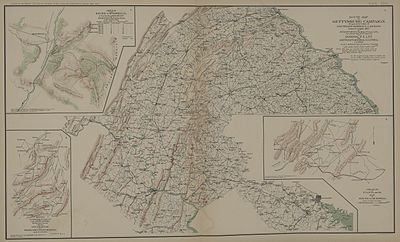
Northern Virginia, Maryland and Pennsylvania (1861–1865)
Gettysburg Campaign, (1863)
Battlefield of Gettysburg, (1863)
The Battle of Gettysburg was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. The battle involved the largest number of casualties of the entire war and is often described as the war's turning point. Union Maj. Gen. George Meade's Army of the Potomac defeated attacks by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia, halting Lee's invasion of the North.
After his success at Chancellorsville in Virginia in May 1863, Lee led his army through the Shenandoah Valley to begin his second invasion of the North—the Gettysburg Campaign.
With his army in high spirits, Lee intended to shift the focus of the
summer campaign from war-ravaged northern Virginia and hoped to
influence Northern politicians to give up their prosecution of the war
by penetrating as far as Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, or even Philadelphia. Prodded by President Abraham Lincoln, Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker moved his army in pursuit, but was relieved of command just three days before the battle and replaced by Meade.
Elements of the two armies initially collided at Gettysburg on
July 1, 1863, as Lee urgently concentrated his forces there, his
objective being to engage the Union army and destroy it. Low ridges to
the northwest of town were defended initially by a Union cavalry
division under Brig. Gen. John Buford, and soon reinforced with two corps of Union infantry.
However, two large Confederate corps assaulted them from the northwest
and north, collapsing the hastily developed Union lines, sending the
defenders retreating through the streets of the town to the hills just
to the south.
On the second day of battle, most of both armies had assembled.
The Union line was laid out in a defensive formation resembling a
fishhook. In the late afternoon of July 2, Lee launched a heavy assault
on the Union left flank, and fierce fighting raged at Little Round Top, the Wheatfield, Devil's Den, and the Peach Orchard. On the Union right, Confederate demonstrations escalated into full-scale assaults on Culp's Hill and Cemetery Hill. All across the battlefield, despite significant losses, the Union defenders held their lines.
On the third day of battle, fighting resumed on Culp's Hill, and
cavalry battles raged to the east and south, but the main event was a
dramatic infantry assault by 12,500 Confederates against the center of
the Union line on Cemetery Ridge, known as Pickett's Charge. The charge was repulsed by Union rifle and artillery fire, at great loss to the Confederate army.
Lee led his army on a torturous retreat back to Virginia. Between 46,000 and 51,000 soldiers from both armies were casualties in the three-day battle, the most costly in US history.
On November 19, President Lincoln used the dedication ceremony for the Gettysburg National Cemetery to honor the fallen Union soldiers and redefine the purpose of the war in his historic Gettysburg Address.
Background
Military situation
Gettysburg Campaign (through July 3); cavalry movements shown with dashed lines
Confederate
Union
This
1863 oval-shaped map depicts Gettysburg Battlefield during July 1–3,
1863, showing troop and artillery positions and movements, relief hachures, drainage, roads, railroads, and houses with the names of residents at the time of the Battle of Gettysburg.
A Harper's Weekly
illustration showing Confederate troops escorting captured African
American civilians south into slavery. En route to Gettysburg, the Army
of Northern Virginia kidnapped approximately 40 black civilians and sent
them south into slavery.
Shortly after the Army of Northern Virginia won a major victory over the Army of the Potomac at the Battle of Chancellorsville (April 30 – May 6, 1863), Robert E. Lee decided upon a second invasion of the North (the first was the unsuccessful Maryland Campaign of September 1862, which ended in the bloody Battle of Antietam). Such a move would upset the Union's plans for the summer campaigning season and possibly reduce the pressure on the besieged Confederate garrison at Vicksburg. The invasion would allow the Confederates to live off the bounty of the rich Northern farms while giving war-ravaged Virginia a much-needed rest. In addition, Lee's 72,000-man army could threaten Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Washington, and possibly strengthen the growing peace movement in the North.
Initial movements to battle
Thus, on June 3, Lee's army began to shift northward from Fredericksburg, Virginia. Following the death of Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, Lee reorganized his two large corps into three new corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. James Longstreet (First Corps), Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell (Second), and Lt. Gen. A.P. Hill
(Third); both Ewell and Hill, who had formerly reported to Jackson as
division commanders, were new to this level of responsibility. The
Cavalry Division remained under the command of Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart.
The Union Army of the Potomac, under Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker,
consisted of seven infantry corps, a cavalry corps, and an Artillery
Reserve, for a combined strength of more than 100,000 men.
The first major action of the campaign took place on June 9 between cavalry forces at Brandy Station, near Culpeper, Virginia. The 9,500 Confederate cavalrymen under Stuart were surprised by Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton's combined arms
force of two cavalry divisions (8,000 troopers) and 3,000 infantry, but
Stuart eventually repulsed the Union attack. The inconclusive battle,
the largest predominantly cavalry engagement of the war, proved for the
first time that the Union horse soldier was equal to his Southern
counterpart.
By mid-June, the Army of Northern Virginia was poised to cross the Potomac River and enter Maryland. After defeating the Union garrisons at Winchester and Martinsburg,
Ewell's Second Corps began crossing the river on June 15. Hill's and
Longstreet's corps followed on June 24 and 25. Hooker's army pursued,
keeping between Washington, D.C. and Lee's army. The Union army crossed
the Potomac from June 25 to 27.
Lee gave strict orders for his army to minimize any negative impacts on the civilian population.
Food, horses, and other supplies were generally not seized outright,
although quartermasters reimbursing Northern farmers and merchants with Confederate money were not well received. Various towns, most notably York, Pennsylvania,
were required to pay indemnities in lieu of supplies, under threat of
destruction. During the invasion, the Confederates seized some 40
northern African Americans. A few of them were escaped fugitive slaves, but most were freemen; all were sent south into slavery under guard.
On June 26, elements of Maj. Gen. Jubal Early's division of Ewell's Corps occupied the town of Gettysburg after chasing off newly raised Pennsylvania militia
in a series of minor skirmishes. Early laid the borough under tribute,
but did not collect any significant supplies. Soldiers burned several
railroad cars and a covered bridge, and destroyed nearby rails and telegraph lines. The following morning, Early departed for adjacent York County.
Meanwhile, in a controversial move, Lee allowed J.E.B. Stuart to
take a portion of the army's cavalry and ride around the east flank of
the Union army. Lee's orders gave Stuart much latitude, and both
generals share the blame for the long absence of Stuart's cavalry, as
well as for the failure to assign a more active role to the cavalry left
with the army. Stuart and his three best brigades were absent from the
army during the crucial phase of the approach to Gettysburg and the
first two days of battle. By June 29, Lee's army was strung out in an
arc from Chambersburg (28 miles (45 km) northwest of Gettysburg) to Carlisle (30 miles (48 km) north of Gettysburg) to near Harrisburg and Wrightsville on the Susquehanna River.
In a dispute over the use of the forces defending the Harpers Ferry garrison, Hooker offered his resignation, and Abraham Lincoln and General-in-Chief Henry W. Halleck,
who were looking for an excuse to rid themselves of him, immediately
accepted. They replaced Hooker early on the morning of June 28 with Maj.
Gen. George Gordon Meade, then commander of the V Corps.
On June 29, when Lee learned that the Army of the Potomac had
crossed the Potomac River, he ordered a concentration of his forces
around Cashtown, located at the eastern base of South Mountain and eight miles (13 km) west of Gettysburg. On June 30, while part of Hill's Corps was in Cashtown, one of Hill's brigades, North Carolinians under Brig. Gen. J. Johnston Pettigrew, ventured toward Gettysburg. In his memoirs, Maj. Gen. Henry Heth, Pettigrew's division commander, claimed that he sent Pettigrew to search for supplies in town—especially shoes.
When Pettigrew's troops approached Gettysburg on June 30, they noticed Union cavalry under Brig. Gen. John Buford
arriving south of town, and Pettigrew returned to Cashtown without
engaging them. When Pettigrew told Hill and Heth what he had seen,
neither general believed that there was a substantial Union force in or
near the town, suspecting that it had been only Pennsylvania militia.
Despite General Lee's order to avoid a general engagement until his
entire army was concentrated, Hill decided to mount a significant reconnaissance in force
the following morning to determine the size and strength of the enemy
force in his front. Around 5 a.m. on Wednesday, July 1, two brigades of
Heth's division advanced to Gettysburg.
Opposing forces
Union
| Key commanders (Army of the Potomac) |
|---|
|
The Army of the Potomac, initially under Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker (Maj. Gen. George Meade replaced Hooker in command on June 28), consisted of more than 100,000 men in the following organization:
- I Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. John F. Reynolds, with divisions commanded by Brig. Gen. James S. Wadsworth, Brig. Gen. John C. Robinson, and Maj. Gen. Abner Doubleday.
- II Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. Winfield Scott Hancock, with divisions commanded by Brig. Gens. John C. Caldwell, John Gibbon, and Alexander Hays.
- III Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. Daniel Sickles, with divisions commanded by Maj. Gen. David B. Birney and Maj. Gen. Andrew A. Humphreys.
- V Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. George Sykes (George G. Meade until June 28), with divisions commanded by Brig. Gens. James Barnes, Romeyn B. Ayres, and Samuel W. Crawford.
- VI Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. John Sedgwick, with divisions commanded by Brig. Gen. Horatio G. Wright, Brig. Gen. Albion P. Howe, and Maj. Gen. John Newton.
- XI Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. Oliver Otis Howard, with divisions commanded by Brig. Gen. Francis C. Barlow, Brig. Gen. Adolph von Steinwehr, and Maj. Gen. Carl Schurz.
- XII Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. Henry W. Slocum, with divisions commanded by Brig. Gens. Alpheus S. Williams and John W. Geary.
- Cavalry Corps, commanded by Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton, with divisions commanded by Brig. Gens. John Buford, David McM. Gregg, and H. Judson Kilpatrick.
- Artillery Reserve, commanded by Brig. Gen. Robert O. Tyler. (The preeminent artillery officer at Gettysburg was Brig. Gen. Henry J. Hunt, chief of artillery on Meade's staff.)
During the advance on Gettysburg, Maj. Gen. Reynolds was in
operational command of the left, or advanced, wing of the Army,
consisting of the I, III, and XI Corps.
Note that many other Union units (not part of the Army of the Potomac)
were actively involved in the Gettysburg Campaign, but not directly
involved in the Battle of Gettysburg. These included portions of the
Union IV Corps, the militia and state troops of the Department of the Susquehanna, and various garrisons, including that at Harpers Ferry.
Confederate
| Key commanders (Army of Northern Virginia) |
|---|
|
In reaction to the death of Lt. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson after Chancellorsville, Lee reorganized his Army of Northern Virginia (75,000 men) from two infantry corps into three.
- First Corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. James Longstreet, with divisions commanded by Maj. Gens. Lafayette McLaws, George Pickett, and John Bell Hood.
- Second Corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell, with divisions commanded by Maj. Gens. Jubal A. Early, Edward "Allegheny" Johnson, and Robert E. Rodes.
- Third Corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. A.P. Hill, with divisions commanded by Maj. Gens. Richard H. Anderson, Henry Heth, and W. Dorsey Pender.
- Cavalry division, commanded by Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart, with brigades commanded by Brig. Gens. Wade Hampton, Fitzhugh Lee, Beverly H. Robertson, Albert G. Jenkins, William E. "Grumble" Jones, and John D. Imboden, and Col. John R. Chambliss.
First day of battle
Overview map of the first day of the Battle of Gettysburg, July 1, 1863
Herr Ridge, McPherson Ridge and Seminary Ridge
Anticipating that the Confederates would march on Gettysburg from the
west on the morning of July 1, Buford laid out his defenses on three
ridges west of the town: Herr Ridge, McPherson Ridge and Seminary Ridge.
These were appropriate terrain for a delaying action by his small
cavalry division against superior Confederate infantry forces, meant to
buy time awaiting the arrival of Union infantrymen who could occupy the
strong defensive positions south of town at Cemetery Hill, Cemetery Ridge, and Culp's Hill.
Buford understood that if the Confederates could gain control of these
heights, Meade's army would have difficulty dislodging them.
First shot monument
Confederate General Henry Heth's division advanced with two brigades forward, commanded by Brig. Gens. James J. Archer and Joseph R. Davis.
They proceeded easterly in columns along the Chambersburg Pike. Three
miles (5 km) west of town, about 7:30 a.m. on July 1, the two brigades
met light resistance from vedettes of Union cavalry, and deployed into line. According to lore, the Union soldier to fire the first shot of the battle was Lt. Marcellus Jones. Lt. Jones later returned to Gettysburg, in 1886 erecting a monument marking the spot where he fired the first shot. Eventually, Heth's men reached dismounted troopers of Col. William Gamble's
cavalry brigade, who raised determined resistance and delaying tactics
from behind fence posts with fire from their breechloading carbines. Still, by 10:20 a.m., the Confederates had pushed the Union cavalrymen east to McPherson Ridge, when the vanguard of the I Corps (Maj. Gen. John F. Reynolds) finally arrived.
North of the pike, Davis gained a temporary success against Brig. Gen. Lysander Cutler's
brigade but was repulsed with heavy losses in an action around an
unfinished railroad bed cut in the ridge. South of the pike, Archer's
brigade assaulted through Herbst (also known as McPherson's) Woods. The
Union Iron Brigade under Brig. Gen. Solomon Meredith enjoyed initial success against Archer, capturing several hundred men, including Archer himself.
General Reynolds was shot and killed early in the fighting while
directing troop and artillery placements just to the east of the woods.
Shelby Foote wrote that the Union cause lost a man considered by many to
be "the best general in the army." Maj. Gen. Abner Doubleday
assumed command. Fighting in the Chambersburg Pike area lasted until
about 12:30 p.m. It resumed around 2:30 p.m., when Heth's entire
division engaged, adding the brigades of Pettigrew and Col. John M. Brockenbrough.
As Pettigrew's North Carolina Brigade came on line, they flanked
the 19th Indiana and drove the Iron Brigade back. The 26th North
Carolina (the largest regiment in the army with 839 men) lost heavily,
leaving the first day's fight with around 212 men. By the end of the
three-day battle, they had about 152 men standing, the highest casualty
percentage for one battle of any regiment, North or South. Slowly the Iron Brigade was pushed out of the woods toward Seminary Ridge. Hill added Maj. Gen. William Dorsey Pender's division to the assault, and the I Corps was driven back through the grounds of the Lutheran Seminary and Gettysburg streets.
As the fighting to the west proceeded, two divisions of Ewell's
Second Corps, marching west toward Cashtown in accordance with Lee's
order for the army to concentrate in that vicinity, turned south on the
Carlisle and Harrisburg roads toward Gettysburg, while the Union XI Corps (Maj. Gen. Oliver O. Howard)
raced north on the Baltimore Pike and Taneytown Road. By early
afternoon, the Union line ran in a semicircle west, north, and northeast
of Gettysburg.
However, the Union did not have enough troops; Cutler, whose
brigade was deployed north of the Chambersburg Pike, had his right flank
in the air. The leftmost division of the XI Corps was unable to deploy
in time to strengthen the line, so Doubleday was forced to throw in
reserve brigades to salvage his line.
Around 2 p.m., the Confederate Second Corps divisions of Maj. Gens. Robert E. Rodes
and Jubal Early assaulted and out-flanked the Union I and XI Corps
positions north and northwest of town. The Confederate brigades of Col. Edward A. O'Neal and Brig. Gen. Alfred Iverson suffered severe losses assaulting the I Corps division of Brig. Gen. John C. Robinson south of Oak Hill. Early's division profited from a blunder by Brig. Gen. Francis C. Barlow,
when he advanced his XI Corps division to Blocher's Knoll (directly
north of town and now known as Barlow's Knoll); this represented a salient
in the corps line, susceptible to attack from multiple sides, and
Early's troops overran Barlow's division, which constituted the right
flank of the Union Army's position. Barlow was wounded and captured in
the attack.
As Union positions collapsed both north and west of town, Gen.
Howard ordered a retreat to the high ground south of town at Cemetery
Hill, where he had left the division of Brig. Gen. Adolph von Steinwehr in reserve. Maj. Gen. Winfield S. Hancock assumed command of the battlefield, sent by Meade when he heard that Reynolds had been killed. Hancock, commander of the II Corps
and Meade's most trusted subordinate, was ordered to take command of
the field and to determine whether Gettysburg was an appropriate place
for a major battle.
Hancock told Howard, "I think this the strongest position by nature
upon which to fight a battle that I ever saw." When Howard agreed,
Hancock concluded the discussion: "Very well, sir, I select this as the
battle-field." Hancock's determination had a morale-boosting effect on
the retreating Union soldiers, but he played no direct tactical role on
the first day.
General Lee understood the defensive potential to the Union if
they held this high ground. He sent orders to Ewell that Cemetery Hill
be taken "if practicable." Ewell, who had previously served under
Stonewall Jackson, a general well known for issuing peremptory orders,
determined such an assault was not practicable and, thus, did not
attempt it; this decision is considered by historians to be a great
missed opportunity.
The first day at Gettysburg, more significant than simply a
prelude to the bloody second and third days, ranks as the 23rd biggest
battle of the war by number of troops engaged. About one quarter of
Meade's army (22,000 men) and one third of Lee's army (27,000) were
engaged.
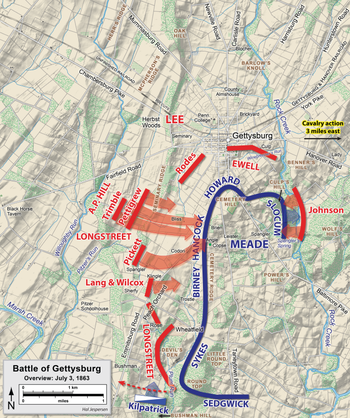
Second day of battle
Robert E. Lee's plan for July 2, 1863
Plans and movement to battle
Throughout the evening of July 1 and morning of July 2, most of the
remaining infantry of both armies arrived on the field, including the
Union II, III, V, VI, and XII Corps. Two of Longstreet's divisions were on the road: Brig. Gen. George Pickett,
had begun the 22 mile (35 km) march from Chambersburg, while Brig. Gen.
E. M. Law had begun the march from Guilford. Both arrived late in the
morning. Law completed his 28-mile (45 km) march in eleven hours.
The Union line ran from Culp's Hill southeast of the town,
northwest to Cemetery Hill just south of town, then south for nearly two
miles (3 km) along Cemetery Ridge, terminating just north of Little
Round Top. Most of the XII Corps was on Culp's Hill; the remnants of I
and XI Corps defended Cemetery Hill; II Corps covered most of the
northern half of Cemetery Ridge; and III Corps was ordered to take up a
position to its flank. The shape of the Union line is popularly
described as a "fishhook" formation.
The Confederate line paralleled the Union line about a mile
(1,600 m) to the west on Seminary Ridge, ran east through the town, then
curved southeast to a point opposite Culp's Hill. Thus, the Union army
had interior lines, while the Confederate line was nearly five miles
(8 km) long.
Lee's battle plan for July 2 called for a general assault of
Meade's positions. On the right, Longstreet's First Corps was to
position itself to attack the Union left flank, facing northeast
astraddle the Emmitsburg Road, and to roll up the Union line. The attack sequence was to begin with Maj. Gens. John Bell Hood's and Lafayette McLaws's divisions, followed by Maj. Gen. Richard H. Anderson's division of Hill's Third Corps.
On the left, Lee instructed Ewell to position his Second Corps to
attack Culp's Hill and Cemetery Hill when he heard the gunfire from
Longstreet's assault, preventing Meade from shifting troops to bolster
his left. Though it does not appear in either his or Lee's Official
Report, Ewell claimed years later that Lee had changed the order to
simultaneously attack, calling for only a "diversion", to be turned into
a full-scale attack if a favorable opportunity presented itself.
Lee's plan, however, was based on faulty intelligence,
exacerbated by Stuart's continued absence from the battlefield. Though
Lee personally reconnoitered his left during the morning, he did not
visit Longstreet's position on the Confederate right. Even so, Lee
rejected suggestions that Longstreet move beyond Meade's left and attack
the Union flank, capturing the supply trains and effectively blocking
Meade's escape route.
Lee did not issue orders for the attack until 11:00 a.m.
About noon, General Anderson's advancing troops were discovered by
General Sickles' outpost guard and the Third Corps–upon which
Longstreet's First Corps was to form–did not get into position until
1:00 p.m.
Hood and McLaws, after their long march, were not yet in position
and did not launch their attacks until just after 4 p.m. and 5 p.m.,
respectively.
Attacks on the Union left flank
Overview map of the second day of the Battle of Gettysburg, July 2, 1863
As Longstreet's left division, under Maj. Gen. Lafayette McLaws, advanced, they unexpectedly found Maj. Gen. Daniel Sickles's
III Corps directly in their path. Sickles had been dissatisfied with
the position assigned him on the southern end of Cemetery Ridge. Seeing
ground better suited for artillery positions a half mile (800 m) to the
west— centered at the Sherfy farm's Peach Orchard—he violated orders and
advanced his corp to the slightly higher ground along the Emmitsburg
Road, moving away from Cemetery Ridge. The new line ran from Devil's
Den, northwest to the Peach Orchard, then northeast along the Emmitsburg
Road to south of the Codori farm. This created an untenable salient at
the Peach Orchard; Brig. Gen. Andrew A. Humphreys's division (in position along the Emmitsburg Road) and Maj. Gen. David B. Birney's
division (to the south) were subject to attacks from two sides and were
spread out over a longer front than their small corps could defend
effectively. The Confederate artillery was ordered to open fire at 3:00 p.m.
After failing to attend a meeting at this time of Meade's corps
commanders, Meade rode to Sickles' position and demanded an explanation
of the situation. Knowing a Confederate attack was imminent and a
retreat would be endangered, Meade refused Sickles' offer to withdraw.
Meade was forced to send 20,000 reinforcements: the entire V Corps, Brig. Gen. John C. Caldwell's
division of the II Corps, most of the XII Corps, and portions of the
newly arrived VI Corps. Hood's division moved more to the east than
intended, losing its alignment with the Emmitsburg Road,
attacking Devil's Den and Little Round Top. McLaws, coming in on Hood's
left, drove multiple attacks into the thinly stretched III Corps in the
Wheatfield and overwhelmed them in Sherfy's Peach Orchard. McLaws's attack eventually reached Plum Run Valley (the "Valley of Death") before being beaten back by the Pennsylvania Reserves
division of the V Corps, moving down from Little Round Top. The III
Corps was virtually destroyed as a combat unit in this battle, and
Sickles's leg was amputated after it was shattered by a cannonball.
Caldwell's division was destroyed piecemeal in the Wheatfield.
Anderson's division, coming from McLaws's left and starting forward
around 6 p.m., reached the crest of Cemetery Ridge, but could not hold
the position in the face of counterattacks from the II Corps, including
an almost suicidal bayonet charge by the 1st Minnesota regiment against a Confederate brigade, ordered in desperation by Hancock to buy time for reinforcements to arrive.
As fighting raged in the Wheatfield and Devil's Den, Col. Strong Vincent
of V Corps had a precarious hold on Little Round Top, an important hill
at the extreme left of the Union line. His brigade of four relatively
small regiments was able to resist repeated assaults by Brig. Gen. Evander M. Law's brigade of Hood's division. Meade's chief engineer, Brig. Gen. Gouverneur K. Warren,
had realized the importance of this position, and dispatched Vincent's
brigade, an artillery battery, and the 140th New York to occupy Little
Round Top mere minutes before Hood's troops arrived. The defense of
Little Round Top with a bayonet charge by the 20th Maine, ordered by Col. Joshua L. Chamberlain but possibly led by Lt. Holman S. Melcher, was one of the most fabled episodes in the Civil War and propelled Col. Chamberlain into prominence after the war.
Attacks on the Union right flank
Union breastworks on Culp's Hill
Ewell interpreted his orders as calling only for a cannonade.
His 32 guns, along with A. P. Hill's 55 guns, engaged in a two-hour
artillery barrage at extreme range that had little effect. Finally,
about six o'clock, Ewell sent orders to each of his division commanders
to attack the Union lines in his front.
Maj. Gen. Edward "Allegheny" Johnson's
Division "had not been pushed close to [Culp's Hill] in preparation for
an assault, although one had been contemplated all day. It now had a
full mile (1,600 m) to advance and Rock Creek had to be crossed. This
could only be done at few places and involved much delay. Only three of
Johnson's four brigades moved to the attack."
Most of the hill's defenders, the Union XII Corps, had been sent to the
left to defend against Longstreet's attacks, leaving only a brigade of
New Yorkers under Brig. Gen. George S. Greene
behind strong, newly constructed defensive works. With reinforcements
from the I and XI Corps, Greene's men held off the Confederate
attackers, though giving up some of the lower earthworks on the lower
part of Culp's Hill.
Early was similarly unprepared when he ordered Harry T. Hays' and Isaac E. Avery's Brigades to attack the Union XI Corps positions on East Cemetery Hill. Once started, fighting was fierce: Col. Andrew L. Harris
of the Union 2nd Brigade, 1st Division, came under a withering attack,
losing half his men. Avery was wounded early on, but the Confederates
reached the crest of the hill and entered the Union breastworks,
capturing one or two batteries. Seeing he was not supported on his
right, Hays withdrew. His right was to be supported by Robert E. Rodes'
Division, but Rodes—like Early and Johnson—had not been ordered up in
preparation for the attack. He had twice as far to travel as Early; by
the time he came in contact with the Union skirmish line, Early's troops
had already begun to withdraw.
Jeb Stuart and his three cavalry brigades arrived in Gettysburg around noon but had no role in the second day's battle. Brig. Gen. Wade Hampton's brigade fought a minor engagement with newly promoted 23-year-old Brig. Gen. George Armstrong Custer's Michigan cavalry near Hunterstown to the northeast of Gettysburg.
Third day of battle
Overview map of the third day of the Battle of Gettysburg, July 3, 1863
Lee's plan
General Lee wished to renew the attack on Friday, July 3, using the
same basic plan as the previous day: Longstreet would attack the Union
left, while Ewell attacked Culp's Hill.
However, before Longstreet was ready, Union XII Corps troops started a
dawn artillery bombardment against the Confederates on Culp's Hill in an
effort to regain a portion of their lost works. The Confederates
attacked, and the second fight for Culp's Hill ended around 11 a.m.
Harry Pfanz judged that, after some seven hours of bitter combat, "the
Union line was intact and held more strongly than before."
Lee was forced to change his plans. Longstreet would command
Pickett's Virginia division of his own First Corps, plus six brigades
from Hill's Corps, in an attack on the Union II Corps position at the
right center of the Union line on Cemetery Ridge. Prior to the attack,
all the artillery the Confederacy could bring to bear on the Union
positions would bombard and weaken the enemy's line.
Much has been made over the years of General Longstreet's
objections to General Lee's plan. In his memoirs, Longstreet described
their discussion as follows:
[Lee] rode over after sunrise and gave his orders. His plan was to assault the enemy's left centre by a column to be composed of McLaws's and Hood's divisions reinforced by Pickett's brigades. I thought that it would not do; that the point had been fully tested the day before, by more men, when all were fresh; that the enemy was there looking for us, as we heard him during the night putting up his defences; that the divisions of McLaws and Hood were holding a mile [1,600 m] along the right of my line against twenty thousand men, who would follow their withdrawal, strike the flank of the assaulting column, crush it, and get on our rear towards the Potomac River; that thirty thousand men was the minimum of force necessary for the work; that even such force would need close co-operation on other parts of the line; that the column as he proposed to organize it would have only about thirteen thousand men (the divisions having lost a third of their numbers the day before); that the column would have to march a mile [1,600 m] under concentrating battery fire, and a thousand yards [900 m] under long-range musketry; that the conditions were different from those in the days of Napoleon, when field batteries had a range of six hundred yards [550 m] and musketry about sixty yards [55 m]. He said the distance was not more than fourteen hundred yards [1280 m]. General Meade's estimate was a mile or a mile and a half [1.6 or 2.4 km] (Captain Long, the guide of the field of Gettysburg in 1888, stated that it was a trifle over a mile). He then concluded that the divisions of McLaws and Hood could remain on the defensive line; that he would reinforce by divisions of the Third Corps and Pickett's brigades, and stated the point to which the march should be directed. I asked the strength of the column. He stated fifteen thousand. Opinion was then expressed that the fifteen thousand men who could make successful assault over that field had never been arrayed for battle; but he was impatient of listening, and tired of talking, and nothing was left but to proceed.
The
"High Water Mark" on Cemetery Ridge as it appears today. The monument
to the 72nd Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry Regiment ("Baxter's
Philadelphia Fire Zouaves") appears at right, the Copse of Trees to the
left.
The largest artillery bombardment of the war
Around 1 p.m., from 150 to 170 Confederate guns began an artillery
bombardment that was probably the largest of the war. In order to save
valuable ammunition for the infantry attack that they knew would follow,
the Army of the Potomac's artillery, under the command of Brig. Gen. Henry Jackson Hunt,
at first did not return the enemy's fire. After waiting about 15
minutes, about 80 Union cannons added to the din. The Army of Northern
Virginia was critically low on artillery ammunition, and the cannonade
did not significantly affect the Union position.
Pickett's Charge
Around 3 p.m., the cannon fire subsided, and 12,500 Southern soldiers
stepped from the ridgeline and advanced the three-quarters of a mile
(1,200 m) to Cemetery Ridge in what is known to history as "Pickett's Charge".
As the Confederates approached, there was fierce flanking artillery
fire from Union positions on Cemetery Hill and north of Little Round
Top, and musket and canister fire from Hancock's II Corps. In the Union
center, the commander of artillery had held fire during the Confederate
bombardment (in order to save it for the infantry assault, which Meade
had correctly predicted the day before), leading Southern commanders to
believe the Northern cannon batteries had been knocked out. However,
they opened fire on the Confederate infantry during their approach with
devastating results. Nearly one half of the attackers did not return to
their own lines.
Although the Union line wavered and broke temporarily at a jog
called the "Angle" in a low stone fence, just north of a patch of
vegetation called the Copse of Trees, reinforcements rushed into the
breach, and the Confederate attack was repulsed. The farthest advance of
Brig. Gen. Lewis A. Armistead's brigade of Maj. Gen. George Pickett's division at the Angle is referred to as the "High-water mark of the Confederacy".
Union and Confederate soldiers locked in hand-to-hand combat, attacking
with their rifles, bayonets, rocks and even their bare hands. Armistead
ordered his Confederates to turn two captured cannons against Union
troops, but discovered that there was no ammunition left, the last double canister shots having been used against the charging Confederates. Armistead was wounded shortly afterward three times.
Cavalry battles
There were two significant cavalry engagements on July 3. Stuart was
sent to guard the Confederate left flank and was to be prepared to
exploit any success the infantry might achieve on Cemetery Hill by
flanking the Union right and hitting their trains and lines of
communications. Three miles (5 km) east of Gettysburg, in what is now
called "East Cavalry Field" (not shown on the accompanying map, but
between the York and Hanover Roads), Stuart's forces collided with Union
cavalry: Brig. Gen. David McMurtrie Gregg's
division and Brig. Gen. Custer's brigade. A lengthy mounted battle,
including hand-to-hand sabre combat, ensued. Custer's charge, leading
the 1st Michigan Cavalry, blunted the attack by Wade Hampton's brigade, blocking Stuart from achieving his objectives in the Union rear.
Aftermath
Casualties
"The Harvest of Death": Union dead on the battlefield at Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, photographed July 5 or July 6, 1863, by Timothy H. O'Sullivan
The two armies suffered between 46,000 and 51,000 casualties, nearly
one third of all total troops engaged, 28% of the Army of the Potomac
and 37% of the Army of Northern Virginia. Union casualties were 23,055 (3,155 killed, 14,531 wounded, 5,369 captured or missing),
while Confederate casualties are more difficult to estimate. Many
authors have referred to as many as 28,000 Confederate casualties, and Busey and Martin's more recent 2005 work, Regimental Strengths and Losses at Gettysburg, documents 23,231 (4,708 killed, 12,693 wounded, 5,830 captured or missing). Nearly a third of Lee's general officers were killed, wounded, or captured. The casualties for both sides during the entire campaign were 57,225.
In addition to being the deadliest battle of the war, Gettysburg
also had the highest number of generals killed in action. The
Confederacy lost generals Paul Jones Semmes, William Barksdale, William Dorsey Pender, Richard Garnett, and Lewis Armistead, as well as J. Johnston Pettigrew during the retreat after the battle. The Union lost Generals John Reynolds, Samuel K. Zook, Stephen H. Weed, and Elon J. Farnsworth, as well as Strong Vincent,
who after being mortally wounded was given a deathbed promotion to
brigadier general. Additional senior officer casualties included the
wounding of Union Generals Dan Sickles (lost a leg), Francis C. Barlow, Daniel Butterfield, and Winfield Scott Hancock. For the Confederacy, Major General John Bell Hood lost the use of his left arm, while Major General Henry Heth
received a shot to the head on the first day of battle (though
incapacitated for the rest of the battle, he remarkably survived without
long-term injuries, credited in part due to his hat stuffed full of
paper dispatches). Confederate Generals James L. Kemper and Isaac R. Trimble were severely wounded during Pickett's charge and captured during the Confederate retreat. General James J. Archer,
in command of a brigade that most likely was responsible for killing
Reynolds, was taken prisoner shortly after Reynolds' death.
The following tables summarize casualties by corps for the Union and Confederate forces during the three-day battle.
John L. Burns, veteran of the War of 1812, civilian who fought at the Battle of Gettysburg with Union troops, standing with bayoneted musket. Mathew Brady's
National Photographic Portrait Galleries, photographer. From the
Liljenquist Family Collection of Civil War Photographs, Prints and
Photographs Division, Library of Congress
| Union Corps | Casualties (k/w/m) |
|---|---|
| I Corps | 6059 (666/3231/2162) |
| II Corps | 4369 (797/3194/378) |
| III Corps | 4211 (593/3029/589) |
| V Corps | 2187 (365/1611/211) |
| VI Corps | 242 (27/185/30) |
| XI Corps | 3807 (369/1924/1514) |
| XII Corps | 1082 (204/812/66) |
| Cavalry Corps | 852 (91/354/407) |
| Artillery Reserve | 242 (43/187/12) |
| Confederate Corps | Casualties (k/w/m) |
|---|---|
| First Corps | 7665 (1617/4205/1843) |
| Second Corps | 6686 (1301/3629/1756) |
| Third Corps | 8495 (1724/4683/2088) |
| Cavalry Corps | 380 (66/174/140) |
Bruce Catton wrote, "The town of Gettysburg looked as if some universal moving day had been interrupted by catastrophe." But there was only one documented civilian death during the battle: Ginnie Wade
(also widely known as Jennie), 20 years old, was hit by a stray bullet
that passed through her kitchen in town while she was making bread. Another notable civilian casualty was John L. Burns,
a 69-year old veteran of the War of 1812 who walked to the front lines
on the first day of battle and participated in heavy combat as a
volunteer, receiving numerous wounds in the process. Despite his age and
injuries, Burns survived the battle and lived until 1872.
Nearly 8,000 had been killed outright; these bodies, lying in the hot
summer sun, needed to be buried quickly. Over 3,000 horse carcasses were burned in a series of piles south of town; townsfolk became violently ill from the stench.
Meanwhile, the town of Gettysburg, with its population of just 2,400,
found itself tasked with taking care of 14,000 wounded Union troops and
an additional 8,000 Confederate prisoners.
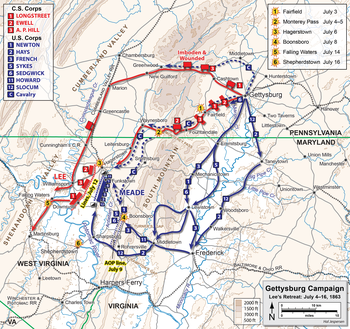
Confederate retreat
Gettysburg Campaign (July 5 – July 14, 1863)
The armies stared at one another in a heavy rain across the bloody
fields on July 4, the same day that, some 900 miles (1,500 km) away, the
Vicksburg garrison surrendered to Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant.
Lee had reformed his lines into a defensive position on Seminary Ridge
the night of July 3, evacuating the town of Gettysburg. The Confederates
remained on the battlefield, hoping that Meade would attack, but the
cautious Union commander decided against the risk, a decision for which
he would later be criticized. Both armies began to collect their
remaining wounded and bury some of the dead. A proposal by Lee for a
prisoner exchange was rejected by Meade.
Lee started his Army of Northern Virginia in motion late the evening of July 4 towards Fairfield and Chambersburg. Cavalry under Brig. Gen. John D. Imboden
was entrusted to escort the miles-long wagon train of supplies and
wounded men that Lee wanted to take back to Virginia with him, using the
route through Cashtown and Hagerstown to Williamsport, Maryland.
Meade's army followed, although the pursuit was half-spirited. The
recently rain-swollen Potomac trapped Lee's army on the north bank of
the river for a time, but when the Union troops finally caught up, the
Confederates had forded the river. The rear-guard action at Falling Waters on July 14 added some more names to the long casualty lists, including General Pettigrew, who was mortally wounded. General James L. Kemper, severely wounded during Pickett's charge, was captured during Lee's retreat.
In a brief letter to Maj. Gen. Henry W. Halleck written on July
7, Lincoln remarked on the two major Union victories at Gettysburg and
Vicksburg. He continued:
Now, if Gen. Meade can complete his work so gloriously prosecuted thus far, by the literal or substantial destruction of Lee's army, the rebellion will be over.
Halleck then relayed the contents of Lincoln's letter to Meade in a
telegram. However, the Army of the Potomac was exhausted by days of
fighting and heavy losses. Furthermore, Meade was forced to detach
4,000 troops North to suppress the New York City Draft Riots,
further reducing the effectiveness of his pursuit. Despite repeated
pleas from Lincoln and Halleck, which continued over the next week,
Meade did not pursue Lee's army aggressively enough to destroy it before
it crossed back over the Potomac River to safety in the South. The
campaign continued into Virginia with light engagements until July 23,
in the minor Battle of Manassas Gap, after which Meade abandoned any attempts at pursuit and the two armies took up positions across from each other on the Rappahannock River.
Union reaction to the news of the victory
The news of the Union victory electrified the North. A headline in The Philadelphia Inquirer proclaimed "VICTORY! WATERLOO ECLIPSED!" New York diarist George Templeton Strong wrote:
The results of this victory are priceless. ... The charm of Robert E. Lee's invincibility is broken. The Army of the Potomac has at last found a general that can handle it, and has stood nobly up to its terrible work in spite of its long disheartening list of hard-fought failures. ... Copperheads are palsied and dumb for the moment at least. ... Government is strengthened four-fold at home and abroad.
— George Templeton Strong, Diary, p. 330.
However, the Union enthusiasm soon dissipated as the public realized
that Lee's army had escaped destruction and the war would continue.
Lincoln complained to Secretary of the Navy Gideon Welles that "Our army held the war in the hollow of their hand and they would not close it!" Brig. Gen. Alexander S. Webb wrote to his father on July 17, stating that such Washington politicians as "Chase, Seward and others," disgusted with Meade, "write to me that Lee really won that Battle!"
Effect on the Confederacy
In fact, the Confederates had lost militarily and also politically.
During the final hours of the battle, Confederate Vice President Alexander Stephens was approaching the Union lines at Norfolk, Virginia, under a flag of truce. Although his formal instructions from Confederate President Jefferson Davis had limited his powers to negotiate on prisoner exchanges and other procedural matters, historian James M. McPherson
speculates that he had informal goals of presenting peace overtures.
Davis had hoped that Stephens would reach Washington from the south
while Lee's victorious army was marching toward it from the north.
President Lincoln, upon hearing of the Gettysburg results, refused
Stephens's request to pass through the lines. Furthermore, when the news
reached London, any lingering hopes of European recognition of the
Confederacy were finally abandoned. Henry Adams,
whose father was serving as the U.S ambassador to the United Kingdom at
the time, wrote, "The disasters of the rebels are unredeemed by even
any hope of success. It is now conceded that all idea of intervention is
at an end."
Compounding the effects of the defeat would be the end of the Siege of Vicksburg, which surrendered to Grant's Federal armies in the West on July 4, the day after the Gettysburg battle.
The immediate reaction of the Southern military and public
sectors was that Gettysburg was a setback, not a disaster. The sentiment
was that Lee had been successful on July 1 and had fought a valiant
battle on July 2–3, but could not dislodge the Union Army from the
strong defensive position to which it fled. The Confederates
successfully stood their ground on July 4 and withdrew only after they
realized Meade would not attack them. The withdrawal to the Potomac that
could have been a disaster was handled masterfully. Furthermore, the
Army of the Potomac had been kept away from Virginia farmlands for the
summer and all predicted that Meade would be too timid to threaten them
for the rest of the year. Lee himself had a positive view of the
campaign, writing to his wife that the army had returned "rather sooner
than I had originally contemplated, but having accomplished what I
proposed on leaving the Rappahannock, viz., relieving the Valley of the
presence of the enemy and drawing his Army north of the Potomac." He was
quoted as saying to Maj. John Seddon, brother of the Confederate
secretary of war, "Sir, we did whip them at Gettysburg, and it will be
seen for the next six months that that army will be as quiet as a sucking dove." Some Southern publications, such as the Charleston Mercury, were critical of Lee's actions. On August 8, Lee offered his resignation to President Davis, who quickly rejected it.
Gettysburg became a postbellum focus of the "Lost Cause",
a movement by writers such as Edward A. Pollard and Jubal Early to
explain the reasons for the Confederate defeat in the war. A fundamental
premise of their argument was that the South was doomed because of the
overwhelming advantage in manpower and industrial might possessed by the
North. They also contend that Robert E. Lee, who up until this time had
been almost invincible, was betrayed by the failures of some of his key
subordinates at Gettysburg: Ewell, for failing to seize Cemetery Hill
on July 1; Stuart, for depriving the army of cavalry intelligence for a
key part of the campaign; and especially Longstreet, for failing to
attack on July 2 as early and as forcefully as Lee had originally
intended. In this view, Gettysburg was seen as a great lost opportunity,
in which a decisive victory by Lee could have meant the end of the war
in the Confederacy's favor.
After the war, General Pickett was asked why Confederates lost at
Gettysburg. He was reported to have said, "I always thought the Yankees
had something to do with it."
Gettysburg Address
Gettysburg, November 19, 1863. Crowd of citizens, soldiers, and etc., with a red arrow indicating Abraham Lincoln
The ravages of war were still evident in Gettysburg more than four months later when, on November 19, the Soldiers' National Cemetery was dedicated. During this ceremony, President Abraham Lincoln honored the fallen and redefined the purpose of the war in his historic Gettysburg Address.
Medal of Honor
There were 72 Medals of Honor
awarded for the Gettysburg Campaign. 64 of the awards were for actions
taken during the battle itself, with the first recipient being awarded
in December 1864. The last Medal of Honor was posthumously awarded to
Lieutenant Alonzo Cushing in 2014.
Historical assessment
Decisive victory controversies
The nature of the result of the Battle of Gettysburg has been the
subject of controversy. Although not seen as overwhelmingly significant
at the time, particularly since the war continued for almost two years,
in retrospect it has often been cited as the "turning point", usually in combination with the fall of Vicksburg the following day.
This is based on the observation that, after Gettysburg, Lee's army
conducted no more strategic offensives—his army merely reacted to the
initiative of Ulysses S. Grant
in 1864 and 1865—and by the speculative viewpoint of the Lost Cause
writers that a Confederate victory at Gettysburg might have resulted in
the end of the war.
[The Army of the
Potomac] had won a victory. It might be less of a victory than Mr.
Lincoln had hoped for, but it was nevertheless a victory—and, because of
that, it was no longer possible for the Confederacy to win the war. The
North might still lose it, to be sure, if the soldiers or the people
should lose heart, but outright defeat was no longer in the cards.
Bruce Catton, Glory Road
It is currently a widely held view that Gettysburg was a decisive victory
for the Union, but the term is considered imprecise. It is inarguable
that Lee's offensive on July 3 was turned back decisively and his
campaign in Pennsylvania was terminated prematurely (although the
Confederates at the time argued that this was a temporary setback and
that the goals of the campaign were largely met). However, when the more
common definition of "decisive victory" is intended—an indisputable
military victory of a battle that determines or significantly influences
the ultimate result of a conflict—historians are divided. For example, David J. Eicher called Gettysburg a "strategic loss for the Confederacy" and James M. McPherson
wrote that "Lee and his men would go on to earn further laurels. But
they never again possessed the power and reputation they carried into
Pennsylvania those palmy summer days of 1863."
However, Herman Hattaway and Archer Jones wrote that the
"strategic impact of the Battle of Gettysburg was ... fairly limited."
Steven E. Woodworth wrote that "Gettysburg proved only the near
impossibility of decisive action in the Eastern theater." Edwin
Coddington pointed out the heavy toll on the Army of the Potomac and
that "after the battle Meade no longer possessed a truly effective
instrument for the accomplishments of his task. The army needed a
thorough reorganization with new commanders and fresh troops, but these
changes were not made until Grant appeared on the scene in March 1864."
Joseph T. Glatthaar wrote that "Lost opportunities and near successes
plagued the Army of Northern Virginia during its Northern invasion," yet
after Gettysburg, "without the distractions of duty as an invading
force, without the breakdown of discipline, the Army of Northern
Virginia [remained] an extremely formidable force." Ed Bearss
wrote, "Lee's invasion of the North had been a costly failure.
Nevertheless, at best the Army of the Potomac had simply preserved the
strategic stalemate in the Eastern Theater ..."
Furthermore, the Confederacy soon proved it was still capable of
winning significant victories over the Northern forces in both the East (Battle of Cold Harbor) and West (Battle of Chickamauga).
Peter Carmichael refers to the military context for the armies,
the "horrendous losses at Chancellorsville and Gettysburg, which
effectively destroyed Lee's offensive capacity," implying that these
cumulative losses were not the result of a single battle. Thomas Goss,
writing in the U.S. Army's Military Review journal on the
definition of "decisive" and the application of that description to
Gettysburg, concludes: "For all that was decided and accomplished, the
Battle of Gettysburg fails to earn the label 'decisive battle'." The military historian John Keegan
agrees. Gettysburg was a landmark battle, the largest of the war and it
would not be surpassed. The Union had restored to it the belief in
certain victory, and the loss dispirited the Confederacy. If "not
exactly a decisive battle", Gettysburg was the end of Confederate use of
Northern Virginia as a military buffer zone, the setting for Grant's Overland Campaign.
Lee vs. Meade
George G. Meade
Prior to Gettysburg, Robert E. Lee had established a reputation as an
almost invincible general, achieving stunning victories against
superior numbers—although usually at the cost of high casualties to his
army—during the Seven Days, the Northern Virginia Campaign (including the Second Battle of Bull Run), Fredericksburg, and Chancellorsville. Only the Maryland Campaign, with its tactically inconclusive Battle of Antietam,
had been less than successful. Therefore, historians have attempted to
explain how Lee's winning streak was interrupted so dramatically at
Gettysburg. Although the issue is tainted by attempts to portray history
and Lee's reputation in a manner supporting different partisan goals,
the major factors in Lee's loss arguably can be attributed to: (1) his
overconfidence in the invincibility of his men; (2) the performance of
his subordinates, and his management thereof; (3) his failing health,
and (4) the performance of his opponent, George G. Meade, and the Army
of the Potomac.
Robert E. Lee
Throughout the campaign, Lee was influenced by the belief that his
men were invincible; most of Lee's experiences with the Army of Northern
Virginia had convinced him of this, including the great victory at
Chancellorsville in early May and the rout of the Union troops at
Gettysburg on July 1. Since morale plays an important role in military
victory when other factors are equal, Lee did not want to dampen his
army's desire to fight and resisted suggestions, principally by
Longstreet, to withdraw from the recently captured Gettysburg to select a
ground more favorable to his army. War correspondent Peter W. Alexander
wrote that Lee "acted, probably, under the impression that his troops
were able to carry any position however formidable. If such was the
case, he committed an error, such however as the ablest commanders will
sometimes fall into." Lee himself concurred with this judgment, writing
to President Davis, "No blame can be attached to the army for its
failure to accomplish what was projected by me, nor should it be
censured for the unreasonable expectations of the public—I am alone to
blame, in perhaps expecting too much of its prowess and valor."
The most controversial assessments of the battle involve the
performance of Lee's subordinates. The dominant theme of the Lost Cause
writers and many other historians is that Lee's senior generals failed
him in crucial ways, directly causing the loss of the battle; the
alternative viewpoint is that Lee did not manage his subordinates
adequately, and did not thereby compensate for their shortcomings. Two of his corps commanders—Richard S. Ewell and A.P. Hill—had
only recently been promoted and were not fully accustomed to Lee's
style of command, in which he provided only general objectives and
guidance to their former commander, Stonewall Jackson; Jackson translated these into detailed, specific orders to his division commanders. All four of Lee's principal commanders received criticism during the campaign and battle:
- James Longstreet suffered most severely from the wrath of the Lost Cause authors, not the least because he directly criticized Lee in postbellum writings and became a Republican after the war. His critics accuse him of attacking much later than Lee intended on July 2, squandering a chance to hit the Union Army before its defensive positions had firmed up. They also question his lack of motivation to attack strongly on July 2 and 3 because he had argued that the army should have maneuvered to a place where it would force Meade to attack them. The alternative view is that Lee was in close contact with Longstreet during the battle, agreed to delays on the morning of July 2, and never criticized Longstreet's performance. (There is also considerable speculation about what an attack might have looked like before Dan Sickles moved the III Corps toward the Peach Orchard.)
- J.E.B. Stuart deprived Lee of cavalry intelligence during a good part of the campaign by taking his three best brigades on a path away from the army's. This arguably led to Lee's surprise at Hooker's vigorous pursuit; the engagement on July 1 that escalated into the full battle prematurely; and it also prevented Lee from understanding the full disposition of the enemy on July 2. The disagreements regarding Stuart's culpability for the situation originate in the relatively vague orders issued by Lee, but most modern historians agree that both generals were responsible to some extent for the failure of the cavalry's mission early in the campaign.
- Richard S. Ewell has been universally criticized for failing to seize the high ground on the afternoon of July 1. Once again the disagreement centers on Lee's orders, which provided general guidance for Ewell to act "if practicable." Many historians speculate that Stonewall Jackson, if he had survived Chancellorsville, would have aggressively seized Culp's Hill, rendering Cemetery Hill indefensible, and changing the entire complexion of the battle. A differently worded order from Lee might have made the difference with this subordinate.
- A.P. Hill has received some criticism for his ineffective performance. His actions caused the battle to begin and then escalate on July 1, despite Lee's orders not to bring on a general engagement (although historians point out that Hill kept Lee well informed of his actions during the day). However, Hill's illness minimized his personal involvement in the remainder of the battle, and Lee took the explicit step of temporarily removing troops from Hill's corps and giving them to Longstreet for Pickett's Charge.
Winfield S. Hancock
In addition to Hill's illness, Lee's performance was affected by
heart troubles, which would eventually lead to his death in 1870; he had
been diagnosed with pericarditis by his staff physicians in March 1863, though modern doctors believe he had in fact suffered a heart attack.
He wrote to Jefferson Davis that his physical condition prevented him
from offering full supervision in the field, and said, "I am so dull
that in making use of the eyes of others I am frequently misled."
As a final factor, Lee faced a new and formidable opponent in George G. Meade,
and the Army of the Potomac fought well on its home territory. Although
new to his army command, Meade deployed his forces relatively
effectively; relied on strong subordinates such as Winfield S. Hancock
to make decisions where and when they were needed; took great advantage
of defensive positions; nimbly shifted defensive resources on interior
lines to parry strong threats; and, unlike some of his predecessors,
stood his ground throughout the battle in the face of fierce Confederate
attacks.
Lee was quoted before the battle as saying Meade "would commit no
blunders on my front and if I make one ... will make haste to take
advantage of it." That prediction proved to be correct at Gettysburg.
Stephen Sears wrote, "The fact of the matter is that George G. Meade,
unexpectedly and against all odds, thoroughly outgeneraled Robert E. Lee
at Gettysburg." Edwin B. Coddington wrote that the soldiers of the Army
of the Potomac received a "sense of triumph which grew into an
imperishable faith in [themselves]. The men knew what they could do
under an extremely competent general; one of lesser ability and courage
could well have lost the battle."
Meade had his own detractors as well. Similar to the situation
with Lee, Meade suffered partisan attacks about his performance at
Gettysburg, but he had the misfortune of experiencing them in person.
Supporters of his predecessor, Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker, lambasted Meade before the U.S. Congress's Joint Committee on the Conduct of the War, where Radical Republicans suspected that Meade was a Copperhead and tried in vain to relieve him from command. Daniel E. Sickles and Daniel Butterfield
accused Meade of planning to retreat from Gettysburg during the battle.
Most politicians, including Lincoln, criticized Meade for what they
considered to be his half-hearted pursuit of Lee after the battle. A
number of Meade's most competent subordinates—Winfield S. Hancock, John Gibbon, Gouverneur K. Warren, and Henry J. Hunt, all heroes of the battle—defended Meade in print, but Meade was embittered by the overall experience.
Battlefield preservation

M1857 12-Pounder "Napoleon" at Gettysburg National Military Park
Gettysburg, Pennsylvania.
| |
| Location | Adams, Pennsylvania, United States |
|---|---|
| Website | Park Home (NPS.gov) |
Today, the Gettysburg National Cemetery and Gettysburg National Military Park are maintained by the U.S. National Park Service
as two of the nation's most revered historical landmarks. Although
Gettysburg is one of the best known of all Civil War battlefields, it
too faces threats to its preservation and interpretation. Many
historically significant locations on the battlefield lie outside the
boundaries of Gettysburg National Military Park and are vulnerable to residential or commercial development.
On July 20, 2009, a Comfort Inn and Suites opened on Cemetery Hill, adjacent to Evergreen Cemetery,
just one of many modern edifices infringing on the historic field. The
Baltimore Pike corridor attracts development that concerns
preservationists.
Some preservation successes have emerged in recent years. Two
proposals to open a casino at Gettysburg were defeated in 2006 and most
recently in 2011, when public pressure forced the Pennsylvania Gaming Control Board to reject the proposed gambling hub at the intersection of Routes 15 and 30, near East Cavalry Field. The Civil War Trust also successfully purchased and transferred 95 acres at the former site of the Gettysburg Country Club to the control of the U.S. Department of the Interior in 2011.
Less than half of the over 11,500 acres on the old Gettysburg Battlefield have been preserved for posterity thus far. The Civil War Trust (a division of the American Battlefield Trust) and its partners have acquired and preserved 1,022 acres (4.14 km2) of the battlefield in more than 30 separate transactions since 1997. Some of these acres are now among the 4,998 acres of the Gettysburg National Military Park.
In 2015, the Trust made one of its most important and expensive
acquisitions, paying $6 million for a four-acre parcel that included the
stone house that Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee used as his
headquarters during the battle. The Trust razed a motel, restaurant and
other buildings within the parcel to restore Lee's Headquarters and the
site to their wartime appearance, adding interpretive signs. It opened
the site to the public in October, 2016.
Commemoration in U.S. postage and coinage
The 1936 Battle of Gettysburg half dollar
Gettysburg Centennial Commemorative issue of 1963
Gettysburg National Military Park Quarter, issued 2011
During the Civil War Centennial,
the U.S. Post Office issued five postage stamps commemorating the 100th
anniversaries of famous battles, as they occurred over a four-year
period, beginning with the Battle of Fort Sumter Centennial issue of 1961. The Battle of Shiloh commemorative stamp was issued in 1962, the Battle of Gettysburg in 1963, the Battle of the Wilderness in 1964, and the Appomattox Centennial commemorative stamp in 1965.
A commemorative half dollar for the battle was produced in 1936. As was typical for the period, mintage for the coin was very low, just 26,928. On January 24, 2011, the America the Beautiful quarters
released a 25-cent coin commemorating Gettysburg National Military Park
and the Battle of Gettysburg. The reverse side of the coin depicts the
monument on Cemetery Ridge to the 72nd Pennsylvania Infantry.
In popular culture
Film records survive of two Gettysburg reunions, held on the battlefield. At the 50th anniversary (1913),
veterans re-enacted Pickett's Charge in a spirit of reconciliation, a
meeting that carried great emotional force for both sides. At the 75th anniversary (1938),
2500 veterans attended, and there was a ceremonial mass hand-shake
across a stone wall. This was recorded on sound film, and some
Confederates can be heard giving the Rebel Yell.
The Battle of Gettysburg was depicted in the 1993 film Gettysburg, based on Michael Shaara's 1974 novel The Killer Angels. The film and novel focused primarily on the actions of Joshua Lawrence Chamberlain, John Buford, Robert E. Lee, and James Longstreet during the battle. The first day focused on Buford's cavalry defense, the second day on Chamberlain's defense at Little Round Top, and the third day on Pickett's Charge.
The south winning the Battle of Gettysburg is a popular premise for a point of divergence in American Civil War alternate histories.
Here are some examples which either depict or make significant
reference to an alternate Battle of Gettysburg (sometimes simply
inserting fantasy or sci-fi elements in an account of the battle):
- Novels: Bring the Jubilee by Ward Moore; If the South Had Won the Civil War by Mackinlay Kantor; Civil War Trilogy (Gettysburg, Grant Comes East, Never Call Retreat) by Newt Gingrich, William R. Forstchen, and Albert S. Hanser; Stonewall Jackson at Gettysburg by Douglas Lee Gibboney; By Force of Arms by Billy Bennett. Also: Harry Turtledove's Southern Victory series has an analogous battle taking place at Camp Hill, another southeast Pennsylvania town.
- Short fiction: "If Lee Had NOT Won the Battle of Gettysburg" by Winston Churchill in If It Had Happened Otherwise and If, or History Rewritten, "Sidewise in Time" by Murray Leinster in various collections, "A Hard Day for Mother" by William R. Forstchen in Alternate Generals 1, "An Old Man's Summer" by Esther Friesner also in AG 1, "If the Lost Order Hadn't Been Lost" by James M. McPherson in What If? and What Ifs? of American History, "East of Appomattox" by Lee Allred in Alternate Generals