 |
| This article is part of a series on |
| Anatomical terminology |
|---|
Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors.
Anatomical terminology uses many unique terms, suffixes, and prefixes deriving from Ancient Greek and Latin. These terms can be confusing to those unfamiliar with them, but can be more precise, reducing ambiguity and errors. Also, since these anatomical terms are not used in everyday conversation, their meanings are less likely to change, and less likely to be misinterpreted.
To illustrate how inexact day-to-day language can be: a scar "above the wrist" could be located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand or at the base of the hand; and could be on the palm-side or back-side of the arm. By using precise anatomical terminology such ambiguity is eliminated.
An international standard for anatomical terminology, Terminologia Anatomica has been created.
Word formation
Anatomical terminology has quite regular morphology: the same prefixes and suffixes are used to add meanings to different roots. The root of a term often refers to an organ or tissue. For example, the Latin names of structures such as musculus biceps brachii can be split up and refer to, musculus for muscle, biceps for "two-headed", brachii as in the brachial region of the arm. The first word describes what is being spoken about, the second describes it, and the third points to location.
When describing the position of anatomical structures, structures may be described according to the anatomical landmark they are near. These landmarks may include structures, such as the umbilicus or sternum, or anatomical lines, such as the midclavicular line from the centre of the clavicle. The cephalon or cephalic region refers to the head. This area is further differentiated into the cranium (skull), facies (face), frons (forehead), oculus (eye area), auris (ear), bucca (cheek), nasus (nose), os (mouth), and mentum (chin). The neck area is called the cervix or cervical region. Examples of structures named according to this include the frontalis muscle, submental lymph nodes, buccal membrane and orbicularis oculi muscle.
Sometimes, unique terminology is used to reduce confusion in different parts of the body. For example, different terms are used when it comes to the skull in compliance with its embryonic origin and its tilted position compared to in other animals. Here, rostral refers to proximity to the front of the nose, and is particularly used when describing the skull. Similarly, different terminology is often used in the arms, in part to reduce ambiguity as to what the "front", "back", "inner" and "outer" surfaces are. For this reason, the terms below are used:
- Radial referring to the radius bone, seen laterally in the standard anatomical position.
- Ulnar referring to the ulna bone, medially positioned when in the standard anatomical position.
Other terms are also used to describe the movement and actions of the hands and feet, and other structures such as the eye.
History
International morphological terminology is used by the colleges of medicine and dentistry and other areas of the health sciences. It facilitates communication and exchanges between scientists from different countries of the world and it is used daily in the fields of research, teaching and medical care. The international morphological terminology refers to morphological sciences as a biological sciences' branch. In this field, the form and structure are examined as well as the changes or developments in the organism. It is descriptive and functional. Basically, it covers the gross anatomy and the microscopic (histology and cytology) of living beings. It involves both development anatomy (embryology) and the anatomy of the adult. It also includes comparative anatomy between different species. The vocabulary is extensive, varied and complex, and requires a systematic presentation.
Within the international field, a group of experts reviews, analyzes and discusses the morphological terms of the structures of the human body, forming today's Terminology Committee (FICAT) from the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA). It deals with the anatomical, histological and embryologic terminology. In the Latin American field, there are meetings called Iberian Latin American Symposium Terminology (SILAT), where a group of experts of the Pan American Association of Anatomy (PAA) that speak Spanish and Portuguese, disseminates and studies the international morphological terminology.
The current international standard for human anatomical terminology is based on the Terminologia Anatomica (TA). It was developed by the Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) and the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) and was released in 1998. It supersedes the previous standard, Nomina Anatomica. Terminologia Anatomica contains terminology for about 7500 human gross (macroscopic) anatomical structures. For microanatomy, known as histology, a similar standard exists in Terminologia Histologica, and for embryology, the study of development, a standard exists in Terminologia Embryologica. These standards specify generally accepted names that can be used to refer to histological and embryological structures in journal articles, textbooks, and other areas. As of September 2016, two sections of the Terminologia Anatomica, including central nervous system and peripheral nervous system, were merged to form the Terminologia Neuroanatomica.
Recently, the Terminologia Anatomica has been perceived with a considerable criticism regarding its content including coverage, grammar and spelling mistakes, inconsistencies, and errors.
Location
Anatomical terminology is often chosen to highlight the relative location of body structures. For instance, an anatomist might describe one band of tissue as "inferior to" another or a physician might describe a tumor as "superficial to" a deeper body structure.
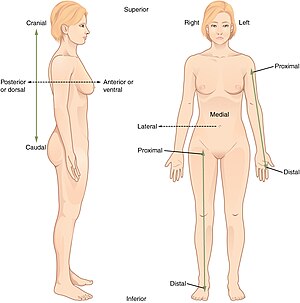
Anatomical position
Anatomical terms used to describe location are based on a body positioned in what is called the standard anatomical position. This position is one in which a person is standing, feet apace, with palms forward and thumbs facing outwards. Just as maps are normally oriented with north at the top, the standard body "map," or anatomical position, is that of the body standing upright, with the feet at shoulder width and parallel, toes forward. The upper limbs are held out to each side, and the palms of the hands face forward.
Using the standard anatomical position reduces confusion. It means that regardless of the position of a body, the position of structures within it can be described without ambiguity.
Regions
In terms of anatomy, the body is divided into regions. In the front, the trunk is referred to as the "thorax" and "abdomen". The back as a general area is the dorsum or dorsal area, and the lower back is the lumbus or lumbar region. The shoulder blades are the scapular area and the breastbone is the sternal region. The abdominal area is the region between the chest and the pelvis. The breast is also called the mammary region, the armpit as the axilla and axillary, and the navel as the umbilicus and umbilical. The pelvis is the lower torso, between the abdomen and the thighs. The groin, where the thigh joins the trunk, are the inguen and inguinal area.
The entire arm is referred to as the brachium and brachial, the front of the elbow as the antecubitis and antecubital, the back of the elbow as the olecranon or olecranal, the forearm as the antebrachium and antebrachial, the wrist as the carpus and carpal area, the hand as the manus and manual, the palm as the palma and palmar, the thumb as the pollex, and the fingers as the digits, phalanges, and phalangeal. The buttocks are the gluteus or gluteal region and the pubic area is the pubis.
Anatomists divide the lower limb into the thigh (the part of the limb between the hip and the knee) and the leg (which refers only to the area of the limb between the knee and the ankle). The thigh is the femur and the femoral region. The kneecap is the patella and patellar while the back of the knee is the popliteus and popliteal area. The leg (between the knee and the ankle) is the crus and crural area, the lateral aspect of the leg is the peroneal area, and the calf is the sura and sural region. The ankle is the tarsus and tarsal, and the heel is the calcaneus or calcaneal. The foot is the pes and pedal region, and the sole of the foot is the planta and plantar. As with the fingers, the toes are also called the digits, phalanges, and phalangeal area. The big toe is referred to as the hallux.
Abdomen
To promote clear communication, for instance about the location of a patient’s abdominal pain or a suspicious mass, the abdominal cavity can be divided into either nine regions or four quadrants.
- Quadrants
The abdomen may be divided into four quadrants, more commonly used in medicine, subdivides the cavity with one horizontal and one vertical line that intersect at the patient’s umbilicus (navel). The right upper quadrant (RUQ) includes the lower right ribs, right side of the liver, and right side of the transverse colon. The left upper quadrant (LUQ) includes the lower left ribs, stomach, spleen, and upper left area of the transverse colon. The right lower quadrant (RLQ) includes the right half of the small intestines, ascending colon, right pelvic bone and upper right area of the bladder. The left lower quadrant (LLQ) contains the left half of the small intestine and left pelvic bone.
- Regions
The more detailed regional approach subdivides the cavity into nine regions, with two vertical and two horizontal lines drawn according to landmark structures. The vertical; or midclavicular lines, are drawn as if dropped from the midpoint of each clavicle. The superior horizontal line is the subcostal line, drawn immediately inferior to the ribs. The inferior horizontal line is called the intertubercular line, and is to cross the iliac tubercles, found at the superior aspect of the pelvis. The upper right square is the right hypochondriac region and contains the base of the right ribs. The upper left square is the left hypochondriac region and contains the base of the left ribs.
The epigastric region is the upper central square and contains the bottom edge of the liver as well as the upper areas of the stomach. The diaphragm curves like an upside down U over these three regions. The central right region is called the right lumbar region and contains the ascending colon and the right edge of the small intestines. The central square contains the transverse colon and the upper regions of the small intestines. The left lumbar region contains the left edge of the transverse colon and the left edge of the small intestine. The lower right square is the right iliac region and contains the right pelvic bones and the ascending colon. The lower left square is the left iliac region and contains the left pelvic bone and the lower left regions of the small intestine. The lower central square contains the bottom of the pubic bones, upper regions of the bladder and the lower region of the small intestine.
Standard terms
When anatomists refer to the right and left of the body, it is in reference to the right and left of the subject, not the right and left of the observer. When observing a body in the anatomical position, the left of the body is on the observer’s right, and vice versa.
These standardized terms avoid confusion. Examples of terms include:
- Anterior and posterior, which describe structures at the front (anterior) and back (posterior) of the body. For example, the toes are anterior to the heel, and the popliteus is posterior to the patella.
- Superior and inferior, which describe a position above (superior) or below (inferior) another part of the body. For example, the orbits are superior to the oris, and the pelvis is inferior to the abdomen.
- Proximal and distal, which describe a position that is closer to (proximal) or farther from (distal) the trunk of the body. For example, the shoulder is proximal to the arm, and the foot is distal to the knee.
- Superficial and deep, which describe structures that are closer to (superficial) or farther from (deep) the surface of the body. For example, the skin is superficial to the bones, and the brain is deep to the skull. Sometimes profound is used synonymously with deep.
- Medial and lateral, which describe a position that is closer to (medial) or farther from (lateral) the midline of the body. For example, the shoulders are lateral to the heart, and the umbilicus is medial to the hips. The medial side of the left knee is the side toward the opposite knee.
- Radial and ulnar, which describe only structures at or distal to the elbow and may be used interchangeably with medial and lateral in that particular area because they are less confusing. Examples: The thumb is on the radial side of the hand (the same as saying the lateral side); the ulnar side of the wrist is the side toward the little finger (medial side).
- Ventral and dorsal, which describe structures derived from the front (ventral) and back (dorsal) of the embryo, before limb rotation.
- Rostral and caudal, which describe structures close to (rostral) or farther from (caudal) the nose. For example, the eyes are rostral to the back of the skull, and the tailbone is caudal to the chest.
- Cranial and caudal, which describe structures close to the top of the skull (cranial), and towards the bottom of the body (caudal).
- Occasionally, sinister for left, and dexter for right are used.
- Paired, referring to a structure that is present on both sides of the body. For example, the hands are paired structures.
Axes
Each locational term above can define the direction of a vector, and pairs of them can define axes, that is, lines of orientation. For example, blood can be said to flow in a proximal or distal direction, and anteroposterior, mediolateral, and inferosuperior axes are lines along which the body extends, like the X, Y, and Z axes of a Cartesian coordinate system. An axis can be projected to a corresponding plane.
Planes
Anatomy is often described in planes, referring to two-dimensional sections of the body. A section is a two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut. A plane is an imaginary two-dimensional surface that passes through the body. Three planes are commonly referred to in anatomy and medicine:
- The sagittal plane is the plane that divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides. If this vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body, it is called the midsagittal or median plane. If it divides the body into unequal right and left sides, it is called a parasagittal plane, or less commonly a longitudinal section.
- The frontal plane is the plane that divides the body or an organ into an anterior (front) portion and a posterior (rear) portion. The frontal plane is often referred to as a coronal plane, following Latin corona, which means "crown".
- The transverse plane is the plane that divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions. Transverse planes produce images referred to as cross sections.
Functional state
Anatomical terms may be used to describe the functional state of an organ:
- Anastomoses refers to the connection between two structures previously branched out, such as blood vessels or leaf veins.
- Patent, meaning a structure such as an artery or vein that abnormally remains open, such as a patent ductus arteriosus, referring to the ductus arteriosus which normally becomes ligamentum arteriosum within three weeks of birth. Something that is patent may also refer to a channel such as a blood vessel, section of bowel, collecting system or duct that is not occluded and remains open to free flow. Such obstructions may include a calculus (i.e. a kidney stone or gallstone), plaque (like that encountered in vital arteries such as coronary arteries and cerebral arteries), or another unspecified obstruction, such as a mass or bowel obstruction.
- A plexus refers to a net-like arrangement of a nerve.
Anatomical variation
The term anatomical variation is used to refer to a difference in anatomical structures that is not regarded as a disorder. Many structures vary slightly between people, for example muscles that attach in slightly different places. For example, the presence or absence of the palmaris longus tendon. Anatomical variation is unlike congenital anomalies, which are considered a disorder.
Movement
Joints, especially synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles that are attached to the bones on either side of the articulation. The type of movement that can be produced at a synovial joint is determined by its structural type.
Movement types are generally paired, with one being the opposite of the other. Body movements are always described in relation to the anatomical position of the body: upright stance, with upper limbs to the side of body and palms facing forward.
General motion
Terms describing motion in general include:
- Flexion and extension, which refer to a movement that decreases (flexion) or increases (extension) the angle between body parts. For example, when standing up, the knees are extended.
- Abduction and adduction refers to a motion that pulls a structure away from (abduction) or towards (adduction) the midline of the body or limb. For example, a star jump requires the legs to be abducted.
- Internal rotation (or medial rotation) and external rotation (or lateral rotation) refers to rotation towards (internal) or away from (external) the center of the body. For example, the Lotus position posture in yoga requires the legs to be externally rotated.
- Elevation and depression refer to movement in a superior (elevation) or inferior (depression) direction. Primarily refers to movements involving the scapula and mandible.
Special motions of the hands and feet
These terms refer to movements that are regarded as unique to the hands and feet:
- Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion refers to flexion (dorsiflexion) or extension of the foot at the ankle. For example, plantarflexion occurs when pressing the brake pedal of a car.
- Palmarflexion and dorsiflexion refer to movement of the flexion (palmarflexion) or extension (dorsiflexion) of the hand at the wrist. For example, prayer is often conducted with the hands dorsiflexed.
- Pronation and supination refer to rotation of the forearm or foot so that in the anatomical position the palm or sole is facing anteriorly (supination) or posteriorly (pronation). For example, if a person is holding a bowl of soup in one hand, the hand is "supinated" and the thumb will point away from the body midline and the palm will be superior; if the hands are typing on a computer keyboard, they will be "pronated" with the thumbs toward the body midline and the palms inferior.
- Eversion and inversion refer to movements that tilt the sole of the foot away from (eversion) or towards (inversion) the midline of the body.
Muscles
Muscle action that moves the axial skeleton work over a joint with an origin and insertion of the muscle on respective side. The insertion is on the bone deemed to move towards the origin during muscle contraction. Muscles are often present that engage in several actions of the joint; able to perform for example both flexion and extension of the forearm as in the biceps and triceps respectively. This is not only to be able to revert actions of muscles, but also brings on stability of the actions though muscle coactivation.
Agonist and antagonist muscles
The muscle performing an action is the agonist, while the muscle which contraction brings about an opposite action is the antagonist. For example, an extension of the lower arm is performed by the triceps as the agonist and the biceps as the antagonist (which contraction will perform flexion over the same joint). Muscles that work together to perform the same action are called synergists. In the above example synergists to the biceps can be the brachioradialis and the brachialis muscle.
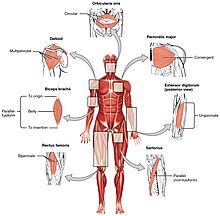
Skeletal and smooth muscle
The gross anatomy of a muscle is the most important indicator of its role in the body. One particularly important aspect of gross anatomy of muscles is pennation or lack thereof. In most muscles, all the fibers are oriented in the same direction, running in a line from the origin to the insertion. In pennate muscles, the individual fibers are oriented at an angle relative to the line of action, attaching to the origin and insertion tendons at each end. Because the contracting fibers are pulling at an angle to the overall action of the muscle, the change in length is smaller, but this same orientation allows for more fibers (thus more force) in a muscle of a given size. Pennate muscles are usually found where their length change is less important than maximum force, such as the rectus femoris.
Skeletal muscle is arranged in discrete muscles, an example of which is the biceps brachii. The tough, fibrous epimysium of skeletal muscle is both connected to and continuous with the tendons. In turn, the tendons connect to the periosteum layer surrounding the bones, permitting the transfer of force from the muscles to the skeleton. Together, these fibrous layers, along with tendons and ligaments, constitute the deep fascia of the body.
Joints
Movement is not limited to only synovial joints, although they allow for most freedom. Muscles also run over symphysis, which allow for movement in for example the vertebral column by compression of the intervertebral discs. Additionally, synovial joints can be divided into different types, depending on their axis of movement.
Membranes
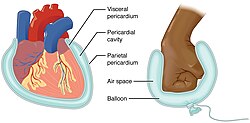
A serous membrane (also referred to as a serosa) is a thin membrane that covers the walls of organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities. The serous membranes have two layers; parietal and visceral, surrounding a fluid filled space. The visceral layer of the membrane covers the organ (the viscera), and the parietal layer lines the walls of the body cavity (pariet- refers to a cavity wall). Between the parietal and visceral layers is a very thin, fluid-filled serous space, or cavity. For example, the pericardium is the serous cavity which surrounds the heart.
Additional images
Older set of terminology shown in Parts of the Human Body: Posterior and Anterior View from the 1933 edition of Sir Henry Morris' Human Anatomy. See also List of human anatomical regions § Deprecated or older regions.






















![{\displaystyle \int _{L\subset \mathbb {R} ^{n}}\!\!\!\nabla \varphi \cdot d\mathbf {r} \ =\ \varphi \left(\mathbf {q} \right)-\varphi \left(\mathbf {p} \right)\ \ {\text{ for }}\ \ L=L[p\to q]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e6256210d4ba35dd4b15ebac17aaa3445b8ee38a)









