biological anthropology, herpetology, ornithology, and ichthyology seek to identify and classify species and study the structures and mechanisms specific to those groups. The rest of the animal kingdom is dealt with by invertebrate zoology, a vast and very diverse group of animals that includes sponges, echinoderms, tunicates, worms, molluscs, arthropods and many other phyla, but single-celled organisms or protists are not usually included.
Structural zoology
Cell biology studies the structural and physiological properties of cells, including their behavior, interactions, and environment. This is done on both the microscopic and molecular levels for single-celled organisms such as bacteria as well as the specialized cells in multicellular organisms such as humans. Understanding the structure and function of cells is fundamental to all of the biological sciences. The similarities and differences between cell types are particularly relevant to molecular biology.
Anatomy considers the forms of macroscopic structures such as organs and organ systems. It focuses on how organs and organ systems work together in the bodies of humans and animals, in addition to how they work independently. Anatomy and cell biology are two studies that are closely related, and can be categorized under "structural" studies. Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different groups. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the evolution of species).
Physiology
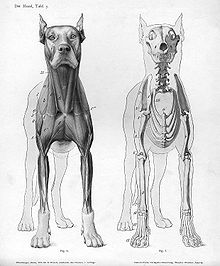
Physiology studies the mechanical, physical, and biochemical processes of living organisms by attempting to understand how all of the structures function as a whole. The theme of "structure to function" is central to biology. Physiological studies have traditionally been divided into plant physiology and animal physiology, but some principles of physiology are universal, no matter what particular organism is being studied. For example, what is learned about the physiology of yeast cells can also apply to human cells. The field of animal physiology extends the tools and methods of human physiology to non-human species. Physiology studies how, for example, the nervous, immune, endocrine, respiratory, and circulatory systems function and interact.
Developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the processes by which animals and plants reproduce and grow. The discipline includes the study of embryonic development, cellular differentiation, regeneration, asexual and sexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Development of both animals and plants is further considered in the articles on evolution, population genetics, heredity, genetic variability, Mendelian inheritance, and reproduction.
Evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. Evolutionary research is concerned with the origin and descent of species, as well as their change over time, and includes scientists from many taxonomically oriented disciplines. For example, it generally involves scientists who have special training in particular organisms such as mammalogy, ornithology, herpetology, or entomology, but use those organisms as systems to answer general questions about evolution.
Evolutionary biology is partly based on paleontology, which uses the fossil record to answer questions about the mode and tempo of evolution, and partly on the developments in areas such as population genetics and evolutionary theory. Following the development of DNA fingerprinting techniques in the late 20th century, the application of these techniques in zoology has increased the understanding of animal populations. In the 1980s, developmental biology re-entered evolutionary biology from its initial exclusion from the modern synthesis through the study of evolutionary developmental biology. Related fields often considered part of evolutionary biology are phylogenetics, systematics, and taxonomy.
Ethology

Ethology is the scientific and objective study of animal behavior under natural conditions, as opposed to behaviorism, which focuses on behavioral response studies in a laboratory setting. Ethologists have been particularly concerned with the evolution of behavior and the understanding of behavior in terms of the theory of natural selection. In one sense, the first modern ethologist was Charles Darwin, whose book, The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals, influenced many future ethologists.
A subfield of ethology is behavioral ecology which attempts to answer Nikolaas Tinbergen's four questions with regard to animal behavior: what are the proximate causes of the behavior, the developmental history of the organism, the survival value and phylogeny of the behavior? Another area of study is animal cognition, which uses laboratory experiments and carefully controlled field studies to investigate an animal's intelligence and learning.
Biogeography
Biogeography studies the spatial distribution of organisms on the Earth, focusing on topics like dispersal and migration, plate tectonics, climate change, and cladistics. It is an integrative field of study, uniting concepts and information from evolutionary biology, taxonomy, ecology, physical geography, geology, paleontology and climatology. The origin of this field of study is widely accredited to Alfred Russel Wallace, a British biologist who had some of his work jointly published with Charles Darwin.
Molecular biology

Molecular biology studies the common genetic and developmental mechanisms of animals and plants, attempting to answer the questions regarding the mechanisms of genetic inheritance and the structure of the gene. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick described the structure of DNA and the interactions within the molecule, and this publication jump-started research into molecular biology and increased interest in the subject. While researchers practice techniques specific to molecular biology, it is common to combine these with methods from genetics and biochemistry. Much of molecular biology is quantitative, and recently a significant amount of work has been done using computer science techniques such as bioinformatics and computational biology. Molecular genetics, the study of gene structure and function, has been among the most prominent sub-fields of molecular biology since the early 2000s. Other branches of biology are informed by molecular biology, by either directly studying the interactions of molecules in their own right such as in cell biology and developmental biology, or indirectly, where molecular techniques are used to infer historical attributes of populations or species, as in fields in evolutionary biology such as population genetics and phylogenetics. There is also a long tradition of studying biomolecules "from the ground up", or molecularly, in biophysics.

![1520 Sedgwick Avenue where DJ Kool Herc threw his first parties in the Bronx, New York City in 1973, considered to be the birth of hip-hop.[24]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6c/1520_Sedwick_Ave.%2C_Bronx%2C_New_York1.JPG/90px-1520_Sedwick_Ave.%2C_Bronx%2C_New_York1.JPG)
![The cast of The Jeffersons in 1976. The Jeffersons ran from 1975 to 1985, and was the second-longest running TV series with a mainly African-American cast.[25][26]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e8/Sherman_Hemsley_Isabel_Sanford_Zara_Cully_The_Jeffersons_1976.JPG/95px-Sherman_Hemsley_Isabel_Sanford_Zara_Cully_The_Jeffersons_1976.JPG)


![Michael Jackson's 1982 album Thriller became the best selling album of all time.[39]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/04/Michael_Jackson_1984.jpg/79px-Michael_Jackson_1984.jpg)
![Track and field star Florence Griffith Joyner won three gold and one silver medal at the 1988 Summer Olympics.[38]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/89/Florence_Griffith_Joyner2.jpg/92px-Florence_Griffith_Joyner2.jpg)

![Michael Jordan was the most dominant basketball player of the 1990s, becoming a global cultural icon.[45]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5c/Jordan_elgrafico_1992.jpg/98px-Jordan_elgrafico_1992.jpg)