Corporate signature used since 1993
| |||||||||
 USPS Headquarters | |||||||||
| Agency overview | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formed | July 1, 1971 Washington, D.C., U.S. | ||||||||
| Type | Independent | ||||||||
| Headquarters | 475 L'Enfant Plaza SW Washington, D.C. 20260-0004 U.S. | ||||||||
| Employees | 633,108 (496,934 career personnel, 136,174 non-career personnel) as of 2019 | ||||||||
| Agency executives |
| ||||||||
| Key document | |||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The full eagle logo, used in various versions from 1970 to 1993
The United States Postal Service (USPS; also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service) is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the United States, including its insular areas and associated states. It is one of the few government agencies explicitly authorized by the United States Constitution.
The USPS traces its roots to 1775 during the Second Continental Congress, when Benjamin Franklin was appointed the first postmaster general. The Post Office Department was created in 1792 with the passage of the Postal Service Act. It was elevated to a cabinet-level department in 1872, and was transformed by the Postal Reorganization Act of 1970 into the United States Postal Service as an independent agency.
Since the early 1980s, many direct tax subsidies to the USPS (with the
exception of subsidies for costs associated with disabled and overseas
voters) have been reduced or eliminated.
The USPS, as of 2019, has 469,934 career employees and 136,174
non-career employees. The Postal Service is legally obligated to serve
all Americans, regardless of geography, at uniform price and quality.
The Post Office has exclusive access to letter boxes marked "U.S. Mail" and personal letterboxes in the United States, but has to compete against private package delivery services, such as United Parcel Service, FedEx, and Amazon.
History
On March 18, 1970,
postal workers in New York City—upset over low wages and poor working
conditions, and emboldened by the Civil Rights Movement—organized a strike
against the United States government. The strike initially involved
postal workers in only New York City, but it eventually gained support
of over 210,000 United States Post Office Department workers across the nation.
While the strike ended without any concessions from the Federal
government, it did ultimately allow for postal worker unions and the
government to negotiate a contract which gave the unions most of what
they wanted, as well as the signing of the Postal Reorganization Act by President Richard Nixon
on August 12, 1970. The act replaced the cabinet-level Post Office
Department with a new federal agency, the United States Postal Service, and took effect on July 1, 1971.
Since the 1990s, Republicans have been discussing the idea of privatizing the U.S. Postal Service. The Donald Trump
administration proposed turning USPS into "a private postal operator"
as part of a June 2018 governmental reorganization plan, although there
was strong bipartisan opposition to the idea in Congress.
Current operations
The United States Postal Service employs 633,188 workers, making it
the third-largest civilian employer in the United States behind the
federal government and Walmart. In a 2006 U.S. Supreme Court
decision, the Court noted: "Each day, according to the Government's
submissions here, the United States Postal Service delivers some 660
million pieces of mail to as many as 142 million delivery points."
As of 2017, the USPS operates 30,825 post offices and locations in the
U.S., and delivers 149.5 billion pieces of mail annually.
The USPS operates one of the largest civilian vehicle fleets in the world, with an estimated 227,896 vehicles, the majority of which are the easily identified Chevrolet/Grumman LLV
(long-life vehicle), and the newer Ford/Utilimaster FFV (flex-fuel
vehicle), originally also referred to as the CRV (carrier route
vehicle). Made from 1987 to 1994 and with no air conditioning, no
airbags, no anti-lock brakes, and lacking space for the large modern
volume of e-commerce packages, the Grumman fleet ended its expected
lifespan in fiscal year 2017. The replacement process began in 2015, and
prototypes have been produced by various bidders, but due to delays as
of May 2020, a final contract for replacement trucks has not been
awarded.
It is by geography and volume the globe's largest postal system, delivering 47% of the world's mail. For every penny increase in the national average price of gasoline, the USPS spends an extra US$8 million per year to fuel its fleet.
A Grumman LLV, the USPS’ main type of delivery truck
The number of gallons of fuel used in 2009 was 444 million, at a cost of US$1.1 billion. The fleet is notable in that many of its vehicles are right-hand drive, an arrangement intended to give drivers the easiest access to roadside mailboxes. Some rural letter carriers use personal vehicles. All contractors use personal vehicles. Standard postal-owned vehicles do not have license plates. These vehicles are identified by a seven-digit number displayed on the front and rear.
A fleet of post office vehicles at the James Griffith Station in Spring Branch, Houston
The Department of Defense and the USPS jointly operate a postal system to deliver mail for the military; this is known as the Army Post Office (for Army and Air Force postal facilities) and the Fleet Post Office (for Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard postal facilities).
In February 2013, the Postal Service announced that on Saturdays
it would only deliver packages, mail-order medicines, Priority Mail, and
Express Mail, effective August 10, 2013. However, this change was reversed by federal law in the Consolidated and Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2013. They now deliver packages on Sunday—only for Amazon.com — meaning that carriers make parcel deliveries seven days a week.
During the four weeks preceding Christmas since 2013, packages from all
mail classes and senders were delivered on Sunday in some areas.
Parcels are also delivered on holidays, with the exception of Thanksgiving and Christmas.
The period between Thanksgiving and Christmas is the busiest time
of the year for the USPS with the agency delivering an estimated
900 million packages during the period of 2018.
In May 2019, the Postal Service announced that it will be
releasing a pilot of self-driving trucks to haul mail across the U.S.
The 18-wheelers were developed by startup company, TuSimple. The pilot
will last two weeks, making five total round trips to cities across the
country.
In early May 2020, the USPS's board of governors confirmed that Louis DeJoy would be the new postmaster general.
Operation and budget
In 2016, the Postal Service collected $71.5 billion in revenue.
Revenue decline and planned cuts
In
2016, the USPS had its fifth straight annual operating loss, in the
amount of $5.6 billion, of which $5.8 billion was the accrual of unpaid
mandatory retiree health payments.
Declining mail volume
First-class mail volume peaked in 2001, declining by 43% as of 2017 due to the increasing use of email and the World Wide Web for correspondence and business transactions.
Private courier services, such as FedEx and United Parcel Service (UPS), directly compete with USPS for the delivery of urgent letters and packages.
Lower volume means lower revenues to support the fixed commitment
to deliver to every address once a day, six days a week. According to
an official report on November 15, 2012, the U.S. Postal Service lost
$15.9 billion its 2012 fiscal year.
Internal streamlining and delivery slowdown
In response, the USPS has increased productivity each year from 2000 to 2007, through increased automation, route re-optimization, and facility consolidation. Despite these efforts, the organization saw an $8.5 billion budget shortfall in 2010, and was losing money at a rate of about $3 billion per quarter in 2011.
On December 5, 2011, the USPS announced it would close more than
half of its mail processing centers, eliminate 28,000 jobs and reduce
overnight delivery of First-Class Mail. This will close down 252 of its
461 processing centers. (At peak mail volume in 2006, the USPS operated 673 facilities.)
As of May 2012, the plan was to start the first round of consolidation
in summer 2012, pause from September to December, and begin a second
round in February 2014; 80% of first-class mail would still be delivered
overnight through the end of 2013.
New delivery standards were issued in January 2015, and the majority of
single-piece (not presorted) first-class mail is now being delivered in
two days instead of one.
Large commercial mailers can still have first-class mail delivered
overnight if delivered directly to a processing center in the early
morning, though as of 2014 this represented only 11% of first-class
mail. Unsorted first-class mail will continue to be delivered anywhere in the contiguous United States within three days.
Post office closures
In
July 2011, the USPS announced a plan to close about 3,700 small post
offices. Various representatives in Congress protested, and the Senate
passed a bill that would have kept open all post offices farther than 10
miles (16 km) from the next office.
In May 2012, the service announced it had modified its plan. Instead,
rural post offices would remain open with reduced retail hours (some as
little as two hours per day) unless there was a community preference for
a different option.
In a survey of rural customers, 54% preferred the new plan of retaining
rural post offices with reduced hours, 20% preferred the "Village Post
Office" replacement (where a nearby private retail store would provide
basic mail services with expanded hours), 15% preferred merger with
another Post Office, and 11% preferred expanded rural delivery services. Approximately 40% of postal revenue already comes from online purchases or private retail partners including Walmart, Staples, Office Depot, Walgreens, Sam's Club, Costco, and grocery stores. The National Labor Relations Board
agreed to hear the American Postal Workers Union's arguments that these
counters should be manned by postal employees who earn far more and
have "a generous package of health and retirement benefits".
Elimination of Saturday delivery averted
On January 28, 2009, Postmaster General John E. Potter testified before the Senate
that, if the Postal Service could not readjust its payment toward the
contractually funding earned employee retiree health benefits, as
mandated by the Postal Accountability & Enhancement Act of 2006, the USPS would be forced to consider cutting delivery to five days per week during June, July, and August.
H.R. 22, addressing this issue, passed the House of Representatives and Senate and was signed into law on September 30, 2009. However, Postmaster General Potter continued to advance plans to eliminate Saturday mail delivery.
On June 10, 2009, the National Rural Letter Carriers' Association
(NRLCA) was contacted for its input on the USPS's current study of the
effect of five-day delivery along with developing an implementation plan
for a five-day service plan. A team of Postal Service headquarters
executives and staff has been given a time frame of sixty days to
complete the study. The current concept examines the effect of five-day
delivery with no business or collections on Saturday, with Post Offices
with current Saturday hours remaining open.
On Thursday, April 15, 2010, the House Committee on Oversight and
Government Reform held a hearing to examine the status of the Postal
Service and recent reports on short and long-term strategies for the
financial viability and stability of the USPS entitled "Continuing to
Deliver: An Examination of the Postal Service's Current Financial Crisis
and its Future Viability". At which, PMG Potter testified that by the
year 2020, the USPS cumulative losses could exceed $238 billion, and
that mail volume could drop 15 percent from 2009.
In February 2013, the USPS announced that in order to save about
$2 billion per year, Saturday delivery service would be discontinued
except for packages, mail-order medicines, Priority Mail, Express Mail,
and mail delivered to Post Office boxes, beginning August 10, 2013. However, the Consolidated and Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2013, passed in March, reversed the cuts to Saturday delivery.
Retirement funding and payment defaults
The Postal Accountability and Enhancement Act of 2006 (PAEA)
obligates the USPS to fund the present value of earned retirement
obligations (essentially past promises which have not yet come due)
within a ten-year time span. In contrast, private businesses in the
United States have no legal obligation to pay for retirement costs at
promise-time rather than retirement-time, but about one quarter do.
The Office of Personnel Management (OPM)
is the main bureaucratic organization responsible for the human
resources aspect of many federal agencies and their employees. The PAEA
created the Postal Service Retiree Health Benefit Fund (PSRHB) after
Congress removed the Postal Service contribution to the Civil Service
Retirement System (CSRS). Most other employees that contribute to the
CSRS have 7% deducted from their wages. Currently all new employees
contribute into Federal Employee Retirement System (FERS) once they
become a full-time regular employees.
On September 30, 2014, the USPS failed to make a $5.7 billion payment on this debt, the fourth such default.
On February 5, 2020, the House passed The USPS Fairness Act (H.R. 2382)
with 309 Yeas and 106 Nays meeting the 2/3rd rule. The measure
eliminates the requirement going forward and forgives all payments on
which USPS has defaulted. It was moved to the Senate on February 10, 2020 and is awaiting action by senators.
Rate increases
Congress has limited rate increases for First-Class Mail to the cost of inflation, unless approved by the Postal Regulatory Commission.
A three-cent surcharge above inflation increased the 1 oz (28 g) rate
to 49¢ in January 2014, but this was approved by the commission for two
years only.
As of January 2019, first-class postage for up to 1 ounce is $0.55.
Reform proposals and delivery changes
Comprehensive reform packages considered in the 113th Congress include S.1486 and H.R.2748. These include the efficiency measure, supported by Postmaster General Patrick Donahoe of ending door-to-door delivery of mail for some or most of the
35 million addresses that currently receive it, replacing that with
either curbside boxes or nearby "cluster boxes". This would save
$4.5 billion per year out of the $30 billion delivery budget;
door-to-door city delivery costs annually on average $353 per stop,
curbside $224, and cluster box $160 (and for rural delivery, $278, $176,
and $126, respectively).
S.1486, also with the support of Postmaster Donahoe,
would also allow the USPS to ship alcohol in compliance with state law,
from manufacturers to recipients with ID to show they are over 21. This
is projected to raise approximately $50 million per year. (Shipping alcoholic beverages is currently illegal under 18 U.S.C. § 1716(f).)
In 2014, the Postal Service was requesting reforms to workers'
compensation, moving from a pension to defined contribution retirement
savings plan, and paying senior retiree health care costs out of Medicare funds, as is done for private-sector workers.
As part of a June 2018 governmental reorganization plan, the Donald Trump
administration proposed turning USPS into "a private postal operator"
which could save costs through measures like delivering mail fewer days
per week, or delivering to central locations instead of door to door.
There was strong bipartisan opposition to the idea in Congress.
In April 2020 Congress approved a $10 billion loan from the Treasury to the post office. According to the Washington Post, officials under Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin
suggested using the loan as leverage to give the Treasury Department
more influence on USPS operations, including making them raise their
charges for package deliveries, a change long sought by President Trump.
In May 2020 Louis DeJoy
was appointed Postmaster General and immediately began taking measures
to reduce costs, such as banning overtime and extra trips to deliver
mail.
While DeJoy admitted that these measures were causing delays in mail delivery, he said they would eventually improve service. More than 600 high-speed mail sorting machines were dismantled and removed from postal facilities without explanation, raising concerns that mailed ballots for the November 3 election might not reach election offices on time.
Mail collection boxes were removed from the streets in many cities;
after photos of boxes being removed were spread on social media, a
postal service spokesman said they were being moved to higher traffic
areas but that the removals would stop until after the election. The inspector general for the postal service has opened an investigation into recent changes.
Voting by mail has become an increasingly common practice in the
United States, with 25% of voters nationwide mailing their ballots in
2016 and 2018. The coronavirus pandemic
of 2020 has been predicted to cause a large increase in mail voting
because of the possible danger of congregating at polling places.
For the 2020 election, a state-by-state analysis concluded that 76% of
Americans are eligible to vote by mail in 2020, a record number. The
analysis predicted that 80 million ballots could be cast by mail in 2020
- more than double the number in 2016.
The Postal Service sent a letter to 46 states in July 2020, warning
that the service might not be able to meet the state's deadlines for
requesting and casting last-minute absentee ballots.
The House of Representatives voted to include an emergency grant
of $25 billion to the post office to facilitate the predicted flood of
mail ballots.
Trump conceded that the post office would need additional funds to
handle the additional mail-in voting, but said he would oppose any
additional funding so that "universal mail-in voting" would not be
possible. On August 14, 2020, President
Trump says he's willing to approve USPS funding if concessions are made to some funding asks in coronavirus relief package.
Governance and organization
The Board of Governors of the United States Postal Service sets policy, procedure, and postal rates for services rendered. It has a similar role to a corporate board of directors. Of the eleven members of the Board, nine are appointed by the president and confirmed by the United States Senate (see 39 U.S.C. § 202). The nine appointed members then select the United States postmaster general,
who serves as the board's tenth member, and who oversees the day-to-day
activities of the service as chief executive officer (see 39 U.S.C. §§ 202–203).
The ten-member board then nominates a deputy postmaster general, who
acts as chief operating officer, to the eleventh and last remaining open
seat.
The independent Postal Regulatory Commission
(formerly the Postal Rate Commission) is also controlled by appointees
of the president confirmed by the Senate. It oversees postal rates and
related concerns, having the authority to approve or reject USPS
proposals.
The USPS is often mistaken for a state-owned enterprise or government-owned corporation (e.g., Amtrak)
because it operates much like a business. It is, however, an
"establishment of the executive branch of the Government of the United
States", (39 U.S.C. § 201) as it is controlled by presidential appointees and the postmaster general. As a government agency, it has many special privileges, including sovereign immunity, eminent domain powers, powers to negotiate postal treaties
with foreign nations, and an exclusive legal right to deliver
first-class and third-class mail. Indeed, in 2004, the U.S. Supreme
Court ruled in a unanimous decision “The Postal Service is not subject
to antitrust liability. In both form and function, it is not a separate
antitrust person from the United States but is part of the Government,
and so is not controlled by the antitrust laws.” Sherman Antitrust Act.
Unlike a state-owned enterprise, the USPS lacks a transparent ownership
structure and isn't subject to standard rules and norms that apply to
commercial entities. The USPS also lacks commercial discretion and
control.
The U.S. Supreme Court has also upheld the USPS's statutory monopoly on access to letter boxes against a First Amendment freedom of speech challenge; it thus remains illegal in the U.S. for anyone, other than the employees and agents of the USPS, to deliver mailpieces to letter boxes marked "U.S. Mail".
The Postal Service also has a Mailers' Technical Advisory
Committee and local Postal Customer Councils, which are advisory and
primarily involve business customers.
Privatization proposals
On December 17, 2017, President Donald Trump criticized the postal service's relationship with Amazon. In a post on Twitter,
he stated: "Why is the United States Post Office, which is losing many
billions of dollars a year, while charging Amazon and others so little
to deliver their packages, making Amazon richer and the Post Office
dumber and poorer? Should be charging MUCH MORE!" Amazon maintains that the Postal Service makes a profit from its contract with the company.
On June 21, 2018, Trump proposed a sweeping government
reorganization that would sharpen the focus on workforce training,
consolidate government-assistance programs and shrink federal agencies.
As part of this proposal, he recommended restructuring the postal
service with an eye toward privatization. According to his proposal,
privatization would cut costs and give the financially burdened agency
greater flexibility in adjusting to the digital age.
Universal service obligation and monopoly status
Legal basis and rationale
Article I, section 8, Clause 7 of the United States Constitution grants Congress the power to establish post offices and post roads,
which has been interpreted as a de facto Congressional monopoly over
the delivery of first-class residential mail—which has been defined as
non-urgent residential letters (not packages). Accordingly, no other
system for delivering first-class residential mail—public or private—has
been tolerated, absent Congress's consent.
The mission of the Postal Service is to provide the American
public with trusted universal postal service. While not explicitly
defined, the Postal Service's universal service obligation
(USO) is broadly outlined in statute and includes multiple dimensions:
geographic scope, range of products, access to services and facilities,
delivery frequency, affordable and uniform pricing, service quality, and
security of the mail. While other carriers may claim to voluntarily
provide delivery on a broad basis, the Postal Service is the only
carrier with a legal obligation to provide all the various aspects of universal service.
Proponents of universal service principles claim that since any
obligation must be matched by the financial capability to meet that
obligation, the postal monopoly was put in place as a funding mechanism
for the USO, and it has been in place for over a hundred years. It
consists of two parts: the Private Express Statutes
(PES) and the mailbox access rule. The PES refer to the Postal
Service's monopoly on the delivery of letters, and the mailbox rule
refers to the Postal Service's exclusive access to customer mailboxes.
Proponents of universal service principles further claim that
eliminating or reducing the PES or mailbox rule would affect the ability
of the Postal Service to provide affordable universal service. If, for
example, the PES and the mailbox rule were to be eliminated, and the USO
maintained, then either billions of dollars in tax revenues or some
other source of funding would have to be found.
Some proponents
of universal service principles suggest that private communications
that are protected by the veil of government promote the exchange of
free ideas and communications. This separates private communications
from the ability of a private for-profit or non-profit organization to
corrupt. Security for the individual is in this way protected by the
United States Post Office, maintaining confidentiality and anonymity, as
well as government employees being much less likely to be instructed by
superiors to engage in nefarious spying. It is seen by some
as a dangerous step to extract the universal service principle from the
post office, as the untainted nature of private communications is
preserved as assurance of the protection of individual freedom of
privacy.
However, as the recent notice of a termination of mail service to residents of the Frank Church—River of No Return Wilderness indicates, mail service has been contracted to private firms such as Arnold Aviation for many decades. KTVB-TV reported:
"We cannot go out every week and pick up our mail ... it's impossible", said Heinz Sippel. "Everyone gets their mail. Why can't we?" said Sue Anderson. Getting mail delivered, once a week, by airplane is not a luxury, it's a necessity for those who live in Idaho's vast wilderness—those along the Salmon and Selway rivers. It's a service that's been provided to them for more than half a century—mostly by Ray Arnold of Arnold Aviation. The decision was reversed; U.S. Postmaster General John Potter indicated that acceptable service to back country customers could not be achieved in any other fashion than continuing an air mail contract with Arnold Aviation to deliver the mail.
2008 report on universal postal service and the postal monopoly
The Postal Act of 2006 required the Postal Regulatory Commission
(PRC) to submit a report to the president and Congress on universal
postal service and the postal monopoly in December 2008. The report must
include any recommended changes. The Postal Service report supports the
requirement that the PRC is to consult with and solicit written
comments from the Postal Service. In addition, the Government
Accountability Office is required to evaluate broader business model
issues by 2011.
On October 15, 2008, the Postal Service submitted a report
to the PRC on its position related to the Universal Service Obligation
(USO). It said no changes to the USO and restriction on mailbox access
were necessary at this time, but increased regulatory flexibility was
required to ensure affordable universal service in the future. In 2013,
the Postal Service announced that starting August 2013, Saturday
delivery would be discontinued.
Obligations of the USO include uniform prices, quality of
service, access to services, and six-day delivery to every part of the
country. To assure financial support for these obligations, the postal
monopoly provides the Postal Service the exclusive right to deliver
letters and restricts mailbox access solely for mail. The report argued
that eliminating or reducing either aspect of the monopoly "would have a
devastating impact on the ability ... to provide the affordable
universal service that the country values so highly". Relaxing access to
the mailbox would also pose security concerns, increase delivery costs,
and hurt customer service, according to the Post Office. The report
notes:
It is somewhat misleading to characterize the mailbox rule as a "monopoly," because the enforcement of 18 U.S.C. § 1725 leaves customers with ample alternative means of delivering their messages. Customers can deliver their messages either by paying postage, by placing messages on or under a door or a doormat, by using newspaper or non-postal boxes, by telephoning or emailing, by engaging in person-to-person delivery in public areas, by tacking or taping their notices on a door post, or by placing advertisements in local newspapers. These methods are comparable in efficacy to communication via the mailbox.
Most of these alternatives are not actually free in some communities. For example, in the Chicago metropolitan area and many other major metros one must get a background check from police and pay a daily fee for the right to solicit or post commercial messages on private property.
Regarding the monopoly on delivery of letters, the report notes
that the monopoly is not complete, as there is an exception for letters
where either the amount paid for private carriage of the letter
equals at least six times the current rate for the first ounce of a
single-piece First-Class Mail letter (also known as the "base rate" or
"base tariff") or the letter weighs at least 12.5 ounces.
The Postal Service said that the USO should continue to be
broadly defined and there should be no changes to the postal monopoly.
Any changes would have far-reaching effects on customers and the
trillion dollar mailing industry. "A more rigidly defined USO would ...
ultimately harm the American public and businesses," according to the
report, which cautions that any potential change must be studied
carefully and the effects fully understood.
Competitors
USPS Terminal Annex building in Los Angeles
FedEx and United Parcel Service
(UPS) directly compete with USPS Express Mail and package delivery
services, making nationwide deliveries of urgent letters and packages.
Due to the postal monopoly, they are not allowed to deliver non-urgent
letters and may not directly ship to U.S. Mail boxes at residential and
commercial destinations. However, both companies have transit agreements
with the USPS in which an item can be dropped off with either FedEx or
UPS who will then provide shipment up to the destination post office
serving the intended recipient where it will be transferred for delivery
to the U.S. Mail destination, including Post Office Box destinations. These services also deliver packages which are larger and heavier than USPS will accept. DHL Express was the third major competitor until February 2009, when it ceased domestic delivery operations in the United States.
A variety of other transportation companies in the United States
move cargo around the country, but either have limited geographic scope
for delivery points, or specialize in items too large to be mailed.
Many of the thousands of courier companies focus on same-day delivery, for example, by bicycle messenger.
Although USPS and FedEx are direct competitors, USPS contracts with FedEx for air transport of 2–3 Day Priority Mail and Priority Mail Express (typically delivered overnight).
Alternative transmission methods
The Post Office Department owned and operated the first public telegraph lines
in the United States, starting in 1844 from Washington to Baltimore,
and eventually extending to New York, Boston, Buffalo, and Philadelphia.
In 1847, the telegraph system was privatized, except for a period
during World War I, when it was used to accelerate the delivery of
letters arriving at night.
Between 1942 and 1945, "V-Mail" (for "Victory Mail") service was available for military mail. Letters were converted into microfilm and reprinted near the destination, to save room on transport vehicles for military cargo.
In 1970, Western Union in co-operation with the Postal Service introduced the "Mailgram", a special type of telegram
offered by Western Union intended for bulk mailing to multiple
addressees. The sender would contact WU and submit to them the message
to be sent and a list of addressees to mail the requested Mailgrams to.
The message and address data were then sent electronically over Western
Union's terrestrial network normally used for standard telegrams, with
WU's Westar 1
satellite used instead starting in 1974 with its launch, for Mailgram
transmission to participating Postal Service centers, who would then
print and mail the Mailgrams to the requested addressees.
Similar to WU's Mailgrams was Electronic Computer Originated
Mail, offered by the Postal Service from 1982 to 1985. Also known as E-COM,
it too was used for bulk mailings. Text was transmitted electronically
to one of 25 post offices nationwide. The Postal Service would print
the mail and put it in special envelopes bearing a blue E-COM logo.
Delivery was assured within 2 days.
To improve accuracy and efficiency, the Postal Service introduced the Intelligent Mail program to complement the ZIP code system. This system, which was intended to replace the deprecated POSTNET
system, allows bulk mailers to use pre-printed bar codes to assist in
mail delivery and sorting. Additional features, called Enhanced, or
Full-Service, Intelligent Mail Barcodes allow for mail tracking of bulk
mail through the postal system up to the final delivery Post Office.
Criticism of the universal service requirement and the postal monopoly
Critics
of the universal service requirement and the statutory postal monopoly
include several professional economists advocating for the privatization
of the mail delivery system, or at least a relaxation of the universal
service model that currently exists. Rick Geddes argued in 2000:
- First, basic economics implies that rural customers are unlikely to be without service under competition; they would simply have to pay the true cost of delivery to them, which may or may not be lower than under monopoly.
- Second, basic notions of fairness imply that the cross-subsidy should be eliminated. To the extent that people make choices about where they live, they should assume the costs of that decision.
- Third, there is no reason why the government monopoly is necessary to ensure service to sparsely populated areas. The government could easily award competitive contracts to private firms for that service.
- Fourth, early concerns that rural residents of the United States would somehow become isolated without federally subsidized mail delivery today are simply unfounded. ... Once both sender and receiver have access to a computer, the marginal cost of sending an electronic message is close to zero.
Furthermore, some economists have argued that because public
enterprises may pursue objectives different than profit maximization,
they might have more of an incentive than profit-maximizing firms to
behave anticompetitively through policies such as predatory pricing,
misstating costs, and creating barriers to entry. To resolve those issues, one economist proposes a cost-allocation model that would determine the optimal allocation of USPS's common costs by finding the share of costs that would maximize USPS profits from its competitive products.
Postal regulators could use such a cost model to ensure that the Postal
Service is not abusing its statutory monopoly by subsidizing price cuts
in competitive product markets with revenue obtained from the
monopolized market.
Law enforcement agencies
Under the Mail Cover Program
USPS photographs the front and back of every piece of U.S. mail as part
of the sorting process, enabling law enforcement to obtain address
information and images of the outsides of mail as part of an
investigation without the need for a warrant.
The Food and Drug Administration inspects packages for illegal drug shipments
Postal Inspection Service
The United States Postal Inspection Service (USPIS) is one of the oldest law enforcement agencies in the U.S. Founded by Benjamin Franklin
on August 7, 1775, its mission is to protect the Postal Service, its
employees, and its customers from crime and protect the nation's mail
system from criminal misuse.
Postal Inspectors enforce over 200 federal laws providing for the protection of mail in investigations of crimes that may adversely affect or fraudulently use the U.S. Mail, the postal system or postal employees.
The USPIS has the power to enforce the USPS monopoly by
conducting search and seizure raids on entities they suspect of sending
non-urgent mail through overnight delivery competitors. According to the
American Enterprise Institute, a private conservative think tank, the USPIS raided Equifax offices in 1993 to ascertain if the mail they were sending through Federal Express was truly "extremely urgent". It was found that the mail was not, and Equifax was fined $30,000.
The PIS oversees the activities of the Postal Police Force who patrol and secure major postal facilities in the United States.
Office of Inspector General
The United States Postal Service Office of Inspector General
(OIG) was authorized by law in 1996. Prior to the 1996 legislation, the
Postal Inspection Service performed the duties of the OIG. The
inspector general, who is independent of postal management, is appointed
by and reports directly to the nine presidentially appointed, Senate–confirmed members of the Board of Governors of the United States Postal Service.
The primary purpose of the OIG is to prevent, detect and report
fraud, waste and program abuse, and promote efficiency in the operations
of the Postal Service. The OIG has "oversight" responsibility for all
activities of the Postal Inspection Service.
How delivery services work
Elements of addressing and preparing domestic mail
All mailable articles (e.g., letters, flats, machinable parcels,
irregular parcels, etc.) shipped within the United States must comply
with an array of standards published in the USPS Domestic Mail Manual
(DMM).
Before addressing the mailpiece, one must first comply with the various
mailability standards relating to attributes of the actual mailpiece
such as: minimum/maximum dimensions
and weight, acceptable mailing containers, proper mailpiece
sealing/closure, utilization of various markings, and restrictions
relating to various hazardous (e.g., explosives, flammables, etc.) and
restricted (e.g., cigarettes, smokeless tobacco, etc.) materials, as
well as others articulated in § 601 of the DMM.
The USPS specifies the following key elements when preparing the face of a mailpiece:
- Proper Placement: The Delivery Address should be left-justified and located roughly in the center of mailpiece's largest side. More precisely, on a letter-size piece, the recommended address placement is within the optical character reader (OCR) read area, which is a space on the address side of the mailpiece defined by these boundaries: Left – 1/2 inch (13 mm) from the left edge of the piece; Right – 1/2 inch (13 mm) from the right edge of the piece; Top – 2-3/4 inches (70 mm) from the bottom edge of the piece; Bottom – 5/8 inch (16 mm) from the bottom edge of the piece. Preferred placement of a return address is in the upper left portion of the mailpiece—on the side of the piece bearing postage. Finally, postage (e.g., stamps, meter imprints, information-based indicia [IBI], etc.) is to be affixed in the upper right corner of the address side of the mail cover. Any stamp/indicia partly concealed or otherwise obscured by an overlapping stamp/indicia may not be counted as valid postage.
- Delivery Address (party receiving mail): The mail piece must have the address of the intended recipient, visible and legible, only on the side of the mail piece bearing postage. Generally, the name of the addressee should be included above the address itself. A ZIP+4 code will facilitate delivery.
- Return Address (party sending mail): A return address tells the USPS where the sender wants the mail returned if it is undeliverable. Usage of a return address is required for some postal services (including Priority Mail, Express Mail, Periodicals in envelopes or wrappers, Insured Mail, Registered Mail, and parcel services).
- Postage Payment: All mailpieces must include appropriate valid postage. Postage payment may be in the form of stamps, stamped stationery, precanceled stamps, postage meter imprints & PC Postage products ("Postage Evidencing Systems"), or permit imprint (indicia). Members of the U.S. Congress, among others, have franking privileges, which require only a signature.
Domestic First-Class Mail costs 55¢ for envelopes (35¢ for post cards) and upwards, depending on the weight and dimensions of the letter and the class.
Mail going to naval vessels is known as the Fleet Post Office (FPO) and to Army or Air Force installations use the city abbreviation APO (Army Post Office or Air Force Post Office).
Undeliverable mail that cannot be readily returned, including mail without a return address, is treated as dead mail at a Mail Recovery Center in Atlanta, Georgia or Saint Paul, Minnesota.
Sticker promoting ZIP code use
- The format of the address is as follows
- Line 1: Name of recipient
- Line 2: Street address or P.O. Box
- Line 3: City, State (ISO 3166-2:US code or APO/FPO code) and ZIP+4 code
- Example
- Clifford Clavin
- 84 Beacon Street
- Boston MA 02108-3496
The USPS maintains a list of proper abbreviations.
The format of a return address is similar. Though some style manuals
recommend using a comma between the city and state name when
typesetting addresses in other contexts, for optimal automatic character
recognition, the Post Office does not recommend this when addressing
mail. The official recommendation is to use all upper case block letters
with proper formats and abbreviations, and leave out all punctuation
except for the hyphen
in the ZIP+4 code. If the address is unusually formatted or illegible
enough, it will require hand-processing, delaying that particular item.
The USPS publishes the entirety of their postal addressing standards.
Postal address verification
tools and services are offered by the USPS and third party companies to
help ensure mail is deliverable by fixing formatting, appending
information such as ZIP code and validating the address is a valid delivery point.
Customers can look up ZIP codes and verify addresses using USPS Web
Tools available on the official USPS website and Facebook page, as well
as on third-party sites.
Delivery Point Validation
Delivery
Point Validation (DPV) provides the highest level of address accuracy
checking. In a DPV process, the address is checked against the AMS data
file to ensure that it exists as an active delivery point.
The USPS does not offer DPV validation on their website; however, there
are companies that offer services to perform DPV verification.
Paying postage
The actual postage can be paid via:
- Stamps purchased online at usps.com, at a post office, from a stamp vending machine or "Automated Postal Center" which can also handle packages, or from a third party (such as a grocery store)
- Pre-cancelled stamps for bulk mailings
- Postal meter
- Prepaid envelope
- Shipping label purchased online and printed by the customer on standard paper (e.g. with Click-N-Ship, or via a third-party such as PayPal or Amazon shipping)
All unused U.S. postage stamps
issued since 1861 are still valid as postage at their indicated value.
Stamps with no value shown or denominated by a letter are also still
valid, although the value depends upon the particular stamp. For some
stamps issued without a printed value, the current value is the original
value. But some stamps beginning in 1988 or earlier, including Forever Stamps
(issued from April 2007) and all first-class, first-ounce stamps issued
from January 21, 2011, the value is the current value of a
first-class-mail first-ounce stamp. The USPS calls these Forever Stamps
but the generic name is non-denominated postage.
Forever stamps are sold at the First-Class Mail postage rate at
the time of purchase, but will always be valid for First-Class Mail, up
to 1 ounce (28 g), no matter how rates rise in the future.
Britain has had a similar stamp since 1989. The cost of mailing a 1 oz
(28 g) First-Class letter increased to 55 cents on January 26, 2020.
Postage meters
A postage meter is a mechanical device used to create and apply
physical evidence of postage (or franking) to mailed matter. Postage
meters are regulated by a country's postal authority; for example, in
the United States, the United States Postal Service specifies the rules
for the creation, support, and use of postage meters. A postage meter
imprints an amount of postage, functioning as a postage stamp, a
cancellation and a dated postmark all in one. The meter stamp serves as
proof of payment and eliminates the need for adhesive stamps.
PC Postage
In
addition to using standard stamps, postage can now be printed in the
form of an electronic stamp, or e-stamp, from a personal computer using a
system called Information Based Indicia.
This online PC Postage method relies upon application software on the
customer's computer contacting a postal security device at the office of
the postal service.
PC Postage providers include:
- Stamps.com (founded 1996, headquartered in El Segundo, CA)
- EasyPost (founded 2012, headquartered in San Francisco, CA)
Other electronic postage payment methods
Electronic Verification System (eVS)
is the Postal Service's integrated mail management technology that
centralizes payment processing and electronic postage reports. Part of
an evolving suite of USPS electronic payment services called PostalOne!,
eVS allows mailers shipping large volumes of parcels through the Postal
Service a way to circumvent use of hard-copy manifests, postage
statements and drop-shipment verification forms. Instead, mailers can
pay postage automatically through a centralized account and track
payments online.
Beginning in August 2007, the Postal Service began requiring
mailers shipping Parcel Select packages using a permit imprint to use
eVS for manifesting their packages.
Stamp copyright and reproduction
All U.S. postage stamps issued under the former United States Post Office Department
and other postage items that were released before 1978 are not subject
to copyright, but stamp designs since 1978 are copyrighted. The United States Copyright Office in section 313.6(C)(1) of the Third Edition of the Compendium of U.S. Copyright Office Practices
holds that "Works prepared by officers or employees of the U.S. Postal
Service ... are not considered works of the U.S. Government"
and are therefore eligible for registration. Thus, the USPS holds
copyright to such materials released since 1978 under Title 17 of the United States Code.
Written permission is required for use of copyrighted postage stamp
images, although under USPS rules, permission is "generally" not
required for "educational use", "news reporting" or "philatelic
advertising use," but users must cite USPS as the source of the image
and include language such as "© United States Postal Service. All rights
reserved."
Service level choices
General domestic services
Former Tyvek envelope design for Express Mail before July 28, 2013
As of April 2011, domestic postage levels for low-volume mailers include:
- Priority Mail Express (Formerly Express Mail): Overnight delivery guaranteed to most locations
- Sunday, holiday and 10:30 am delivery available for additional charge.
- $100 insurance included.
- Tracking included.
- Flat Rate envelopes are available. Otherwise, pricing varies by weight and distance.
- Priority Mail: Day specific delivery service ranging from 1–3 days depending on origin of shipment (not guaranteed)
- As of January 27, 2013, tracking via Delivery Confirmation is now included on all Priority Mail shipments.
- Flat Rate envelopes and boxes (various sizes) are available free from the Postal Store. Otherwise, pricing varies by weight, size and distance.
- $50 insurance for retail/$100 insurance for commercial starting on July 28, 2013.
- Tracking Included
- First-Class Mail
- 2- to 3-day delivery.
- In most cases for letters and small packages.
- Rate varies by size and weight, but not distance.
- Postcards (5" × 3.5" × 0.007 to 6" × 4.25" × 0.016" [127 × 89 × 0.18 to 152 × 108 × 0.4 mm]): 35¢
- Letters (up to 11.5" × 6.125" × 0.25", 3.5 oz [292 × 156 × 6.4 mm, 100 g]): 55¢ + 15¢ for each additional ounce stamped, 50¢ + 15¢ for each additional ounce metered
- Large Envelope or Flat (up to 15" × 12" × 0.75", 13 oz [381 × 305 × 19 mm, 370 g]): $1.00 + 15¢ each additional ounce (28 g). Must be rectangular, uniformly thick, and not too rigid.
- 2- to 3-day delivery.
- First class package service
- Rate varies by weight and distance.
- Package/Parcel (Up to 108 inches (270 cm) length plus girth, 13 ounces (370 g): $3.80-$4.20 up to 4 ounces, $4.60-$5.00 up to 8 ounces, $5.90-$6.50 up to 13 ounces
- Rate varies by weight and distance.
- USPS Retail Ground (formerly Parcel Post)
- Slowest but cheapest service for packages too large or heavy for First Class—uses surface transport.
- 2- to 9-day service to contiguous U.S., 4–14 days internal to AK/HI/territories, 3–6 weeks between mainland and outlying areas (travels by ship).
- Variable pricing by weight, size and distance.
- Free forwarding if recipient has filed change-of-address form, or return if the item is undeliverable.
- Media Mail—formerly "Book Rate"
- Books and recorded media only.
- No advertising.
- Pricing by weight only.
- Transit time similar to Parcel Post.
- Cheaper than Parcel Post but only due to increased restrictions on package contents.
- Library Mail
- Similar to Media Mail, but cheaper and restricted to academic institutions, public libraries, museums, etc.
The Post Office will not deliver packages heavier than 70 pounds
(32 kg) or if the length (the package's longest dimension) plus the
girth (the measurement around the package at its largest point in the
two shorter dimensions) is greater than 108 inches (270 cm) combined
(130 inches [330 cm] for Parcel Post)
Bulk mail
USPS Dodge Caravan used for residential delivery in Omaha, Nebraska
USPS-operated minivan serving in the LLV's role
Discounts are available for large volumes of mail. Depending on the
postage level, certain conditions might be required or optional for an
additional discount:
- Minimum number of pieces
- Weight limits
- Ability for the USPS to process by machine
- Addresses formatting standardized
- USPS-readable barcode
- Sorted by three-digit ZIP code prefix, five-digit ZIP code, ZIP+4, or 11-digit delivery point
- Delivered in trays, bundles, or pallets partitioned by destination
- Delivered directly to a regional Bulk Mail Center, destination SCF, or destination Post Office
- Certification of mailing list accuracy and freshness (e.g. correct ZIP codes, purging of stale addresses, processing of change-of-address notifications)
In addition to bulk discounts on Express, Priority, and First-Class
Mail, the following postage levels are available for bulk mailers:
- Periodicals
- Standard Mail (A)
- Automation
- Enhanced Carrier Route
- Regular
- Standard Mail (B)
- Parcel Post
- Bound Printed Matter – Cheaper than Media Mail, for advertising catalogs, phone books, etc. up to 15 lb
- Special Standard Mail
- Library Mail
- Nonprofit
Extra services
A Long Life Vehicle seen in Guam
Depending on the type of mail, additional services are available for an additional fee:
- Certificate of Mailing provides proof of the date a package was mailed.
- Certified Mail provides proof of mailing, and a delivery record. Used for serving legal documents and for sending U.S. Government classified information, up to the "confidential" level.
- Collect on Delivery (C.O.D.) allows merchants to offer customers an option to pay upon delivery, up to $1000. Includes insurance.
- USPS Tracking provides proof of delivery to sorting facilities, local post office and destination, but no signature is required.
- Insurance is shipping insurance against loss or damage for the value of the goods mailed. Amount of coverage can be specified, up to $5,000.
- Registered Mail is used for highly valuable or irreplaceable items, and classified information up to the "secret" level.[148] Registered mail is transported separately from other mail, in locked containers. Tracking is included and insurance up to $25,000 is available.[149]
- Restricted Delivery requires delivery to a specific person or their authorized agent, not just to a mailbox.
- Return Receipt actively sends signature confirmation back to the sender by postcard or emailed PDF (as opposed to merely putting this information into the online tracking system).
- Signature Confirmation requires a delivery signature, which is kept on file. The online tracking system displays the first initial and last name of the signatory.
- Special Handling is for unusual items, like live animals.
International services
Packages awaiting inspection at the International Mail Facility in JFK airport
In May 2007, the USPS restructured international service names to
correspond with domestic shipping options. Formerly, USPS International
services
were categorized as Airmail (Letter Post), Economy (Surface) Parcel
Post, Airmail Parcel Post, Global Priority, Global Express, and Global
Express Guaranteed Mail. The former Airmail (Letter Post) is now
First-Class Mail International, and includes small packages weighing up to four pounds (1.8 kg).
Economy Parcel Post was discontinued for international service, while
Airmail Parcel Post was replaced by Priority Mail International.
Priority Mail International Flat-Rate packaging in various sizes was
introduced, with the same conditions of service previously used for
Global Priority. Global Express is now Express Mail International, while
Global Express Guaranteed is unchanged. The international mailing
classes with a tracking ability are Express, Express Guaranteed, and
Priority (except that tracking is not available for Priority Mail
International Flat Rate Envelopes or Priority Mail International Small
Flat Rate Boxes).
One of the major changes in the new naming and services
definitions is that USPS-supplied mailing boxes for Priority and Express
mail are now allowed for international use. These services are offered
to ship letters and packages to almost every country and territory on
the globe. The USPS provides much of this service by contracting with a
private parcel service, FedEx.
An m-bag
The USPS provides an M-bag service for international shipment of printed matter; previously surface M-bags existed, but with the 2007 elimination of surface mail, only airmail M-bags remain.
The term "M-bag" is not expanded in USPS publications; M-bags are
simply defined as "direct sacks of printed matter ... sent to a single
foreign addressee at a single address";
however, the term is sometimes referred to informally as "media bag",
as the bag can also contain "discs, tapes, and cassettes", in addition
to books, for which the usual umbrella term is "media"; some also refer
to them as "mail bags".
Military mail
is billed at domestic rates when being sent from the United States to a
military outpost, and is free when sent by deployed military personnel.
The overseas logistics are handled by the Military Postal Service Agency in the Department of Defense.
Outside of forward areas and active operations, military mail
First-Class takes 7–10 days, Priority 10–15 days, and Parcel Post about
24 days.
Three independent countries with a Compact of Free Association with the U.S. (Palau, the Marshall Islands, and the Federated States of Micronesia) have a special relationship with the United States Postal Service:
- Each associated state maintains its own government-run mail service for delivery to and pickup from retail customers.
- The associated states are integrated into the USPS addressing and ZIP code system.
- The USPS is responsible for transporting mail between the United States and the associated states, and between the individual states of the Federated States of Micronesia.
- The associated states synchronize postal services and rates with the USPS.
- The USPS treats mail to and from the associated states as domestic mail. Incoming mail does require customs declarations because, like some U.S. territories, the associated states are outside the main customs territory of the United States.
The discontinuation of international surface mail
In 2007, the US Postal Service discontinued its outbound international surface mail ("sea mail") service,
mainly because of increased costs. Returned undeliverable surface
parcels had become an expensive problem for the USPS, since it was often
required to take such parcels back.
Domestic surface mail (now "Retail Ground" or "Commercial Parcel Select") remains available.
Alternatives to international surface mail include:
- International Surface Air Lift (ISAL). The service includes neither tracking nor insurance; but it may be possible to purchase shipping insurance from a third-party company.
- USPS Commercial ePacket. The service is trackable.
- Ordinary first-class international airmail.
Senders can access the International Surface Air Lift and ePacket
services through postal wholesalers. Some examples of such wholesalers
include:
- Asendia USA (accessible through the Shippo website to users who have an Asendia account),
- Globegistics (now owned by Asendia), and
- APC Postal Logistics.
If a sender sends an ISAL mailing directly through the USPS (without a
wholesaler as an intermediary), the minimum weight is 50 pounds per
mailing.
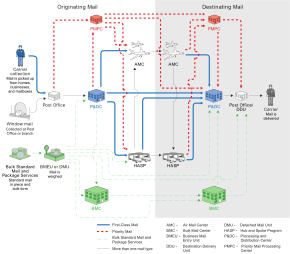
Sorting and delivery process
Mail flow through national infrastructure
Processing of standard sized envelopes and cards is highly automated,
including reading of handwritten addresses. Mail from individual
customers and public postboxes is collected by letter carriers into
plastic tubs, which are taken to one of approximately 251 Processing and Distribution Centers (P&DC)
across the United States. Each P&DC sorts mail for a given region
(typically with a radius of around 200 miles (320 km)) and connects with
the national network for interregional mail.
The USPS has consolidated mail sorting for large regions into the
P&DCs on the basis that most mail is addressed to faraway
destinations,
but for cities at the edge of a P&DC's region, this means all
locally addressed mail must now travel long distances (that is, to and
from the P&DC for sorting) to reach nearby addresses.
At the P&DC, mail is emptied into hampers which are then
automatically dumped into a Dual Pass Rough Cull System (DPRCS). As mail
travels through the DPRCS, large items, such as packages and mail
bundles, are removed from the stream. As the remaining mail enters the
first machine for processing standard mail, the Advanced Facer-Canceler System
(AFCS), pieces that passed through the DPRCS but do not conform to
physical dimensions for processing in the AFCS (e.g., large envelopes or
overstuffed standard envelopes) are automatically diverted from the
stream. Mail removed from the DPRCS and AFCS is manually processed or
sent to parcel sorting machines.
In contrast to the previous system, which merely canceled and
postmarked the upper right corner of the envelope, thereby missing any
stamps which were inappropriately placed, the Advanced Facer-Canceler
System locates indicia (stamp or metered postage mark), regardless of the orientation of the mail as it enters the machine, and cancels it by applying a postmark.
Detection of indicia enables the AFCS to determine the orientation of
each mailpiece and sort it accordingly, rotating pieces as necessary so
all mail is sorted right-side up and faced in the same direction in each
output bin.
Mail is output by the machine into three categories: mail already affixed with a bar code
and addressed (such as business reply envelopes and cards); mail with
machine printed (typed) addresses; and mail with handwritten addresses.
Additionally, machines with a recent Optical Character Recognition
(OCR) upgrade have the capability to read the address information,
including handwritten, and sort the mail based on local or outgoing ZIP
codes.
Mail with typed addresses goes to a Multiline Optical Character Reader
(MLOCR) which reads the ZIP Code and address information and prints the
appropriate bar code onto the envelope. Mail (actually the scanned
image of the mail) with handwritten addresses (and machine-printed ones
that are not easily recognized) goes to the Remote Bar Coding System.
It also corrects spelling errors and, where there is an error,
omission, or conflict in the written address, identifies the most likely
correct address.
When it has decided on a correct address, it prints the
appropriate bar code onto the envelopes, similarly to the MLOCR system.
RBCS also has facilities in place, called Remote Encoding Centers,
that have humans look at images of mail pieces and enter the address
data. The address data is associated with the image via an ID Tag, a fluorescent barcode printed by mail processing equipment on the back of mail pieces.
Processed mail is imaged by the Mail Isolation Control and Tracking
(MICT) system to allow easier tracking of hazardous substances. Images
are taken at more than 200 mail processing centers, and are destroyed
after being retained for 30 days.
If a customer has filed a change of address card and his or her
mail is detected in the mailstream with the old address, the mailpiece
is sent to a machine that automatically connects to a Computerized
Forwarding System database to determine the new address. If this address
is found, the machine will paste a label over the former address with
the current address. The mail is returned to the mailstream to forward
to the new location.
Mail with addresses that cannot be resolved by the automated
system are separated for human intervention. If a local postal worker
can read the address, he or she manually sorts it out according to the
ZIP code on the article. If the address cannot be read, mail is either
returned to the sender (First-Class Mail with a valid return address) or
is sent to the Mail Recovery Center in Atlanta, Georgia (formerly known
as the dead letter office).
At this office, the mail is opened to try to find an address to forward
to. If an address is found, the contents are resealed and delivered.
Otherwise, the items are held for 90 days in case of inquiry by the
customer; if they are not claimed, they are either destroyed or
auctioned off at the monthly Postal Service Unclaimed Parcel auction to
raise money for the service.
Once the mail is bar coded, it is automatically sorted by a Delivery Bar Code Sorter
(DBCS) that reads the bar code, identifies the destination of the
mailpiece, and sends it to an appropriate tray that corresponds to the
next segment of its journey.
Regional mail is either trucked to the appropriate local post
office, or kept in the building for carrier routes served directly from
the P&DC. Out-of-region mail is trucked to the airport and then
flown, usually as baggage on commercial airlines, to the airport nearest
the destination station. At the destination P&DC, mail is once
again read by a DBCS which sorts items to local post offices; this
includes grouping mailpieces by individual letter-carrier route.
At the carrier route level, 95% of letters arrive pre-sorted;
the remaining mail must be sorted by hand. The Post Office is working
to increase the percentage of automatically sorted mail, including a
pilot program to sort "flats".
FedEx provides air transport service to USPS for Priority and
Express Mail. Priority Mail and Express Mail are transported from
Priority Mail processing centers to the closest FedEx-served airport,
where they are handed off to FedEx. FedEx then flies them to the
destination airport and hands them back to USPS for transport to the
local post office and delivery.
Types of postal facilities
Historic main post office in Tomah, Wisconsin
A typical post office station in the Spring Branch area of Houston, Texas
Floating post office, Halibut Cove, Alaska
Although its customer service centers are called post offices in
regular speech, the USPS recognizes several types of postal facilities,
including the following:
- A main post office (formerly known as a general post office) is the primary postal facility in a community.
- A station or post office station is a postal facility that is not the main post office, but that is within the corporate limits of the community.
- A branch or post office branch is a postal facility that is not the main post office and that is outside the corporate limits of the community.
- A classified unit is a station or branch operated by USPS employees in a facility owned or leased by the USPS.
- A contract postal unit (or CPU) is a station or branch operated by a contractor, typically in a store or other place of business.
- A community post office (or CPO) is a contract postal unit providing services in a small community in which other types of post office facilities have been discontinued.
- A finance unit is a station or branch that provides window services and accepts mail, but does not provide delivery.
- A village post office (VPO) is an entity such as a local business or government center that provides postal services through a contract with the USPS. First introduced in 2011 as an integral part of the USPS plan to close low volume post offices, village post offices will fill the role of the post office within a ZIP code.
- A processing and distribution center (P&DC, or processing and distribution facility, formerly known as a General Mail Facility) is a central mail facility that processes and dispatches incoming and outgoing mail to and from a designated service area (251 nationwide).
- A sectional center facility (SCF) is a P&DC for a designated geographical area defined by one or more three-digit ZIP code prefixes.
- An international service center (ISC) is an international mail processing facility. There are only five such USPS facilities in the continental United States, located in Chicago, New York, Miami, Los Angeles and San Francisco.
- A network distribution center, formerly known as a bulk mail center (BMC), is a central mail facility that processes bulk rate parcels as the hub in a hub and spoke network.
- An auxiliary sorting facility (ASF) is a central mail facility that processes bulk rate parcels as spokes in a hub and spoke network.
- A remote encoding center (REC) is a facility at which clerks receive images of problem mail pieces (those with hard-to-read addresses, etc.) via secure Internet-type feeds and manually type the addresses they can decipher, using a special encoding protocol. The mail pieces are then sprayed with the correct addresses or are sorted for further handling according to the instructions given via encoding. The total number of RECs is down from 55 in 1998 to just 1 center in December 2016. The last REC is in Salt Lake City, Utah.
While common usage refers to all types of postal facilities as
"substations", the USPS Glossary of Postal Terms does not define or even
list that word.
Post Offices often share facilities with other governmental
organizations located within a city's central business district. In
those locations, often Courthouses and Federal Buildings, the building
is owned by the General Services Administration while the U.S. Postal Services operates as a tenant. The USPS retail system has approximately 36,000 post offices, stations, and branches.
Automated Postal Centers
A 24-hour Automated Postal Center kiosk inside the Webster, Texas main post office
In the year 2004, the USPS began deploying Automated Postal Centers (APCs). APCs are unattended kiosks that are capable of weighing, franking,
and storing packages for later pickup as well as selling domestic and
international postage stamps. Since its introduction, APCs do not take
cash payments – they only accept credit or debit cards. Similarly,
traditional vending machines are available at many post offices to purchase stamps, though these are being phased out in many areas.
Due to increasing use of Internet services, as of June 2009, no retail
post office windows are open 24 hours; overnight services are limited to
those provided by an Automated Postal Center.
Evolutionary Network Development (END) program
In
February 2006, the USPS announced that they plan to replace the nine
existing facility-types with five processing facility-types:
- Regional Distribution Centers (RDCs), which will process all classes of parcels and bundles and serve as Surface Transfer Centers;
- Local Processing Centers (LPCs), which will process single-piece letters and flats and cancel mail;
- Destination Processing Centers (DPC), sort the mail for individual letter-carrier route;
- Airport Transfer Centers (ATCs), which will serve as transfer points only; and
- Remote Encoding Centers (RECs).
Over a period of years, these facilities are expected to replace
Processing & Distribution Centers, Customer Service Facilities, Bulk
Mail Centers, Logistic and Distribution Centers, annexes, the Hub and
Spoke Program, Air Mail Centers, and International Service Centers.
The changes are a result of the declining volumes of single-piece
First-Class Mail, population shifts, the increase in drop shipments by
advertising mailers at destinating postal facilities, advancements in
equipment and technology, redundancies in the existing network, and the
need for operational flexibility.
The program was ended in early 2007 after an analysis revealed
that the significant amount of capital investment required to implement
the END network concept would not generate the benefits originally
anticipated.
Airline and rail division
A former United States Postal Service Boeing 727-200 aircraft at Miami International Airport in 1999
The United States Postal Service does not directly own or operate any
aircraft or trains, although both were formerly operated. The mail and
packages are flown on airlines with which the Postal Service has a
contractual agreement. The contracts change periodically. Contract
airlines have included: UPS, Emery Worldwide, Ryan International Airlines, FedEx Express, American Airlines, United Airlines, and Express One International. Amtrak carried some mail between cities, such as Chicago and Minneapolis–Saint Paul, but this terminated in October 2004.
The last air delivery route in the continental U.S., to residents in the Frank Church–River of No Return Wilderness, was scheduled to be ended in June 2009. The weekly bush plane route, contracted out to an air taxi
company, had in its final year an annual cost of $46,000, or $2400/year
per residence, over ten times the average cost of delivering mail to a
residence in the United States. This decision has been reversed by the U.S. postmaster general.
Parcel forwarding and private interchange
Private
US parcel forwarding or US mail forwarding companies focusing on
personal shopper, relocation, Ex-pat and mail box services often
interface with the United States Postal Service for transporting of mail
and packages for their customers.
Delivery timing
USPS contractor-driven semi-trailer truck seen near Mendota, California
1998 United States Postal Service Ford Windstar, showing the larger driver's side door
Delivery days
From
1810, mail was delivered seven days a week. In 1828, local religious
leaders noticed a decline in Sunday-morning church attendance because of
local post offices' doubling as gathering places. These leaders
appealed to the government to intervene and close post offices on
Sundays. The government, however, declined, and mail was delivered 7
days a week until 1912.
Today, U.S. Mail (with the exception of Express Mail) is not delivered on Sunday.
Saturday delivery was temporarily suspended in April 1957, because of lack of funds, but quickly restored.
Budget problems prompted consideration of dropping Saturday
delivery starting around 2009. This culminated in a 2013 announcement
that regular mail services would be cut to five days a week, which was
reversed by Congress before it could take effect. (See the section Revenue decline and planned cuts.)
Direct delivery vs. customer pickup
Originally,
mail was not delivered to homes and businesses, but to post offices. In
1863, "city delivery" began in urban areas with enough customers to
make this economical. This required streets to be named, houses to be
numbered, with sidewalks and lighting provided, and these street
addresses to be added to envelopes. The number of routes served expanded over time. In 1891, the first experiments with Rural Free Delivery began in less densely populated areas. There is currently an effort to reduce direct delivery in favor of mailbox clusters.
To compensate for high mail volume and slow long-distance
transportation which saw mail arrive at post offices throughout the day,
deliveries were made multiple times a day. This ranged from twice for
residential areas to up to seven times for the central business district
of Brooklyn, New York.
In the late 19th century, mail boxes were encouraged, saving carriers
the time it took to deliver directly to the addressee in person; in the
1910s and 1920s, they were phased in as a requirement for service.
In the 1940s, multiple daily deliveries began to be reduced, especially
on Saturdays. By 1990, the last twice-daily deliveries in New York City
were eliminated.
Today, mail is delivered once a day on-site to most private homes
and businesses. The USPS still distinguishes between city delivery
(where carriers generally walk and deliver to mailboxes hung on exterior
walls or porches, or to commercial reception areas) and rural delivery
(where carriers generally drive).
With "curbside delivery", mailboxes are at the ends of driveways, on
the nearest convenient road. "Central point delivery" is used in some
locations, where several nearby residences share a "cluster" of
individual mailboxes in a single housing.
Some customers choose to use post office boxes
for an additional fee, for privacy or convenience. This provides a
locked box at the post office to which mail is addressed and delivered
(usually earlier in the day than home delivery). Customers in less
densely populated areas where there is no city delivery and who do not
qualify for rural delivery may receive mail only through post office
boxes. High-volume business customers can also arrange for special
pick-up. Another option is the old-style general delivery,
for people who have neither post office boxes nor street addresses.
Mail is held at the post office until they present identification and
pick it up.
Some customers receive free post office boxes if the USPS
declines to provide door-to-door delivery to their location or a nearby
box. People with medical problems can request door-to-door delivery. Homeless people are also eligible for post office boxes at the discretion of the local postmaster, or can use general delivery.
Special delivery
From 1885 to 1997, a service called special delivery was available, which caused a separate delivery to the final location earlier in the day than the usual daily rounds.
Same-day trials
In
December 2012, the USPS began a limited one-year trial of same-day
deliveries directly from retailers or distribution hubs to residential
addresses in the same local area, a service it dubbed "Metro Post". The trial was initially limited to San Francisco and the only retailer to participate in the first few weeks was 1-800-FLOWERS.
In March 2013, the USPS faced new same-day competition for e-commerce deliveries from Google Shopping Express.
In November 2013, the Postal Service began regular package delivery on Sundays for Amazon customers in New York and Los Angeles, which it expanded to 15 cities in May 2014. Amazon Sunday delivery has now been expanded to most major markets as of September 2015.
Other competition in this area includes online grocers such as AmazonFresh, Webvan, and delivery services operated by grocery stores like Peapod and Safeway.
Forwarding and holds
Residential
customers can fill out a form to forward mail to a new address, and can
also send pre-printed forms to any of their frequent correspondents.
They can also put their mail on "hold", for example, while on vacation.
The Post Office will store mail during the hold, instead of letting it
overflow in the mailbox. These services are not available to large
buildings and customers of a commercial mail receiving agency, where mail is subsorted by non-Post Office employees into individual mailboxes.
Financial services
Postal money orders provide a safe alternative to sending cash through the mail, and are available in any amount up to $1,000. Like a bank cheque,
money orders are cashable only by the recipient. Unlike a personal bank
check, they are prepaid and therefore cannot be returned because of
insufficient funds. Money orders are a declining business for the USPS, as companies like PayPal, Venmo and others are offering electronic replacements.
From 1911 to 1967, the Postal Service also operated the United States Postal Savings System, not unlike a savings and loan association with the amount of the deposit limited.
A January 2014 report by the inspector general of the USPS
suggested that the agency could earn $8.9 billion per year in revenue by
providing financial services, especially in areas where there are no
local banks but there is a local post office, and to customers who
currently do not have bank accounts.
Employment
A Rural Letter Carrier from Fort Myers, Florida
The Postal Service is the nation's second-largest civilian employer. As of 2019, it employed 633,108 personnel, divided into offices, processing centers, and actual post offices. The United States Postal Service would rank 44th on the 2019 Fortune 500 list, if considered a private company and ranks 136 on Global Fortune 500 list.
Labor unions representing USPS employees include: The American Postal Workers Union
(APWU), which represents postal clerks and maintenance, motor vehicle,
mail equipment shops, material distribution centers, and operating
services and facilities services employees, postal nurses, and IT and
accounting; the National Association of Letter Carriers (NALC), which represents city letter carriers; the National Rural Letter Carriers' Association (NRLCA), which represents rural letter carriers; and the National Postal Mail Handlers Union (NPMHU).
USPS employees are divided into major crafts according to the work they engage in:
- letter carriers, also referred to as mailmen or mail carriers, prepare and deliver mail and parcels. They are divided into two categories: City Letter Carriers, who are represented by the NALC, and Rural Letter Carriers, who are represented by the NRLCA. City Carriers are paid hourly with automatic overtime paid after 8 hours or 40 hours a week of duty. City Carriers are required to work in any kind of weather, daylight or dark and carry three bundles of mail (letters in one hand with magazines and other larger mail pieces) on the forearm carrying the mail. Advertisement mail, Every door direct (EDD) and smaller parcels all go in the carriers satchel). Larger parcels, up to a total of 70 lbs. may be delivered at various times of the day or with the mail. Mail routes are outfitted with a number of scanpoints (mailbox barcodes) on random streets every 30 to 40 minutes apart to keep track of the carriers whereabouts in real-time.
- Rural carriers are under a form of salary called "evaluated hours", usually with overtime built into their pay. The evaluated hours are created by having all mail counted for a period of two or four weeks, and a formula used to create the set dollar amount they will be paid for each day worked until the next time the route is counted.
- Mail handlers and processors, prepare, separate, load and unload mail and parcels, by delivery ZIP code and station, for the clerks. They work almost exclusively at the plants or larger mail facilities now after having their duties excessed and reassigned to clerks in Post Offices and Station branches.
- Clerks, have a dual function by design of where their assignment is. Window clerks directly handle customer service needs at the counter, sort box mail and also sort first-class letters, standard and bulk-rate mail for the carriers on the work floor. Clerks may also work alongside mail handlers in large sorting facilities, outside of the public view, sorting mail. Data Conversion Operators, who encode address information at Remote Encoding Centers, are also members of the clerk craft. Mail handlers and Clerks are represented by the NPMHU and the APWU, respectively.
Other non-managerial positions in the USPS include:
- Maintenance and custodians, who see to the overall operation and cleaning of mail sorting machines, work areas, public parking and general facility operations.
- City Carrier Assistants. (CCAs) With the Das Arbitration award the designation of PTF City Carrier has been abolished. TE City Carriers will have the opportunity to become CCAs. A CCA is a non-career employee who is hired for a 360-day term, similar to what TEs had. CCAs earn annual leave. CCAs, unlike TEs do have a direct path to becoming career employees. When excess City Carrier positions exist the CCA in that work installation with the highest "relative standing" will be promoted to a career employee and be assigned to the vacant position.
- Career, Part Time Flexible and Transitional employees (Career, PTF & TE) There are a variety of other non-managerial positions in such crafts as accounting, information technology, and the remote encoding center. These are under a different contract than plant workers or letter carriers.
- Contractors are not USPS employees, but work for the USPS under a written contract and usually paid per mile. They do not get benefits including health insurance, leave, life insurance, and pension. They must use their own vehicle and pay any cost to maintain, insure, or replace. Contractors generally make less than employees. Just like regular carriers they deliver packages and letters to mailboxes and doors.
Though the USPS employs many individuals, as more Americans send
information via email, fewer postal workers are needed to work dwindling
amounts of mail. Post offices and mail facilities are constantly
downsizing, replacing craft positions with new machines and
consolidating mail routes through the MIARAP (Modified Interim Alternate
Route Adjustment Process) agreement. A major round of job cuts, early
retirements, and a construction freeze were announced on March 20, 2009.
Workplace violence
In the early 1990s, widely publicized workplace shootings
by disgruntled employees at USPS facilities led to a Human Resource
effort to provide care for stressed workers and resources for coworker
conflicts. Due to media coverage, postal employees gained a reputation among the general public as more likely to be mentally ill.
The USPS Commission on a Safe and Secure Workplace found that "Postal
workers are only a third as likely as those in the national workforce to
be victims of homicide at work." In the documentary Murder by Proxy: How America Went Postal, it was argued that this number failed to factor out workers killed by external subjects rather than by fellow employees.
This series of events in turn has influenced American culture, as seen in the slang term "going postal" and the computer game Postal. Also, in the opening sequence of Naked Gun 33 1⁄3: The Final Insult,
a yell of "Disgruntled postal workers" is heard, followed by the
arrival of postal workers with machine guns. In an episode of Seinfeld, the mailman character, Newman, explained in a dramatic monologue that postal workers "go crazy and kill everyone" because the mail never stops. In The Simpsons episode "Sunday, Cruddy Sunday," Nelson Muntz
asks Postmaster Bill if he has "ever gone on a killing spree"; Bill
replies, "The day of the gun-toting, disgruntled postman shooting up the
place went out with the Macarena".
The series of massacres led the USPS to issue a rule prohibiting
the possession of any type of firearms (except for those issued to
Postal Inspectors) in all designated USPS facilities.
In 2016, video footage was released showing a group of police officers from the New York City Police Department
(NYPD) arresting a USPS worker while he was in the middle of his
deliveries. The footage showed that the officers were dressed in
civilian clothing. The NYPD is reportedly investigating alleged disorderly conduct.
In fiction
- In the film Miracle on 34th Street (1947), the identity of Kris Kringle (played by Edmund Gwenn) as the one and only "Santa Claus" was validated by a state court, based on the delivery of 21 bags of mail (famously carried into the courtroom) to the character in question. The contention was that it would have been illegal for the United States Post Office to deliver mail that was addressed to "Santa Claus" to the character "Kris Kringle" unless he were, in fact, the one and only Santa Claus. Judge Henry X. Harper (played by Gene Lockhart) ruled that since the U.S. Government had demonstrated through the delivery of the bags of mail that Kris Kringle was Santa Claus, the State of New York did not have the authority to overrule that decision.
- The novel Post Office (1971), written by poet and novelist Charles Bukowski, is a semi-autobiographical account of his life over the years as a letter carrier. Bukowski would, under duress, quit and years later return as a mail clerk. His personal account would detail the work at lengths as frustrating, menial, boring, and degrading.
- David Brin's novel The Postman (1985) portrays the USPS and its returned services as a staple to revive the United States government in a post-apocalyptic world. It was adapted as a film starring Kevin Costner and Larenz Tate in 1997.
- The comedy film Dear God (1996), starring Greg Kinnear and Laurie Metcalf, portrays a group of quirky postal workers in a dead letter office that handle letters addressed to the Easter Bunny, Elvis, and even God himself.
- In 2015, The Inspectors, which depicts a group of postal inspectors investigating postal crimes, debuted on CBS. The series uses the USPIS seal and features messages and tips from the Chief Postal Inspector at the end of each episode.
- Signed, Sealed, Delivered (original title: Dead Letters), also known as Lost Letter Mysteries, is an American-Canadian drama/romantic comedy television series that aired on the Hallmark Channel from April 20 through June 22, 2014.
- In the NBC sitcom Cheers, Cliff Clavin (played by John Ratzenberger) was a know-it-all bar regular and letter carrier.