From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Rice is the seed of the grass species Oryza sativa (Asian rice) or Oryza glaberrima (African rice). As a cereal grain, it is the most widely consumed staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in Asia. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production, after sugarcane and maize, according to data of FAOSTAT 2012.[1]
Since a large portion of maize crops are grown for purposes other than human consumption, rice is the most important grain with regard to human nutrition and caloric intake, providing more than one fifth of the calories consumed worldwide by humans.[2]
Chinese legends attribute the domestication of rice to Shennong, the legendary Emperor of China and inventor of Chinese agriculture.[3] Genetic evidence has shown that rice originates from a single domestication 8,200–13,500 years ago[4] in the Pearl River valley region of China.[5] Previously, archaeological evidence had suggested that rice was domesticated in the Yangtze River valley region in China.[4] From East Asia, rice was spread to Southeast and South Asia.[5] Rice was introduced to Europe through Western Asia, and to the Americas through European colonization.
There are many varieties of rice and culinary preferences tend to vary regionally. In some areas such as the Far East or Spain, there is a preference for softer and stickier varieties.
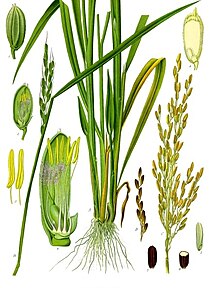
Rice, a monocot, is normally grown as an annual plant, although in tropical areas it can survive as a perennial and can produce a ratoon crop for up to 30 years.[6] The rice plant can grow to 1–1.8 m (3.3–5.9 ft) tall, occasionally more depending on the variety and soil fertility. It has long, slender leaves 50–100 cm (20–39 in) long and 2–2.5 cm (0.79–0.98 in) broad. The small wind-pollinated flowers are produced in a branched arching to pendulous inflorescence 30–50 cm (12–20 in) long. The edible seed is a grain (caryopsis) 5–12 mm (0.20–0.47 in) long and 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in) thick.
Rice cultivation is well-suited to countries and regions with low labor costs and high rainfall, as it is labor-intensive to cultivate and requires ample water. However, rice can be grown practically anywhere, even on a steep hill or mountain area with the use of water-controlling terrace systems. Although its parent species are native to Asia and certain parts of Africa, centuries of trade and exportation have made it commonplace in many cultures worldwide.
The traditional method for cultivating rice is flooding the fields while, or after, setting the young seedlings. This simple method requires sound planning and servicing of the water damming and channeling, but reduces the growth of less robust weed and pest plants that have no submerged growth state, and deters vermin. While flooding is not mandatory for the cultivation of rice, all other methods of irrigation require higher effort in weed and pest control during growth periods and a different approach for fertilizing the soil.
The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera Zizania and Porteresia, both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of Oryza.
Etymology
First used in English in the middle of the 13th century, the word "rice" derives from the Old French ris, which comes from Italian riso, in turn from the Latin oriza, which derives from the Greek ὄρυζα (oruza). The Greek word is the source of all European words (cf. Welsh reis, German Reis, Lithuanian ryžiai, Serbo-Croatian riža, Polish ryż, Dutch rijst, Hungarian rizs, Romanian orez).[7][8][9]The origin of the Greek word is unclear. It is sometimes held to be from the Tamil word அரிசி (arisi), or rather Old Tamil arici.[10][11] However, Krishnamurti[12] disagrees with the notion that Old Tamil arici is the source of the Greek term, and proposes that it was borrowed from descendants of Proto-Dravidian *wariñci instead. Mayrhofer[13] suggests that the immediate source of the Greek word is to be sought in Old Iranian words of the types *vrīz- or *vrinj-, but these are ultimately traced back to Indo-Aryan (as in Sanskrit vrīhí-) and subsequently to Dravidian by Witzel and others.
Cooking
The varieties of rice are typically classified as long-, medium-, and short-grained.[14] The grains of long-grain rice (high in amylose) tend to remain intact after cooking; medium-grain rice (high in amylopectin) becomes more sticky. Medium-grain rice is used for sweet dishes, for risotto in Italy, and many rice dishes, such as arròs negre, in Spain. Some varieties of long-grain rice that are high in amylopectin, known as Thai Sticky rice, are usually steamed.[15] A stickier medium-grain rice is used for sushi; the stickiness allows rice to hold its shape when molded. Short-grain rice is often used for rice pudding.Instant rice differs from parboiled rice in that it is fully cooked and then dried, though there is a significant degradation in taste and texture. Rice flour and starch often are used in batters and breadings to increase crispiness.
Preparation

A: Rice with chaff
B: Brown rice
C: Rice with germ
D: White rice with bran residue
E: Musenmai (Japanese: 無洗米), "Polished and ready to boil rice", literally, non-wash rice
(1): Chaff
(2): Bran
(3): Bran residue
(4): Cereal germ
(5): Endosperm
B: Brown rice
C: Rice with germ
D: White rice with bran residue
E: Musenmai (Japanese: 無洗米), "Polished and ready to boil rice", literally, non-wash rice
(1): Chaff
(2): Bran
(3): Bran residue
(4): Cereal germ
(5): Endosperm
Rice is typically rinsed before cooking to remove excess starch. Rice produced in the US is usually fortified with vitamins and minerals, and rinsing will result in a loss of nutrients. Rice may be rinsed repeatedly until the rinse water is clear to improve the texture and taste.
Rice may be soaked to decrease cooking time, conserve fuel, minimize exposure to high temperature, and reduce stickiness. For some varieties, soaking improves the texture of the cooked rice by increasing expansion of the grains. Rice may be soaked for 30 minutes up to several hours.
Brown rice may be soaked in warm water for 20 hours to stimulate germination. This process, called germinated brown rice (GBR),[16] activates enzymes and enhances amino acids including gamma-aminobutyric acid to improve the nutritional value of brown rice. This method is a result of research carried out for the United Nations International Year of Rice.
Processing
Rice is cooked by boiling or steaming, and absorbs water during cooking. With the absorption method, rice may be cooked in a volume of water similar to the volume of rice. With the rapid-boil method, rice may be cooked in a large quantity of water which is drained before serving. Rapid-boil preparation is not desirable with enriched rice, as much of the enrichment additives are lost when the water is discarded. Electric rice cookers, popular in Asia and Latin America, simplify the process of cooking rice. Rice (or any other grain) is sometimes quickly fried in oil or fat before boiling (for example saffron rice or risotto); this makes the cooked rice less sticky, and is a cooking style commonly called pilaf in Iran and Afghanistan or biryani (Dam-pukhtak) in India and Pakistan.Dishes
In Arab cuisine, rice is an ingredient of many soups and dishes with fish, poultry, and other types of meat. It is also used to stuff vegetables or is wrapped in grape leaves (dolma). When combined with milk, sugar, and honey, it is used to make desserts. In some regions, such as Tabaristan, bread is made using rice flour. Medieval Islamic texts spoke of medical uses for the plant.[17] Rice may also be made into congee (also called rice porridge, fawrclaab, okayu, Xifan, jook, or rice gruel) by adding more water than usual, so that the cooked rice is saturated with water, usually to the point that it disintegrates. Rice porridge is commonly eaten as a breakfast food, and is also a traditional food for the sick.Nutrition and health
Nutrients and the nutritional importance of rice
 |
|
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 1,527 kJ (365 kcal) |
80 g
|
|
| Sugars | 0.12 g |
| Dietary fiber | 1.3 g |
0.66 g
|
|
7.13 g
|
|
| Vitamins | |
| Thiamine (B1) |
(6%)
0.0701 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(1%)
0.0149 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(11%)
1.62 mg |
(20%)
1.014 mg |
|
| Vitamin B6 |
(13%)
0.164 mg |
| Trace metals | |
| Calcium |
(3%)
28 mg |
| Iron |
(6%)
0.80 mg |
| Magnesium |
(7%)
25 mg |
| Manganese |
(52%)
1.088 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(16%)
115 mg |
| Potassium |
(2%)
115 mg |
| Zinc |
(11%)
1.09 mg |
| Other constituents | |
| Water | 11.61 g |
|
|
| Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|
Rice is the staple food of over half the world's population. It is the predominant dietary energy source for 17 countries in Asia and the Pacific, 9 countries in North and South America and 8 countries in Africa. Rice provides 20% of the world’s dietary energy supply, while wheat supplies 19% and maize (corn) 5%.[18]
A detailed analysis of nutrient content of rice suggests that the nutrition value of rice varies based on a number of factors. It depends on the strain of rice, that is between white, brown, black, red and purple varieties of rice – each prevalent in different parts of the world. It also depends on nutrient quality of the soil rice is grown in, whether and how the rice is polished or processed, the manner it is enriched, and how it is prepared before consumption.[19]
An illustrative comparison between white and brown rice of protein quality, mineral and vitamin quality, carbohydrate and fat quality suggests that neither is a complete nutrition source. Between the two, there is a significant difference in fiber content and minor differences in other nutrients.[20]
Brilliantly colored rice strains, such as purple rice, derive their color from anthocyanins and tocols. Scientific studies suggest that these color pigments have antioxidant properties that may be useful to human health. In purple rice bran, hydrophilic antioxidants are in greater quantity and have higher free radical scavenging activity than lipophilic antioxidants. Anthocyanins and γ-tocols in purple rice are largely located in the inner portion of purple rice bran.[21]
Comparative nutrition studies on red, black and white varieties of rice suggest that pigments in red and black rice varieties may offer nutritional benefits. Red or black rice consumption was found to reduce or retard the progression of atherosclerotic plaque development, induced by dietary cholesterol, in mammals. White rice consumption offered no similar benefits, which the study suggests may be due in part to a lack of antioxidants found in red and black varieties of rice.[22]
Comparison of rice to other major staple foods
The table below shows the nutrient content of major staple foods in a raw form. Raw grains, however, are not edible and can not be digested. These must be sprouted, or prepared and cooked for human consumption. In sprouted and cooked form, the relative nutritional and anti-nutritional contents of each of these grains is remarkably different from that of raw form of these grains reported in this table.| STAPLE: | Maize / Corn[A] | Rice (white)[B] | Rice (brown)[I] | Wheat[C] | Potato[D] | Cassava[E] | Soybean (Green)[F] | Sweet potato[G] | Sorghum[H] | Yam[Y] | Plantain[Z] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component (per 100g portion) | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount |
| Water (g) | 10 | 12 | 10 | 13 | 79 | 60 | 68 | 77 | 9 | 70 | 65 |
| Energy (kJ) | 1528 | 1528 | 1549 | 1369 | 322 | 670 | 615 | 360 | 1419 | 494 | 511 |
| Protein (g) | 9.4 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 12.6 | 2.0 | 1.4 | 13.0 | 1.6 | 11.3 | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| Fat (g) | 4.74 | 0.66 | 2.92 | 1.54 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 6.8 | 0.05 | 3.3 | 0.17 | 0.37 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 74 | 80 | 77 | 71 | 17 | 38 | 11 | 20 | 75 | 28 | 32 |
| Fiber (g) | 7.3 | 1.3 | 3.5 | 12.2 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 4.2 | 3 | 6.3 | 4.1 | 2.3 |
| Sugar (g) | 0.64 | 0.12 | 0.85 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 1.7 | 0 | 4.18 | 0 | 0.5 | 15 |
| Calcium (mg) | 7 | 28 | 23 | 29 | 12 | 16 | 197 | 30 | 28 | 17 | 3 |
| Iron (mg) | 2.71 | 0.8 | 1.47 | 3.19 | 0.78 | 0.27 | 3.55 | 0.61 | 4.4 | 0.54 | 0.6 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 127 | 25 | 143 | 126 | 23 | 21 | 65 | 25 | 0 | 21 | 37 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 210 | 115 | 333 | 288 | 57 | 27 | 194 | 47 | 287 | 55 | 34 |
| Potassium (mg) | 287 | 115 | 223 | 363 | 421 | 271 | 620 | 337 | 350 | 816 | 499 |
| Sodium (mg) | 35 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 14 | 15 | 55 | 6 | 9 | 4 |
| Zinc (mg) | 2.21 | 1.09 | 2.02 | 2.65 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.99 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.24 | 0.14 |
| Copper (mg) | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.15 | - | 0.18 | 0.08 | |
| Manganese (mg) | 0.49 | 1.09 | 3.74 | 3.99 | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0.55 | 0.26 | - | 0.40 | - |
| Selenium (μg) | 15.5 | 15.1 | 70.7 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.7 | 1.5 | |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.7 | 20.6 | 29 | 2.4 | 0 | 17.1 | 18.4 |
| Thiamin (mg) | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Niacin (mg) | 3.63 | 1.6 | 5.09 | 5.46 | 1.05 | 0.85 | 1.65 | 0.56 | 2.93 | 0.55 | 0.69 |
| Pantothenic acid (mg) | 0.42 | 1.01 | 1.49 | 0.95 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.80 | - | 0.31 | 0.26 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 0.3 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.21 | - | 0.29 | 0.30 |
| Folate Total (μg) | 19 | 8 | 20 | 38 | 16 | 27 | 165 | 11 | 0 | 23 | 22 |
| Vitamin A (IU) | 214 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 13 | 180 | 14187 | 0 | 138 | 1127 |
| Vitamin E, alpha-tocopherol (mg) | 0.49 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 1.01 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0 | 0.26 | 0 | 0.39 | 0.14 |
| Vitamin K1 (μg) | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 0 | 1.8 | 0 | 2.6 | 0.7 |
| Beta-carotene (μg) | 97 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 8509 | 0 | 83 | 457 | |
| Lutein+zeaxanthin (μg) | 1355 | 0 | 220 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 | |
| Saturated fatty acids (g) | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.58 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 0.46 | 0.04 | 0.14 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids (g) | 1.25 | 0.21 | 1.05 | 0.2 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.28 | 0.00 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids (g) | 2.16 | 0.18 | 1.04 | 0.63 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 3.20 | 0.01 | 1.37 | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| A corn, yellow | B rice, white, long-grain, regular, raw, unenriched | ||||||||
| C wheat, hard red winter | D potato, flesh and skin, raw | ||||||||
| E cassava, raw | F soybeans, green, raw | ||||||||
| G sweet potato, raw, unprepared | H sorghum, raw | ||||||||
| Y yam, raw | Z plantains, raw | ||||||||
| I rice, brown, long-grain, raw |
Arsenic concerns
Rice and rice products contain arsenic, a known poison and Group 1 carcinogen.[24] There is no safe level of arsenic, but, as of 2012, a limit of 10 parts per billion has been established in the United States for drinking water, twice the level of 5 parts per billion originally proposed by the EPA.
Consumption of one serving of some varieties of rice gives more exposure to arsenic than consumption of 1 liter of water that contains 5 parts per billion arsenic; however, the amount of arsenic in rice varies widely with the greatest concentration in brown rice and rice grown on land formerly used to grow cotton; in the United States, Arkansas, Louisiana, Missouri, and Texas.[25] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is studying this issue, but has not established a limit.[26] China has set a limit of 150 ppb for arsenic in rice.[27]
White rice grown in Arkansas, Louisiana, Missouri, and Texas, which account for 76 percent of American-produced rice had higher levels of arsenic than other regions of the world studied, possibly because of past use of arsenic-based pesticides to control cotton weevils.[28] Jasmine rice from Thailand and Basmati rice from Pakistan and India contain the least arsenic among rice varieties in one study.[29]
There have been plenty of debates on the origins of the domesticated rice. Genetic evidence published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) shows that all forms of Asian rice, both indica and japonica, spring from a single domestication that occurred 8,200–13,500 years ago in China of the wild rice Oryza rufipogon.[4] A 2012 study published in Nature, through a map of rice genome variation, indicated that the domestication of rice occurred in the Pearl River valley region of China based on the genetic evidence. From East Asia, rice was spread to South and Southeast Asia.[5] Before this research, the commonly accepted view, based on archaeological evidence, is that rice was first domesticated in the region of the Yangtze River valley in China.[35][36]
Morphological studies of rice phytoliths from the Diaotonghuan archaeological site clearly show the transition from the collection of wild rice to the cultivation of domesticated rice. The large number of wild rice phytoliths at the Diaotonghuan level dating from 12,000–11,000 BP indicates that wild rice collection was part of the local means of subsistence. Changes in the morphology of Diaotonghuan phytoliths dating from 10,000–8,000 BP show that rice had by this time been domesticated.[37] Soon afterwards the two major varieties of indica and japonica rice were being grown in Central China.[36] In the late 3rd millennium BC, there was a rapid expansion of rice cultivation into mainland Southeast Asia and westwards across India and Nepal.[36]
In 2003, Korean archaeologists claimed to have discovered the world's oldest domesticated rice.[38] Their 15,000-year old age challenges the accepted view that rice cultivation originated in China about 12,000 years ago.[38] These findings were received by academia with strong skepticism,[39] and the results and their publicizing has been cited as being driven by a combination of nationalist and regional interests.[40] In 2011, a combined effort by the Stanford University, New York University, Washington University in St. Louis, and Purdue University has provided the strongest evidence yet that there is only one single origin of domesticated rice, in the Yangtze Valley of China.[41][42]
Rice spread to the Middle East where, according to Zohary and Hopf (2000, p. 91), O. sativa was recovered from a grave at Susa in Iran (dated to the 1st century AD).

African rice has been cultivated for 3500 years. Between 1500 and 800 BC, Oryza glaberrima propagated from its original centre, the Niger River delta, and extended to Senegal. However, it never developed far from its original region. Its cultivation even declined in favour of the Asian species, which was introduced to East Africa early in the common era and spread westward.[44] African rice helped Africa conquer its famine of 1203.[45]
Today, the majority of all rice produced comes from China, India, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Thailand, Myanmar, Pakistan, Philippines, Korea and Japan. Asian farmers still account for 87% of the world's total rice production.
Traditional rice varieties are now making a comeback with the recent interest in green foods.
The northern region has both low lands and high lands. The farmers’ usual crop is non-glutinous rice [48] such as Niew Sun Pah Tong rice seeds. This rice is naturally protected from leaf disease, and the paddy has a brown color.[49] The northeastern region has a large area, where farmers can cultivate about 36 million square meters of rice. Although most of them are plains and dry areas,[50] they can grow the white jasmine rice 105 which is the most famous Thai rice. The white jasmine rice was developed in Chonburi province first and after that it was grown in many areas in the country but the rice from this region has a high quality, because it's softer, whiter and more fragrant.[51] This rice can resist drought, acidic soil, and alkaline soil.[52]
The central region is mostly composed of plains. Most farmers grow Jao rice.[50] For example the Pathum Thani 1 rice which has qualities similar to the white jasmine 105 rice. Their paddy has the color of thatch and their cooked rice has fragrant grains also.[53]
In the southern region, most farmers transplant around boundaries to the flood of plain or plain between mountains. Farming is the region is slower than other regions because the rainy season comes late.[54] The popular rice varieties in this area are the Leb Nok Pattani seeds, a type of Jao rice. Their paddy has the color of thatch and it can be processed to make noodles.[55]
The Moors brought Asiatic rice to the Iberian Peninsula in the 10th century. Records indicate it was grown in Valencia and Majorca. In Majorca, rice cultivation seems to have stopped after the Christian conquest, although historians are not certain.[57]
Muslims also brought rice to Sicily, where it was an important crop[57] long before it is noted in the plain of Pisa (1468) or in the Lombard plain (1475), where its cultivation was promoted by Ludovico Sforza, Duke of Milan, and demonstrated in his model farms.[59]
After the 15th century, rice spread throughout Italy and then France, later propagating to all the continents during the age of European exploration.
In European Russia, a short-grain, starchy rice similar to the Italian varieties, has been grown in the Krasnodar Krai, and known in Russia as "Kuban Rice" or "Krasnodar Rice". In the Russian Far East several japonica cultivars are grown in Primorye around the Khanka lake. Increasing scale of rice production in the region has recently brought criticism towards growers' alleged bad practices in regards to the environment.
The Native Americans of what is now the Eastern United States may have practiced extensive agriculture with forms of wild rice (Zizania palustris), which looks similar to but it not directly related to rice.
In 1694, rice arrived in South Carolina, probably originating from Madagascar.[60]
In the United States, colonial South Carolina and Georgia grew and amassed great wealth from the slave labor obtained from the Senegambia area of West Africa and from coastal Sierra Leone. At the port of Charleston, through which 40% of all American slave imports passed, slaves from this region of Africa brought the highest prices due to their prior knowledge of rice culture, which was put to use on the many rice plantations around Georgetown, Charleston, and Savannah.
From the enslaved Africans, plantation owners learned how to dyke the marshes and periodically flood the fields. At first the rice was laboriously milled by hand using large mortars and pestles made of wood, then winnowed in sweetgrass baskets (the making of which was another skill brought by slaves from Africa). The invention of the rice mill increased profitability of the crop, and the addition of water power for the mills in 1787 by millwright Jonathan Lucas was another step forward.
Rice culture in the southeastern U.S. became less profitable with the loss of slave labor after the American Civil War, and it finally died out just after the turn of the 20th century. Today, people can visit the only remaining rice plantation in South Carolina that still has the original winnowing barn and rice mill from the mid-19th century at the historic Mansfield Plantation in Georgetown, South Carolina. The predominant strain of rice in the Carolinas was from Africa and was known as "Carolina Gold." The cultivar has been preserved and there are current attempts to reintroduce it as a commercially grown crop.[62]
In the southern United States, rice has been grown in southern Arkansas, Louisiana, and east Texas since the mid-19th century. Many Cajun farmers grew rice in wet marshes and low lying prairies where they could also farm crayfish when the fields were flooded.[63] In recent years rice production has risen in North America, especially in the Mississippi embayment in the states of Arkansas and Mississippi (see also Arkansas Delta and Mississippi Delta).
Rice cultivation began in California during the California Gold Rush, when an estimated 40,000 Chinese laborers immigrated to the state and grew small amounts of the grain for their own consumption. However, commercial production began only in 1912 in the town of Richvale in Butte County.[64] By 2006, California produced the second largest rice crop in the United States,[65] after Arkansas, with production concentrated in six counties north of Sacramento.[66] Unlike the Arkansas–Mississippi Delta region, California's production is dominated by short- and medium-grain japonica varieties, including cultivars developed for the local climate such as Calrose, which makes up as much as 85% of the state's crop.[67]
References to wild rice in the Americas are to the unrelated Zizania palustris
More than 100 varieties of rice are commercially produced primarily in six states (Arkansas, Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, and California) in the U.S.[68] According to estimates for the 2006 crop year, rice production in the U.S. is valued at $1.88 billion, approximately half of which is expected to be exported. The U.S. provides about 12% of world rice trade.[68] The majority of domestic utilization of U.S. rice is direct food use (58%), while 16% is used in each of processed foods and beer. 10% is found in pet food.[68]
Although attempts to grow rice in the well-watered north of Australia have been made for many years, they have consistently failed because of inherent iron and manganese toxicities in the soils and destruction by pests.
In the 1920s it was seen as a possible irrigation crop on soils within the Murray-Darling Basin that were too heavy for the cultivation of fruit and too infertile for wheat.[69]
Because irrigation water, despite the extremely low runoff of temperate Australia,[70] was (and remains) very cheap, the growing of rice was taken up by agricultural groups over the following decades. Californian varieties of rice were found suitable for the climate in the Riverina,[69] and the first mill opened at Leeton in 1951.
Even before this Australia's rice production greatly exceeded local needs,[69] and rice exports to Japan have become a major source of foreign currency. Above-average rainfall from the 1950s to the middle 1990s[71] encouraged the expansion of the Riverina rice industry, but its prodigious water use in a practically waterless region began to attract the attention of environmental scientists. These became severely concerned with declining flow in the Snowy River and the lower Murray River.
Although rice growing in Australia is highly profitable due to the cheapness of land, several recent years of severe drought have led many to call for its elimination because of its effects on extremely fragile aquatic ecosystems. The Australian rice industry is somewhat opportunistic, with the area planted varying significantly from season to season depending on water allocations in the Murray and Murrumbidgee irrigation regions.

The world dedicated 162.3 million hectares in 2012 for rice cultivation and the total production was about 738.1 million tonnes.[73] The average world farm yield for rice was 4.5 tonnes per hectare, in 2012.[73]
Rice farms in Egypt were the most productive in 2012, with a nationwide average of 9.5 tonnes per hectare.[74] Second place: Australia – 8.9 tonnes per hectare.[74] Third place: USA – 8.3 tonnes per hectare.[74]
Rice is a major food staple and a mainstay for the rural population and their food security. It is mainly cultivated by small farmers in holdings of less than 1 hectare. Rice is also a wage commodity for workers in the cash crop or non-agricultural sectors. Rice is vital for the nutrition of much of the population in Asia, as well as in Latin America and the Caribbean and in Africa; it is central to the food security of over half the world population. Developing countries account for 95% of the total production, with China and India alone responsible for nearly half of the world output.[75]
World production of rice has risen steadily from about 200 million tonnes of paddy rice in 1960 to over 678 million tonnes in 2009. The three largest producers of rice in 2009 were China (197 million tonnes), India (131 Mt), and Indonesia (64 Mt). Among the six largest rice producers, the most productive farms for rice, in 2009, were in China producing 6.59 tonnes per hectare.[76]
Many rice grain producing countries have significant losses post-harvest at the farm and because of poor roads, inadequate storage technologies, inefficient supply chains and farmer's inability to bring the produce into retail markets dominated by small shopkeepers. A World Bank – FAO study claims 8% to 26% of rice is lost in developing nations, on average, every year, because of post-harvest problems and poor infrastructure. Some sources claim the post-harvest losses to exceed 40%.,[75][77] Not only do these losses reduce food security in the world, the study claims that farmers in developing countries such as China, India and others lose approximately US$89 billion of income in preventable post-harvest farm losses, poor transport, the lack of proper storage and retail. One study claims that if these post-harvest grain losses could be eliminated with better infrastructure and retail network, in India alone enough food would be saved every year to feed 70 to 100 million people over a year.[78] However, other writers have warned against dramatic assessments of post-harvest food losses, arguing that "worst-case scenarios" tend to be used rather than realistic averages and that in many cases the cost of avoiding losses exceeds the value of the food saved.[79]
The seeds of the rice plant are first milled using a rice huller to remove the chaff (the outer husks of the grain). At this point in the process, the product is called brown rice. The milling may be continued, removing the bran, i.e., the rest of the husk and the germ, thereby creating white rice. White rice, which keeps longer, lacks some important nutrients; moreover, in a limited diet which does not supplement the rice, brown rice helps to prevent the disease beriberi.
Either by hand or in a rice polisher, white rice may be buffed with glucose or talc powder (often called polished rice, though this term may also refer to white rice in general), parboiled, or processed into flour. White rice may also be enriched by adding nutrients, especially those lost during the milling process. While the cheapest method of enriching involves adding a powdered blend of nutrients that will easily wash off (in the United States, rice which has been so treated requires a label warning against rinsing), more sophisticated methods apply nutrients directly to the grain, coating the grain with a water-insoluble substance which is resistant to washing.
In some countries, a popular form, parboiled rice, is subjected to a steaming or parboiling process while still a brown rice grain. This causes nutrients from the outer husk, especially thiamine, to move into the grain itself. The parboil process causes a gelatinisation of the starch in the grains. The grains become less brittle, and the color of the milled grain changes from white to yellow. The rice is then dried, and can then be milled as usual or used as brown rice. Milled parboiled rice is nutritionally superior to standard milled rice. Parboiled rice has an additional benefit in that it does not stick to the pan during cooking, as happens when cooking regular white rice. This type of rice is eaten in parts of India and countries of West Africa are also accustomed to consuming parboiled rice.
Despite the hypothetical health risks of talc (such as stomach cancer),[80][81] talc-coated rice remains the norm in some countries due to its attractive shiny appearance, but it has been banned in some, and is no longer widely used in others (such as the United States). Even where talc is not used, glucose, starch, or other coatings may be used to improve the appearance of the grains.
Rice bran, called nuka in Japan, is a valuable commodity in Asia and is used for many daily needs. It is a moist, oily inner layer which is heated to produce oil. It is also used as a pickling bed in making rice bran pickles and takuan.
Raw rice may be ground into flour for many uses, including making many kinds of beverages, such as amazake, horchata, rice milk, and rice wine. Rice flour does not contain gluten, so is suitable for people on a gluten-free diet. Rice may also be made into various types of noodles. Raw, wild, or brown rice may also be consumed by raw-foodist or fruitarians if soaked and sprouted (usually a week to 30 days – gaba rice).
Processed rice seeds must be boiled or steamed before eating. Boiled rice may be further fried in cooking oil or butter (known as fried rice), or beaten in a tub to make mochi.
Rice is a good source of protein and a staple food in many parts of the world, but it is not a complete protein: it does not contain all of the essential amino acids in sufficient amounts for good health, and should be combined with other sources of protein, such as nuts, seeds, beans, fish, or meat.[82]
Rice, like other cereal grains, can be puffed (or popped). This process takes advantage of the grains' water content and typically involves heating grains in a special chamber. Further puffing is sometimes accomplished by processing puffed pellets in a low-pressure chamber. The ideal gas law means either lowering the local pressure or raising the water temperature results in an increase in volume prior to water evaporation, resulting in a puffy texture. Bulk raw rice density is about 0.9 g/cm³. It decreases to less than one-tenth that when puffed.

Unmilled rice, known as paddy (Indonesia and Malaysia: padi; Philippines, palay), is usually harvested when the grains have a moisture content of around 25%. In most Asian countries, where rice is almost entirely the product of smallholder agriculture, harvesting is carried out manually, although there is a growing interest in mechanical harvesting. Harvesting can be carried out by the farmers themselves, but is also frequently done by seasonal labour groups. Harvesting is followed by threshing, either immediately or within a day or two. Again, much threshing is still carried out by hand but there is an increasing use of mechanical threshers. Subsequently, paddy needs to be dried to bring down the moisture content to no more than 20% for milling.
A familiar sight in several Asian countries is paddy laid out to dry along roads. However, in most countries the bulk of drying of marketed paddy takes place in mills, with village-level drying being used for paddy to be consumed by farm families. Mills either sun dry or use mechanical driers or both. Drying has to be carried out quickly to avoid the formation of moulds. Mills range from simple hullers, with a throughput of a couple of tonnes a day, that simply remove the outer husk, to enormous operations that can process 4,000 tonnes a day and produce highly polished rice. A good mill can achieve a paddy-to-rice conversion rate of up to 72% but smaller, inefficient mills often struggle to achieve 60%. These smaller mills often do not buy paddy and sell rice but only service farmers who want to mill their paddy for their own consumption.
Developing countries are the main players in the world rice trade, accounting for 83% of exports and 85% of imports. While there are numerous importers of rice, the exporters of rice are limited. Just five countries – Thailand, Vietnam, China, the United States and India – in decreasing order of exported quantities, accounted for about three-quarters of world rice exports in 2002.[75] However, this ranking has been rapidly changing in recent years. In 2010, the three largest exporters of rice, in decreasing order of quantity exported were Thailand, Vietnam and India. By 2012, India became the largest exporter of rice with a 100% increase in its exports on year to year basis, and Thailand slipped to third position.[85][86] Together, Thailand, Vietnam and India accounted for nearly 70% of the world rice exports.
The primary variety exported by Thailand and Vietnam were Jasmine rice, while exports from India included aromatic Basmati variety. China, an exporter of rice in early 2000s, was a net importer of rice in 2010 and will become the largest net importer, surpassing Nigeria, in 2013.[84][87] According to a USDA report, the world's largest exporters of rice in 2012 were India (9.75 million tonnes), Vietnam (7 million tonnes), Thailand (6.5 million tonnes), Pakistan (3.75 million tonnes) and the United States (3.5 million tonnes).[88]
Major importers usually include Nigeria, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brazil and some African and Persian Gulf countries. In common with other West African countries, Nigeria is actively promoting domestic production. However, its very heavy import duties (110%) open it to smuggling from neighboring countries.[89] Parboiled rice is particularly popular in Nigeria. Although China and India are the two largest producers of rice in the world, both countries consume the majority of the rice produced domestically, leaving little to be traded internationally.
Australian rice farms were the most productive in 2010, with a nationwide average of 10.8 tonnes per hectare.[90]
Yuan Longping of China National Hybrid Rice Research and Development Center, China, set a world record for rice yield in 2010 at 19 tonnes per hectare on a demonstration plot. In 2011, this record was surpassed by an Indian farmer, Sumant Kumar, with 22.4 tonnes per hectare in Bihar. Both these farmers claim to have employed newly developed rice breeds and System of Rice Intensification (SRI), a recent innovation in rice farming. SRI is claimed to have set new national records in rice yields, within the last 10 years, in many countries. The claimed Chinese and Indian yields have yet to be demonstrated on seven-hectare lots and to be reproducible over two consecutive years on the same farm.[91][92][93][94]
On April 30, 2008, Thailand announced plans for the creation of the Organisation of Rice Exporting Countries (OREC) with the intention that this should develop into a price-fixing cartel for rice.[96][97] However, little progress had been made by mid-2011 to achieve this.
As of 2009 world food consumption of rice was 531.6 million metric tons of paddy equivalent (354,603 of milled equivalent), while the far largest consumers were China consuming 156.3 million metric tons of paddy equivalent (29.4% of the world consumption) and India consuming 123.5 million metric tons of paddy equivalent (23.3% of the world consumption).[98] Between 1961 and 2002, per capita consumption of rice increased by 40%.
Rice is the most important crop in Asia. In Cambodia, for example, 90% of the total agricultural area is used for rice production.[99]
U.S. rice consumption has risen sharply over the past 25 years, fueled in part by commercial applications such as beer production.[100] Almost one in five adult Americans now report eating at least half a serving of white or brown rice per day.[101]

Rice cultivation on wetland rice fields is thought to be responsible for 1.5% of the anthropogenic methane emissions.[102] Rice requires slightly more water to produce than other grains.[103] Rice production uses almost a third of Earth’s fresh water.[104]
Long-term flooding of rice fields cuts the soil off from atmospheric oxygen and causes anaerobic fermentation of organic matter in the soil.[105] Methane production from rice cultivation contributes ~1.5% of anthropogenic greenhouse gases.[106] Methane is twenty times more potent a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide.[107]
A 2010 study found that, as a result of rising temperatures and decreasing solar radiation during the later years of the 20th century, the rice yield growth rate has decreased in many parts of Asia, compared to what would have been observed had the temperature and solar radiation trends not occurred.[108][109] The yield growth rate had fallen 10–20% at some locations. The study was based on records from 227 farms in Thailand, Vietnam, Nepal, India, China, Bangladesh, and Pakistan. The mechanism of this falling yield was not clear, but might involve increased respiration during warm nights, which expends energy without being able to photosynthesize.
White rice grown in Arkansas, Louisiana, Missouri, and Texas, which account for 76 percent of American-produced rice had higher levels of arsenic than other regions of the world studied, possibly because of past use of arsenic-based pesticides to control cotton weevils.[28] Jasmine rice from Thailand and Basmati rice from Pakistan and India contain the least arsenic among rice varieties in one study.[29]
Bacillus cereus
Cooked rice can contain Bacillus cereus spores, which produce an emetic toxin when left at 4–60 °C (39–140 °F). When storing cooked rice for use the next day, rapid cooling is advised to reduce the risk of toxin production.[30] One of the enterotoxins produced by Bacillus cereus is heat-resistant; reheating contaminated rice kills the bacteria, but does not destroy the toxin already present.Rice-growing environments
Rice can be grown in different environments, depending upon water availability.[31] Generally, rice does not thrive in a waterlogged area, yet it can survive and grow herein[32] and it can also survive flooding.[33]- Lowland, rainfed, which is drought prone, favors medium depth; waterlogged, submergence, and flood prone
- Lowland, irrigated, grown in both the wet season and the dry season
- Deep water or floating rice
- Coastal Wetland
- Upland rice is also known as Ghaiya rice, well known for its drought tolerance[34]
History of domestication and cultivation
Morphological studies of rice phytoliths from the Diaotonghuan archaeological site clearly show the transition from the collection of wild rice to the cultivation of domesticated rice. The large number of wild rice phytoliths at the Diaotonghuan level dating from 12,000–11,000 BP indicates that wild rice collection was part of the local means of subsistence. Changes in the morphology of Diaotonghuan phytoliths dating from 10,000–8,000 BP show that rice had by this time been domesticated.[37] Soon afterwards the two major varieties of indica and japonica rice were being grown in Central China.[36] In the late 3rd millennium BC, there was a rapid expansion of rice cultivation into mainland Southeast Asia and westwards across India and Nepal.[36]
In 2003, Korean archaeologists claimed to have discovered the world's oldest domesticated rice.[38] Their 15,000-year old age challenges the accepted view that rice cultivation originated in China about 12,000 years ago.[38] These findings were received by academia with strong skepticism,[39] and the results and their publicizing has been cited as being driven by a combination of nationalist and regional interests.[40] In 2011, a combined effort by the Stanford University, New York University, Washington University in St. Louis, and Purdue University has provided the strongest evidence yet that there is only one single origin of domesticated rice, in the Yangtze Valley of China.[41][42]
Rice spread to the Middle East where, according to Zohary and Hopf (2000, p. 91), O. sativa was recovered from a grave at Susa in Iran (dated to the 1st century AD).
Regional history
In a recent study,[43] scientist have found a link for differences in human culture based on either wheat or rice cultivating races since ancient times.Africa

African rice has been cultivated for 3500 years. Between 1500 and 800 BC, Oryza glaberrima propagated from its original centre, the Niger River delta, and extended to Senegal. However, it never developed far from its original region. Its cultivation even declined in favour of the Asian species, which was introduced to East Africa early in the common era and spread westward.[44] African rice helped Africa conquer its famine of 1203.[45]
Asia
Today, the majority of all rice produced comes from China, India, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Thailand, Myanmar, Pakistan, Philippines, Korea and Japan. Asian farmers still account for 87% of the world's total rice production.
Sri Lanka
Rice is the staple food amongst all the ethnic groups in Sri Lanka. Agriculture in Sri Lanka mainly depends on the rice cultivation. Rice production is acutely dependent on rainfall and government supply necessity of water through irrigation channels throughout the cultivation seasons. The principal cultivation season, known as "Maha", is from October to March and the subsidiary cultivation season, known as "Yala", is from April to September. During Maha season, there is usually enough water to sustain the cultivation of all rice fields, nevertheless in Yala season there is only enough water for cultivation of half of the land extent.Traditional rice varieties are now making a comeback with the recent interest in green foods.
Thailand
Rice is the main export of Thailand, especially the white jasmine rice 105 (Dok Mali 105).[46] Thailand has a large number of rice varieties, 3,500 kinds with different characters, and 5 kinds of wild rice cultivates.[47] In each region of the country there are different rice seed types. Their use depends on weather, atmosphere, and topography.[48]The northern region has both low lands and high lands. The farmers’ usual crop is non-glutinous rice [48] such as Niew Sun Pah Tong rice seeds. This rice is naturally protected from leaf disease, and the paddy has a brown color.[49] The northeastern region has a large area, where farmers can cultivate about 36 million square meters of rice. Although most of them are plains and dry areas,[50] they can grow the white jasmine rice 105 which is the most famous Thai rice. The white jasmine rice was developed in Chonburi province first and after that it was grown in many areas in the country but the rice from this region has a high quality, because it's softer, whiter and more fragrant.[51] This rice can resist drought, acidic soil, and alkaline soil.[52]
The central region is mostly composed of plains. Most farmers grow Jao rice.[50] For example the Pathum Thani 1 rice which has qualities similar to the white jasmine 105 rice. Their paddy has the color of thatch and their cooked rice has fragrant grains also.[53]
In the southern region, most farmers transplant around boundaries to the flood of plain or plain between mountains. Farming is the region is slower than other regions because the rainy season comes late.[54] The popular rice varieties in this area are the Leb Nok Pattani seeds, a type of Jao rice. Their paddy has the color of thatch and it can be processed to make noodles.[55]
Companion plant
One of the earliest known examples of companion planting is the growing of rice with Azolla, the mosquito fern, which covers the top of a fresh rice paddy's water, blocking out any competing plants, as well as fixing nitrogen from the atmosphere for the rice to use. The rice is planted when it is tall enough to poke out above the azolla. This method has been used for at least a thousand years.Middle East
Rice was grown in some areas of southern Iraq. With the rise of Islam it moved north to Nisibin, the southern shores of the Caspian Sea(Iran)[56] and then beyond the Muslim world into the valley of the Volga. In Egypt, rice is mainly grown in the Nile Delta. In Israel, rice came to be grown in the Jordan Valley. Rice is also grown in Saudi Arabia at Al-hasa Oasis and in Yemen.[57]Europe
Rice was known to the Classical world, being imported from Egypt, and perhaps west Asia. It was known to Greece by returning soldiers from Alexander the Great's military expedition to Asia. Large deposits of rice from the first century A.D. have been found in Roman camps in Germany.[58]The Moors brought Asiatic rice to the Iberian Peninsula in the 10th century. Records indicate it was grown in Valencia and Majorca. In Majorca, rice cultivation seems to have stopped after the Christian conquest, although historians are not certain.[57]
Muslims also brought rice to Sicily, where it was an important crop[57] long before it is noted in the plain of Pisa (1468) or in the Lombard plain (1475), where its cultivation was promoted by Ludovico Sforza, Duke of Milan, and demonstrated in his model farms.[59]
After the 15th century, rice spread throughout Italy and then France, later propagating to all the continents during the age of European exploration.
In European Russia, a short-grain, starchy rice similar to the Italian varieties, has been grown in the Krasnodar Krai, and known in Russia as "Kuban Rice" or "Krasnodar Rice". In the Russian Far East several japonica cultivars are grown in Primorye around the Khanka lake. Increasing scale of rice production in the region has recently brought criticism towards growers' alleged bad practices in regards to the environment.
Caribbean and Latin America
Rice is not native to the Americas but was introduced to Latin America and the Caribbean by European colonizers at an early date with Spanish colonizers introducing Asian rice to Mexico in the 1520s at Veracruz and the Portuguese and their African slaves introducing it at about the same time to colonial Brazil.[60] Recent scholarship suggests that enslaved Africans played an active role in the establishment of rice in the New World and that African rice was an important crop from an early period.[61] Varieties of rice and bean dishes that were a staple dish along the peoples of West Africa remained a staple among their descendants subjected to slavery in the Spanish New World colonies, Brazil and elsewhere in the Americas.[45]The Native Americans of what is now the Eastern United States may have practiced extensive agriculture with forms of wild rice (Zizania palustris), which looks similar to but it not directly related to rice.
United States
In 1694, rice arrived in South Carolina, probably originating from Madagascar.[60]
In the United States, colonial South Carolina and Georgia grew and amassed great wealth from the slave labor obtained from the Senegambia area of West Africa and from coastal Sierra Leone. At the port of Charleston, through which 40% of all American slave imports passed, slaves from this region of Africa brought the highest prices due to their prior knowledge of rice culture, which was put to use on the many rice plantations around Georgetown, Charleston, and Savannah.
From the enslaved Africans, plantation owners learned how to dyke the marshes and periodically flood the fields. At first the rice was laboriously milled by hand using large mortars and pestles made of wood, then winnowed in sweetgrass baskets (the making of which was another skill brought by slaves from Africa). The invention of the rice mill increased profitability of the crop, and the addition of water power for the mills in 1787 by millwright Jonathan Lucas was another step forward.
Rice culture in the southeastern U.S. became less profitable with the loss of slave labor after the American Civil War, and it finally died out just after the turn of the 20th century. Today, people can visit the only remaining rice plantation in South Carolina that still has the original winnowing barn and rice mill from the mid-19th century at the historic Mansfield Plantation in Georgetown, South Carolina. The predominant strain of rice in the Carolinas was from Africa and was known as "Carolina Gold." The cultivar has been preserved and there are current attempts to reintroduce it as a commercially grown crop.[62]
In the southern United States, rice has been grown in southern Arkansas, Louisiana, and east Texas since the mid-19th century. Many Cajun farmers grew rice in wet marshes and low lying prairies where they could also farm crayfish when the fields were flooded.[63] In recent years rice production has risen in North America, especially in the Mississippi embayment in the states of Arkansas and Mississippi (see also Arkansas Delta and Mississippi Delta).
Rice cultivation began in California during the California Gold Rush, when an estimated 40,000 Chinese laborers immigrated to the state and grew small amounts of the grain for their own consumption. However, commercial production began only in 1912 in the town of Richvale in Butte County.[64] By 2006, California produced the second largest rice crop in the United States,[65] after Arkansas, with production concentrated in six counties north of Sacramento.[66] Unlike the Arkansas–Mississippi Delta region, California's production is dominated by short- and medium-grain japonica varieties, including cultivars developed for the local climate such as Calrose, which makes up as much as 85% of the state's crop.[67]
References to wild rice in the Americas are to the unrelated Zizania palustris
More than 100 varieties of rice are commercially produced primarily in six states (Arkansas, Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, and California) in the U.S.[68] According to estimates for the 2006 crop year, rice production in the U.S. is valued at $1.88 billion, approximately half of which is expected to be exported. The U.S. provides about 12% of world rice trade.[68] The majority of domestic utilization of U.S. rice is direct food use (58%), while 16% is used in each of processed foods and beer. 10% is found in pet food.[68]
Australia
Rice was one of the earliest crops planted in Australia by British settlers, who had experience with rice plantations in the Americas and India.Although attempts to grow rice in the well-watered north of Australia have been made for many years, they have consistently failed because of inherent iron and manganese toxicities in the soils and destruction by pests.
In the 1920s it was seen as a possible irrigation crop on soils within the Murray-Darling Basin that were too heavy for the cultivation of fruit and too infertile for wheat.[69]
Because irrigation water, despite the extremely low runoff of temperate Australia,[70] was (and remains) very cheap, the growing of rice was taken up by agricultural groups over the following decades. Californian varieties of rice were found suitable for the climate in the Riverina,[69] and the first mill opened at Leeton in 1951.
Even before this Australia's rice production greatly exceeded local needs,[69] and rice exports to Japan have become a major source of foreign currency. Above-average rainfall from the 1950s to the middle 1990s[71] encouraged the expansion of the Riverina rice industry, but its prodigious water use in a practically waterless region began to attract the attention of environmental scientists. These became severely concerned with declining flow in the Snowy River and the lower Murray River.
Although rice growing in Australia is highly profitable due to the cheapness of land, several recent years of severe drought have led many to call for its elimination because of its effects on extremely fragile aquatic ecosystems. The Australian rice industry is somewhat opportunistic, with the area planted varying significantly from season to season depending on water allocations in the Murray and Murrumbidgee irrigation regions.
Production and commerce
| Top 20 Rice Producers by Country—2012 (million metric ton)[72] |
|
|---|---|
| 204.3 | |
| 152.6 | |
| 69.0 | |
| 43.7 | |
| 37.8 | |
| 33.9 | |
| 33.0 | |
| 18.0 | |
| 11.5 | |
| 10.7 | |
| 9.4 | |
| 9.3 | |
| 9.0 | |
| 6.4 | |
| 5.9 | |
| 5.1 | |
| 4.8 | |
| 4.0 | |
| 3.8 | |
| 3.5 | |
| Source: Food and Agriculture Organization | |
Production

Burning of rice residues after harvest, to quickly prepare the land for wheat planting, around Sangrur, Punjab, India.
The world dedicated 162.3 million hectares in 2012 for rice cultivation and the total production was about 738.1 million tonnes.[73] The average world farm yield for rice was 4.5 tonnes per hectare, in 2012.[73]
Rice farms in Egypt were the most productive in 2012, with a nationwide average of 9.5 tonnes per hectare.[74] Second place: Australia – 8.9 tonnes per hectare.[74] Third place: USA – 8.3 tonnes per hectare.[74]
Rice is a major food staple and a mainstay for the rural population and their food security. It is mainly cultivated by small farmers in holdings of less than 1 hectare. Rice is also a wage commodity for workers in the cash crop or non-agricultural sectors. Rice is vital for the nutrition of much of the population in Asia, as well as in Latin America and the Caribbean and in Africa; it is central to the food security of over half the world population. Developing countries account for 95% of the total production, with China and India alone responsible for nearly half of the world output.[75]
World production of rice has risen steadily from about 200 million tonnes of paddy rice in 1960 to over 678 million tonnes in 2009. The three largest producers of rice in 2009 were China (197 million tonnes), India (131 Mt), and Indonesia (64 Mt). Among the six largest rice producers, the most productive farms for rice, in 2009, were in China producing 6.59 tonnes per hectare.[76]
Many rice grain producing countries have significant losses post-harvest at the farm and because of poor roads, inadequate storage technologies, inefficient supply chains and farmer's inability to bring the produce into retail markets dominated by small shopkeepers. A World Bank – FAO study claims 8% to 26% of rice is lost in developing nations, on average, every year, because of post-harvest problems and poor infrastructure. Some sources claim the post-harvest losses to exceed 40%.,[75][77] Not only do these losses reduce food security in the world, the study claims that farmers in developing countries such as China, India and others lose approximately US$89 billion of income in preventable post-harvest farm losses, poor transport, the lack of proper storage and retail. One study claims that if these post-harvest grain losses could be eliminated with better infrastructure and retail network, in India alone enough food would be saved every year to feed 70 to 100 million people over a year.[78] However, other writers have warned against dramatic assessments of post-harvest food losses, arguing that "worst-case scenarios" tend to be used rather than realistic averages and that in many cases the cost of avoiding losses exceeds the value of the food saved.[79]
The seeds of the rice plant are first milled using a rice huller to remove the chaff (the outer husks of the grain). At this point in the process, the product is called brown rice. The milling may be continued, removing the bran, i.e., the rest of the husk and the germ, thereby creating white rice. White rice, which keeps longer, lacks some important nutrients; moreover, in a limited diet which does not supplement the rice, brown rice helps to prevent the disease beriberi.
Either by hand or in a rice polisher, white rice may be buffed with glucose or talc powder (often called polished rice, though this term may also refer to white rice in general), parboiled, or processed into flour. White rice may also be enriched by adding nutrients, especially those lost during the milling process. While the cheapest method of enriching involves adding a powdered blend of nutrients that will easily wash off (in the United States, rice which has been so treated requires a label warning against rinsing), more sophisticated methods apply nutrients directly to the grain, coating the grain with a water-insoluble substance which is resistant to washing.
In some countries, a popular form, parboiled rice, is subjected to a steaming or parboiling process while still a brown rice grain. This causes nutrients from the outer husk, especially thiamine, to move into the grain itself. The parboil process causes a gelatinisation of the starch in the grains. The grains become less brittle, and the color of the milled grain changes from white to yellow. The rice is then dried, and can then be milled as usual or used as brown rice. Milled parboiled rice is nutritionally superior to standard milled rice. Parboiled rice has an additional benefit in that it does not stick to the pan during cooking, as happens when cooking regular white rice. This type of rice is eaten in parts of India and countries of West Africa are also accustomed to consuming parboiled rice.
Despite the hypothetical health risks of talc (such as stomach cancer),[80][81] talc-coated rice remains the norm in some countries due to its attractive shiny appearance, but it has been banned in some, and is no longer widely used in others (such as the United States). Even where talc is not used, glucose, starch, or other coatings may be used to improve the appearance of the grains.
Rice bran, called nuka in Japan, is a valuable commodity in Asia and is used for many daily needs. It is a moist, oily inner layer which is heated to produce oil. It is also used as a pickling bed in making rice bran pickles and takuan.
Raw rice may be ground into flour for many uses, including making many kinds of beverages, such as amazake, horchata, rice milk, and rice wine. Rice flour does not contain gluten, so is suitable for people on a gluten-free diet. Rice may also be made into various types of noodles. Raw, wild, or brown rice may also be consumed by raw-foodist or fruitarians if soaked and sprouted (usually a week to 30 days – gaba rice).
Processed rice seeds must be boiled or steamed before eating. Boiled rice may be further fried in cooking oil or butter (known as fried rice), or beaten in a tub to make mochi.
Rice is a good source of protein and a staple food in many parts of the world, but it is not a complete protein: it does not contain all of the essential amino acids in sufficient amounts for good health, and should be combined with other sources of protein, such as nuts, seeds, beans, fish, or meat.[82]
Rice, like other cereal grains, can be puffed (or popped). This process takes advantage of the grains' water content and typically involves heating grains in a special chamber. Further puffing is sometimes accomplished by processing puffed pellets in a low-pressure chamber. The ideal gas law means either lowering the local pressure or raising the water temperature results in an increase in volume prior to water evaporation, resulting in a puffy texture. Bulk raw rice density is about 0.9 g/cm³. It decreases to less than one-tenth that when puffed.
Harvesting, drying and milling

After the harvest, rice straw is gathered in the traditional way from small paddy fields in Mae Wang District, Chiang Mai Province, Thailand
A familiar sight in several Asian countries is paddy laid out to dry along roads. However, in most countries the bulk of drying of marketed paddy takes place in mills, with village-level drying being used for paddy to be consumed by farm families. Mills either sun dry or use mechanical driers or both. Drying has to be carried out quickly to avoid the formation of moulds. Mills range from simple hullers, with a throughput of a couple of tonnes a day, that simply remove the outer husk, to enormous operations that can process 4,000 tonnes a day and produce highly polished rice. A good mill can achieve a paddy-to-rice conversion rate of up to 72% but smaller, inefficient mills often struggle to achieve 60%. These smaller mills often do not buy paddy and sell rice but only service farmers who want to mill their paddy for their own consumption.
Distribution
Because of the importance of rice to human nutrition and food security in Asia, the domestic rice markets tend to be subject to considerable state involvement. While the private sector plays a leading role in most countries, agencies such as BULOG in Indonesia, the NFA in the Philippines, VINAFOOD in Vietnam and the Food Corporation of India are all heavily involved in purchasing of paddy from farmers or rice from mills and in distributing rice to poorer people. BULOG and NFA monopolise rice imports into their countries while VINAFOOD controls all exports from Vietnam.[83]Trade
World trade figures are very different from those for production, as less than 8% of rice produced is traded internationally.[84] In economic terms, the global rice trade was a small fraction of 1% of world mercantile trade. Many countries consider rice as a strategic food staple, and various governments subject its trade to a wide range of controls and interventions.Developing countries are the main players in the world rice trade, accounting for 83% of exports and 85% of imports. While there are numerous importers of rice, the exporters of rice are limited. Just five countries – Thailand, Vietnam, China, the United States and India – in decreasing order of exported quantities, accounted for about three-quarters of world rice exports in 2002.[75] However, this ranking has been rapidly changing in recent years. In 2010, the three largest exporters of rice, in decreasing order of quantity exported were Thailand, Vietnam and India. By 2012, India became the largest exporter of rice with a 100% increase in its exports on year to year basis, and Thailand slipped to third position.[85][86] Together, Thailand, Vietnam and India accounted for nearly 70% of the world rice exports.
The primary variety exported by Thailand and Vietnam were Jasmine rice, while exports from India included aromatic Basmati variety. China, an exporter of rice in early 2000s, was a net importer of rice in 2010 and will become the largest net importer, surpassing Nigeria, in 2013.[84][87] According to a USDA report, the world's largest exporters of rice in 2012 were India (9.75 million tonnes), Vietnam (7 million tonnes), Thailand (6.5 million tonnes), Pakistan (3.75 million tonnes) and the United States (3.5 million tonnes).[88]
Major importers usually include Nigeria, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Malaysia, the Philippines, Brazil and some African and Persian Gulf countries. In common with other West African countries, Nigeria is actively promoting domestic production. However, its very heavy import duties (110%) open it to smuggling from neighboring countries.[89] Parboiled rice is particularly popular in Nigeria. Although China and India are the two largest producers of rice in the world, both countries consume the majority of the rice produced domestically, leaving little to be traded internationally.
World's most productive rice farms and farmers
The average world yield for rice was 4.3 tonnes per hectare, in 2010.Australian rice farms were the most productive in 2010, with a nationwide average of 10.8 tonnes per hectare.[90]
Yuan Longping of China National Hybrid Rice Research and Development Center, China, set a world record for rice yield in 2010 at 19 tonnes per hectare on a demonstration plot. In 2011, this record was surpassed by an Indian farmer, Sumant Kumar, with 22.4 tonnes per hectare in Bihar. Both these farmers claim to have employed newly developed rice breeds and System of Rice Intensification (SRI), a recent innovation in rice farming. SRI is claimed to have set new national records in rice yields, within the last 10 years, in many countries. The claimed Chinese and Indian yields have yet to be demonstrated on seven-hectare lots and to be reproducible over two consecutive years on the same farm.[91][92][93][94]
Price
In late 2007 to May 2008, the price of grains rose greatly due to droughts in major producing countries (particularly Australia), increased use of grains for animal feed and US subsidies for bio-fuel production. Although there was no shortage of rice on world markets this general upward trend in grain prices led to panic buying by consumers, government rice export bans (in particular, by Vietnam and India) and inflated import orders by the Philippines marketing board, the National Food Authority. This caused significant rises in rice prices. In late April 2008, prices hit 24 US cents a pound, twice the price of seven months earlier.[95] Over the period of 2007 to 2013, the Chinese government has substantially increased the price it pays domestic farmers for their rice, rising to US$500 per metric ton by 2013.[84] The 2013 price of rice originating from other southeast Asian countries was a comparably low US$350 per metric ton.[84]On April 30, 2008, Thailand announced plans for the creation of the Organisation of Rice Exporting Countries (OREC) with the intention that this should develop into a price-fixing cartel for rice.[96][97] However, little progress had been made by mid-2011 to achieve this.
Worldwide consumption
| Food consumption of rice by country – 2009 (million metric ton of paddy equivalent)[98] |
|
|---|---|
| World Total | 531.6 |
| 156.3 | |
| 123.5 | |
| 45.3 | |
| 38.2 | |
| 18.4 | |
| 17.0 | |
| 13.7 | |
| 10.2 | |
| 10.0 | |
| 10.0 | |
| 5.8 | |
| 4.8 | |
| 4.6 | |
| 4.3 | |
| 3.8 | |
| 3.5 | |
| 3.4 | |
| 3.2 | |
| 3.2 | |
| 3.1 | |
| 2.8 | |
Rice is the most important crop in Asia. In Cambodia, for example, 90% of the total agricultural area is used for rice production.[99]
U.S. rice consumption has risen sharply over the past 25 years, fueled in part by commercial applications such as beer production.[100] Almost one in five adult Americans now report eating at least half a serving of white or brown rice per day.[101]
Environmental impacts

Work by the International Center for Tropical Agriculture to measure the greenhouse gas emissions of rice production.
Rice cultivation on wetland rice fields is thought to be responsible for 1.5% of the anthropogenic methane emissions.[102] Rice requires slightly more water to produce than other grains.[103] Rice production uses almost a third of Earth’s fresh water.[104]
Long-term flooding of rice fields cuts the soil off from atmospheric oxygen and causes anaerobic fermentation of organic matter in the soil.[105] Methane production from rice cultivation contributes ~1.5% of anthropogenic greenhouse gases.[106] Methane is twenty times more potent a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide.[107]
A 2010 study found that, as a result of rising temperatures and decreasing solar radiation during the later years of the 20th century, the rice yield growth rate has decreased in many parts of Asia, compared to what would have been observed had the temperature and solar radiation trends not occurred.[108][109] The yield growth rate had fallen 10–20% at some locations. The study was based on records from 227 farms in Thailand, Vietnam, Nepal, India, China, Bangladesh, and Pakistan. The mechanism of this falling yield was not clear, but might involve increased respiration during warm nights, which expends energy without being able to photosynthesize.
Rainfall
Temperature
Rice requires high temperature above 20 °C but not more than 35 to 40 °C. Optimum temperature is around 30 °C (Tmax) and 20 °C (Tmin).[110]Solar radiation
The amount of solar radiation received during 45 days after harvest determines final crop output.[110]Atmospheric water vapour
High water vapour content (in humid tropics) subjects unusual stress which favours the spread of fungal and bacterial diseases.[110]Wind
Light wind transports CO2 to the leaf canopy but strong wind cause severe damage and may lead to sterility (due to pollen dehydration, spikelet sterility, and abortive endosperms).[110]Pests and diseases
Rice pests are any organisms or microbes with the potential to reduce the yield or value of the rice crop (or of rice seeds).[111] Rice pests include weeds, pathogens, insects, nematode, rodents, and birds. A variety of factors can contribute to pest outbreaks, including climatic factors, improper irrigation, the overuse of insecticides and high rates of nitrogen fertilizer application.[112] Weather conditions also contribute to pest outbreaks. For example, rice gall midge and army worm outbreaks tend to follow periods of high rainfall early in the wet season, while thrips outbreaks are associated with drought.[113]Insects
Major rice insect pests include: the brown planthopper (BPH),[114] several spp. of stemborers – including those in the genera Scirpophaga and Chilo,[115] the rice gall midge,[116] several spp. of rice bugs[117] – notably in the genus Leptocorisa,[118] the rice leafroller and rice weevils.Diseases
Rice blast, caused by the fungus Magnaporthe grisea,[119] is the most significant disease affecting rice cultivation. Other major rice diseases include: sheath blight, rice ragged stunt (vector: BPH), and tungro (vector: Nephotettix spp).[120] There is also an ascomycete fungus, Cochliobolus miyabeanus, that causes brown spot disease in rice.[121][122]Nematodes
Several nematode species infect rice crops, causing diseases such as Ufra (Ditylenchus dipsaci), White tip disease (Aphelenchoide bessei), and root knot disease (Meloidogyne graminicola). Some nematode species such as Pratylenchus spp. are most dangerous in upland rice of all parts of the world. Rice root nematode (Hirschmanniella oryzae) is a migratory endoparasite which on higher inoculum levels will lead to complete destruction of a rice crop. Beyond being obligate parasites, they also decrease the vigor of plants and increase the plants' susceptibility to other pests and diseases.Other Pests
These include: the apple snail Pomacea canaliculata, panicle rice mite, rats,[123] and the weed Echinochloa crusgali.[124]Integrated Pest Management
Crop protection scientists are trying to develop rice pest management techniques which are sustainable. In other words, to manage crop pests in such a manner that future crop production is not threatened.[125] Sustainable pest management is based on four principles: biodiversity, host plant resistance (HPR), landscape ecology, and hierarchies in a landscape – from biological to social.[126]
At present, rice pest management includes cultural techniques, pest-resistant rice varieties, and pesticides (which include insecticide). Increasingly, there is evidence that farmers' pesticide applications are often unnecessary, and even facilitate pest outbreaks.[127][128][129][130] By reducing the populations of natural enemies of rice pests,[131] misuse of insecticides can actually lead to pest outbreaks.[132] The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) demonstrated in 1993 that an 87.5% reduction in pesticide use can lead to an overall drop in pest numbers.[133] IRRI also conducted two campaigns in 1994 and 2003, respectively, which discouraged insecticide misuse and smarter pest management in Vietnam.[134][135]
Rice plants produce their own chemical defenses to protect themselves from pest attacks. Some synthetic chemicals, such as the herbicide 2,4-D, cause the plant to increase the production of certain defensive chemicals and thereby increase the plant’s resistance to some types of pests.[136] Conversely, other chemicals, such as the insecticide imidacloprid, can induce changes in the gene expression of the rice that cause the plant to become more susceptible to attacks by certain types of pests.[137] 5-Alkylresorcinols are chemicals that can also be found in rice.[138]
Botanicals, so-called "natural pesticides", are used by some farmers in an attempt to control rice pests. Botanicals include extracts of leaves, or a mulch of the leaves themselves. Some upland rice farmers in Cambodia spread chopped leaves of the bitter bush (Chromolaena odorata) over the surface of fields after planting. This practice probably helps the soil retain moisture and thereby facilitates seed germination. Farmers also claim the leaves are a natural fertilizer and helps suppress weed and insect infestations.[139]
Among rice cultivars, there are differences in the responses to, and recovery from, pest damage.[117][140] Many rice varieties have been selected for resistance to insect pests.[141][142] Therefore, particular cultivars are recommended for areas prone to certain pest problems. The genetically based ability of a rice variety to withstand pest attacks is called resistance. Three main types of plant resistance to pests are recognized as nonpreference, antibiosis, and tolerance.[143] Nonpreference (or antixenosis) describes host plants which insects prefer to avoid; antibiosis is where insect survival is reduced after the ingestion of host tissue; and tolerance is the capacity of a plant to produce high yield or retain high quality despite insect infestation.[144]
Over time, the use of pest resistant rice varieties selects for pests that are able to overcome these mechanisms of resistance. When a rice variety is no longer able to resist pest infestations, resistance is said to have broken down. Rice varieties that can be widely grown for many years in the presence of pests and retain their ability to withstand the pests are said to have durable resistance. Mutants of popular rice varieties are regularly screened by plant breeders to discover new sources of durable resistance.[143][145]

While most rice is bred for crop quality and productivity, there are varieties selected for characteristics such as texture, smell, and firmness. There are four major categories of rice worldwide: indica, japonica, aromatic and glutinous. The different varieties of rice are not considered interchangeable, either in food preparation or agriculture, so as a result, each major variety is a completely separate market from other varieties. It is common for one variety of rice to rise in price while another one drops in price.[147]
Rice cultivars also fall into groups according to environmental conditions, season of planting, and season of harvest, called ecotypes. Some major groups are the Japan-type (grown in Japan), "buly" and "tjereh" types (Indonesia); "aman" (main winter crop), "aus" ("aush", summer), and "boro" (spring) (Bengal and Assam).[148][149] Cultivars exist that are adapted to deep flooding, and these are generally called "floating rice".[150]
The largest collection of rice cultivars is at the International Rice Research Institute[151] in the Philippines, with over 100,000 rice accessions[152] held in the International Rice Genebank.[153] Rice cultivars are often classified by their grain shapes and texture. For example, Thai Jasmine rice is long-grain and relatively less sticky, as some long-grain rice contains less amylopectin than short-grain cultivars. Chinese restaurants often serve long-grain as plain unseasoned steamed rice though short-grain rice is common as well. Japanese mochi rice and Chinese sticky rice are short-grain. Chinese people use sticky rice which is properly known as "glutinous rice" (note: glutinous refer to the glue-like characteristic of rice; does not refer to "gluten") to make zongzi. The Japanese table rice is a sticky, short-grain rice. Japanese sake rice is another kind as well.
Indian rice cultivars include long-grained and aromatic Basmati (ਬਾਸਮਤੀ) (grown in the North), long and medium-grained Patna rice, and in South India (Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka) short-grained Sona Masuri (also called as Bangaru theegalu). In the state of Tamil Nadu, the most prized cultivar is ponni which is primarily grown in the delta regions of the Kaveri River. Kaveri is also referred to as ponni in the South and the name reflects the geographic region where it is grown. In the Western Indian state of Maharashtra, a short grain variety called Ambemohar is very popular. This rice has a characteristic fragrance of Mango blossom.
Aromatic rices have definite aromas and flavors; the most noted cultivars are Thai fragrant rice, Basmati, Patna rice, Vietnamese fragrant rice, and a hybrid cultivar from America, sold under the trade name Texmati. Both Basmati and Texmati have a mild popcorn-like aroma and flavor. In Indonesia, there are also red and black cultivars.
High-yield cultivars of rice suitable for cultivation in Africa and other dry ecosystems, called the new rice for Africa (NERICA) cultivars, have been developed. It is hoped that their cultivation will improve food security in West Africa.
Draft genomes for the two most common rice cultivars, indica and japonica, were published in April 2002. Rice was chosen as a model organism for the biology of grasses because of its relatively small genome (~430 megabase pairs). Rice was the first crop with a complete genome sequence.[154]
On December 16, 2002, the UN General Assembly declared the year 2004 the International Year of Rice. The declaration was sponsored by more than 40 countries.
Scientists have identified and cloned many genes involved in the gibberellin signaling pathway, including GAI1 (Gibberellin Insensitive) and SLR1 (Slender Rice).[156] Disruption of gibberellin signaling can lead to significantly reduced stem growth leading to a dwarf phenotype. Photosynthetic investment in the stem is reduced dramatically as the shorter plants are inherently more stable mechanically. Assimilates become redirected to grain production, amplifying in particular the effect of chemical fertilizers on commercial yield. In the presence of nitrogen fertilizers, and intensive crop management, these varieties increase their yield two to three times.
The International Rice Research Institute is currently further developing and evaluating Golden Rice as a potential new way to help address vitamin A deficiency.[159]
Rice containing these added proteins can be used as a component in oral rehydration solutions which are used to treat diarrheal diseases, thereby shortening their duration and reducing recurrence. Such supplements may also help reverse anemia.[161]
In response to this hazard, a variety of rice named Swarna Sub1 was developed via marker-assisted selection, with the ability to withstand prolonged periods of around 14 days beneath a flooded plain.[162][164] The submergence tolerance ability of this variety is conferred by the presence of the Sub1A gene, introgressed from the Indian cultivar FR13A into the flood-vulnerable (but high yielding) cultivar Swarna.[162][164] Swarna Sub1 effectively enters a dormant, energy conserving state upon being submerged in a flooded rice paddy, a process that involves the finely controlled metabolism of enzymes such amylases, starch phosphorylase and alcohol dehydrogenase, allowing the plant to survive with limited oxygen and sunlight unlike its standard variety relatives.[162][164] Given that the presence of the Sub1A gene does not impact upon the quality or quantity of the rice obtained,[162] this variety has been very popular, with 1.7 million hectares of land in India having Swarna Sub1 and other flood resistant varieties used instead of conventional rice crops.[165]
The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) conducts research into developing drought tolerant rice varieties, including the varieties 5411 and Sookha dhan, currently being employed by farmers in the Philippines and Nepal respectively.[167] In addition, in 2013 the Japanese National Institute for Agrobiological Sciences led a team which successfully inserted the DEEPER ROOTING 1 (DRO1), from the Philippine upland rice variety Kinandang Patong, into the popular commercial rice variety IR64, giving rise to a far deeper root system in the resulting plants.[168] This facilitates an improved ability for the rice plant to derive its required nutrients in times of drought via accessing deeper layers of soil, a feature demonstrated by trials which saw the IR64 + DRO1 rice yields drop by 10% under moderate drought conditions, compared to 60% for the unmodified IR64 variety.[168] [169]
Progress has been made, however, in developing rice varieties capable of tolerating such conditions; the hybrid created from the cross between the commercial rice variety IR56 and the wild rice species Oryza coarctata is one example.[173] O. coarctata is capable of successful growth in soils with double the limit of salinity of normal varieties, but lacks the ability to produce edible rice.[173] Developed by the International Rice Research Institute, the hybrid variety can utilise specialised leaf glands that allow for the removal of salt into the atmosphere. It was initially produced from one successful embryo out of 34,000 crosses between the two species; this was then backcrossed to IR56 with the aim of preserving the genes responsible for salt tolerance that were inherited from O. coarctata.[171] Furthermore, extensive trials are planned prior to the new variety being available to farmers by approximately 2017–18.[171]
Rice plays an important role in certain religions and popular beliefs. In many cultures relatives will scatter rice during or towards the end of a wedding ceremony in front of the bride and groom.[178]
The pounded rice ritual is conducted during weddings in Nepal. The bride gives a leafplate full of pounded rice to the groom after he requests it politely from her.[179]
In the Philippines rice wine, popularly known as tapuy, is used for important occasions such as weddings, rice harvesting ceremonies and other celebrations.[180]
Dewi Sri is the traditional rice goddess of the Javanese, Sundanese, and Balinese people in Indonesia. Most rituals involving Dewi Sri are associated with the mythical origin attributed to the rice plant, the staple food of the region.[181] [182] In Thailand a similar rice deity is known as Phosop; she is a deity more related to ancient local folklore than a goddess of a structured, mainstream religion.[183] The same female rice deity is known as Po Ino Nogar in Cambodia and as Nang Khosop in Laos. Ritual offerings are made during the different stages of rice production to propitiate the Rice Goddess in the corresponding cultures.
Rice plants produce their own chemical defenses to protect themselves from pest attacks. Some synthetic chemicals, such as the herbicide 2,4-D, cause the plant to increase the production of certain defensive chemicals and thereby increase the plant’s resistance to some types of pests.[136] Conversely, other chemicals, such as the insecticide imidacloprid, can induce changes in the gene expression of the rice that cause the plant to become more susceptible to attacks by certain types of pests.[137] 5-Alkylresorcinols are chemicals that can also be found in rice.[138]
Botanicals, so-called "natural pesticides", are used by some farmers in an attempt to control rice pests. Botanicals include extracts of leaves, or a mulch of the leaves themselves. Some upland rice farmers in Cambodia spread chopped leaves of the bitter bush (Chromolaena odorata) over the surface of fields after planting. This practice probably helps the soil retain moisture and thereby facilitates seed germination. Farmers also claim the leaves are a natural fertilizer and helps suppress weed and insect infestations.[139]
Among rice cultivars, there are differences in the responses to, and recovery from, pest damage.[117][140] Many rice varieties have been selected for resistance to insect pests.[141][142] Therefore, particular cultivars are recommended for areas prone to certain pest problems. The genetically based ability of a rice variety to withstand pest attacks is called resistance. Three main types of plant resistance to pests are recognized as nonpreference, antibiosis, and tolerance.[143] Nonpreference (or antixenosis) describes host plants which insects prefer to avoid; antibiosis is where insect survival is reduced after the ingestion of host tissue; and tolerance is the capacity of a plant to produce high yield or retain high quality despite insect infestation.[144]
Over time, the use of pest resistant rice varieties selects for pests that are able to overcome these mechanisms of resistance. When a rice variety is no longer able to resist pest infestations, resistance is said to have broken down. Rice varieties that can be widely grown for many years in the presence of pests and retain their ability to withstand the pests are said to have durable resistance. Mutants of popular rice varieties are regularly screened by plant breeders to discover new sources of durable resistance.[143][145]
Parasitic weeds
Rice is parasitized by the weed eudicot Striga hermonthica.[146] which is of local importance for this crop.Ecotypes and cultivars

Rice seed collection from IRRI
While most rice is bred for crop quality and productivity, there are varieties selected for characteristics such as texture, smell, and firmness. There are four major categories of rice worldwide: indica, japonica, aromatic and glutinous. The different varieties of rice are not considered interchangeable, either in food preparation or agriculture, so as a result, each major variety is a completely separate market from other varieties. It is common for one variety of rice to rise in price while another one drops in price.[147]
Rice cultivars also fall into groups according to environmental conditions, season of planting, and season of harvest, called ecotypes. Some major groups are the Japan-type (grown in Japan), "buly" and "tjereh" types (Indonesia); "aman" (main winter crop), "aus" ("aush", summer), and "boro" (spring) (Bengal and Assam).[148][149] Cultivars exist that are adapted to deep flooding, and these are generally called "floating rice".[150]
The largest collection of rice cultivars is at the International Rice Research Institute[151] in the Philippines, with over 100,000 rice accessions[152] held in the International Rice Genebank.[153] Rice cultivars are often classified by their grain shapes and texture. For example, Thai Jasmine rice is long-grain and relatively less sticky, as some long-grain rice contains less amylopectin than short-grain cultivars. Chinese restaurants often serve long-grain as plain unseasoned steamed rice though short-grain rice is common as well. Japanese mochi rice and Chinese sticky rice are short-grain. Chinese people use sticky rice which is properly known as "glutinous rice" (note: glutinous refer to the glue-like characteristic of rice; does not refer to "gluten") to make zongzi. The Japanese table rice is a sticky, short-grain rice. Japanese sake rice is another kind as well.
Indian rice cultivars include long-grained and aromatic Basmati (ਬਾਸਮਤੀ) (grown in the North), long and medium-grained Patna rice, and in South India (Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka) short-grained Sona Masuri (also called as Bangaru theegalu). In the state of Tamil Nadu, the most prized cultivar is ponni which is primarily grown in the delta regions of the Kaveri River. Kaveri is also referred to as ponni in the South and the name reflects the geographic region where it is grown. In the Western Indian state of Maharashtra, a short grain variety called Ambemohar is very popular. This rice has a characteristic fragrance of Mango blossom.
Aromatic rices have definite aromas and flavors; the most noted cultivars are Thai fragrant rice, Basmati, Patna rice, Vietnamese fragrant rice, and a hybrid cultivar from America, sold under the trade name Texmati. Both Basmati and Texmati have a mild popcorn-like aroma and flavor. In Indonesia, there are also red and black cultivars.
High-yield cultivars of rice suitable for cultivation in Africa and other dry ecosystems, called the new rice for Africa (NERICA) cultivars, have been developed. It is hoped that their cultivation will improve food security in West Africa.
Draft genomes for the two most common rice cultivars, indica and japonica, were published in April 2002. Rice was chosen as a model organism for the biology of grasses because of its relatively small genome (~430 megabase pairs). Rice was the first crop with a complete genome sequence.[154]
On December 16, 2002, the UN General Assembly declared the year 2004 the International Year of Rice. The declaration was sponsored by more than 40 countries.
Biotechnology
High-yielding varieties
The high-yielding varieties are a group of crops created intentionally during the Green Revolution to increase global food production. This project enabled labor markets in Asia to shift away from agriculture, and into industrial sectors. The first "Rice Car", IR8 was produced in 1966 at the International Rice Research Institute which is based in the Philippines at the University of the Philippines' Los Baños site. IR8 was created through a cross between an Indonesian variety named "Peta" and a Chinese variety named "Dee Geo Woo Gen."[155]Scientists have identified and cloned many genes involved in the gibberellin signaling pathway, including GAI1 (Gibberellin Insensitive) and SLR1 (Slender Rice).[156] Disruption of gibberellin signaling can lead to significantly reduced stem growth leading to a dwarf phenotype. Photosynthetic investment in the stem is reduced dramatically as the shorter plants are inherently more stable mechanically. Assimilates become redirected to grain production, amplifying in particular the effect of chemical fertilizers on commercial yield. In the presence of nitrogen fertilizers, and intensive crop management, these varieties increase their yield two to three times.
Future potential
As the UN Millennium Development project seeks to spread global economic development to Africa, the "Green Revolution" is cited as the model for economic development. With the intent of replicating the successful Asian boom in agronomic productivity, groups like the Earth Institute are doing research on African agricultural systems, hoping to increase productivity. An important way this can happen is the production of "New Rices for Africa" (NERICA). These rices, selected to tolerate the low input and harsh growing conditions of African agriculture, are produced by the African Rice Center, and billed as technology "from Africa, for Africa". The NERICA have appeared in The New York Times (October 10, 2007) and International Herald Tribune (October 9, 2007), trumpeted as miracle crops that will dramatically increase rice yield in Africa and enable an economic resurgence. Ongoing research in China to develop perennial rice could result in enhanced sustainability and food security.Golden rice
Rice kernels do not contain vitamin A, so people who obtain most of their calories from rice are at risk of vitamin A deficiency. German and Swiss researchers have genetically engineered rice to produce beta-carotene, the precursor to vitamin A, in the rice kernel. The beta-carotene turns the processed (white) rice a "gold" color, hence the name "golden rice." The beta-carotene is converted to vitamin A in humans who consume the rice.[157] Although some rice strains produce beta-carotene in the hull, no non-genetically engineered strains have been found that produce beta-carotene in the kernel, despite the testing of thousands of strains. Additional efforts are being made to improve the quantity and quality of other nutrients in golden rice.[158]The International Rice Research Institute is currently further developing and evaluating Golden Rice as a potential new way to help address vitamin A deficiency.[159]
Expression of human proteins
Ventria Bioscience has genetically modified rice to express lactoferrin, lysozyme which are proteins usually found in breast milk, and human serum albumin, These proteins have antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal effects.[160]Rice containing these added proteins can be used as a component in oral rehydration solutions which are used to treat diarrheal diseases, thereby shortening their duration and reducing recurrence. Such supplements may also help reverse anemia.[161]
Flood tolerant rice
Flooding is an issue that many rice growers face, especially in South and South East Asia where flooding annually affects 20 million hectares.[162] Standard rice varieties cannot withstand stagnant flooding of more than about a week,[163] mainly as it disallows the plant access to necessary requirements such as sunlight and essential gas exchanges, inevitably leading to plants being unable to recover.[162] In the past, this has led to a massive losses in yields, such as in the Philippines, where in 2006, rice crops worth $65 million were lost to flooding.[164]In response to this hazard, a variety of rice named Swarna Sub1 was developed via marker-assisted selection, with the ability to withstand prolonged periods of around 14 days beneath a flooded plain.[162][164] The submergence tolerance ability of this variety is conferred by the presence of the Sub1A gene, introgressed from the Indian cultivar FR13A into the flood-vulnerable (but high yielding) cultivar Swarna.[162][164] Swarna Sub1 effectively enters a dormant, energy conserving state upon being submerged in a flooded rice paddy, a process that involves the finely controlled metabolism of enzymes such amylases, starch phosphorylase and alcohol dehydrogenase, allowing the plant to survive with limited oxygen and sunlight unlike its standard variety relatives.[162][164] Given that the presence of the Sub1A gene does not impact upon the quality or quantity of the rice obtained,[162] this variety has been very popular, with 1.7 million hectares of land in India having Swarna Sub1 and other flood resistant varieties used instead of conventional rice crops.[165]
Drought tolerant rice
Drought represents a significant environmental stress for rice production, with 19–23 million hectares of rainfed rice production in South and South East Asia often at risk.[166][167] Under drought conditions, without sufficient water to afford them the ability to obtain the required levels of nutrients from the soil, conventional commercial rice varieties can be severely impacted – for example yield losses as high as 40% have affected some parts of India, with resulting losses of around US$800 million annually.[168]The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) conducts research into developing drought tolerant rice varieties, including the varieties 5411 and Sookha dhan, currently being employed by farmers in the Philippines and Nepal respectively.[167] In addition, in 2013 the Japanese National Institute for Agrobiological Sciences led a team which successfully inserted the DEEPER ROOTING 1 (DRO1), from the Philippine upland rice variety Kinandang Patong, into the popular commercial rice variety IR64, giving rise to a far deeper root system in the resulting plants.[168] This facilitates an improved ability for the rice plant to derive its required nutrients in times of drought via accessing deeper layers of soil, a feature demonstrated by trials which saw the IR64 + DRO1 rice yields drop by 10% under moderate drought conditions, compared to 60% for the unmodified IR64 variety.[168] [169]
Salt tolerant rice
Soil salinity poses a major threat to rice crop productivity, particularly along low-lying coastal areas during the dry season[166] – for example, roughly 1 million hectares of the coastal areas of Bangladesh are affected by saline soils.[170] These high concentrations of salt can severely impact upon rice plants’ normal physiology, especially during early stages of growth, and as such farmers are often forced to abandon these otherwise potentially usable areas.[171][172]Progress has been made, however, in developing rice varieties capable of tolerating such conditions; the hybrid created from the cross between the commercial rice variety IR56 and the wild rice species Oryza coarctata is one example.[173] O. coarctata is capable of successful growth in soils with double the limit of salinity of normal varieties, but lacks the ability to produce edible rice.[173] Developed by the International Rice Research Institute, the hybrid variety can utilise specialised leaf glands that allow for the removal of salt into the atmosphere. It was initially produced from one successful embryo out of 34,000 crosses between the two species; this was then backcrossed to IR56 with the aim of preserving the genes responsible for salt tolerance that were inherited from O. coarctata.[171] Furthermore, extensive trials are planned prior to the new variety being available to farmers by approximately 2017–18.[171]
Meiosis and DNA repair
Rice is used as a model organism for investigating the molecular mechanisms of meiosis and DNA repair in higher plants. Meiosis is a key stage of the sexual cycle in which diploid cells in the ovule (female structure) and the anther (male structure) produce haploid cells that develop further into gametophytes and gametes. So far, 28 meiotic genes of rice have been characterized.[174] Studies of rice gene OsRAD51C showed that this gene is necessary for homologous recombinational repair of DNA, particularly the accurate repair of DNA double-strand breaks during meiosis.[175] Rice gene OsDMC1 was found to be essential for pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis,[176] and rice gene OsMRE11 was found to be required for both synapsis of homologous chromosomes and repair of double-strand breaks during meiosis.[177]Cultural roles of rice
Rice plays an important role in certain religions and popular beliefs. In many cultures relatives will scatter rice during or towards the end of a wedding ceremony in front of the bride and groom.[178]
The pounded rice ritual is conducted during weddings in Nepal. The bride gives a leafplate full of pounded rice to the groom after he requests it politely from her.[179]
In the Philippines rice wine, popularly known as tapuy, is used for important occasions such as weddings, rice harvesting ceremonies and other celebrations.[180]
Dewi Sri is the traditional rice goddess of the Javanese, Sundanese, and Balinese people in Indonesia. Most rituals involving Dewi Sri are associated with the mythical origin attributed to the rice plant, the staple food of the region.[181] [182] In Thailand a similar rice deity is known as Phosop; she is a deity more related to ancient local folklore than a goddess of a structured, mainstream religion.[183] The same female rice deity is known as Po Ino Nogar in Cambodia and as Nang Khosop in Laos. Ritual offerings are made during the different stages of rice production to propitiate the Rice Goddess in the corresponding cultures.