From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
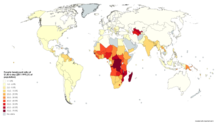
World Development Indicators have improved relative to the year 1990.
International development or global development is a broad concept denoting the idea that societies and countries have differing levels of economic or human development on an international scale. It is the basis for international classifications such as developed country, developing country and least developed country,
and for a field of practice and research that in various ways engages
with international development processes. There are, however, many
schools of thought and conventions regarding which are the exact
features constituting the "development" of a country.
Historically, development was largely synonymous with economic
development, and especially its convenient but flawed quantification
(see parable of the broken window) through readily gathered (for developed countries) or estimated monetary proxies (estimated for severely undeveloped or isolationist countries) such as gross domestic product (GDP), often viewed alongside actuarial measures such as life expectancy.
More recently, writers and practitioners have begun to discuss
development in the more holistic and multi-disciplinary sense of human
development. Other related concepts are, for instance, competitiveness, quality of life or subjective well-being.
"International development" is different from the simple concept
of "development". Whereas the latter, at its most basic, denotes simply
the idea of change through time, international development has come to
refer to a distinct field of practice, industry, and research; the
subject of university courses and professional categorisations. It
remains closely related to the set of institutions—especially the Bretton Woods Institutions—that
arose after the Second World War with a focus on economic growth,
alleviating poverty, and improving living conditions in previously
colonised countries. The international community has codified development aims in, for instance, the Millennium Development Goals (2000 to 2015) and the Sustainable Development Goals (2015 to 2030).
Global Goals
Sustainable Development Goals (2015 to 2030)
The MDGs served a successful framework to guide international
development efforts, having achieved progress on some of the 8 goals.
For example, by 2015 the extreme poverty rate had already been cut into
half. Other targets achieved include access to safe drinking water, malaria, and gender equality in schooling.
Yet, some scholars have argued that the MDGs lack the critical
perspectives required to alleviate poverty and structures of inequality,
reflected in the serious lags to achieving numerous other goals.
As the MDG era came to an end, 2015 marked the year that the
United Nations General Assembly adopted a new agenda for development.
Former UN Secretary General Ban Ki Moon referred to this as a "defining
moment in history" calling on states to "act in solidarity". Succeeding the MDG agenda, 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were created, with 169 indicators.
UN resolution 70/1 adopted on September 25, 2015 was titled
"Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development",
solidifying 17 new goals that had been in motion since 2014. The goals came into force in January 2016, focusing on areas of climate
change, economic inequality, democracy, poverty, and peacebuilding.
Although the SDGs were built on the foundation of the MDGs, there
are some key differences in both processes. Before adoption, unlike the
MDGs, the SDGs had been in discussion for months, involving civil
society actors, NGOs, as well as an opening summit involving
intergovernmental negotiations.
The new global development agenda places a greater emphasis on
collective action, combining the efforts of multiple stakeholders to
increase the sustainability of the goals. This emphasis on
sustainability has also led to more cross-sector partnerships, and
combined international efforts across areas of environmental, social,
cultural, political, and economic development.
Millennium Development Goals (2000 to 2015)
In 2000, United Nations signed the United Nations Millennium Declaration,
which includes eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) to be achieved
by 2015. This represented the first time that a holistic strategy to
meet the development needs of the world has been established, with
measurable targets and defined indicators.
Because the MDGs were agreed as global targets to be achieved by
the global community, they are independent of, but by no means unrelated
to, individual national interests. The goals imply that every state has
a set of obligations to the world community to meet and that other
states, who have achieved those goals, have an obligation to help those
who have not. As such they may represent an extension of the concept of
human rights.
The first seven Millennium Development Goals present measurable
goals, while the eighth lists a number of 'stepping stone' goals – ways
in which progress towards the first seven goals could be made. Each goal
uses indicators based on statistical series collected and maintained
by respected organisations in each relevant field (usually the UN agency
responsible but also the OECD, IMF and World Bank)
The MDGs have catalysed a significant amount of action, including new initiatives such as Millennium Promise.
Most of these initiatives however work in small scale interventions
which do not reach the millions of people required by the MDGs.
Recent praise has been that it will be impossible to meet the first seven goals without meeting the eighth by forming a Global Partnership for Development.
No current organisation has the capacity to dissolve the enormous
problems of the developing world alone – especially in cities, where an
increasing number of poor people live – as demonstrated by the almost
nonexistent progress on the goal of improving the lives of at least 100
Million slum dwellers.
The Institution of Civil Engineers Engineering Without Frontiers panel and its recommendations, and the 2007 Brunel Lecture by the ICE's 2009–2010 president Paul Jowitt,
are representative of a change of approach in the UK at least to start
drawing together the huge capacity available to western governments,
industry, academia and charity to develop such a partnership.
Other goals
International
development also aims to improve general government policies of these
developing countries. "State building" is the strengthening of regional
institutions necessary to support long-term economic, social, and
political development. Education is another important aspect of
international development. It is a good example of how the focus today
is on sustainable development in these countries; education gives people
the skills required to keep themselves out of poverty.
Concepts
International development is related to the concept of international aid, but is distinct from, disaster relief and humanitarian aid.
While these two forms of international support seek to alleviate some
of the problems associated with a lack of development, they are most
often short term fixes – they are not necessarily long-term solutions.
International development, on the other hand, seeks to implement
long-term solutions to problems by helping developing countries create
the necessary capacity needed to provide such sustainable solutions to
their problems. A truly sustainable development
project is one which will be able to carry on indefinitely with no
further international involvement or support, whether it be financial or
otherwise.
International development projects may consist of a single,
transformative project to address a specific problem or a series of
projects targeted at several aspects of society. Promoted projects are
ones which involve problem solving that reflects the unique culture,
politics, geography, and economy of a region. More recently, the focus
in this field has been projects that aim towards empowering women,
building local economies, and caring for the environment.
In context of human development it usually encompasses foreign aid, governance, healthcare, education, poverty reduction, gender equality, disaster preparedness, infrastructure, economics, human rights, environment and issues associated with these.
During recent decades, development thinking has shifted from modernization and structural adjustment programs to poverty reduction.
Under the former system, poor countries were encouraged to undergo
social and economical structural transformations as part of their
development, creating industrialization
and intentional industrial policy. Poverty reduction rejects this
notion, consisting instead of direct budget support for social welfare
programs that create macroeconomic stability leading to an increase in
economic growth.
The concept of poverty can apply to different circumstances
depending on context. Poverty is the condition of lacking economic
access to fundamental human needs such as food, shelter and safe
drinking water. While some define poverty primarily in economic terms,
others consider social and political arrangements also to be intrinsic –
often manifested in a lack of dignity.
Theories
There are a number of theories about how desirable change in society
is best achieved. Such theories draw on a variety of social scientific
disciplines and approaches, and include historical theories such as:
International economic inequality
Global share of
wealth by wealth group, Credit Suisse, 2021
Global share of
wealth by wealth group, Credit Suisse, 2017
International development institutions and international organisations such as the UN promote the realisation of the fact that economic practices such as rapid globalisation and certain aspects of international capitalism
can lead to, and, allegedly, have led to an economic divide between
countries, sometimes called the North-South divide. Such organisations
often make it a goal and to help reduce these divides by encouraging
co-operation amongst the Global South and other practices and policies that can accomplish this.
International development can also cause inequality between
richer and poorer factions of one nation's society. For example, when
economic growth boosts development and industrialisation, it can create a class divide
by creating demand for more educated people in order to maintain
corporate and industrial profitability. Thus the popular demand for
education, which in turn drives the cost of education higher through the
principle of supply and demand,
as people would want to be part of the new economic elite. Higher costs
for education lead to a situation where only the people with enough
money to pay for education can receive sufficient education to qualify
for the better-paying jobs that mass-development brings about. This
restricts poorer people to lesser-paying jobs but technological
development makes some of these jobs obsolete (for example, by
introducing electronic machines to take over a job, such as creating a
series of machines such as lawn mowers to make people such as gardeners
obsolete). This leads to a situation where poorer people cannot improve
their lives as easily as they could have in a less developed society. That is partially why institutions such as the Center for Global Development are searching for "pro-poor" economic policies.
Dignity
Modern poverty reduction and development programmes often have
dignity as a central theme. Dignity is also a central theme of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the very first article of which starts with:
- "All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights."
The concept of dignity in development has been extensively explored
by many, and related to all of the development sectors. For example, in Development with Dignity Amit Bhaduri argues that full employment with dignity for all is both important and possible in India, while the UN Millennium Project's task force on Water and Sanitation links the sector directly to dignity in the report Health, Dignity and Development: What will it take?. The Asian Human Rights Commission released a statement in 2006 claiming that:
Human dignity is the true measure of human development.
— Asian Human Rights Commission & People's Vigilance Committee for Human Rights press release
Participation
The concept of participation is concerned with ensuring that the
intended beneficiaries of development projects and programmes are
themselves involved in the planning and execution of those projects and
programmes. This is considered important as it empowers the recipients
of development projects to influence and manage their own development –
thereby removing any culture of dependency. It is widely considered to be one of the most important concepts in modern development theory. The UN System Network on Rural Development and Food Security describes participation as:
one of the ends as well as one of the means of development
— UN System Network on Rural Development and Food Security
Local participants in development projects are often products of oral communities. This has led to efforts to design project planning and organizational development methods, such as participatory rural appraisal, which are accessible to non-literate people.
Appropriateness
The concept of something being appropriate is concerned with ensuring
that a development project or programme is of the correct scale and
technical level, and is culturally and socially suitable for its
beneficiaries. This should not be confused with ensuring something is
low-technology, cheap or basic – a project is appropriate if it is
acceptable to its recipients and owners, economically affordable and
sustainable in the context in which it is executed.
For example, in a rural sub-Saharan community it may not be
appropriate to provide a chlorinated and pumped water system because it
cannot be maintained or controlled adequately – simple hand pumps may be
better; while in a big city in the same country it would be
inappropriate to provide water with hand pumps, and the chlorinated
system would be the correct response.
The economist E. F. Schumacher championed the cause of appropriate technology
and founded the organization ITDG (Intermediate Technology Design
Group), which develops and provides appropriate technologies for
development (ITDG has now been renamed Practical Action).
The concept of right-financing has been developed to reflect the
need for public and private financial support systems that foster and
enable development, rather than hinder it.
Sustainable development
Sustainable business practices lead to economic growth and empowerment for farming communities in northern Uganda.
Capacity building
Capacity building
(or capacity development, capacity strengthening) is the improvement in
an individual's or organization's facility (or capability) "to produce,
perform or deploy". The terms capacity building and capacity development have often been used interchangeably, although a publication by OECD-DAC stated in 2006 that capacity development was the preferable term. Since the 1950s, international organizations, governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and communities use the concept of capacity building as part of "social and economic development" in national and subnational plans. The United Nations Development Programme defines itself by "capacity development" in the sense of "'how UNDP works" to fulfill its mission. The UN system applies it in almost every sector, including several of the Sustainable Development Goals to be achieved by 2030. For example, the Sustainable Development Goal 17 advocates for enhanced international support for capacity building in developing countries to support national plans to implement the 2030 Agenda.
Under the codification of international development law, capacity
building is a "cross cutting modality of international intervention". It
often overlaps or is part of interventions in
public administration reform,
good governance and education in line sectors of
public services.
Rights-based approach
Rights-based approach to development has been adopted by many nongovernmental organizations and the United Nations
as the new approach to international development. Rights-based approach
combines many different concepts of international development, such as capacity building, human rights, participation, and sustainability.
The goal of the rights-based approach to development is to empower the
rights-holders, or the group that does not exercise full rights, and
strengthen the capacity of the duty-bearers, or the institution or
government obligated to fill these rights.
Practice
Measurement
The judging of how developed a country or a community is highly
subjective, often highly controversial, and very important in judging
what further development is necessary or desirable.
There are many different measures of human development, many of them related to the different sectors above. Some of them are:
An interesting way of seeing development is through modernization.
This includes electronification of households and increases in phone
plans. This does not accurately convey social development although it is
hard to precisely measure, and institutions differ greatly in their
methods.
This goes into the debate on whether economic growth causes social
growth or vice versa. Indicators of social change can be used to
complement economic factors as indicators of development and in
formulating development policies.
In a multi-country review of development progress, improved
outcomes on these measures has generally been found to be driven by a
combination of smart leadership, policies, institutions, and social
networks, according to the Overseas Development Institute.
Migration and remittance
Migration has throughout history also led to significant
international development. As people move, their culture, knowledge,
skills and technologies move with them. Migrants' ties with their past
homes and communities lead to international relationships and further
flows of goods, capital and knowledge. The value of remittances sent home by migrants in modern times is much greater than the total in international aid given.
Sectors
International
development and disaster relief are both often grouped into sectors,
which correlate with the major themes of international development (and
with the Millennium Development Goals – which are included in the
descriptions below). There is no clearly defined list of sectors, but
some of the more established and universally accepted sectors are
further explored here. The sectors are highly interlinked, illustrating
the complexity of the problems they seek to deal with.
Water and sanitation
In development, this is the provision of water and sanitation (toilets, bathing facilities, a healthy environment) of sufficient quantity and quality to supply an acceptable standard of living.
This is different from a relief response, where it is the provision of
water and sanitation in sufficient quantity and quality to maintain
life.
The provision of water and sanitation is an engineering challenge, as well as a societal and political challenge as it includes education and behaviour change elements and is closely connected with shelter, politics and human rights.
The seventh Millennium Development Goal was to ensure environmental sustainability, including reducing by half the proportion of people without sustainable access to safe drinking water and achieving significant improvement in lives of at least 100 million slum dwellers, by 2020. UN-Water, a body of 26 UN agencies that work on water issues, is responsible for the triennial UN World Water Development Report which monitors progress towards the Millennium Development Goals
related to water. The World Water Assessment Programme, which produces
the Report, has articulated how eight of the MDGs are linked to water
resources.
Health
This is provision of access to quality healthcare
to the population in an efficient and consistent manner and according
to their needs. The standard and level of provision that is acceptable
or appropriate depends on many factors and is highly specific to country
and location. For example, in a large city (whether in a 'developing' country or not), it is appropriate and often practical to provide a high standard hospital which can offer a full range of treatments; in a remote rural community it may be more appropriate and practical to provide a visiting healthworker on a periodic basis, possibly with a rural clinic serving several different communities.
The provision of access to healthcare is both an engineering challenge as it requires infrastructure
such as hospitals and transport systems and an education challenge as
it requires qualified healthworkers and educated consumers.
The fourth Millennium Development Goal is to reduce by two thirds the mortality rate among children under five.
The fifth Millennium Development Goal is to reduce by three quarters the maternal mortality ratio.
The sixth Millennium Development Goal is to halt and begin to reverse the spread of HIV/AIDS and to halt and begin to reverse the incidence of malaria and other major diseases.
Reaching these goals is also a management challenge. Health
services need to make the best use of limited resources while providing
the same quality of care to every man, woman and child everywhere.
Achieving this level of services requires innovation, quality
improvement and expansion of public health services and programs. The
main goal is to make public health truly public.
Examples of organizations working in health are:
Education
The provision of education often focuses on providing free primary level education, but also covers secondary and higher education.
A lack of access to education is one of the primary limits on human
development, and is related closely to every one of the other sectors.
Almost every development project includes an aspect of education as
development by its very nature requires a change in the way people live.
The second Millennium Development Goal is to Provide universal primary education.
The provision of education is itself an education challenge, as it requires qualified teachers
who must be trained in higher education institutions. However, donors
are unwilling to provide support to higher education because their
policies now target the MDG.
The result is that students are not educated by qualified professionals
and worse, when they graduate from primary school they are inducted
into a secondary school system that is not able to accommodate them.
Shelter
The provision of appropriate shelter is concerned with providing suitable housing for families and communities. It is highly specific to context of culture, location, climate
and other factors. In development, it is concerned with providing
housing of an appropriate quality and type to accommodate people in the
long term. This is distinct from shelter in relief, which is concerned
with providing sufficient shelter to maintain life.
Examples of organisations specialising in shelter are:
Human rights
The provision of human rights is concerned with ensuring that all people everywhere receive the rights conferred on them by International human rights instruments. There are many of these, but the most important for international development are:
Human rights covers a huge range of topics. Some of those more
relevant to international development projects include rights associated
with gender equality, justice, employment, social welfare and culture.
The third Millennium Development Goal was to "promote gender
equality and empower women" by "eliminating gender disparity in primary
and secondary education preferably by 2005, and at all levels by 2015."
Accomplishing this goal could assist in the achievement of five
of the other eight Millennium Development Goals. Goals 1–6 are in direct
correlation with the status of women in the communities of problem
countries such as The Democratic Republic of Congo, Sub-Saharan Africa
and many of the developing nations. The low social stature of a woman
inhibits her abilities to truly impact her community in astonishing
ways. Noting the relationship between mother and offspring, Goals 1, 4
and 5 are ones to feel the wrath of poor social status. An unhealthy
mother simply cannot bear a healthy child, let alone nurse a sickly one
back to health, without access to adequate nutrition. A mother
characteristically takes most of the care of a child, therefore must
have the resources available to not only support herself but another
human as well. Without these resources, if she has not already succumbed
to birthing complications, a woman cannot survive the perils of poverty
and hunger and support her child simultaneously.
In a different spectrum of societal norms the Goals 2 and 6 are
being threatened by an age old privilege. Historically females have been
refused education in pardon of males, resulting in lesser opportunity
to thrive economically. Giving women equal access to an adequate
education brings the global community steps closer to achieving
universal primary education. Along with this education will come proper
spread of knowledge regarding safe practices in disease avoidance. Women
are increasingly falling victim to HIV/AIDS for reasons easily evaded.
Increasing the availability of a proper education to women will be
remarkably beneficial on a variety of fronts. To promote gender equality
is to promote progress towards global development.
Livelihoods
This is concerned with ensuring that all people are able to make a
living for themselves and provide themselves with an adequate standard
of living, without compromising their human rights and while maintaining
dignity.
The first Millennium Development Goal is to reduce by half the proportion of people living on less than a dollar a day and reduce by half the proportion of people who suffer from hunger.
The concept of livelihoods is directly drawn from the Sustainable
Livelihoods Approach (SLA) to international development. The approach
and subsequent practical framework is credited to Robert Chambers, who,
writing from the mid-1980s and onward, was interested in fostering
efficiency in development cooperation. The approach was later developed
and utilized by the United Kingdom's Department for International
Development (DFID). The approach is considered to be more comprehensive
than previous theories and methodology of "conventional" development
initiatives. The core concepts include: taking a holistic view, building
on community and individual strengths, focusing on linking both macro
and micro-level thinking, sustainability, and maintaining a dynamic and
ever-evolving framework.
Finance
Several organisations and initiatives exist which are concerned with
providing financial systems and frameworks which allow people to
organise or purchase services, items or projects for their own
development.
The 2006 Nobel Peace Prize was awarded jointly to Muhammad Yunus and the Grameen Bank, which he founded, for their work in providing microcredit to the poor.
Concerns
The terms "developed" and "developing" (or "underdeveloped") have proven problematic in forming policy as they ignore issues of wealth distribution and the lingering effects of colonialism. Some theorists see development efforts as fundamentally neo-colonial, in which a wealthier nation forces its industrial and economic structure on a poorer nation, which will then become a consumer of the developed nation's goods and services. Post-developmentalists, for example, see development as a form of Western cultural imperialism
that hurts the people of poor countries and endangers the environment
to such an extent that they suggest rejection of development altogether.
Other scholars have sought to widen the notion of "developing" to encompass all countries,
as even the wealthiest and most industrialised of countries face
problems of social exclusion and inequality. This points to the
widespread critiques of the language of development practice, from the
Cold War-era terminology of "Third World" to the subsequent bifurcation
of "developed" and "developing" countries. The phrases "Global North"
and "Global South"
are similarly imprecise (particularly from a geographical standpoint,
as Australia, for instance, is considered part of the Global North).
Other terms currently in use as synonyms for "Global South" include
"majority world"
and "low- and middle-income countries". The latter term allows for
greater specificity, for instance in differentiating between
lower-middle and upper-middle-income countries, but it has the downside
of overemphasising the economic aspects of development at the expense of
social, political and cultural rights and freedoms. These linguistic
issues reflect conceptual tensions related to the framing of
development.
History
Although international relations and international trade
have existed for thousands of years, it is only in the past century
that international development theory emerged as a separate body of
ideas. More specifically, it has been suggested that 'the theory and practice of development is inherently technocratic, and remains rooted in the high modernist period of political thought that existed in the immediate aftermath of the Second World War'.
Throughout the 20th century, before the concept of international
development became a common word, four aspects were used to describe the
idea:
- political and economic liberalism, and the significance of "free markets"
- social evolution in extremely hierarchical environment
- Marxist critiques of class and imperialism
- anti-colonial take on cultural differences and national self-determination
After World War 2
The second half of the 20th century has been called the 'era of development'. The origins of this era have been attributed to
- the need for reconstruction in the immediate aftermath of World War II
- the evolution of colonialism or "colonization" into globalization and the establishment of new free trade policies between so-called 'developed' and 'underdeveloped' nations
- the start of the Cold War and the desire of the United States and its allies to prevent the Third World from drifting towards communism
International Development in its very meaning is geared towards
colonies that gained independence. The governance of the newly
independent states should be constructed so that the inhabitants enjoy
freedom from poverty, hunger, and insecurity.
It has been argued that this era was launched on January 20, 1949, when Harry S. Truman made these remarks in his inaugural address
We must embark on a bold new
program for making the benefits of our scientific advances and
industrial progress available for the improvement and growth of
underdeveloped areas. The old imperialism—exploitation for foreign
profit—has no place in our plans. What we envisage is a program of
development based on the concept of democratic fair dealing.
— Harry S. Truman, 1949
Before this date, however, the United States had already taken a leading role in the creation of the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (now part of the World Bank Group) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), both established in 1944, and in the United Nations in 1945.
The launch of the Marshall Plan
was another important step in setting the agenda for international
development, combining humanitarian goals with the creation of a
political and economic bloc in Europe that was allied to the U.S. This
agenda was given conceptual support during the 1950s in the form of modernization theory espoused by Walt Rostow and other American economists.
The changes in the 'developed' world's approach to international
development were further necessitated by the gradual collapse of Western
Europe's empires over the next decades; now independent ex-colonies no
longer received support in return for their subordinate role.
By the late 1960s, dependency theory arose analysing the evolving relationship between the West and the Third World. In the 1970s and early 1980s, the modernists at the World Bank and IMF adopted the neoliberal ideas of economists such as Milton Friedman or Béla Balassa, which were implemented in the form of structural adjustment programs, while their opponents were promoting various 'bottom-up' approaches, ranging from civil disobedience and critical consciousness to appropriate technology and Rapid Rural Appraisal.
In response, various parts of the UN system led a counter movement, which in the long run has proved to be successful. They were led initially by the International Labour Organization (ILO), influenced by Paul Streeten, then by United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF). Then United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) put forward the concept of Human Development, thanks to Mahboub ul Haq and Amartya Sen, thus changing the nature of the development dialogue to focus on human needs and capabilities.
By the 1990s, there were some writers for whom development theory had reached an impasse and some academics were "imagining a postdevelopment era".
The Cold War had ended, capitalism had become the dominant mode of
social organization, and UN statistics showed that living standards
around the world had improved over the past 40 years. Nevertheless, a large portion of the world's population were still living in poverty, their governments were crippled by debt and concerns about the environmental impact of globalization were rising.
In response to the impasse, the rhetoric of development is now focusing on the issue of poverty, with the metanarrative of modernization being replaced by shorter-term vision embodied by the Millennium Development Goals and the Human Development approach. At the same time, some development agencies are exploring opportunities for public-private partnerships and promoting the idea of Corporate social responsibility with the apparent aim of integrating international development with the process of economic globalization.
The critics have suggested that this integration has always been part of the underlying agenda of development. They argue that poverty can be equated with powerlessness and that the way to overcome poverty is through emancipatory social movements and civil society, not paternalistic aid programmes or corporate charity.
While some critics have been debating the end of development others have predicted a development revival as part of the War on Terrorism.
To date, however, there is limited evidence to support the notion that
aid budgets are being used to counter Islamic fundamentalism in the same
way that they were used 40 years ago to counter communism.
 Sikkim (became a state within the Republic of India in 1975)
Sikkim (became a state within the Republic of India in 1975) Botswana (graduated from LDC status in December 1994)
Botswana (graduated from LDC status in December 1994) Cape Verde (graduated in December 2007)
Cape Verde (graduated in December 2007) Maldives (graduated in January 2011)
Maldives (graduated in January 2011) Samoa (graduated in January 2014)
Samoa (graduated in January 2014) Equatorial Guinea (graduated in June 2017)
Equatorial Guinea (graduated in June 2017) Vanuatu (graduated in December 2020)
Vanuatu (graduated in December 2020)