From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation".[1][2] A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light coherently. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum, i.e., they can emit a single color of light. Temporal coherence can be used to produce pulses of light as short as a femtosecond.
Amongst their many applications, lasers are used in optical disk drives, laser printers, and barcode scanners; fiber-optic and free-space optical communication; laser surgery and skin treatments; cutting and welding materials; military and law enforcement devices for marking targets and measuring range and speed; and laser lighting displays in entertainment.
Fundamentals
Lasers are distinguished from other light sources by their coherence. Spatial coherence is typically expressed through the output being a narrow beam, which is diffraction-limited. Laser beams can be focused to very tiny spots, achieving a very high irradiance, or they can have very low divergence in order to concentrate their power at a great distance.Temporal (or longitudinal) coherence implies a polarized wave at a single frequency whose phase is correlated over a relatively great distance (the coherence length) along the beam.[3] A beam produced by a thermal or other incoherent light source has an instantaneous amplitude and phase that vary randomly with respect to time and position, thus having a short coherence length.
Lasers are characterized according to their wavelength in a vacuum. Most "single wavelength" lasers actually produce radiation in several modes having slightly differing frequencies (wavelengths), often not in a single polarization. Although temporal coherence implies monochromaticity, there are lasers that emit a broad spectrum of light or emit different wavelengths of light simultaneously. There are some lasers that are not single spatial mode and consequently have light beams that diverge more than is required by the diffraction limit. However, all such devices are classified as "lasers" based on their method of producing light, i.e., stimulated emission. Lasers are employed in applications where light of the required spatial or temporal coherence could not be produced using simpler technologies.
Terminology
The word laser started as an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". In modern usage, the term "light" includes electromagnetic radiation of any frequency, not only visible light, hence the terms infrared laser, ultraviolet laser, X-ray laser, and so on. Because the microwave predecessor of the laser, the maser, was developed first, devices of this sort operating at microwave and radio frequencies are referred to as "masers" rather than "microwave lasers" or "radio lasers". In the early technical literature, especially at Bell Telephone Laboratories, the laser was called an optical maser; this term is now obsolete.[4]
A laser that produces light by itself is technically an optical oscillator rather than an optical amplifier as suggested by the acronym. It has been humorously noted that the acronym LOSER, for "light oscillation by stimulated emission of radiation", would have been more correct.[5] With the widespread use of the original acronym as a common noun, optical amplifiers have come to be referred to as "laser amplifiers", notwithstanding the apparent redundancy in that designation.
The back-formed verb to lase is frequently used in the field, meaning "to produce laser light,"[6] especially in reference to the gain medium of a laser; when a laser is operating it is said to be "lasing." Further use of the words laser and maser in an extended sense, not referring to laser technology or devices, can be seen in usages such as astrophysical maser and atom laser.
Design
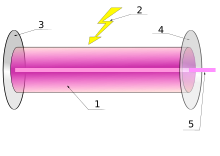
Components of a typical laser:
1. Gain medium
2. Laser pumping energy
3. High reflector
4. Output coupler
5. Laser beam
1. Gain medium
2. Laser pumping energy
3. High reflector
4. Output coupler
5. Laser beam
For the gain medium to amplify light, it needs to be supplied with energy in a process called pumping. The energy is typically supplied as an electrical current or as light at a different wavelength. Pump light may be provided by a flash lamp or by another laser.
The most common type of laser uses feedback from an optical cavity—a pair of mirrors on either end of the gain medium. Light bounces back and forth between the mirrors, passing through the gain medium and being amplified each time. Typically one of the two mirrors, the output coupler, is partially transparent. Some of the light escapes through this mirror. Depending on the design of the cavity (whether the mirrors are flat or curved), the light coming out of the laser may spread out or form a narrow beam. In analogy to electronic oscillators, this device is sometimes called a laser oscillator.
Most practical lasers contain additional elements that affect properties of the emitted light, such as the polarization, wavelength, and shape of the beam.
Laser physics
Electrons and how they interact with electromagnetic fields are important in our understanding of chemistry and physics.Stimulated emission
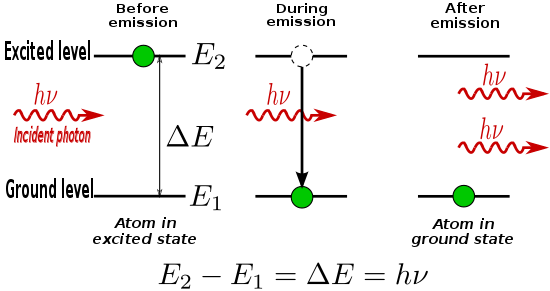
In the classical view, the energy of an electron orbiting an atomic nucleus is larger for orbits further from the nucleus of an atom. However, quantum mechanical effects force electrons to take on discrete positions in orbitals. Thus, electrons are found in specific energy levels of an atom, two of which are shown below:When an electron absorbs energy either from light (photons) or heat (phonons), it receives that incident quantum of energy. But transitions are only allowed in between discrete energy levels such as the two shown above. This leads to emission lines and absorption lines.
When an electron is excited from a lower to a higher energy level, it will not stay that way forever. An electron in an excited state may decay to a lower energy state which is not occupied, according to a particular time constant characterizing that transition. When such an electron decays without external influence, emitting a photon, that is called "spontaneous emission". The phase associated with the photon that is emitted is random. A material with many atoms in such an excited state may thus result in radiation which is very spectrally limited (centered around one wavelength of light), but the individual photons would have no common phase relationship and would emanate in random directions. This is the mechanism of fluorescence and thermal emission.
An external electromagnetic field at a frequency associated with a transition can affect the quantum mechanical state of the atom. As the electron in the atom makes a transition between two stationary states (neither of which shows a dipole field), it enters a transition state which does have a dipole field, and which acts like a small electric dipole, and this dipole oscillates at a characteristic frequency. In response to the external electric field at this frequency, the probability of the atom entering this transition state is greatly increased. Thus, the rate of transitions between two stationary states is enhanced beyond that due to spontaneous emission. Such a transition to the higher state is called absorption, and it destroys an incident photon (the photon's energy goes into powering the increased energy of the higher state). A transition from the higher to a lower energy state, however, produces an additional photon; this is the process of stimulated emission.
Gain medium and cavity

A helium–neon laser demonstration at the Kastler-Brossel Laboratory at Univ. Paris 6. The pink-orange glow running through the center of the tube is from the electric discharge which produces incoherent light, just as in a neon tube. This glowing plasma is excited and then acts as the gain medium through which the internal beam passes, as it is reflected between the two mirrors. Laser radiation output through the front mirror can be seen to produce a tiny (about 1mm in diameter) intense spot on the screen, to the right. Although it is a deep and pure red color, spots of laser light are so intense that cameras are typically overexposed and distort their color.

Spectrum of a helium neon laser illustrating its very high spectral purity (limited by the measuring apparatus). The .002 nm bandwidth of the lasing medium is well over 10,000 times narrower than the spectral width of a light-emitting diode (whose spectrum is shown here for comparison), with the bandwidth of a single longitudinal mode being much narrower still.
The gain medium is excited by an external source of energy into an excited state. In most lasers this medium consists of population of atoms which have been excited into such a state by means of an outside light source, or an electrical field which supplies energy for atoms to absorb and be transformed into their excited states.
The gain medium of a laser is normally a material of controlled purity, size, concentration, and shape, which amplifies the beam by the process of stimulated emission described above. This material can be of any state: gas, liquid, solid, or plasma. The gain medium absorbs pump energy, which raises some electrons into higher-energy ("excited") quantum states. Particles can interact with light by either absorbing or emitting photons. Emission can be spontaneous or stimulated. In the latter case, the photon is emitted in the same direction as the light that is passing by. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in some lower-energy state, population inversion is achieved and the amount of stimulated emission due to light that passes through is larger than the amount of absorption. Hence, the light is amplified. By itself, this makes an optical amplifier. When an optical amplifier is placed inside a resonant optical cavity, one obtains a laser oscillator.[8]
In a few situations it is possible to obtain lasing with only a single pass of EM radiation through the gain medium, and this produces a laser beam without any need for a resonant or reflective cavity (see for example nitrogen laser).[9] Thus, reflection in a resonant cavity is usually required for a laser, but is not absolutely necessary.
The optical resonator is sometimes referred to as an "optical cavity", but this is a misnomer: lasers use open resonators as opposed to the literal cavity that would be employed at microwave frequencies in a maser. The resonator typically consists of two mirrors between which a coherent beam of light travels in both directions, reflecting back on itself so that an average photon will pass through the gain medium repeatedly before it is emitted from the output aperture or lost to diffraction or absorption. If the gain (amplification) in the medium is larger than the resonator losses, then the power of the recirculating light can rise exponentially. But each stimulated emission event returns an atom from its excited state to the ground state, reducing the gain of the medium. With increasing beam power the net gain (gain minus loss) reduces to unity and the gain medium is said to be saturated. In a continuous wave (CW) laser, the balance of pump power against gain saturation and cavity losses produces an equilibrium value of the laser power inside the cavity; this equilibrium determines the operating point of the laser. If the applied pump power is too small, the gain will never be sufficient to overcome the resonator losses, and laser light will not be produced. The minimum pump power needed to begin laser action is called the lasing threshold. The gain medium will amplify any photons passing through it, regardless of direction; but only the photons in a spatial mode supported by the resonator will pass more than once through the medium and receive substantial amplification.
The light emitted
The light generated by stimulated emission is very similar to the input signal in terms of wavelength, phase, and polarization. This gives laser light its characteristic coherence, and allows it to maintain the uniform polarization and often monochromaticity established by the optical cavity design.The beam in the cavity and the output beam of the laser, when travelling in free space (or a homogeneous medium) rather than waveguides (as in an optical fiber laser), can be approximated as a Gaussian beam in most lasers; such beams exhibit the minimum divergence for a given diameter.
However some high power lasers may be multimode, with the transverse modes often approximated using Hermite–Gaussian or Laguerre-Gaussian functions. It has been shown that unstable laser resonators (not used in most lasers) produce fractal shaped beams.[10] Near the beam "waist" (or focal region) it is highly collimated: the wavefronts are planar, normal to the direction of propagation, with no beam divergence at that point. However due to diffraction, that can only remain true well within the Rayleigh range. The beam of a single transverse mode (gaussian beam) laser eventually diverges at an angle which varies inversely with the beam diameter, as required by diffraction theory. Thus, the "pencil beam" directly generated by a common helium–neon laser would spread out to a size of perhaps 500 kilometers when shone on the Moon (from the distance of the earth). On the other hand the light from a semiconductor laser typically exits the tiny crystal with a large divergence: up to 50°. However even such a divergent beam can be transformed into a similarly collimated beam by means of a lens system, as is always included, for instance, in a laser pointer whose light originates from a laser diode. That is possible due to the light being of a single spatial mode. This unique property of laser light, spatial coherence, cannot be replicated using standard light sources (except by discarding most of the light) as can be appreciated by comparing the beam from a flashlight (torch) or spotlight to that of almost any laser.
Quantum vs. classical emission processes
The mechanism of producing radiation in a laser relies on stimulated emission, where energy is extracted from a transition in an atom or molecule. This is a quantum phenomenon discovered by Einstein who derived the relationship between the A coefficient describing spontaneous emission and the B coefficient which applies to absorption and stimulated emission. However in the case of the free electron laser, atomic energy levels are not involved; it appears that the operation of this rather exotic device can be explained without reference to quantum mechanics.Continuous and pulsed modes of operation
A laser can be classified as operating in either continuous or pulsed mode, depending on whether the power output is essentially continuous over time or whether its output takes the form of pulses of light on one or another time scale. Of course even a laser whose output is normally continuous can be intentionally turned on and off at some rate in order to create pulses of light. When the modulation rate is on time scales much slower than the cavity lifetime and the time period over which energy can be stored in the lasing medium or pumping mechanism, then it is still classified as a "modulated" or "pulsed" continuous wave laser. Most laser diodes used in communication systems fall in that category.
Continuous wave operation
Some applications of lasers depend on a beam whose output power is constant over time. Such a laser is known as continuous wave (CW). Many types of lasers can be made to operate in continuous wave mode to satisfy such an application. Many of these lasers actually lase in several longitudinal modes at the same time, and beats between the slightly different optical frequencies of those oscillations will in fact produce amplitude variations on time scales shorter than the round-trip time (the reciprocal of the frequency spacing between modes), typically a few nanoseconds or less. In most cases these lasers are still termed "continuous wave" as their output power is steady when averaged over any longer time periods, with the very high frequency power variations having little or no impact in the intended application. (However the term is not applied to mode-locked lasers, where the intention is to create very short pulses at the rate of the round-trip time).For continuous wave operation it is required for the population inversion of the gain medium to be continually replenished by a steady pump source. In some lasing media this is impossible. In some other lasers it would require pumping the laser at a very high continuous power level which would be impractical or destroy the laser by producing excessive heat. Such lasers cannot be run in CW mode.
Pulsed operation
Pulsed operation of lasers refers to any laser not classified as continuous wave, so that the optical power appears in pulses of some duration at some repetition rate. This encompasses a wide range of technologies addressing a number of different motivations. Some lasers are pulsed simply because they cannot be run in continuous mode.In other cases the application requires the production of pulses having as large an energy as possible. Since the pulse energy is equal to the average power divided by the repetition rate, this goal can sometimes be satisfied by lowering the rate of pulses so that more energy can be built up in between pulses. In laser ablation for example, a small volume of material at the surface of a work piece can be evaporated if it is heated in a very short time, whereas supplying the energy gradually would allow for the heat to be absorbed into the bulk of the piece, never attaining a sufficiently high temperature at a particular point.
Other applications rely on the peak pulse power (rather than the energy in the pulse), especially in order to obtain nonlinear optical effects. For a given pulse energy, this requires creating pulses of the shortest possible duration utilizing techniques such as Q-switching.
The optical bandwidth of a pulse cannot be narrower than the reciprocal of the pulse width. In the case of extremely short pulses, that implies lasing over a considerable bandwidth, quite contrary to the very narrow bandwidths typical of CW lasers. The lasing medium in some dye lasers and vibronic solid-state lasers produces optical gain over a wide bandwidth, making a laser possible which can thus generate pulses of light as short as a few femtoseconds (10−15 s).
Q-switching
In a Q-switched laser, the population inversion is allowed to build up by introducing loss inside the resonator which exceeds the gain of the medium; this can also be described as a reduction of the quality factor or 'Q' of the cavity. Then, after the pump energy stored in the laser medium has approached the maximum possible level, the introduced loss mechanism (often an electro- or acousto-optical element) is rapidly removed (or that occurs by itself in a passive device), allowing lasing to begin which rapidly obtains the stored energy in the gain medium. This results in a short pulse incorporating that energy, and thus a high peak power.Mode-locking
A mode-locked laser is capable of emitting extremely short pulses on the order of tens of picoseconds down to less than 10 femtoseconds. These pulses will repeat at the round trip time, that is, the time that it takes light to complete one round trip between the mirrors comprising the resonator. Due to the Fourier limit (also known as energy-time uncertainty), a pulse of such short temporal length has a spectrum spread over a considerable bandwidth. Thus such a gain medium must have a gain bandwidth sufficiently broad to amplify those frequencies. An example of a suitable material is titanium-doped, artificially grown sapphire (Ti:sapphire) which has a very wide gain bandwidth and can thus produce pulses of only a few femtoseconds duration.Such mode-locked lasers are a most versatile tool for researching processes occurring on extremely short time scales (known as femtosecond physics, femtosecond chemistry and ultrafast science), for maximizing the effect of nonlinearity in optical materials (e.g. in second-harmonic generation, parametric down-conversion, optical parametric oscillators and the like) due to the large peak power, and in ablation applications.[citation needed] Again, because of the extremely short pulse duration, such a laser will produce pulses which achieve an extremely high peak power.
Pulsed pumping
Another method of achieving pulsed laser operation is to pump the laser material with a source that is itself pulsed, either through electronic charging in the case of flash lamps, or another laser which is already pulsed. Pulsed pumping was historically used with dye lasers where the inverted population lifetime of a dye molecule was so short that a high energy, fast pump was needed. The way to overcome this problem was to charge up large capacitors which are then switched to discharge through flashlamps, producing an intense flash. Pulsed pumping is also required for three-level lasers in which the lower energy level rapidly becomes highly populated preventing further lasing until those atoms relax to the ground state. These lasers, such as the excimer laser and the copper vapor laser, can never be operated in CW mode.History
Foundations
In 1917, Albert Einstein established the theoretical foundations for the laser and the maser in the paper Zur Quantentheorie der Strahlung (On the Quantum Theory of Radiation) via a re-derivation of Max Planck's law of radiation, conceptually based upon probability coefficients (Einstein coefficients) for the absorption, spontaneous emission, and stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. In 1928, Rudolf W. Ladenburg confirmed the existence of the phenomena of stimulated emission and negative absorption.[11] In 1939, Valentin A. Fabrikant predicted the use of stimulated emission to amplify "short" waves.[12] In 1947, Willis E. Lamb and R. C. Retherford found apparent stimulated emission in hydrogen spectra and effected the first demonstration of stimulated emission.[11] In 1950, Alfred Kastler (Nobel Prize for Physics 1966) proposed the method of optical pumping, experimentally confirmed, two years later, by Brossel, Kastler, and Winter.[13]Maser

In 1953, Charles Hard Townes and graduate students James P. Gordon and Herbert J. Zeiger produced the first microwave amplifier, a device operating on similar principles to the laser, but amplifying microwave radiation rather than infrared or visible radiation. Townes's maser was incapable of continuous output.[citation needed] Meanwhile, in the Soviet Union, Nikolay Basov and Aleksandr Prokhorov were independently working on the quantum oscillator and solved the problem of continuous-output systems by using more than two energy levels. These gain media could release stimulated emissions between an excited state and a lower excited state, not the ground state, facilitating the maintenance of a population inversion. In 1955, Prokhorov and Basov suggested optical pumping of a multi-level system as a method for obtaining the population inversion, later a main method of laser pumping.
Townes reports that several eminent physicists – among them Niels Bohr, John von Neumann, Isidor Rabi, Polykarp Kusch, and Llewellyn Thomas — argued the maser violated Heisenberg's uncertainty principle and hence could not work.[14] In 1964 Charles H. Townes, Nikolay Basov, and Aleksandr Prokhorov shared the Nobel Prize in Physics, "for fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics, which has led to the construction of oscillators and amplifiers based on the maser–laser principle".
Laser
In 1957, Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow, then at Bell Labs, began a serious study of the infrared laser. As ideas developed, they abandoned infrared radiation to instead concentrate upon visible light. The concept originally was called an "optical maser". In 1958, Bell Labs filed a patent application for their proposed optical maser; and Schawlow and Townes submitted a manuscript of their theoretical calculations to the Physical Review, published that year in Volume 112, Issue No. 6.
LASER notebook: First page of the notebook wherein Gordon Gould coined the LASER acronym, and described the technologic elements for constructing the device.
Simultaneously, at Columbia University, graduate student Gordon Gould was working on a doctoral thesis about the energy levels of excited thallium. When Gould and Townes met, they spoke of radiation emission, as a general subject; afterwards, in November 1957, Gould noted his ideas for a "laser", including using an open resonator (later an essential laser-device component). Moreover, in 1958, Prokhorov independently proposed using an open resonator, the first published appearance (the USSR) of this idea. Elsewhere, in the U.S., Schawlow and Townes had agreed to an open-resonator laser design – apparently unaware of Prokhorov's publications and Gould's unpublished laser work.
At a conference in 1959, Gordon Gould published the term LASER in the paper The LASER, Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.[1][5] Gould's linguistic intention was using the "-aser" word particle as a suffix – to accurately denote the spectrum of the light emitted by the LASER device; thus x-rays: xaser, ultraviolet: uvaser, et cetera; none established itself as a discrete term, although "raser" was briefly popular for denoting radio-frequency-emitting devices.
Gould's notes included possible applications for a laser, such as spectrometry, interferometry, radar, and nuclear fusion. He continued developing the idea, and filed a patent application in April 1959.
The U.S. Patent Office denied his application, and awarded a patent to Bell Labs, in 1960. That provoked a twenty-eight-year lawsuit, featuring scientific prestige and money as the stakes. Gould won his first minor patent in 1977, yet it was not until 1987 that he won the first significant patent lawsuit victory, when a Federal judge ordered the U.S. Patent Office to issue patents to Gould for the optically pumped and the gas discharge laser devices. The question of just how to assign credit for inventing the laser remains unresolved by historians.[15]
On May 16, 1960, Theodore H. Maiman operated the first functioning laser,[16][17] at Hughes Research Laboratories, Malibu, California, ahead of several research teams, including those of Townes, at Columbia University, Arthur Schawlow, at Bell Labs,[18] and Gould, at the TRG (Technical Research Group) company. Maiman's functional laser used a solid-state flashlamp-pumped synthetic ruby crystal to produce red laser light, at 694 nanometres wavelength; however, the device only was capable of pulsed operation, because of its three-level pumping design scheme. Later in 1960, the Iranian physicist Ali Javan, and William R. Bennett, and Donald Herriott, constructed the first gas laser, using helium and neon that was capable of continuous operation in the infrared (U.S. Patent 3,149,290); later, Javan received the Albert Einstein Award in 1993. Basov and Javan proposed the semiconductor laser diode concept. In 1962, Robert N. Hall demonstrated the first laser diode device, made of gallium arsenide and emitted at 850 nm the near-infrared band of the spectrum. Later, in 1962, Nick Holonyak, Jr. demonstrated the first semiconductor laser with a visible emission. This first semiconductor laser could only be used in pulsed-beam operation, and when cooled to liquid nitrogen temperatures (77 K). In 1970, Zhores Alferov, in the USSR, and Izuo Hayashi and Morton Panish of Bell Telephone Laboratories also independently developed room-temperature, continual-operation diode lasers, using the heterojunction structure.
Recent innovations
Since the early period of laser history, laser research has produced a variety of improved and specialized laser types, optimized for different performance goals, including:
- new wavelength bands
- maximum average output power
- maximum peak pulse energy
- maximum peak pulse power
- minimum output pulse duration
- maximum power efficiency
- minimum cost
Lasing without maintaining the medium excited into a population inversion[dubious ] was discovered in 1992 in sodium gas and again in 1995 in rubidium gas by various international teams.[citation needed] This was accomplished by using an external maser to induce "optical transparency" in the medium by introducing and destructively interfering the ground electron transitions between two paths, so that the likelihood for the ground electrons to absorb any energy has been cancelled.
Types and operating principles
Gas lasers
Following the invention of the HeNe gas laser, many other gas discharges have been found to amplify light coherently. Gas lasers using many different gases have been built and used for many purposes. The helium–neon laser (HeNe) is able to operate at a number of different wavelengths, however the vast majority are engineered to lase at 633 nm; these relatively low cost but highly coherent lasers are extremely common in optical research and educational laboratories. Commercial carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers can emit many hundreds of watts in a single spatial mode which can be concentrated into a tiny spot. This emission is in the thermal infrared at 10.6 µm; such lasers are regularly used in industry for cutting and welding. The efficiency of a CO2 laser is unusually high: over 30%.[19] Argon-ion lasers can operate at a number of lasing transitions between 351 and 528.7 nm. Depending on the optical design one or more of these transitions can be lasing simultaneously; the most commonly used lines are 458 nm, 488 nm and 514.5 nm. A nitrogen transverse electrical discharge in gas at atmospheric pressure (TEA) laser is an inexpensive gas laser, often home-built by hobbyists, which produces rather incoherent UV light at 337.1 nm.[20] Metal ion lasers are gas lasers that generate deep ultraviolet wavelengths. Helium-silver (HeAg) 224 nm and neon-copper (NeCu) 248 nm are two examples. Like all low-pressure gas lasers, the gain media of these lasers have quite narrow oscillation linewidths, less than 3 GHz (0.5 picometers),[21] making them candidates for use in fluorescence suppressed Raman spectroscopy.Chemical lasers
Chemical lasers are powered by a chemical reaction permitting a large amount of energy to be released quickly. Such very high power lasers are especially of interest to the military, however continuous wave chemical lasers at very high power levels, fed by streams of gasses, have been developed and have some industrial applications. As examples, in the hydrogen fluoride laser (2700–2900 nm) and the deuterium fluoride laser (3800 nm) the reaction is the combination of hydrogen or deuterium gas with combustion products of ethylene in nitrogen trifluoride.Excimer lasers
Excimer lasers are a special sort of gas laser powered by an electric discharge in which the lasing medium is an excimer, or more precisely an exciplex in existing designs. These are molecules which can only exist with one atom in an excited electronic state. Once the molecule transfers its excitation energy to a photon, therefore, its atoms are no longer bound to each other and the molecule disintegrates. This drastically reduces the population of the lower energy state thus greatly facilitating a population inversion. Excimers currently used are all noble gas compounds; noble gasses are chemically inert and can only form compounds while in an excited state. Excimer lasers typically operate at ultraviolet wavelengths with major applications including semiconductor photolithography and LASIK eye surgery. Commonly used excimer molecules include ArF (emission at 193 nm), KrCl (222 nm), KrF (248 nm), XeCl (308 nm), and XeF (351 nm).[22] The molecular fluorine laser, emitting at 157 nm in the vacuum ultraviolet is sometimes referred to as an excimer laser, however this appears to be a misnomer inasmuch as F2 is a stable compound.Solid-state lasers

A frequency-doubled green laser pointer, showing internal construction. Two AAA cells and electronics power the laser module (lower diagram) This contains a powerful 808 nm IR diode laser that optically pumps a Nd:YVO4 crystal inside a laser cavity. That laser produces 1064 nm (infrared) light which is mainly confined inside the resonator. Also inside the laser cavity, however, is a non-linear KTP crystal which causes frequency doubling, resulting in green light at 532 nm. The front mirror is transparent to this visible wavelength which is then expanded and collimated using two lenses (in this particular design).
Solid-state lasers use a crystalline or glass rod which is "doped" with ions that provide the required energy states. For example, the first working laser was a ruby laser, made from ruby (chromium-doped corundum). The population inversion is actually maintained in the dopant. These materials are pumped optically using a shorter wavelength than the lasing wavelength, often from a flashtube or from another laser. The usage of the term "solid-state" in laser physics is narrower than in typical use. Semiconductor lasers (laser diodes) are typically not referred to as solid-state lasers.
Neodymium is a common dopant in various solid-state laser crystals, including yttrium orthovanadate (Nd:YVO4), yttrium lithium fluoride (Nd:YLF) and yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG). All these lasers can produce high powers in the infrared spectrum at 1064 nm. They are used for cutting, welding and marking of metals and other materials, and also in spectroscopy and for pumping dye lasers. These lasers are also commonly frequency doubled, tripled or quadrupled to produce 532 nm (green, visible), 355 nm and 266 nm (UV) beams, respectively. Frequency-doubled diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) lasers are used to make bright green laser pointers.
Ytterbium, holmium, thulium, and erbium are other common "dopants" in solid-state lasers. Ytterbium is used in crystals such as Yb:YAG, Yb:KGW, Yb:KYW, Yb:SYS, Yb:BOYS, Yb:CaF2, typically operating around 1020–1050 nm. They are potentially very efficient and high powered due to a small quantum defect. Extremely high powers in ultrashort pulses can be achieved with Yb:YAG. Holmium-doped YAG crystals emit at 2097 nm and form an efficient laser operating at infrared wavelengths strongly absorbed by water-bearing tissues. The Ho-YAG is usually operated in a pulsed mode, and passed through optical fiber surgical devices to resurface joints, remove rot from teeth, vaporize cancers, and pulverize kidney and gall stones.
Titanium-doped sapphire (Ti:sapphire) produces a highly tunable infrared laser, commonly used for spectroscopy. It is also notable for use as a mode-locked laser producing ultrashort pulses of extremely high peak power.
Thermal limitations in solid-state lasers arise from unconverted pump power that heats the medium. This heat, when coupled with a high thermo-optic coefficient (dn/dT) can cause thermal lensing and reduce the quantum efficiency. Diode-pumped thin disk lasers overcome these issues by having a gain medium that is much thinner than the diameter of the pump beam. This allows for a more uniform temperature in the material. Thin disk lasers have been shown to produce beams of up to one kilowatt.[23]
Fiber lasers
Solid-state lasers or laser amplifiers where the light is guided due to the total internal reflection in a single mode optical fiber are instead called fiber lasers. Guiding of light allows extremely long gain regions providing good cooling conditions; fibers have high surface area to volume ratio which allows efficient cooling. In addition, the fiber's waveguiding properties tend to reduce thermal distortion of the beam. Erbium and ytterbium ions are common active species in such lasers.Quite often, the fiber laser is designed as a double-clad fiber. This type of fiber consists of a fiber core, an inner cladding and an outer cladding. The index of the three concentric layers is chosen so that the fiber core acts as a single-mode fiber for the laser emission while the outer cladding acts as a highly multimode core for the pump laser. This lets the pump propagate a large amount of power into and through the active inner core region, while still having a high numerical aperture (NA) to have easy launching conditions.
Pump light can be used more efficiently by creating a fiber disk laser, or a stack of such lasers.
Fiber lasers have a fundamental limit in that the intensity of the light in the fiber cannot be so high that optical nonlinearities induced by the local electric field strength can become dominant and prevent laser operation and/or lead to the material destruction of the fiber. This effect is called photodarkening. In bulk laser materials, the cooling is not so efficient, and it is difficult to separate the effects of photodarkening from the thermal effects, but the experiments in fibers show that the photodarkening can be attributed to the formation of long-living color centers.[citation needed]
Photonic crystal lasers
Photonic crystal lasers are lasers based on nano-structures that provide the mode confinement and the density of optical states (DOS) structure required for the feedback to take place.[clarification needed] They are typical micrometre-sized[dubious ] and tunable on the bands of the photonic crystals.[24][clarification needed]Semiconductor lasers
Semiconductor lasers are diodes which are electrically pumped. Recombination of electrons and holes created by the applied current introduces optical gain. Reflection from the ends of the crystal form an optical resonator, although the resonator can be external to the semiconductor in some designs.
Commercial laser diodes emit at wavelengths from 375 nm to 3500 nm.[25] Low to medium power laser diodes are used in laser pointers, laser printers and CD/DVD players. Laser diodes are also frequently used to optically pump other lasers with high efficiency. The highest power industrial laser diodes, with power up to 10 kW (70 dBm)[citation needed], are used in industry for cutting and welding. External-cavity semiconductor lasers have a semiconductor active medium in a larger cavity. These devices can generate high power outputs with good beam quality, wavelength-tunable narrow-linewidth radiation, or ultrashort laser pulses.
In 2012, Nichia and OSRAM developed and manufactured commercial high-power green laser diodes (515/520 nm), which compete with traditional diode-pumped solid-state lasers.[26][27]
Vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) are semiconductor lasers whose emission direction is perpendicular to the surface of the wafer. VCSEL devices typically have a more circular output beam than conventional laser diodes. As of 2005, only 850 nm VCSELs are widely available, with 1300 nm VCSELs beginning to be commercialized,[28] and 1550 nm devices an area of research. VECSELs are external-cavity VCSELs. Quantum cascade lasers are semiconductor lasers that have an active transition between energy sub-bands of an electron in a structure containing several quantum wells.
The development of a silicon laser is important in the field of optical computing. Silicon is the material of choice for integrated circuits, and so electronic and silicon photonic components (such as optical interconnects) could be fabricated on the same chip. Unfortunately, silicon is a difficult lasing material to deal with, since it has certain properties which block lasing. However, recently teams have produced silicon lasers through methods such as fabricating the lasing material from silicon and other semiconductor materials, such as indium(III) phosphide or gallium(III) arsenide, materials which allow coherent light to be produced from silicon. These are called hybrid silicon laser. Another type is a Raman laser, which takes advantage of Raman scattering to produce a laser from materials such as silicon.
Dye lasers
Dye lasers use an organic dye as the gain medium. The wide gain spectrum of available dyes, or mixtures of dyes, allows these lasers to be highly tunable, or to produce very short-duration pulses (on the order of a few femtoseconds). Although these tunable lasers are mainly known in their liquid form, researchers have also demonstrated narrow-linewidth tunable emission in dispersive oscillator configurations incorporating solid-state dye gain media.[29] In their most prevalent form these solid state dye lasers use dye-doped polymers as laser media.
Free-electron lasers
Free-electron lasers, or FELs, generate coherent, high power radiation that is widely tunable, currently ranging in wavelength from microwaves through terahertz radiation and infrared to the visible spectrum, to soft X-rays. They have the widest frequency range of any laser type. While FEL beams share the same optical traits as other lasers, such as coherent radiation, FEL operation is quite different. Unlike gas, liquid, or solid-state lasers, which rely on bound atomic or molecular states, FELs use a relativistic electron beam as the lasing medium, hence the term free-electron.
Exotic media
In September 2007, the BBC News reported that there was speculation about the possibility of using positronium annihilation to drive a very powerful gamma ray laser.[30] Dr. David Cassidy of the University of California, Riverside proposed that a single such laser could be used to ignite a nuclear fusion reaction, replacing the banks of hundreds of lasers currently employed in inertial confinement fusion experiments.[30]Space-based X-ray lasers pumped by a nuclear explosion have also been proposed as antimissile weapons.[31][32] Such devices would be one-shot weapons.
Living cells have been used to produce laser light.[33][34] The cells were genetically engineered to produce green fluorescent protein (GFP). The GFP is used as the laser's "gain medium", where light amplification takes place. The cells were then placed between two tiny mirrors, just 20 millionths of a metre across, which acted as the "laser cavity" in which light could bounce many times through the cell. Upon bathing the cell with blue light, it could be seen to emit directed and intense green laser light.
Uses

Lasers range in size from microscopic diode lasers (top) with numerous applications, to football field sized neodymium glass lasers (bottom) used for inertial confinement fusion, nuclear weapons research and other high energy density physics experiments.
The first use of lasers in the daily lives of the general population was the supermarket barcode scanner, introduced in 1974. The laserdisc player, introduced in 1978, was the first successful consumer product to include a laser but the compact disc player was the first laser-equipped device to become common, beginning in 1982 followed shortly by laser printers.
Some other uses are:
- Medicine: Bloodless surgery, laser healing, surgical treatment, kidney stone treatment, eye treatment, dentistry
- Industry: Cutting, welding, material heat treatment, marking parts, non-contact measurement of parts
- Military: Marking targets, guiding munitions, missile defence, electro-optical countermeasures (EOCM), alternative to radar, blinding troops.
- Law enforcement: used for latent fingerprint detection in the forensic identification field[36][37]
- Research: Spectroscopy, laser ablation, laser annealing, laser scattering, laser interferometry, lidar, laser capture microdissection, fluorescence microscopy
- Product development/commercial: laser printers, optical discs (e.g. CDs and the like), barcode scanners, thermometers, laser pointers, holograms, bubblegrams.
- Laser lighting displays: Laser light shows
- Cosmetic skin treatments: acne treatment, cellulite and striae reduction, and hair removal.
Examples by power
Different applications need lasers with different output powers. Lasers that produce a continuous beam or a series of short pulses can be compared on the basis of their average power. Lasers that produce pulses can also be characterized based on the peak power of each pulse. The peak power of a pulsed laser is many orders of magnitude greater than its average power. The average output power is always less than the power consumed.
| Power | Use |
|---|---|
| 1–5 mW | Laser pointers |
| 5 mW | CD-ROM drive |
| 5–10 mW | DVD player or DVD-ROM drive |
| 100 mW | High-speed CD-RW burner |
| 250 mW | Consumer 16× DVD-R burner |
| 400 mW | Burning through a jewel case including disc within 4 seconds[40] |
| DVD 24× dual-layer recording.[41] | |
| 1 W | Green laser in current Holographic Versatile Disc prototype development |
| 1–20 W | Output of the majority of commercially available solid-state lasers used for micro machining |
| 30–100 W | Typical sealed CO2 surgical lasers[42] |
| 100–3000 W | Typical sealed CO2 lasers used in industrial laser cutting |
- 700 TW (700×1012 W) – National Ignition Facility, a 192-beam, 1.8-megajoule laser system adjoining a 10-meter-diameter target chamber.[43]
- 1.3 PW (1.3×1015 W) – world's most powerful laser as of 1998, located at the Lawrence Livermore Laboratory[44]
Hobby uses
In recent years, some hobbyists have taken interests in lasers. Lasers used by hobbyists are generally of class IIIa or IIIb (see Safety), although some have made their own class IV types.[45] However, compared to other hobbyists, laser hobbyists are far less common, due to the cost and potential dangers involved. Due to the cost of lasers, some hobbyists use inexpensive means to obtain lasers, such as salvaging laser diodes from broken DVD players (red), Blu-ray players (violet), or even higher power laser diodes from CD or DVD burners.[46]Hobbyists also have been taking surplus pulsed lasers from retired military applications and modifying them for pulsed holography. Pulsed Ruby and pulsed YAG lasers have been used.
Safety
Even the first laser was recognized as being potentially dangerous. Theodore Maiman characterized the first laser as having a power of one "Gillette" as it could burn through one Gillette razor blade.Today, it is accepted that even low-power lasers with only a few milliwatts of output power can be hazardous to human eyesight when the beam hits the eye directly or after reflection from a shiny surface. At wavelengths which the cornea and the lens can focus well, the coherence and low divergence of laser light means that it can be focused by the eye into an extremely small spot on the retina, resulting in localized burning and permanent damage in seconds or even less time.
Lasers are usually labeled with a safety class number, which identifies how dangerous the laser is:
- Class 1 is inherently safe, usually because the light is contained in an enclosure, for example in CD players.
- Class 2 is safe during normal use; the blink reflex of the eye will prevent damage. Usually up to 1 mW power, for example laser pointers.
- Class 3R (formerly IIIa) lasers are usually up to 5 mW and involve a small risk of eye damage within the time of the blink reflex. Staring into such a beam for several seconds is likely to cause damage to a spot on the retina.
- Class 3B can cause immediate eye damage upon exposure.
- Class 4 lasers can burn skin, and in some cases, even scattered light can cause eye and/or skin damage. Many industrial and scientific lasers are in this class.
Infrared lasers with wavelengths longer than about 1.4 micrometres are often referred to as "eye-safe", because the cornea strongly absorbs light at these wavelengths, protecting the retina from damage. The label "eye-safe" can be misleading, however, as it only applies to relatively low power continuous wave beams; a high power or Q-switched laser at these wavelengths can burn the cornea, causing severe eye damage, and even moderate power lasers can injure the eye.
As weapons
Lasers of all but the lowest powers can potentially be used as incapacitating weapons, through their ability to produce temporary or permanent vision loss in varying degrees when aimed at the eyes. The degree, character, and duration of vision impairment caused by eye exposure to laser light varies with the power of the laser, the wavelength(s), the collimation of the beam, the exact orientation of the beam, and the duration of exposure. Lasers of even a fraction of a watt in power can produce immediate, permanent vision loss under certain conditions, making such lasers potential non-lethal but incapacitating weapons. The extreme handicap that laser-induced blindness represents makes the use of lasers even as non-lethal weapons morally controversial, and weapons designed to cause blindness have been banned by the Protocol on Blinding Laser Weapons. Incidents of pilots being exposed to lasers while flying have prompted aviation authorities to implement special procedures to deal with such hazards.[47]
Laser weapons capable of directly damaging or destroying a target in combat are still in the experimental stage. The general idea of laser-beam weaponry is to hit a target with a train of brief pulses of light. The rapid evaporation and expansion of the surface causes shockwaves that damage the target.[citation needed] The power needed to project a high-powered laser beam of this kind is beyond the limit of current mobile power technology, thus favoring chemically powered gas dynamic lasers. Example experimental systems include MIRACL and the Tactical High Energy Laser.
The United States Air Force was working on the Boeing YAL-1, an airborne laser mounted in a Boeing 747. It was intended to be used to shoot down incoming ballistic missiles over enemy territory. On March 18, 2009 Northrop Grumman claimed that its engineers in Redondo Beach had successfully built and tested an electrically powered solid state laser capable of producing a 100-kilowatt beam, powerful enough to destroy an airplane. According to Brian Strickland, manager for the United States Army's Joint High Power Solid State Laser program, an electrically powered laser is capable of being mounted in an aircraft, ship, or other vehicle because it requires much less space for its supporting equipment than a chemical laser.[48] However, the source of such a large electrical power in a mobile application remains unclear. The YAL-1 program was canceled due to infeasibility in December 2011.
The United States Navy is developing a laser weapon referred to as the Laser Weapon System or LaWS.[49]
Fictional predictions

Several novelists described devices similar to lasers, prior to the discovery of stimulated emission:
- A very early example is the Heat-Ray featured in H. G. Wells' novel The War of the Worlds (1898).[50]
- A laser-like device was described in Alexey Tolstoy's science fiction novel The Hyperboloid of Engineer Garin in 1927.
- Mikhail Bulgakov exaggerated the biological effect (laser bio stimulation) of intense red light in his science fiction novel Fatal Eggs (1925), without any reasonable description of the source of this red light. (In that novel, the red light first appears occasionally from the illuminating system of an advanced microscope; then the protagonist Prof. Persikov arranges a special set-up for generation of the red light.)