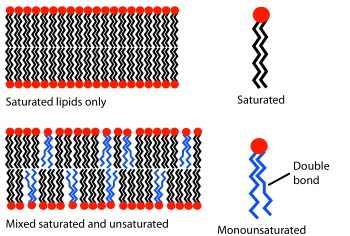
This fluid lipid bilayer cross section is made up entirely of phosphatidylcholine.
The three main structures phospholipids form in solution; the liposome (a closed bilayer), the micelle and the bilayer.
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and other membranes surrounding sub-cellular structures. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins
and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from
diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are
ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps.
Biological bilayers are usually composed of amphiphilic phospholipids that have a hydrophilic phosphate head and a hydrophobic
tail consisting of two fatty acid chains. Phospholipids with certain
head groups can alter the surface chemistry of a bilayer and can, for
example, serve as signals as well as "anchors" for other molecules in
the membranes of cells. Just like the heads, the tails of lipids can also affect membrane properties, for instance by determining the phase of the bilayer. The bilayer can adopt a solid gel phase state at lower temperatures but undergo phase transition to a fluid state
at higher temperatures, and the chemical properties of the lipids'
tails influence at which temperature this happens. The packing of lipids
within the bilayer also affects its mechanical properties, including
its resistance to stretching and bending. Many of these properties have
been studied with the use of artificial "model" bilayers produced in a
lab. Vesicles made by model bilayers have also been used clinically to deliver drugs.
Biological membranes typically include several types of molecules other than phospholipids. A particularly important example in animal cells is cholesterol, which helps strengthen the bilayer and decrease its permeability. Cholesterol also helps regulate the activity of certain integral membrane proteins.
Integral membrane proteins function when incorporated into a lipid
bilayer, and they are held tightly to lipid bilayer with the help of an annular lipid shell.
Because bilayers define the boundaries of the cell and its
compartments, these membrane proteins are involved in many intra- and
inter-cellular signaling processes. Certain kinds of membrane proteins
are involved in the process of fusing two bilayers together. This fusion
allows the joining of two distinct structures as in the fertilization of an egg by sperm or the entry of a virus
into a cell. Because lipid bilayers are quite fragile and invisible in
a traditional microscope, they are a challenge to study. Experiments on
bilayers often require advanced techniques like electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy.
Structure and organization
When
phospholipids are exposed to water, they self-assemble into a
two-layered sheet with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the center
of the sheet. This arrangement results in two “leaflets” that are each a
single molecular layer. The center of this bilayer contains almost no
water and excludes molecules like sugars or salts that dissolve in water. The assembly process is driven by interactions between hydrophobic molecules (also called the hydrophobic effect).
An increase in interactions between hydrophobic molecules (causing
clustering of hydrophobic regions) allows water molecules to bond more
freely with each other, increasing the entropy of the system. This
complex process includes non-covalent interactions such as van der Waals forces, electrostatic and hydrogen bonds.
Schematic
cross sectional profile of a typical lipid bilayer. There are three
distinct regions: the fully hydrated headgroups, the fully dehydrated
alkane core and a short intermediate region with partial hydration.
Although the head groups are neutral, they have significant dipole
moments that influence the molecular arrangement.
Cross section analysis
The
lipid bilayer is very thin compared to its lateral dimensions. If a
typical mammalian cell (diameter ~10 micrometers) were magnified to the
size of a watermelon (~1 ft/30 cm), the lipid bilayer making up the plasma membrane
would be about as thick as a piece of office paper. Despite being only a
few nanometers thick, the bilayer is composed of several distinct
chemical regions across its cross-section. These regions and their
interactions with the surrounding water have been characterized over the
past several decades with x-ray reflectometry, neutron scattering and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques.
The first region on either side of the bilayer is the hydrophilic
headgroup. This portion of the membrane is completely hydrated and is
typically around 0.8-0.9 nm thick. In phospholipid bilayers the phosphate group is located within this hydrated region, approximately 0.5 nm outside the hydrophobic core.
In some cases, the hydrated region can extend much further, for
instance in lipids with a large protein or long sugar chain grafted to
the head. One common example of such a modification in nature is the lipopolysaccharide coat on a bacterial outer membrane, which helps retain a water layer around the bacterium to prevent dehydration.
TEM
image of a bacterium. The furry appearance on the outside is due to a
coat of long-chain sugars attached to the cell membrane. This coating
helps trap water to prevent the bacterium from becoming dehydrated.
Next to the hydrated region is an intermediate region that is only
partially hydrated. This boundary layer is approximately 0.3 nm thick.
Within this short distance, the water concentration drops from 2M on the
headgroup side to nearly zero on the tail (core) side. The hydrophobic core of the bilayer is typically 3-4 nm thick, but this value varies with chain length and chemistry. Core thickness also varies significantly with temperature, in particular near a phase transition.
Asymmetry
In many naturally occurring bilayers, the compositions of the inner and outer membrane leaflets are different. In human red blood cells, the inner (cytoplasmic) leaflet is composed mostly of phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol and its phosphorylated derivatives. By contrast, the outer (extracellular) leaflet is based on phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin and a variety of glycolipids, In some cases, this asymmetry is based on where the lipids are made in the cell and reflects their initial orientation.
The biological functions of lipid asymmetry are imperfectly understood,
although it is clear that it is used in several different situations.
For example, when a cell undergoes apoptosis,
the phosphatidylserine — normally localised to the cytoplasmic
leaflet — is transferred to the outer surface: There, it is recognised
by a macrophage that then actively scavenges the dying cell.
Lipid asymmetry arises, at least in part, from the fact that most
phospholipids are synthesised and initially inserted into the inner
monolayer: those that constitute the outer monolayer are then
transported from the inner monolayer by a class of enzymes called flippases.
Other lipids, such as sphingomyelin, appear to be synthesised at the
external leaflet. Flippases are members of a larger family of lipid
transport molecules that also includes floppases, which transfer lipids
in the opposite direction, and scramblases, which randomize lipid
distribution across lipid bilayers (as in apoptotic cells). In any case,
once lipid asymmetry is established, it does not normally dissipate
quickly because spontaneous flip-flop of lipids between leaflets is
extremely slow.
It is possible to mimic this asymmetry in the laboratory in model bilayer systems. Certain types of very small artificial vesicle
will automatically make themselves slightly asymmetric, although the
mechanism by which this asymmetry is generated is very different from
that in cells. By utilizing two different monolayers in Langmuir-Blodgett deposition or a combination of Langmuir-Blodgett and vesicle rupture deposition
it is also possible to synthesize an asymmetric planar bilayer. This
asymmetry may be lost over time as lipids in supported bilayers can be
prone to flip-flop.
Phases and phase transitions
Diagram
showing the effect of unsaturated lipids on a bilayer. The lipids with
an unsaturated tail (blue) disrupt the packing of those with only
saturated tails (black). The resulting bilayer has more free space and
is, as a consequence, more permeable to water and other small molecules.
At a given temperature a lipid bilayer can exist in either a liquid
or a gel (solid) phase. All lipids have a characteristic temperature at
which they transition (melt) from the gel to liquid phase. In both
phases the lipid molecules are prevented from flip-flopping across the
bilayer, but in liquid phase bilayers a given lipid will exchange
locations with its neighbor millions of times a second. This random walk exchange allows lipid to diffuse and thus wander across the surface of the membrane. Unlike liquid phase bilayers, the lipids in a gel phase bilayer have less mobility.
The phase behavior of lipid bilayers is determined largely by the strength of the attractive Van der Waals
interactions between adjacent lipid molecules. Longer-tailed lipids
have more area over which to interact, increasing the strength of this
interaction and, as a consequence, decreasing the lipid mobility. Thus,
at a given temperature, a short-tailed lipid will be more fluid than an
otherwise identical long-tailed lipid. Transition temperature can also be affected by the degree of unsaturation of the lipid tails. An unsaturated double bond can produce a kink in the alkane
chain, disrupting the lipid packing. This disruption creates extra free
space within the bilayer that allows additional flexibility in the
adjacent chains.
An example of this effect can be noted in everyday life as butter,
which has a large percentage saturated fats, is solid at room
temperature while vegetable oil, which is mostly unsaturated, is liquid.
Most natural membranes are a complex mixture of different lipid
molecules. If some of the components are liquid at a given temperature
while others are in the gel phase, the two phases can coexist in
spatially separated regions, rather like an iceberg floating in the
ocean. This phase separation plays a critical role in biochemical
phenomena because membrane components such as proteins can partition
into one or the other phase and thus be locally concentrated or activated. One particularly important component of many mixed phase systems is cholesterol, which modulates bilayer permeability, mechanical strength, and biochemical interactions.
Surface chemistry
While
lipid tails primarily modulate bilayer phase behavior, it is the
headgroup that determines the bilayer surface chemistry. Most natural
bilayers are composed primarily of phospholipids, but sphingolipids and sterols such as cholesterol are also important components. Of the phospholipids, the most common headgroup is phosphatidylcholine (PC), accounting for about half the phospholipids in most mammalian cells. PC is a zwitterionic
headgroup, as it has a negative charge on the phosphate group and a
positive charge on the amine but, because these local charges balance,
no net charge.
Other headgroups are also present to varying degrees and can include phosphatidylserine (PS) phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylglycerol
(PG). These alternate headgroups often confer specific biological
functionality that is highly context-dependent. For instance, PS
presence on the extracellular membrane face of erythrocytes is a marker of cell apoptosis, whereas PS in growth plate vesicles is necessary for the nucleation of hydroxyapatite crystals and subsequent bone mineralization.
Unlike PC, some of the other headgroups carry a net charge, which can
alter the electrostatic interactions of small molecules with the
bilayer.
Biological roles
Containment and separation
The primary role of the lipid bilayer in biology is to separate aqueous
compartments from their surroundings. Without some form of barrier
delineating “self” from “non-self,” it is difficult to even define the
concept of an organism or of life. This barrier takes the form of a
lipid bilayer in all known life forms except for a few species of archaea that utilize a specially adapted lipid monolayer. It has even been proposed that the very first form of life may have been a simple lipid vesicle with virtually its sole biosynthetic capability being the production of more phospholipids. The partitioning ability of the lipid bilayer is based on the fact that hydrophilic molecules cannot easily cross the hydrophobic
bilayer core, as discussed in Transport across the bilayer below. The
nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts have two lipid bilayers, while
other sub-cellular structures are surrounded by a single lipid bilayer
(such as the plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticula, Golgi apparatus and
lysosomes).
Prokaryotes have only one lipid bilayer- the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane). Many prokaryotes also have a cell wall, but the cell wall is composed of proteins or long chain carbohydrates, not lipids. In contrast, eukaryotes have a range of organelles including the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes and endoplasmic reticulum.
All of these sub-cellular compartments are surrounded by one or more
lipid bilayers and, together, typically comprise the majority of the
bilayer area present in the cell. In liver hepatocytes
for example, the plasma membrane accounts for only two percent of the
total bilayer area of the cell, whereas the endoplasmic reticulum
contains more than fifty percent and the mitochondria a further thirty
percent.
Signaling
Probably the most familiar form of cellular signaling is synaptic transmission, whereby a nerve impulse that has reached the end of one neuron is conveyed to an adjacent neuron via the release of neurotransmitters. This transmission is made possible by the action of synaptic vesicles loaded with the neurotransmitters to be released. These vesicles fuse
with the cell membrane at the pre-synaptic terminal and release its
contents to the exterior of the cell. The contents then diffuse across
the synapse to the post-synaptic terminal.
Lipid bilayers are also involved in signal transduction through their role as the home of integral membrane proteins. This is an extremely broad and important class of biomolecule. It is estimated that up to a third of the human proteome may be membrane proteins. Some of these proteins are linked to the exterior of the cell membrane. An example of this is the CD59 protein, which identifies cells as “self” and thus inhibits their destruction by the immune system. The HIV virus evades the immune system in part by grafting these proteins from the host membrane onto its own surface.
Alternatively, some membrane proteins penetrate all the way through the
bilayer and serve to relay individual signal events from the outside to
the inside of the cell. The most common class of this type of protein
is the G protein-coupled receptor
(GPCR). GPCRs are responsible for much of the cell’s ability to sense
its surroundings and, because of this important role, approximately 40%
of all modern drugs are targeted at GPCRs.
In addition to protein- and solution-mediated processes, it is
also possible for lipid bilayers to participate directly in signaling. A
classic example of this is phosphatidylserine-triggered phagocytosis.
Normally, phosphatidylserine is asymmetrically distributed in the cell
membrane and is present only on the interior side. During programmed
cell death a protein called a scramblase
equilibrates this distribution, displaying phosphatidylserine on the
extracellular bilayer face. The presence of phosphatidylserine then
triggers phagocytosis to remove the dead or dying cell.
Characterization methods
Human red blood cells viewed through a fluorescence microscope. The cell membrane has been stained with a fluorescent dye. Scale bar is 20μm.
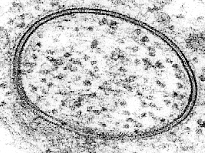
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) image of a lipid vesicle.
The two dark bands around the edge are the two leaflets of the bilayer.
Historically, similar images confirmed that the cell membrane is a
bilayer
The lipid bilayer is a very difficult structure to study because it
is so thin and fragile. In spite of these limitations dozens of
techniques have been developed over the last seventy years to allow
investigations of its structure and function.
Electrical measurements are a straightforward way to characterize
an important function of a bilayer: its ability to segregate and
prevent the flow of ions in solution. By applying a voltage across the
bilayer and measuring the resulting current, the resistance of the bilayer is determined. This resistance is typically quite high (108 Ohm-cm2 or more) since the hydrophobic core is impermeable to charged species. The
presence of even a few nanometer-scale holes results in a dramatic
increase in current. The sensitivity of this system is such that even the activity of single ion channels can be resolved.
Electrical measurements do not provide an actual picture like
imaging with a microscope can. Lipid bilayers cannot be seen in a
traditional microscope because they are too thin. In order to see
bilayers, researchers often use fluorescence microscopy.
A sample is excited with one wavelength of light and observed in a
different wavelength, so that only fluorescent molecules with a matching
excitation and emission profile will be seen. Natural lipid bilayers
are not fluorescent, so a dye is used that attaches to the desired
molecules in the bilayer. Resolution is usually limited to a few hundred
nanometers, much smaller than a typical cell but much larger than the
thickness of a lipid bilayer.
3d-Adapted AFM images showing formation of transmembrane pores (holes) in supported lipid bilayer
Illustration of a typical AFM
scan of a supported lipid bilayer. The pits are defects in the bilayer,
exposing the smooth surface of the substrate underneath.
Electron microscopy offers a higher resolution image. In an electron microscope, a beam of focused electrons
interacts with the sample rather than a beam of light as in traditional
microscopy. In conjunction with rapid freezing techniques, electron
microscopy has also been used to study the mechanisms of inter- and
intracellular transport, for instance in demonstrating that exocytotic vesicles are the means of chemical release at synapses.
31P-NMR(nuclear magnetic resonance) spectroscopy is
widely used for studies of phospholipid bilayers and biological
membranes in native conditions. The analysis of 31P-NMR
spectra of lipids could provide a wide range of information about lipid
bilayer packing, phase transitions (gel phase, physiological liquid
crystal phase, ripple phases, non bilayer phases), lipid head group
orientation/dynamics, and elastic properties of pure lipid bilayer and
as a result of binding of proteins and other biomolecules.
A new method to study lipid bilayers is Atomic force microscopy
(AFM). Rather than using a beam of light or particles, a very small
sharpened tip scans the surface by making physical contact with the
bilayer and moving across it, like a record player needle. AFM is a
promising technique because it has the potential to image with nanometer
resolution at room temperature and even under water or physiological
buffer, conditions necessary for natural bilayer behavior. Utilizing
this capability, AFM has been used to examine dynamic bilayer behavior
including the formation of transmembrane pores (holes) and phase transitions in supported bilayers. Another advantage is that AFM does not require fluorescent or isotopic
labeling of the lipids, since the probe tip interacts mechanically with
the bilayer surface. Because of this, the same scan can image both
lipids and associated proteins, sometimes even with single-molecule
resolution.[38][42] AFM can also probe the mechanical nature of lipid bilayers.
Lipid bilayers exhibit high levels of birefringence where the refractive index in the plane of the bilayer differs from that perpendicular by as much as 0.1 refractive index units. This has been used to characterise the degree of order and disruption in bilayers using dual polarisation interferometry to understand mechanisms of protein interaction.
Lipid bilayers are complicated molecular systems with many
degrees of freedom. Thus atomistic simulation of membrane and in
particular ab initio
calculations of its properties is difficult and computationally
expensive. Quantum chemical calculations has recently been successfully
performed to estimate dipole and quadrupole moments of lipid membranes.
Transport across the bilayer
Passive diffusion
Most polar molecules have low solubility in the hydrocarbon
core of a lipid bilayer and, as a consequence, have low permeability
coefficients across the bilayer. This effect is particularly pronounced
for charged species, which have even lower permeability coefficients
than neutral polar molecules. Anions typically have a higher rate of diffusion through bilayers than cations. Compared to ions, water molecules actually have a relatively large permeability through the bilayer, as evidenced by osmotic swelling.
When a cell or vesicle with a high interior salt concentration is
placed in a solution with a low salt concentration it will swell and
eventually burst. Such a result would not be observed unless water was
able to pass through the bilayer with relative ease. The anomalously
large permeability of water through bilayers is still not completely
understood and continues to be the subject of active debate.
Small uncharged apolar molecules diffuse through lipid bilayers many
orders of magnitude faster than ions or water. This applies both to fats
and organic solvents like chloroform and ether. Regardless of their polar character larger molecules diffuse more slowly across lipid bilayers than small molecules.
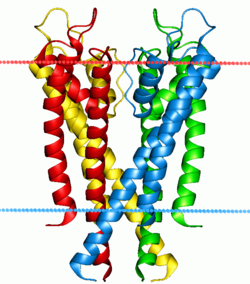
Structure of a potassium ion channel. The alpha helices penetrate the bilayer (boundaries indicated by red and blue lines), opening a hole through which potassium ions can flow
Ion pumps and channels
Two special classes of protein deal with the ionic gradients found across cellular and sub-cellular membranes in nature- ion channels and ion pumps. Both pumps and channels are integral membrane proteins
that pass through the bilayer, but their roles are quite different. Ion
pumps are the proteins that build and maintain the chemical gradients
by utilizing an external energy source to move ions against the
concentration gradient to an area of higher chemical potential. The energy source can be ATP, as is the case for the Na+-K+ ATPase. Alternatively, the energy source can be another chemical gradient already in place, as in the Ca2+/Na+ antiporter. It is through the action of ion pumps that cells are able to regulate pH via the pumping of protons.
In contrast to ion pumps, ion channels do not build chemical
gradients but rather dissipate them in order to perform work or send a
signal. Probably the most familiar and best studied example is the voltage-gated Na+ channel, which allows conduction of an action potential along neurons.
All ion pumps have some sort of trigger or “gating” mechanism. In the
previous example it was electrical bias, but other channels can be
activated by binding a molecular agonist or through a conformational
change in another nearby protein.
Schematic illustration of pinocytosis, a type of endocytosis
Endocytosis and exocytosis
Some molecules or particles are too large or too hydrophilic to pass
through a lipid bilayer. Other molecules could pass through the bilayer
but must be transported rapidly in such large numbers that channel-type
transport is impractical. In both cases, these types of cargo can be
moved across the cell membrane through fusion or budding of vesicles.
When a vesicle is produced inside the cell and fuses with the plasma
membrane to release its contents into the extracellular space, this
process is known as exocytosis. In the reverse process, a region of the
cell membrane will dimple inwards and eventually pinch off, enclosing a
portion of the extracellular fluid to transport it into the cell.
Endocytosis and exocytosis rely on very different molecular machinery to
function, but the two processes are intimately linked and could not
work without each other. The primary mechanism of this interdependence
is the sheer volume of lipid material involved.
In a typical cell, an area of bilayer equivalent to the entire plasma
membrane will travel through the endocytosis/exocytosis cycle in about
half an hour.
If these two processes were not balancing each other, the cell would
either balloon outward to an unmanageable size or completely deplete its
plasma membrane within a matter of minutes.
Exocytosis of outer membrane vesicles (MV) liberated from inflated periplasmic pockets (p) on surface of human Salmonella 3,10:r:- pathogens docking on plasma membrane of macrophage cells (M) in chicken ileum, for host-pathogen signaling in vivo.
Exocytosis in prokaryotes: Membrane vesicular exocytosis, popularly known as membrane vesicle trafficking, a Nobel prize-winning (year, 2013) process, is traditionally regarded as a prerogative of eukaryotic cells. This myth was however broken with the revelation that nanovesicles, popularly known as bacterial outer membrane vesicles, released by gram-negative microbes, translocate bacterial signal molecules to host or target cells to carry out multiple processes in favour of the secreting microbe e.g., in host cell invasion and microbe-environment interactions, in general.
Electroporation
Electroporation is the rapid increase in bilayer permeability induced
by the application of a large artificial electric field across the
membrane. Experimentally, electroporation is used to introduce
hydrophilic molecules into cells. It is a particularly useful technique
for large highly charged molecules such as DNA, which would never passively diffuse across the hydrophobic bilayer core. Because of this, electroporation is one of the key methods of transfection as well as bacterial transformation. It has even been proposed that electroporation resulting from lightning strikes could be a mechanism of natural horizontal gene transfer.
This increase in permeability primarily affects transport of ions
and other hydrated species, indicating that the mechanism is the
creation of nm-scale water-filled holes in the membrane. Although
electroporation and dielectric breakdown
both result from application of an electric field, the mechanisms
involved are fundamentally different. In dielectric breakdown the
barrier material is ionized, creating a conductive pathway. The material
alteration is thus chemical in nature. In contrast, during
electroporation the lipid molecules are not chemically altered but
simply shift position, opening up a pore that acts as the conductive
pathway through the bilayer as it is filled with water.
Mechanics
Schematic
showing two possible conformations of the lipids at the edge of a pore.
In the top image the lipids have not rearranged, so the pore wall is
hydrophobic. In the bottom image some of the lipid heads have bent over,
so the pore wall is hydrophilic.
Lipid bilayers are large enough structures to have some of the
mechanical properties of liquids or solids. The area compression modulus
Ka, bending modulus Kb, and edge energy , can be used to describe them. Solid lipid bilayers also have a shear modulus,
but like any liquid, the shear modulus is zero for fluid bilayers.
These mechanical properties affect how the membrane functions. Ka and Kb affect the ability of proteins and small molecules to insert into the bilayer, and bilayer mechanical properties have been shown to alter the function of mechanically activated ion channels.
Bilayer mechanical properties also govern what types of stress a cell
can withstand without tearing. Although lipid bilayers can easily bend,
most cannot stretch more than a few percent before rupturing.
As discussed in the Structure and organization section, the
hydrophobic attraction of lipid tails in water is the primary force
holding lipid bilayers together. Thus, the elastic modulus of the
bilayer is primarily determined by how much extra area is exposed to
water when the lipid molecules are stretched apart. It is not surprising given this understanding of the forces involved that studies have shown that Ka varies strongly with osmotic pressure but only weakly with tail length and unsaturation. Because the forces involved are so small, it is difficult to experimentally determine Ka. Most techniques require sophisticated microscopy and very sensitive measurement equipment.
In contrast to Ka, which is a measure of how much energy is needed to stretch the bilayer, Kb
is a measure of how much energy is needed to bend or flex the bilayer.
Formally, bending modulus is defined as the energy required to deform a
membrane from its intrinsic curvature to some other curvature. Intrinsic
curvature is defined by the ratio of the diameter of the head group to
that of the tail group. For two-tailed PC lipids, this ratio is nearly
one so the intrinsic curvature is nearly zero. If a particular lipid has
too large a deviation from zero intrinsic curvature it will not form a
bilayer and will instead form other phases such as micelles or inverted micelles. Addition of small hydrophilic molecules like sucrose into mixed lipid lamellar liposomes made from galactolipid-rich thylakoid membranes destabilises bilayers into micellar phase. Typically, Kb is not measured experimentally but rather is calculated from measurements of Ka and bilayer thickness, since the three parameters are related.
is a measure of how much energy it takes to expose a bilayer edge to
water by tearing the bilayer or creating a hole in it. The origin of
this energy is the fact that creating such an interface exposes some of
the lipid tails to water, but the exact orientation of these border
lipids is unknown. There is some evidence that both hydrophobic (tails
straight) and hydrophilic (heads curved around) pores can coexist.
Fusion
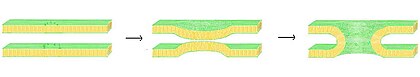
Illustration
of lipid vesicles fusing showing two possible outcomes: hemifusion and
full fusion. In hemifusion, only the outer bilayer leaflets mix. In full
fusion both leaflets as well as the internal contents mix.
Fusion
is the process by which two lipid bilayers merge, resulting in one
connected structure. If this fusion proceeds completely through both
leaflets of both bilayers, a water-filled bridge is formed and the
solutions contained by the bilayers can mix. Alternatively, if only one
leaflet from each bilayer is involved in the fusion process, the
bilayers are said to be hemifused. Fusion is involved in many cellular
processes, in particular in eukaryotes, since the eukaryotic cell is extensively sub-divided by lipid bilayer membranes. Exocytosis, fertilization of an egg by sperm and transport of waste products to the lysozome
are a few of the many eukaryotic processes that rely on some form of
fusion. Even the entry of pathogens can be governed by fusion, as many
bilayer-coated viruses have dedicated fusion proteins to gain entry into the host cell.
There are four fundamental steps in the fusion process.
First, the involved membranes must aggregate, approaching each other to
within several nanometers. Second, the two bilayers must come into very
close contact (within a few angstroms). To achieve this close contact,
the two surfaces must become at least partially dehydrated, as the bound
surface water normally present causes bilayers to strongly repel. The
presence of ions, in particular divalent cations like magnesium and
calcium, strongly affects this step.
One of the critical roles of calcium in the body is regulating membrane
fusion. Third, a destabilization must form at one point between the two
bilayers, locally distorting their structures. The exact nature of this
distortion is not known. One theory is that a highly curved "stalk"
must form between the two bilayers. Proponents of this theory believe that it explains why phosphatidylethanolamine, a highly curved lipid, promotes fusion.
Finally, in the last step of fusion, this point defect grows and the
components of the two bilayers mix and diffuse away from the site of
contact.
Schematic illustration of the process of fusion through stalk formation.
Diagram
of the action of SNARE proteins docking a vesicle for exocytosis.
Complementary versions of the protein on the vesicle and the target
membrane bind and wrap around each other, drawing the two bilayers close
together in the process.
The situation is further complicated when considering fusion in vivo since biological fusion is almost always regulated by the action of membrane-associated proteins. The first of these proteins to be studied were the viral fusion proteins, which allow an enveloped virus
to insert its genetic material into the host cell (enveloped viruses
are those surrounded by a lipid bilayer; some others have only a protein
coat). Eukaryotic cells also use fusion proteins, the best-studied of which are the SNAREs. SNARE proteins are used to direct all vesicular
intracellular trafficking. Despite years of study, much is still
unknown about the function of this protein class. In fact, there is
still an active debate regarding whether SNAREs are linked to early
docking or participate later in the fusion process by facilitating
hemifusion.
In studies of molecular and cellular biology it is often desirable to artificially induce fusion. The addition of polyethylene glycol
(PEG) causes fusion without significant aggregation or biochemical
disruption. This procedure is now used extensively, for example by
fusing B-cells with myeloma cells. The resulting “hybridoma” from this combination expresses a desired antibody
as determined by the B-cell involved, but is immortalized due to the
melanoma component. Fusion can also be artificially induced through electroporation in a process known as electrofusion. It is believed that this phenomenon results from the energetically active edges formed during electroporation, which can act as the local defect point to nucleate stalk growth between two bilayers.
Model systems
Lipid bilayers can be created artificially in the lab to allow
researchers to perform experiments that cannot be done with natural
bilayers. They can also be used in the field of Synthetic Biology, to define the boundaries of artificial cells.
These synthetic systems are called model lipid bilayers. There are many
different types of model bilayers, each having experimental advantages
and disadvantages. They can be made with either synthetic or natural
lipids. Among the most common model systems are:
- Black lipid membranes (BLM)
- Supported lipid bilayers (SLB)
- Tethered Bilayer Lipid Membranes (t-BLM)
- Vesicles
- Droplet Interface Bilayers (DIBs)
Commercial applications
To date, the most successful commercial application of lipid bilayers has been the use of liposomes for drug delivery, especially for cancer treatment. (Note- the term “liposome” is in essence synonymous with “vesicle”
except that vesicle is a general term for the structure whereas
liposome refers to only artificial not natural vesicles) The basic idea
of liposomal drug delivery is that the drug is encapsulated in solution
inside the liposome then injected into the patient. These drug-loaded
liposomes travel through the system until they bind at the target site
and rupture, releasing the drug. In theory, liposomes should make an
ideal drug delivery system since they can isolate nearly any hydrophilic
drug, can be grafted with molecules to target specific tissues and can
be relatively non-toxic since the body possesses biochemical pathways
for degrading lipids.
The first generation of drug delivery liposomes had a simple
lipid composition and suffered from several limitations. Circulation in
the bloodstream was extremely limited due to both renal clearing and phagocytosis.
Refinement of the lipid composition to tune fluidity, surface charge
density, and surface hydration resulted in vesicles that adsorb fewer
proteins from serum and thus are less readily recognized by the immune system. The most significant advance in this area was the grafting of polyethylene glycol
(PEG) onto the liposome surface to produce “stealth” vesicles, which
circulate over long times without immune or renal clearing.
The first stealth liposomes were passively targeted at tumor tissues. Because tumors induce rapid and uncontrolled angiogenesis they are especially “leaky” and allow liposomes to exit the bloodstream at a much higher rate than normal tissue would. More recently work has been undertaken to graft antibodies or other molecular markers onto the liposome surface in the hope of actively binding them to a specific cell or tissue type. Some examples of this approach are already in clinical trials.
Another potential application of lipid bilayers is the field of biosensors.
Since the lipid bilayer is the barrier between the interior and
exterior of the cell, it is also the site of extensive signal
transduction. Researchers over the years have tried to harness this
potential to develop a bilayer-based device for clinical diagnosis or
bioterrorism detection. Progress has been slow in this area and,
although a few companies have developed automated lipid-based detection
systems, they are still targeted at the research community. These
include Biacore (now GE Healthcare Life Sciences), which offers a
disposable chip for utilizing lipid bilayers in studies of binding
kinetics and Nanion Inc., which has developed an automated patch clamping system. Other, more exotic applications are also being pursued such as the use of lipid bilayer membrane pores for DNA sequencing by Oxford Nanolabs. To date, this technology has not proven commercially viable.
A supported lipid bilayer (SLB) as described above has achieved
commercial success as a screening technique to measure the permeability
of drugs. This parallel artificial membrane permeability assay PAMPA technique measures the permeability across specifically formulated lipid cocktail(s) found to be highly correlated with Caco-2 cultures, the gastrointestinal tract, blood–brain barrier and skin.
History
By the early twentieth century scientists had come to believe that cells are surrounded by a thin oil-like barrier,
but the structural nature of this membrane was not known. Two
experiments in 1925 laid the groundwork to fill in this gap. By
measuring the capacitance of erythrocyte solutions, Hugo Fricke determined that the cell membrane was 3.3 nm thick.
Although the results of this experiment were accurate, Fricke
misinterpreted the data to mean that the cell membrane is a single
molecular layer. Prof. Dr. Evert Gorter
(1881–1954) and F. Grendel of Leiden University approached the problem
from a different perspective, spreading the erythrocyte lipids as a
monolayer on a Langmuir-Blodgett trough. When they compared the area of the monolayer to the surface area of the cells, they found a ratio of two to one.
Later analyses showed several errors and incorrect assumptions with
this experiment but, serendipitously, these errors canceled out and from
this flawed data Gorter and Grendel drew the correct conclusion- that
the cell membrane is a lipid bilayer.
This theory was confirmed through the use of electron microscopy in the late 1950s. Although he did not publish the first electron microscopy study of lipid bilayers
J. David Robertson was the first to assert that the two dark
electron-dense bands were the headgroups and associated proteins of two
apposed lipid monolayers.
In this body of work, Robertson put forward the concept of the “unit
membrane.” This was the first time the bilayer structure had been
universally assigned to all cell membranes as well as organelle membranes.
Around the same time, the development of model membranes
confirmed that the lipid bilayer is a stable structure that can exist
independent of proteins. By “painting” a solution of lipid in organic
solvent across an aperture, Mueller and Rudin were able to create an
artificial bilayer and determine that this exhibited lateral fluidity,
high electrical resistance and self-healing in response to puncture, all of which are properties of a natural cell membrane. A few years later, Alec Bangham showed that bilayers, in the form of lipid vesicles, could also be formed simply by exposing a dried lipid sample to water. This was an important advance, since it demonstrated that lipid bilayers form spontaneously via self assembly and do not require a patterned support structure.
In 1977, a totally synthetic bilayer membrane was prepared by
Kunitake and Okahata, from a single organic compound,
didodecyldimethylammonium bromide. It clearly shows that the bilayer membrane was assembled by the van der Waals interaction.