The mathematical constant π is an irrational number that is much represented in popular culture.
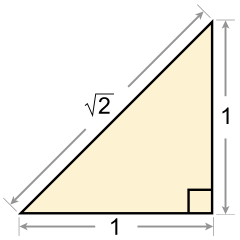
The number √2 is irrational.
In mathematics, the irrational numbers are all the real numbers which are not rational numbers, the latter being the numbers constructed from ratios (or fractions) of integers. When the ratio of lengths of two line segments is an irrational number, the line segments are also described as being incommensurable, meaning that they share no "measure" in common, that is, there is no length ("the measure"), no matter how short, that could be used to express the lengths of both of the two given segments as integer multiples of itself.
Among irrational numbers are the ratio π of a circle's circumference to its diameter, Euler's number e, the golden ratio φ, and the square root of two; in fact all square roots of natural numbers, other than of perfect squares, are irrational.
It can be shown that irrational numbers, when expressed in a positional numeral system (e.g. as decimal numbers, or with any other natural basis), do not terminate, nor do they repeat, i.e., do not contain a subsequence of digits, the repetition of which makes up the tail of the representation. For example, the decimal representation of the number π starts with 3.14159, but no finite number of digits can represent π exactly, nor does it repeat. The proof that the decimal expansion of a rational number must terminate or repeat is distinct from the proof that a decimal expansion that terminates or repeats must be a rational number, and although elementary and not lengthy, both proofs take some work. Mathematicians do not generally take "terminating or repeating" to be the definition of the concept of rational number.
Irrational numbers may also be dealt with via non-terminating continued fractions.
As a consequence of Cantor's proof that the real numbers are uncountable and the rationals countable, it follows that almost all real numbers are irrational.
History
Set
of real numbers (R), which include the rationals (Q), which include the
integers (Z), which include the natural numbers (N). The real numbers
also include the irrationals (R\Q).
Ancient Greece
The first proof of the existence of irrational numbers is usually attributed to a Pythagorean (possibly Hippasus of Metapontum), who probably discovered them while identifying sides of the pentagram. The then-current Pythagorean method would have claimed that there must be some sufficiently small, indivisible unit that could fit evenly into one of these lengths as well as the other. However, Hippasus, in the 5th century BC, was able to deduce that there was in fact no common unit of measure, and that the assertion of such an existence was in fact a contradiction. He did this by demonstrating that if the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle was indeed commensurable with a leg, then one of those lengths measured in that unit of measure must be both odd and even, which is impossible. His reasoning is as follows:- Start with an isosceles right triangle with side lengths of integers a, b, and c. The ratio of the hypotenuse to a leg is represented by c:b.
- Assume a, b, and c are in the smallest possible terms (i.e. they have no common factors).
- By the Pythagorean theorem: c2 = a2+b2 = b2+b2 = 2b2. (Since the triangle is isosceles, a = b).
- Since c2 = 2b2, c2 is divisible by 2, and therefore even.
- Since c2 is even, c must be even.
- Since c is even, dividing c by 2 yields an integer. Let y be this integer (c = 2y).
- Squaring both sides of c = 2y yields c2 = (2y)2, or c2 = 4y2.
- Substituting 4y2 for c2 in the first equation (c2 = 2b2) gives us 4y2= 2b2.
- Dividing by 2 yields 2y2 = b2.
- Since y is an integer, and 2y2 = b2, b2 is divisible by 2, and therefore even.
- Since b2 is even, b must be even.
- We have just shown that both b and c must be even. Hence they have a common factor of 2. However this contradicts the assumption that they have no common factors. This contradiction proves that c and b cannot both be integers, and thus the existence of a number that cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers.
The discovery of incommensurable ratios was indicative of another problem facing the Greeks: the relation of the discrete to the continuous. Brought into light by Zeno of Elea, who questioned the conception that quantities are discrete and composed of a finite number of units of a given size. Past Greek conceptions dictated that they necessarily must be, for “whole numbers represent discrete objects, and a commensurable ratio represents a relation between two collections of discrete objects.” However Zeno found that in fact “[quantities] in general are not discrete collections of units; this is why ratios of incommensurable [quantities] appear….[Q]uantities are, in other words, continuous.” What this means is that, contrary to the popular conception of the time, there cannot be an indivisible, smallest unit of measure for any quantity. That in fact, these divisions of quantity must necessarily be infinite. For example, consider a line segment: this segment can be split in half, that half split in half, the half of the half in half, and so on. This process can continue infinitely, for there is always another half to be split. The more times the segment is halved, the closer the unit of measure comes to zero, but it never reaches exactly zero. This is just what Zeno sought to prove. He sought to prove this by formulating four paradoxes, which demonstrated the contradictions inherent in the mathematical thought of the time. While Zeno’s paradoxes accurately demonstrated the deficiencies of current mathematical conceptions, they were not regarded as proof of the alternative. In the minds of the Greeks, disproving the validity of one view did not necessarily prove the validity of another, and therefore further investigation had to occur.
The next step was taken by Eudoxus of Cnidus, who formalized a new theory of proportion that took into account commensurable as well as incommensurable quantities. Central to his idea was the distinction between magnitude and number. A magnitude “...was not a number but stood for entities such as line segments, angles, areas, volumes, and time which could vary, as we would say, continuously. Magnitudes were opposed to numbers, which jumped from one value to another, as from 4 to 5.” Numbers are composed of some smallest, indivisible unit, whereas magnitudes are infinitely reducible. Because no quantitative values were assigned to magnitudes, Eudoxus was then able to account for both commensurable and incommensurable ratios by defining a ratio in terms of its magnitude, and proportion as an equality between two ratios. By taking quantitative values (numbers) out of the equation, he avoided the trap of having to express an irrational number as a number. “Eudoxus’ theory enabled the Greek mathematicians to make tremendous progress in geometry by supplying the necessary logical foundation for incommensurable ratios.” This incommensurability is dealt with in Euclid's Elements, Book X, Proposition 9.
As a result of the distinction between number and magnitude, geometry became the only method that could take into account incommensurable ratios. Because previous numerical foundations were still incompatible with the concept of incommensurability, Greek focus shifted away from those numerical conceptions such as algebra and focused almost exclusively on geometry. In fact, in many cases algebraic conceptions were reformulated into geometrical terms. This may account for why we still conceive of x2 or x3 as x squared and x cubed instead of x second power and x third power. Also crucial to Zeno’s work with incommensurable magnitudes was the fundamental focus on deductive reasoning that resulted from the foundational shattering of earlier Greek mathematics. The realization that some basic conception within the existing theory was at odds with reality necessitated a complete and thorough investigation of the axioms and assumptions that underlie that theory. Out of this necessity, Eudoxus developed his method of exhaustion, a kind of reductio ad absurdum that “…established the deductive organization on the basis of explicit axioms…” as well as “…reinforced the earlier decision to rely on deductive reasoning for proof.” This method of exhaustion is the first step in the creation of calculus.
Theodorus of Cyrene proved the irrationality of the surds of whole numbers up to 17, but stopped there probably because the algebra he used could not be applied to the square root of 17.
It was not until Eudoxus developed a theory of proportion that took into account irrational as well as rational ratios that a strong mathematical foundation of irrational numbers was created.
India
Geometrical and mathematical problems involving irrational numbers such as square roots were addressed very early during the Vedic period in India. There are references to such calculations in the Samhitas, Brahmanas, and the Shulba Sutras (800 BC or earlier). (See Bag, Indian Journal of History of Science, 25(1-4), 1990).It is suggested that the concept of irrationality was implicitly accepted by Indian mathematicians since the 7th century BC, when Manava (c. 750 – 690 BC) believed that the square roots of numbers such as 2 and 61 could not be exactly determined. However, historian Carl Benjamin Boyer writes that "such claims are not well substantiated and unlikely to be true".
It is also suggested that Aryabhata (5th century AD), in calculating a value of pi to 5 significant figures, used the word āsanna (approaching), to mean that not only is this an approximation but that the value is incommensurable (or irrational).
Later, in their treatises, Indian mathematicians wrote on the arithmetic of surds including addition, subtraction, multiplication, rationalization, as well as separation and extraction of square roots.
Mathematicians like Brahmagupta (in 628 AD) and Bhaskara I (in 629 AD) made contributions in this area as did other mathematicians who followed. In the 12th century Bhaskara II evaluated some of these formulas and critiqued them, identifying their limitations.
During the 14th to 16th centuries, Madhava of Sangamagrama and the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics discovered the infinite series for several irrational numbers such as π and certain irrational values of trigonometric functions. Jyeṣṭhadeva provided proofs for these infinite series in the Yuktibhāṣā.
Middle Ages
In the Middle ages, the development of algebra by Muslim mathematicians allowed irrational numbers to be treated as algebraic objects. Middle Eastern mathematicians also merged the concepts of "number" and "magnitude" into a more general idea of real numbers, criticized Euclid's idea of ratios, developed the theory of composite ratios, and extended the concept of number to ratios of continuous magnitude. In his commentary on Book 10 of the Elements, the Persian mathematician Al-Mahani (d. 874/884) examined and classified quadratic irrationals and cubic irrationals. He provided definitions for rational and irrational magnitudes, which he treated as irrational numbers. He dealt with them freely but explains them in geometric terms as follows:"It will be a rational (magnitude) when we, for instance, say 10, 12, 3%, 6%, etc., because its value is pronounced and expressed quantitatively. What is not rational is irrational and it is impossible to pronounce and represent its value quantitatively. For example: the roots of numbers such as 10, 15, 20 which are not squares, the sides of numbers which are not cubes etc."In contrast to Euclid's concept of magnitudes as lines, Al-Mahani considered integers and fractions as rational magnitudes, and square roots and cube roots as irrational magnitudes. He also introduced an arithmetical approach to the concept of irrationality, as he attributes the following to irrational magnitudes:
"their sums or differences, or results of their addition to a rational magnitude, or results of subtracting a magnitude of this kind from an irrational one, or of a rational magnitude from it."The Egyptian mathematician Abū Kāmil Shujā ibn Aslam (c. 850 – 930) was the first to accept irrational numbers as solutions to quadratic equations or as coefficients in an equation, often in the form of square roots, cube roots and fourth roots. In the 10th century, the Iraqi mathematician Al-Hashimi provided general proofs (rather than geometric demonstrations) for irrational numbers, as he considered multiplication, division, and other arithmetical functions. Iranian mathematician, Abū Ja'far al-Khāzin (900–971) provides a definition of rational and irrational magnitudes, stating that if a definite quantity is:
"contained in a certain given magnitude once or many times, then this (given) magnitude corresponds to a rational number. . . . Each time when this (latter) magnitude comprises a half, or a third, or a quarter of the given magnitude (of the unit), or, compared with (the unit), comprises three, five, or three fifths, it is a rational magnitude. And, in general, each magnitude that corresponds to this magnitude (i.e. to the unit), as one number to another, is rational. If, however, a magnitude cannot be represented as a multiple, a part (l/n), or parts (m/n) of a given magnitude, it is irrational, i.e. it cannot be expressed other than by means of roots."Many of these concepts were eventually accepted by European mathematicians sometime after the Latin translations of the 12th century. Al-Hassār, a Moroccan mathematician from Fez specializing in Islamic inheritance jurisprudence during the 12th century, first mentions the use of a fractional bar, where numerators and denominators are separated by a horizontal bar. In his discussion he writes, "..., for example, if you are told to write three-fifths and a third of a fifth, write thus, ." This same fractional notation appears soon after in the work of Leonardo Fibonacci in the 13th century.
Modern period
The 17th century saw imaginary numbers become a powerful tool in the hands of Abraham de Moivre, and especially of Leonhard Euler. The completion of the theory of complex numbers in the 19th century entailed the differentiation of irrationals into algebraic and transcendental numbers, the proof of the existence of transcendental numbers, and the resurgence of the scientific study of the theory of irrationals, largely ignored since Euclid. The year 1872 saw the publication of the theories of Karl Weierstrass (by his pupil Ernst Kossak), Eduard Heine (Crelle's Journal, 74), Georg Cantor (Annalen, 5), and Richard Dedekind. Méray had taken in 1869 the same point of departure as Heine, but the theory is generally referred to the year 1872. Weierstrass's method has been completely set forth by Salvatore Pincherle in 1880, and Dedekind's has received additional prominence through the author's later work (1888) and the endorsement by Paul Tannery (1894). Weierstrass, Cantor, and Heine base their theories on infinite series, while Dedekind founds his on the idea of a cut (Schnitt) in the system of all rational numbers, separating them into two groups having certain characteristic properties. The subject has received later contributions at the hands of Weierstrass, Leopold Kronecker (Crelle, 101), and Charles Méray.Continued fractions, closely related to irrational numbers (and due to Cataldi, 1613), received attention at the hands of Euler, and at the opening of the 19th century were brought into prominence through the writings of Joseph-Louis Lagrange. Dirichlet also added to the general theory, as have numerous contributors to the applications of the subject.
Johann Heinrich Lambert proved (1761) that π cannot be rational, and that en is irrational if n is rational (unless n = 0). While Lambert's proof is often called incomplete, modern assessments support it as satisfactory, and in fact for its time it is unusually rigorous. Adrien-Marie Legendre (1794), after introducing the Bessel–Clifford function, provided a proof to show that π2 is irrational, whence it follows immediately that π is irrational also. The existence of transcendental numbers was first established by Liouville (1844, 1851). Later, Georg Cantor (1873) proved their existence by a different method, which showed that every interval in the reals contains transcendental numbers. Charles Hermite (1873) first proved e transcendental, and Ferdinand von Lindemann (1882), starting from Hermite's conclusions, showed the same for π. Lindemann's proof was much simplified by Weierstrass (1885), still further by David Hilbert (1893), and was finally made elementary by Adolf Hurwitz and Paul Gordan.
Examples
Square roots
The square root of 2 was the first number proved irrational, and that article contains a number of proofs. The golden ratio is another famous quadratic irrational and there is a simple proof of its irrationality in its article. The square roots of all natural numbers which are not perfect squares are irrational and a proof may be found in quadratic irrationals.General roots
The proof above for the square root of two can be generalized using the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. This asserts that every integer has a unique factorization into primes. Using it we can show that if a rational number is not an integer then no integral power of it can be an integer, as in lowest terms there must be a prime in the denominator that does not divide into the numerator whatever power each is raised to. Therefore, if an integer is not an exact kth power of another integer then its kth root is irrational.Logarithms
Perhaps the numbers most easy to prove irrational are certain logarithms. Here is a proof by contradiction that log2 3 is irrational. Notice that log2 3 ≈ 1.58 > 0.Assume log2 3 is rational. For some positive integers m and n, we have
Cases such as log10 2 can be treated similarly.
Transcendental and algebraic irrationals
Almost all irrational numbers are transcendental and all real transcendental numbers are irrational (there are also complex transcendental numbers): the article on transcendental numbers lists several examples. So e r and π r are irrational for all nonzero rational r, and, e.g., eπ is irrational, too.Irrational numbers can also be found within the countable set of real algebraic numbers (essentially defined as the real roots of polynomials with integer coefficients), i.e., as real solutions of polynomial equations
Because the algebraic numbers form a subfield of the real numbers, many irrational real numbers can be constructed by combining transcendental and algebraic numbers. For example, 3π + 2, π + √2 and e√3 are irrational (and even transcendental).
Decimal expansions
The decimal expansion of an irrational number never repeats or terminates (the latter being equivalent to repeating zeroes), unlike any rational number. The same is true for binary, octal or hexadecimal expansions, and in general for expansions in every positional notation with natural bases.To show this, suppose we divide integers n by m (where m is nonzero). When long division is applied to the division of n by m, only m remainders are possible. If 0 appears as a remainder, the decimal expansion terminates. If 0 never occurs, then the algorithm can run at most m − 1 steps without using any remainder more than once. After that, a remainder must recur, and then the decimal expansion repeats.
Conversely, suppose we are faced with a repeating decimal, we can prove that it is a fraction of two integers. For example, consider:
Therefore, when we subtract the 10A equation from the 10,000A equation, the tail end of 10A cancels out the tail end of 10,000A leaving us with:
Irrational powers
Dov Jarden gave a simple non-constructive proof that there exist two irrational numbers a and b, such that ab is rational:Consider √2√2; if this is rational, then take a = b = √2. Otherwise, take a to be the irrational number √2√2 and b = √2. Then ab = (√2√2)√2 = √2√2·√2 = √22 = 2, which is rational.
Although the above argument does not decide between the two cases, the Gelfond–Schneider theorem shows that √2√2 is transcendental, hence irrational. This theorem states that if a and b are both algebraic numbers, and a is not equal to 0 or 1, and b is not a rational number, then any value of ab is a transcendental number (there can be more than one value if complex number exponentiation is used).
An example that provides a simple constructive proof is
A stronger result is the following: Every rational number in the interval can be written either as aa for some irrational number a or as nn for some natural number n. Similarly, every positive rational number can be written either as for some irrational number a or as for some natural number n.
Open questions
It is not known whether π + e (or π − e) is irrational. In fact, there is no pair of non-zero integers m and n for which it is known whether mπ + ne is irrational. Moreover, it is not known whether the set {π, e} is algebraically independent over Q.It is not known whether πe, π/e, 2e, πe, π√2, ln π, Catalan's constant, or the Euler–Mascheroni gamma constant γ are irrational. It is not known if the tetrations nπ or ne are rational for some positive integer n > 1, respectively.
Set of all irrationals
Since the reals form an uncountable set, of which the rationals are a countable subset, the complementary set of irrationals is uncountable.Under the usual (Euclidean) distance function d(x, y) = |x − y|, the real numbers are a metric space and hence also a topological space. Restricting the Euclidean distance function gives the irrationals the structure of a metric space. Since the subspace of irrationals is not closed, the induced metric is not complete. However, being a G-delta set—i.e., a countable intersection of open subsets—in a complete metric space, the space of irrationals is completely metrizable: that is, there is a metric on the irrationals inducing the same topology as the restriction of the Euclidean metric, but with respect to which the irrationals are complete. One can see this without knowing the aforementioned fact about G-delta sets: the continued fraction expansion of an irrational number defines a homeomorphism from the space of irrationals to the space of all sequences of positive integers, which is easily seen to be completely metrizable.
Furthermore, the set of all irrationals is a disconnected metrizable space. In fact, the irrationals have a basis of clopen sets so the space is zero-dimensional.