In addition to the many unresolved arguments about the
construction techniques, there have been disagreements as to the kind of
workforce used. The Greeks, many years after the event, believed that the pyramids must have been built by slave labor. Archaeologists now believe that the Great Pyramid of Giza
(at least) was built by tens of thousands of skilled workers who camped
near the pyramids and worked for a salary or as a form of tax payment
(levy) until the construction was completed, pointing to workers'
cemeteries discovered in 1990 by archaeologists Zahi Hawass and Mark Lehner. For the Middle Kingdom Pyramid of Amenemhat II, there is evidence from the annal stone of the king that foreigners from Canaan were used.
Pseudoscientific theories have proliferated in the vacuum of official construction explanations.
Pseudoscientific theories have proliferated in the vacuum of official construction explanations.
Historical hypotheses
Third through Fifth Dynasties
During
the earliest period, pyramids were constructed wholly of stone. Locally
quarried limestone was the material of choice for the main body of
these pyramids, while a higher quality of limestone quarried at Tura (near modern Cairo) was used for the outer casing. Granite, quarried near Aswan, was used to construct some architectural elements, including the portcullis
(a type of gate) and the roofs and walls of the burial chamber.
Occasionally, granite was used in the outer casing as well, such as in
the Pyramid of Menkaure. In the early pyramids, the layers of stone (called courses)
forming the pyramid body were laid sloping inwards; however, this
configuration was found to be less stable than simply stacking the
stones horizontally on top of each other. The Bent Pyramid at Dahshur
seems to indicate acceptance of a new technique at a transition between
these two building techniques. Its lower section is built of sloping
courses while in its upper section the stones are laid horizontally.
Middle Kingdom and onward
During the Middle Kingdom,
pyramid construction techniques changed again. Most pyramids built then
were little more than mountains of mud brick encased in a veneer of
polished limestone. In several cases, later pyramids were built on top
of natural hills to further reduce the volume of material needed in
their construction. The materials and methods of construction used in
the earliest pyramids have ensured their survival in a generally much
better state of preservation than for the pyramid monuments of the later
pharaohs.
Construction method hypotheses
Building the pyramids from quarried stone blocks
One
of the major problems faced by the early pyramid builders was the need
to move huge quantities of stone. The Twelfth Dynasty tomb of Djehutihotep
has an illustration of 172 men pulling an alabaster statue of him on a
sledge. The statue is estimated to weigh 60 tons and Denys Stocks
estimated that 45 workers would be required to start moving a 16,300 kg
(35,900 lb; 16.3 t) lubricated block, or eight workers to move a
2,750 kg (6,060 lb; 2.75 t) block. Dr R H G Parry
has suggested a method for rolling the stones, using a cradle-like
machine that had been excavated in various new kingdom temples. Four of
those objects could be fitted around a block so it could be rolled
easily. Experiments done by the Obayashi Corporation, with concrete
blocks 0.8 metres (2 ft 7 in) square by 1.6 metres (5 ft 3 in) long and
weighing 2.5 tonnes (2,500 kg; 5,500 lb), showed how 18 men could drag
the block over a 1-in-4 incline ramp, at a rate of 18 metres per minute
(1 ft/s). This idea was previously described by John Bush in 1977, and is mentioned in the Closing Remarks section of Parry's book. Vitruvius in De architectura
described a similar method for moving irregular weights. It is still
not known whether the Egyptians used this method but the experiments
indicate it could have worked using stones of this size. Egyptologists
generally accept this for the 2.5 ton blocks mostly used but do not
agree over the methods used for the 15+ ton and several 70 to 80 ton
blocks.
As the stones forming the core of the pyramids were roughly cut, especially in the Great Pyramid, the material used to fill the gaps was another problem. Huge quantities of gypsum and rubble were needed.
The filling has almost no binding properties, but it was necessary to
stabilize the construction. To make the gypsum mortar, it had to be
dehydrated by heating which requires large quantities of wood. According
to Egyptologists, the findings of both the 1984 and 1995 David H. Koch
Pyramids Radiocarbon Projects
may suggest that Egypt had to strip its forest and scrap every bit of
wood it had to build the pyramids of Giza and other even earlier 4th
Dynasty pyramids. Carbon dating samples from core blocks and other
materials revealed that dates from the 1984 study averaged 374 years
earlier than currently accepted and the 1995 dating averaging 100–200
years. As suggested by team members, "We thought that it was unlikely
that the pyramid builders consistently used centuries-old wood as fuel
in preparing mortar. The 1984 results left us with too little data to
conclude that the historical chronology of the Old Kingdom was wrong by
nearly 400 years, but we considered this at least a possibility". To
explain this discrepancy, Egyptologists proposed the "old wood" theory
claiming the earlier dates were possibly derived from recycling large
amounts of centuries old wood and other earlier materials.
There is good information concerning the location of the
quarries, some of the tools used to cut stone in the quarries,
transportation of the stone to the monument, leveling the foundation,
and leveling the subsequent tiers of the developing superstructure.
Workmen probably used copper chisels, drills, and saws to cut softer
stone, such as most of the limestone. The harder stones, such as
granite, granodiorite, syenite, and basalt, cannot be cut with copper
tools alone; instead they were worked with time-consuming methods like
pounding with dolerite, drilling, and sawing with the aid of an abrasive, such as quartz sand. Blocks were transported by sledge likely lubricated by water.
Leveling the foundation may have been accomplished by use of
water-filled trenches as suggested by Mark Lehner and I.E.S. Edwards or
through the use of a crude square level and experienced surveyors.
Thales's method (intercept theorem) to determine the height of Cheops pyramid
The diary of Merer,
logbooks written more than 4,500 years ago by an Egyption official and
found in 2013 by a French archeology team under the direction of Pierre Tallet in a cave in Wadi al-Jarf, describes the transportation of limestone from the quarry in Tora to Giza.
Writings of Herodotus and Diodorus Siculus
The
unknowns of pyramid construction chiefly center on the question of how
the blocks were moved up the superstructure. There is no known accurate
historical or archaeological evidence that definitively resolves the
question. Therefore, most discussion on construction methods involves
functional possibilities that are supported by limited historical and
archaeological evidence.
Historical accounts for the construction of the Egyptian pyramids
do little to point definitively to methods to lift the blocks; yet most
Egyptologists refer to these accounts when discussing this portion of
pyramid construction. Thales, according to the philosopher Hieronymus (3rd century BC) visited the Egyptian pyramids during the 7th century BC and by using the intercept theorem,
also known as Thales's theorem, measured their height and thus their
volume. The first historical accounts of the construction of these
monuments came centuries after the era of pyramid construction, by Herodotus in the 5th century BC and Diodorus Siculus in the 1st century BC. Herodotus's account states:
This pyramid was made like stairs, which some call steps and others, tiers. When this, its first form, was completed, the workmen used short wooden logs as levers to raise the rest of the stones; they heaved up the blocks from the ground onto the first tier of steps; when the stone had been raised, it was set on another lever that stood on the first tier, and the lever again used to lift it from this tier to the next. It may be that there was a new lever on each tier of steps, or perhaps there was only one lever, quite portable, which they carried up to each tier in turn; I leave this uncertain, as both possibilities were mentioned. But this is certain, that the upper part of the pyramid was finished off first, then the next below it, and last of all the base and the lowest part.
Diodorus Siculus's account states:
And 'tis said the stone was transported a great distance from Arabia, and that the edifices were raised by means of earthen ramps, since machines for lifting had not yet been invented in those days; and most surprising it is, that although such large structures were raised in an area surrounded by sand, no trace remains of either ramps or the dressing of the stones, so that it seems not the result of the patient labor of men, but rather as if the whole complex were set down entire upon the surrounding sand by some god. Now Egyptians try to make a marvel of these things, alleging that the ramps were made of salt and natron and that, when the river was turned against them, it melted them clean away and obliterated their every trace without the use of human labor. But in truth, it most certainly was not done this way! Rather, the same multitude of workmen who raised the mounds returned the entire mass again to its original place; for they say that three hundred and sixty thousand men were constantly employed in the prosecution of their work, yet the entire edifice was hardly finished at the end of twenty years.
Diodorus Siculus's description of the shipment of the stone from
Arabia is correct since the term "Arabia" those days implied the land
between the Nile and the Red Sea where the limestone blocks have been transported from quarries across the river Nile.
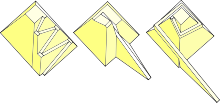
Different kinds of ramps
Example of a large straight ramp
From left to right: Zig-zagging ramp (Uvo Hölscher), ramp using the incomplete part of the superstructure (Dieter Arnold), and a spiraling ramp supported by the superstructure (Mark Lehner)
Most Egyptologists acknowledge that ramps are the most tenable of the
methods to raise the blocks, yet they acknowledge that it is an
incomplete method that must be supplemented by another device.
Archaeological evidence for the use of ramps has been found at the Great Pyramid of Giza and other pyramids. The method most accepted for assisting ramps is levering (Lehner 1997: 222). The archaeological record
gives evidence of only small ramps and inclined causeways, not
something that could have been used to construct even a majority of the
monument. To add to the uncertainty, there is considerable evidence
demonstrating that non-standardized or ad hoc construction methods were used in pyramid construction (Arnold 1991: 98, Lehner 1997: 223).
Therefore, there are many proposed ramps and there is a
considerable amount of discrepancy regarding what type of ramp was used
to build the pyramids.
One of the widely discredited ramping methods is the large straight
ramp, and it is routinely discredited on functional grounds for its
massive size, lack of archaeological evidence, huge labor cost, and
other problems (Arnold 1991: 99, Lehner 1997: 215, Isler 2001: 213).
Other ramps serve to correct these problems of ramp size, yet
either run into critiques of functionality and limited archaeological
evidence. There are zig-zagging ramps, straight ramps using the
incomplete part of the superstructure (Arnold 1991), spiraling ramps
supported by the superstructure and spiraling ramps leaning on the
monument as a large accretion are proposed. Mark Lehner speculated that a spiraling ramp, beginning in the stone quarry
to the southeast and continuing around the exterior of the pyramid, may
have been used. The stone blocks may have been drawn on sleds along the
ramps lubricated by water or milk.
Levering
methods are considered to be the most tenable solution to complement
ramping methods, partially due to Herodotus's description; and partially
to the Shadoof;
an irrigation device first depicted in Egypt during the New Kingdom,
and found concomitantly with the Old Kingdom in Mesopotamia. In Lehner's
(1997: 222) point of view, levers should be employed to lift the top 3%
of the material of the superstructure. It is important to note that the
top 4% of this material comprises 1⁄3
of the total height of the monument. In other words, in Lehner's view,
levers should be employed to lift a small amount of material and a great
deal of vertical height of the monument.
In the milieu of levering methods, there are those that lift the
block incrementally, as in repeatedly prying up alternating sides of the
block and inserting a wooden or stone shims to gradually move the stone
up one course; and there are other methods that use a larger lever to
move the block up one course in one lifting procedure. Since the
discussion of construction techniques to lift the blocks attempts to
resolve a gap in the archaeological and historical record with a
plausible functional explanation, the following examples by Isler,
Keable, and Hussey-Pailos
list experimentally tested methods. Isler's method (1985, 1987) is an
incremental method and, in the Nova experiment (1992), used wooden shims
or cribbing. Isler was able to lift a block up one tier in approximately one hour and 30 minutes. Peter Hodges's and Julian Keable's
method is similar to Isler's method and instead used small manufactured
concrete blocks as shims, wooden pallets, and a pit where their
experimental tests were performed. Keable was able to perform his method
in approximately 2 minutes. Scott Hussey-Pailos's (2005) method
uses a simple levering device to lift a block up a course in one
movement. This method was tested with materials of less strength than
historical analogs (tested with materials weaker than those available in
ancient Egypt), a factor of safety of 2, and lifted a 2500-pound block
up one course in under a minute. This method is presented as a levering
device to work complementary with Mark Lehner's idea of a combined ramp
and levering techniques.
Jean-Pierre Houdin's "internal ramp" hypothesis
Houdin's father was an architect who, in 1999, thought of a
construction method that, it seemed to him, made more sense than any
existing method proposed for building pyramids. To develop this
hypothesis, Jean-Pierre Houdin, also an architect, gave up his job and
set about drawing the first fully functional CAD architectural model of the Great Pyramid.
His/their scheme involves using a regular external ramp to build the
first 30% of the pyramid, with an "internal ramp" taking stones up
beyond that height.
The stones of the external ramp are re-cycled into the upper stories,
thus explaining the otherwise puzzling lack of evidence for ramps.
After 4 years working alone, Houdin was joined by a team of engineers from the French 3D software company Dassault Systemes, who used the most modern computer-aided design
technology available to further refine and test the hypothesis, making
it (according to Houdin) the only one proven to be a viable technique. In 2006 Houdin announced it in a book: Khufu: The Secrets Behind the Building of the Great Pyramid, and in 2008 he and Egyptologist Bob Brier wrote a second one: The Secret of the Great Pyramid.
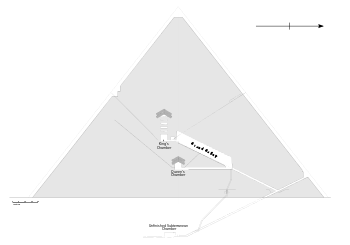
In Houdin's method, each ramp inside the pyramid ended at an open
space, a notch temporarily left open in the edge of the
construction.(see diagram)
This 10-square-meter clear space housed a crane that lifted and rotated
each 2.5-ton block, to ready it for eight men to drag up the next
internal ramp. There is a notch of sorts in one of the right places, and
in 2008 Houdin's co-author Bob Brier, with a National Geographic film
crew, entered a previously unremarked chamber that could be the start of
one of these internal ramps. In 1986 a member of the French team (see below) saw a desert fox at this notch, rather as if it had ascended internally.
Houdin's thesis remains unproven and in 2007, UCL Egyptologist David Jeffreys described the internal spiral hypothesis as "far-fetched and horribly complicated", while Oxford University's John Baines, declared he was "suspicious of any theory that seeks to explain only how the Great Pyramid was built".
Houdin has another hypothesis developed from his architectural
model, one that could finally explain the internal "Grand Gallery"
chamber that otherwise appears to have little purpose. He believes the
gallery acted as a trolley chute/guide for counterbalance weights. It
enabled the raising of the five 60-ton granite beams that roof the
King's Chamber. Houdin and Brier and the Dassault team are already
credited with proving for the first time that cracks in beams appeared
during construction, were examined and tested at the time and declared
relatively harmless.
Limestone concrete hypothesis
Materials scientist Joseph Davidovits has claimed that the blocks of the pyramid are not carved stone, but mostly a form of limestone concrete and that they were "cast" as with modern concrete. According to this hypothesis, soft limestone with a high kaolinite content was quarried in the wadi
on the south of the Giza Plateau. The limestone was then dissolved in
large, Nile-fed pools until it became a watery slurry. Lime (found in
the ash of cooking fires) and natron (also used by the Egyptians in mummification)
were mixed in. The pools were then left to evaporate, leaving behind a
moist, clay-like mixture. This wet "concrete" would be carried to the
construction site where it would be packed into reusable wooden moulds
and in a few days would undergo a chemical reaction similar to the
curing of concrete. New blocks, he suggests, could be cast in place, on
top of and pressed against the old blocks. Proof-of-concept tests using
similar compounds were carried out at a geopolymer
institute in northern France and it was found that a crew of five to
ten, working with simple hand tools, could agglomerate a structure of
five, 1.3 to 4.5 ton blocks in a couple of weeks. He also claims that the Famine Stele, along with other hieroglyphic texts, describe the technology of stone agglomeration.
Davidovits's method is not accepted by the academic mainstream.
His method does not explain the granite stones, weighing well over 10
tons, above the King's Chamber, which he agrees were carved. Geologists
have carefully scrutinized Davidovits's suggested technique and
concluded his concrete came from natural limestone quarried in the
Mokattam Formation.
However, Davidovits alleges that the bulk of the soft limestone came
from the same natural Mokkatam Formation quarries found by geologists,
and insists that ancient Egyptians used the soft marly layer instead of
the hard layer to re-agglomerate stones.
Davidovits's hypothesis gained support from Michel Barsoum, a materials science researcher. Michel Barsoum and his colleagues at Drexel University published their findings supporting Davidovits's hypothesis in the Journal of the American Ceramic Society in 2006. Using scanning electron microscopy,
they discovered in samples of the limestone pyramid blocks mineral
compounds and air bubbles that do not occur in natural limestone.
Dipayan Jana, a petrographer, made a presentation to the ICMA (International Cement Microscopy Association) in 2007 and gave a paper
in which he discusses Davidovits's and Barsoum's work and concludes "we
are far from accepting even as a remote possibility a 'man-made' origin
of pyramid stones."
NOVA pyramid building experiment
In 1997, Mark Lehner and stonemason Roger Hopkins conducted a three-week pyramid-building experiment for a NOVA
television episode. They built a pyramid 6 metres (20 ft) high by 9
metres (30 ft) wide, consisting of a total of 162 cubic metres
(5,700 cu ft), or about 405 tons. It was made out of 186 stones weighing
an average of 2.2 tons each. Twelve quarrymen carved 186 stones in 22 days, and the structure was erected using 44 men. They used iron hammers, chisels and levers (this is a modern shortcut, as the ancient Egyptians were limited to using copper and later bronze and wood).
But Lehner and Hopkins did experiments with copper tools, noting that
they were adequate for the job in hand, provided that additional
manpower was available to constantly resharpen the ancient tools. They
estimated they would have needed around 20 extra men for this
maintenance. Another shortcut taken was the use of a front-end loader or fork lift
truck, but modern machinery was not used to finish the construction.
They used levers to lift the capstone to a height of 20 feet (6.1 m).
Four or five men were able to use levers on stones less than one ton to
flip them over and transport them by rolling, but larger stones had to
be towed. Lehner and Hopkins found that by putting the stones on wooden
sledges and sliding the sledges on wooden tracks, they were able to tow a
two-ton stone with 12 to 20 men. The wood for these sledges and tracks
would have to have been imported from Lebanon
at great cost since there was little, if any, wood in ancient Egypt.
While the builders failed to duplicate the precise jointing created by
the ancient Egyptians, Hopkins was confident that this could have been
achieved with more practice.
Great Pyramid
Some research suggests alternate estimates to the accepted workforce size. For instance, mathematician Kurt Mendelssohn calculated that the workforce may have been 50,000 men at most, while Ludwig Borchardt and Louis Croon placed the number at 36,000. According to Miroslav Verner,
a workforce of no more than 30,000 was needed in the Great Pyramid's
construction. Evidence suggests that around 5,000 were permanent workers
on salaries with the balance working three- or four-month shifts in
lieu of taxes while receiving subsistence "wages" of ten loaves of bread
and a jug of beer per day. Zahi Hawass
believes that the majority of workers may have been volunteers. It is
estimated that only 4,000 of the total workforce were labourers who
quarried the stone, hauled blocks to the pyramid and set the blocks in
place. The vast majority of the workforce provided support services such
as scribes, toolmakers and other backup services. The tombs of
supervisors contain inscriptions regarding the organisation of the
workforce. There were two crews of approximately 2,000 workers
sub-divided into named gangs of 1,000. The gangs were divided into five
phyles of 200 which were in turn split into groups of around 20 workers
grouped according to their skills, with each group having their own
project leader and a specific task.
A construction management study carried out by the firm Daniel, Mann, Johnson, & Mendenhall in association with Mark Lehner,
and other Egyptologists, estimates that the total project required an
average workforce of 14,567 people and a peak workforce of 40,000.
Without the use of pulleys, wheels, or iron tools, they used critical path analysis to suggest the Great Pyramid was completed from start to finish in approximately 10 years.
Their study estimates the number of blocks used in construction was
between 2 and 2.8 million (an average of 2.4 million), but settles on a
reduced finished total of 2 million after subtracting the estimated
volume of the hollow spaces of the chambers and galleries. Most sources agree on this number of blocks somewhere above 2.3 million.
Their calculations suggest the workforce could have sustained a rate of
180 blocks per hour (3 blocks/minute) with ten-hour work days for
putting each individual block in place. They derived these estimates
from modern third-world construction projects that did not use modern
machinery, but conclude it is still unknown exactly how the Great
Pyramid was built. As Dr. Craig Smith of the team points out:
The logistics of construction at the Giza site are staggering when you think that the ancient Egyptians had no pulleys, no wheels, and no iron tools. Yet, the dimensions of the pyramid are extremely accurate and the site was leveled within a fraction of an inch over the entire 13.1-acre base. This is comparable to the accuracy possible with modern construction methods and laser leveling. That's astounding. With their 'rudimentary tools,' the pyramid builders of ancient Egypt were about as accurate as we are today with 20th-century technology.
Average
core blocks of the Great Pyramid weigh about 1.5 tons each, and the
granite blocks used to roof the burial chambers are estimated to weigh
up to 80 tons each.
The entire Giza Plateau
is believed to have been constructed over the reign of five pharaohs in
less than a hundred years, which generally includes: the Great Pyramid,
Khafre and Menkaure's pyramids, the Great Sphinx, the Sphinx and Valley
Temples, 35 boat pits cut out of solid bedrock, and several causeways,
as well as paving nearly the entire plateau with large stones. This does
not include Khafre's brother Djedefre's northern pyramid, Abu Rawash,
which would have also been built during this time frame of 100 years. In
the hundred years prior to Giza—beginning with Djoser,
who ruled from 2687–2667 BC, and amongst dozens of other temples,
smaller pyramids, and general construction projects—four other massive
pyramids were built: the Step pyramid of Saqqara (believed to be the first Egyptian pyramid), the pyramid of Meidum, the Bent Pyramid, and the Red Pyramid. Also during this period (between 2686 and 2498 BC) the Sadd el-Kafara dam, which used an estimated 100,000 cubic meters of rock and rubble, was built.
In October 2018, a team of archaeologists from the Institut Français d'Archéologie Orientale and University of Liverpool had announced the discovery of the remains of a 4,500-year-old ramp contraption at Hatnub,
excavated since 2012. This method which aided in lifting the heavy
alabaster stones up from their quarries, may have been used to build
Egypt's Great Pyramid as well. Yannis Gourdon, co-director of the joint mission at Hatnub, said:
This system is composed of a central ramp flanked by two staircases with numerous post holes, using a sled which carried a stone block and was attached with ropes to these wooden posts, ancient Egyptians were able to pull up the alabaster blocks out of the quarry on very steep slopes of 20 percent or more ... As this system dates back at least to Khufu's reign, that means that during the time of Khufu, ancient Egyptians knew how to move huge blocks of stone using very steep slopes. Therefore, they could have used it for the construction [of] his pyramid.