The Holodomor (Ukrainian: Голодомо́р, romanized: Holodomór, IPA: [ɦolodoˈmor]; derived from морити голодом, moryty holodom, 'to kill by starvation'), also known as the Terror-Famine and sometimes referred to as the Great Famine, was a famine in Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The term Holodomor emphasises the famine's man-made and intentional aspects such as rejection of outside aid, confiscation of all household foodstuffs and restriction of population movement. As part of the wider Soviet famine of 1932–1933 which affected the major grain-producing areas of the country, millions of inhabitants of Ukraine, the majority of whom were ethnic Ukrainians, died of starvation in a peacetime catastrophe unprecedented in the history of Ukraine. Since 2006, the Holodomor has been recognized by Ukraine and 15 other countries as a genocide of the Ukrainian people carried out by the Soviet government.
Early estimates of the death toll by scholars and government officials varied greatly. A United Nations joint statement signed by 25 countries in 2003 declared that 7–10 million perished. Current scholarship estimates a range of 4 to 7 million victims, with more precise estimates ranging from 3.3 to 7.5 million. According to the findings of the Court of Appeal of Kyiv in 2010, the demographic losses due to the famine amounted to 10 million, with 3.9 million direct famine deaths, and a further 6.1 million birth deficits.
Whether the Holodomor was genocide is still the subject of academic debate, as are the causes of the famine and intentionality of the deaths. Some scholars believe that the famine was planned by Joseph Stalin to eliminate a Ukrainian independence movement. Others suggest that the man-made famine was a consequence of Soviet industrialisation.
Etymology
The word Holodomor literally translated from Ukrainian means "death by hunger", "killing by hunger, killing by starvation", or sometimes "murder by hunger or starvation." It is a compound of the Ukrainian words holod, 'hunger'; and mor, 'plague'. The expression moryty holodom means "to inflict death by hunger." The Ukrainian verb moryty (морити) means "to poison, to drive to exhaustion, or to torment." The perfective form of moryty is zamoryty, 'kill or drive to death by hunger, exhausting work.' In English, the Holodomor has also been referred to as the artificial famine, famine genocide, terror famine, and terror-genocide.
The word was used in print in the 1930s in Ukrainian diaspora publications in Czechoslovakia as Haladamor and by Ukrainian immigrant organisations in the United States and Canada by 1978; in the Soviet Union, of which Ukraine was a constituent republic, any references to the famine were dismissed as anti-Soviet propaganda, even after de-Stalinization in 1956, until the declassification and publication of historical documents in the late 1980s made continued denial of the catastrophe unsustainable.
Discussion of the Holodomor became possible as part of the glasnost policy of openness. In Ukraine, the first official use of the word was a December 1987 speech by Volodymyr Shcherbytskyi, First Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Ukraine, on the occasion of the republic's 17th anniversary. An early public usage in the Soviet Union was in a February 1988 speech by Oleksiy Musiyenko, Deputy Secretary for ideological matters of the party organisation of the Kyiv branch of the Union of Soviet Writers in Ukraine. The term may have first appeared in print in the Soviet Union on 18 July 1988, when his article on the topic was published. Holodomor is now an entry in the modern, two-volume dictionary of the Ukrainian language, published in 2004, described as "artificial hunger, organised on a vast scale by a criminal regime against a country's population."
According to Elazar Barkan, Elizabeth A. Cole and Kai Struve, there is a competition among victims in constructing an "Ukrainian Holocaust", stating that since the 1990s the term Holodomor has been adopted by anti-Communists due to its similarity to Holocaust in an attempt to promote the narrative that the Communists killed 10 million Ukrainians while the Nazis only killed 6 million Jews. They stated that the term Holodomor was "introduced and popularized by the Ukrainian diaspora in North America before Ukraine became independent" and that "the term 'Holocaust' is not explained at all." According to them, this has been used to create a "victimized national narrative" and "compete with the Jewish narrative in order to obscure the 'dark sides' of Ukraine's national history and to counter accusations that their fathers collaborated with the Germans."
History
Scope and duration
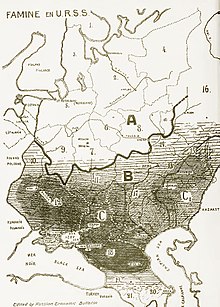
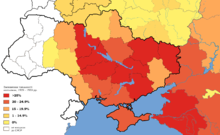
The famine affected the Ukrainian SSR as well as the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (a part of the Ukrainian SSR at the time) in spring 1932 and from February to July 1933, with the most victims recorded in spring 1933. The consequences are evident in demographic statistics: between 1926 and 1939, the Ukrainian population increased by only 6.6%, whereas Russia and Belarus grew by 16.9% and 11.7%, respectively.
From the 1932 harvest, Soviet authorities were able to procure only 4.3 million tons as compared with 7.2 million tons obtained from the 1931 harvest. Rations in towns were drastically cut back, and in winter 1932–33 and spring 1933, people in many urban areas starved. Urban workers were supplied by a rationing system and therefore could occasionally assist their starving relatives in the countryside, but rations were gradually cut; and by spring 1933, urban residents also faced starvation. At the same time, workers were shown agitprop movies depicting peasants as counterrevolutionaries who hid grain and potatoes at a time when workers, who were constructing the "bright future" of socialism, were starving.
The first reports of mass malnutrition and deaths from starvation emerged from two urban areas of the city of Uman, reported in January 1933 by Vinnytsia and Kyiv oblasts. By mid-January 1933, there were reports about mass "difficulties" with food in urban areas, which had been undersupplied through the rationing system, and deaths from starvation among people who were refused rations, according to the December 1932 decree of the Central Committee of the Ukrainian Communist Party. By the beginning of February 1933, according to reports from local authorities and Ukrainian GPU (secret police), the most affected area was Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, which also suffered from epidemics of typhus and malaria. Odessa and Kyiv oblasts were second and third, respectively. By mid-March, most of the reports of starvation originated from Kyiv Oblast.
By mid-April 1933, Kharkiv Oblast reached the top of the most affected list, while Kyiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Odessa, Vinnytsia, and Donetsk oblasts, and Moldavian SSR were next on the list. Reports about mass deaths from starvation, dated mid-May through the beginning of June 1933, originated from raions in Kyiv and Kharkiv oblasts. The "less affected" list noted Chernihiv Oblast and northern parts of Kyiv and Vinnytsia oblasts. The Central Committee of the CP(b) of Ukraine Decree of 8 February 1933 said no hunger cases should have remained untreated. Local authorities had to submit reports about the numbers suffering from hunger, the reasons for hunger, number of deaths from hunger, food aid provided from local sources, and centrally provided food aid required. The GPU managed parallel reporting and food assistance in the Ukrainian SSR. Many regional reports and most of the central summary reports are available from present-day central and regional Ukrainian archives. The Ukrainian Weekly, which was tracking the situation in 1933, reported the difficulties in communications and the appalling situation in Ukraine.
Cannibalism
Evidence of widespread cannibalism was documented during the Holodomor:
Survival was a moral as well as a physical struggle. A woman doctor wrote to a friend in June 1933 that she had not yet become a cannibal, but was "not sure that I shall not be one by the time my letter reaches you." The good people died first. Those who refused to steal or to prostitute themselves died. Those who gave food to others died. Those who refused to eat corpses died. Those who refused to kill their fellow man died. Parents who resisted cannibalism died before their children did.
The Soviet regime printed posters declaring: "To eat your own children is a barbarian act." More than 2,500 people were convicted of cannibalism during the Holodomor.
Causes
The reasons for the famine are a subject of scholarly and political debate. Some scholars suggest that the man-made famine was a consequence of the economic problems associated with changes implemented during the period of Soviet industrialisation. There are also those who blame a systematic set of policies perpetrated by the Soviet government under Stalin designed to exterminate the Ukrainians.
According to some scholars collectivization policies of the Soviet Union
and lack of favored industries were primary contributors to famine
mortality (52% of excess deaths), and some evidence shows there was
discrimination against ethnic Ukrainians and Germans. The collectivisation policy
was enforced, entailing extreme crisis and contributing to the famine.
In 1929–30, peasants were induced to transfer land and livestock to
state-owned farms, on which they would work as day-labourers for payment
in kind. Collectivization in the Soviet Union, including the Ukrainian SSR, was not popular among the peasantry and forced collectivisation led to numerous peasant revolts. The first five-year plan changed the output expected from Ukrainian farms, from the familiar crop of grain to unfamiliar crops like sugar beets and cotton.
In addition, the situation was exacerbated by poor administration of
the plan and the lack of relevant general management. Significant
amounts of grain remained unharvested, and—even when harvested—a
significant percentage was lost during processing, transportation, or
storage.
In the summer of 1930, the government instituted a program of food requisitioning, ostensibly to increase grain exports. Food theft was made punishable by death or 10 years imprisonment. Food exports continued during the famine, albeit at a reduced rate.
It has been proposed that the Soviet leadership used the man-made famine to attack Ukrainian nationalism, and thus it could fall under the legal definition of genocide. For example, special and particularly lethal policies were adopted in and largely limited to Soviet Ukraine at the end of 1932 and 1933. According to Snyder, "each of them may seem like an anodyne administrative measure, and each of them was certainly presented as such at the time, and yet each had to kill." Under the collectivism policy, for example, farmers were not only deprived of their properties but a large swath of these were also exiled in Siberia with no means of survival. Those who were left behind and attempted to escape the zones of famine were ordered shot. There were foreign individuals who witnessed this atrocity or its effects. For example, there was the account of Arthur Koestler, a Hungarian-British journalist, which described the peak years of Holodomor in these words:
At every [train] station there was a crowd of peasants in rags, offering icons and linen in exchange for a loaf of bread. The women were lifting up their infants to the compartment windows—infants pitiful and terrifying with limbs like sticks, puffed bellies, big cadaverous heads lolling on thin necks.
Aftermath and immediate reception
Despite attempts by the Soviet authorities to hide the scale of the disaster, it became known abroad thanks to the publications of journalists Gareth Jones, Malcolm Muggeridge, Ewald Ammende, Rhea Clyman, photographs made by engineer Alexander Wienerberger, etc. In response, the Soviet Union launched a counter-propaganda campaign, whereby celebrities such as Bernard Shaw, Edouard Herriot, and several others traveled to the USSR, and then made statements that they had not seen hunger.
During the German occupation of Ukraine, the occupation authorities allowed the publication of articles in local newspapers about Holodomor and other communist crimes, but they also did not want to pay too much attention to this issue in order to avoid stirring national sentiment. In 1942, Stepan Sosnovy, an agronomist in Kharkiv, published a comprehensive statistical research on the number of Holodomor casualties, based on documents from Soviet archives.
In the post-war period, the Ukrainian diaspora disseminated information about the Holodomor in Europe and North America. At first, the public attitude was rather cautious, as the information came from people who had lived in the occupied territories, but it gradually changed in the 1950s. Scientific study of the Holodomor, based on the growing number of memoirs published by survivors, began in the 1950s.
Death toll
The Soviet Union long denied that the famine had taken place. The NKVD (and later KGB) controlled the archives for the Holodomor period and made relevant records available very slowly. The exact number of the victims remains unknown and is probably impossible to estimate, even within a margin of error of a hundred thousand. However, by the end of 1933, millions of people had starved to death or otherwise died unnaturally in the Soviet republics. In 2001, based on a range of official demographic data, historian Stephen G. Wheatcroft noted that official death statistics for this period were systematically repressed and showed that that many deaths were un-registered. Estimates vary in their coverage, with some using the 1933 Ukraine borders, some of the current borders, and some counting ethnic Ukrainians. Some extrapolate on the basis of deaths in a given area, while others use archival data. Some historians question the accuracy of Soviet censuses, as they may reflect Soviet propaganda. Other estimates come from recorded discussions between world leaders. In an August 1942 conversation, Stalin gave Winston Churchill his estimates of the number of "kulaks" who were repressed for resisting collectivisation as 10 million, in all of the Soviet Union, rather than only in Ukraine. When using this number, Stalin implied that it included not only those who lost their lives but also those who were forcibly deported. Additionally, there are variations in opinion as to whether deaths in Gulag labour camps should be counted or only those who starved to death at home. Estimates before archival opening varied widely such as: 2.5 million (Volodymyr Kubiyovych); 4.8 million (Vasyl Hryshko); and 5 million (Robert Conquest).
In the 1980s, dissident demographer and historian Alexander P. Babyonyshev (writing as Sergei Maksudov) estimated officially non-accounted child mortality in 1933 by 150,000, leading to a calculation that the number of births for 1933 should be increased from 471,000 to 621,000 (down from 1,184,000 in 1927). Given the decreasing birth rates and assuming the natural mortality rates in 1933 to be equal to the average annual mortality rate in 1927–1930 (524,000 per year), a natural population growth for 1933 would have been 97,000 (as opposed to the recorded decrease of 1,379,000). This was five times less than the growth in the previous three years (1927–1930). Straight-line extrapolation of population (continuation of the previous net change) between census takings in 1927 and 1936 would have been +4.043 million, which compares to a recorded -538,000 change. Overall change in birth and death amounts to 4.581 million fewer people but whether through factors of choice, disease or starvation will never be fully known.
In the 2000s, there were debates among historians and in civil society about the number of deaths as Soviet files were released and tension built between Russia and the Ukrainian president Viktor Yushchenko. Yushchenko and other Ukrainian politicians described fatalities as in the region of seven to ten million. Yushchenko stated in a speech to the United States Congress that the Holodomor "took away 20 million lives of Ukrainians," while former Canadian Prime Minister Stephen Harper issued a public statement giving the death toll at about 10 million. Some Ukrainian and Western historians use similar figures. Historian David R. Marples gave a figure of 7.5 million in 2007. During an international conference held in Ukraine in 2016, Holodomor 1932–1933 loss of the Ukrainian nation, at the National University of Kyiv Taras Shevchenko, it was claimed that during the Holodomor 7 million Ukrainians were killed, and in total, 10 million people died of starvation across the USSR.
However, the use of the 7 to 20 million figures has been criticized by historians Timothy D. Snyder and Stephen G. Wheatcroft. Snyder wrote: "President Viktor Yushchenko does his country a grave disservice by claiming ten million deaths, thus exaggerating the number of Ukrainians killed by a factor of three; but it is true that the famine in Ukraine of 1932–1933 was a result of purposeful political decisions, and killed about three million people." In an email to Postmedia News, Wheatcroft wrote: "I find it regrettable that Stephen Harper and other leading Western politicians are continuing to use such exaggerated figures for Ukrainian famine mortality" and "[t]here is absolutely no basis for accepting a figure of 10 million Ukrainians dying as a result of the famine of 1932–33." In 2001, Wheatfcroft had calculated total population loss (including stillbirth) across the Union at 10 million and possibly up to 15 million between 1931 and 1934, including 2.8 million (and possibly up to 4.8 million excess deaths) and 3.7 million (up to 6.7 million) population losses including birth losses in Ukraine.
| Year | Births | Deaths | Natural change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1927 | 1,184 | 523 | 661 |
| 1928 | 1,139 | 496 | 643 |
| 1929 | 1,081 | 539 | 542 |
| 1930 | 1,023 | 536 | 487 |
| 1931 | 975 | 515 | 460 |
| 1932 | 782 | 668 | 114 |
| 1933 | 471 | 1,850 | −1,379 |
| 1934 | 571 | 483 | 88 |
| 1935 | 759 | 342 | 417 |
| 1936 | 895 | 361 | 534 |
In 2002, Ukrainian historian Stanislav Kulchytsky, using demographic data including those recently unclassified, narrowed the losses to about 3.2 million or, allowing for the lack of precise data, 3 million to 3.5 million. The number of recorded excess deaths extracted from the birth/death statistics from Soviet archives is contradictory. The data fail to add up to the differences between the results of the 1926 Census and the 1937 Census. Kulchytsky summarized the declassified Soviet statistics as showing a decrease of 538,000 people in the population of Soviet Ukraine between 1926 census (28,926,000) and 1937 census (28,388,000). Similarly, Wheatcroft's work from Soviet archives showed that excess deaths in Ukraine in 1932–1933 numbered a minimum of 1.8 million (2.7 including birth losses): "Depending upon the estimations made concerning unregistered mortality and natality, these figures could be increased to a level of 2.8 million to a maximum of 4.8 million excess deaths and to 3.7 million to a maximum of 6.7 million population losses (including birth losses)".
A 2002 study by French demographer Jacques Vallin and colleagues utilising some similar primary sources to Kulchytsky, and performing an analysis with more sophisticated demographic tools with forward projection of expected growth from the 1926 census and backward projection from the 1939 census estimates the number of direct deaths for 1933 as 2.582 million. This number of deaths does not reflect the total demographic loss for Ukraine from these events as the fall of the birth rate during the crisis and the out-migration contribute to the latter as well. The total population shortfall from the expected value between 1926 and 1939 estimated by Vallin amounted to 4.566 million. Of this number, 1.057 million is attributed to the birth deficit, 930,000 to forced out-migration, and 2.582 million to the combination of excess mortality and voluntary out-migration. With the latter assumed to be negligible, this estimate gives the number of deaths as the result of the 1933 famine about 2.2 million. According to this study the life expectancy for those born in 1933 sharply fell to 10.8 years for females and to 7.3 years for males and remained abnormally low for 1934 but, as commonly expected for the post-crisis peaked in 1935–36.
According to historian Snyder in 2010, the recorded figure of excess deaths was 2.4 million. However, Snyder claims that this figure is "substantially low" due to many deaths going unrecorded. Snyder states that demographic calculations carried out by the Ukrainian government provide a figure of 3.89 million dead, and opined that the actual figure is likely between these two figures, approximately 3.3 million deaths to starvation and disease related to the starvation in Ukraine from 1932 to 1933. Snyder also estimates that of the million people who died in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic from famine at the same time, approximately 200,000 were ethnic Ukrainians due to Ukrainian-inhabited regions being particularly hard hit in Russia. As a child, Mikhail Gorbachev, born into a mixed Russian-Ukrainian family, experienced the famine in Stavropol, Russia. He recalled in a memoir that "In that terrible year [in 1933] nearly half the population of my native village, Privolnoye, starved to death, including two sisters and one brother of my father."
Wheatcroft and R. W. Davies concluded that disease was the cause of a large number of deaths: in 1932–1933, there were 1.2 million cases of typhus and 500,000 cases of typhoid fever. Malnourishment increases fatality rates from many diseases, and are not counted by some historians. From 1932 to 1934, the largest rate of increase was recorded for typhus, commonly spread by lice. In conditions of harvest failure and increased poverty, lice are likely to increase. Gathering numerous refugees at railway stations, on trains and elsewhere facilitates the spread. In 1933, the number of recorded cases was 20 times the 1929 level. The number of cases per head of population recorded in Ukraine in 1933 was already considerably higher than in the USSR as a whole. By June 1933, the incidence in Ukraine had increased to nearly 10 times the January level, and it was much higher than in the rest of the USSR.
Estimates of the human losses due to famine must account for the numbers involved in migration (including forced resettlement). According to Soviet statistics, the migration balance for the population in Ukraine for 1927–1936 period was a loss of 1.343 million people. Even when the data were collected, the Soviet statistical institutions acknowledged that the precision was less than for the data of the natural population change. The total number of deaths in Ukraine due to unnatural causes for the given ten years was 3.238 million; accounting for the lack of precision, estimates of the human toll range from 2.2 million to 3.5 million deaths.
According to Babyonyshev's 1981 estimate, about 81.3% of the famine victims in the Ukrainian SSR were ethnic Ukrainians, 4.5% Russians, 1.4% Jews and 1.1% were Poles. Many Belarusians, Volga Germans and other nationalities became victims as well. The Ukrainian rural population was the hardest hit by the Holodomor. Since the peasantry constituted a demographic backbone of the Ukrainian nation, the tragedy deeply affected the Ukrainians for many years. In an October 2013 opinion poll (in Ukraine) 38.7% of those polled stated "my families had people affected by the famine", 39.2% stated they did not have such relatives, and 22.1% did not know.
There was also migration in to Ukraine as a response to the famine: in response to the demographic collapse, the Soviet authorities ordered large-scale resettlements, with over 117,000 peasants from remote regions of the Soviet Union taking over the deserted farms.
Genocide question
Scholars continue to debate "whether the man-made Soviet famine was a central act in a campaign of genocide, or whether it was designed to simply cow Ukrainian peasants into submission, drive them into the collectives and ensure a steady supply of grain for Soviet industrialization." Whether the Holodomor is a genocide is a significant issue in modern politics and there is no international consensus on whether Soviet policies would fall under the legal definition of genocide.
Scholarly positions are diverse. Raphael Lemkin, James Mace, Norman Naimark, Timothy Snyder and Anne Applebaum considered the Holodomor a genocide and the intentional result of Stalinist policies. Michael Ellman considers the Holodomor a crime against humanity, but does not use the term genocide. Robert Conquest and Steven Rosefielde consider the deaths to be primarily due to intentional state policy, not poor harvests. Robert Davies, Stephen Kotkin, and Stephen Wheatcroft reject the notion that Stalin intentionally wanted to kill the Ukrainians, but exacerbated the situation by enacting bad policies and ignorance of the problem. In 1991, American historian Mark Tauger considered the Holodomor primarily the result of natural conditions and failed economic policy, not intentional state policy. Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn opined on 2 April 2008 in Izvestia that the 1930s famine in the Ukraine was similar to the Russian famine of 1921–22 as both were caused by the ruthless robbery of peasants by Bolshevik grain procurements.
Soviet and Western denial
Holodomor denial is the assertion that the 1932–1933 genocide in Soviet Ukraine either did not occur or did occur but was not a premeditated act. Denying the existence of the famine was the Soviet state's position and reflected in both Soviet propaganda and the work of some Western journalists and intellectuals including George Bernard Shaw, Walter Duranty, and Louis Fischer. In the Soviet Union, authorities all but banned discussion of the famine, and Ukrainian historian Stanislav Kulchytsky stated the Soviet government ordered him to falsify his findings and depict the famine as an unavoidable natural disaster, to absolve the Communist Party and uphold the legacy of Stalin.
In modern politics
Whether the Holodomor was a genocide or ethnicity-blind, was man-made or natural, and was intentional or unintentional are issues of significant modern debate. The event is considered a genocide by Ukraine, a crime against humanity by the European Parliament, and the lower house of parliament of Russia condemned the Soviet regime's "disregard for the lives of people".
On 10 November 2003 at the United Nations, 25 countries, including Russia, Ukraine, and United States signed a joint statement on the seventieth anniversary of the Holodomor with the following preamble:
In the former Soviet Union millions of men, women and children fell victims to the cruel actions and policies of the totalitarian regime. The Great Famine of 1932–1933 in Ukraine (Holodomor), took from 7 million to 10 million innocent lives and became a national tragedy for the Ukrainian people. In this regard, we note activities in observance of the seventieth anniversary of this Famine, in particular organized by the Government of Ukraine. Honouring the seventieth anniversary of the Ukrainian tragedy, we also commemorate the memory of millions of Russians, Kazakhs and representatives of other nationalities who died of starvation in the Volga River region, Northern Caucasus, Kazakhstan and in other parts of the former Soviet Union, as a result of civil war and forced collectivisation, leaving deep scars in the consciousness of future generations.
The Ukrainian parliament first recognized the Holodomor as a genocide in 2003, and criminalized both Holodomor denial and Holocaust denial in 2006. In 2010, the Kyiv Court of Appeal ruled that the Holodomor was an act of genocide and held Joseph Stalin, Vyacheslav Molotov, Lazar Kaganovich, Stanislav Kosior, Pavel Postyshev, Mendel Khatayevich, Vlas Chubar and other Bolshevik leaders responsible.
The Holodomor has been compared to the Irish Famine of 1845-1849 that took place in Ireland under British rule, which has been the subject of similar controversy and debate.
Remembrance
To honour those who perished in the Holodomor, monuments have been dedicated and public events held annually in Ukraine and worldwide.
Ukraine
Since 2006, Ukraine has officially observed a Holodomor Remembrance Day on the fourth Saturday of November.
In 2006, the Holodomor Remembrance Day took place on 25 November. Ukraine President Viktor Yushchenko directed, in Decree No. 868/2006, that a minute of silence should be observed at 4 o'clock in the afternoon on that Saturday. The document specified that flags in Ukraine should fly at half-staff as a sign of mourning. In addition, the decree directed that entertainment events are to be restricted and television and radio programming adjusted accordingly.
In 2007, the 74th anniversary of the Holodomor was commemorated in Kyiv for three days on the Maidan Nezalezhnosti. As part of the three-day event, from 23 to 25 November, video testimonies of the communist regime's crimes in Ukraine, and documentaries by famous domestic and foreign film directors were shown. In addition, experts and scholars gave lectures on the topic. As well, on 23 November 2007, the National Bank of Ukraine issued a set of two commemorative coins remembering the Holodomor.
As of 2009, Ukrainian schoolchildren take a more extensive course of the history of the Holodomor.
The National Museum "Memorial to Holodomor victims" was erected on the slopes of the Dnieper river in 2008, welcoming its first visitors on 22 November 2008. The ceremony of the memorial's opening was dedicated to the 75th anniversary of the Holodomor.
In an October 2013 opinion poll, 33.7% of Ukrainians fully agreed and 30.4% rather agreed with the statement "The Holodomor was the result of actions committed by the Soviet authorities, along with Soviet dictator Joseph Stalin, and was the result of human actions". In the same poll, 22.9% of those polled fully or partially agreed with the view that the famine was caused by natural circumstances, but 50.5% disagreed with that. Furthermore, 45.4% of respondents believed that the Holodomor was "a deliberate attempt to destroy the Ukrainian nation" and 26.2% rather or completely disagreed with this.
Canada
The first public monument to the Holodomor was erected and dedicated in 1983 outside City Hall in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, to mark the 50th anniversary of the famine-genocide. Since then, the fourth Saturday in November has in many jurisdictions been marked as the official day of remembrance for people who died as a result of the 1932–33 Holodomor and political repression.
On 22 November 2008, Ukrainian Canadians marked the beginning of National Holodomor Awareness Week. Citizenship, Immigration, and Multiculturalism Minister Jason Kenney attended a vigil in Kyiv. In November 2010, Prime Minister Stephen Harper visited the Holodomor memorial in Kyiv, although Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych did not join him.
Saskatchewan became the first jurisdiction in North America and the first province in Canada to recognize the Holodomor as a genocide. The Ukrainian Famine and Genocide (Holodomor) Memorial Day Act was introduced in the Saskatchewan Legislature on 6 May 2008, and received royal assent on 14 May 2008.
On 9 April 2009, the Province of Ontario unanimously passed bill 147, "The Holodomor Memorial Day Act", which calls for the fourth Saturday in November to be a day of remembrance. This was the first piece of legislation in the Province's history to be introduced with Tri-Partisan sponsorship: the joint initiators of the bill were Dave Levac, MPP for Brant (Liberal Party); Cheri DiNovo, MPP for Parkdale–High Park (NDP); and Frank Klees, MPP for Newmarket–Aurora (PC). MPP Levac was made a chevalier of Ukraine's Order of Merit.
On 2 June 2010, the Province of Quebec unanimously passed bill 390, "Memorial Day Act on the great Ukrainian famine and genocide (the Holodomor)".
On 25 September 2010, a new Holodomor monument was unveiled at St. Mary's Ukrainian Catholic Church, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, bearing the inscription "Holodomor: Genocide By Famine in Ukraine 1932–1933" and a section in Ukrainian bearing mention of the 10 million victims.
On 21 September 2014, a statue entitled "Bitter Memories of Childhood" was unveiled outside the Manitoba Legislative Building in Winnipeg to memorialize the Holodomor.
A monument to the Holodomor has been erected on Calgary's Memorial Drive, itself originally designated to honour Canadian servicemen of the First World War. The monument is located in the district of Renfrew near Ukrainian Pioneer Park, which pays tribute to the contributions of Ukrainian immigrants to Canada.
On 21 October 2018, a memorial statue was unveiled on Canada Boulevard in Exhibition Place of Toronto. The site provides a place for an annual memorial on the fourth Saturday of November.
Poland
On 16 March 2006, the Senate of the Republic of Poland paid tribute to the victims of the Great Famine and declared it an act of genocide, expressing solidarity with the Ukrainian nation and its efforts to commemorate this crime.
On 22 January 2015, a Holodomor monument was erected in the city of Lublin.
United States
The Ukrainian Weekly reported a meeting taking place on 27 February 1982 in the parish center of the Ukrainian Catholic National Shrine of the Holy Family in commemoration of the 50th Anniversary of the Great Famine caused by the Soviet authorities. On 20 March 1982, the Ukrainian Weekly also reported a multi-ethnic community meeting that was held on 15 February on the North Shore Drive at the Ukrainian Village in Chicago to commemorate the famine which took the lives of seven million Ukrainians. Other events in commemoration were held in other places around the United States as well.
On 29 May 2008, the city of Baltimore held a candlelight commemoration for the Holodomor at the War Memorial Plaza in front of City Hall. This ceremony was part of the larger international journey of the "International Holodomor Remembrance Torch", which began in Kyiv and made its way through thirty-three countries. Twenty-two other US cities were also visited during the tour. Then-Mayor Sheila Dixon presided over the ceremony and declared 29 May to be "Ukrainian Genocide Remembrance Day in Baltimore". She referred to the Holodomor "among the worst cases of man's inhumanity towards man".
On 2 December 2008, a ceremony was held in Washington, D.C., for the Holodomor Memorial. On 13 November 2009, U.S. President Barack Obama released a statement on Ukrainian Holodomor Remembrance Day. In this, he said that "remembering the victims of the man-made catastrophe of Holodomor provides us an opportunity to reflect upon the plight of all those who have suffered the consequences of extremism and tyranny around the world". NSC Spokesman Mike Hammer released a similar statement on 20 November 2010.
In 2011, the American day of remembrance of Holodomor was held on 19 November. The statement released by the White House Press Secretary reflects on the significance of this date, stating that "in the wake of this brutal and deliberate attempt to break the will of the people of Ukraine, Ukrainians showed great courage and resilience. The establishment of a proud and independent Ukraine twenty years ago shows the remarkable depth of the Ukrainian people's love of freedom and independence".
On 7 November 2015, the Holodomor Genocide Memorial was opened in Washington D.C.
In the 115th Congress, both the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives adopted resolutions commemorating the 85th anniversary of the Holodomor, "the Soviet Union's manmade famine that it committed against the people of Ukraine in 1932 and 1933." The Senate Resolution, S. Res. 435 (115th Congress) was adopted on 3 October 2018 and stated that the U.S. Senate "solemnly remembers the 85th anniversary of the Holodomor of 1932–1933 and extends its deepest sympathies to the victims, survivors, and families of this tragedy." On 11 December 2018, the United States House of Representatives adopted H. Res. 931 (115th Congress), a resolution extending the House's "deepest sympathies to the victims and survivors of the Holodomor of 1932–1933, and their families" and condemned "the systematic violations of human rights, including the freedom of self-determination and freedom of speech, of the Ukrainian people by the Soviet Government."