Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species.
Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the hindlimbs of the snake and whale.
Overview

Vestigial features may take various forms; for example, they may be patterns of behavior, anatomical structures, or biochemical processes. Like most other physical features, however functional, vestigial features in a given species may successively appear, develop, and persist or disappear at various stages within the life cycle of the organism, ranging from early embryonic development to late adulthood.

Vestigiality, biologically speaking, refers to organisms retaining organs that have seemingly lost their original function. Vestigial organs are common evolutionary knowledge. In addition, the term vestigiality is useful in referring to many genetically determined features, either morphological, behavioral, or physiological; in any such context, however, it need not follow that a vestigial feature must be completely useless. A classic example at the level of gross anatomy is the human vermiform appendix, vestigial in the sense of retaining no significant digestive function.
Similar concepts apply at the molecular level—some nucleic acid sequences in eukaryotic genomes have no known biological function; some of them may be "junk DNA", but it is a difficult matter to demonstrate that a particular sequence in a particular region of a given genome is truly nonfunctional. The simple fact that it is noncoding DNA does not establish that it is functionless. Furthermore, even if an extant DNA sequence is functionless, it does not follow that it has descended from an ancestral sequence of functional DNA. Logically such DNA would not be vestigial in the sense of being the vestige of a functional structure. In contrast pseudogenes have lost their protein-coding ability or are otherwise no longer expressed in the cell. Whether they have any extant function or not, they have lost their former function and in that sense, they do fit the definition of vestigiality.
Vestigial structures are often called vestigial organs, although many of them are not actually organs. Such vestigial structures typically are degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary, and tend to be much more variable than homologous non-vestigial parts. Although structures commonly regarded "vestigial" may have lost some or all of the functional roles that they had played in ancestral organisms, such structures may retain lesser functions or may have become adapted to new roles in extant populations.
It is important to avoid confusion of the concept of vestigiality with that of exaptation. Both may occur together in the same example, depending on the relevant point of view. In exaptation, a structure originally used for one purpose is modified for a new one. For example, the wings of penguins would be exaptational in the sense of serving a substantial new purpose (underwater locomotion), but might still be regarded as vestigial in the sense of having lost the function of flight. In contrast Darwin argued that the wings of emus would be definitely vestigial, as they appear to have no major extant function; however, function is a matter of degree, so judgments on what is a "major" function are arbitrary; the emu does seem to use its wings as organs of balance in running. Similarly, the ostrich uses its wings in displays and temperature control, though they are undoubtedly vestigial as structures for flight.
Vestigial characters range from detrimental through neutral to favorable in terms of selection. Some may be of some limited utility to an organism but still degenerate over time if they do not confer a significant enough advantage in terms of fitness to avoid the effects of genetic drift or competing selective pressures. Vestigiality in its various forms presents many examples of evidence for biological evolution.
History

Vestigial structures have been noticed since ancient times, and the reason for their existence was long speculated upon before Darwinian evolution provided a widely accepted explanation. In the 4th century BC, Aristotle was one of the earliest writers to comment, in his History of Animals, on the vestigial eyes of moles, calling them "stunted in development" due to the fact that moles can scarcely see. However, only in recent centuries have anatomical vestiges become a subject of serious study. In 1798, Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire noted on vestigial structures:
Whereas useless in this circumstance, these rudiments... have not been eliminated, because Nature never works by rapid jumps, and She always leaves vestiges of an organ, even though it is completely superfluous, if that organ plays an important role in the other species of the same family.
His colleague, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, named a number of vestigial structures in his 1809 book Philosophie Zoologique. Lamarck noted "Olivier's Spalax, which lives underground like the mole, and is apparently exposed to daylight even less than the mole, has altogether lost the use of sight: so that it shows nothing more than vestiges of this organ."
Charles Darwin was familiar with the concept of vestigial structures, though the term for them did not yet exist. He listed a number of them in The Descent of Man, including the muscles of the ear, wisdom teeth, the appendix, the tail bone, body hair, and the semilunar fold in the corner of the eye. Darwin also noted, in On the Origin of Species, that a vestigial structure could be useless for its primary function, but still retain secondary anatomical roles: "An organ serving for two purposes, may become rudimentary or utterly aborted for one, even the more important purpose, and remain perfectly efficient for the other.... [A]n organ may become rudimentary for its proper purpose, and be used for a distinct object."
In the first edition of On the Origin of Species, Darwin briefly mentioned inheritance of acquired characters under the heading "Effects of Use and Disuse", expressing little doubt that use "strengthens and enlarges certain parts, and disuse diminishes them; and that such modifications are inherited". In later editions he expanded his thoughts on this, and in the final chapter of the 6th edition concluded that species have been modified "chiefly through the natural selection of numerous successive, slight, favorable variations; aided in an important manner by the inherited effects of the use and disuse of parts".
In 1893, Robert Wiedersheim published The Structure of Man, a book on human anatomy and its relevance to man's evolutionary history. The Structure of Man contained a list of 86 human organs that Wiedersheim described as, "Organs having become wholly or in part functionless, some appearing in the Embryo alone, others present during Life constantly or inconstantly. For the greater part Organs which may be rightly termed Vestigial." Since his time, the function of some of these structures have been discovered, while other anatomical vestiges have been unearthed, making the list primarily of interest as a record of the knowledge of human anatomy at the time. Later versions of Wiedersheim's list were expanded to as many as 180 human "vestigial organs". This is why the zoologist Horatio Newman said in a written statement read into evidence in the Scopes Trial that "There are, according to Wiedersheim, no less than 180 vestigial structures in the human body, sufficient to make of a man a veritable walking museum of antiquities."
Common descent and evolutionary theory
Vestigial structures are often homologous to structures that are functioning normally in other species. Therefore, vestigial structures can be considered evidence for evolution, the process by which beneficial heritable traits arise in populations over an extended period of time. The existence of vestigial traits can be attributed to changes in the environment and behavior patterns of the organism in question. Through an examination of these various traits, it is clear that evolution had a hard role in the development of organisms. Every anatomical structure or behavior response has origins in which they were, at one time, useful. As time progressed, the ancient common ancestor organisms did as well. Evolving with time, natural selection played a huge role. More advantageous structures were selected, while others were not. With this expansion, some traits were left to the wayside. As the function of the trait is no longer beneficial for survival, the likelihood that future offspring will inherit the "normal" form of it decreases. In some cases, the structure becomes detrimental to the organism (for example the eyes of a mole can become infected). In many cases the structure is of no direct harm, yet all structures require extra energy in terms of development, maintenance, and weight, and are also a risk in terms of disease (e.g., infection, cancer), providing some selective pressure for the removal of parts that do not contribute to an organism's fitness. A structure that is not harmful will take longer to be 'phased out' than one that is. However, some vestigial structures may persist due to limitations in development, such that complete loss of the structure could not occur without major alterations of the organism's developmental pattern, and such alterations would likely produce numerous negative side-effects. The toes of many animals such as horses, which stand on a single toe, are still evident in a vestigial form and may become evident, although rarely, from time to time in individuals.
The vestigial versions of the structure can be compared to the original version of the structure in other species in order to determine the homology of a vestigial structure. Homologous structures indicate common ancestry with those organisms that have a functional version of the structure. Douglas Futuyma has stated that vestigial structures make no sense without evolution, just as spelling and usage of many modern English words can only be explained by their Latin or Old Norse antecedents.
Vestigial traits can still be considered adaptations. This is because an adaptation is often defined as a trait that has been favored by natural selection. Adaptations, therefore, need not be adaptive, as long as they were at some point.
Examples
Non-human animals
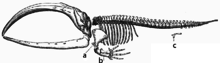
Vestigial characters are present throughout the animal kingdom, and an almost endless list could be given. Darwin said that "it would be impossible to name one of the higher animals in which some part or other is not in a rudimentary condition."
The wings of ostriches, emus and other flightless birds are vestigial; they are remnants of their flying ancestors' wings. These birds go through the effort of developing wings, even though most birds are too large to use the wings successfully. Seeing vestigial wings in birds is also common when they no longer need to fly to escape predators, such as birds on the Galapagos Islands. The eyes of certain cavefish and salamanders are vestigial, as they no longer allow the organism to see, and are remnants of their ancestors' functional eyes. Animals that reproduce without sex (via asexual reproduction) generally lose their sexual traits, such as the ability to locate/recognize the opposite sex and copulation behavior.
Boas and pythons have vestigial pelvis remnants, which are externally visible as two small pelvic spurs on each side of the cloaca. These spurs are sometimes used in copulation, but are not essential, as no colubrid snake (the vast majority of species) possesses these remnants. Furthermore, in most snakes, the left lung is greatly reduced or absent. Amphisbaenians, which independently evolved limblessness, also retain vestiges of the pelvis as well as the pectoral girdle, and have lost their right lung.

A case of vestigial organs was described in polyopisthocotylean Monogeneans (parasitic flatworms). These parasites usually have a posterior attachment organ with several clamps, which are sclerotised organs attaching the worm to the gill of the host fish. These clamps are extremely important for the survival of the parasite. In the family Protomicrocotylidae, species have either normal clamps, simplified clamps, or no clamps at all (in the genus Lethacotyle). After a comparative study of the relative surface of clamps in more than 100 Monogeneans, this has been interpreted as an evolutionary sequence leading to the loss of clamps. Coincidentally, other attachment structures (lateral flaps, transverse striations) have evolved in protomicrocotylids. Therefore, clamps in protomicrocotylids were considered vestigial organs.
In the foregoing examples the vestigiality is generally the (sometimes incidental) result of adaptive evolution. However, there are many examples of vestigiality as the product of drastic mutation, and such vestigiality is usually harmful or counter-adaptive. One of the earliest documented examples was that of vestigial wings in Drosophila. Many examples in many other contexts have emerged since.
Humans

Human vestigiality is related to human evolution, and includes a variety of characters occurring in the human species. Many examples of these are vestigial in other primates and related animals, whereas other examples are still highly developed. The human caecum is vestigial, as often is the case in omnivores, being reduced to a single chamber receiving the content of the ileum into the colon. The ancestral caecum would have been a large, blind diverticulum in which resistant plant material such as cellulose would have been fermented in preparation for absorption in the colon. Analogous organs in other animals similar to humans continue to perform similar functions. The coccyx, or tailbone, though a vestige of the tail of some primate ancestors, is functional as an anchor for certain pelvic muscles including: the levator ani muscle and the largest gluteal muscle, the gluteus maximus.
Other structures that are vestigial include the plica semilunaris on the inside corner of the eye (a remnant of the nictitating membrane); and (as seen at right) muscles in the ear. Other organic structures (such as the occipitofrontalis muscle) have lost their original functions (to keep the head from falling) but are still useful for other purposes (facial expression).
Humans also bear some vestigial behaviors and reflexes. The formation of goose bumps in humans under stress is a vestigial reflex; its function in human ancestors was to raise the body's hair, making the ancestor appear larger and scaring off predators. The arrector pili (muscle that connects the hair follicle to connective tissue) contracts and creates goosebumps on skin.
There are also vestigial molecular structures in humans, which are no longer in use but may indicate common ancestry with other species. One example of this is a gene that is functional in most other mammals and which produces L-gulonolactone oxidase, an enzyme that can make vitamin C. A documented mutation deactivated the gene in an ancestor of the modern infraorder of monkeys, and apes, and it now remains in their genomes, including the human genome, as a vestigial sequence called a pseudogene.
The shift in human diet towards soft and processed food over time caused a reduction in the number of powerful grinding teeth, especially the third molars (also known as wisdom teeth), which were highly prone to impaction.
Plants and fungi
Plants also have vestigial parts, including functionless stipules and carpels, leaf reduction of Equisetum, paraphyses of Fungi. Well known examples are the reductions in floral display, leading to smaller and/or paler flowers, in plants that reproduce without outcrossing, for example via selfing or obligate clonal reproduction.
Objects

Many objects in daily use contain vestigial structures. While not the result of natural selection through random mutation, much of the process is the same. Product design, like evolution, is iterative; it builds on features and processes that already exist, with limited resources available to make tweaks. To spend resources on completely weeding out a form that serves no purpose (if at the same time it is not an obstruction either) is not economically astute. These vestigial structures differ from the concept of skeuomorphism in that a skeuomorph is a design feature that has been specifically implemented as a reference to the past, enabling users to acclimatise quicker. A vestigial feature does not exist intentionally, or even usefully.
For example, men's business suits often contain a row of buttons at the bottom of the sleeve. These used to serve a purpose, allowing the sleeve to be split and rolled up. The feature has been lost entirely, though most suits still give the impression that it is possible, complete with fake button holes. There is also an example of exaptation to be found in the business suit: it was previously possible to button a jacket up all the way to the top. As it became the fashion to fold the lapel over, the top half of buttons and their accompanying buttonholes disappeared, save for a single hole at the top; it has since found a new use as a place to fasten pins, badges, or boutonnières.
As a final example, soldiers in ceremonial or parade uniform can sometimes be seen wearing a gorget: a small decorative piece of metal suspended around the neck with a chain. The gorget serves no protection to the wearer, yet there exists an unbroken lineage from the gorget to the full suits of armour of the middle ages. With the introduction of gunpowder weapons, armour increasingly lost its usefulness on the battlefield. At the same time, military men were keen to retain the status it provided them. The result: a breastplate that "shrank" away over time, but never disappeared completely.