Thunderstorm near Garajau, Madeira
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the lowest level of the atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.
Weather is driven by air pressure, temperature and moisture
differences between one place and another. These differences can occur
due to the sun's angle at any particular spot, which varies with latitude. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the largest scale atmospheric circulations: the Hadley Cell, the Ferrel Cell, the Polar Cell, and the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight
is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On
Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F)
annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.
Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure
differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes, as most
atmospheric heating is due to contact with the Earth's surface while
radiative losses to space are mostly constant. Weather forecasting is
the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The Earth's weather system is a chaotic system;
as a result, small changes to one part of the system can grow to have
large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather
have occurred throughout history, and there is evidence that human
activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather
patterns.
Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful
in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona
is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very
thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass
ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.
Causes
Cumulus mediocris cloud surrounded by stratocumulus
On Earth, the common weather phenomena include wind, cloud, rain, snow, fog and dust storms. Less common events include natural disasters such as tornadoes, hurricanes, typhoons and ice storms. Almost all familiar weather phenomena occur in the troposphere (the lower part of the atmosphere).
Weather does occur in the stratosphere and can affect weather lower
down in the troposphere, but the exact mechanisms are poorly understood.
Weather occurs primarily due to air pressure, temperature and moisture differences between one place to another. These differences can occur due to the sun
angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the
tropics. In other words, the farther from the tropics one lies, the
lower the sun angle is, which causes those locations to be cooler due
the spread of the sunlight over a greater surface. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the large scale atmospheric circulation cells and the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Weather systems in the tropics, such as monsoons or organized thunderstorm systems, are caused by different processes.
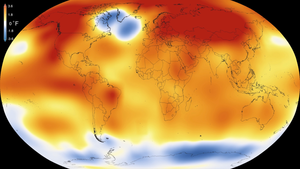
2015 – Warmest Global Year on Record (since 1880) – Colors indicate temperature anomalies (NASA/NOAA; 20 January 2016).
Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. In June the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, so at any given Northern Hemisphere latitude sunlight falls more directly on that spot than in December.
This effect causes seasons. Over thousands to hundreds of thousands of
years, changes in Earth's orbital parameters affect the amount and
distribution of solar energy received by the Earth and influence long-term climate.
The uneven solar heating (the formation of zones of temperature and moisture gradients, or frontogenesis) can also be due to the weather itself in the form of cloudiness and precipitation.
Higher altitudes are typically cooler than lower altitudes, which the
result of higher surface temperature and radiational heating, which
produces the adiabatic lapse rate. In some situations, the temperature actually increases with height. This phenomenon is known as an inversion and can cause mountaintops to be warmer than the valleys below. Inversions can lead to the formation of fog and often act as a cap that suppresses
thunderstorm development. On local scales, temperature differences can
occur because different surfaces (such as oceans, forests, ice sheets, or man-made objects) have differing physical characteristics such as reflectivity, roughness, or moisture content.
Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure
differences. A hot surface warms the air above it causing it to expand
and lower the density and the resulting surface air pressure. The resulting horizontal pressure gradient
moves the air from higher to lower pressure regions, creating a wind,
and the Earth's rotation then causes deflection of this air flow due to
the Coriolis effect. The simple systems thus formed can then display emergent behaviour to produce more complex systems and thus other weather phenomena. Large scale examples include the Hadley cell while a smaller scale example would be coastal breezes.
The atmosphere is a chaotic system.
As a result, small changes to one part of the system can accumulate and
magnify to cause large effects on the system as a whole. This atmospheric instability makes weather forecasting less predictable than tides or eclipses. Although it is difficult to accurately predict weather more than a few days in advance, weather forecasters are continually working to extend this limit through meteorological
research and refining current methodologies in weather prediction.
However, it is theoretically impossible to make useful day-to-day predictions more than about two weeks ahead, imposing an upper limit to potential for improved prediction skill.
Shaping the planet Earth
Weather is one of the fundamental processes that shape the Earth. The
process of weathering breaks down the rocks and soils into smaller
fragments and then into their constituent substances.
During rains precipitation, the water droplets absorb and dissolve
carbon dioxide from the surrounding air. This causes the rainwater to be
slightly acidic, which aids the erosive properties of water. The
released sediment and chemicals are then free to take part in chemical reactions that can affect the surface further (such as acid rain), and sodium and chloride ions (salt)
deposited in the seas/oceans. The sediment may reform in time and by
geological forces into other rocks and soils. In this way, weather plays
a major role in erosion of the surface.
Effect on humans
Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all
humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least
while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed
understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it
has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.
Effects on populations
New Orleans, Louisiana, after being struck by Hurricane Katrina. Katrina was a Category 3 hurricane when it struck although it had been a category 5 hurricane in the Gulf of Mexico.
Weather has played a large and sometimes direct part in human history. Aside from climatic changes that have caused the gradual drift of populations (for example the desertification of the Middle East, and the formation of land bridges during glacial periods), extreme weather
events have caused smaller scale population movements and intruded
directly in historical events. One such event is the saving of Japan
from invasion by the Mongol fleet of Kublai Khan by the Kamikaze winds in 1281. French claims to Florida came to an end in 1565 when a hurricane destroyed the French fleet, allowing Spain to conquer Fort Caroline. More recently, Hurricane Katrina redistributed over one million people from the central Gulf coast elsewhere across the United States, becoming the largest diaspora in the history of the United States.
The Little Ice Age caused crop failures and famines
in Europe. The 1690s saw the worst famine in France since the Middle
Ages. Finland suffered a severe famine in 1696–1697, during which about
one-third of the Finnish population died.
Forecasting
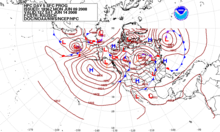
Forecast
of surface pressures five days into the future for the north Pacific,
North America, and north Atlantic Ocean as on 9 June 2008
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere
for a future time and a given location. Human beings have attempted to
predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since at
least the nineteenth century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere and using scientific understanding of atmospheric processes to project how the atmosphere will evolve.
Once an all-human endeavor based mainly upon changes in barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky condition, forecast models
are now used to determine future conditions. On the other hand, human
input is still required to pick the best possible forecast model to base
the forecast upon, which involve many disciplines such as pattern
recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and knowledge of model biases.
The chaotic
nature of the atmosphere, the massive computational power required to
solve the equations that describe the atmosphere, error involved in
measuring the initial conditions, and an incomplete understanding of
atmospheric processes mean that forecasts become less accurate as the
difference in current time and the time for which the forecast is being
made (the range of the forecast) increases. The use of ensembles
and model consensus helps to narrow the error and pick the most likely
outcome.
There are a variety of end users to weather forecasts. Weather
warnings are important forecasts because they are used to protect life
and property. Forecasts based on temperature and precipitation are important to agriculture,
and therefore to commodity traders within stock markets. Temperature
forecasts are used by utility companies to estimate demand over coming
days.
In some areas, people use weather forecasts to determine what to
wear on a given day. Since outdoor activities are severely curtailed by
heavy rain, snow and the wind chill, forecasts can be used to plan activities around these events, and to plan ahead to survive through them.
Modification
The aspiration to control the weather is evident throughout human history: from ancient rituals intended to bring rain for crops to the U.S. Military Operation Popeye, an attempt to disrupt supply lines by lengthening the North Vietnamese monsoon. The most successful attempts at influencing weather involve cloud seeding; they include the fog- and low stratus dispersion techniques employed by major airports, techniques used to increase winter precipitation over mountains, and techniques to suppress hail. A recent example of weather control was China's preparation for the 2008 Summer Olympic Games. China shot 1,104 rain dispersal rockets from 21 sites in the city of Beijing
in an effort to keep rain away from the opening ceremony of the games
on 8 August 2008. Guo Hu, head of the Beijing Municipal Meteorological
Bureau (BMB), confirmed the success of the operation with 100
millimeters falling in Baoding City of Hebei Province, to the southwest and Beijing's Fangshan District recording a rainfall of 25 millimeters.
Whereas there is inconclusive evidence for these techniques'
efficacy, there is extensive evidence that human activity such as
agriculture and industry results in inadvertent weather modification:
- Acid rain, caused by industrial emission of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, adversely affects freshwater lakes, vegetation, and structures.
- Anthropogenic pollutants reduce air quality and visibility.
- Climate change caused by human activities that emit greenhouse gases into the air is expected to affect the frequency of extreme weather events such as drought, extreme temperatures, flooding, high winds, and severe storms.
- Heat, generated by large metropolitan areas have been shown to minutely affect nearby weather, even at distances as far as 1,600 kilometres (990 mi).
The effects of inadvertent weather modification may pose serious threats to many aspects of civilization, including ecosystems, natural resources, food and fiber production, economic development, and human health.
Microscale meteorology
Microscale meteorology is the study of short-lived atmospheric phenomena smaller than mesoscale, about 1 km or less. These two branches of meteorology are sometimes grouped together as "mesoscale and microscale meteorology" (MMM) and together study all phenomena smaller than synoptic scale; that is they study features generally too small to be depicted on a weather map. These include small and generally fleeting cloud "puffs" and other small cloud features.
Extremes on Earth
Early morning sunshine over Bratislava, Slovakia. February 2008.
The same area, just three hours later, after light snowfall
On Earth, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (100 °F to −40 °F)
annually. The range of climates and latitudes across the planet can
offer extremes of temperature outside this range. The coldest air
temperature ever recorded on Earth is −89.2 °C (−128.6 °F), at Vostok Station, Antarctica on 21 July 1983. The hottest air temperature ever recorded was 57.7 °C (135.9 °F) at 'Aziziya, Libya, on 13 September 1922, but that reading is queried. The highest recorded average annual temperature was 34.4 °C (93.9 °F) at Dallol, Ethiopia. The coldest recorded average annual temperature was −55.1 °C (−67.2 °F) at Vostok Station, Antarctica.
The coldest average annual temperature in a permanently inhabited location is at Eureka, Nunavut, in Canada, where the annual average temperature is −19.7 °C (−3.5 °F).
Extraterrestrial within the Solar System
Jupiter's Great Red Spot in February 1979, photographed by the unmanned Voyager 1 NASA space probe.
Studying how the weather works on other planets has been seen as helpful in understanding how it works on Earth.
Weather on other planets follows many of the same physical principles
as weather on Earth, but occurs on different scales and in atmospheres
having different chemical composition. The Cassini–Huygens mission to Titan discovered clouds formed from methane or ethane which deposit rain composed of liquid methane and other organic compounds. Earth's atmosphere includes six latitudinal circulation zones, three in each hemisphere. In contrast, Jupiter's banded appearance shows many such zones, Titan has a single jet stream near the 50th parallel north latitude, and Venus has a single jet near the equator.
One of the most famous landmarks in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. On other gas giants,
the lack of a surface allows the wind to reach enormous speeds: gusts
of up to 600 metres per second (about 2,100 km/h or 1,300 mph) have been
measured on the planet Neptune. This has created a puzzle for planetary scientists. The weather is ultimately created by solar energy and the amount of energy received by Neptune is only about 1⁄900 of that received by Earth, yet the intensity of weather phenomena on Neptune is far greater than on Earth. The strongest planetary winds discovered so far are on the extrasolar planet HD 189733 b, which is thought to have easterly winds moving at more than 9,600 kilometres per hour (6,000 mph).
Space weather
Weather is not limited to planetary bodies. Like all stars, the sun's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind. Inconsistencies in this wind and larger events on the surface of the star, such as coronal mass ejections,
form a system that has features analogous to conventional weather
systems (such as pressure and wind) and is generally known as space weather. Coronal mass ejections have been tracked as far out in the solar system as Saturn. The activity of this system can affect planetary atmospheres and occasionally surfaces. The interaction of the solar wind with the terrestrial atmosphere can produce spectacular aurorae, and can play havoc with electrically sensitive systems such as electricity grids and radio signals.