From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Health_care_reforms_proposed_during_the_Obama_administration
The first of these reform proposals to be passed by the United States Congress is the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, which originated in the Senate and was later passed by the House of Representatives in amended form on March 21, 2010 (with a vote of 219–212). President Obama signed the reforms into law on March 23, 2010. Reuters and CNN summarized the reforms and the year in which they take effect.
Overview




A variety of specific types of reform have been suggested to improve the United States health care system. These range from increased use of health care technology through changing the anti-trust rules governing health insurance companies and tort-reform to rationing of care. Different overall strategies have been suggested as well.
The Institute of Medicine reported in September 2012 that approximately $750B per year in U.S. health care costs are avoidable or wasted. This included: unnecessary services ($210 billion annually); inefficient delivery of care ($130 billion); excess administrative costs ($190 billion); inflated prices ($105 billion); prevention failures ($55 billion), and fraud ($75 billion).
During a June 2009 speech, President Barack Obama outlined his strategy for reform. He mentioned electronic record-keeping, preventing expensive conditions, reducing obesity, refocusing doctor incentives from quantity of care to quality, bundling payments for treatment of conditions rather than specific services, better identifying and communicating the most cost-effective treatments, and reducing defensive medicine.
President Obama further described his plan in a September 2009 speech to a joint session of Congress. His plan mentions: deficit neutrality; not allowing insurance companies to discriminate based on pre-existing conditions; capping out of pocket expenses; creation of an insurance exchange for individuals and small businesses; tax credits for individuals and small companies; independent commissions to identify fraud, waste and abuse; and malpractice reform projects, among other topics.
In November 2009, then-OMB Director Peter Orszag described aspects of the Obama administration's strategy during an interview: "In order to help contain [ Medicare and Medicaid ] cost growth over the long term, we need a new health care system that has digitized information...in which that information is used to assess what’s working and what’s not more intelligently, and in which we’re paying for quality rather than quantity while also encouraging prevention and wellness." He also argued for bundling payments and accountable care organizations, which reward doctors for teamwork and patient outcomes.
Mayo Clinic President and CEO Denis Cortese has advocated an overall strategy to guide reform efforts. He argued that the U.S. has an opportunity to redesign its healthcare system and that there is a wide consensus that reform is necessary. He articulated four "pillars" of such a strategy:
- Focus on value, which he defined as the ratio of quality of service provided relative to cost;
- Pay for and align incentives with value;
- Cover everyone;
- Establish mechanisms for improving the healthcare service delivery system over the long-term, which is the primary means through which value would be improved.
Writing in The New Yorker, surgeon Atul Gawande further distinguished between the delivery system, which refers to how medical services are provided to patients, and the payment system, which refers to how payments for services are processed. He argued that reform of the delivery system is critical to getting costs under control, but that payment system reform (e.g., whether the government or private insurers process payments) is considerably less important yet gathers a disproportionate share of attention. Gawande argued that dramatic improvements and savings in the delivery system will take "at least a decade." He recommended changes that address the over-utilization of healthcare; the refocusing of incentives on value rather than profits; and comparative analysis of the cost of treatment across various healthcare providers to identify best practices. He argued this would be an iterative, empirical process and should be administered by a "national institute for healthcare delivery" to analyze and communicate improvement opportunities. A report published by the Commonwealth Fund in December 2007 examined 15 federal policy options and concluded that, taken together, they had the potential to reduce future increases in health care spending by $1.5 trillion over the next 10 years. These options included increased use of health information technology, research and incentives to improve medical decision making, reduced tobacco use and obesity, reforming the payment of providers to encourage efficiency, limiting the tax federal exemption for health insurance premiums, and reforming several market changes such as resetting the benchmark rates for Medicare Advantage plans and allowing the Department of Health and Human Services to negotiate drug prices. The authors based their modeling on the effect of combining these changes with the implementation of universal coverage. The authors concluded that there are no magic bullets for controlling health care costs, and that a multifaceted approach will be needed to achieve meaningful progress.
During February 2010, President Obama updated his reform proposal, with modifications to the bills that had passed as of that time.
Cost overview

Health spending accounted for 17.6% of GDP in the United States in 2010, down slightly from 2009 (17.7%) and by far the highest share in the OECD, and a full eight percentage points higher than the OECD average of 9.5%. Following the United States were the Netherlands (at 12.0% of GDP), and France and Germany (both at 11.6% of GDP). The United States spent $8,233 on health per capita in 2010, two-and-a-half times more than the OECD average of $3,268 (adjusted for purchasing power parity). Following the United States were Norway and Switzerland which spent over $5,250 per capita. Americans spent more than twice as much as relatively rich European countries such as France, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
The annual rate of cost increases slowed during 2010 and 2011. The causes are disputed, ranging from recession-related delays in visiting doctors to more long-term trends in moderating insurance premiums and reduced spending on structures and equipment.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services reported in 2013 that the rate of increase in annual healthcare costs has fallen since 2002. However, costs per capita continue to rise. Per capita cost increases have averaged 5.4% annually since 2000. Costs relative to GDP have risen from 13.8% in 2000 to 17.9% by 2009, but remained at that level in 2010 and 2011.
Several studies have attempted to explain the reduction in the rate of annual increase. Reasons include, among others:
- Higher unemployment due to the 2008-2012 recession, which has limited the ability of consumers to purchase healthcare;
- Rising out-of-pocket payments;
- Deductibles (the amount a person pays before insurance begins to cover claims) have risen sharply. Workers must pay a larger share of their own health costs, and generally forces them to spend less; and
- The proportion of workers with employer-sponsored health insurance enrolled in a plan that required a deductible climbed to about three-quarters in 2012 from about half in 2006.
Increasing healthcare costs also contribute to wage stagnation, as corporations pay for benefits rather than wages. Bloomberg reported in January 2013: "If there’s a consensus among health economists about anything, it’s that employer-provided health benefits come out of wages. If health insurance were cheaper, or the marketplace were structured so that most people bought health coverage for themselves rather than getting it with their jobs, people would be paid more and raises would be higher."
Best practices
Independent advisory panels
President Obama has proposed an "Independent Medicare Advisory Panel" (IMAC) to make recommendations on Medicare reimbursement policy and other reforms. Comparative effectiveness research would be one of many tools used by the IMAC. The IMAC concept was endorsed in a letter from several prominent healthcare policy experts, as summarized by OMB Director Peter Orszag:
Their support of the IMAC proposal underscores what most serious health analysts have recognized for some time: that moving toward a health system emphasizing quality rather than quantity will require continual effort, and that a key objective of legislation should be to put in place structures (like the IMAC) that facilitate such change over time. And ultimately, without a structure in place to help contain health care costs over the long term as the health market evolves, nothing else we do in fiscal policy will matter much, because eventually rising health care costs will overwhelm the federal budget.
Both Mayo Clinic CEO Dr. Denis Cortese and Surgeon/Author Atul Gawande have argued that such panel(s) will be critical to reform of the delivery system and improving value. Washington Post columnist David Ignatius has also recommended that President Obama engage someone like Cortese to have a more active role in driving reform efforts.
Comparative effectiveness research

Overutilization refers to when a patient overuses a doctor or to a doctor ordering more tests or services than may be required to address a particular condition effectively. Several treatment alternatives may be available for a given medical condition, with significantly different costs yet no statistical difference in outcome. Such scenarios offer the opportunity to maintain or improve the quality of care, while significantly reducing costs, through comparative effectiveness research. According to economist Peter A. Diamond and research cited by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the cost of healthcare per person in the U.S. also varies significantly by geography and medical center, with little or no statistical difference in outcome. Comparative effectiveness research has shown that significant cost reductions are possible. Former OMB Director Peter Orszag stated: "Nearly thirty percent of Medicare's costs could be saved without negatively affecting health outcomes if spending in high- and medium-cost areas could be reduced to the level of low-cost areas."
Pilot programs
Gawande wrote that Obamacare contains a variety of pilot programs that may have a significant impact on cost and quality over the long-run, although these have not been factored into CBO cost estimates. He stated these pilot programs cover nearly every idea healthcare experts advocate, except malpractice/tort reform. He described how the U.S. faced a cost problem with agriculture, with nearly 40% of household disposable income absorbed by food costs in 1900. With a central oversight panel (the U.S.D.A.) and many pilot programs, the U.S. was able to vastly improve the productivity of its food production and reduce these costs over time. He wrote:
Medicare and Medicaid currently pay clinicians the same amount regardless of results. But there is a pilot program to increase payments for doctors who deliver high-quality care at lower cost, while reducing payments for those who deliver low-quality care at higher cost. There’s a program that would pay bonuses to hospitals that improve patient results after heart failure, pneumonia, and surgery. There’s a program that would impose financial penalties on institutions with high rates of infections transmitted by health-care workers. Still another would test a system of penalties and rewards scaled to the quality of home health and rehabilitation care. Other experiments try moving medicine away from fee-for-service payment altogether. A bundled-payment provision would pay medical teams just one thirty-day fee for all the outpatient and inpatient services related to, say, an operation. This would give clinicians an incentive to work together to smooth care and reduce complications. One pilot would go even further, encouraging clinicians to band together into “Accountable Care Organizations” that take responsibility for all their patients’ needs, including prevention—so that fewer patients need operations in the first place. These groups would be permitted to keep part of the savings they generate, as long as they meet quality and service thresholds. The bill has ideas for changes in other parts of the system, too. Some provisions attempt to improve efficiency through administrative reforms, by, for example, requiring insurance companies to create a single standardized form for insurance reimbursement, to alleviate the clerical burden on clinicians. There are tests of various kinds of community wellness programs. The legislation also continues a stimulus-package program that funds comparative-effectiveness research—testing existing treatments for a condition against one another—because fewer treatment failures should mean lower costs.
Preventive strategies
Increased use of preventive care (e.g., regular doctor visits) is one way of reducing health care spending. Official budget scores of universal health care proposals state that most of its savings would be from providing preventative care to the uninsured. Canadian physicians, who provide universal health care including preventative care, found that they could lower their total health care expenditures by 40% simply by increasing appropriate and reducing inappropriate preventative care measures. A single uninsured cancer patient diagnosed at stage four can incur over half a million dollars in hospital bills in a few months, which must be borne by all other health care consumers, when the same diagnosis at stage one with preventative screening would cost much less. However, preventive care is typically provided to many people who would never become ill, and for those who would have become ill, it is partially offset by the health care costs during additional years of life.
Preventing obesity and overweight conditions presents a significant opportunity to reduce costs. The Centers for Disease Control reported that approximately 9% of healthcare costs in 1998 were attributable to overweight and obesity, or as much as $92.6 billion in 2002 dollars. Nearly half of these costs were paid for by the government via Medicare or Medicaid. However, by 2008 the CDC estimated these costs had nearly doubled to $147 billion. The CDC identified a series of expensive conditions more likely to occur due to obesity. The CDC released a series of strategies to prevent obesity and overweight, including: making healthy foods and beverages more available; supporting healthy food choices; encouraging kids to be more active; and creating safe communities to support physical activity. An estimated 25.6% of U.S. adults in 2007 were obese, versus 23.9% in 2005. State obesity rates ranged from 18.7% to 30%. Obesity rates were roughly equal among men and women. Some have proposed a so-called "fat tax" to provide incentives for healthier behavior, either by levying the tax on products (such as soft drinks) that are thought to contribute to obesity, or to individuals based on body measures, as they do in Japan. A study released in October, 2010 had a similar cost estimate, of $168 billion, nearly 17% of U.S. medical costs. This is an estimated $2,400 per obese person. The study was performed by researchers at Cornell and Emory universities.
However, in contrast to yearly costs, lifetime costs can be highest among healthy people, who live longer. One study in the Netherlands indicated that: "Until the age of 56, yearly health costs were highest for obese people and lowest for healthy-living people. At older ages, the highest yearly costs were incurred by the smoking group. However, because of differences in life expectancy (life expectancy at age 20 was 5 years less for the obese group, and 8 years less for the smoking group, compared to the healthy-living group), total lifetime health spending was greatest for the healthy-living people, lowest for the smokers, and intermediate for the obese people."
Eliminate unnecessary tests
During April 2012, nine physician groups identified 45 tests that were commonly used but that provided no proven benefits to patients or could actually be harmful. This was done at the urging of a Dr. Howard Brody, who published this recommendation in a 2010 article. The nine groups (medical societies) developed the lists after months of analyses and reviews of the medical literature by expert committees. The New York Times editorial board wrote: "Eliminating needless care is not rationing. It is sound medicine and sound economics."
One July 2012 proposal advocated that consumers of healthcare always have "skin in the game" such that their costs rise as more services are provided.
Address expensive chronic cases
The CBO reported in May 2005: "Medicare spending is highly concentrated, with a small number of beneficiaries accounting for a large proportion of the Medicare program's annual expenditures. In 2001, the costliest 5 percent of beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare's fee-for-service (FFS) sector accounted for 43 percent of total spending, while the costliest 25 percent...accounted for fully 85 percent of spending...These high-cost beneficiaries, compared with beneficiaries in the bottom 75 percent in terms of their spending, were slightly older, more likely to suffer from chronic conditions, such as coronary artery disease and diabetes, and more likely to die in a given year." Such concentration offers opportunities to focus on key ailments and treatment approaches. Peter Orszag wrote in May 2011: "The truth is that constraining future health care costs will require a variety of approaches, but in particular it will mean improving the information that providers have about their patients and best practices, and the incentives that providers are given to deliver better care, especially in expensive cases."
Market-based solutions
Privatize Medicare with a voucher system
Rep. Paul Ryan (R) has proposed the Roadmap for America's Future, which is a series of budgetary reforms. His January 2010 version of the plan includes the transition of Medicare to a voucher system, meaning individuals would receive a voucher which could be used to purchase health insurance in the private market. This would not affect those near retirement or currently enrolled in Medicare. A series of graphs and charts summarizing the impact of the plan are included. Economists have both praised and criticized particular features of the plan. The CBO also partially scored the bill.
Medicaid recipients could also be provided with tax credits or subsidies to purchase their own private insurance, reducing incentives for them to remain in the program.
Insurance company antitrust reforms
Some conservatives advocate free market reforms such as breaking up state monopolies on insurance and licensing and allowing consumers to purchase health insurance licensed by other states.
The GAO reported in 2002 (using 2000 data) the following statistics regarding insurance competition in state markets: "The median number of licensed carriers in the small group market per state was 28, with a range from 4 in Hawaii to 77 in Indiana. The median market share of the largest carrier was about 33 percent, with a range from about 14 percent in Texas to about 89 percent in North Dakota. The five largest carriers, when combined, represented three-quarters or more of the market in 19 of the 34 states supplying information, and they represented more than 90 percent in 7 of these states. Twenty-five of 37 states supplying information identified a Blue Cross and Blue Shield (BCBS) carrier as the largest carrier offering health insurance in the small group market, and in all but one of the remaining 12 states, a BCBS carrier was among the five largest. The median market share of all the BCBS carriers in the 34 states supplying information was about 34 percent, with a range from about 3 percent in Vermont to about 89 percent in North Dakota; in 9 of these states BCBS carriers combined for half or more of the market."
The GAO reported in 2008 (using 2007 data for the most part) the following statistics: "The median number of licensed carriers in the small group market per state was 27. The median market share of the largest carrier in the small group market was about 47 percent, with a range from about 21 percent in Arizona to about 96 percent in Alabama. In 31 of the 39 states supplying market share information, the top carrier had a market share of a third or more. The five largest carriers in the small group market, when combined, represented three quarters or more of the market in 34 of the 39 states supplying this information, and they represented 90 percent or more in 23 of these states. Thirty-six of the 44 states supplying information on the top carrier identified a Blue Cross and Blue Shield (BCBS) carrier as the largest carrier, and in all but 1 of the remaining 8 states, a BCBS carrier was among the five largest carriers. The median market share of all the BCBS carriers in the 38 states supplying this information was about 51 percent, with a range of less than 5 percent in Vermont and Wisconsin and more than 90 percent in Alabama and North Dakota...the median market share of all the BCBS carriers in 38 states reporting this information in 2008 was about 51 percent, compared to the 44 percent reported in 2005 and the 34 percent reported in 2002 for the 34 states supplying information in each of these years."
Economist Paul Krugman argued that allowing interstate competition would create a "race to the bottom," in which "[t]he states with the weakest regulations – for example, those that allow insurance companies to deny coverage to victims of domestic violence – would set the standards for the nation as a whole. The result would be to afflict the afflicted, to make the lives of Americans with pre-existing conditions even harder."
Reform of doctor's incentives
Critics have argued that the healthcare system has several incentives that drive costly behavior. Two of these include:
- Doctors are typically paid for services provided rather than with a salary. This provides a financial incentive to increase the costs of treatment provided.
- Patients that are fully insured have no financial incentive to minimize the cost when choosing among alternatives. The overall effect is to increase insurance premiums for all.
Gawande argued: "Our fee-for-service system, doling out separate payments for everything and everyone involved in a patient’s care, has all the wrong incentives: it rewards doing more over doing right, it increases paperwork and the duplication of efforts, and it discourages clinicians from working together for the best possible results."
Gawande quoted one surgeon who stated: "We took a wrong turn when doctors stopped being doctors and became businessmen." Gawande identified various revenue-enhancing approaches and profit-based incentives that doctors were using in high-cost areas that may have caused the over-utilization of healthcare. He contrasted this with lower-cost areas that used salaried doctors and other techniques to reward value, referring to this as a "battle for the soul of American medicine."
One option involves an integrated series of healthcare providers charging a premium or flat fee to patients to participate in the network, rather than a fee for each individual service. This modifies the doctor's incentive from ordering more services to solving the problem efficiently (i.e., more care to more cost-efficient care). The provider network would also purchase insurance for catastrophic (extremely high cost) cases.
Medical malpractice liability costs and tort reform
Critics have argued that medical malpractice costs (insurance and lawsuits, for example) are significant and should be addressed via tort reform.
How much these costs are is a matter of debate. Some have argued that malpractice lawsuits are a major driver of medical costs. A 2005 study estimated the cost around 0.2%, and in 2009 insurer WellPoint Inc. said "liability wasn’t driving premiums." A 2006 study found neurologists in the United States ordered more tests in theoretical clinical situations posed than their German counterparts; U.S. clinicians are more likely to fear litigation which may be due to the teaching of defensive strategies which are reported more often in U.S. teaching programs. Counting both direct and indirect costs, other studies estimate the total cost of malpractice "is linked to" between 5% and 10% of total U.S. medical costs.
A 2004 report by the Congressional Budget Office put medical malpractice costs at 2 percent of U.S. health spending and "even significant reductions" would do little to reduce the growth of health care expenses. A 2009 CBO report estimated that approximately $54 billion could be saved over ten years by limiting medical malpractice lawsuits. A tort reform package that includes caps on jury awards of $500,000 for punitive damages and $250,000 for "pain and suffering" damages would lower liability insurance premiums by about 10 percent.
In August 2009, physician and former Democratic National Committee Chairman Howard Dean explained why tort reform was omitted from the Congressional health care reform bills then under consideration: "When you go to pass a really enormous bill like that, the more stuff you put in it, the more enemies you make, right?...And the reason tort reform is not on the bill is because the people who wrote it did not want to take on the trial lawyers in addition to everybody else they were taking on. That is the plain and simple truth."
Others have argued that even successful tort reform might not lead to lower aggregate liability. For example, the current contingent fee system skews litigation towards high-value cases while ignoring meritorious small cases; aligning litigation more closely with merit might thus increase the number of small awards, offsetting any reduction in large awards. A New York study found that only 1.5% of hospital negligence led to claims; moreover, the CBO observed that "health care providers are generally not exposed to the financial cost of their own malpractice risk because they carry liability insurance, and the premiums for that insurance do not reflect the records or practice styles of individual providers but more-general factors such as location and medical specialty." Given that total liability is small relative to the amount doctors pay in malpractice insurance premiums, alternative mechanisms have been proposed to reform malpractice insurance.
In 2004, the CBO studied restrictions on malpractice awards proposed by the George W. Bush Administration and members of Congress; CBO concluded that "the evidence available to date does not make a strong case that restricting malpractice liability would have a significant effect, either positive or negative, on economic efficiency." Empirical data and reporting have since shown that some of the highest medical costs are now in states where tort reform had already caused malpractice premiums and lawsuits to drop substantially; unnecessary and injurious procedures are instead caused by a system "often driven to maximize revenues over patient needs."
One option proposed includes specialized healthcare courts rather than the jury system. Such courts exist in other disciplines. In administrative health courts, an expert judge would decide cases based on best medical practice, writing an opinion that is subject to appeal to an appellate health court. There would also be a requirement of full disclosure by hospitals, and all facts would be fed back into the health care system so providers learn from their mistakes. Such an approach has been opposed by trial lawyer lobbyists.
Addressing the shortage of doctors and nurses
The U.S. is facing shortages of doctors and nurses that are projected to grow worse as America ages, which may drive up the price of these services. Writing in The Washington Post, cardiologist Arthur Feldman cited various studies that indicate the U.S. is facing a "critical" shortage of doctors, including an estimated 1,300 general surgeons by 2010.
The American Academy of Family Physicians predicts a shortage of 40,000 primary care doctors (including family practice, internal medicine, pediatrics and obstetrics/gynecology) by 2020. The number of medical students choosing the primary care specialty has dropped by 52% since 1997. Currently, only 2% of medical school graduates choose primary care as a career. An amendment to the Senate health bill includes $2 billion in funds over 10 years to create 2,000 new residency training slots geared toward primary care medicine and general surgery. Writing in Forbes, a physician argued that this is a "tiny band-aid at best," advocating full loan repayments and guaranteed positions upon graduation.
Physicians wrote a NYT Op Ed in May 2011 stating that doctors typically graduate with an average of $155,000 in debt from Medical school, with over 80% owing debt of some type. This drives some doctors into higher paying specialties as opposed to primary care. As specialists, they prescribe more expensive treatments. About $2.5 billion/year would be required to make Medical school free, which the writers estimated at one-thousandth the total annual healthcare costs. Making medical school free would help address the shortage in their view.
The U.S. had 2.3 doctors per 1,000 people in 2002, ranking 52nd. Germany and France had approximately 3.4 and ranked in the top 25. The OECD average in 2008 was 3.1 doctors per 1,000 people, while the U.S. had 2.4.
The American Association of Colleges of Nurses cited studies estimating that a shortage of registered nurses would reach 230,000 by 2025 as America ages, with over 135,000 open positions during 2007. An additional 30% more nurses would have to graduate annually to keep up with demand. A study by Price Waterhouse advanced several strategies for addressing the nursing shortage, including developing more public-private partnerships, federal and state-level grants for nursing students and educators, creating healthy work environments, using technology as a training tool, and designing more flexible roles for advanced practice nurses given their increased use as primary care providers.
Newsweek wrote: "Lately, some policymakers have argued that instead of having a primary-care doctor, more people—especially young, healthy patients with simple medical needs—should see a nurse or physician assistant who administers routine care and kicks more complex problems up to a doctor when they arise. 'If you're just coming in to have your blood pressure checked and your pulse taken, you really don't need to see a doctor, and you might not need to see a nurse, either,' says David Barrett, president and CEO of the Lahey Clinic in Burlington, Mass. "There are three-stripe military sergeants with two-year degrees who can provide excellent primary care. There's absolutely no reason to force all primary-care providers to have an M.D."
Tax reform

The Congressional Budget Office has described how the tax treatment of insurance premiums may affect behavior:
One factor perpetuating inefficiencies in health care is a lack of clarity regarding the cost of health insurance and who bears that cost, especially employment-based health insurance. Employers’ payments for employment-based health insurance and nearly all payments by employees for that insurance are excluded from individual income and payroll taxes. Although both theory and evidence suggest that workers ultimately finance their employment-based insurance through lower take-home pay, the cost is not evident to many workers...If transparency increases and workers see how much their income is being reduced for employers’contributions and what those contributions are paying for, there might be a broader change in cost-consciousness that shifts demand.
Peter Singer wrote in The New York Times that the current exclusion of insurance premiums from compensation represents a $200 billion subsidy for the private insurance industry and that it would likely not exist without it. In November 2009, The Economist estimated that taxing employer-provided health insurance (which is presently exempt from tax) would add $215 billion per year to federal tax revenue.
Employer-provided health insurance receives uncapped tax benefits. According to the OECD, it "encourages the purchase of more generous insurance plans, notably plans with little cost sharing, thus exacerbating moral hazard". Consumers want unfettered access to medical services; they also prefer to pay through insurance or tax rather than out of pocket. These two needs create cost-efficiency challenges for health care. Some studies have found no consistent and systematic relationship between the type of financing of health care and cost containment.
Some have proposed an "excise tax" for high cost 'Cadillac' insurance plans. A study published in Health Affairs in December 2009 found that high-cost health plans do not provide unusually rich benefits to enrollees. The researchers found that only 3.7% of the variation in the cost of family coverage in employer-sponsored health plans is attributable to differences in the actuarial value of benefits. Only 6.1% of the variation is attributable to the combination of benefit design and plan type (e.g., PPO, HMO, etc.). The employer's industry and regional variations in health care cost explain part of the variation, but most is unexplained. The researchers conclude ". . . that analysts should not equate high-cost plans with Cadillac plans, . . . [w]ithout appropriate adjustments, a simple cap may exacerbate rather than ameliorate current inequities"
Premium tax subsidies to help individuals purchase their own health insurance have also been suggested as a way to increase coverage rates. Research confirms that consumers in the individual health insurance market are sensitive to price. It appears that price sensitivity varies among population subgroups and is generally higher for younger individuals and lower income individuals. However, research also suggests that subsidies alone are unlikely to solve the uninsured problem in the U.S.
Government action
Address Medicare fraud
The Government Accountability Office lists Medicare as a "high-risk" government program due to its vulnerability to improper payments. Estimates of Medicare fraud or "improper payments" vary. The Office of Management and Budget reported that $54 billion in "improper payments" were made to Medicare ($24B), Medicaid ($18B) and Medicaid Advantage ($12B) during FY2009. This was 9.4% of the $573 billion spent in these categories. GAO reported in 2000: "The Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General has reported that $13.5 billion of processed Medicare fee-for-service claim payments for fiscal year 1999 may have been improperly paid for reasons that ranged from inadvertent error to outright fraud and abuse." Fewer than 5% of Medicare claims are audited. CBO reported in October 2014 that it is difficult to quantify healthcare fraud related to government programs. CBO reported that: "According to HHS, since 2009 the HEAT Medicare task force has filed criminal and civil charges against more than 1,700 defendants who falsely billed the Medicare program for more than $5.5 billion." However, false billing is a partial measure of fraud, as much of it is undetected.
According to CBS News, Medicare fraud accounts for an estimated $60 billion in Medicare payments each year, and "has become one of, if not the most profitable, crimes in America." Criminals set up phony companies, then invoice Medicare for fraudulent services provided to valid Medicare patients who never receive the services. These costs appear on the Medicare statements provided to Medicare card holders. The program pays out over $430 billion per year via over 1 billion claims, making enforcement challenging. Its enforcement budget is "extremely limited" according to one Medicare official. U.S. Attorney General Eric Holder said in an interview: "Clearly more auditing needs to be done and it needs to be done in real time." The Obama administration is providing Medicare with an additional $200 million to fight fraud as part of its stimulus package, and billions of dollars to computerize medical records and upgrade networks, which should assist Medicare in identifying fraudulent claims.
During July 2010, President Obama signed into law the Improper Payments Elimination and Recovery Act of 2010, citing approximately $110 billion in unauthorized payments of all types, including Medicare and Medicaid. President Obama has directed his administration to reduce these payments by $50 million annually by 2012, less than 1%.
Coverage mandates
Reforming or restructuring the private health insurance market is often suggested as a means for achieving health care reform in the U.S. Insurance market reform has the potential to increase the number of Americans with insurance, but is unlikely to significantly reduce the rate of growth in health care spending. Careful consideration of basic insurance principles is important when considering insurance market reform, in order to avoid unanticipated consequences and ensure the long-term viability of the reformed system. According to one study conducted by the Urban Institute, if not implemented on a systematic basis with appropriate safeguards, market reform has the potential to cause more problems than it solves.
Since most Americans with private coverage receive it through employer-sponsored plans, many have suggested employer "pay or play" requirements as a way to increase coverage levels (i.e., employers that do not provide insurance would have to pay a tax instead). However, research suggests that current pay or play proposals are limited in their ability to increase coverage among the working poor. These proposals generally exclude small firms, do not distinguish between individuals who have access to other forms of coverage and those who do not, and increase the overall compensation costs to employers.
In October 2009 the Wall Street Journal reported that while requirements to purchase health insurance were central to proposals in both the House and Senate, these coverage mandates were "under fire from both ends of the political spectrum, with some liberals saying the penalties are too harsh for those who refuse and conservatives denouncing the whole concept." According to the article, however, "[h]ealth-policy experts . . .say there is a good reason for the mandate." Proposed reforms would prohibit health insurers from denying coverage to individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. Insurers said that, to keep premiums from rising for everyone, it is necessary for healthier people to pay into the insurance pools to balance out the cost of these higher cost individuals.
Arguing against requiring individuals to buy coverage, the Cato Institute has asserted that the Massachusetts law forcing everyone to buy insurance has increased costs: "Premiums are growing 21 to 46 percent faster than the national average, in part because Massachusetts' individual mandate has effectively outlawed affordable health plans." They say that "the mandate gives politicians enormous power to dictate the content of every American's health plan – a power that health care providers inevitably capture and use to increase the required level of insurance" and state that providers were successful in persuading legislators to include an additional 16 benefit mandates in the required benefit package during the first three years after the coverage mandate was enacted. They also say that by prohibiting the use of health status in pricing, the Massachusetts law "further increase[s] premiums for the young and healthy" and, as the result of adverse selection, drives more comprehensive health plans out of the market. The conclusion they draw is that "[T]he most sweeping provision . . . is an 'individual mandate' that makes health insurance compulsory. Massachusetts shows that such a mandate would oust millions from their low-cost health plans and force them to pay higher premiums."
Writing in the New York Times opinion blog "Room for Debate" the single-payer health care advocate Marcia Angell, former editor-in-chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, said that a coverage mandate would not be necessary within a single-payer system and that even within the context of current system she was "troubled by the notion of an individual mandate." She described the Massachusetts mandates as "a windfall for the insurance industry" and wrote, "Premiums are rising much faster than income, benefit packages are getting skimpier, and deductibles and co-payments are going up."
In April 2009 the Boston Globe reported that the number of people seeking emergency room care and the cost of emergency room visits increased after the 2006 mandates went into effect (comparing 2005 to 2007). The number of visits increased by 7% during that period, while costs rose by 17%. State officials cautioned that it was too early to determine if the state's new coverage mandate had failed to reduce the emergency room use, but several physicians and policymakers said that it was unlikely that a coverage mandate alone could solve the problems of emergency room crowding and overuse. In August 2009 the Boston Globe reported that Massachusetts had "the most expensive family health insurance premiums in the country." Premiums in Massachusetts increased by 40 percent from 2003 to 2008, compared to a national average increase of 33%. The report did not break out the amount of the increase since 2006, but as the Massachusetts reforms are often taken as a model for national reform, "advocates on various sides of the issue said the report underscores the urgency of including cost controls in any large-scale federal or state overhaul." Karen Davenport, director of health policy at the Center for American Progress, has argued that "before making coverage mandatory, we need to reform the health insurance market, strengthen public health insurance programs, and finance premium subsidies for people who can’t afford coverage on their own."
Addressing the issue when it was proposed in 1994, CBO wrote: "A mandate requiring all individuals to purchase health insurance would be an unprecedented form of federal action. The government has never required people to buy any good or service as a condition of lawful residence in the United States." There is also disagreement as to whether federal mandates would be constitutional, and state initiatives opposing federal mandates may lead to litigation and delay.
On June 28, 2012, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the individual mandate provision as Constitutional.
Rationing of care
President Barack Obama argues that U.S. healthcare is rationed, based on income, type of employment, and pre-existing medical conditions, with nearly 46 million uninsured. He argues that millions of Americans are denied coverage or face higher premiums as a result of pre-existing medical conditions.
Peter Singer and David Leonhardt have each separately noted that health care rationing is not a choice, but an economic necessity. All health care resources are finite and have to be allocated in some way or other. The issue is which way is the most sensible way to do it.
Former Republican Secretary of Commerce Peter G. Peterson has also argued that some form of rationing is inevitable and desirable considering the state of U.S. finances and the trillions of dollars of unfunded Medicare liabilities. He estimated that 25–33% of healthcare services are provided to those in the last months or year of life and advocated restrictions in cases where quality of life cannot be improved. He also recommended that a budget be established for government healthcare expenses, through establishing spending caps and pay-as-you-go rules that require tax increases for any incremental spending. He has indicated that a combination of tax increases and spending cuts will be required. All of these issues would be addressed under the aegis of a fiscal reform commission.
Rationing by price means accepting that there is no triage according to need. Thus in the private sector it is accepted that some people get expensive surgeries such as liver transplants or non life-threatening ones such as cosmetic surgery, when others fail to get cheaper and much more cost effective care such as prenatal care, which could save the lives of many fetuses and newborn children. Some places, like Oregon for example, do explicitly ration Medicaid resources using medical priorities.
Politicians on the right tend to be fearful of democratically elected governments becoming involved in rationing decision. Former House Speaker Newt Gingrich (R-GA) argued that the reform plans supported by President Obama expand the control of government over healthcare decisions, which he referred to as a type of healthcare rationing. Senator Charles Grassley (R-IA) makes similar arguments claiming for example that people like the late Senator Edward Kennedy received health care in the U.S. that would have been denied in countries which have government controlled health care, a claim that The Economist magazine said was "dangerous" and went on to say that "The reality is that America, like Britain, already makes extensive use of rationing.
Better usage of healthcare technology
Automation of patient records
The Congressional Budget Office has concluded that increased use of health information technology has great potential to significantly reduce overall health care spending and realize large improvements in health care quality providing that the system is integrated. The use of health IT in an unintegrated setting will not realize all the projected savings.
Treatment registries
One application of healthcare technology is the creation of registries or databases to relate treatments to outcomes. Useful treatments could be identified and those less useful could be avoided to reduce costs.
Payment system reform
The payment system refers to the billing and payment for medical services, which is distinct from the delivery system through which the services are provided. The over 1,300 U.S. health insurance companies have different forms and processes for billing and reimbursement, requiring enormous costs on the part of service providers (mainly doctors and hospitals) to process payments. For example, the Cleveland Clinic, considered a low-cost, best-practices hospital system, has 1,400 billing clerks to support 2,000 doctors. Further, the insurance companies have their own overhead functions and profit margins, much of which could be eliminated with a single payer system. Economist Paul Krugman estimated in 2005 that converting from the current private insurance system to a single-payer system would enable $200 billion per year in cost savings, primarily via insurance company overhead. One advocacy group estimated savings as high as $400 billion annually for 2009 and beyond.
Proponents of health care reform argue that moving to a single-payer system would reallocate the money currently spent on the administrative overhead required to run the hundreds of insurance companies in the U.S. to provide universal care. An often-cited study by Harvard Medical School and the Canadian Institute for Health Information determined that some 31 percent of U.S. health care dollars, or more than $1,000 per person per year, went to health care administrative costs. Other estimates are lower. One study of the billing and insurance-related (BIR) costs borne not only by insurers but also by physicians and hospitals found that BIR among insurers, physicians, and hospitals in California represented 20–22% of privately insured spending in California acute care settings.
Advocates of "single-payer" argue that shifting the U.S. to a single-payer health care system would provide universal coverage, give patients free choice of providers and hospitals, and guarantee comprehensive coverage and equal access for all medically necessary procedures, without increasing overall spending. Shifting to a single-payer system, by this view, would also eliminate oversight by managed care reviewers, restoring the traditional doctor-patient relationship. Among the organizations in support of single-payer health care in the U.S. is Physicians for a National Health Program (PNHP), an organization of some 17,000 American physicians, medical students, and health professionals.
Reduce costs of imaging technology
During 2009, Medicare spent $11.7 billion for medical imaging, such as CT scans and MRI's. From 2005 to 2009, usage of scans grew at an annual rate of 14%, but may have slowed since due to a combination of changing incentives and saturation of usage. Initially, demanding patients insisted on scans; doctors feared malpractice suits if they refused; and doctors and hospitals wanted to maximize revenues. One study indicated that changing incentives may have reduced cost growth. From 2006 to 2010, the share of workers with deductibles exceeding $1,000 grew from 10 percent to 27 percent. Increased out-of-pocket expenses have made patients and physicians more cost conscious. Further, a combination of prior notification, higher patient co-payments and restrained reimbursements may have contributed to slowing cost growth.
Motivation
International comparisons of healthcare have found that the United States spends more per-capita than other similarly developed nations but falls below similar countries in various health metrics, suggesting inefficiency and waste. In addition, the United States has significant underinsurance and significant impending unfunded liabilities from its aging demographic and its social insurance programs Medicare and Medicaid (Medicaid provides free long-term care to the elderly poor). The fiscal and human impact of these issues have motivated reform proposals.
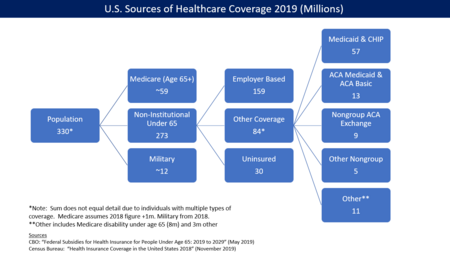
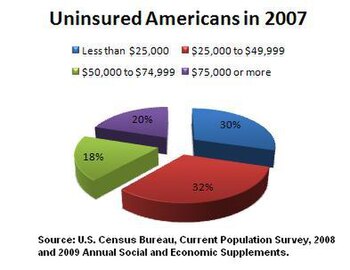
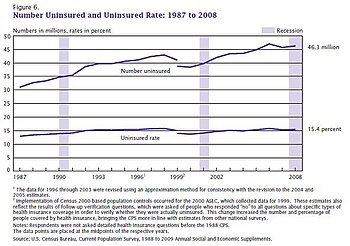
According to 2009 World Bank statistics, the U.S. had the highest healthcare costs relative to the size of the economy (GDP) in the world, even though estimated 50.2 million citizens (approximately 15.6% of the September 2011 estimated population of 312 million) lacked insurance. In March 2010, billionaire Warren Buffett commented that the high costs paid by U.S. companies for their employees' health care put them at a competitive disadvantage.
Further, an estimated 77 million Baby Boomers are reaching retirement age, which combined with significant annual increases in healthcare costs per person will place enormous budgetary strain on U.S. state and federal governments, particularly through Medicare and Medicaid spending (Medicaid provides long-term care for the elderly poor). Maintaining the long-term fiscal health of the U.S. federal government is significantly dependent on healthcare costs being controlled.
Insurance cost and availability
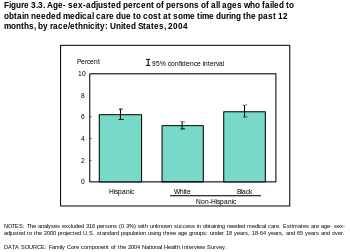
In addition, the number of employers who offer health insurance has declined and costs for employer-paid health insurance are rising: from 2001 to 2007, premiums for family coverage increased 78%, while wages rose 19% and prices rose 17%, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. Even for those who are employed, the private insurance in the US varies greatly in its coverage; one study by the Commonwealth Fund published in Health Affairs estimated that 16 million U.S. adults were underinsured in 2003. The underinsured were significantly more likely than those with adequate insurance to forgo health care, report financial stress because of medical bills, and experience coverage gaps for such items as prescription drugs. The study found that underinsurance disproportionately affects those with lower incomes — 73% of the underinsured in the study population had annual incomes below 200% of the federal poverty level. However, a study published by the Kaiser Family Foundation in 2008 found that the typical large employer preferred provider organization (PPO) plan in 2007 was more generous than either Medicare or the Federal Employees Health Benefits Program Standard Option. One indicator of the consequences of Americans' inconsistent health care coverage is a study in Health Affairs that concluded that half of personal bankruptcies involved medical bills, although other sources dispute this.
There are health losses from insufficient health insurance. A 2009 study found more than 44,800 excess deaths annually in the United States due to Americans lacking health insurance. More broadly, estimates of the total number of people in the United States, whether insured or uninsured, who die because of lack of medical care were estimated in a 1997 analysis to be nearly 100,000 per year. A study of the effects of the Massachusetts universal health care law (which took effect in 2006) found a 3% drop in mortality among people 20–64 years old - 1 death per 830 people with insurance. Other studies, just as those examining the randomized distribution of Medicaid insurance to low-income people in Oregon in 2008, found no change in death rate.
The cost of insurance has been a primary motivation in the reform of the US healthcare system, and many different explanations have been proposed in the reasons for high insurance costs and how to remedy them. One critique and motivation for healthcare reform has been the development of the medical–industrial complex. This relates to moral arguments for health care reform, framing healthcare as a social good, one that is fundamentally immoral to deny to people based on economic status. The motivation behind healthcare reform in response to the medical-industrial complex also stems from issues of social inequity, promotion of medicine over preventative care. The medical-industrial complex, defined as a network of health insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, and the like, plays a role in the complexity of the US insurance market and a fine line between government and industry within it. Likewise, critiques of insurance markets being conducted under a capitalistic, free-market model also include that medical solutions, as opposed to preventative healthcare measures, are promoted to maintain this medical-industrial complex. Arguments for a market-based approach to health insurance include the Grossman model, which is based on an ideal competitive model, but others have critiqued this, arguing that fundamentally, this means that people in higher socioeconomic levels will receive a better quality of healthcare.
Uninsured rate
Another concern is the rate of uninsured people in the US. In June 2014, Gallup–Healthways Well–Being conducted a survey and found that the uninsured rate is going down. 13.4 percent of U.S. adults are uninsured in 2014. This is a decrease from the percentage at 17.1 percent in January 2014 and translates to roughly 10 million to 11 million individuals who gained coverage. The survey also looked at the major demographic groups and found each is making progress towards getting health insurance. However, Hispanics, who have the highest uninsured rate of any racial or ethnic group, are lagging in their progress. Under the new health care reform, Latinos were expected to be major beneficiaries of the new health care law. Gallup found that the biggest drop in the uninsured rate (2.8 percentage points) was among households making less than $36,000 a year.
Waste and fraud
In December 2011 the outgoing Administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Donald Berwick, asserted that 20% to 30% of health care spending is waste. He listed five causes for the waste: (1) overtreatment of patients, (2) the failure to coordinate care, (3) the administrative complexity of the health care system, (4) burdensome rules and (5) fraud.
An estimated 3%–10% of all health care expenditures in the U.S. are fraudulent. In 2011, Medicare and Medicaid made $65 billion in improper payments (including both error and fraud). Government efforts to reduce fraud include $4.2 billion in fraudulent payments recovered by the Department of Justice and the FBI in 2012, longer jail sentences specified by the Affordable Care Act, and Senior Medicare Patrols—volunteers trained to identify and report fraud.
International comparisons
The International Federation of Health Plans provides a comparative annual survey of costs for drugs, devices and medical services across countries. According to their 2013 report, the U.S. pays considerably more than other countries in 22 of 23 categories. For example, the average cost of a hip replacement in the U.S. was $40,364, with other countries ranging from $3,365 (Argentina) to $27,810 (Australia). An MRI averaged $1,121 in the U.S. versus $280 in France. The reasons for these differences are driven by higher prices per unit of service, rather than a higher volume of usage. In other countries, governments intervene more forcefully in setting prices. In countries such as Canada and Britain, prices are set by the government. In others, such as Germany and Japan, they're set by providers and insurers sitting in a room and coming to an agreement, with the government stepping in to set prices if they fail.
Other topics
Importation of prescription drugs
Congressional proponents argue that drugs manufactured overseas by U.S. companies could be imported and purchased more cheaply in the U.S. Drug manufacturers argue that certain foreign countries have price controls, which they recoup by charging higher prices in the U.S. Whitehouse spokesman Robert Gibbs said President Obama is supportive of importing drugs, provided safety concerns related to the drugs can be addressed. This is because drugs manufactured outside the country may be held to different standards. According to Bloomberg News, drugmakers agreed in June 2009 to contribute $80 billion over 10 years, largely to help the elderly afford medicines, in return for staving off other profit-endangering proposals such as drug importation.