Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic media, especially published materials, should be considered a right to be exercised freely. Such freedom implies the absence of interference from an overreaching state; its preservation may be sought through the constitution or other legal protection and security. It is in opposition to paid press, where communities, police organizations, and governments are paid for their copyrights.
Without respect to governmental information, any government may distinguish which materials are public or protected from disclosure to the public. State materials are protected due to either one of two reasons: the classification of information as sensitive, classified, or secret, or the relevance of the information to protecting the national interest. Many governments are also subject to "sunshine laws" or freedom of information legislation that define the ambit of national interest and enable citizens to request access to government-held information.
The United Nations' 1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights states: "Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; this right includes freedom to hold opinions without interference, and to seek, receive, and impart information and ideas through any media regardless of frontiers."
This philosophy is usually accompanied by legislation ensuring various degrees of freedom of scientific research (known as scientific freedom), publishing, and the press. The depth to which these laws are entrenched in a country's legal system can go as far down as its constitution. The concept of freedom of speech is often covered by the same laws as freedom of the press, thereby giving equal treatment to spoken and published expression. Freedom of the press was formally established in Great Britain with the lapse of the Licensing Act in 1695. Sweden was the first country in the world to adopt freedom of the press into its constitution with the Freedom of the Press Act of 1766.
Relationship to self-publishing
Freedom of the press is not construed as an absence of interference by outside entities, such as a government or religious organization, but rather as a right for authors to have their works published by other people. This idea was famously summarized by the 20th-century American journalist, A. J. Why, who wrote, "Freedom of the press is guaranteed only to those who own one". Freedom of the press gives the printer or publisher exclusive control over what the publisher chooses to publish, including the right to refuse to print anything for any reason. If the author cannot reach a voluntary agreement with a publisher to produce the author's work, then the author must turn to self-publishing.
Status of press freedom worldwide
Beyond legal definitions, several non-governmental organizations use other criteria to judge the level of press freedom worldwide. Some create subjective lists, while others are based on quantitative data:
- Reporters Without Borders considers the number of journalists murdered, expelled, or harassed, the existence of a state monopoly on TV and radio, as well as the existence of censorship and self-censorship in the media, and the overall independence of media as well as the difficulties that foreign reporters may face to rank countries in levels of press freedom.
- The Committee to Protect Journalists (CPJ) systematically tracks the number of journalists killed and imprisoned in reprisal for their work. It says it uses the tools of journalism to help journalists by tracking press freedom issues through independent research, fact-finding missions, and a network of foreign correspondents, including local working journalists in countries worldwide. CPJ shares information on breaking cases with other press freedom organizations worldwide through the International Freedom of Expression Exchange, a global network of more than 119 free expression organizations. CPJ also tracks impunity in cases of journalist murders. CPJ staff applies strict criteria for each case; researchers independently investigate and verify the circumstances behind each death or imprisonment.
- Freedom House studies the more general political and economic environments of each nation in order to determine whether relationships of dependence exist that limit in practice the level of press freedom that might exist in theory. Panels of experts assess the press freedom score and draft each country summary according to a weighted scoring system that analyzes the political, economic, legal and safety situation for journalists based on a 100-point scale. It then categorizes countries as having a free, partly free, or not free press.
Annual report on journalists killed and Prison Census
Each year, The Committee to Protect Journalists produces a comprehensive list of all working journalists killed in relation to their employment, including profiles of each deceased journalist within an exhaustive database, and an annual census of incarcerated journalists (as of midnight, December 1). The year 2017 reported record findings of jailed journalists, reaching 262. Turkey, China, and Egypt account for more than half of all global journalists jailed.
As per a 2019 special report by the Committee to Protect Journalists, approximately 25 journalists were murdered on duty in 2019. The figure is claimed to be the lowest since 2002, a year in which at least 21 journalists were killed while they were reporting from the field. Meanwhile, Reporters Without Borders (RSF) reported 49 killings, the lowest since 2003, when almost 36 journalists were killed. Leading press watchdogs fear persisting danger for the life of journalists. The drop in the murder of in-field journalists came across during the "global attention on the issue of impunity in journalist murders", focusing on the assassination of Saudi journalist Jamal Khashoggi in October 2018 and Daphne Caruana Galizia, a Maltese blogger in October 2017.
Every year, Reporters Without Borders establish a subjective ranking of countries in terms of their freedom of the press. The Press Freedom Index list is based on responses to surveys sent to journalists that are members of partner organizations of the RWB, as well as related specialists such as researchers, jurists, and human rights activists. The survey asks questions about direct attacks on journalists and the media and other indirect sources of pressure against the free press, such as non-governmental groups.
In 2022, the eight countries with the most press freedom are, in order: Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Estonia, Finland, Ireland, Portugal, and Costa Rica. The ten countries with the least press freedom are, in order: North Korea, Eritrea, Iran, Turkmenistan, Myanmar, China, Vietnam, Cuba, Iraq, and Syria.
Freedom of the Press
Freedom of the Press is a yearly report by the US-based non-profit organization Freedom House. It is known to subjectively measure the level of freedom and editorial independence that is enjoyed by the press in every nation and significant disputed territories around the world. Levels of freedom are scored on a scale from 1 (most free) to 100 (least free). Depending on the basics, the nations are then classified as "Free", "Partly Free", or "Not Free".
Democratic states
A free and independent press has been theorized to be a key mechanism of a functioning, healthy democracy. In the absence of censorship, journalism exists as a watchdog of private and government action, providing information to maintain an informed citizenry of voters. In this perspective, "government efforts to influence published or broadcasted news content, either via media control or by inducing self-censorship, represent a threat to the access of important and necessary information to the public and affect the quality of democracy". An independent press "serves to increase political knowledge, participation, and voter turnout", acting as an essential driver of civic participation.
Non-democratic states
Turkey, China, Egypt, Eritrea, and Saudi Arabia accounted for 70% of all journalists that were imprisoned in 2018. CPJ reported that "After China, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt, the worst jailers are Eritrea, Vietnam, and Iran."
According to Reporters Without Borders, more than a third of the world's people live in countries where there is no press freedom. Overwhelmingly, these people live in countries where there is no system of democracy or where there are serious deficiencies in the democratic process.
Freedom of the press is an extremely problematic problem/concept for most non-democratic systems of government since, in the modern age, strict control of access to information is critical to the existence of most non-democratic governments and their associated control systems and security apparatus. To this end, most non-democratic societies employ state-run news organizations to promote the propaganda critical to maintaining an existing political power base and suppress (often very brutally, through the use of police, military, or intelligence agencies) any significant attempts by the media or individual journalists to challenge the approved "government line" on contentious issues. In such countries, journalists operating on the fringes of what is deemed to be acceptable will very often find themselves the subject of considerable intimidation by agents of the state. This can range from simple threats to their professional careers (firing, professional blacklisting) to death threats, kidnapping, torture, and assassination.
- The Lira Baysetova case in Kazakhstan.
- The Georgiy R. Gongadze case in Ukraine
- In Nepal, Eritrea, and mainland China, journalists may spend years in jail simply for using the "wrong" word or photo.
History
Europe
Central, Northern, and Western Europe have a long tradition of freedom of speech, including freedom of the press. After World War II, Hugh Baillie, the president of the United Press wire service based in the U.S., promoted freedom of news dissemination. In 1944, he called for an open system of news sources and transmission, and a minimum of government regulation of the news. His proposals were aired at the Geneva Conference on Freedom of Information in 1948 but were blocked by the Soviets and the French.
Media freedom is a fundamental right that applies to all member states of the European Union and its citizens, as defined in the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights as well as the European Convention on Human Rights. Within the EU enlargement process, guaranteeing media freedom is named a "key indicator of a country's readiness to become part of the EU".
United Kingdom
According to the New York Times, "Britain has a long tradition of a free, inquisitive press", but "[u]nlike the United States, Britain has no constitutional guarantee of press freedom." Freedom of the press was established in Great Britain in 1695, with Alan Rusbridger, former editor of The Guardian, stating: "When people talk about licensing journalists or newspapers the instinct should be to refer them to history. Read about how licensing of the press in Britain was abolished in 1695. Remember how the freedoms won here became a model for much of the rest of the world, and be conscious of how the world still watches us to see how we protect those freedoms."
Until 1694, Great Britain had an elaborate system of licensing; the most recent was seen in the Licensing of the Press Act, 1662. No publication was allowed without the accompaniment of a government-granted license. Fifty years earlier, at a time of civil war, John Milton wrote his pamphlet Areopagitica (1644). In this work Milton argued forcefully against this form of government censorship and parodied the idea, writing "when as debtors and delinquents may walk abroad without a keeper, but inoffensive books must not stir forth without a visible jailer in their title." Although at the time it did little to halt the practice of licensing, it would be viewed later a significant milestone as one of the most eloquent defenses of press freedom.
Milton's central argument was that the individual is capable of using reason and distinguishing right from wrong, and good from bad. In order to be able to exercise this ration right, the individual must have unlimited access to the ideas of his fellow men in "a free and open encounter." Milton's writings developed the concept of the open marketplace of ideas, the idea that when people argue against each other, good arguments will prevail. One form of speech that was widely restricted in Great Britain was seditious libel, and laws were in place that made criticizing the government a crime. The king was above public criticism and statements critical of the government were forbidden, according to the English court of the Star Chamber. The truth was not a defense to seditious libel because the goal was to prevent and punish all condemnation of the government.
Locke contributed to the lapse of the Licensing Act in 1695, whereupon the press needed no license. Still, some libels were tried throughout the 18th century, until "the Society of the Bill of Rights" led by John Horne Tooke and John Wilkes organized a campaign to publish Parliamentary Debates. This culminated in three defeats of the Crown in the 1770 cases of Almon, Miller and Woodfall, who all had published one of the Letters of Junius, and the unsuccessful arrest of John Wheble in 1771. Thereafter the Crown was much more careful in the application of libel; for example, in the aftermath of the Peterloo Massacre, Burdett was convicted, whereas by contrast, the Junius affair was over a satire and sarcasm about the non-lethal conduct and policies of the government.
In Britain's American colonies, the first editors discovered their readers enjoyed it when they criticized the local governor; the governors discovered they could shut down the newspapers. The most dramatic confrontation came in New York in 1734, where the governor brought John Peter Zenger to trial for criminal libel after the publication of satirical attacks. The defense lawyers argued that according to English common law, the truth was a valid defense against libel. The jury acquitted Zenger, who became the iconic American hero for freedom of the press. The result was an emerging tension between the media and the government. By the mid-1760s, there were 24 weekly newspapers in the 13 colonies, and the satirical attack on the government became common features in American newspapers.
In the Victorian era, the press became more influential than it had been previously, to the dismay of some readers. Thomas Carlyle, in his essay "Signs of the Times" (1829), said that the "true Church of England, at this moment, lies in the Editors of its Newspapers. These preach to the people daily, weekly; admonishing kings themselves; advising peace or war, with an authority which only the first Reformers, and a long-past class of Popes, were possessed of". Similarly, Charles Dickens, in his Pickwick Papers (1837), caricatured the newspapers as but the "chosen organ and representative" of either the Whigs or the Tories, and that they were "essentially and indispensably necessary" to the parties' operations.
John Stuart Mill in 1869 in his book On Liberty approached the problem of authority versus liberty from the viewpoint of a 19th-century utilitarian: The individual has the right of expressing himself so long as he does not harm other individuals. The good society is one in which the greatest number of persons enjoy the greatest possible amount of happiness. Applying these general principles of liberty to freedom of expression, Mill states that if we silence an opinion, we may silence the truth. The individual freedom of expression is therefore essential to the well-being of society. Mill wrote:
- If all mankind minus one, were of one opinion, and one, and only one person were of the contrary opinion, mankind would be no more justified in silencing that one person, than he, if he had the power, would be justified in silencing mankind.
The December 1817 Trials of writer and satirist William Hone for publishing three political pamphlets is considered a landmark in the fight for a free press.
Denmark–Norway
Between September 4, 1770 and October 7, 1771 the kingdom of Denmark–Norway had the most unrestricted freedom of press of any country in Europe. This occurred during the regime of Johann Friedrich Struensee, whose second act was to abolish the old censorship laws. However, due to the great amount of mostly anonymous pamphlets published that was critical and often slanderous towards Struensee's own regime, he reinstated some restrictions regarding the freedom of press a year later, October 7, 1771.
Italy
After the Italian unification in 1861, the Albertine Statute of 1848 was adopted as the constitution of the Kingdom of Italy. The Statute granted the freedom of the press with some restrictions in case of abuses and in religious matters, as stated in Article 28:
The press shall be free, but the law may suppress abuses of this freedom. However, Bibles, catechisms, liturgical and prayer books shall not be printed without the prior permission of the Bishop.
After the abolition of the monarchy in 1946 and the abrogation of the Statute in 1948, the Constitution of the Republic of Italy guarantees the freedom of the press, as stated in Article 21, Paragraphs 2 and 3.
The press may not be subjected to any authorisation or censorship. Seizure may be permitted only by judicial order stating the reason and only for offences expressly determined by the law on the press or in case of violation of the obligation to identify the persons responsible for such offences.
The Constitution allows the warrantless confiscation of periodicals in cases of absolute urgency, when the Judiciary cannot timely intervene, on the condition that a judicial validation must be obtained within 24 hours. Article 21 also gives restrictions against those publications considered offensive by public morality, as stated in Paragraph 6:
Publications, performances, and other exhibits offensive to public morality shall be prohibited. Measures of preventive and repressive measure against such violations shall be established by law.
Nazi Germany (1933–1945)
In 1933, freedom of the press was suppressed in Nazi Germany by the Reichstag Fire Decree of President Paul von Hindenburg, just as Adolf Hitler was coming to power. Hitler suppressed freedom of the press through Joseph Goebbels' Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda. The Ministry acted as a central control point for all media, issuing orders as to what stories could be run and what stories would be suppressed. Anyone involved in the film industry, from directors to the lowliest assistant, had to sign an oath of loyalty to the Nazi Party due to the opinion-changing power Goebbels perceived movies to have; Goebbels himself maintained some personal control over every single film made in Nazi Europe. Journalists who crossed the Propaganda Ministry were routinely imprisoned.
Sweden
One of the world's first freedom of the press acts was introduced in Sweden in 1766 (Swedish Freedom of the Press Act), mainly due to classical liberal member of parliament, Ostrobothnian priest, Anders Chydenius. Excepted and liable to prosecution was only vocal opposition to the king and the Church of Sweden. The act was largely rolled back after King Gustav's coup d'état in 1772, restored after the overthrowing of his son, Gustav IV of Sweden in 1809, and fully recognized with the abolition of the king's prerogative to cancel licenses in the 1840s.
Russia
The US Secretary of State, Mike Pompeo, criticized Russia for limiting the activities of VOA and Radio Free Europe in Russia with a governmental order demanding reviewing the subject by Moscow.
Romania
Until 1989, Romania was part of the communist bloc, with no freedom of speech and only a handful of newspapers, all controlled by the communist regime. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty was the only connection with the rest of Europe, but it was highly illegal, and people were afraid to listen to it. In 1990, with the regime's fall, Romania tried to find out what free media meant. The old communist newspapers were revamped, most of them having "freedom" in their names: Romania Libera (Free Romania), Cuvantul Libertatii (The word of Freedom), and Libertatea (Freedom), to name just a few.
1990–2000
For the first ten years, as the media outlets were trying to find out their audience, strange articles and news were part of the everyday news delivery. But, as Romania was struggling with post-communist corruption, investigative reporters developed and more investigations were published. At the same time, violence against journalists began. Even though there are not many English papers that wrote about it, an article written by Christina Pirvulescu in AP News on June 14, 1990, shows how fragile the media was in front of aggression. During this time, the two biggest media conglomerates are also founded in Romania, Antena 1 (1994), and ProTV (1995). The media world was fragile during these times, and journalists were always prosecuted by government organizations.
In 1992, President Ion Illiescu had a nervous meltdown and called a journalist an "animal" for asking him tough questions.
One of the most notorious cases was of Tiberiu Patru (died in 2017), the editor of Ora. The editor-in-chief of the local newspaper was arrested in the summer of 1999 while finalizing a contract for advertising space. Before his arrest, Patru was about to publish a huge investigation about an entire department from the Attorney General Office, Dolj, who was caught in a striptease club, most of them almost completely naked and harassing the employees. To stop the investigation from being published, the Attorney General Office, Dolj, sent Sorin Sarbu of the Romanian Federation for Democracy to trick Patru. Sarbu had a meeting with Patru, saying he wanted an advertising contract. Before signing the papers, Sarbu insisted that Patru should count the money to see that the entire amount was there. The moment Patru touched the money, the police arrested him. The investigation was published a week after the arrest of Tiberiu Patru, while he was still in jail. The entire team of Ora moved the newsroom in front of The National Theater of Craiova to protest the abusive arrest of the editor-in-chief and called to be arrested too.
Another journalist, Silviu Sergiu, a reporter at Jurnalul National at the time, was beaten and held hostage for hours by Sorin Sarbu while investigating what was happening. Patru was set free after 13 days.
2000–2010
For many Romanian journalists, the years between 2000 and 2010 represent the romantic era of the press. More and more newspapers were starting to appear during these years, and the country saw a rise in the number of televisions, radios, and newspapers. More and more investigations are published, especially since the country was asked, as a condition to be part of the European Union, to get rid of the corruption. It is also when the journalists face more aggression, especially from authorities. Since no law states the freedom of media or speech in the country, abuses were done every day. Many of these cases are undocumented since the country had low or no internet access during these years, but also because the government tried to hide most of the cases.
Until 2007, when Romania became part of the European Union, the Romanian journalists were living a very dangerous life, government and mafia alike trying to stop them from doing their job. The financial crisis in 2010 made a lot of journals and televisions to accept the implication of political parties into their newsroom, and the freedom so hard gained by the press was lost again. The political parties started to include their own agenda into the editorial policy, while the media outlets had no other option but to accept since no money came from advertising during the crisis.
Turkey
More than 120 journalists remained in prison in Turkey in 2019, making it the most prolific incarcerator of journalists in the world.
Americas
United States
The First Amendment of the United States Constitution states:
Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the government for a redress of grievances.
Canada
Section 2(b) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms states that everyone has "the freedom of thought, belief, opinion and expression, including freedom of the press and other media of communication."
The open court principle ensures the freedom of the press by requiring that court proceedings presumptively be open and accessible to the public and to the media.
Mexico
see Freedom of the press in Mexico and mass media in Mexico
Guatemala
Nicaragua
See Freedom of the press in Nicaragua and Mass media in Nicaragua
Argentina
See History of Argentina#New democracy (1983–present) and Mass media in Argentina
Bolivia
See History of Bolivia (1982–present) and Mass media in Bolivia
Brazil
See History of Brazil (1985–present)
Chile
Colombia
See History of Colombia#From 2004 and on and Mass media in Colombia
Ecuador
See History of Ecuador#Ecuador since 2000
Guyana
See Guyana#UNASUR
Paraguay
See History of Paraguay#Modern Paraguay and Mass media in Paraguay
Peru
See Freedom of the press in Peru and Mass media in Peru
Suriname
See History of Suriname's Independence
Uruguay
See History of Uruguay#Recent history and Mass media in Uruguay
Venezuela
See History of Venezuela (1999–present) and Mass media in Venezuela
Asia
Bahrain
According to Reporters without Borders, a number of reporters in Bahrain were jailed. Some were also tortured or were exiled.
Iran
According to the reports of the RSF in 2007, the freedom of Press in Iran ranked 166 among 169 states. The report reads the Iranian journalists face the "extreme harsh behavior of the Iranian regime that prevent them criticizing authorities or expressing political and social demands.
After shutting down of a Ukrainian airliner, the agents of the Iranian Intelligent Service raided the houses and offices of many Iranian journalists seeking for their PCs, cell phones, books, and documents. These journalists had revealed the lies of the Iranian regime. Some of the journalists received warnings by the authorities and forced to shut down their accounts in Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook.
Demanding promotion of the global Freedom of Media, in December 1993, UNESCO called the 3rd of April as "International day for Freedom of Media". This is while the RSF reported at least 860 journalists have been detained and imprisoned from 1979 to 2009 in Iran.
On April 21, 2020 Paris-based Reporters Without Borders (RSF) said in its annual press freedom rankings that the pandemic was "highlighting many crises" already casting a shadow on press freedom, around the world, with authoritarian states including Iran suppressing details of the outbreak.
RSF accused Iran—in 173rd place—of censoring major coronavirus outbreaks.
On May 2, 2020, on the occasion of the 3rd of May, the International Day of Freedom of Press, in a statement, the Iranian Writer Association emphasized on the existence of censorships and violation of freedom of speech and its destructive impacts on the structure and vital foundation of the society. It reminded that during the past decades, the rulers in the country imprisoned more than 890 journalists and reporters, some of whom have been executed. The Iranian Writer Association expressed its regret when Iran ranked 173 among 180 states due to freedom of speech.
On 7 February 2020, the International Federation of Journalists in a statement condemned "raiding of Iranian Security Forces upon the houses of six Iranian journalists, holding the forces of "IRGC's Intelligence" responsible for recent pressures on the journalists. The secretary-general of the federation, Anthony Blunker, said that intimidating and threatening journalists are unpleasant tools to silence the public opinion of the administration.
On November 26, 2019, the RSF condemned the pressure on families of reporters by the Iranian regime, saying Iran ranked 170 among 180 states regarding Freedom of Press in 2019.
In its 2019 annual report, the Committee to Protect Journalists found at least 250 journalists in jail in relation to their work, and stated that the number of imprisoned journalists in Iran was 11, citing the crackdown on protests by the Iranian people over rising gasoline prices. The report named Eritrea, Vietnam and Iran as "the worst prisons for journalists" after China, Turkey, Saudi Arabia and Egypt.
On September 8, 2020, Reporters Without Borders expressed concern about the continuing detention and repression of journalists in Iran, and warned for the journalists and Reporters who have been arrested for their activities and subjected to harassment. "The Human Rights Council must take more serious action to protect and defend journalists," said an official.
On Monday, November 9, 2020, Ralph Nestmeyer, Vice President of the German Section of the Pen Association, referred to the repressive methods of authoritarian regimes: "Freedom of expression has declined in many parts of the world." He added that dictatorial regimes respond to any criticism with violence and imprisonment. This year the World Pen Association (Pen), will concentrate on the fate of writers in Iran, China, Turkey, Peru and Uganda.
Human Rights Watch condemned the punishment of the death penalty and demanded that it be prevented at all cost, following the December 12 execution of an Iranian dissident on vague charges. Rouhallah Zam, the founder of Telegram channel Amadnews, was allegedly detained when he was visiting Iran in October 2019. He was deported forcibly to Iran and convicted of vague national security charges, as per Human Rights Watch. Zam faced trial for his ‘activism’ after being deported to Iran. The Iranian Supreme Court confirmed his verdict on December 8 and the journalist was executed on December 12.
Palestine
In October 2019, the Palestinian Authority blocked 59 websites, claiming that they were critical of the government. These websites were both Palestinian and Arabic, and were identified to have been publishing material that "threaten national security and civil peace." Quds News Network, among the blocked sites, stated that the move reflected the Palestinian Authority's repression of the press.
China
Critics argue that the Communist Party in China has failed to live up to its promises about the freedom of the mainland Chinese media. Freedom House consistently ranks China as 'Not Free' in its annual press freedom survey, including the 2014 report. PRC journalist He Qinglian says that the PRC's media are controlled by directives from the Communist Party's propaganda department, and are subjected to intense monitoring which threatens punishment for violators, rather than to pre-publication censorship. In 2008, ITV News reporter John Ray was arrested while covering a 'Free Tibet' protest. International media coverage of Tibetan protests only a few months before the Beijing Olympics in 2008 triggered a strong reaction inside China. Chinese media practitioners took the opportunity to argue with propaganda authorities for more media freedom: one journalist asked, 'If not even Chinese journalists are allowed to report about the problems in Tibet, how can foreign journalists know about the Chinese perspective about the events?' Foreign journalists also reported that their access to certain websites, including those of human rights organizations, was restricted.
International Olympic Committee president Jacques Rogge stated at the end of the 2008 Olympic Games that "The regulations [governing foreign media freedom during the Olympics] might not be perfect but they are a sea-change compared to the situation before. We hope that they will continue." The Foreign Correspondents Club of China (FCCC) issued a statement during the Olympics that 'despite welcome progress in terms of accessibility and the number of press conferences within the Olympic facilities, the FCCC has been alarmed at the use of violence, intimidation and harassment outside. The club has confirmed more than 30 cases of reporting interference since the formal opening of the Olympic media centre on 25 July, and is checking at least 20 other reported incidents.'
Since the Chinese state continues to exert a considerable amount of control over media, public support for domestic reporting has come as a surprise to many observers. Not much is known about the extent to which the Chinese citizenry believe the official statements of the CPC, nor about which media sources they perceive as credible and why. So far, research on the media in China has focused on the changing relationship between media outlets and the state during the reform era. Nor is much known about how China's changing media environment has affected the government's ability to persuade media audiences. Research on political trust reveals that exposure to the media correlates positively with support for the government in some instances, and negatively in others. The research has been cited as evidence that the Chinese public believes propaganda transmitted to them through the news media, but also that they disbelieve it. These contradictory results can be explained by realizing that ordinary citizens consider media sources to be credible to a greater or lesser degree, depending on the extent to which media outlets have undergone reform.
In 2012 the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights urged the Chinese government to lift restrictions on media access to the region and allow independent and impartial monitors to visit and assess conditions in Tibet. The Chinese government did not change its position.
Pakistan
Article 19 of the constitution of the Pakistan states that : "Every citizen shall have the right to freedom of speech and expression, and there shall be freedom of the press, subject to any reasonable restrictions imposed by law in the interest of the glory of Islam or the integrity, security or defense of Pakistan or any part thereof, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, decency or morality, or in relation to contempt of court, commission of or incitement to an offence." Since independence the electronic media in Pakistan remained dominated by the state-run Pakistan Television and Pakistan Broadcasting CorporationsIronically, press freedom in Pakistan flourished for the first time in 2002 during Gen R Prevaiz Musharraf's era.
To a large extent the media enjoys freedom of expression in spite of political pressure and direct bans sometimes administered by political stake holders. Political pressure on media is mostly done indirectly. One tool widely used by the government is to cut off 'unfriendly' media from governmental advertising. Using draconian laws the government has also banned or officially silenced popular television channels. The Pakistan Electronic Media Regulatory Authority (PEMRA) has been used to silence the broadcast media by either suspending licenses or by simply threatening to do so. In addition, media is also threatened by non-state actors involved in the current conflict. The security situation of journalists has improved and the number of journalists killed in Pakistan has also declined considerably. However, press freedom in Pakistan along with India continues to decline.
In its 2018 Press Freedom Index, Reporters Without Borders ranked Pakistan number 139 out of 180 countries based on freedom of the press. The report implied considerable improvement in the freedom of press compared to the preceding years.
Malaysia
The press in Malaysia is controlled and journalists cannot have a conversation about certain things. For instance, a British reporter in Malaysia was arrested after she reported on the 1Malaysia Development Berhad scandal and published details of the alleged transfer of $681 million from 1MDB to bank accounts held by Najib Razak.
Singapore
Singapore's media environment is considered to be controlled by the government.
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia does not tolerate dissidents and it can impose penalties on such people. Saudi Arabia is also responsible for executing Saudi-American journalist, Jamal Khashoggi in 2018. As he entered a Saudi embassy in Turkey, a group of Saudi assassins got rid of him.
India
The Indian Constitution, while not mentioning the word "press", provides for "the right to freedom of speech and expression" (Article 19(1) a). However this right is subject to restrictions under sub clause, whereby this freedom can be restricted for reasons of "sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, preserving decency, preserving morality, in relation to contempt, court, defamation, or incitement to an offense". Laws such as the Official Secrets Act and Prevention of Terrorist Activities Act (PoTA) have been used to limit press freedom. Under PoTA, person could be detained for up to six months for being in contact with a terrorist or terrorist group. PoTA was repealed in 2006, but the Official Secrets Act 1923 continues.
For the first half-century of independence, media control by the state was the major constraint on press freedom. Indira Gandhi famously stated in 1975 that All India Radio is "a Government organ, it is going to remain a Government organ..." With the liberalization starting in the 1990s, private control of media has burgeoned, leading to increasing independence and greater scrutiny of government.
It ranks poorly at 142nd rank out of 180 listed countries in the Press Freedom Index 2021 released by Reporters Without Borders (RSF). Analytically India's press freedom, as could be deduced by the Press Freedom Index, has constantly reduced since 2002, when it culminated in terms of apparent freedom, achieving a rank of 80 among the reported countries. In 2018, India's freedom of press ranking declined two placed to 138. In explaining the decline, RSF cited growing intolerance from Hindu nationalist supporters of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, and the murders of journalists such as Gauri Lankesh.
Bangladesh
Bangladeshi media is reportedly following self-censorship due to the controversial Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Act. Under this act, 25 journalists and several hundred bloggers and Facebook users are reportedly prosecuted in Bangladesh in 2017.
Bangladesh ranks poorly at 146th rank out of 180 listed countries in the Press Freedom Index 2018 released by Reporters Without Borders (RWB). Bangladeshi media has faced many problems in 2018. The country's most popular online newspaper bdnews24.com was blocked for a few hours on June 18, 2018 by Bangladesh's regulatory authority. Another newspaper The Daily Star's website was blocked for 22 hours on June 2, 2018 after it had published a report about a victim of an extrajudicial execution in the southeastern city of Cox's Bazar.
During the road-safety protests in 2018, Bangladeshi government switched off 3G and 4G mobile data and also arrested a photographer named Shahidul Alam under ICT act, after he had given an interview with Al Jazeera.
Africa
Tanzania
As of 2018, online content providers must be licensed and pay an annual fee to the government.
South Africa
Following the transition to democracy in 1994, the post-apartheid Constitution of South Africa guarantees the freedom of the press.
Implications of new technologies
Many of the traditional means of delivering information are being slowly superseded by the increasing pace of modern technological advance. Almost every conventional mode of media and information dissemination has a modern counterpart that offers significant potential advantages to journalists seeking to maintain and enhance their freedom of speech. A few simple examples of such phenomena include:
- Satellite television versus terrestrial television: Whilst terrestrial television is relatively easy to manage and manipulate, satellite television is much more difficult to control as journalistic content can easily be broadcast from other jurisdictions beyond the control of individual governments. An example of this in the Middle East is the satellite broadcaster Al Jazeera. This Arabic-language media channel operates out of Qatar, whose government is relatively liberal compared to many of its neighboring states. As such, its views and content are often problematic to a number of governments in the region and beyond. However, because of the increased affordability and miniaturisation of satellite technology (e.g. dishes and receivers) it is simply not practicable for most states to control popular access to the channel.
- Internet-based publishing (e.g., blogging, social media) vs. traditional publishing: Traditional magazines and newspapers rely on physical resources (e.g., offices, printing presses) that can easily be targeted and forced to close down. Internet-based publishing systems can be run using ubiquitous and inexpensive equipment and can operate from any global jurisdiction. Nations and organisations are increasingly resorting to legal measures to take control of online publications, using national security, anti-terror measures and copyright laws to issue takedown notices and restrict opposition speech.
- Internet, anonymity software and strong cryptography: In addition to Internet-based publishing, the Internet (in combination with anonymity software such as Tor and cryptography) allows for sources to remain anonymous and sustain confidentiality while delivering information to or securely communicating with journalists anywhere in the world in an instant (e.g. SecureDrop, WikiLeaks).
- Voice over Internet protocol (VOIP) vs. conventional telephony: Although conventional telephony systems are easily tapped and recorded, modern VOIP technology can employ low-cost strong cryptography to evade surveillance. As VOIP and similar technologies become more widespread they are likely to make the effective monitoring of journalists (and their contacts and activities) a very difficult task for governments.
Governments are responding to the challenges posed by new media technologies by deploying increasingly sophisticated technology of their own (a notable example being China's attempts to impose control through a state-run internet service provider that controls access to the Internet).
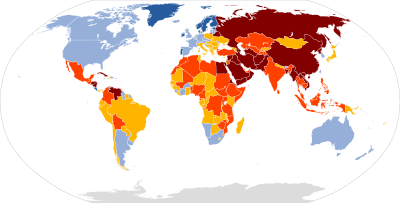
World ranking
World ranking 2015
On February 12, 2015, the Reporters without Borders (RSF) published its annual report. In this report, 180 states have been reviewed based on the freedom of press, independent media and also the situation of reporters and journalists. Iran is at the 173rd of this list that indicates, despite the Rouhani's promises, freedom of speeches and journalists has not been improved; the RSF concerns continue. According to the report, Iran ranked third on the list on the imprisonment of journalists.
World ranking 2016
On December 13, 2016, the Reporters without Borders (RSF) published its annual report. The report reads: 348 journalists have been detained and 52 taken hostage in Iran in 2016. Following Turkey, the countries China, Syria, Egypt, and Iran have almost two-thirds of detained journalists.
World ranking 2017
Based on the 2017 annual report on RSF, Iran along with China, Turkey, Vietnam, and Syria are the largest prison for reporters and media activists. The report says during 2017, among professional journalists, 50 have been killed and 326 detained; 54 reporters have been taken hostage.
World ranking 2018
The RSF in its annual report in 2018 documented deadly violence and misbehavior against reporters saying for one year 80 reporters have been killed, 348 detained, and 60 taken hostage which indicates an unprecedented hostility against media staff. This organization recognizes Iran as one of the five states which is called "prison of reporters" along with China, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Turkey. Based on this report Iran is ranked 144th and is still one of the greatest prisons for journalists.
World ranking 2019
On April 18, the RSF published its annual report, Indication for Free Media in the world. In this report, among 180 states, Norway was the freest and safest country in the world. Finland and Sweden are the next. Meanwhile, Iran lost its position in the list- compare to 2018- and is among the 11 countries that suppress the freedom of the media. Iran is on the bottom of the list, ranked as the 170th state.
World ranking 2020
On April 21, the RSF in its 2020 annual report published the latest ranking of Freedom of Media. The Islamic Republic of Iran is the 173rd in the list, declining three steps compared to 2019. The three Iranian allied countries, Syria, China, and North Korea are 174th, 177th, and 180th. This organization accuses China and Iran of censorship of news about an outbreak of coronavirus.
World ranking 2021
The World Press Freedom Index 2021, compiled by Reporters Without Borders, shows that journalism is completely blocked or severely restricted in 73 countries and restricted in 59 others. According to the report, Norway ranks first among 180 countries for the fifth year in a row. Finland is second and Sweden third. In this index, Iran is ranked 174th with a decline. Russia, China, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Syria ranked consequently 150th, 177th, 170th, 166th and 173rd.