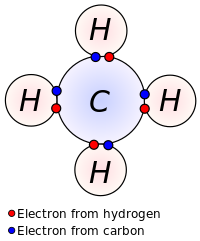
A covalent bond forming H2 (right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons
A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules,
the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a
full outer shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration.
Covalent bonding includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, and three-center two-electron bonds. The term covalent bond dates from 1939. The prefix co- means jointly, associated in action, partnered to a lesser degree, etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share "valence", such as is discussed in valence bond theory.
In the molecule H
2, the hydrogen atoms share the two electrons via covalent bonding. Covalency is greatest between atoms of similar electronegativities. Thus, covalent bonding does not necessarily require that the two atoms be of the same elements, only that they be of comparable electronegativity. Covalent bonding that entails sharing of electrons over more than two atoms is said to be delocalized.
2, the hydrogen atoms share the two electrons via covalent bonding. Covalency is greatest between atoms of similar electronegativities. Thus, covalent bonding does not necessarily require that the two atoms be of the same elements, only that they be of comparable electronegativity. Covalent bonding that entails sharing of electrons over more than two atoms is said to be delocalized.
History
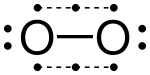
Early concepts in covalent bonding arose from this kind of image of the molecule of methane. Covalent bonding is implied in the Lewis structure by indicating electrons shared between atoms.
The term covalence in regard to bonding was first used in 1919 by Irving Langmuir in a Journal of the American Chemical Society article entitled "The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules". Langmuir wrote that "we shall denote by the term covalence the number of pairs of electrons that a given atom shares with its neighbors."
The idea of covalent bonding can be traced several years before 1919 to Gilbert N. Lewis, who in 1916 described the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. He introduced the Lewis notation or electron dot notation or Lewis dot structure,
in which valence electrons (those in the outer shell) are represented
as dots around the atomic symbols. Pairs of electrons located between
atoms represent covalent bonds. Multiple pairs represent multiple bonds,
such as double bonds and triple bonds. An alternative form of representation, not shown here, has bond-forming electron pairs represented as solid lines.
Lewis proposed that an atom forms enough covalent bonds to form a
full (or closed) outer electron shell. In the diagram of methane shown
here, the carbon atom has a valence of four and is, therefore,
surrounded by eight electrons (the octet rule),
four from the carbon itself and four from the hydrogens bonded to it.
Each hydrogen has a valence of one and is surrounded by two electrons (a
duet rule) – its own one electron plus one from the carbon. The numbers
of electrons correspond to full shells in the quantum theory of the
atom; the outer shell of a carbon atom is the n = 2 shell, which can hold eight electrons, whereas the outer (and only) shell of a hydrogen atom is the n = 1 shell, which can hold only two.
While the idea of shared electron pairs provides an effective qualitative picture of covalent bonding, quantum mechanics is needed to understand the nature of these bonds and predict the structures and properties of simple molecules. Walter Heitler and Fritz London are credited with the first successful quantum mechanical explanation of a chemical bond (molecular hydrogen) in 1927.
Their work was based on the valence bond model, which assumes that a
chemical bond is formed when there is good overlap between the atomic orbitals of participating atoms.
Types of covalent bonds
Atomic orbitals (except for s orbitals) have specific directional properties leading to different types of covalent bonds. Sigma (σ) bonds are the strongest covalent bonds and are due to head-on overlapping of orbitals on two different atoms. A single bond is usually a σ bond. Pi (π) bonds are weaker and are due to lateral overlap between p (or d) orbitals. A double bond between two given atoms consists of one σ and one π bond, and a triple bond is one σ and two π bonds.
Covalent bonds are also affected by the electronegativity of the connected atoms which determines the chemical polarity
of the bond. Two atoms with equal electronegativity will make nonpolar
covalent bonds such as H–H. An unequal relationship creates a polar
covalent bond such as with H−Cl. However polarity also requires geometric asymmetry, or else dipoles may cancel out resulting in a non-polar molecule.
Covalent structures
There are several types of structures for covalent substances, including individual molecules, molecular structures, macromolecular
structures and giant covalent structures. Individual molecules have
strong bonds that hold the atoms together, but there are negligible
forces of attraction between molecules. Such covalent substances are
usually gases, for example, HCl, SO2, CO2, and CH4.
In molecular structures, there are weak forces of attraction. Such
covalent substances are low-boiling-temperature liquids (such as ethanol), and low-melting-temperature solids (such as iodine and solid CO2).
Macromolecular structures have large numbers of atoms linked by
covalent bonds in chains, including synthetic polymers such as polyethylene and nylon, and biopolymers such as proteins and starch. Network covalent structures (or giant covalent structures) contain large numbers of atoms linked in sheets (such as graphite), or 3-dimensional structures (such as diamond and quartz). These substances have high melting and boiling points, are frequently brittle, and tend to have high electrical resistivity. Elements that have high electronegativity, and the ability to form three or four electron pair bonds, often form such large macromolecular structures.
One- and three-electron bonds
Lewis and MO diagrams of an individual 2e bond and 3e bond
Bonds with one or three electrons can be found in radical species, which have an odd number of electrons. The simplest example of a 1-electron bond is found in the dihydrogen cation, H+
2. One-electron bonds often have about half the bond energy of a 2-electron bond, and are therefore called "half bonds". However, there are exceptions: in the case of dilithium, the bond is actually stronger for the 1-electron Li+
2 than for the 2-electron Li2. This exception can be explained in terms of hybridization and inner-shell effects.
2. One-electron bonds often have about half the bond energy of a 2-electron bond, and are therefore called "half bonds". However, there are exceptions: in the case of dilithium, the bond is actually stronger for the 1-electron Li+
2 than for the 2-electron Li2. This exception can be explained in terms of hybridization and inner-shell effects.
The simplest example of three-electron bonding can be found in the helium dimer cation, He+
2. It is considered a "half bond" because it consists of only one shared electron (rather than two); in molecular orbital terms, the third electron is in an anti-bonding orbital which cancels out half of the bond formed by the other two electrons. Another example of a molecule containing a 3-electron bond, in addition to two 2-electron bonds, is nitric oxide, NO. The oxygen molecule, O2 can also be regarded as having two 3-electron bonds and one 2-electron bond, which accounts for its paramagnetism and its formal bond order of 2. Chlorine dioxide and its heavier analogues bromine dioxide and iodine dioxide also contain three-electron bonds.
2. It is considered a "half bond" because it consists of only one shared electron (rather than two); in molecular orbital terms, the third electron is in an anti-bonding orbital which cancels out half of the bond formed by the other two electrons. Another example of a molecule containing a 3-electron bond, in addition to two 2-electron bonds, is nitric oxide, NO. The oxygen molecule, O2 can also be regarded as having two 3-electron bonds and one 2-electron bond, which accounts for its paramagnetism and its formal bond order of 2. Chlorine dioxide and its heavier analogues bromine dioxide and iodine dioxide also contain three-electron bonds.
Molecules with odd-electron bonds are usually highly reactive.
These types of bond are only stable between atoms with similar
electronegativities.
Resonance
There are situations whereby a single Lewis structure
is insufficient to explain the electron configuration in a molecule,
hence a superposition of structures are needed. The same two atoms in
such molecules can be bonded differently in different structures (a
single bond in one, a double bond in another, or even none at all),
resulting in a non-integer bond order. The nitrate ion is one such example with three equivalent structures. The bond between the nitrogen
and each oxygen is a double bond in one structure and a single bond in
the other two, so that the average bond order for each N–O interaction
is 2 + 1 + 1/3 = 4/3.
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, when a molecule with a planar ring obeys Hückel's rule, where the number of π electrons fit the formula 4n + 2 (where n is an integer), it attains extra stability and symmetry. In benzene, the prototypical aromatic compound, there are 6 π bonding electrons (n = 1, 4n + 2 = 6). These occupy three delocalized π molecular orbitals (molecular orbital theory) or form conjugate π bonds in two resonance structures that linearly combine (valence bond theory), creating a regular hexagon exhibiting a greater stabilization than the hypothetical 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene.
In the case of heterocyclic aromatics and substituted benzenes,
the electronegativity differences between different parts of the ring
may dominate the chemical behaviour of aromatic ring bonds, which
otherwise are equivalent.
Hypervalence
Certain molecules such as xenon difluoride and sulfur hexafluoride have higher co-ordination numbers than would be possible due to strictly covalent bonding according to the octet rule. This is explained by the three-center four-electron bond ("3c–4e") model which interprets the molecular wavefunction in terms of non-bonding highest occupied molecular orbitals in molecular orbital theory and resonance of sigma bonds in valence bond theory.
Electron deficiency
In three-center two-electron bonds ("3c–2e") three atoms share two electrons in bonding. This type of bonding occurs in electron deficient compounds like diborane. Each such bond (2 per molecule in diborane) contains a pair of electrons which connect the boron atoms to each other in a banana
shape, with a proton (nucleus of a hydrogen atom) in the middle of the
bond, sharing electrons with both boron atoms. In certain cluster compounds, so-called four-center two-electron bonds also have been postulated.
Quantum mechanical description
After the development of quantum mechanics, two basic theories were
proposed to provide a quantum description of chemical bonding: valence bond (VB) theory and molecular orbital (MO) theory. A more recent quantum description is given in terms of atomic contributions to the electronic density of states.
Comparison of VB and MO theories
The two theories represent two ways to build up the electron configuration of the molecule. For valence bond theory, the atomic hybrid orbitals
are filled with electrons first to produce a fully bonded valence
configuration, followed by performing a linear combination of
contributing structures (resonance) if there are several of them. In contrast, for molecular orbital theory a linear combination of atomic orbitals is performed first, followed by filling of the resulting molecular orbitals with electrons.
The two approaches are regarded as complementary, and each
provides its own insights into the problem of chemical bonding. As
valence bond theory builds the molecular wavefunction out of localized
bonds, it is more suited for the calculation of bond energies and the understanding of reaction mechanisms.
As molecular orbital theory builds the molecular wavefunction out of
delocalized orbitals, it is more suited for the calculation of ionization energies and the understanding of spectral absorption bands.
At the qualitative level, both theories contain incorrect
predictions. Simple (Heitler–London) valence bond theory correctly
predicts the dissociation of homonuclear diatomic molecules into
separate atoms, while simple (Hartree–Fock) molecular orbital theory
incorrectly predicts dissociation into a mixture of atoms and ions. On
the other hand, simple molecular orbital theory correctly predicts Hückel's rule
of aromaticity, while simple valence bond theory incorrectly predicts
that cyclobutadiene has a larger resonance energy than benzene.
Although the wavefunctions generated by both theories at the
qualitative level do not agree and do not match the stabilization energy
by experiment, they can be corrected by configuration interaction.
This is done by combining the valence bond covalent function with the
functions describing all possible ionic structures or by combining the
molecular orbital ground state function with the functions describing
all possible excited states using unoccupied orbitals. It can then be
seen that the simple molecular orbital approach overestimates the weight
of the ionic structures while the simple valence bond approach neglects
them. This can also be described as saying that the simple molecular
orbital approach neglects electron correlation while the simple valence bond approach overestimates it.
Modern calculations in quantum chemistry
usually start from (but ultimately go far beyond) a molecular orbital
rather than a valence bond approach, not because of any intrinsic
superiority in the former but rather because the MO approach is more
readily adapted to numerical computations. Molecular orbitals are
orthogonal, which significantly increases feasibility and speed of
computer calculations compared to nonorthogonal valence bond orbitals.
However, better valence bond programs are now available.
Covalency from atomic contribution to the electronic density of states
In COOP, COHP and BCOOP,
evaluation of bond covalency is dependent on the basis set. To overcome
this issue, an alternative formulation of the bond covalency can be
provided in this way.
The center mass cm(n,l,ml,ms) of an atomic orbital |n,l,ml,ms⟩,
with quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms, for atom A is defined as
where gA
|n,l,ml,ms⟩(E) is the contribution of the atomic orbital |n,l,ml,ms⟩ of the atom A to the total electronic density of states g(E) of the solid
|n,l,ml,ms⟩(E) is the contribution of the atomic orbital |n,l,ml,ms⟩ of the atom A to the total electronic density of states g(E) of the solid
where the outer sum runs over all atoms A of the unit cell. The energy window [E0,E1]
is chosen in such a way that it encompasses all relevant bands
participating in the bond. If the range to select is unclear, it can be
identified in practice by examining the molecular orbitals that describe
the electron density along the considered bond.
The relative position CnAlA,nBlB of the center mass of |nA,lA⟩ levels of atom A with respect to the center mass of |nB,lB⟩ levels of atom B is given as
where the contributions of the magnetic and spin quantum numbers are
summed. According to this definition, the relative position of the A
levels with respect to the B levels is
where, for simplicity, we may omit the dependence from the principal quantum number n in the notation referring to CnAlA,nBlB.
In this formalism, the greater the value of CA,B,
the higher the overlap of the selected atomic bands, and thus the
electron density described by those orbitals gives a more covalent A–B
bond. The quantity CA,B is denoted as the covalency of the A–B bond, which is specified in the same units of the energy E.