A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures. A failure to pay, along with evasion of or resistance to taxation, is punishable by law. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labour equivalent. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC.
Most countries have a tax system in place, in order to pay for public, common, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some levy a flat percentage rate of taxation on personal annual income, but most scale taxes are progressive based on brackets of annual income amounts. Most countries charge a tax on an individual's income as well as on corporate income. Countries or subunits often also impose wealth taxes, inheritance taxes, estate taxes, gift taxes, property taxes, sales taxes, use taxes, payroll taxes, duties and/or tariffs.
In economic terms, taxation transfers wealth from households or businesses to the government. This has effects that can both increase and reduce economic growth and economic welfare. Consequently, taxation is a highly debated topic.
Overview
The legal definition and the economic definition of taxes differ in some ways such that economists do not regard many transfers to governments as taxes. For example, some transfers to the public sector are comparable to prices. Examples include tuition at public universities and fees for utilities provided by local governments. Governments also obtain resources by "creating" money and coins (for example, by printing bills and by minting coins), through voluntary gifts (for example, contributions to public universities and museums), by imposing penalties (such as traffic fines), by borrowing and confiscating criminal proceeds. From the view of economists, a tax is a non-penal, yet compulsory transfer of resources from the private to the public sector, levied on a basis of predetermined criteria and without reference to specific benefits received.
In modern taxation systems, governments levy taxes in money; but in-kind and corvée taxation are characteristic of traditional or pre-capitalist states and their functional equivalents. The method of taxation and the government expenditure of taxes raised is often highly debated in politics and economics. Tax collection is performed by a government agency such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States, Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs (HMRC) in the United Kingdom, the Canada Revenue Agency or the Australian Taxation Office. When taxes are not fully paid, the state may impose civil penalties (such as fines or forfeiture) or criminal penalties (such as incarceration) on the non-paying entity or individual.
Purposes and effects
The levying of taxes aims to raise revenue to fund governing or to alter prices in order to affect demand. States and their functional equivalents throughout history have used the money provided by taxation to carry out many functions. Some of these include expenditures on economic infrastructure (roads, public transportation, sanitation, legal systems, public security, public education, public health systems), military, scientific research & development, culture and the arts, public works, distribution, data collection and dissemination, public insurance, and the operation of government itself. A government's ability to raise taxes is called its fiscal capacity.
When expenditures exceed tax revenue, a government accumulates debt. A portion of taxes may be used to service past debts. Governments also use taxes to fund welfare and public services. These services can include education systems, pensions for the elderly, unemployment benefits, transfer payments, subsidies and public transportation. Energy, water and waste management systems are also common public utilities.
According to the proponents of the chartalist theory of money creation, taxes are not needed for government revenue, as long as the government in question is able to issue fiat money. According to this view, the purpose of taxation is to maintain the stability of the currency, express public policy regarding the distribution of wealth, subsidizing certain industries or population groups or isolating the costs of certain benefits, such as highways or social security.
Effects of taxes can be divided into two fundamental categories:
- Taxes cause an income effect because they reduce purchasing power to taxpayers.
- Taxes cause a substitution effect when taxation causes a substitution between taxed goods and untaxed goods.
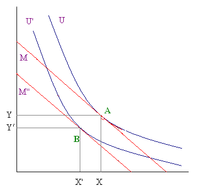
If we consider, for instance, two normal goods, x and y, whose prices are respectively px and py and an individual budget constraint given by the equation xpx + ypy = Y, where Y is the income, the slope of the budget constraint, in a graph where is represented good x on the vertical axis and good y on the horizontal axes, is equal to -py/px . The initial equilibrium is in the point (C), in which budget constraint and indifference curve are tangent, introducing an ad valorem tax on the y good (budget constraint: pxx + py(1 + τ)y = Y), the budget constraint's slope becomes equal to -py(1 + τ)/px. The new equilibrium is now in the tangent point (A) with a lower indifferent curve.
As can be noticed the tax's introduction causes two consequences:
- It changes the consumers' real income (less purchasing power)
- It raises the relative price of y good.
The income effect shows the variation of y good quantity given by the change of real income. The substitution effect shows the variation of y good determined by relative prices' variation. This kind of taxation (that causes the substitution effect) can be considered distortionary.
Another example can be the introduction of an income lump-sum tax (xpx + ypy = Y - T), with a parallel shift downward of the budget constraint, can be produced a higher revenue with the same loss of consumers' utility compared with the property tax case, from another point of view, the same revenue can be produced with a lower utility sacrifice. The lower utility (with the same revenue) or the lower revenue (with the same utility) given by a distortionary tax are called excess pressure. The same result, reached with an income lump-sum tax, can be obtained with these following types of taxes (all of them cause only a budget constraint's shift without causing a substitution effect), the budget constraint's slope remains the same (-px/py):
- A general tax on consumption: (Budget constraint: px(1 + τ)x + py(1 + τ)y = Y)
- A proportional income tax: (Budget constraint: xpx + ypy = Y(1 - t))
When the t and τ rates are chosen respecting this equation (where t is the rate of income tax and tau is the consumption tax's rate):
the effects of the two taxes are the same.
A tax effectively changes the relative prices of products. Therefore, most economists, especially neoclassical economists, argue that taxation creates market distortion and results in economic inefficiency unless there are (positive or negative) externalities associated with the activities that are taxed that need to be internalized to reach an efficient market outcome. They have therefore sought to identify the kind of tax system that would minimize this distortion. Recent scholarship suggests that in the United States of America, the federal government effectively taxes investments in higher education more heavily than it subsidizes higher education, thereby contributing to a shortage of skilled workers and unusually high differences in pre-tax earnings between highly educated and less-educated workers.
Taxes can even have effects on labor supply: we can consider a model in which the consumer chooses the number of hours spent working and the amount spent on consumption. Let us suppose that only one good exists and no income is saved.
Consumers have a given number of hours (H) that is divided between work (L) and free time (F = H - L). The hourly wage is called w and it tells us the free time's opportunity cost, i.e. the income to which the individual renounces consuming an additional hour of free time. Consumption and hours of work have a positive relationship, more hours of work mean more earnings and, assuming that workers don't save money, more earnings imply an increase in consumption (Y = C = wL). Free time and consumption can be considered as two normal goods (workers have to decide between working one hour more, that would mean consuming more or having one more hour of free time) and the budget constraint is negatively inclined (Y = w(H - F)). The indifference curve related to these two goods has a negative slope and free time becomes more and more important with high levels of consumption. This is because a high level of consumption means that people are already spending many hours working, so, in this situation, they need more free time than consume and it implies that they have to be paid with a higher salary to work an additional hour. A proportional income tax, changing budget constraint's slope (now Y = w(1 - t)(H - F)), implies both substitution and income effects. The problem now is that the two effects go in opposite ways: the income effect tells us that, with an income tax, the consumer feels poorer and for this reason he wants to work more, causing an increase in labor offer. On the other hand, the substitution effect tells us that free time, being a normal good, is now more convenient compared to consume and it implies a decrease in labor offer. Therefore, the total effect can be both an increase or a decrease of labor offer, depending on the indifference curve's shape.
The Laffer curve depicts the amount of government revenue as a function of the rate of taxation. It shows that for a tax rate above a certain critical rate, government revenue starts decreasing as the tax rate rises, as a consequence of a decline in labor supply. This theory supports that, if the tax rate is above that critical point, a decrease in the tax rate should imply a rise in labor supply that in turn would lead to an increase in government revenue.
Governments use different kinds of taxes and vary the tax rates. They do this in order to distribute the tax burden among individuals or classes of the population involved in taxable activities, such as the business sector, or to redistribute resources between individuals or classes in the population. Historically, taxes on the poor supported the nobility; modern social-security systems aim to support the poor, the disabled, or the retired by taxes on those who are still working. In addition, taxes are applied to fund foreign aid and military ventures, to influence the macroeconomic performance of the economy (a government's strategy for doing this is called its fiscal policy; see also tax exemption), or to modify patterns of consumption or employment within an economy, by making some classes of the transaction more or less attractive.
A state's tax system often reflects its communal values and the values of those in current political power. To create a system of taxation, a state must make choices regarding the distribution of the tax burden—who will pay taxes and how much they will pay—and how the taxes collected will be spent. In democratic nations where the public elects those in charge of establishing or administering the tax system, these choices reflect the type of community that the public wishes to create. In countries where the public does not have a significant amount of influence over the system of taxation, that system may reflect more closely the values of those in power.
All large businesses incur administrative costs in the process of delivering revenue collected from customers to the suppliers of the goods or services being purchased. Taxation is no different, as governments are large organizations; the resource collected from the public through taxation is always greater than the amount which can be used by the government. The difference is called the compliance cost and includes (for example) the labor cost and other expenses incurred in complying with tax laws and rules. The collection of a tax in order to spend it on a specified purpose, for example collecting a tax on alcohol to pay directly for alcoholism-rehabilitation centers, is called hypothecation. Finance ministers often dislike this practice, since it reduces their freedom of action. Some economic theorists regard hypothecation as intellectually dishonest since, in reality, money is fungible. Furthermore, it often happens that taxes or excises initially levied to fund some specific government programs are then later diverted to the government general fund. In some cases, such taxes are collected in fundamentally inefficient ways, for example, through highway tolls.
Since governments also resolve commercial disputes, especially in countries with common law, similar arguments are sometimes used to justify a sales tax or value added tax. Some (libertarians, for example) portray most or all forms of taxes as immoral due to their involuntary (and therefore eventually coercive or violent) nature. The most extreme anti-tax view, anarcho-capitalism, holds that all social services should be voluntarily bought by the people using them.
Types
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) publishes an analysis of the tax systems of member countries. As part of such analysis, OECD has developed a definition and system of classification of internal taxes, generally followed below. In addition, many countries impose taxes (tariffs) on the import of goods.
Income
Income tax
Many jurisdictions tax the income of individuals and of business entities, including corporations. Generally, the authorities impose a tax on net profits from a business, on net gains, and on other income. Computation of income subject to tax may be determined under accounting principles used in the jurisdiction, which tax-law principles in the jurisdiction may modify or replace. The incidence of taxation varies by system, and some systems may be viewed as progressive or regressive. Rates of tax may vary or be constant (flat) by income level. Many systems allow individuals certain personal allowances and other non-business reductions to taxable income, although business deductions tend to be favored over personal deductions.
Tax-collection agencies often collect personal income tax on a pay-as-you-earn basis, with corrections made after the end of the tax year. These corrections take one of two forms:
- payments to the government, from taxpayers who have not paid enough during the tax year
- tax refunds from the government to those who have overpaid
Income-tax systems often make deductions available that reduce the total tax liability by reducing total taxable income. They may allow losses from one type of income to count against another - for example, a loss on the stock market may be deducted against taxes paid on wages. Other tax systems may isolate the loss, such that business losses can only be deducted against business income tax by carrying forward the loss to later tax years.
Negative income tax
In economics, a negative income tax (abbreviated NIT) is a progressive income tax system where people earning below a certain amount receive supplemental payment from the government instead of paying taxes to the government.
Capital gains
Most jurisdictions imposing an income tax treat capital gains as part of income subject to tax. Capital gain is generally a gain on sale of capital assets—that is, those assets not held for sale in the ordinary course of business. Capital assets include personal assets in many jurisdictions. Some jurisdictions provide preferential rates of tax or only partial taxation for capital gains. Some jurisdictions impose different rates or levels of capital-gains taxation based on the length of time the asset was held. Because tax rates are often much lower for capital gains than for ordinary income, there is widespread controversy and dispute about the proper definition of capital.
Corporate
Corporate tax refers to income tax, capital tax, net-worth tax, or other taxes imposed on corporations. Rates of tax and the taxable base for corporations may differ from those for individuals or for other taxable persons.
Social-security contributions
Many countries provide publicly funded retirement or healthcare systems. In connection with these systems, the country typically requires employers and/or employees to make compulsory payments. These payments are often computed by reference to wages or earnings from self-employment. Tax rates are generally fixed, but a different rate may be imposed on employers than on employees. Some systems provide an upper limit on earnings subject to the tax. A few systems provide that the tax is payable only on wages above a particular amount. Such upper or lower limits may apply for retirement but not for health-care components of the tax. Some have argued that such taxes on wages are a form of "forced savings" and not really a tax, while others point to redistribution through such systems between generations (from newer cohorts to older cohorts) and across income levels (from higher income levels to lower income-levels) which suggests that such programs are really taxed and spending programs.
Payroll or workforce
Unemployment and similar taxes are often imposed on employers based on the total payroll. These taxes may be imposed in both the country and sub-country levels.
Wealth
A wealth tax is levied on the total value of personal assets, including: bank deposits, real estate, assets in insurance and pension plans, ownership of unincorporated businesses, financial securities, and personal trusts. Typically liabilities (primarily mortgages and other loans) are deducted, hence it is sometimes called a net wealth tax.
Property
Recurrent property taxes may be imposed on immovable property (real property) and on some classes of movable property. In addition, recurrent taxes may be imposed on the net wealth of individuals or corporations. Many jurisdictions impose estate tax, gift tax or other inheritance taxes on property at death or at the time of gift transfer. Some jurisdictions impose taxes on financial or capital transactions.
Property taxes
A property tax (or millage tax) is an ad valorem tax levy on the value of a property that the owner of the property is required to pay to a government in which the property is situated. Multiple jurisdictions may tax the same property. There are three general varieties of property: land, improvements to land (immovable man-made things, e.g. buildings), and personal property (movable things). Real estate or realty is the combination of land and improvements to the land.
Property taxes are usually charged on a recurrent basis (e.g., yearly). A common type of property tax is an annual charge on the ownership of real estate, where the tax base is the estimated value of the property. For a period of over 150 years from 1695, the government of England levied a window tax, with the result that one can still see listed buildings with windows bricked up in order to save their owner's money. A similar tax on hearths existed in France and elsewhere, with similar results. The two most common types of event-driven property taxes are stamp duty, charged upon change of ownership, and inheritance tax, which many countries impose on the estates of the deceased.
In contrast with a tax on real estate (land and buildings), a land-value tax (or LVT) is levied only on the unimproved value of the land ("land" in this instance may mean either the economic term, i.e., all-natural resources, or the natural resources associated with specific areas of the Earth's surface: "lots" or "land parcels"). Proponents of the land-value tax argue that it is economically justified, as it will not deter production, distort market mechanisms or otherwise create deadweight losses the way other taxes do.
When real estate is held by a higher government unit or some other entity not subject to taxation by the local government, the taxing authority may receive a payment in lieu of taxes to compensate it for some or all of the foregone tax revenues.
In many jurisdictions (including many American states), there is a general tax levied periodically on residents who own personal property (personalty) within the jurisdiction. Vehicle and boat registration fees are subsets of this kind of tax. The tax is often designed with blanket coverage and large exceptions for things like food and clothing. Household goods are often exempt when kept or used within the household. Any otherwise non-exempt object can lose its exemption if regularly kept outside the household. Thus, tax collectors often monitor newspaper articles for stories about wealthy people who have lent art to museums for public display, because the artworks have then become subject to personal property tax. If an artwork had to be sent to another state for some touch-ups, it may have become subject to personal property tax in that state as well.
Inheritance
Inheritance tax, estate tax, and death tax or duty are the names given to various taxes that arise on the death of an individual. In United States tax law, there is a distinction between an estate tax and an inheritance tax: the former taxes the personal representatives of the deceased, while the latter taxes the beneficiaries of the estate. However, this distinction does not apply in other jurisdictions; for example, if using this terminology UK inheritance tax would be an estate tax.
Expatriation
An expatriation tax is a tax on individuals who renounce their citizenship or residence. The tax is often imposed based on a deemed disposition of all the individual's property. One example is the United States under the American Jobs Creation Act, where any individual who has a net worth of $2 million or an average income-tax liability of $127,000 who renounces his or her citizenship and leaves the country is automatically assumed to have done so for tax avoidance reasons and is subject to a higher tax rate.
Transfer
Historically, in many countries, a contract needs to have a stamp affixed to make it valid. The charge for the stamp is either a fixed amount or a percentage of the value of the transaction. In most countries, the stamp has been abolished but stamp duty remains. Stamp duty is levied in the UK on the purchase of shares and securities, the issue of bearer instruments, and certain partnership transactions. Its modern derivatives, stamp duty reserve tax and stamp duty land tax, are respectively charged on transactions involving securities and land. Stamp duty has the effect of discouraging speculative purchases of assets by decreasing liquidity. In the United States, transfer tax is often charged by the state or local government and (in the case of real property transfers) can be tied to the recording of the deed or other transfer documents.
Wealth (net worth)
Some countries' governments will require a declaration of the taxpayers' balance sheet (assets and liabilities), and from that exact a tax on net worth (assets minus liabilities), as a percentage of the net worth, or a percentage of the net worth exceeding a certain level. The tax may be levied on "natural" or "legal persons."
Goods and services
Value added
A value-added tax (VAT), also known as Goods and Services Tax (G.S.T), Single Business Tax, or Turnover Tax in some countries, applies the equivalent of a sales tax to every operation that creates value. To give an example, sheet steel is imported by a machine manufacturer. That manufacturer will pay the VAT on the purchase price, remitting that amount to the government. The manufacturer will then transform the steel into a machine, selling the machine for a higher price to a wholesale distributor. The manufacturer will collect the VAT on the higher price but will remit to the government only the excess related to the "value-added" (the price over the cost of the sheet steel). The wholesale distributor will then continue the process, charging the retail distributor the VAT on the entire price to the retailer, but remitting only the amount related to the distribution mark-up to the government. The last VAT amount is paid by the eventual retail customer who cannot recover any of the previously paid VAT. For a VAT and sales tax of identical rates, the total tax paid is the same, but it is paid at differing points in the process.
VAT is usually administrated by requiring the company to complete a VAT return, giving details of VAT it has been charged (referred to as input tax) and VAT it has charged to others (referred to as output tax). The difference between output tax and input tax is payable to the Local Tax Authority.
Many tax authorities have introduced automated VAT which has increased accountability and auditability, by utilizing computer systems, thereby also enabling anti-cybercrime offices as well.
Sales
Sales taxes are levied when a commodity is sold to its final consumer. Retail organizations contend that such taxes discourage retail sales. The question of whether they are generally progressive or regressive is a subject of much current debate. People with higher incomes spend a lower proportion of them, so a flat-rate sales tax will tend to be regressive. It is therefore common to exempt food, utilities, and other necessities from sales taxes, since poor people spend a higher proportion of their incomes on these commodities, so such exemptions make the tax more progressive. This is the classic "You pay for what you spend" tax, as only those who spend money on non-exempt (i.e. luxury) items pay the tax.
A small number of U.S. states rely entirely on sales taxes for state revenue, as those states do not levy a state income tax. Such states tend to have a moderate to a large amount of tourism or inter-state travel that occurs within their borders, allowing the state to benefit from taxes from people the state would otherwise not tax. In this way, the state is able to reduce the tax burden on its citizens. The U.S. states that do not levy a state income tax are Alaska, Tennessee, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Texas, Washington state, and Wyoming. Additionally, New Hampshire and Tennessee levy state income taxes only on dividends and interest income. Of the above states, only Alaska and New Hampshire do not levy a state sales tax. Additional information can be obtained at the Federation of Tax Administrators website.
In the United States, there is a growing movement for the replacement of all federal payroll and income taxes (both corporate and personal) with a national retail sales tax and monthly tax rebate to households of citizens and legal resident aliens. The tax proposal is named FairTax. In Canada, the federal sales tax is called the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and now stands at 5%. The provinces of British Columbia, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Prince Edward Island also have a provincial sales tax [PST]. The provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Newfoundland & Labrador, and Ontario have harmonized their provincial sales taxes with the GST—Harmonized Sales Tax [HST], and thus is a full VAT. The province of Quebec collects the Quebec Sales Tax [QST] which is based on the GST with certain differences. Most businesses can claim back the GST, HST, and QST they pay, and so effectively it is the final consumer who pays the tax.
Excises
An excise duty is an indirect tax imposed upon goods during the process of their manufacture, production or distribution, and is usually proportionate to their quantity or value. Excise duties were first introduced into England in the year 1643, as part of a scheme of revenue and taxation devised by parliamentarian John Pym and approved by the Long Parliament. These duties consisted of charges on beer, ale, cider, cherry wine, and tobacco, to which list were afterward added paper, soap, candles, malt, hops, and sweets. The basic principle of excise duties was that they were taxes on the production, manufacture, or distribution of articles which could not be taxed through the customs house, and revenue derived from that source is called excise revenue proper. The fundamental conception of the term is that of a tax on articles produced or manufactured in a country. In the taxation of such articles of luxury as spirits, beer, tobacco, and cigars, it has been the practice to place a certain duty on the importation of these articles (a customs duty).
Excises (or exemptions from them) are also used to modify consumption patterns of a certain area (social engineering). For example, a high excise is used to discourage alcohol consumption, relative to other goods. This may be combined with hypothecation if the proceeds are then used to pay for the costs of treating illness caused by alcohol use disorder. Similar taxes may exist on tobacco, pornography, etc., and they may be collectively referred to as "sin taxes". A carbon tax is a tax on the consumption of carbon-based non-renewable fuels, such as petrol, diesel-fuel, jet fuels, and natural gas. The object is to reduce the release of carbon into the atmosphere. In the United Kingdom, vehicle excise duty is an annual tax on vehicle ownership.
Tariff
An import or export tariff (also called customs duty or impost) is a charge for the movement of goods through a political border. Tariffs discourage trade, and they may be used by governments to protect domestic industries. A proportion of tariff revenues is often hypothecated to pay the government to maintain a navy or border police. The classic ways of cheating a tariff are smuggling or declaring a false value of goods. Tax, tariff and trade rules in modern times are usually set together because of their common impact on industrial policy, investment policy, and agricultural policy. A trade bloc is a group of allied countries agreeing to minimize or eliminate tariffs against trade with each other, and possibly to impose protective tariffs on imports from outside the bloc. A customs union has a common external tariff, and the participating countries share the revenues from tariffs on goods entering the customs union.
In some societies, tariffs also could be imposed by local authorities on the movement of goods between regions (or via specific internal gateways). A notable example is the likin, which became an important revenue source for local governments in the late Qing China.
Other
License fees
Occupational taxes or license fees may be imposed on businesses or individuals engaged in certain businesses. Many jurisdictions impose a tax on vehicles.
Poll
A poll tax, also called a per capita tax, or capitation tax, is a tax that levies a set amount per individual. It is an example of the concept of fixed tax. One of the earliest taxes mentioned in the Bible of a half-shekel per annum from each adult Jew (Ex. 30:11–16) was a form of the poll tax. Poll taxes are administratively cheap because they are easy to compute and collect and difficult to cheat. Economists have considered poll taxes economically efficient because people are presumed to be in fixed supply and poll taxes, therefore, do not lead to economic distortions. However, poll taxes are very unpopular because poorer people pay a higher proportion of their income than richer people. In addition, the supply of people is in fact not fixed over time: on average, couples will choose to have fewer children if a poll tax is imposed. The introduction of a poll tax in medieval England was the primary cause of the 1381 Peasants' Revolt. Scotland was the first to be used to test the new poll tax in 1989 with England and Wales in 1990. The change from progressive local taxation based on property values to a single-rate form of taxation regardless of ability to pay (the Community Charge, but more popularly referred to as the Poll Tax), led to widespread refusal to pay and to incidents of civil unrest, known colloquially as the 'Poll Tax Riots'.
Other
Some types of taxes have been proposed but not actually adopted in any major jurisdiction. These include:
- Bank tax
- Financial transaction taxes including currency transaction taxes
Descriptive labels
Ad valorem and per unit
An ad valorem tax is one where the tax base is the value of a good, service, or property. Sales taxes, tariffs, property taxes, inheritance taxes, and value-added taxes are different types of ad valorem tax. An ad valorem tax is typically imposed at the time of a transaction (sales tax or value-added tax (VAT)) but it may be imposed on an annual basis (property tax) or in connection with another significant event (inheritance tax or tariffs).
In contrast to ad valorem taxation is a per unit tax, where the tax base is the quantity of something, regardless of its price. An excise tax is an example.
Consumption
Consumption tax refers to any tax on non-investment spending and can be implemented by means of a sales tax, consumer value-added tax, or by modifying an income tax to allow for unlimited deductions for investment or savings.
Environmental
This includes natural resources consumption tax, greenhouse gas tax (Carbon tax), "sulfuric tax", and others. The stated purpose is to reduce the environmental impact by repricing. Economists describe environmental impacts as negative externalities. As early as 1920, Arthur Pigou suggested a tax to deal with externalities (see also the section on Increased economic welfare below). The proper implementation of environmental taxes has been the subject of a long-lasting debate.
Proportional, progressive, regressive, and lump-sum
An important feature of tax systems is the percentage of the tax burden as it relates to income or consumption. The terms progressive, regressive, and proportional are used to describe the way the rate progresses from low to high, from high to low, or proportionally. The terms describe a distribution effect, which can be applied to any type of tax system (income or consumption) that meets the definition.
- A progressive tax is a tax imposed so that the effective tax rate increases as the amount to which the rate is applied increases.
- The opposite of a progressive tax is a regressive tax, where the effective tax rate decreases as the amount to which the rate is applied increases. This effect is commonly produced where means testing is used to withdraw tax allowances or state benefits.
- In between is a proportional tax, where the effective tax rate is fixed, while the amount to which the rate is applied increases.
- A lump-sum tax is a tax that is a fixed amount, no matter the change in circumstance of the taxed entity. This in actuality is a regressive tax as those with lower income must use a higher percentage of their income than those with higher income and therefore the effect of the tax reduces as a function of income.
The terms can also be used to apply meaning to the taxation of select consumption, such as a tax on luxury goods and the exemption of basic necessities may be described as having progressive effects as it increases a tax burden on high end consumption and decreases a tax burden on low end consumption.
Direct and indirect
Taxes are sometimes referred to as "direct taxes" or "indirect taxes". The meaning of these terms can vary in different contexts, which can sometimes lead to confusion. An economic definition, by Atkinson, states that "...direct taxes may be adjusted to the individual characteristics of the taxpayer, whereas indirect taxes are levied on transactions irrespective of the circumstances of buyer or seller." According to this definition, for example, income tax is "direct", and sales tax is "indirect".
In law, the terms may have different meanings. In U.S. constitutional law, for instance, direct taxes refer to poll taxes and property taxes, which are based on simple existence or ownership. Indirect taxes are imposed on events, rights, privileges, and activities. Thus, a tax on the sale of the property would be considered an indirect tax, whereas the tax on simply owning the property itself would be a direct tax.
Fees and effective
Governments may charge user fees, tolls, or other types of assessments in exchange of particular goods, services, or use of property. These are generally not considered taxes, as long as they are levied as payment for a direct benefit to the individual paying. Such fees include:
- Tolls: a fee charged to travel via a road, bridge, tunnel, canal, waterway or other transportation facilities. Historically tolls have been used to pay for public bridge, road, and tunnel projects. They have also been used in privately constructed transport links. The toll is likely to be a fixed charge, possibly graduated for vehicle type, or for distance on long routes.
- User fees, such as those charged for use of parks or other government-owned facilities.
- Ruling fees charged by governmental agencies to make determinations in particular situations.
Some scholars refer to certain economic effects as taxes, though they are not levies imposed by governments. These include:
- Inflation tax: the economic disadvantage suffered by holders of cash and cash equivalents in one denomination of currency due to the effects of expansionary monetary policy
- Financial repression: Government policies such as interest-rate caps on government debt, financial regulations such as reserve requirements and capital controls, and barriers to entry in markets where the government owns or controls businesses.
History
The first known system of taxation was in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC, in the First Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. The earliest and most widespread forms of taxation were the corvée and the tithe. The corvée was forced labour provided to the state by peasants too poor to pay other forms of taxation (labor in ancient Egyptian is a synonym for taxes). Records from the time document that the Pharaoh would conduct a biennial tour of the kingdom, collecting tithes from the people. Other records are granary receipts on limestone flakes and papyrus. Early taxation is also described in the Bible. In Genesis (chapter 47, verse 24 – the New International Version), it states "But when the crop comes in, give a fifth of it to Pharaoh. The other four-fifths you may keep as seed for the fields and as food for yourselves and your households and your children". Samgharitr is the name mentioned for the Tax collector in the Vedic texts. In Hattusa, the capital of the Hittite Empire, grains were collected as a tax from the surrounding lands, and stored in silos as a display of the king's wealth.
In the Persian Empire, a regulated and sustainable tax system was introduced by Darius I the Great in 500 BC; the Persian system of taxation was tailored to each Satrapy (the area ruled by a Satrap or provincial governor). At differing times, there were between 20 and 30 Satrapies in the Empire and each was assessed according to its supposed productivity. It was the responsibility of the Satrap to collect the due amount and to send it to the treasury, after deducting his expenses (the expenses and the power of deciding precisely how and from whom to raise the money in the province, offer maximum opportunity for rich pickings). The quantities demanded from the various provinces gave a vivid picture of their economic potential. For instance, Babylon was assessed for the highest amount and for a startling mixture of commodities; 1,000 silver talents and four months supply of food for the army. India, a province fabled for its gold, was to supply gold dust equal in value to the very large amount of 4,680 silver talents. Egypt was known for the wealth of its crops; it was to be the granary of the Persian Empire (and, later, of the Roman Empire) and was required to provide 120,000 measures of grain in addition to 700 talents of silver. This tax was exclusively levied on Satrapies based on their lands, productive capacity and tribute levels.
The Rosetta Stone, a tax concession issued by Ptolemy V in 196 BC and written in three languages "led to the most famous decipherment in history—the cracking of hieroglyphics".
Islamic rulers imposed Zakat (a tax on Muslims) and Jizya (a poll tax on conquered non-Muslims). In India this practice began in the 11th century.
Trends
Numerous records of government tax collection in Europe since at least the 17th century are still available today. But taxation levels are hard to compare to the size and flow of the economy since production numbers are not as readily available. Government expenditures and revenue in France during the 17th century went from about 24.30 million livres in 1600–10 to about 126.86 million livres in 1650–59 to about 117.99 million livres in 1700–10 when government debt had reached 1.6 billion livres. In 1780–89, it reached 421.50 million livres. Taxation as a percentage of production of final goods may have reached 15–20% during the 17th century in places such as France, the Netherlands, and Scandinavia. During the war-filled years of the eighteenth and early nineteenth century, tax rates in Europe increased dramatically as war became more expensive and governments became more centralized and adept at gathering taxes. This increase was greatest in England, Peter Mathias and Patrick O'Brien found that the tax burden increased by 85% over this period. Another study confirmed this number, finding that per capita tax revenues had grown almost sixfold over the eighteenth century, but that steady economic growth had made the real burden on each individual only double over this period before the industrial revolution. Effective tax rates were higher in Britain than France the years before the French Revolution, twice in per capita income comparison, but they were mostly placed on international trade. In France, taxes were lower but the burden was mainly on landowners, individuals, and internal trade and thus created far more resentment.
Taxation as a percentage of GDP 2016 was 45.9% in Denmark, 45.3% in France, 33.2% in the United Kingdom, 26% in the United States, and among all OECD members an average of 34.3%.
Forms
In monetary economies prior to fiat banking, a critical form of taxation was seigniorage, the tax on the creation of money.
Other obsolete forms of taxation include:
- Scutage, which is paid in lieu of military service; strictly speaking, it is a commutation of a non-tax obligation rather than a tax as such but functioning as a tax in practice.
- Tallage, a tax on feudal dependents.
- Tithe, a tax-like payment (one-tenth of one's earnings or agricultural produce), paid to the Church (and thus too specific to be a tax in strict technical terms). This should not be confused with the modern practice of the same name which is normally voluntary.
- (Feudal) aids, a type of tax or due that was paid by a vassal to his lord during feudal times.
- Danegeld, a medieval land tax originally raised to pay off raiding Danes and later used to fund military expenditures.
- Carucage, a tax which replaced the Danegeld in England.
- Tax farming, the principle of assigning the responsibility for tax revenue collection to private citizens or groups.
- Socage, a feudal tax system based on land rent.
- Burgage, a feudal tax system based on land rent.
Some principalities taxed windows, doors, or cabinets to reduce consumption of imported glass and hardware. Armoires, hutches, and wardrobes were employed to evade taxes on doors and cabinets. In some circumstances, taxes are also used to enforce public policy like congestion charge (to cut road traffic and encourage public transport) in London. In Tsarist Russia, taxes were clamped on beards. Today, one of the most-complicated taxation systems worldwide is in Germany. Three-quarters of the world's taxation literature refers to the German system. Under the German system, there are 118 laws, 185 forms, and 96,000 regulations, spending €3.7 billion to collect the income tax. In the United States, the IRS has about 1,177 forms and instructions, 28.4111 megabytes of Internal Revenue Code which contained 3.8 million words as of 1 February 2010, numerous tax regulations in the Code of Federal Regulations, and supplementary material in the Internal Revenue Bulletin. Today, governments in more advanced economies (i.e. Europe and North America) tend to rely more on direct taxes, while developing economies (i.e. several African countries) rely more on indirect taxes.
Economic effects
In economic terms, taxation transfers wealth from households or businesses to the government of a nation. Adam Smith writes in The Wealth of Nations that
- "…the economic incomes of private people are of three main types: rent, profit, and wages. Ordinary taxpayers will ultimately pay their taxes from at least one of these revenue sources. The government may intend that a particular tax should fall exclusively on rent, profit, or wages – and that another tax should fall on all three private income sources jointly. However, many taxes will inevitably fall on resources and persons very different from those intended … Good taxes meet four major criteria. They are (1) proportionate to incomes or abilities to pay (2) certain rather than arbitrary (3) payable at times and in ways convenient to the taxpayers and (4) cheap to administer and collect."
The side-effects of taxation (such as economic distortions) and theories about how best to tax are an important subject in microeconomics. Taxation is almost never a simple transfer of wealth. Economic theories of taxation approach the question of how to maximize economic welfare through taxation.
A 2019 study looking at the impact of tax cuts for different income groups, it was tax cuts for low-income groups that had the greatest positive impact on employment growth. Tax cuts for the wealthiest top 10% had a small impact.
Incidence
Law establishes from whom a tax is collected. In many countries, taxes are imposed on businesses (such as corporate taxes or portions of payroll taxes). However, who ultimately pays the tax (the tax "burden") is determined by the marketplace as taxes become embedded into production costs. Economic theory suggests that the economic effect of tax does not necessarily fall at the point where it is legally levied. For instance, a tax on employment paid by employers will impact the employee, at least in the long run. The greatest share of the tax burden tends to fall on the most inelastic factor involved—the part of the transaction which is affected least by a change in price. So, for instance, a tax on wages in a town will (at least in the long run) affect property-owners in that area.
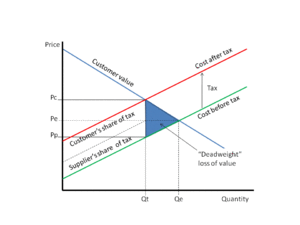
Depending on how quantities supplied and demanded to vary with price (the "elasticities" of supply and demand), a tax can be absorbed by the seller (in the form of lower pre-tax prices), or by the buyer (in the form of higher post-tax prices). If the elasticity of supply is low, more of the tax will be paid by the supplier. If the elasticity of demand is low, more will be paid by the customer; and, contrariwise for the cases where those elasticities are high. If the seller is a competitive firm, the tax burden is distributed over the factors of production depending on the elasticities thereof; this includes workers (in the form of lower wages), capital investors (in the form of loss to shareholders), landowners (in the form of lower rents), entrepreneurs (in the form of lower wages of superintendence) and customers (in the form of higher prices).
To show this relationship, suppose that the market price of a product is $1.00 and that a $0.50 tax is imposed on the product that, by law, is to be collected from the seller. If the product has an elastic demand, a greater portion of the tax will be absorbed by the seller. This is because goods with elastic demand cause a large decline in quantity demanded a small increase in price. Therefore, in order to stabilize sales, the seller absorbs more of the additional tax burden. For example, the seller might drop the price of the product to $0.70 so that, after adding in the tax, the buyer pays a total of $1.20, or $0.20 more than he did before the $0.50 tax was imposed. In this example, the buyer has paid $0.20 of the $0.50 tax (in the form of a post-tax price) and the seller has paid the remaining $0.30 (in the form of a lower pre-tax price).
Increased economic welfare
Government spending
The purpose of taxation is to provide for government spending without inflation. The provision of public goods such as roads and other infrastructure, schools, a social safety net, public health systems, national defense, law enforcement, and a courts system increases the economic welfare of society if the benefit outweighs the costs involved.
Pigovian
The existence of a tax can increase economic efficiency in some cases. If there is a negative externality associated with a good (meaning that it has negative effects not felt by the consumer) then a free market will trade too much of that good. By taxing the good, the government can raise revenue to address specific problems while increasing overall welfare.
The goal is to tax people when they're creating societal costs in addition to their personal costs. By taxing goods with negative externalities, the government attempts to increase economic efficiency while raising revenues.
This type of tax is called a Pigovian tax, after economist Arthur Pigou who wrote about it in his 1920 book "The Economics of Welfare".
Pigovian taxes might target the undesirable production of greenhouse gases which cause climate change (namely a carbon tax), polluting fuels (such as petrol), water or air pollution (namely an ecotax), goods which incur public healthcare costs (such as alcohol or tobacco), and excess demand of certain public goods (such as traffic congestion pricing). The idea is to aim taxes at people that cause an above-average amount of societal harm so the free market incorporates all costs as opposed to only personal costs, with the benefit of lowering the overall tax burden for people who cause less societal harm.
Reduced inequality
Progressive taxation generally reduces economic inequality, even when the tax revenue is not redistributed from higher-income individuals to lower-income individuals. However, in a highly specific condition, progressive taxation increases economic inequality when lower-income individuals consume goods and services produced by higher-income individuals, who in turn consume only from other higher-income individuals (trickle-up effect).
Reduced economic welfare
Most taxes (see below) have side effects that reduce economic welfare, either by mandating unproductive labor (compliance costs) or by creating distortions to economic incentives (deadweight loss and perverse incentives).
Cost of compliance
Although governments must spend money on tax collection activities, some of the costs, particularly for keeping records and filling out forms, are borne by businesses and by private individuals. These are collectively called costs of compliance. More complex tax systems tend to have higher compliance costs. This fact can be used as the basis for practical or moral arguments in favor of tax simplification (such as the FairTax or OneTax, and some flat tax proposals).
Deadweight costs
In the absence of negative externalities, the introduction of taxes into a market reduces economic efficiency by causing deadweight loss. In a competitive market, the price of a particular economic good adjusts to ensure that all trades which benefit both the buyer and the seller of a good occur. The introduction of a tax causes the price received by the seller to be less than the cost to the buyer by the amount of the tax. This causes fewer transactions to occur, which reduces economic welfare; the individuals or businesses involved are less well off than before the tax. The tax burden and the amount of deadweight cost is dependent on the elasticity of supply and demand for the good taxed.
Most taxes—including income tax and sales tax—can have significant deadweight costs. The only way to avoid deadweight costs in an economy that is generally competitive is to refrain from taxes that change economic incentives. Such taxes include the land value tax, where the tax is on a good in completely inelastic supply. By taxing the value of unimproved land as opposed to what's built on it, a land value tax does not increase taxes on landowners for improving their land. This is opposed to traditional property taxes which reward land abandonment and disincentivize construction, maintenance, and repair. Another example of a tax with few deadweight costs is a lump sum tax such as a poll tax (head tax) which is paid by all adults regardless of their choices. Arguably a windfall profits tax which is entirely unanticipated can also fall into this category.
Deadweight loss does not account for the effect taxes have in leveling the business playing field. Businesses that have more money are better suited to fend off competition. It is common that an industry with a small amount of very large corporations has a very high barrier of entry for new entrants coming into the marketplace. This is due to the fact that the larger the corporation, the better its position to negotiate with suppliers. Also, larger companies may be able to operate at low or even negative profits for extended periods of time, thus pushing out competition. More progressive taxation of profits, however, would reduce such barriers for new entrants, thereby increasing competition and ultimately benefiting consumers.
Perverse incentives
Complexity of the tax code in developed economies offers perverse tax incentives. The more details of tax policy there are, the more opportunities for legal tax avoidance and illegal tax evasion. These not only result in lost revenue but involve additional costs: for instance, payments made for tax advice are essentially deadweight costs because they add no wealth to the economy. Perverse incentives also occur because of non-taxable 'hidden' transactions; for instance, a sale from one company to another might be liable for sales tax, but if the same goods were shipped from one branch of a corporation to another, no tax would be payable.
To address these issues, economists often suggest simple and transparent tax structures that avoid providing loopholes. Sales tax, for instance, can be replaced with a value added tax which disregards intermediate transactions.
In developing countries
Following Nicolas Kaldor's research, public finance in developing countries is strongly tied to state capacity and financial development. As state capacity develops, states not only increase the level of taxation but also the pattern of taxation. With the increase of larger tax bases and the diminish of the importance of trading tax, while income tax gains more importance. According to Tilly's argument, state capacity evolves as a response to the emergence of war. War is an incentive for states to raise taxes and strengthen states' capacity. Historically, many taxation breakthroughs took place during wartime. The introduction of income tax in Britain was due to the Napoleonic War in 1798. The US first introduced income tax during the Civil War. Taxation is constrained by the fiscal and legal capacities of a country. Fiscal and legal capacities also complement each other. A well-designed tax system can minimize efficiency loss and boost economic growth. With better compliance and better support to financial institutions and individual property, the government will be able to collect more tax. Although wealthier countries have higher tax revenue, economic growth does not always translate to higher tax revenue. For example, in India, increases in exemptions lead to the stagnation of income tax revenue at around 0.5% of GDP since 1986.
Researchers for EPS PEAKS stated that the core purpose of taxation is revenue mobilisation, providing resources for National Budgets, and forming an important part of macroeconomic management. They said economic theory has focused on the need to 'optimize' the system through balancing efficiency and equity, understanding the impacts on production, and consumption as well as distribution, redistribution, and welfare.
They state that taxes and tax reliefs have also been used as a tool for behavioral change, to influence investment decisions, labor supply, consumption patterns, and positive and negative economic spill-overs (externalities), and ultimately, the promotion of economic growth and development. The tax system and its administration also play an important role in state-building and governance, as a principal form of 'social contract' between the state and citizens who can, as taxpayers, exert accountability on the state as a consequence.
The researchers wrote that domestic revenue forms an important part of a developing country's public financing as it is more stable and predictable than Overseas Development Assistance and necessary for a country to be self-sufficient. They found that domestic revenue flows are, on average, already much larger than ODA, with aid worth less than 10% of collected taxes in Africa as a whole.
However, in a quarter of African countries Overseas Development Assistance does exceed tax collection, with these more likely to be non-resource-rich countries. This suggests countries making the most progress replacing aid with tax revenue tend to be those benefiting disproportionately from rising prices of energy and commodities.
The author found tax revenue as a percentage of GDP varying greatly around a global average of 19%. This data also indicates countries with higher GDP tend to have higher tax to GDP ratios, demonstrating that higher income is associated with more than proportionately higher tax revenue. On average, high-income countries have tax revenue as a percentage of GDP of around 22%, compared to 18% in middle-income countries and 14% in low-income countries.
In high-income countries, the highest tax-to-GDP ratio is in Denmark at 47% and the lowest is in Kuwait at 0.8%, reflecting low taxes from strong oil revenues. The long-term average performance of tax revenue as a share of GDP in low-income countries has been largely stagnant, although most have shown some improvement in more recent years. On average, resource-rich countries have made the most progress, rising from 10% in the mid-1990s to around 17% in 2008. Non-resource-rich countries made some progress, with average tax revenues increasing from 10% to 15% over the same period.
Many low-income countries have a tax-to-GDP ratio of less than 15% which could be due to low tax potentials, such as a limited taxable economic activity, or low tax effort due to policy choice, non-compliance, or administrative constraints.
Some low-income countries have relatively high tax-to-GDP ratios due to resource tax revenues (e.g. Angola) or relatively efficient tax administration (e.g. Kenya, Brazil) whereas some middle-income countries have lower tax-to-GDP ratios (e.g. Malaysia) which reflect a more tax-friendly policy choice.
While overall tax revenues have remained broadly constant, the global trend shows trade taxes have been declining as a proportion of total revenues(IMF, 2011), with the share of revenue shifting away from border trade taxes towards domestically levied sales taxes on goods and services. Low-income countries tend to have a higher dependence on trade taxes, and a smaller proportion of income and consumption taxes when compared to high-income countries.
One indicator of the taxpaying experience was captured in the 'Doing Business' survey, which compares the total tax rate, time spent complying with tax procedures, and the number of payments required through the year, across 176 countries. The 'easiest' countries in which to pay taxes are located in the Middle East with the UAE ranking first, followed by Qatar and Saudi Arabia, most likely reflecting low tax regimes in those countries. Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa are among the 'hardest' to pay with the Central African Republic, Republic of Congo, Guinea and Chad in the bottom 5, reflecting higher total tax rates and a greater administrative burden to comply.
Key facts
The below facts were compiled by EPS PEAKS researchers:
- Trade liberalisation has led to a decline in trade taxes as a share of total revenues and GDP.
- Resource-rich countries tend to collect more revenue as a share of GDP, but this is more volatile. Sub-Saharan African countries that are resource-rich have performed better tax collecting than non-resource-rich countries, but revenues are more volatile from year to year. By strengthening revenue management, there are huge opportunities for investment for development and growth.
- Developing countries have an informal sector representing an average of around 40%, perhaps up to 60% in some. Informal sectors feature many small informal traders who may not be efficient in bringing into the tax net since the cost of collection is high and revenue potential limited (although there are broader governance benefits). There is also an issue of non-compliant companies who are 'hard to tax', evading taxes and should be brought into the tax net.
- In many low-income countries, the majority of revenue is collected from a narrow tax base, sometimes because of a limited range of taxable economic activities. There is therefore dependence on few taxpayers, often multinationals, that can exacerbate the revenue challenge by minimizing their tax liability, in some cases abusing a lack of capacity in revenue authorities, sometimes through transfer pricing abuse.
- Developing and developed countries face huge challenges in taxing multinationals and international citizens. Estimates of tax revenue losses from evasion and avoidance in developing countries are limited by a lack of data and methodological shortcomings, but some estimates are significant.
- Countries use incentives to attract investment but doing this may be unnecessarily giving up revenue as evidence suggests that investors are influenced more by economic fundamentals like market size, infrastructure, and skills, and only marginally by tax incentives (IFC investor surveys). For example, even though the Armenian government supports the IT sector and improves the investment climate, the small size of the domestic market, low wages, low demand for productivity enhancement tools, financial constraints, high software piracy rates, and other factors make growth in this sector a slow process. Meaning that tax incentives do not contribute to the development of the sector as much as it is thought to contribute.
- In low-income countries, compliance costs are high, they are lengthy processes, frequent tax payments, bribes and corruption.
- Administrations are often under-resourced, resources aren't effectively targeted on areas of greatest impact, and mid-level management is weak. Coordination between domestic and customs is weak, which is especially important for VAT. Weak administration, governance, and corruption tend to be associated with low revenue collections (IMF, 2011).
- Evidence on the effect of aid on tax revenues is inconclusive. Tax revenue is more stable and sustainable than aid. While a disincentive effect of aid on revenue may be expected and was supported by some early studies, recent evidence does not support that conclusion, and in some cases, points towards higher tax revenue following support for revenue mobilization.
- Of all regions, Africa has the highest total tax rates borne by the business at 57.4% of the profit on average but has reduced the most since 2004, from 70%, partly due to introducing VAT and this is likely to have a beneficial effect on attracting investment.
- Fragile states are less able to expand tax revenue as a percentage of GDP and any gains are more difficult to sustain. Tax administration tends to collapse if conflict reduces state-controlled territory or reduces productivity. As economies are rebuilt after conflicts, there can be good progress in developing effective tax systems. Liberia expanded from 10.6% of GDP in 2003 to 21.3% in 2011. Mozambique increased from 10.5% of GDP in 1994 to around 17.7% in 2011.
Summary
Aid interventions in revenue can support revenue mobilization for growth, improve tax system design and administrative effectiveness, and strengthen governance and compliance. The author of the Economics Topic Guide found that the best aid modalities for revenue depend on country circumstances, but should aim to align with government interests and facilitate effective planning and implementation of activities under evidence-based tax reform. Lastly, she found that identifying areas for further reform requires country-specific diagnostic assessment: broad areas for developing countries identified internationally (e.g. IMF) include, for example, property taxation for local revenues, strengthening expenditure management, and effective taxation of extractive industries and multinationals.
Views
Support
Every tax, however, is, to the person who pays it, a badge, not of slavery, but of liberty. – Adam Smith (1776), Wealth of Nations
According to most political philosophies, taxes are justified as they fund activities that are necessary and beneficial to society. Additionally, progressive taxation can be used to reduce economic inequality in a society. According to this view, taxation in modern nation-states benefit the majority of the population and social development. A common presentation of this view, paraphrasing various statements by Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. is "Taxes are the price of civilization".
It can also be argued that in a democracy, because the government is the party performing the act of imposing taxes, society as a whole decides how the tax system should be organized. The American Revolution's "No taxation without representation" slogan implied this view. For traditional conservatives, the payment of taxation is justified as part of the general obligations of citizens to obey the law and support established institutions. The conservative position is encapsulated in perhaps the most famous adage of public finance, "An old tax is a good tax". Conservatives advocate the "fundamental conservative premise that no one should be excused from paying for government, lest they come to believe that government is costless to them with the certain consequence that they will demand more government 'services'." Social democrats generally favor higher levels of taxation to fund public provision of a wide range of services such as universal health care and education, as well as the provision of a range of welfare benefits. As argued by Anthony Crosland and others, the capacity to tax income from capital is a central element of the social democratic case for a mixed economy as against Marxist arguments for comprehensive public ownership of capital. American libertarians recommend a minimal level of taxation in order to maximize the protection of liberty.
Compulsory taxation of individuals, such as income tax, is often justified on grounds including territorial sovereignty, and the social contract. Defenders of business taxation argue that it is an efficient method of taxing income that ultimately flows to individuals, or that separate taxation of business is justified on the grounds that commercial activity necessarily involves the use of publicly established and maintained economic infrastructure, and that businesses are in effect charged for this use. Georgist economists argue that all of the economic rent collected from natural resources (land, mineral extraction, fishing quotas, etc.) is unearned income, and belongs to the community rather than any individual. They advocate a high tax (the "Single Tax") on land and other natural resources to return this unearned income to the state, but no other taxes.
Against
Because payment of tax is compulsory and enforced by the legal system, rather than voluntary like crowdfunding, some political philosophies view taxation as theft, extortion, (or as slavery, or as a violation of property rights), or tyranny, accusing the government of levying taxes via force and coercive means. Objectivists, anarcho-capitalists, and right-wing libertarians see taxation as government aggression (see non-aggression principle). The view that democracy legitimizes taxation is rejected by those who argue that all forms of government, including laws chosen by democratic means, are fundamentally oppressive. According to Ludwig von Mises, "society as a whole" should not make such decisions, due to methodological individualism. Libertarian opponents of taxation claim that governmental protection, such as police and defense forces might be replaced by market alternatives such as private defense agencies, arbitration agencies or voluntary contributions.
Socialism
Karl Marx assumed that taxation would be unnecessary after the advent of communism and looked forward to the "withering away of the state". In socialist economies such as that of China, taxation played a minor role, since most government income was derived from the ownership of enterprises, and it was argued by some that monetary taxation was not necessary. While the morality of taxation is sometimes questioned, most arguments about taxation revolve around the degree and method of taxation and associated government spending, not taxation itself.
Choice
Tax choice is the theory that taxpayers should have more control with how their individual taxes are allocated. If taxpayers could choose which government organizations received their taxes, opportunity cost decisions would integrate their partial knowledge. For example, a taxpayer who allocated more of his taxes on public education would have less to allocate on public healthcare. Supporters argue that allowing taxpayers to demonstrate their preferences would help ensure that the government succeeds at efficiently producing the public goods that taxpayers truly value. This would end real estate speculation, business cycles, unemployment and distribute wealth much more evenly. Joseph Stiglitz's Henry George Theorem predicts its sufficiency because—as George also noted—public spending raises land value.
Geoism
Geoists (Georgists and geolibertarians) state that taxation should primarily collect economic rent, in particular the value of land, for both reasons of economic efficiency as well as morality. The efficiency of using economic rent for taxation is (as economists agree) due to the fact that such taxation cannot be passed on and does not create any dead-weight loss, and that it removes the incentive to speculate on land. Its morality is based on the Geoist premise that private property is justified for products of labour but not for land and natural resources.
Economist and social reformer Henry George opposed sales taxes and protective tariffs for their negative impact on trade. He also believed in the right of each person to the fruits of their own labour and productive investment. Therefore, income from labour and proper capital should remain untaxed. For this reason many Geoists—in particular those that call themselves geolibertarian—share the view with libertarians that these types of taxation (but not all) are immoral and even theft. George stated there should be one single tax: the Land Value Tax, which is considered both efficient and moral. Demand for specific land is dependent on nature, but even more so on the presence of communities, trade, and government infrastructure, particularly in urban environments. Therefore, the economic rent of land is not the product of one particular individual and it may be claimed for public expenses. According to George, this would end real estate bubbles, business cycles, unemployment and distribute wealth much more evenly. Joseph Stiglitz's Henry George Theorem predicts its sufficiency for financing public goods because those raise land value.
John Locke stated that whenever labour is mixed with natural resources, such as is the case with improved land, private property is justified under the proviso that there must be enough other natural resources of the same quality available to others. Geoists state that the Lockean proviso is violated wherever land value is greater than zero. Therefore, under the assumed principle of equal rights of all people to natural resources, the occupier of any such land must compensate the rest of society to the amount of that value. For this reason, geoists generally believe that such payment cannot be regarded as a true 'tax', but rather a compensation or fee. This means that while Geoists also regard taxation as an instrument of social justice, contrary to social democrats and social liberals they do not regard it as an instrument of redistribution but rather a 'predistribution' or simply a correct distribution of the commons.
Modern geoists note that land in the classical economic meaning of the word referred to all natural resources, and thus also includes resources such as mineral deposits, water bodies and the electromagnetic spectrum, to which privileged access also generates economic rent that must be compensated. Under the same reasoning most of them also consider pigouvian taxes as compensation for environmental damage or privilege as acceptable and even necessary.
Theories
Laffer curve
In economics, the Laffer curve is a theoretical representation of the relationship between government revenue raised by taxation and all possible rates of taxation. It is used to illustrate the concept of taxable income elasticity (that taxable income will change in response to changes in the rate of taxation). The curve is constructed by thought experiment. First, the amount of tax revenue raised at the extreme tax rates of 0% and 100% is considered. It is clear that a 0% tax rate raises no revenue, but the Laffer curve hypothesis is that a 100% tax rate will also generate no revenue because at such a rate there is no longer any incentive for a rational taxpayer to earn any income, thus the revenue raised will be 100% of nothing. If both a 0% rate and 100% rate of taxation generate no revenue, it follows from the extreme value theorem that there must exist at least one rate in between where tax revenue would be a maximum. The Laffer curve is typically represented as a graph that starts at 0% tax, zero revenue, rises to a maximum rate of revenue raised at an intermediate rate of taxation, and then falls again to zero revenue at a 100% tax rate.
One potential result of the Laffer curve is that increasing tax rates beyond a certain point will become counterproductive for raising further tax revenue. A hypothetical Laffer curve for any given economy can only be estimated and such estimates are sometimes controversial. The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics reports that estimates of revenue-maximizing tax rates have varied widely, with a mid-range of around 70%.
Optimal
Most governments take revenue that exceeds that which can be provided by non-distortionary taxes or through taxes that give a double dividend. Optimal taxation theory is the branch of economics that considers how taxes can be structured to give the least deadweight costs, or to give the best outcomes in terms of social welfare. The Ramsey problem deals with minimizing deadweight costs. Because deadweight costs are related to the elasticity of supply and demand for a good, it follows that putting the highest tax rates on the goods for which there are most inelastic supply and demand will result in the least overall deadweight costs. Some economists sought to integrate optimal tax theory with the social welfare function, which is the economic expression of the idea that equality is valuable to a greater or lesser extent. If individuals experience diminishing returns from income, then the optimum distribution of income for society involves a progressive income tax. Mirrlees optimal income tax is a detailed theoretical model of the optimum progressive income tax along these lines. Over the last years the validity of the theory of optimal taxation was discussed by many political economists.
Rates
Taxes are most often levied as a percentage, called the tax rate. An important distinction when talking about tax rates is to distinguish between the marginal rate and the effective tax rate. The effective rate is the total tax paid divided by the total amount the tax is paid on, while the marginal rate is the rate paid on the next dollar of income earned. For example, if income is taxed on a formula of 5% from $0 up to $50,000, 10% from $50,000 to $100,000, and 15% over $100,000, a taxpayer with income of $175,000 would pay a total of $18,750 in taxes.
- Tax calculation
- (0.05*50,000) + (0.10*50,000) + (0.15*75,000) = 18,750
- The "effective rate" would be 10.7%:
- 18,750/175,000 = 0.107
- The "marginal rate" would be 15%.