
Green infrastructure or blue-green infrastructure refers to a network that provides the “ingredients” for solving urban and climatic challenges by building with nature. The main components of this approach include stormwater management, climate adaptation, the reduction of heat stress, increasing biodiversity, food production, better air quality, sustainable energy production, clean water, and healthy soils, as well as more anthropocentric functions, such as increased quality of life through recreation and the provision of shade and shelter in and around towns and cities. Green infrastructure also serves to provide an ecological framework for social, economic, and environmental health of the surroundings. More recently scholars and activists have also called for green infrastructure that promotes social inclusion and equity rather than reinforcing pre-existing structures of unequal access to nature-based services.
Green infrastructure is considered a subset of "Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure", which is defined in standards such as SuRe, the Standard for Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure. However, green infrastructure can also mean "low-carbon infrastructure" such as renewable energy infrastructure and public transportation systems (See "low-carbon infrastructure"). Blue-green infrastructure can also be a component of "sustainable drainage systems" or "sustainable urban drainage systems" (SuDS or SUDS) designed to manage water quantity and quality, while providing improvements to biodiversity and amenity.
Introduction
Green infrastructure

Nature can be used to provide important services for communities by protecting them against flooding or excessive heat, or helping to improve air, soil and water quality. When nature is harnessed by people and used as an infrastructural system it is called “green infrastructure”. Many such efforts take as their model prairies, where absorbent soil prevents runoff and vegetation filters out pollutants. Green infrastructure occurs at all scales. It is most often associated with green stormwater management systems, which are smart and cost-effective. However, green infrastructure acts as a supplemental component to other related concepts, and ultimately provides an ecological framework for social, economic, and environmental health of the surroundings.
Blue infrastructure
"Blue infrastructure" refers to urban infrastructure relating to water. Blue infrastructure is commonly associated with green infrastructure in urban environments and may be referred to as "blue-green infrastructure" when being viewed in combination. Rivers, streams, ponds, and lakes may exist as natural features within cities, or be added to an urban environment as an aspect of its design. Coastal urban developments may also utilize pre-existing features of the coastline specifically employed in their design. Harbours, quays, piers, and other extensions of the urban environment are also often added to capture benefits associated with the marine environment. Blue infrastructure can support unique aquatic biodiversity in urban areas, including aquatic insects, amphibians, and water birds. There may considerable co-benefits to the health and wellbeing of populations with access to blue spaces in the urban context. Accessible blue infrastructure in urban areas is also referred as to blue spaces.
Terminology
Ideas for green urban structures began in the 1870s with concepts of urban farming and garden allotments. Alternative terminology includes stormwater best management practices, source controls, and low impact development (LID) practices.
Green infrastructure concepts originated in mid-1980s proposals for best management practices that would achieve more holistic stormwater quantity management goals for runoff volume reduction, erosion prevention, and aquifer recharge. In 1987, amendments to the U.S. Clean Water Act introduced new provisions for management of diffuse pollutant sources from urban land uses, establishing the regulatory need for practices that unlike conventional drainage infrastructure managed runoff "at source." The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) published its initial regulations for municipal separate storm sewer systems ("MS4") in 1990, requiring large MS4s to develop stormwater pollution prevention plans and implement "source control practices". EPA's 1993 handbook, Urban Runoff Pollution Prevention and Control Planning, identified best management practices to consider in such plans, including vegetative controls, filtration practices and infiltration practices (trenches, porous pavement). Regulations covering smaller municipalities were published in 1999. MS4s serve over 80% of the US population and provide drainage for 4% of the land area.
Green infrastructure is a concept that highlights the importance of the natural environment in decisions about land-use planning. However, the term does not have a widely recognized definition. Also known as “blue-green infrastructure”, or “green-blue urban grids” the terms are used by many design-, conservation- and planning-related disciplines and commonly feature stormwater management, climate adaptation and multifunctional green space.
The term "green infrastructure" is sometimes expanded to "multifunctional" green infrastructure. Multifunctionality in this context refers to the integration and interaction of different functions or activities on the same piece of land.
The EPA extended the concept of “green infrastructure” to apply to the management of stormwater runoff at the local level through the use of natural systems, or engineered systems that mimic natural systems, to treat polluted runoff. This use of the term "green infrastructure" to refer to urban "green" best management practices contributes to the overall health of natural ecosystems, even though it is not central to the larger concept.
However, it is apparent that the term “blue-green infrastructure” is applied in an urban context and places a greater emphasis on the management of stormwater as an integral part of creating a sustainable, multifunctional urban environment. At the building level, the term "blue-green architecture" is used, which implements the same principles on a smaller scale. The focus here is on building greening with water management from alternative water resources such as grey water and rainwater.
History
Green Infrastructure as a term did not appear until the early 1990s, although ideas of Green Infrastructure had been used long before that. The first coined use of the term was seen in a 1994 report by Buddy MacKay, chair of the Florida Greenways Commission, to Florida governor Lawton Chiles about a Green Infrastructure project undertaken in 1991: Florida Greenways Project. MacKay states, "Just as we carefully plan the infrastructure our communities need to support the people who live there—the roads, water and electricity—so must we begin to plan and manage Florida’s green infrastructure”.
Ancient China
Chinese literary gardens are an example of a sustainable lawn that showcased natural beauty in suburban areas. These gardens, dating back to the Shang Dynasty (1600–1046 BC), were designed to allow native plant species to thrive in their natural conditions and appear untouched by humans. This created ecological havens within the city.
8th Century BC - 1st Century BC
Greece was an early adopter of the concept of green Infrastructure with the invention of Greek agora. Agoras were meeting spaces that were built for social conversations and allowed Greeks to converse in public. Many were built across Greece, and some incorporated nature as a design aspect, giving nature a space among the public.
5th century - 15th century
A common urban habitat, the lawn, consists of short grass and sometimes herbaceous plants. While modern artificial lawns have been connected to a negative environmental impact, lawns in the past have been more sustainable, and they promoted biodiversity and the growth of native plants. These historical lawns are impacting lawn design today to create more sustainable ‘alternative lawns’.
In Medieval Europe, lawns rich with flowers and herbaceous plants known as ‘flower meads’ are a good example of a more sustainable lawn. Since then, this idea has been used. In the Edwardian Era, lawns full of thyme, whose flowers attracted insects and pollinators, created biodiversity. A 20th century take on this lawn, the ‘enamelled mead’, has been used in England, and has the purpose of both aesthetics and for stormwater management.
During the height of the Renaissance, public areas became more common in new cities and infrastructure. These areas were carefully selected and would often be urban parks and gardens for the public to converse and relax at. Other than social uses, urban parks and gardens were used to improve the aesthetic of the urban environment they were present in. Urban spaces had environmental uses for the implementation of fresh air and reduced urban heating.
17th Century – 18th Century
Green Infrastructure can be traced as far back as the 17th century in European society beginning in France. France used the presence of nature to provide social and spatial organization to their towns. Originally, nature in cities was used to provide social areas to interact, and plants were grown in these spaces to provide food in close proximity to the inhabitants. In this period, Large open spaces were used to provide a calm setting that could give "sites of power with sites of sanctity" across France. These sites were used by the French elites to bring rural country town house beauty to their new urban houses in a showcase of power and elaborate display of wealth. The French implemented many different types of infrastructure throughout the 17th century that involved incorporating nature in some shape or form. Another example would be the use of promenades that were used by the French elites to flee the unhealthy living conditions of the cities and to avoid the filthy public areas available to the common folks. These areas were lush gardens that had a wide variety of vegetation and foliage that kept the air clean for the wealthy while allowing them to relax away from the poorer members of French society. Again, Mathis goes on to state, "The first cours [or promenades] were established in the capital at the instigation of Marie de Medici: the Mail de l'Arsenal (1604) and above all the Allée du Cours-la-Reine (1616), 1300 mètres long and lined with elms, running along the Seine, from the Tuileries Garden to the high ground of Chaillot," establishing the use of nature as a symbol of power and achievement amongst French royalty and the common people at the time.
Keeping and making cities green were at the forefront for city planners in France. They often incorporated design elements blending urbanism and nature, forming a relationship that showcased how the French grew alongside nature and often made it a key aspect of their expansion.
In 18th Century France, Citizens were able to request to have old and battered city walls destroyed to make room for new gardens, vegetation sites, and green walkways. This opened up new areas to the city landscape and incorporated greenery into the new areas where the walls were torn down. Along with this, the town hall as well as the city center were elaborately decorated with different types of vegetation and trees, especially rare and unique species that had been brought from other countries. Mathis goes on to state, "A French-style garden is linked to the town hall to make the view of it more sublime", showing the use of foliage as a way to impress and beautify French cities.
19th Century
In 1847, a speech by George Perkins Marsh called attention to negative human impacts such as deforestation. Marsh later wrote Man and Nature in 1864 based on his idea for conserving forests. Around the same time, Henry David Thoreau's Walden of 1860 discussed preservation of nature and applied these ideas to urban planning saying, “I think every town should have a park,” and stated the “importance of preserving some portions of nature herself unimpaired.” Frederick Law Olmsted, a landscape architect, agreed with these ideas and planned many parks, areas of preserved land, and scenic roads, and in 1887, The Emerald Necklace of Boston, MA. The Emerald Necklace is a system of public parks linked by parkways that serves as a home to diverse wildlife and provides environmental benefits such as flood protection and water storage.
In Europe, Ebenezer Howard led the garden city movement to balance development with nature. He planned agricultural greenbelts and wide, radiating boulevards surrounded by trees and shrubbery for Victoria, England. One of Howard's concepts was of the "marriage of town and country" to promote sustainable relationships between human society and nature through the planning of garden cities.
The US government became more involved in conservation and land preservation in the late 1800s. This was seen in the 1864 legislation to preserve the Yosemite Valley as a California public park, and 8 years later, the United States’ first national park.
20th Century
Many industrial leaders in the 19th century had the goal of increasing worker's quality of life through quality sanitation and outdoor activity, which would in turn create increased productivity in the workforce. These ideas carried into the 20th century where efforts in green infrastructure were seen in industrial parks, integrated landscaping, and suburban gardens.
The Anaconda Copper Mining Company was responsible for environmental damage in Montana, but a refinery in Great Falls saw this impact and used the surrounding land to create a green open space that was also used for recreation. This natural haven included a golf course, flower beds, picnic areas, a lily pond, and pedestrian paths.
The role of water: blue spaces and blue infrastructure

Proximity and access to water have been key factors in human settlement through history. Water, along with the spaces around it, create a potential for transport, trade, and power generation. They also provide the human population with resources like recreation and tourism in addition to drinking water and food. Many of the world's largest cities are located near water sources, and networks of urban "blue infrastructure", such as canals, harbors and so forth, have been constructed to capture the benefits and minimize risks. Globally, cities are facing severe water uncertainties such as floods, droughts, and upstream activities on trans-boundary rivers. The increasing pressure, intensity, and speed of urbanization has led to the disappearance of any visible form of water infrastructure in most cities. Urban coastal populations are growing, and many cities have seen an extensive post-industrial transformation of canals, riversides, docks, etc. following changes in global trading patterns. The potential implications of such waterside regeneration in terms of public health have only recently been scientifically investigated. A systematic review conducted in 2017 found consistent evidence of positive associations between exposure of people to blue space and mental health and physical activity.
One-fifth of the world's population, 1.2 billion people, live in areas of water scarcity. Climate change and water-related disasters will place increasing demands on urban systems and will result in increased migration to urban areas. Cities require a very large input of freshwater and in turn have a huge impact on freshwater systems. Urban and industrial water use is projected to double by 2050.
In 2010 the United Nations declared that access to clean water and sanitation is a human right. New solutions for improving the sustainability of cities are being explored. Good urban water management is complex and requires not only water and wastewater infrastructure, but also pollution control and flood prevention. It requires coordination across many sectors, and between different local authorities and changes in governance, that lead to more sustainable and equitable use of urban water resources.
Types of green infrastructure
Urban forests
Urban forests are forests located in cities. They are an important component of urban green infrastructure systems. Urban forests use appropriate tree and vegetation species, instead of noxious and invasive kinds, which reduce the need of maintenance and irrigation. In addition, native species also provide aesthetic value while reducing cost. Diversity of plant species should also be considered in design of urban forests to avoid monocultures; this makes the urban forests more durable and resilient to pests and other harms.
- Benefits
- Energy use: According to a study conducted by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Sacramento Municipal Utility District, it was found that strategically located shade trees planted around houses can provide up to 47% energy savings for heating and cooling.
- Urban heat island mitigation: Maximum air temperature for tree groves were found to be lower than that of open areas without trees. This is contributed to by the principal processes of evaporative cooling from transpiration, radiation interception from the shading effect of canopies, and increasing urban surface roughness to enhance its convective cooling efficiency.
- Water management: Urban forests helps with city water management on diverting storm water from water channels. Trees intercept a large amount of rainfall that hit them.
- Property values: In response to fluctuating demand from residents wanting increased amounts of urban greenery, increasing vegetation like tree cover within urban areas can result in the surrounding areas of real estate to increase in value.
- Public health: Urban greenery can also improve mental health and well-being. Creating urban forests affects public health in many ways. Urban heat islands are created by the condensation of heat due to the materials and infrastructure used in metropolitan areas, which can negatively impact human health. Urban forests provide natural shading structures at a fraction of the cost of artificial shading structures and it counters the negative health impacts of increasing global temperatures. Beyond countering the negative impacts of man-made infrastructure, green infrastructure has the potential to enhance existing ecosystems and make them more stable, which has been historically done in traditional Japanese agriculture. Green infrastructure in an urbanized area can help restore and enhance the resiliency of an ecosystem to natural disturbances and disasters that disrupt the lives of residents. Building new urban forests in an existing metropolitan area creates new labor jobs that do not require a high level of education, which can decrease unemployment in the working class which benefits society. Furthermore, green infrastructure helps states to implement the principles of the 1992 Rio Declaration on Environment and Development that was designed to alleviate the social and economic consequences of environmental degradation.
Constructed wetlands
Constructed wetlands are manmade wetlands, which work as a bio-filtration system. They contain wetland vegetation and are mostly built on uplands and floodplains. Constructed wetlands are built this way to avoid connection or damage to natural wetlands and other aquatic resources. There are two main categories of constructed wetlands: subsurface flow system and free water surface system. Proper planning and operating can help avoid possible harm done to the wetlands, which are caused by alteration of natural hydrology and introduction of invasive species.
- Benefits
- Water efficiency: Constructed wetlands try to replicate natural wetland ecosystems. They are built to improve water efficiency and water quality. They also create wildlife habitats by using natural processes of plants, soils, and associated microorganisms. In these types of wetlands, vegetation can trap parts of suspended solids and slow down water flow; the microorganisms that live there process some other pollutants.
- Cost-effective: Wetlands have low operating and maintenance costs. They can also help with fluctuating water levels. Aesthetically, constructed wetlands are able to add greenery to its surrounding environment. It also helps to reduce unpleasing odors of wastewater.[60][61]
Green and blue roofs
Green roofs improve air and water quality while reducing energy cost. The implementation of green roofs in some regions have correlated with increased albedo, providing slightly cooler temperatures and thus, lower energy consumption. The plants and soil provide more green space and insulation on roofs. Green and blue roofs also help reducing city runoff by retaining rainfall providing a potential solution for the stormwater management in highly concentrated urban areas. The social benefit of green roofs is the rooftop agriculture for the residents.
Green roofs also sequester rain and carbon pollution. Forty to eighty percent of the total volume of rain that falls on green roofs are able to be reserved.[64] The water released from the roofs flow at a slow pace, reducing the amount of runoff entering the watershed at once.
Blue roofs, not technically being green infrastructure, collect and store rainfall, reducing the inrush of runoff water into sewer systems. Blue roofs use detention ponds, or detention basins, for collecting the rainfall before it gets drained into waterways and sewers at a controlled rate. As well as saving energy by reducing cooling expenses, blue roofs reduce the urban heat island effect when coupled with reflective roofing material.
Rain gardens
Rain gardens are a form of stormwater management using water capture. Rain gardens are shallow depressed areas in the landscape, planted with shrubs and plants that are used to collect rainwater from roofs or pavement and allows for the stormwater to slowly infiltrate into the ground.

Ubiquitous lawn grass is not a solution for controlling runoff, so an alternative is required to reduce urban and suburban first flush (highly toxic) runoff and to slow the water down for infiltration. In residential applications, water runoff can be reduced by 30% with the use of rain gardens in the homeowner's yard. A minimum size of 150 sq. ft. up to a range of 300 sq. ft. is the usual size considered for a private property residence. The cost per square foot is about $5–$25, depending on the type of plants you use and the slope of the property. Native trees, shrubs, and herbaceous perennials of the wetland and riparian zones being the most useful for runoff detoxification.
Downspout disconnection
Downspout disconnection is a form of green infrastructure that separates roof downspouts from the sewer system and redirects roof water runoff into permeable surfaces. It can be used for storing stormwater or allowing the water to penetrate the ground. Downspout disconnection is especially beneficial in cities with combined sewer systems. With high volumes of rain, downspouts on buildings can send 12 gallons of water a minute into the sewer system, which increases the risk of basement backups and sewer overflows. In attempts to reduce the amount of rainwater that enters the combined sewer systems, agencies such as the Milwaukee Metropolitan Sewerage District amended regulations that require downspout disconnection at residential areas.
Bioswales
Bioswales are stormwater runoff systems providing an alternative to traditional storm sewers. Much like rain gardens, bioswales are vegetated or mulched channels commonly placed in long narrow spaces in urban areas. They absorb flows or carry stormwater runoff from heavy rains into sewer channels or directly to surface waters. Vegetated bioswales infiltrate, slow down, and filter stormwater flows that are most beneficial along streets and parking lots.
Green alleys
The Trust for Public Land is working in partnership with the City of Los Angeles' Community Redevelopment Agency, Bureau of Sanitation, the University of Southern California's Center for Sustainable Cities, and Jefferson High School by converting the existing 900 miles of alleys in the city to green alleys. The concept is to re-engineer existing alleyways to reflect more light to mitigate heat island effect, capture storm water, and make the space beautiful and usable by the neighboring communities. The first alley, completed in 2015, saved more than 750,000 gallons in its first year. The Green alleys will provide open space on top of these ecological benefits, converting spaces which used to feel unsafe, or used for dumping into a playground, and walking/biking corridor.
Green school yards
The Trust for Public Land has completed 183 green school yards across the 5 boroughs in New York. Existing asphalt school yards are converted to a more vibrant and exciting place while also incorporating infrastructure to capture and store rainwater: rain garden, rain barrel, tree groves with pervious pavers, and an artificial field with a turf base. The children are engaged in the design process, lending to a sense of ownership and encourages children to take better care of their school yard. Success in New York has allowed other cities like Philadelphia and Oakland to also convert to green school yards.
Low-impact development
Low-impact development (also referred to as green stormwater infrastructure) are systems and practices that use or mimic natural processes that result in the infiltration, evapotranspiration or use of stormwater in order to protect water quality and associated aquatic habitat. LID practices aim to preserve, restore and create green space using soils, vegetation, and rainwater harvest techniques. It is an approach to land development (or re-development) that works with nature to manage stormwater as close to its source as possible. Many low impact development tools integrate vegetation or the existing soil to reduce runoff and let rainfall enter the natural water cycle.
Planning approach
The Green Infrastructure approach analyses the natural environment in a way that highlights its function and subsequently seeks to put in place, through regulatory or planning policy, mechanisms that safeguard critical natural areas. Where life support functions are found to be lacking, plans may propose how these can be put in place through landscaped and/or engineered improvements.
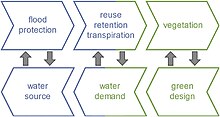
Within an urban context, this can be applied to re-introducing natural waterways and making a city self-sustaining particularly with regard to water, for example, to harvest water locally, recycle it, re-use it and integrate stormwater management into everyday infrastructure.
The multi-functionality of this approach is key to the efficient and sustainable use of land, especially in a compact and bustling country such as England where pressures on land are particularly acute. An example might be an urban edge river floodplain which provides a repository for flood waters, acts as a nature reserve, provides a recreational green space and could also be productively farmed (probably through grazing). There is growing evidence that the natural environment also has a positive effect on human health.
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, Green Infrastructure planning is increasingly recognised as a valuable approach for spatial planning and is now seen in national, regional and local planning and policy documents and strategies, for example in the Milton Keynes and South Midlands Growth area.
In 2009, guidance on green infrastructure planning was published by Natural England. This guidance promotes the importance of green infrastructure in 'place-making', i.e. in recognizing and maintaining the character of a particular location, especially where new developments are planned.
In North West England the former Regional Spatial Strategy had a specific Green Infrastructure Policy (EM3 – Green Infrastructure) as well as other references to the concept in other land use development policies (e.g. DP6). The policy was supported by the North West Green Infrastructure Guide. The Green Infrastructure Think Tank (GrITT) provides the support for policy development in the region and manages the web site that acts as a repository for information on Green Infrastructure.
The Natural Economy Northwest programme has supported a number of projects, commissioned by The Mersey Forest to develop the evidence base for green infrastructure in the region. In particular work has been undertaken to look at the economic value of green infrastructure, the linkage between grey and green infrastructure and also to identify areas where green infrastructure may play critical role in helping to overcome issues such as risks of flood or poor air quality.
In March 2011, a prototype Green Infrastructure Valuation Toolkit was launched. The Toolkit is available under a Creative Commons license, and provides a range of tools that provide economic valuation of green infrastructure interventions. The toolkit has been trialled in a number of areas and strategies, including the Liverpool Green Infrastructure Strategy.
In 2012, the Greater London Authority published the All London Green Grid Supplementary Planning Guidance (ALGG SPG) which proposes an integrated network of green and open spaces together with the Blue Ribbon Network of rivers and waterways. The ALGG SPG aims to promote the concept of green infrastructure, and increase its delivery by boroughs, developers, and communities, to benefit areas such as sustainable travel, flood management, healthy living and the economic and social uplift these support.
Green Infrastructure is being promoted as an effective and efficient response to projected climate change.
Green Infrastructure may include geodiversity objectives.
United States


Green infrastructure programs managed by EPA and partner organizations are intended to improve water quality generally through more extensive management of stormwater runoff. The practices are expected to reduce stress on traditional water drainage infrastructure--storm sewers and combined sewers—which are typically extensive networks of underground pipes and/or surface water channels in U.S. cities, towns and suburban areas. Improved stormwater management is expected to reduce the frequency of combined sewer overflows and sanitary sewer overflows, reduce the impacts of urban flooding, and provide other environmental benefits.
Though green infrastructure is yet to become a mainstream practice, many US cities have initiated its implementation to comply with their MS4 permit requirements. For example, the City of Philadelphia has installed or supported a variety of retrofit projects in neighborhoods throughout the city. Installed improvements include:
- permeable pavements in parks, basketball courts and parking lots
- rain gardens and bioretention systems at schools and other public facilities
- constructed wetlands for management of stormwater runoff.
Some of these facilities reduce the volume of runoff entering the city's aging combined sewer system, and thereby reduce the extent of system overflows during rainstorms.
Another U.S. example is the State of Maryland's promotion of a program called "GreenPrint." GreenPrint Maryland is the first web-enabled map in the nation that shows the relative ecological importance of every parcel of land in the state. Combining color-coded maps, information layers, and aerial photography with public openness and transparency, Greenprint Maryland applies the best environmental science and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to the urgent work of preserving and protecting environmentally critical lands. A valuable new tool not only for making land conservation decisions today, but for building a broader and better informed public consensus for sustainable growth and land preservation decisions into the future. The program was established in 2001 with the objective to "preserve an extensive intertwined network of lands vital to the long-term protection of the State's natural resources, in concert with other Smart Growth initiatives."
In April 2011, EPA announced the Strategic Agenda to Protect Waters and Build More Livable Communities through Green Infrastructure and the selection of the first ten communities to be green infrastructure partners. The communities selected were: Austin, Texas; Chelsea, Massachusetts; the Northeast Ohio Regional Sewer District (Cleveland, Ohio); the City and County of Denver, Colorado; Jacksonville, Florida; Kansas City, Missouri; Los Angeles, California; Puyallup, Washington; Onondaga County and the City of Syracuse, New York; and Washington, D.C.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is also promoting green infrastructure as a means of managing urban flooding (also known as localized flooding).
Singapore
Since 2009, two editions of the ABC (Active, Beautiful, Clean) Waters Design Guidelines have been published by the Public Utilities Board, Singapore. The latest version (2011) contains planning and design considerations for the holistic integration of drains, canals and reservoirs with the surrounding environment. The Public Utilities Board encourages the various stakeholders — landowners, private developers to incorporate ABC Waters design features into their developments, and the community to embrace these infrastructures for recreational & educational purposes.
The main benefits outlined in the ABC Waters Concept include:
- Treating stormwater runoff closer to the source naturally, without the use of chemicals through the use of plants and soil media, so that cleaner water is discharged into waterways and eventually our reservoirs.
- Enhancing biodiversity and site aesthetics.
- Bringing people closer to water, and creating new recreational and community spaces for people to enjoy.
Other states

A 2012 paper by the Overseas Development Institute reviewed evidence of the economic impacts of green infrastructure in fragile states.
Upfront construction costs for GI were up to 8% higher than non-green infrastructure projects. Climate Finance was not adequately captured by Fragile states for GI investments, and governance issues may further hinder capability to take full advantage.
GI Investments needed strong government participation as well as institutional capacities and capabilities that fragile states may not possess. Potential poverty reduction includes improved agricultural yields and higher rural electrification rates, benefits that can be transmitted to other sectors of the economy not directly linked to the GI investment.
Whilst there are examples of GI investments creating new jobs in a number of sectors, it is unclear what the employment opportunities advantages are in respect to traditional infrastructure investments. The correct market conditions (i.e. labour regulations or energy demand) are also required in order to maximise employment creation opportunities.
Such factors that may not be fully exploited by fragile state governments lacking the capacity to do so. GI investments have a number of co-benefits including increased energy security and improved health outcomes, whilst a potential reduction of a country's vulnerability to the negative effects of climate change being arguably the most important co-benefit for such investments in a fragile state context.
There is some evidence that GI options are taken into consideration during project appraisal. Engagement mostly occurs in projects specifically designed with green goals, hence there is no data showing decision making that leads to a shift towards any green alternative. Comparisons of costs, co-benefits, poverty reduction benefits or employment creation benefits between the two typologies are also not evident.
Currently, an international standard for green infrastructure is developed: SuRe – The Standard for Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure is a global voluntary standard which integrates key criteria of sustainability and resilience into infrastructure development and upgrade. SuRe is developed by the Swiss Global Infrastructure Basel Foundation and the French bank Natixis as part of a multi-stakeholder process and will be compliant with ISEAL guidelines. The foundation has also developed the SuRe SmartScan, a simplified version of the SuRe Standard which serves as a self-assessment tool for infrastructure project developers. It provides them with a comprehensive and time-efficient analysis of the various themes covered by the SuRe Standard, offering a solid foundation for projects that are planning to become certified by the SuRe Standard in the future. Upon completion of the SmartScan, project developers receive a spider diagram evaluation, which indicates their project's performance in the different themes and benchmarks the performances with other SmartScan assessed projects.
Examples
Beijing, China
A good example of green infrastructure principles being applied at landscape scale is the Beijing Olympic site. First developed for the 2008 Summer Olympics but used also for the 2022 Winter Olympics, the Beijing Olympic site covers a large area of brownfield redevelopment in the northern sector of the city between the 4th and 5th ring roads. The central green infrastructure feature of the Olympic site is the "Dragon-shaped river" – a complex of retention basins and wetlands covering more than a half million square metres configured to look from the air like a traditional Chinese dragon.

In addition to referencing Chinese culture, the system is capable of significantly reducing nutrient loads from influent waters, which are provided by a nearby wastewater recycling facility.
Surrey, British Columbia
Farmers claimed that flooding of their farmlands was caused by suburban development upstream. The flooding was a result of funneled runoff directed into storm drains by impervious cove, which ran unmitigated and unabsorbed into their farmlands downstream. The farmers were awarded an undisclosed amount of money in the tens of millions as compensation. Low density and highly paved residential communities redirect stormwater from impervious surfaces and pipes to stream at velocities much greater than predevelopment rates. Not only are these practices environmentally damaging, they can be costly and inefficient to maintain. In response, the city of Surrey opted to employ a green infrastructure strategy and chose a 250-hectare site called East Clayton as a demonstration project. The approach reduced the stormwater flowing downstream and allows for infiltration of rainwater closer if not at its point of origin. In result, the stormwater system at East Clayton had the ability to hold one inch of rainfall per day, accounting for 90% of the annual rainfall. The incorporation of green infrastructure at Surrey, British Columbia was able to create a sustainable environment that diminishes runoff and to save around $12,000 per household.
Nya Krokslätt, Sweden
The site of former factory Nya Krokslätt is situated between a mountain and a stream. Danish engineers, Ramboll, have designed a concept of slowing down and guiding storm water in the area with methods such as vegetation combined with ponds, streams and soak-away pits as well as glazed green-blue climate zones surrounding the buildings which delay and clean roof water and greywater. The design concept provides for a multifunctional, rich urban environment, which includes not only technical solutions for energy efficient buildings, but encompasses the implementation of blue-green infrastructure and ecosystem services in an urban area.
Zürich, Switzerland
Since 1991, the city of Zürich has had a law stating all flat roofs (unless used as terraces) must be greened roofed surfaces. The main advantages as a result of this policy include increased biodiversity, rainwater storage and outflow delay, and micro-climatic compensation (temperature extremes, radiation balance, evaporation and filtration efficiency). Roof biotopes are stepping stones which, together with the earthbound green areas and the seeds distributed by wind and birds, make an important contribution to the urban green infrastructure.
Duisburg-Nord, Germany
In the old industrial area of the Ruhr District in Germany, Duisburg-Nord is a landscape park which incorporates former industrial structures and natural biodiversity. The architects Latz + Partner developed the water park which now consists of the old River Emscher, subdivided into five main sections: Klarwasserkanal (Clear Water Canal), the Emschergraben (Dyke), the Emscherrinne (Channel), the Emscherschlucht (Gorge) and the Emscherbach (Stream). The open waste water canal of the “Old Emscher” river is now fed gradually by rainwater collection through a series of barrages and water shoots. This gradual supply means that, even in lengthy dry spells, water can be supplied to the Old Emscher to replenish the oxygen levels. This has allowed the canalised river bed to become a valley with possibilities for nature development and recreation. As a key part of the ecological objectives, much of the overgrown areas of the property were included in the plan as they were found to contain a wide diversity of flora and fauna, including threatened species from the red list. Another important theme in the development of the plan was to make the water system visible, in order to stimulate a relationship between visitors and the water.
New York Sun Works Center, US
The Greenhouse Project was started in 2008 by a small group of public school parents and educators to facilitate hands-on learning, not only to teach about food and nutrition, but also to help children make educated choices regarding their impact on the environment. The laboratory is typically built as a traditional greenhouse on school rooftops and accommodates a hydroponic urban farm and environmental science laboratory. It includes solar panels, hydroponic growing systems, a rainwater catchment system, a weather station and a vermi composting station. Main topics of education include nutrition, water resource management, efficient land use, climate change, biodiversity, conservation, contamination, pollution, waste management, and sustainable development. Students learn the relationship between humans and the environment and gain a greater appreciation of sustainable development and its direct relationship to cultural diversity.
Hammarby Sjöstad, Stockholm, Sweden
In the early 1990s, Hammarby Sjöstad had a reputation for being a run-down, polluted and unsafe industrial and residential area. Now, it is a new district in Stockholm where the city has imposed tough environmental requirements on buildings, technical installations and the traffic environment. An ‘eco-cycle’ solution named the Hammarby Model, developed by Fortum, Stockholm Water Company and the Stockholm Waste Management Administration, is an integral energy, waste and water system for both housing and offices. The goal is to create a residential environment based on sustainable resource usage. Examples include waste heat from the treated wastewater being used for heating up the water in the district heating system, rainwater runoff is returned to the natural cycle through infiltration in green roofs and treatment pools, sludge from the local wastewater treatment is recycled as fertiliser for farming and forestry. This sustainable model has been a source of inspiration to many urban development projects including the Toronto (Canada) Waterfront, London's New Wembley, and a number of cities/city areas in China.
Emeryville, California, US
EPA supported the city of Emeryville, California in the development of "Stormwater Guidelines for Green, Dense Redevelopment." Emeryville, which is a suburb of San Francisco, began in the 1990s reclaiming, remediating and redeveloping the many brownfields within its borders. These efforts sparked a successful economic rebound. The city did not stop there, and decided in the 2000s to harness the redevelopment progress for even better environmental outcomes, in particular that related to stormwater runoff, by requiring in 2005 the use of on-site GI practices in all new private development projects. The city faced several challenges, including a high water table, tidal flows, clay soils, contaminated soil and water, and few absorbent natural areas among the primarily impervious, paved parcels of existing and redeveloped industrial sites. The guidelines, and an accompanying spreadsheet model, were developed to make as much use of redevelopment sites as possible for handling stormwater. The main strategies fell into several categories:
- Reducing the need, space and stormwater impact of motor vehicle parking by way of increased densities, height limits and floor area ratios; shared, stacked, indoor and unbundled automobile parking; making the best use of on-street parking and pricing strategies; car-sharing; free citywide mass transit; requiring one secure indoor bicycle parking space per bedroom and better bicycle and pedestrian roadway infrastructure.
- Sustainable landscape design features, such as tree preservation and minimum rootable soil volumes for new tree planting, use of structural soils, suspended paving systems, bioretention and biofiltration strategies and requiring the use of the holistic practices of Bay-Friendly Landscaping.
- Water storage and harvesting through cisterns and rooftop containers.
- Other strategies to handle or infiltrate water on development and redevelopment sites.
Gowanus Canal Sponge Park, New York, US
The Gowanus Canal, in Brooklyn, New York, is bounded by several communities including Park Slope, Cobble Hill, Carroll Gardens, and Red Hook. The canal empties into New York Harbor. Completed in 1869, the canal was once a major transportation route for the then separate cities of Brooklyn and New York City. Manufactured gas plants, mills, tanneries, and chemical plants are among the many facilities that operated along the canal. As a result of years of discharges, storm water runoff, sewer outflows, and industrial pollutants, the canal has become one of the nation's most extensively contaminated water bodies. Contaminants include PCBs, coal tar wastes, heavy metals, and volatile organics. On March 2, 2010, EPA added the canal to its Superfund National Priorities List (NPL). Placing the canal on the list allows the agency to further investigate contamination at the site and develop an approach to address the contamination.
After the NPL designation, several firms tried to redesign the area surrounding the canal to meet EPA's principles. One of the proposals was the Gowanus Canal Sponge Park, suggested by Susannah Drake of DLANDstudio, an architecture and landscape architecture firm based in Brooklyn. The firm designed a public open space system that slows, absorbs, and filters surface water runoff with the goal of remediating contaminated water, activating the private canal waterfront, and revitalizing the neighborhood. The unique feature of the park is its character as a working landscape that means the ability to improve the environment of the canal over time while simultaneously supporting public engagement with the canal ecosystem. The park was cited in a professional award by the American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA), in the Analysis and Planning category, in 2010.
Lafitte Greenway, New Orleans, Louisiana, US
The Lafitte Greenway in New Orleans, Louisiana, is a post-Hurricane Katrina revitalization effort that utilizes green infrastructure to improve water quality as well as support wildlife habitat. The site was previously an industrial corridor that connected the French Quarter to Bayou St. John and Lake Pontchartrain. Part of the revitalization plan was to incorporate green infrastructure for environmental sustainability. One strategy to mitigate localized flooding was to create recreation fields that are carved out to hold water during times of heavy rains. Another strategy was to restore the native ecology of the corridor, giving special attention to the ecotones that bisect the site. The design proposed retrofitting historic buildings with stormwater management techniques, such as rainwater collection systems, which allows historic buildings to be preserved. This project received the Award of Excellence from the ASLA in 2013.
Geographic information system applications
A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer system for that allows users to capture, store, display, and analyze all kinds of spatial data on Earth. GIS can gather multiple layers of information on one single map regarding streets, buildings, soil types, vegetation, and more. Planners can combine or calculate useful information such as impervious area percentage or vegetation coverage status of a specific region to design or analyze the use of green infrastructure. The continued development of geographic information systems and their increasing level of use is particularly important in the development of Green Infrastructure plans. The plans frequently are based on GIS analysis of many layers of geographic information.
Green Infrastructure Master Plan
According to the "Green Infrastructure Master Plan" developed by Hawkins Partners, civil engineers use GIS to analyze the modeling of impervious surfaces with historical Nashville rainfall data within the CSS (combined sewer system) to find the current rates of runoff. GIS systems are able to help planning teams analyze potential volume reductions at the specific region for green infrastructures, including water harvesting, green roofs, urban trees, and structural control measures.
Implementation
Barriers
Lack of funding is consistently cited as a barrier to the implementation of green infrastructure. One advantage that green infrastructure projects offer, however, is that they generate so many benefits that they can compete for a variety of diverse funding sources. Some tax incentive programs administered by federal agencies can be used to attract financing to green infrastructure projects. Here are two examples of programs whose missions are broad enough to support green infrastructure projects:
- The U.S. Department of Energy administers a range of energy efficiency tax incentives, and green infrastructure could be integrated into project design to claim the incentive. An example of how this might work is found in Oregon's Energy Efficiency Construction Credits. In Eugene, Oregon, a new biofuel station built on an abandoned gas station site included a green roof, bioswales and rain gardens. In this case, nearly $250,000 worth of tax credits reduced income and sales tax for the private company that built and operated the project.
- The U.S. Department of Treasury administers the multibillion-dollar New Markets Tax Credit Program, which encourages private investment for a range of project types (typically real estate or business development projects) in distressed areas. Awards are allocated to non-profit and private entities based on their proposals for distributing these tax benefits.
Benefits

Some people might expect that green spaces are extravagant and excessively difficult to maintain, but high-performing green spaces can provide tangible economic, ecological, and social benefits. For example:
- Urban forestry in an urban environment can supplement stormwater management and reduce associated energy usage costs and runoff.
- Bioretention systems can be applied to the creation of a green transportation system.
- Lawn grass is not an answer to runoff, so an alternative is required to reduce urban and suburban first flush (highly toxic) runoff and to slow the water down for infiltration. In residential applications, water runoff can be reduced by 30% with the use of rain gardens in the homeowner's yard. A minimum size of 150 sq. ft. up to a range of 300 sq. ft. is the usual size considered for a private property residence. The cost per square foot is about $5–$25, depending on the type of plants you use and the slope of your property. Native trees, shrubs, and herbaceous perennials of the wetland and riparian zones being the most useful for runoff detoxification.
As a result, high-performing green spaces work to create a balance between built and natural environments. A higher abundance of green space in communities or neighbourhoods, for example, has been observed to promote participation in physical activities among elderly men, while more green space around one's house is associated with improved mental health.
In addition to these benefits, recent studies have shown that residents highly value the experiential aspects of green infrastructure, emphasizing the importance of aesthetics, wellbeing, and a sense of place. This focus on cultural ecosystem services suggests that the design and implementation of green infrastructure should prioritize these elements, as they significantly contribute to the community's perception of value and overall quality of life.
Economic effects
A 2012 study focusing on 479 green infrastructure projects across the United States found that 44% of green infrastructure projects reduced costs, compared to the 31% that increased the costs. The most notable cost savings were due to reduced stormwater runoff and decreased heating and cooling costs. Green infrastructure is often cheaper than other conventional water management strategies. The city of Philadelphia, for example, discovered that a new green infrastructure plan would cost $1.2 billion over a 25-year period, compared to the $6 billion that would have been needed to finance a grey infrastructure plan.
A comprehensive green infrastructure in Philadelphia is planned to cost just $1.2 billion over the next 25 years, compared to over $6 billion for "grey" infrastructure (concrete tunnels created to move water). Under the new green infrastructure plan it is expected that:
- 250 people will be employed annually in green jobs.
- Up to 1.5 billion pounds of carbon dioxide emission to be avoided or absorbed through green infrastructure each year (the equivalent of removing close to 3,400 vehicles from roadways)
- Air quality will improve due to all the new trees, green roofs, and parks
- Communities will benefit on the social and health side
- About 20 deaths due to asthma will be avoided
- 250 fewer work or school days will be missed
- Deaths due to excessive urban heat could also be cut by 250 over 20 years.
- The new greenery will increase property values by $390 million over 45 years, also boosting the property taxes the city takes in.
A green infrastructure plan in New York City is expected to cost $1.5 billion less than a comparable grey infrastructure approach. Also, the green stormwater management systems alone will save $1 billion, at a cost of about $0.15 less per gallon. The sustainability benefits in New York City range from $139–418 million over the 20 year life of the project. This green plan estimates that “every fully vegetated acre of green infrastructure would provide total annual benefits of $8.522 in reduced energy demand, $166 in reduced CO2 emissions, $1,044 in improved air quality, and $4,725 in increased property value.”
In addition to ambitious infrastructure plans and layouts offering economical and health benefits with the investment of green infrastructure, a study conducted in 2016 within the United Kingdom analyzed the "willingness-to-pay" capacity held by residents in response to green infrastructure. Their findings concluded that, "investment in urban [green infrastructure] that is visibly greener, that facilitates access to [green infrastructure] and other amenities, and that is perceived to promote multiple functions and benefits on a single site (i.e. multi-functionality) generate higher [willingness-to-pay] values." The "willingness-to-pay" obligation is pronounced with the idea that the locations of some living spaces with functionality and aesthetics are more likely to wield larger amounts of social and economical capital. By incentivising residents to invest in green infrastructure within their own zones for development and communities, it allows the potential for increased revenue to be used in order to facilitate further green infrastructure, ultimately increasing the "economic viability" for future projects to occur.
Environmental Justice Impacts
In cities such as Chicago, green infrastructure projects are aimed at enhancing the environment through sustainability and livability, but often they create more social justice concerns like gentrification. This often happens when urban green spaces added in lower income communities attract wealthier residents, which causes the property values to increase and displace the current residence of lower income communities. The impacts of gentrification varies depending on the community, with different implemented infrastructures like greenspaces and transportation avenues along with the size and location of them, which reshapes the demographic and the economic landscape of the community. The challenges with incorporating more green infrastructure with a beneficial goal for social justice is often due to how the government funds and fulfills projects. Many of the projects are managed by nonprofits so they are not the focus nor are the proper skills necessary acquired which creates a larger social justice issue like the decrease in affordable housing. This causes a focus on environmental and recreational improvements and neglects the socioeconomic dimensions of sustainability. The planning process of infrastructure should consider the environmental outcomes while also integrating social equity considerations.
The impacts of green gentrification upon local communities can ultimately contradict the positives brought by sustainable and green infrastructure initially. Green infrastructure like increased green spaces or walkability in cities can potentially improve the well-being of individuals living within the communities, but more often at the expense of dispelling homeless populations or those with decreased housing accessibility living in the future project areas for urban improvement. In order to combat the negative effects of gentrification occurring as a byproduct of haphazard implementation of green infrastructure, different "critical barriers" that act as components prohibiting affordable housing must be addressed. Five major barriers that need to be addressed in future policies and legislation for communities are, "green retrofit-related; land market-related; incentive-related; housing market-related and infrastructural-related barriers."
The success of implementing green infrastructure within communities that have experienced environmental injustice, like excess exposure to pollution or affordable housing, is dependent on the interaction and collaboration of project managers overseeing green infrastructure sites alongside community residents. The most prominent concerns raised by residents in a community in New Jersey cited concerns regarding the maintenance and upkeep of future green stormwater infrastructure (GSI), the necessity for future GSI projects to be multifaceted rather than universal amongst communities, and advocacy for environmental justice to be implemented within project outlines, as "GSI projects, as part of broader community greening initiatives, do not automatically guarantee EJ and health equity, which may be absent in many shrinking cities." It is important to comprehend the environmental and economical capabilities that green infrastructure can provide, but the environmental inequity in respect to being able to access these spaces must be considered in application of green infrastructure within communities. The imperative need to focus on communities with less accessibility to ecosystem services and green infrastructure is a major part of ensuring all communities and residents feel the benefits and effects of implementation.
Initiatives
One program that has integrated green infrastructure into construction projects worldwide is the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification. This system offers a benchmark rating for green buildings and neighborhoods, credibly quantifying a project's environmental responsibility. The LEED program incentivizes development that uses resources efficiently. For example, it offers specific credits for reducing indoor and outdoor water use, optimizing energy performance, producing renewable energy, and minimizing or recycling project waste. Two LEED initiatives that directly promote the use of green infrastructure include the rainwater management and heat island reduction credits. An example of a successfully LEED-certified neighborhood development is the 9th and Berks Street transit-oriented development (TOD) in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, which achieved a Platinum level rating on October 12, 2017.
Another approach to implementing green infrastructure has been developed by the International Living Future Institute. Their Living Community Challenge assesses a community or city in twenty different aspects of sustainability. Notably, the Challenge considers whether the development achieves net positive water and energy uses and utilizes replenishable materials.
