Ethanol is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages. It is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid that acts as a central nervous system depressant. Ethanol can impair different types of memory.
Ethanol
Alcoholic beverages
Mode of actions
Effects on the hippocampus
Alcohol acts as a general central nervous system depressant, but it also
affects some specific areas of the brain to a greater extent than
others. Memory impairment caused by alcohol has been linked to the
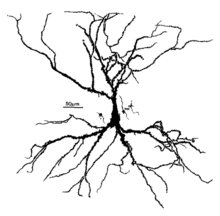
disruption of hippocampal function — particularly affecting gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) neurotransmission which negatively impacts long-term potentiation (LTP). The molecular basis of LTP is associated with learning and memory. Particularly, damage to hippocampal CA1 cells adversely affects memory formation, and this disruption has been linked to dose-dependent levels of alcohol consumption. At higher doses, alcohol significantly inhibits neuronal activity in both the CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cell layers of the hippocampus. This impairs memory encoding, since the hippocampus plays an important role in the formations of new memories.
A Hippocampal Pyramidal Cell
Molecular effects on GABA and NMDA receptors
A GABAA Receptor
Alcohol also acts as a positive allosteric modulator of GABA receptors, specifically type GABAA. Upon activation, these GABA receptors conduct Cl-, resulting in neuronal hyperpolarization. This hyperpolarization decreases the chance of an action potential occurring and thus, it has an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission in the central nervous system. GABAA
receptor subtypes vary in their sensitivities to dosage of alcohol
consumed. Furthermore, acute alcohol intake promotes GABAergic
neurotransmission via the presynaptic release of GABA, the dephosphorylation of GABAA receptors (increasing GABA sensitivity), and the elevation of endogenous GABAergic neuroactive steroids. Protein kinase C (PKC) has been implicated in differentially modulating the response of the GABAA receptor to alcohol, with effects depending on the PKC isozyme. Alcohol effects have also implicated protein kinase A in affecting GABAA receptor function, such as promoting sensitivity. Enhancement of GABAergic transmission due to alcohol consumption can also be brought about by neuroactive steroids, such as allopregnanolone, which act as GABAA receptor agonists.
Both chronic alcohol consumption and alcohol dependence are correlated
with the altered expression, properties, and functions of the GABAA receptor that may contribute to alcohol tolerance. There is still much yet to be discovered about alcohol's specific and varying effects on both the GABAA receptor and its subtypes.
At higher doses, ethanol also affects NMDA receptors (NMDARs) by inhibiting the ion current induced by NMDA, a glutamate receptor agonist.
This inhibition of synaptic excitation by alcohol has been shown to be
dose-dependent (up to a certain point, after which it did not differ by
much). Alcohol appears to produce this inhibition by using a site of the NMDAR that is accessible from the extracellular environment. Therefore, this inhibition of an ion current usually produced by NMDAR activation leads to decreased LTP in hippocampal areas. Alcohol negatively affects LTP to a greater degree in immature versus mature animals.
In adolescents, alcohol decreases the expression of both the NMDAR
NR2A subunit in the hippocampus and the NR1 subunit in the prefrontal
cortex.
Studies have also found that a decrease in phosphorylation of 2B
subunit in the prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus, the nucleus
accumbens, and the striatum. NMDARS may be affected by PKA regulation due to the actions of alcohol. Alcohol's effects on GABAA
neurotransmission may indirectly inhibit the activity of the NMDAR, and
they may contribute to its blockade of LTP induction; however,
alcohol's direct effects on NMDAR alone are sufficient for the
inhibition of LTP. The varying dose-dependent response to alcohol relies on the combined interactions and responses of the GABAA receptors, NMDARs, and metabotropic glutamate receptors subtype 5 (mGluR5). These changes prevent excitatory synaptic transmissions from occurring, affecting synaptic plasticity and, in turn, memory and learning.
However, there is still much yet to be elucidated concerning specific
molecular mechanisms of how alcohol affects memory formation.
Effects on other brain regions
Alcohol also impairs and alters the functioning in the cerebellum, which affects both motor function and coordination. It has a notable inhibitory effect on the neurons of the cerebral cortex,
affecting and altering thought processes, decreasing inhibition, and
increasing the pain threshold. It also decreases sexual performance by
depressing nerve centers in the hypothalamus. Alcohol also has an effect on urine excretion via inhibition of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) secretion of the pituitary gland. Lastly, it depresses breathing and heart rate by inhibiting neuronal functioning of the medulla.
Long-term memory
Long-term memory (LTM) has both a long duration and a large capacity. Memories that are stored in LTM can last from a few days to a lifetime. LTM consists of both explicit memory (requiring conscious awareness) and implicit memory (unconscious awareness). Information selected for LTM goes through three processes. First of all, in the encoding stage, information from the senses is incorporated into mental activity in the form of a memory. Secondly, storage involves taking this information and holding it indefinitely in memory.
Lastly, retrieval is the ability to recall information from the
long-term memory storage. Each of these processes can be affected by
alcohol.
Animation: Hippocampus (red)
Explicit memory
Explicit memory requires conscious and intentional effort for recall. It includes both episodic memory (for specific events, such as a party) and semantic memory (for general information, such as one's name).
Alcohol impairs episodic encoding, specifically for cued recall, recognition of completed word fragments, and free recall. A blackout is an example of a difficulty in encoding episodic memories due to alcohol. Blackouts are caused by a rapid increase in blood alcohol concentration (BAC) which in turn distorts the neurons in the hippocampus. This distortion impairs a person's ability to form new episodic memories.
High doses of alcohol severely disrupt the storage process of semantic memories. Alcohol was found to impair the storage of novel stimuli but not that of previously learned information. Since alcohol affects the central nervous system, it hinders semantic storage functioning by restricting the consolidation of the information from encoding.
Retrieval of explicit memory is significantly impaired by alcohol.
When compared to sober participants, intoxicated participants performed
quite poorly on a recall task for everyday events (i.e., episodic
memory). Intoxicated participants are also slower to respond in reaction time tasks. Alcohol also impairs retrieval in word recognition tasks.
When both encoding and retrieval take place during intoxication, there
are surprisingly more impairments for cued recall than for free recall. In terms of gender differences in retrieval processes, females tend to score lower than males on recall tasks when intoxicated.
Implicit memory
Implicit memory does not require conscious effort or intention for recall. It occurs when previous experience influences performance on a certain task. This is evident in priming experiments. Implicit memory includes procedural memory, which influences our everyday behaviours, such as riding a bike or tying shoes. People can perform these abilities without even thinking about them, which means procedural memory functions automatically. While retrieval of explicit memory is severely impaired by alcohol, retrieval of implicit memory is not. Intoxicated subjects score higher on recognition tasks (involving implicit memory) than they can on recall tasks (involving explicit memory).
Short-term memory
Short-term memory refers to the temporary storage of small amounts of information over short delays. Digit span
refers to the proposed number of pieces of information (5-9) that can
be held in short-term memory. This is also referred to as the magic
number seven – plus or minus two. Any more pieces of information than
this, and newer items replace previous items. Alcohol intoxication has been found to have dissociative effects on both short-term memory and cognitive functioning.
Anterior Cingulate Cortex (yellow)
Animation: Parietal Lobe (red)
Brain areas affected by alcohol
Alcohol affects the functioning of the brain. Neurochemical changes occurring in the anterior cingulate are correlated with altered short-term memory functions in the brains of young alcoholic men. fMRIs
of alcohol-dependent women displayed significantly less blood oxygen in
the frontal and parietal regions, especially in the right hemisphere. This is supported by findings of short-term memory impairment by lesions of both the parietal lobe and the prefrontal cortex. Associations between Third ventricle volume and cognitive performance on memory tests have been found in alcoholics. Specifically, increases in third ventricular volume correlate with a decline in memory performance.
Tasks and intoxication findings
Short-term
memory is commonly tested with visual tasks. Short-term memory,
especially for non-verbal and spatial material, are impaired by
intoxication. Alcohol decreases iconic memory (a type of visual short-term memory). With BACs between 80–84 mg/dl, more intrusion errors occur in a delayed recall task compared to a control group.
Intrusion errors, which represent reflective cognitive functioning,
occur when irrelevant information is produced. Alcoholics have less
control of inhibiting intrusions.
Acute alcohol intoxication in social drinkers caused more intrusion
errors in delayed recall tasks than in immediate free recall tasks.
Acute alcohol intoxication increases the susceptibility to
interference, which allows for more intrusion errors when there is a
short delay. Free recall (given list of words then asked to recall list) is significantly lower and therefore impaired by alcohol intoxication. Encoding deficits were found in verbal free recall and recognition tasks under the influence of alcohol. A discrimination task found significant alcohol-related impairments both in depth perception and in visual short-term memory. State-dependent learning
and relearning studies in male heavy drinkers demonstrate that the
condition of intoxication while learning and sobriety when tested caused
a performance deficit in free recall tasks. These findings are supportive of alcohol-induced storage deficits (not retrieval deficits).
The effects of acute alcohol consumption on visual short-term memory,
stereoscopic depth perception, and attention were all studied. A 33%
alcohol condition showed significant impairments both in depth
perception and in visual short-term memory (assessed by the vernier
discrimination task).
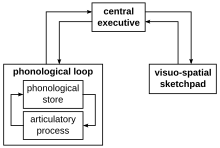
Working
Memory Model. Alcohol intoxication can disrupt rehearsal strategies
which may involve the phonological loop and/or the visuospatial
sketchpad.
Effects on working memory
Working memory allows one to keep things in mind while simultaneously performing complex tasks.
It involves a system for both the temporary storage and the
manipulation of information, subsequently forming a crucial link between
perception and controlled action. Evidence suggests that working memory involves three components: the central executive which controls attention, the visuo-spatial sketchpad which holds and manipulates spatial information, and the phonological loop which performs a similar function for auditory and speech-based information.
In the short term
Alcohol
consumption has substantial, measurable effects on working memory,
although these effects vary greatly between individual responses. Not
much is really known about the neural mechanisms that underlie these
individual differences.
It is also found that alcohol impairs working memory by affecting
mnemonic strategies and executive processes rather than by shrinking the
basic holding capacity of working memory. Isolated acute-moderate
levels of alcohol intoxication do not physically alter the structures
that are critical for working memory function, such as the frontal cortex, the parietal cortex, the anterior cingulate, and parts of the basal ganglia.
One finding regarding the effects of alcohol on working memory points
out that alcohol reduces working memory only in individuals with a high
baseline working memory capacity,
which suggests that alcohol might not uniformly affect working memory
in many different individuals. Alcohol appears to impair the capacity of
working memory to modulate response inhibition. Alcohol disinhibits behaviour, but it only does so in individuals with a low baseline working memory capacity.
An interesting finding is that the incentive to perform well with
working memory measurement tasks while under the influence of alcohol 'does,
in fact, have some effect on working memory, as it boosts scores in the
rate of mental scanning and reaction time to stimulus; however, it did
not reduce the number of errors as opposed to subjects with no incentive
to perform well.
Even acute alcohol intoxication (a blood alcohol concentration of
0.08-0.09%) produces a substantial impairment of working memory
processes that require mnemonic rehearsal strategies. It is less likely for alcohol to impair a working memory task that does not rely on memory rehearsal or associated mnemonic strategies.
Because of this, working memory is very susceptible to falter when an
individual participates in tasks involving retention concerning both
auditory and visual sequences.
An interesting example of this is the failure of guitarists or other
musicians performing concerts to cue in on auditory patterns and make it
known that their performance is hindered by intoxication, whereas
professional basketball (a less sequence-heavy activity for working
memory) standout Ron Artest recently admitted in an interview with Sporting News
to drinking heavily during half-time early in his career and the fact
that it had little — if not any recognizable — effect on his working
memory. His former coach Fran Fraschilla has gone on record saying:
"It's a surprise because every day at practice, he came out in a mood to play. He came out in a basketball rage. He was fully committed; he wanted to let our upperclassmen know that he was the alpha male. It never came up that he had any sort of a problem with alcohol. This is the first I've heard of it."
In the long term
Alcohol has been shown to have just some long-term effects on
working memory. Findings have shown that in order for working memory to
be substantially affected, long-term heavy drinking must be sustained
over a long period of time, as up to one drink per day does not impair
any cognitive function and may actually decrease the risk of a cognitive
decline. Furthermore, chronic alcoholism
is associated with the impairment in both sustained attention and
visual working memory. As a result, alcoholics have reduced ability, but
not necessarily inability, to perform these executive tasks. This is assumed to be subserved by regions of the prefrontal cortex.
While it may not serve as a surprise that chronic alcoholism is linked
to any decreased cognitive function such as working memory, one
surprising finding is not only that even moderate levels of alcohol
consumption during pregnancy were shown to have an adverse effect on the
child's working memory when tested at 7.5 years of age, but also that
working memory may be the most important aspect of attention that is
adversely affected by prenatal alcohol exposure.
Prospective memory
Prospective memory involves remembering to carry out an intended action in the future without an explicit reminder.
Alcohol has been found to impair this ability. Chronic heavy alcohol
users report significantly more prospective forgetting compared to
low-dose and alcohol-free controls.
The Prospective Memory Questionnaire assesses short-term habitual
prospective memory, long-term episodic prospective memory, and
internally cued prospective memory. Chronic heavy alcohol users reported significantly greater deficits for all three aspects of prospective memory.
Individuals that report heavy alcohol use report 24% more difficulties
with prospective memory than those who report that they are light
drinkers and 30% more difficulties than those who report that they never
drink.
The effects of alcohol on prospective memory can also be assessed in
the laboratory by simulating prospective memory tasks that individuals
face in everyday life. Individuals who are given 0.6 g/kg alcohol prior
to performing prospective memory tasks do significantly poorer than a placebo group.
Alcohol can damage the prefrontal and frontal areas of the brain, and
this may be responsible for prospective memory impairments since
prospective memory performance is highly correlated with frontal
executive functions.
In popular culture
The
memory inhibiting effects of alcohol are often a prominent topic in
popular culture. It appears in movies, books, and television shows.
Several movies show characters drinking alcohol to the point of memory
loss and awakening the next morning with a host of problems due to
actions they performed while intoxicated.
One example is The Hangover, where three groomsmen lose the groom during a bachelor party in Las Vegas, so they retrace their steps to find him.
The characters still had functioning implicit/procedural memory, which
allowed them to carry out the many acts they performed that night, but
their episodic memory was impaired and thus they had no recollection of
the events occurring. In addition to alcohol the characters were also
under the influence of flunitrazepam.
Another movie is What Happens in Vegas. After an intoxicated night in "Sin City," two people wake-up to find they got married.
Songs such as Waking Up in Vegas by Katy Perry and Last Name by Carrie Underwood also depict characters waking up and not remembering the night before due to alcohol consumption.
By some accounts, popular culture makes light of the memory problems that can result from alcohol consumption.
The court case R. v. Daviault [1994] concerned the viability of a legal defense based on intoxication.
Law and Order: Special Victims Unit; in season 11 episode 4,
Hammered, a recovering alcoholic was coerced to drink by a business
partner and later wakes up to a dead woman in his bed.