From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology.[1] Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials (materials whose structure is on the scale of nanometers, i.e. billionths of a meter).
Functionalities can be added to nanomaterials by interfacing them with biological molecules or structures. The size of nanomaterials is similar to that of most biological molecules and structures; therefore, nanomaterials can be useful for both in vivo and in vitro biomedical research and applications. Thus far, the integration of nanomaterials with biology has led to the development of diagnostic devices, contrast agents, analytical tools, physical therapy applications, and drug delivery vehicles.
Nanomedicine seeks to deliver a valuable set of research tools and clinically useful devices in the near future.[2][3] The National Nanotechnology Initiative expects new commercial applications in the pharmaceutical industry that may include advanced drug delivery systems, new therapies, and in vivo imaging.[4] Nanomedicine research is receiving funding from the US National Institutes of Health, including the funding in 2005 of a five-year plan to set up four nanomedicine centers.
Nanomedicine is a large industry, with nanomedicine sales reaching $6.8 billion in 2004, and with over 200 companies and 38 products worldwide, a minimum of $3.8 billion in nanotechnology R&D is being invested every year.[5] In April 2006, the journal Nature Materials estimated that 130 nanotech-based drugs and delivery systems were being developed worldwide.[6] As the nanomedicine industry continues to grow, it is expected to have a significant impact on the economy.
Nanotechnology has provided the possibility of delivering drugs to specific cells using nanoparticles.
The overall drug consumption and side-effects may be lowered significantly by depositing the active agent in the morbid region only and in no higher dose than needed. Targeted drug delivery is intended to reduce the side effects of drugs with concomitant decreases in consumption and treatment expenses. Drug delivery focuses on maximizing bioavailability both at specific places in the body and over a period of time. This can potentially be achieved by molecular targeting by nanoengineered devices.[7][8] More than $65 billion are wasted each year due to poor bioavailability.[citation needed] A benefit of using nanoscale for medical technologies is that smaller devices are less invasive and can possibly be implanted inside the body, plus biochemical reaction times are much shorter. These devices are faster and more sensitive than typical drug delivery.[9] The efficacy of drug delivery through nanomedicine is largely based upon: a) efficient encapsulation of the drugs, b) successful delivery of drug to the targeted region of the body, and c) successful release of the drug.[citation needed]
Drug delivery systems, lipid- [10] or polymer-based nanoparticles,[11] can be designed to improve the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of the drug.[12][13][14] However, the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nanomedicine is highly variable among different patients.[15] When designed to avoid the body's defence mechanisms,[16] nanoparticles have beneficial properties that can be used to improve drug delivery. Complex drug delivery mechanisms are being developed, including the ability to get drugs through cell membranes and into cell cytoplasm. Triggered response is one way for drug molecules to be used more efficiently. Drugs are placed in the body and only activate on encountering a particular signal. For example, a drug with poor solubility will be replaced by a drug delivery system where both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments exist, improving the solubility.[17] Drug delivery systems may also be able to prevent tissue damage through regulated drug release; reduce drug clearance rates; or lower the volume of distribution and reduce the effect on non-target tissue. However, the biodistribution of these nanoparticles is still imperfect due to the complex host's reactions to nano- and microsized materials[16] and the difficulty in targeting specific organs in the body. Nevertheless, a lot of work is still ongoing to optimize and better understand the potential and limitations of nanoparticulate systems. While advancement of research proves that targeting and distribution can be augmented by nanoparticles, the dangers of nanotoxicity become an important next step in further understanding of their medical uses.[18]
Nanoparticles can be used in combination therapy for decreasing antibiotic resistance or for their antimicrobial properties.[19][20][21] Nanoparticles might also used to circumvent multidrug resistance (MDR) mechanisms.[22]
Polymeric nano-particles are a competing technology to lipidic (based mainly on Phospholipids) nano-particles. There is an additional risk of toxicity associated with polymers not widely studied or understood. The major advantages of polymers is stability, lower cost and predictable characterisation. However, in the patient's body this very stability (slow degradation) is a negative factor. Phospholipids on the other hand are membrane lipids (already present in the body and surrounding each cell), have a GRAS (Generally Recognised As Safe) status from FDA and are derived from natural sources without any complex chemistry involved. They are not metabolised but rather absorbed by the body and the degradation products are themselves nutrients (fats or micronutrients).
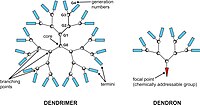
Protein and peptides exert multiple biological actions in the human body and they have been identified as showing great promise for treatment of various diseases and disorders. These macromolecules are called biopharmaceuticals. Targeted and/or controlled delivery of these biopharmaceuticals using nanomaterials like nanoparticles and Dendrimers is an emerging field called nanobiopharmaceutics, and these products are called nanobiopharmaceuticals.
Another vision is based on small electromechanical systems; nanoelectromechanical systems are being investigated for the active release of drugs. Some potentially important applications include cancer treatment with iron nanoparticles or gold shells.Nanotechnology is also opening up new opportunities in implantable delivery systems, which are often preferable to the use of injectable drugs, because the latter frequently display first-order kinetics (the blood concentration goes up rapidly, but drops exponentially over time). This rapid rise may cause difficulties with toxicity, and drug efficacy can diminish as the drug concentration falls below the targeted range.[citation needed]
Another nanoproperty, high surface area to volume ratio, allows many functional groups to be attached to a nanoparticle, which can seek out and bind to certain tumor cells. Additionally, the small size of nanoparticles (10 to 100 nanometers), allows them to preferentially accumulate at tumor sites (because tumors lack an effective lymphatic drainage system).[35] Limitations to conventional cancer chemotherapy include drug resistance, lack of selectivity, and lack of solubility. Nanoparticles have the potential to overcome these problems.[36]
In photodynamic therapy, a particle is placed within the body and is illuminated with light from the outside. The light gets absorbed by the particle and if the particle is metal, energy from the light will heat the particle and surrounding tissue. Light may also be used to produce high energy oxygen molecules which will chemically react with and destroy most organic molecules that are next to them (like tumors). This therapy is appealing for many reasons. It does not leave a "toxic trail" of reactive molecules throughout the body (chemotherapy) because it is directed where only the light is shined and the particles exist. Photodynamic therapy has potential for a noninvasive procedure for dealing with diseases, growth and tumors. Kanzius RF therapy is one example of such therapy.[citation needed] Also, gold nanoparticles have the potential to join numerous therapeutic functions into a single platform, by targeting specific tumor cells, tissues and organs.[37][38]
The small size of nanoparticles endows them with properties that can be very useful in oncology, particularly in imaging. Quantum dots (nanoparticles with quantum confinement properties, such as size-tunable light emission), when used in conjunction with MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), can produce exceptional images of tumor sites. Nanoparticles of cadmium selenide (quantum dots) glow when exposed to ultraviolet light. When injected, they seep into cancer tumors. The surgeon can see the glowing tumor, and use it as a guide for more accurate tumor removal.These nanoparticles are much brighter than organic dyes and only need one light source for excitation. This means that the use of fluorescent quantum dots could produce a higher contrast image and at a lower cost than today's organic dyes used as contrast media. The downside, however, is that quantum dots are usually made of quite toxic elements.[citation needed]
Tracking movement can help determine how well drugs are being distributed or how substances are metabolized. It is difficult to track a small group of cells throughout the body, so scientists used to dye the cells. These dyes needed to be excited by light of a certain wavelength in order for them to light up. While different color dyes absorb different frequencies of light, there was a need for as many light sources as cells. A way around this problem is with luminescent tags. These tags are quantum dots attached to proteins that penetrate cell membranes. The dots can be random in size, can be made of bio-inert material, and they demonstrate the nanoscale property that color is size-dependent. As a result, sizes are selected so that the frequency of light used to make a group of quantum dots fluoresce is an even multiple of the frequency required to make another group incandesce. Then both groups can be lit with a single light source. They have also found a way to insert nanoparticles[39] into the affected parts of the body so that those parts of the body will glow showing the tumor growth or shrinkage or also organ trouble.[40]
Sensor test chips containing thousands of nanowires, able to detect proteins and other biomarkers left behind by cancer cells, could enable the detection and diagnosis of cancer in the early stages from a few drops of a patient's blood.[41]Nanotechnology is helping to advance the use of arthroscopes, which are pencil-sized devices that are used in surgeries with lights and cameras so surgeons can do the surgeries with smaller incisions. The smaller the incisions the faster the healing time which is better for the patients. It is also helping to find a way to make an arthroscope smaller than a strand of hair.[42]
For example, a flesh welder was demonstrated to fuse two pieces of chicken meat into a single piece using a suspension of gold-coated nanoshells activated by an infrared laser. This could be used to weld arteries during surgery.[45] Another example is nanonephrology, the use of nanomedicine on the kidney.
A refuelable strategy implies energy is refilled continuously or periodically with external sonic, chemical, tethered, magnetic, or biological electrical sources, while a nonrefuelable strategy implies that all power is drawn from internal energy storage which would stop when all energy is drained. A nanoscale enzymatic biofuel cell for self-powered nanodevices have been developed that uses glucose from biofluids including human blood and watermelons.[46] One limitation to this innovation is the fact that electrical interference or leakage or overheating from power consumption is possible. The wiring of the structure is extremely difficult because they must be positioned precisely in the nervous system. The structures that will provide the interface must also be compatible with the body's immune system.[47]
Molecular nanotechnology is a speculative subfield of nanotechnology regarding the possibility of engineering molecular assemblers, machines which could re-order matter at a molecular or atomic scale. Nanomedicine would make use of these nanorobots, introduced into the body, to repair or detect damages and infections. Molecular nanotechnology is highly theoretical, seeking to anticipate what inventions nanotechnology might yield and to propose an agenda for future inquiry. The proposed elements of molecular nanotechnology, such as molecular assemblers and nanorobots are far beyond current capabilities.[1][47][48][49]
Functionalities can be added to nanomaterials by interfacing them with biological molecules or structures. The size of nanomaterials is similar to that of most biological molecules and structures; therefore, nanomaterials can be useful for both in vivo and in vitro biomedical research and applications. Thus far, the integration of nanomaterials with biology has led to the development of diagnostic devices, contrast agents, analytical tools, physical therapy applications, and drug delivery vehicles.
Nanomedicine seeks to deliver a valuable set of research tools and clinically useful devices in the near future.[2][3] The National Nanotechnology Initiative expects new commercial applications in the pharmaceutical industry that may include advanced drug delivery systems, new therapies, and in vivo imaging.[4] Nanomedicine research is receiving funding from the US National Institutes of Health, including the funding in 2005 of a five-year plan to set up four nanomedicine centers.
Nanomedicine is a large industry, with nanomedicine sales reaching $6.8 billion in 2004, and with over 200 companies and 38 products worldwide, a minimum of $3.8 billion in nanotechnology R&D is being invested every year.[5] In April 2006, the journal Nature Materials estimated that 130 nanotech-based drugs and delivery systems were being developed worldwide.[6] As the nanomedicine industry continues to grow, it is expected to have a significant impact on the economy.
Drug delivery
Nanoparticles (top), liposomes (middle), and dendrimers (bottom) are some nanomaterials being investigated for use in nanomedicine.
Nanotechnology has provided the possibility of delivering drugs to specific cells using nanoparticles.
The overall drug consumption and side-effects may be lowered significantly by depositing the active agent in the morbid region only and in no higher dose than needed. Targeted drug delivery is intended to reduce the side effects of drugs with concomitant decreases in consumption and treatment expenses. Drug delivery focuses on maximizing bioavailability both at specific places in the body and over a period of time. This can potentially be achieved by molecular targeting by nanoengineered devices.[7][8] More than $65 billion are wasted each year due to poor bioavailability.[citation needed] A benefit of using nanoscale for medical technologies is that smaller devices are less invasive and can possibly be implanted inside the body, plus biochemical reaction times are much shorter. These devices are faster and more sensitive than typical drug delivery.[9] The efficacy of drug delivery through nanomedicine is largely based upon: a) efficient encapsulation of the drugs, b) successful delivery of drug to the targeted region of the body, and c) successful release of the drug.[citation needed]
Drug delivery systems, lipid- [10] or polymer-based nanoparticles,[11] can be designed to improve the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of the drug.[12][13][14] However, the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nanomedicine is highly variable among different patients.[15] When designed to avoid the body's defence mechanisms,[16] nanoparticles have beneficial properties that can be used to improve drug delivery. Complex drug delivery mechanisms are being developed, including the ability to get drugs through cell membranes and into cell cytoplasm. Triggered response is one way for drug molecules to be used more efficiently. Drugs are placed in the body and only activate on encountering a particular signal. For example, a drug with poor solubility will be replaced by a drug delivery system where both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments exist, improving the solubility.[17] Drug delivery systems may also be able to prevent tissue damage through regulated drug release; reduce drug clearance rates; or lower the volume of distribution and reduce the effect on non-target tissue. However, the biodistribution of these nanoparticles is still imperfect due to the complex host's reactions to nano- and microsized materials[16] and the difficulty in targeting specific organs in the body. Nevertheless, a lot of work is still ongoing to optimize and better understand the potential and limitations of nanoparticulate systems. While advancement of research proves that targeting and distribution can be augmented by nanoparticles, the dangers of nanotoxicity become an important next step in further understanding of their medical uses.[18]
Nanoparticles can be used in combination therapy for decreasing antibiotic resistance or for their antimicrobial properties.[19][20][21] Nanoparticles might also used to circumvent multidrug resistance (MDR) mechanisms.[22]
Types of systems used
Two forms of nanomedicine that have already been tested in mice and are awaiting human trials that will be using gold nanoshells to help diagnose and treat cancer,[23] and using liposomes as vaccine adjuvants and as vehicles for drug transport.[24][25] Similarly, drug detoxification is also another application for nanomedicine which has shown promising results in rats.[26] Advances in Lipid nanotechnology was also instrumental in engineering medical nanodevices and novel drug delivery systems as well as in developing sensing applications.[27] Another example can be found in dendrimers and nanoporous materials. Another example is to use block co-polymers, which form micelles for drug encapsulation.[11]Polymeric nano-particles are a competing technology to lipidic (based mainly on Phospholipids) nano-particles. There is an additional risk of toxicity associated with polymers not widely studied or understood. The major advantages of polymers is stability, lower cost and predictable characterisation. However, in the patient's body this very stability (slow degradation) is a negative factor. Phospholipids on the other hand are membrane lipids (already present in the body and surrounding each cell), have a GRAS (Generally Recognised As Safe) status from FDA and are derived from natural sources without any complex chemistry involved. They are not metabolised but rather absorbed by the body and the degradation products are themselves nutrients (fats or micronutrients).
Protein and peptides exert multiple biological actions in the human body and they have been identified as showing great promise for treatment of various diseases and disorders. These macromolecules are called biopharmaceuticals. Targeted and/or controlled delivery of these biopharmaceuticals using nanomaterials like nanoparticles and Dendrimers is an emerging field called nanobiopharmaceutics, and these products are called nanobiopharmaceuticals.
Another vision is based on small electromechanical systems; nanoelectromechanical systems are being investigated for the active release of drugs. Some potentially important applications include cancer treatment with iron nanoparticles or gold shells.Nanotechnology is also opening up new opportunities in implantable delivery systems, which are often preferable to the use of injectable drugs, because the latter frequently display first-order kinetics (the blood concentration goes up rapidly, but drops exponentially over time). This rapid rise may cause difficulties with toxicity, and drug efficacy can diminish as the drug concentration falls below the targeted range.[citation needed]
Applications
Some nanotechnology-based drugs that are commercially available or in human clinical trials include:- Abraxane, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat breast cancer,[28] non-small- cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[29] and pancreatic cancer,[30] is the nanoparticle albumin bound paclitaxel.
- Doxil was originally approved by the FDA for the use on HIV-related Kaposi's sarcoma. It is now being used to also treat ovarian cancer and multiple myeloma. The drug is encased in liposomes, which helps to extend the life of the drug that is being distributed. Liposomes are self-assembling, spherical, closed colloidal structures that are composed of lipid bilayers that surround an aqueous space. The liposomes also help to increase the functionality and it helps to decrease the damage that the drug does to the heart muscles specifically.[31]
- C-dots (Cornell dots) are the smallest silica-based nanoparticles with the size <10 nm. The particles are infused with organic dye which will light up with fluorescence. Clinical trial is underway since 2011 to use the C-dots as diagnostic tool to assist surgeons to identify the location of tumor cells.[32]
- An early phase clinical trial using the platform of ‘Minicell’ nanoparticle for drug delivery have been tested on patients with advanced and untreatable cancer. Built from the membranes of mutant bacteria, the minicells were loaded with paclitaxel and coated with cetuximab, antibodies that bind the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) which is often overexpressed in a number of cancers, as a 'homing' device to the tumor cells. The tumor cells recognize the bacteria from which the minicells have been derived, regard it as invading microorganism and engulf it. Once inside, the payload of anti-cancer drug kills the tumor cells. Measured at 400 nanometers, the minicell is bigger than synthetic particles developed for drug delivery. The researchers indicated that this larger size gives the minicells a better profile in side-effects because the minicells will preferentially leak out of the porous blood vessels around the tumor cells and do not reach the liver, digestive system and skin. This Phase 1 clinical trial demonstrated that this treatment is well tolerated by the patients. As a platform technology, the minicell drug delivery system can be used to treat a number of different cancers with different anti-cancer drugs with the benefit of lower dose and less side-effects.[33][34]
Cancer
Another nanoproperty, high surface area to volume ratio, allows many functional groups to be attached to a nanoparticle, which can seek out and bind to certain tumor cells. Additionally, the small size of nanoparticles (10 to 100 nanometers), allows them to preferentially accumulate at tumor sites (because tumors lack an effective lymphatic drainage system).[35] Limitations to conventional cancer chemotherapy include drug resistance, lack of selectivity, and lack of solubility. Nanoparticles have the potential to overcome these problems.[36]
In photodynamic therapy, a particle is placed within the body and is illuminated with light from the outside. The light gets absorbed by the particle and if the particle is metal, energy from the light will heat the particle and surrounding tissue. Light may also be used to produce high energy oxygen molecules which will chemically react with and destroy most organic molecules that are next to them (like tumors). This therapy is appealing for many reasons. It does not leave a "toxic trail" of reactive molecules throughout the body (chemotherapy) because it is directed where only the light is shined and the particles exist. Photodynamic therapy has potential for a noninvasive procedure for dealing with diseases, growth and tumors. Kanzius RF therapy is one example of such therapy.[citation needed] Also, gold nanoparticles have the potential to join numerous therapeutic functions into a single platform, by targeting specific tumor cells, tissues and organs.[37][38]
Visualization
In vivo imaging is another area where tools and devices are being developed. Using nanoparticle contrast agents, images such as ultrasound and MRI have a favorable distribution and improved contrast. This might be accomplished by self assembled biocompatible nanodevices that will detect, evaluate, treat and report to the clinical doctor automatically.The small size of nanoparticles endows them with properties that can be very useful in oncology, particularly in imaging. Quantum dots (nanoparticles with quantum confinement properties, such as size-tunable light emission), when used in conjunction with MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), can produce exceptional images of tumor sites. Nanoparticles of cadmium selenide (quantum dots) glow when exposed to ultraviolet light. When injected, they seep into cancer tumors. The surgeon can see the glowing tumor, and use it as a guide for more accurate tumor removal.These nanoparticles are much brighter than organic dyes and only need one light source for excitation. This means that the use of fluorescent quantum dots could produce a higher contrast image and at a lower cost than today's organic dyes used as contrast media. The downside, however, is that quantum dots are usually made of quite toxic elements.[citation needed]
Tracking movement can help determine how well drugs are being distributed or how substances are metabolized. It is difficult to track a small group of cells throughout the body, so scientists used to dye the cells. These dyes needed to be excited by light of a certain wavelength in order for them to light up. While different color dyes absorb different frequencies of light, there was a need for as many light sources as cells. A way around this problem is with luminescent tags. These tags are quantum dots attached to proteins that penetrate cell membranes. The dots can be random in size, can be made of bio-inert material, and they demonstrate the nanoscale property that color is size-dependent. As a result, sizes are selected so that the frequency of light used to make a group of quantum dots fluoresce is an even multiple of the frequency required to make another group incandesce. Then both groups can be lit with a single light source. They have also found a way to insert nanoparticles[39] into the affected parts of the body so that those parts of the body will glow showing the tumor growth or shrinkage or also organ trouble.[40]
Sensing
Nanotechnology-on-a-chip is one more dimension of lab-on-a-chip technology. Magnetic nanoparticles, bound to a suitable antibody, are used to label specific molecules, structures or microorganisms. Gold nanoparticles tagged with short segments of DNA can be used for detection of genetic sequence in a sample. Multicolor optical coding for biological assays has been achieved by embedding different-sized quantum dots into polymeric microbeads. Nanopore technology for analysis of nucleic acids converts strings of nucleotides directly into electronic signatures.[citation needed]Sensor test chips containing thousands of nanowires, able to detect proteins and other biomarkers left behind by cancer cells, could enable the detection and diagnosis of cancer in the early stages from a few drops of a patient's blood.[41]Nanotechnology is helping to advance the use of arthroscopes, which are pencil-sized devices that are used in surgeries with lights and cameras so surgeons can do the surgeries with smaller incisions. The smaller the incisions the faster the healing time which is better for the patients. It is also helping to find a way to make an arthroscope smaller than a strand of hair.[42]
Tissue engineering
Nanotechnology may be used as part of tissue engineering to help reproduce or repair damaged tissue using suitable nanomaterial-based scaffolds and growth factors. Tissue engineering if successful may replace conventional treatments like organ transplants or artificial implants. Nanoparticles such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, molybdenum disulfide and tungsten disulfide are being used as reinforcing agents to fabricate mechanically strong biodegradable polymeric nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering applications. The addition of these nanoparticles in the polymer matrix at low concentrations (~0.2 weight %) leads to significant improvements in the compressive and flexural mechanical properties of polymeric nanocomposites.[43][44] Potentially, these nanocomposites may be used as a novel, mechanically strong, light weight composite as bone implants.For example, a flesh welder was demonstrated to fuse two pieces of chicken meat into a single piece using a suspension of gold-coated nanoshells activated by an infrared laser. This could be used to weld arteries during surgery.[45] Another example is nanonephrology, the use of nanomedicine on the kidney.
Medical devices
Neuro-electronic interfacing is a visionary goal dealing with the construction of nanodevices that will permit computers to be joined and linked to the nervous system. This idea requires the building of a molecular structure that will permit control and detection of nerve impulses by an external computer.A refuelable strategy implies energy is refilled continuously or periodically with external sonic, chemical, tethered, magnetic, or biological electrical sources, while a nonrefuelable strategy implies that all power is drawn from internal energy storage which would stop when all energy is drained. A nanoscale enzymatic biofuel cell for self-powered nanodevices have been developed that uses glucose from biofluids including human blood and watermelons.[46] One limitation to this innovation is the fact that electrical interference or leakage or overheating from power consumption is possible. The wiring of the structure is extremely difficult because they must be positioned precisely in the nervous system. The structures that will provide the interface must also be compatible with the body's immune system.[47]
Molecular nanotechnology is a speculative subfield of nanotechnology regarding the possibility of engineering molecular assemblers, machines which could re-order matter at a molecular or atomic scale. Nanomedicine would make use of these nanorobots, introduced into the body, to repair or detect damages and infections. Molecular nanotechnology is highly theoretical, seeking to anticipate what inventions nanotechnology might yield and to propose an agenda for future inquiry. The proposed elements of molecular nanotechnology, such as molecular assemblers and nanorobots are far beyond current capabilities.[1][47][48][49]