Amphetamine
 |
 |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name |
(RS)-1-phenylpropan-2-amine
(RS)-1-phenyl-2-aminopropane |
| Clinical data |
| AHFS/Drugs.com |
entry |
| Licence data |
US FDA:link |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Physical: none
Psychological: moderate |
|
|
Moderate |
|
|
Medical: oral, nasal inhalation
Recreational: oral, nasal inhalation, insufflation, rectal, intravenous |
| Pharmacokinetic data |
| Bioavailability |
Rectal 95–100%; Oral 75–100%[1] |
| Protein binding |
15–40%[2] |
| Metabolism |
CYP2D6,[3] DBH,[4][5][6] FMO3,[7][8] XM-ligase,[9] and ACGNAT[10] |
| Onset of action |
Immediate |
| Half-life |
D-amph:9–11h;[3][11] L-amph:11–14h[3][11] |
| Excretion |
Renal; pH-dependent range: 1–75%[3] |
| Identifiers |
|
|
300-62-9  Y Y |
|
|
N06BA01 |
| PubChem |
CID 3007 |
| IUPHAR ligand |
4804 |
| DrugBank |
DB00182  Y Y |
| ChemSpider |
13852819  Y Y |
| UNII |
CK833KGX7E  Y Y |
| KEGG |
D07445  Y Y |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:2679  Y Y |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL405  Y Y |
| NIAID ChemDB |
018564 |
| Synonyms |
α-methylphenethylamine |
| PDB ligand ID |
FRD (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| Chemical data |
| Formula |
C9H13N |
|
|
135.2084 g/mol |
|
|
| Physical data |
|---|
| Density |
0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Melting point |
11.3 °C (52.3 °F) [12] |
| Boiling point |
203 °C (397 °F) [13] |
 Y (what is this?) (verify) Y (what is this?) (verify) |
Amphetamine[note 1] (
pronunciation:  i//
i//; contracted from
alpha‑methylphenethylamine) is a potent
central nervous system (CNS)
stimulant of the
phenethylamine class that is used in the treatment of
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and
narcolepsy. Amphetamine was discovered in 1887 and exists as two
enantiomers:
levoamphetamine and
dextroamphetamine.
[note 2] Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the
racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers, levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine, in their pure amine forms. However, the term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion, depression, and obesity. Amphetamine is also used as a
performance and
cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an
aphrodisiac and
euphoriant. It is a
prescription medication in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with
substance abuse.
[sources 1]
The first pharmaceutical amphetamine was
Benzedrine, a brand of inhalers used to treat a variety of conditions. Currently, pharmaceutical amphetamine is typically prescribed as
Adderall,
[note 3] dextroamphetamine, or the inactive
prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine, through activation of a
trace amine receptor, increases
biogenic amine and
excitatory neurotransmitter activity in the brain, with its most pronounced effects targeting the
catecholamine neurotransmitters
norepinephrine and
dopamine. At therapeutic doses, this causes emotional and cognitive effects such as euphoria, change in
libido, increased
wakefulness, and improved
cognitive control. It induces physical effects such as decreased reaction time, fatigue resistance, and increased muscle strength.
[sources 2]
Much larger doses of amphetamine are likely to impair cognitive function and induce rapid muscle breakdown.
Drug addiction is a serious risk with large recreational doses, but rarely arises from medical use. Very high doses can result in
psychosis (e.g., delusions and paranoia) which rarely occurs at therapeutic doses even during long-term use. Recreational doses are generally much larger than prescribed therapeutic doses and carry a far greater risk of serious side effects.
[sources 3]
Amphetamine is also the parent compound of its own structural class, the
substituted amphetamines,
[note 4] which includes prominent substances such as
bupropion,
cathinone,
MDMA (ecstasy), and
methamphetamine. As a member of the phenethylamine class, amphetamine is also chemically related to the naturally occurring
trace amine neuromodulators, specifically
phenethylamine[note 5] and
N-methylphenethylamine, both of which are produced within the human body. Phenethylamine is the parent compound of amphetamine, while
N-methylphenethylamine is a
constitutional isomer that differs only in the placement of the methyl group.
[sources 4]
Uses
Medical
Amphetamine is used to treat
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and
narcolepsy (a sleep disorder), and is sometimes prescribed
off-label for its past
medical indications, such as
depression,
obesity, and
nasal congestion.
[11][27] Long-term amphetamine exposure in some animal species is known to produce abnormal
dopamine system development or nerve damage,
[39][40] but, in humans with ADHD, pharmaceutical amphetamines appear to improve brain development and nerve growth.
[41][42][43] Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies suggest that long-term treatment with amphetamine decreases abnormalities in brain structure and function found in subjects with ADHD, and improves function in several parts of the brain, such as the right
caudate nucleus of the
basal ganglia.
[41][42][43]
Reviews of clinical stimulant research have established the safety and effectiveness of long-term amphetamine use for ADHD.
[44][45][46] Controlled trials spanning two years have demonstrated treatment effectiveness and safety.
[44][46] One review highlighted a nine-month
randomized controlled trial in children with ADHD that found an average increase of 4.5
IQ points, continued increases in attention, and continued decreases in disruptive behaviors and hyperactivity.
[44]
Current models of ADHD suggest that it is associated with functional impairments in some of the brain's
neurotransmitter systems;
[47] these functional impairments involve impaired
dopamine neurotransmission in the
mesocorticolimbic projection and
norepinephrine neurotransmission in the
locus coeruleus and
prefrontal cortex.
[47] Psychostimulants like
methylphenidate and amphetamine are effective in treating ADHD because they increase neurotransmitter activity in these systems.
[24][47][48] Approximately 80% of those who use these stimulants see improvements in ADHD symptoms.
[49] Children with ADHD who use stimulant medications generally have better relationships with peers and family members, perform better in school, are less distractible and impulsive, and have longer attention spans.
[50][51] The
Cochrane Collaboration's review
[note 6] on the treatment of adult ADHD with pharmaceutical amphetamines stated that while these drugs improve short-term symptoms, they have higher discontinuation rates than non-stimulant medications due to their adverse
side effects.
[53]
A Cochrane Collaboration review on the treatment of ADHD in children with
tic disorders such as
Tourette syndrome indicated that stimulants in general do not make
tics worse, but high doses of dextroamphetamine could exacerbate tics in some individuals.
[54] Other Cochrane reviews on the use of amphetamine following stroke or acute brain injury indicated that it may improve recovery, but further research is needed to confirm this.
[55][56][57]
Enhancing performance
A 2015
meta-analysis of high quality
clinical trials confirmed that therapeutic doses of amphetamine and methylphenidate result in modest improvements in performance on
working memory,
episodic memory, and
inhibitory control tests in normal healthy adults.
[58] Therapeutic doses of amphetamine also enhance cortical network efficiency, an effect which mediates improvements in working memory in all individuals.
[24][59]
Amphetamine and other ADHD stimulants also improve
task saliency (motivation to perform a task) and increase
arousal (wakefulness), in turn promoting goal-directed behavior.
[24][60][61] Stimulants such as amphetamine can improve performance on difficult and boring tasks and are used by some students as a study and test-taking aid.
[24][60][62] Based upon studies of self-reported illicit stimulant use, students primarily use stimulants such as amphetamine for performance enhancement rather than using them as recreational drugs.
[63] However, high amphetamine doses that are above the therapeutic range can interfere with working memory and other aspects of
cognitive control.
[24][60]
Amphetamine is used by some athletes for its psychological and performance-enhancing effects, such as increased stamina and alertness;
[23][36] however, its use is prohibited at sporting events regulated by collegiate, national, and international anti-doping agencies.
[64][65] In healthy people at oral therapeutic doses, amphetamine has been shown to increase physical strength, acceleration, stamina, and endurance, while reducing
reaction time.
[23][66][67]
Amphetamine improves stamina, endurance, and reaction time primarily through
reuptake inhibition and
effluxion of dopamine in the central nervous system.
[66][67][68] At therapeutic doses, the adverse effects of amphetamine do not impede athletic performance;
[23][66][67] however, at much higher doses, amphetamine can induce effects that severely impair performance, such as
rapid muscle breakdown and
elevated body temperature.
[22][31][66]
Contraindications
According to the
International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) and
United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA),
[note 7] amphetamine is
contraindicated in people with a history of
drug abuse,
heart disease, severe
agitation, or severe anxiety.
[69][70] It is also contraindicated in people currently experiencing
arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries),
glaucoma (increased eye pressure),
hyperthyroidism (excessive production of thyroid hormone), or
hypertension.
[69][70] People who have experienced
allergic reactions to other stimulants in the past or who are taking
monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are advised not to take amphetamine.
[69][70] These agencies also state that anyone with
anorexia nervosa,
bipolar disorder, depression, hypertension, liver or kidney problems,
mania,
psychosis,
Raynaud's phenomenon,
seizures,
thyroid problems,
tics, or
Tourette syndrome should monitor their symptoms while taking amphetamine.
[69][70] Evidence from human studies indicates that therapeutic amphetamine use does not cause developmental abnormalities in the fetus or newborns (i.e., it is not a human
teratogen), but amphetamine abuse does pose risks to the fetus.
[70] Amphetamine has also been shown to pass into breast milk, so the IPCS and USFDA advise mothers to avoid breastfeeding when using it.
[69][70] Due to the potential for reversible growth impairments,
[note 8] the USFDA advises monitoring the height and weight of children and adolescents prescribed an amphetamine pharmaceutical.
[69]
Side effects
The
side effects of amphetamine are varied, and the amount of amphetamine used is the primary factor in determining the likelihood and severity of side effects.
[22][31][36] Amphetamine products such as
Adderall, Dexedrine, and their generic equivalents are currently approved by the USFDA for long-term therapeutic use.
[29][31] Recreational use of amphetamine generally involves much larger doses, which have a greater risk of serious side effects than dosages used for therapeutic reasons.
[36]
Physical
At normal therapeutic doses, the physical side effects of amphetamine vary widely by age and from person to person.
[31] Cardiovascular side effects can include
hypertension or
hypotension from a
vasovagal response,
Raynaud's phenomenon (reduced blood flow to extremities), and
tachycardia (increased heart rate).
[31][36][71] Sexual side effects in males may include
erectile dysfunction, frequent erections, or
prolonged erections.
[31] Abdominal side effects may include stomach pain, loss of appetite, nausea, and weight loss.
[31] Other potential side effects include
dry mouth,
excessive grinding of the teeth, acne, profuse sweating, blurred vision, reduced
seizure threshold, and
tics (a type of movement disorder).
[31][36][71] Dangerous physical side effects are rare at typical pharmaceutical doses.
[36]
Amphetamine stimulates the
medullary respiratory centers, producing faster and deeper breaths.
[36] In a normal person at therapeutic doses, this effect is usually not noticeable, but when respiration is already compromised, it may be evident.
[36] Amphetamine also induces
contraction in the urinary
bladder sphincter, the muscle which controls urination, which can result in difficulty urinating. This effect can be useful in treating
bed wetting and
loss of bladder control.
[36] The effects of amphetamine on the gastrointestinal tract are unpredictable.
[36] If intestinal activity is high, amphetamine may reduce
gastrointestinal motility (the rate at which content moves through the digestive system);
[36] however, amphetamine may increase motility when the
smooth muscle of the tract is relaxed.
[36] Amphetamine also has a slight
analgesic effect and can enhance the pain relieving effects of
opioids.
[36]
USFDA-commissioned studies from 2011 indicate that in children, young adults, and adults there is no association between serious adverse cardiovascular events (
sudden death,
heart attack, and
stroke) and the medical use of amphetamine or other ADHD stimulants.
[sources 5]
Psychological
Common psychological effects of therapeutic doses can include increased
alertness, apprehension,
concentration, decreased sense of fatigue, mood swings (
elated mood followed by mildly
depressed mood), increased initiative,
insomnia or
wakefulness,
self-confidence, and sociability.
[31][36] Less common side effects include
anxiety, change in
libido,
grandiosity,
irritability, repetitive or
obsessive behaviors, and restlessness;
[sources 6] these effects depend on the user's personality and current mental state.
[36] Amphetamine psychosis (e.g., delusions and paranoia) can occur in heavy users.
[22][31][32] Although very rare, this psychosis can also occur at therapeutic doses during long-term therapy.
[22][31][33] According to the USFDA, "there is no systematic evidence" that stimulants produce aggressive behavior or hostility.
[31]
Amphetamine has also been shown to produce a
conditioned place preference in humans taking therapeutic doses,
[53][77] meaning that individuals acquire a preference for spending time in places where they have previously used amphetamine.
[77][78]
Overdose
An amphetamine overdose can lead to many different symptoms, but is rarely fatal with appropriate care.
[70][79] The severity of overdose symptoms increases with dosage and decreases with
drug tolerance to amphetamine.
[36][70] Tolerant individuals have been known to take as much as 5 grams of amphetamine in a day, which is roughly 100 times the maximum daily therapeutic dose.
[70] Symptoms of a moderate and extremely large overdose are listed below; fatal amphetamine poisoning usually also involves convulsions and
coma.
[22][36] In 2013, overdose on amphetamine, methamphetamine, and other compounds implicated in an "
amphetamine use disorder" resulted in an estimated 3,788 deaths worldwide (3,425–4,145 deaths,
95% confidence).
[note 9][80]
Pathological overactivation of the
mesolimbic pathway, a
dopamine pathway that connects the
ventral tegmental area to the
nucleus accumbens, plays a central role in amphetamine addiction.
[81][82] Individuals who frequently overdose on amphetamine during recreational use have a high risk of developing an amphetamine addiction, since repeated overdoses gradually increase the level of
accumbal ΔFosB, a "molecular switch" and "master control protein" for addiction.
[83][84][85] Once nucleus accumbens ΔFosB is sufficiently overexpressed, it begins to increase the severity of addictive behavior (e.g., compulsive drug-seeking).
[83][86] While there are currently no effective drugs for treating amphetamine addiction, regularly engaging in sustained aerobic exercise appears to reduce the risk of developing such an addiction.
[87] Sustained aerobic exercise on a regular basis also appears to be an effective treatment for amphetamine addiction;
[86][87][88] exercise therapy improves
clinical treatment outcomes and may be used as a
combination therapy with
cognitive behavioral therapy, which is currently the best clinical treatment available.
[87][88][89]
Addiction
| • addiction – a state characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, despite adverse consequences |
| • reinforcing stimuli – stimuli that increase the probability of repeating behaviors paired with them |
| • rewarding stimuli – stimuli that the brain interprets as intrinsically positive or as something to be approached |
| • addictive drug – a drug that is both rewarding and reinforcing |
| • addictive behavior – a behavior that is both rewarding and reinforcing |
| • sensitization – an amplified response to a stimulus resulting from repeated exposure to it |
| • drug tolerance – the diminishing effect of a drug resulting from repeated administration at a given dose |
| • drug sensitization or reverse tolerance – the escalating effect of a drug resulting from repeated administration at a given dose |
| • drug dependence – an adaptive state associated with a withdrawal syndrome upon cessation of repeated drug intake |
| • physical dependence – dependence that involves persistent physical–somatic withdrawal symptoms (e.g., fatigue) |
| • psychological dependence – dependence that involves emotional–motivational withdrawal symptoms (e.g., dysphoria and anhedonia) |
| (edit | history) |
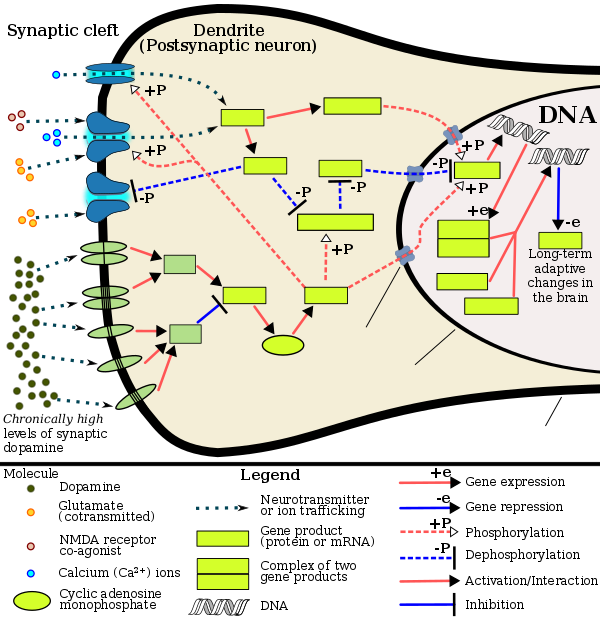
This diagram depicts the signaling events in the
brain's reward center that are induced by chronic high-dose exposure to psychostimulants that increase the concentration of synaptic dopamine, like amphetamine,
methylphenidate, and
phenethylamine. Following presynaptic
dopamine and
glutamate co-release by such psychostimulants,
[92][93] postsynaptic receptors for these
neurotransmitters trigger internal signaling events through a
cAMP pathway and calcium-dependent pathway that ultimately result in increased
CREB phosphorylation.
[81][94] Phosphorylated CREB increases levels of ΔFosB, which in turn represses the c-fos gene with the help of
corepressors;
[94] c-fos
repression acts as a molecular switch that enables the accumulation of ΔFosB in the neuron.
[95] A highly stable (phosphorylated) form of ΔFosB, one that persists in neurons for one or two months, slowly accumulates following repeated exposure to stimulants through this process.
[85][96] ΔFosB functions as "one of the master control proteins" that produces addiction-related
structural changes in the brain, and upon sufficient accumulation, with the help of its downstream targets (e.g.,
nuclear factor kappa B), it induces an addictive state.
[85][96]
Addiction is a serious risk with heavy recreational amphetamine use but is unlikely to arise from typical medical use at therapeutic doses.
[34][35][36] Tolerance develops rapidly in amphetamine abuse (i.e., a recreational amphetamine overdose), so periods of extended use require increasingly larger doses of the drug in order to achieve the same effect.
[97][98]
Biomolecular mechanisms
Current models of addiction from chronic drug use involve alterations in
gene expression in certain parts of the brain, particularly the
nucleus accumbens.
[99][100][101] The most important
transcription factors[note 10] that produce these alterations are
ΔFosB,
cAMP response element binding protein (
CREB), and nuclear factor kappa B (
NFκB).
[100] ΔFosB plays a crucial role in the development of drug addictions, since its overexpression in
D1-type medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens is
necessary and sufficient[note 11] for most of the behavioral and neural adaptations that arise from addiction.
[83][84][100] Once ΔFosB is sufficiently overexpressed, it induces an addictive state that becomes increasingly more severe with further increases in ΔFosB expression.
[83][84] It has been implicated in addictions to
alcohol,
cannabinoids,
cocaine,
nicotine,
opioids,
phencyclidine, and
substituted amphetamines, among others.
[86][100][103]
ΔJunD, a transcription factor, and
G9a, a
histone methyltransferase enzyme, both directly oppose the induction of ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens (i.e., they oppose increases in its expression).
[84][100][104] Sufficiently overexpressing ΔJunD in the nucleus accumbens with
viral vectors can completely block many of the neural and behavioral alterations seen in chronic drug abuse (i.e., the alterations mediated by ΔFosB).
[100] ΔFosB also plays an important role in regulating behavioral responses to
natural rewards, such as palatable food, sex, and exercise.
[86][100][105] Since both natural rewards and addictive drugs
induce expression of ΔFosB (i.e., they cause the brain to produce more of it), chronic acquisition of these rewards can result in a similar pathological state of addiction.
[86][100] Consequently, ΔFosB is the most significant factor involved in both amphetamine addiction and amphetamine-induced
sex addictions, which are compulsive sexual behaviors that result from excessive sexual activity and amphetamine use.
[86][106] These sex addictions are associated with a
dopamine dysregulation syndrome which occurs in some patients taking
dopaminergic drugs.
[86][105][106]
The effects of amphetamine on gene regulation are both dose- and route-dependent.
[101] Most of the research on gene regulation and addiction is based upon animal studies with intravenous amphetamine administration at very high doses.
[101] The few studies that have used equivalent (weight-adjusted) human therapeutic doses and oral administration show that these changes, if they occur, are relatively minor.
[101] This suggests that medical use of amphetamine does not significantly affect gene regulation.
[101]
Pharmacological treatments
As of May 2014
[update], there is no effective
pharmacotherapy for amphetamine addiction.
[107][108][109] Amphetamine addiction is largerly mediated through increased activation of
dopamine receptors and
co-localized NMDA receptors[note 12] in the the nucleus accumbens;
[82] magnesium ions inhibit NMDA receptors by blocking the receptor
calcium channel.
[82][110] One review suggested that, based upon animal testing, pathological (addiction-inducing) amphetamine use significantly reduces the level of intracellular magnesium throughout the brain.
[82] Supplemental magnesium[note 13] and
fluoxetine treatment have been shown to reduce amphetamine
self-administration (doses given to oneself) in humans, but neither is an effective
monotherapy for amphetamine addiction.
[82][111]
Behavioral treatments
Cognitive behavioral therapy is currently the most effective clinical treatment for psychostimulant addiction.
[89]
Additionally, research on the
neurobiological effects of physical exercise suggests that daily aerobic exercise, especially endurance exercise (e.g.,
marathon running), prevents the development of drug addiction and is an effective adjunct (supplemental) treatment for amphetamine addiction.
[86][87][88] Exercise leads to better treatment outcomes when used as an adjunct treatment, particularly for psychostimulant addictions.
[87][88] In particular,
aerobic exercise decreases psychostimulant self-administration, reduces the
reinstatement (i.e., relapse) of drug-seeking, and induces increased
dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) density in the
striatum.
[86] This is the opposite of pathological stimulant use, which induces decreased striatal DRD2 density.
[86]
Dependence and withdrawal
According to another Cochrane Collaboration review on
withdrawal in individuals who compulsively use amphetamine and methamphetamine, "when chronic heavy users abruptly discontinue amphetamine use, many report a time-limited withdrawal syndrome that occurs within 24 hours of their last dose."
[112] This review noted that withdrawal symptoms in chronic, high-dose users are frequent, occurring in up to 87.6% of cases, and persist for three to four weeks with a marked "crash" phase occurring during the first week.
[112] Amphetamine withdrawal symptoms can include anxiety,
drug craving,
depressed mood,
fatigue,
increased appetite, increased movement or
decreased movement, lack of motivation, sleeplessness or sleepiness, and
lucid dreams.
[112] The review indicated that withdrawal symptoms are associated with the degree of dependence, suggesting that therapeutic use would result in far milder discontinuation symptoms.
[112] Manufacturer prescribing information does not indicate the presence of withdrawal symptoms following discontinuation of amphetamine use after an extended period at therapeutic doses.
[113][114][115]
Toxicity and psychosis
In rodents and primates, sufficiently high doses of amphetamine cause dopaminergic
neurotoxicity, or damage to dopamine neurons, which is characterized by reduced transporter and receptor function.
[116] There is no evidence that amphetamine is directly neurotoxic in humans.
[117][118] However, large doses of amphetamine may cause indirect neurotoxicity as a result of increased oxidative stress from
reactive oxygen species and
autoxidation of dopamine.
[39][119][120]
A severe amphetamine overdose can result in a stimulant psychosis that may involve a variety of symptoms, such as
paranoia and
delusions.
[32] A Cochrane Collaboration review on treatment for amphetamine, dextroamphetamine, and methamphetamine psychosis states that about 5–15% of users fail to recover completely.
[32][121] According to the same review, there is at least one trial that shows
antipsychotic medications effectively resolve the symptoms of acute amphetamine psychosis.
[32] Psychosis very rarely arises from therapeutic use.
[33][69]
Interactions
Many types of substances are known to
interact with amphetamine, resulting in altered
drug action or
metabolism of amphetamine, the interacting substance, or both.
[3][122] Inhibitors of the enzymes that metabolize amphetamine (e.g., CYP2D6 and flavin-containing monooxygenase 3) will prolong its
elimination half-life, meaning that its effects will last longer.
[7][122] Amphetamine also interacts with
MAOIs, particularly
monoamine oxidase A inhibitors, since both MAOIs and amphetamine increase plasma catecholamines (i.e., norepinephrine and dopamine);
[122] therefore, concurrent use of both is dangerous.
[122] Amphetamine will modulate the activity of most psychoactive drugs. In particular, amphetamine may decrease the effects of
sedatives and
depressants and increase the effects of
stimulants and
antidepressants.
[122] Amphetamine may also decrease the effects of
antihypertensives and
antipsychotics due to its effects on blood pressure and dopamine respectively.
[122] In general, there is no significant interaction when consuming amphetamine with food, but the
pH of gastrointestinal content and urine affects the absorption and excretion of amphetamine, respectively.
[122] Acidic substances reduce the absorption of amphetamine and increase urinary excretion, and alkaline substances do the opposite.
[122] Due to the effect pH has on absorption, amphetamine also interacts with gastric acid reducers such as
proton pump inhibitors and
H2 antihistamines, which increase gastrointestinal pH (i.e., make it less acidic).
[122]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics of amphetamine enantiomers in a dopamine neuron
Amphetamine enters the presynaptic neuron across the neuronal membrane or through
DAT.
Once inside, it binds to
TAAR1 or enters synaptic vesicles through
VMAT2. When amphetamine enters the synaptic vesicles through VMAT2, dopamine is released into the cytosol (yellow-orange area). When amphetamine binds to TAAR1, it reduces dopamine receptor firing rate via
potassium channels and triggers
protein kinase A (PKA) and
protein kinase C (PKC) signaling, resulting in DAT phosphorylation.
PKA-phosphorylation causes DAT to withdraw into the presynaptic neuron (
internalize) and cease transport.
PKC-phosphorylated DAT may either operate in reverse or, like
PKA-phosphorylated DAT, internalize and cease transport. Amphetamine is also known to increase intracellular calcium, a known effect of TAAR1 activation, which is associated with DAT phosphorylation through a
CAMK-dependent pathway, in turn producing dopamine efflux.
Amphetamine exerts its behavioral effects by altering the use of
monoamines as neuronal signals in the brain, primarily in
catecholamine neurons in the reward and executive function pathways of the brain.
[30][48] The concentrations of the main neurotransmitters involved in reward circuitry and executive functioning, dopamine and norepinephrine, increase dramatically in a dose-dependent manner by amphetamine due to its effects on monoamine transporters.
[30][48][123] The reinforcing and task
saliency effects of amphetamine are mostly due to enhanced dopaminergic activity in the
mesolimbic pathway.
[24]
Amphetamine has been identified as a potent
full agonist of
trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1), a
Gs-coupled and
Gq-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) discovered in 2001, which is important for regulation of brain monoamines.
[30][124] Activation of
TAAR1 increases
cAMP production via
adenylyl cyclase activation and inhibits
monoamine transporter function.
[30][125] Monoamine
autoreceptors (e.g.,
D2 short,
presynaptic α2, and
presynaptic 5-HT1A) have the opposite effect of TAAR1, and together these receptors provide a regulatory system for monoamines.
[30] Notably, amphetamine and
trace amines bind to TAAR1, but not monoamine autoreceptors.
[30] Imaging studies indicate that monoamine reuptake inhibition by amphetamine and trace amines is site specific and depends upon the presence of
TAAR1 co-localization in the associated monoamine neurons.
[30] As of 2010,
[update] co-localization of TAAR1 and the
dopamine transporter (DAT) has been visualized in rhesus monkeys, but
co-localization of TAAR1 with the
norepinephrine transporter (NET) and the
serotonin transporter (SERT) has only been evidenced by
messenger RNA (mRNA) expression.
[30]
In addition to the neuronal monoamine
transporters, amphetamine also inhibits
vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2),
SLC1A1,
SLC22A3, and
SLC22A5.
[sources 8] SLC1A1 is
excitatory amino acid transporter 3 (EAAT3), a glutamate transporter located in neurons, SLC22A3 is an extraneuronal monoamine transporter that is present in
astrocytes and SLC22A5 is a high-affinity
carnitine transporter.
[sources 8] Amphetamine is known to strongly induce
cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART)
gene expression,
[131] a
neuropeptide involved in feeding behavior, stress, and reward, which induces observable increases in neuronal development and survival
in vitro.
[132][133][134] The CART receptor has yet to be identified, but there is significant evidence that CART binds to a unique
Gi/Go-coupled GPCR.
[134][135] Amphetamine also inhibits
monoamine oxidase at very high doses, resulting in less dopamine and phenethylamine metabolism and consequently higher concentrations of synaptic monoamines.
[136] The full profile of amphetamine's short-term drug effects is derived through increased cellular communication or
neurotransmission of
dopamine,
[30] serotonin,
[30] norepinephrine,
[30] epinephrine,
[123] histamine,
[123] CART peptides,
[131] acetylcholine,
[137][138] and
glutamate,
[92][139] which it effects through interactions with
CART,
EAAT3,
TAAR1, and
VMAT2.
[sources 9]
Dextroamphetamine is a more potent agonist of
TAAR1 than levoamphetamine.
[140] Consequently, dextroamphetamine produces greater
CNS stimulation than levoamphetamine, roughly three to four times more, but levoamphetamine has slightly stronger cardiovascular and peripheral effects.
[36][140]
Dopamine
In certain brain regions, amphetamine increases the concentration of dopamine in the
synaptic cleft.
[30] Amphetamine can enter the
presynaptic neuron either through
DAT or by diffusing across the neuronal membrane directly.
[30] As a consequence of DAT uptake, amphetamine produces competitive reuptake inhibition at the transporter.
[30] Upon entering the presynaptic neuron, amphetamine activates
TAAR1 which, through
protein kinase A (PKA) and
protein kinase C (PKC) signaling, causes DAT
phosphorylation.
[30] Phosphorylation by either protein kinase can result in DAT
internalization (
non-competitive reuptake inhibition), but
PKC-mediated phosphorylation alone induces reverse transporter function (dopamine
efflux).
[30][141] Amphetamine is also known to increase intracellular calcium, a known effect of TAAR1 activation, which is associated with DAT phosphorylation through a
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CAMK)-dependent pathway, in turn producing dopamine efflux.
[124][126][142] Through direct activation of
G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels and an indirect increase in dopamine autoreceptor signaling,
TAAR1 reduces the
firing rate of postsynaptic dopamine receptors, preventing a hyper-dopaminergic state.
[143][144][145]
Amphetamine is also a substrate for the presynaptic vesicular monoamine transporter,
VMAT2.
[123] Following amphetamine uptake at VMAT2, the
synaptic vesicle releases dopamine molecules into the
cytosol in exchange.
[123] Subsequently, the cytosolic dopamine molecules exit the presynaptic neuron via reverse transport at
DAT.
[30][123]
Norepinephrine
Similar to dopamine, amphetamine dose-dependently increases the level of synaptic norepinephrine, the direct precursor of
epinephrine.
[38][48] Based upon neuronal
TAAR1 mRNA expression, amphetamine is thought to affect norepinephrine analogously to dopamine.
[30][123][141] In other words, amphetamine induces TAAR1-mediated efflux and
non-competitive reuptake inhibition at phosphorylated
NET, competitive NET reuptake inhibition, and norepinephrine release from
VMAT2.
[30][123]
Serotonin
Amphetamine exerts analogous, yet less pronounced, effects on serotonin as on dopamine and norepinephrine.
[30][48] Amphetamine affects serotonin via
VMAT2 and, like norepinephrine, is thought to phosphorylate
SERT via
TAAR1.
[30][123] Like dopamine, amphetamine has low, micromolar affinity at the human
5-HT1A receptor.
[146][147]
Other neurotransmitters
Amphetamine has no direct effect on
acetylcholine neurotransmission, but several studies have noted that acetylcholine release increases after its use.
[137][138] In lab animals, amphetamine increases acetylcholine levels in certain brain regions as a downstream effect.
[137] In humans, a similar phenomenon occurs via the
ghrelin-mediated
cholinergic–dopaminergic reward link in the
ventral tegmental area.
[138] This heightened
cholinergic activity leads to increased
nicotinic receptor activation in the
CNS, a factor which likely contributes to the
nootropic effects of amphetamine.
[148]
Extracellular levels of
glutamate, the primary
excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, have been shown to increase upon exposure to amphetamine.
[92][139] This
cotransmission effect was found in the mesolimbic pathway, an area of the brain implicated in reward, where amphetamine is known to affect dopamine neurotransmission.
[92][139] Amphetamine also induces effluxion of
histamine from synaptic vesicles in
CNS mast cells and histaminergic neurons through
VMAT2.
[123]
Pharmacokinetics
The oral
bioavailability of amphetamine varies with gastrointestinal pH;
[122] it is well absorbed from the gut, and bioavailability is typically over 75% for dextroamphetamine.
[1] Amphetamine is a weak base with a
pKa of
9–10;
[3] consequently, when the pH is basic, more of the drug is in its
lipid soluble
free base form, and more is absorbed through the lipid-rich
cell membranes of the gut
epithelium.
[3][122] Conversely, an acidic pH means the drug is predominantly in a water soluble
cationic (salt) form, and less is absorbed.
[3] Approximately
15–40% of amphetamine circulating in the bloodstream is bound to
plasma proteins.
[2]
The
half-life of amphetamine enantiomers differ and vary with urine pH.
[3] At normal urine pH, the half-lives of dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine are
9–11 hours and
11–14 hours, respectively.
[3] An acidic diet will reduce the enantiomer half-lives to
8–11 hours; an alkaline diet will increase the range to
16–31 hours.
[149][150] The immediate-release and extended release variants of salts of both isomers reach peak plasma concentrations at 3 hours and 7 hours post-dose respectively.
[3] Amphetamine is eliminated via the kidneys, with
30–40% of the drug being excreted unchanged at normal urinary pH.
[3] When the urinary pH is basic, amphetamine is in its free base form, so less is excreted.
[3] When urine pH is abnormal, the urinary recovery of amphetamine may range from a low of 1% to a high of 75%, depending mostly upon whether urine is too basic or acidic, respectively.
[3] Amphetamine is usually eliminated within two days of the last oral dose.
[149] Apparent half-life and duration of effect increase with repeated use and accumulation of the drug.
[151]
The prodrug lisdexamfetamine is not as sensitive to pH as amphetamine when being absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract;
[152] following absorption into the blood stream, it is converted by red blood cell-associated enzymes to dextroamphetamine via
hydrolysis.
[152] The elimination half-life of lisdexamfetamine is generally less than one hour.
[152]
CYP2D6,
dopamine β-hydroxylase,
flavin-containing monooxygenase 3,
butyrate-CoA ligase, and
glycine N-acyltransferase are the enzymes known to metabolize amphetamine or its metabolites in humans.
[sources 10] Amphetamine has a variety of excreted metabolic products, including
4-hydroxyamfetamine,
4-hydroxynorephedrine,
4-hydroxyphenylacetone,
benzoic acid,
hippuric acid,
norephedrine, and
phenylacetone.
[3][149][153] Among these metabolites, the active
sympathomimetics are
4‑hydroxyamphetamine,
[154] 4‑hydroxynorephedrine,
[155] and norephedrine.
[156] The main metabolic pathways involve aromatic para-hydroxylation, aliphatic alpha- and beta-hydroxylation, N-oxidation, N-dealkylation, and deamination.
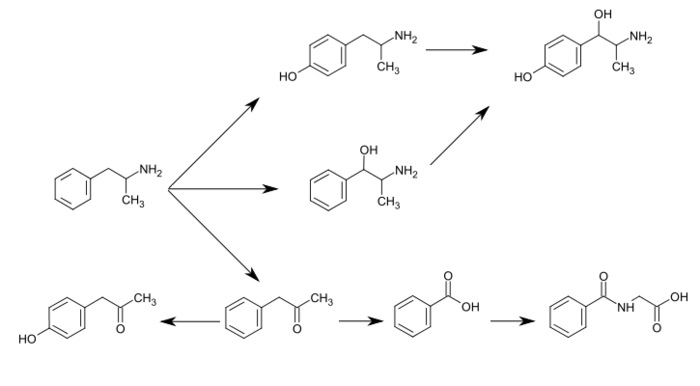
[3][149] The known pathways and detectable metabolites in humans include the following:
[3][7][153]
Metabolic pathways of amphetamine
Amphetamine
Para-
Hydroxylation
Para-
Hydroxylation
Para-
Hydroxylation
Beta-
Hydroxylation
Beta-
Hydroxylation
Oxidative
Deamination
Oxidation
Glycine
Conjugation
The primary active metabolites of amphetamine are
4-hydroxyamphetamine and norephedrine;
[153] at normal urine pH, about
30–40% of amphetamine is excreted unchanged and roughly 50% is excreted as the inactive metabolites (bottom row).
[3] The remaining
10–20% is excreted as the active metabolites.
[3] Benzoic acid is metabolized by butyrate-CoA ligase into an intermediate product,
benzoyl-CoA,
[9] which is then metabolized by glycine N-acyltransferase into hippuric acid.
[10]
Related endogenous compounds
Amphetamine has a very similar structure and function to the
endogenous trace amines, which are naturally occurring
neurotransmitter molecules produced in the human body and brain.
[30][38] Among this group, the most closely related compounds are
phenethylamine, the parent compound of amphetamine, and
N-methylphenethylamine, an
isomer of amphetamine (i.e., it has an identical molecular formula).
[30][38][157] In humans, phenethylamine is produced directly from
L-phenylalanine by the
aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) enzyme, which converts
L-DOPA into dopamine as well.
[38][157] In turn,
N‑methylphenethylamine is metabolized from phenethylamine by
phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, the same enzyme that metabolizes norepinephrine into epinephrine.
[38][157] Like amphetamine, both phenethylamine and
N‑methylphenethylamine regulate monoamine neurotransmission via
TAAR1;
[30][157] unlike amphetamine, both of these substances are broken down by
monoamine oxidase B, and therefore have a shorter half-life than amphetamine.
[38][157]
Physical and chemical properties
A vial of the colorless amphetamine free base
Amphetamine is a
methyl homolog of the mammalian neurotransmitter phenethylamine with the chemical formula
C9H13N. The carbon atom adjacent to the
primary amine is a
stereogenic center, and amphetamine is composed of a
racemic 1:1 mixture of two
enantiomeric mirror images.
[15] This racemic mixture can be separated into its optical isomers:
[note 14] levoamphetamine and
dextroamphetamine.
[15] Physically, at room temperature, the pure free base of amphetamine is a mobile, colorless, and
volatile liquid with a characteristically strong
amine odor, and acrid, burning taste.
[13] Frequently prepared solid salts of amphetamine include amphetamine aspartate,
[22] hydrochloride,
[158] phosphate,
[159] saccharate,
[22] and sulfate,
[22] the last of which is the most common amphetamine salt.
[37] Amphetamine is also the parent compound of
its own structural class, which includes a number of psychoactive
derivatives.
[15] In organic chemistry, amphetamine is an excellent
chiral ligand for the
stereoselective synthesis of
1,1'-bi-2-naphthol.
[160]
Derivatives
Amphetamine derivatives, often referred to as "amphetamines" or "substituted amphetamines", are a broad range of chemicals that contain amphetamine as a "backbone".
[162] The class includes stimulants like methamphetamine, serotonergic
empathogens like
MDMA (ecstasy), and
decongestants like
ephedrine, among other subgroups.
[162] This class of chemicals is sometimes referred to collectively as the "amphetamine family."
[163]
Synthesis
Since the first preparation was reported in 1887,
[164] numerous synthetic routes to amphetamine have been developed.
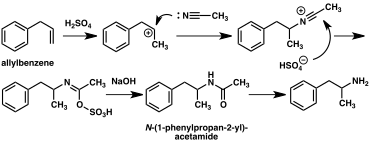
[165][166] Many of these syntheses are based on classic organic reactions. One such example is the
Friedel–Crafts alkylation of
chlorobenzene by
allyl chloride to yield beta chloropropylbenzene which is then reacted with ammonia to produce racemic amphetamine (method 1).
[167] Another example employs the
Ritter reaction (method 2). In this route,
allylbenzene is reacted
acetonitrile in sulfuric acid to yield an
organosulfate which in turn is treated with sodium hydroxide to give amphetamine via an
acetamide intermediate.
[168][169] A third route starts with
ethyl 3-oxobutanoate which through a double alkylation with
methyl iodide followed by
benzyl chloride can be converted into
2-methyl-3-phenyl-propanoic acid. This synthetic intermediate can be transformed into amphetamine using either a
Hofmann or
Curtius rearrangement (method 3).
[170]
A significant number of amphetamine syntheses feature a
reduction of a
nitro,
imine,
oxime or other nitrogen-containing
functional group.
[165] In one such example, a
Knoevenagel condensation of
benzaldehyde with
nitroethane yields
phenyl-2-nitropropene. The double bond and nitro group of this intermediate is
reduced using either catalytic
hydrogenation or by treatment with
lithium aluminium hydride (method 4).
[171][172] Another method is the reaction of
phenylacetone with
ammonia, producing an imine intermediate that is reduced to the primary amine using hydrogen over a palladium catalyst or lithium aluminum hydride (method 5).
[172]
The most common route of both legal and illicit amphetamine synthesis employs a non-metal reduction known as the
Leuckart reaction (method 6).
[37][172] In the first step, a reaction between phenylacetone and
formamide, either using additional
formic acid or formamide itself as a reducing agent, yields
N-formylamphetamine. This intermediate is then hydrolyzed using hydrochloric acid, and subsequently basified, extracted with organic solvent, concentrated, and distilled to yield the free base. The free base is then dissolved in an organic solvent, sulfuric acid added, and amphetamine precipitates out as the sulfate salt.
[172][173]
A number of
chiral resolutions have been developed to separate the two enantiomers of amphetamine.
[166] For example, racemic amphetamine can be treated with
d-tartaric acid to form a
diastereoisomeric salt which is
fractionally crystallized to yield dextroamphetamine.
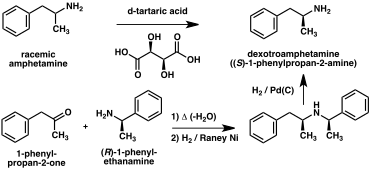
[174] Chiral resolution remains the most economical method for obtaining optically pure amphetamine on a large scale.
[175] In addition, several
enantioselective syntheses of amphetamine have been developed. In one example,
optically pure (R)-1-phenyl-ethanamine is condensed with phenylacetone to yield a chiral
Schiff base. In the key step, this intermediate is reduced by
catalytic hydrogenation with a transfer of chirality to the carbon atom alpha to the amino group. Cleavage of the
benzylic amine bond by hydrogenation yields optically pure dextroamphetamine.
[175]
Amphetamine synthetic routes
Method 1: Synthesis by Friedel–Crafts alkylation
Method 2: Ritter synthesis
Method 3: Synthesis via Hofmann and Curtius rearrangements
Method 4: Synthesis by Knoevenagel condensation
|
|
Method 5: Synthesis using phenylacetone and ammonia
Method 6: Synthesis by the Leuckart reaction
Top: Chiral resolution of amphetamine
Bottom: Stereoselective synthesis of amphetamine
|
|
Detection in body fluids
Amphetamine is frequently measured in urine or blood as part of a
drug test for sports, employment, poisoning diagnostics, and forensics.
[sources 11] Techniques such as
immunoassay, which is the most common form of amphetamine test, may cross-react with a number of sympathomimetic drugs.
[179] Chromatographic methods specific for amphetamine are employed to prevent false positive results.
[180] Chiral separation techniques may be employed to help distinguish the source of the drug, whether prescription amphetamine, prescription amphetamine prodrugs, (e.g.,
selegiline),
over-the-counter drug products (e.g.,
Vicks VapoInhaler, which contains
levomethamphetamine) or illicitly obtained substituted amphetamines.
[180][181][182] Several prescription drugs produce amphetamine as a
metabolite, including
benzphetamine,
clobenzorex,
famprofazone,
fenproporex,
lisdexamfetamine,
mesocarb, methamphetamine,
prenylamine, and
selegiline, among others.
[27][183][184] These compounds may produce positive results for amphetamine on drug tests.
[183][184] Amphetamine is generally only detectable by a standard drug test for approximately 24 hours, although a high dose may be detectable for two to four days.
[179]
For the assays, a study noted that an
enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique (EMIT) assay for amphetamine and methamphetamine may produce more false positives than
liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry.
[181] Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) of amphetamine and methamphetamine with the derivatizing agent
(S)-(−)-trifluoroacetylprolyl chloride allows for the detection of methamphetamine in urine.
[180] GC–MS of amphetamine and methamphetamine with the chiral derivatizing agent
Mosher's acid chloride allows for the detection of both dextroamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine in urine.
[180] Hence, the latter method may be used on samples that test positive using other methods to help distinguish between the various sources of the drug.
[180]
History, society, and culture
Amphetamine was first synthesized in 1887 in Germany by Romanian chemist
Lazăr Edeleanu who named it
phenylisopropylamine;
[164][186][187] its stimulant effects remained unknown until 1927, when it was independently resynthesized by Gordon Alles and reported to have
sympathomimetic properties.
[187] Amphetamine had no pharmacological use until 1934, when
Smith, Kline and French began selling it as an
inhaler under the trade name
Benzedrine as a decongestant.
[28] During World War II, amphetamine and methamphetamine were used extensively by both the Allied and Axis forces for their stimulant and performance-enhancing effects.
[164][188][189] As the addictive properties of the drug became known, governments began to place strict controls on the sale of amphetamine.
[164] For example, during the early 1970s in the United States, amphetamine became a
schedule II controlled substance under the
Controlled Substances Act.
[190] In spite of strict government controls, amphetamine has been used legally or illicitly by people from a variety of backgrounds, including authors,
[191] musicians,
[192] mathematicians,
[193] and athletes.
[23]
Amphetamine is still illegally synthesized today in
clandestine labs and sold on the
black market, primarily in European countries.
[185] Among European Union (EU) member states, 1.2 million young adults used illicit amphetamine or methamphetamine in 2013.
[194] During 2012, approximately 5.9
metric tons of illicit amphetamine were seized within EU member states;
[194] the "street price" of illicit amphetamine within the EU ranged from €6–38 per gram during the same period.
[194] Outside Europe, the illicit market for amphetamine is much smaller than the market for methamphetamine and MDMA.
[185]
Legal status
As a result of the
United Nations 1971
Convention on Psychotropic Substances, amphetamine became a schedule II controlled substance, as defined in the treaty, in all (183) state parties.
[21] Consequently, it is heavily regulated in most countries.
[195][196] Some countries, such as South Korea and Japan, have banned substituted amphetamines even for medical use.
[197][198] In other nations, such as Canada (
schedule I drug),
[199] the United States (
schedule II drug),
[22] Thailand (
category 1 narcotic),
[200] and United Kingdom (
class B drug),
[201] amphetamine is in a restrictive national drug schedule that allows for its use as a medical treatment.
[26][185]
Pharmaceutical products
The only currently prescribed amphetamine formulation that contains both enantiomers is Adderall.
[note 3][15][27] Amphetamine is also prescribed in
enantiopure and
prodrug form as dextroamphetamine and lisdexamfetamine respectively.
[29][202] Lisdexamfetamine is structurally different from amphetamine, and is inactive until it metabolizes into dextroamphetamine.
[202] The free base of racemic amphetamine was previously available as Benzedrine, Psychedrine, and Sympatedrine.
[15][27] Levoamphetamine was previously available as Cydril.
[27] All current amphetamine pharmaceuticals are
salts due to the comparatively high volatility of the free base.
[27][29][37] Some of the current brands and their generic equivalents are listed below.
Amphetamine pharmaceuticals
(D:L) ratio
of salts |
Source |
| Adderall |
– |
3:1 |
tablet |
[27][29] |
| Adderall XR |
– |
3:1 |
capsule |
[27][29] |
| Dexedrine |
dextroamphetamine sulfate |
1:0 |
capsule |
[27][29] |
| ProCentra |
dextroamphetamine sulfate |
1:0 |
liquid |
[29] |
| Vyvanse |
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate |
1:0 |
capsule |
[27][202] |
| Zenzedi |
dextroamphetamine sulfate |
1:0 |
tablet |
[29] |
|

The skeletal structure of lisdexamfetamine
|
|