A sustainable food system is a type of food system that provides healthy food to people and creates sustainable environmental, economic and social systems that surround food. Sustainable food systems start with the development of sustainable agricultural practices, development of more sustainable food distribution systems, creation of sustainable diets and reduction of food waste throughout the system. Sustainable food systems have been argued to be central to many or all 17 Sustainable Development Goals.
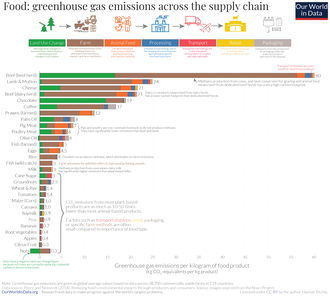
Moving to sustainable food systems, including via shifting consumption to sustainable diets, is an important component of addressing the causes of climate change and adapting to it. A 2020 review conducted for the European Union found that up to 37% of global greenhouse gas emissions could be attributed to the food system, including crop and livestock production, transportation, changing land use (including deforestation) and food loss and waste. Reduction of meat production, which e.g. accounts for ~60% of GHG emissions and ~75% of agriculturally used land, is one major component of this change.
The global food system is facing major interconnected challenges, including mitigating food insecurity, effects from climate change, biodiversity loss, malnutrition, inequity, soil degradation, pest outbreaks, water and energy scarcity, economic and political crises, natural resource depletion and preventable ill-health.
The concept of sustainable food systems is frequently at the center of sustainability-focused policy programs, such as proposed Green New Deal programs.
Definition
There are many different definitions of a sustainable food system.
From a global perspective, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations describes a sustainable food system as follows:
A sustainable food system (SFS) is a food system that delivers food security and nutrition for all in such a way that the economic, social and environmental bases to generate food security and nutrition for future generations are not compromised. This means that:
- It is profitable throughout (economic sustainability);
- It has broad-based benefits for society (social sustainability); and
- It has a positive or neutral impact on the natural environment (environmental sustainability)
The American Public Health Association (APHA) defines a sustainable food system as:
one that provides healthy food to meet current food needs while maintaining healthy ecosystems that can also provide food for generations to come with minimal negative impact to the environment. A sustainable food system also encourages local production and distribution infrastructures and makes nutritious food available, accessible, and affordable to all. Further, it is humane and just, protecting farmers and other workers, consumers, and communities
The European Union's Scientific Advice Mechanism defines a sustainable food system as a system that:
provides and promotes safe, nutritious and healthy food of low environmental impact for all current and future EU citizens in a manner that itself also protects and restores the natural environment and its ecosystem services, is robust and resilient, economically dynamic, just and fair, and socially acceptable and inclusive. It does so without compromising the availability of nutritious and healthy food for people living outside the EU, nor impairing their natural environment
Problems with conventional food systems
Industrial agriculture causes environmental impacts, as well as health problems associated with obesity in the rich world and hunger in the poor world. This has generated a strong movement towards healthy, sustainable eating as a major component of overall ethical consumerism.
Conventional food systems are largely based on the availability of inexpensive fossil fuels, which is necessary for mechanized agriculture, the manufacture or collection of chemical fertilizers, the processing of food products, and the packaging of foods. Food processing began when the number of consumers started growing rapidly. The demand for cheap and efficient calories climbed, which resulted in nutrition decline. Industrialized agriculture, due to its reliance on economies of scale to reduce production costs, often leads to the compromising of local, regional, or even global ecosystems through fertilizer runoff, nonpoint source pollution, deforestation, suboptimal mechanisms affecting consumer product choice, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Options
Based on the location a person may live at it will determine the amount and type of food resources accessible to them. Therefore, not everyone receives the same quality of food. In addition, conventional channels do not distribute food by emergency assistance or charity. Urban residents receive a more sustainable food production from healthier and safer sources than low-income communities. Nonetheless, conventional channels are more sustainable than charitable or welfare food resources. Even though the conventional food system provides easier access and lower prices, their food may not be the best for our environment nor health.
Complications from globalization
Also, the need to reduce production costs in an increasingly global market can cause production of foods to be moved to areas where economic costs (labor, taxes, etc.) are lower or environmental regulations are more lax, which are usually further from consumer markets. For example, the majority of salmon sold in the United States is raised off the coast of Chile, due in large part to less stringent Chilean standards regarding fish feed and regardless of the fact that salmon are not indigenous in Chilean coastal waters. The globalization of food production can result in the loss of traditional food systems in less developed countries, and have negative impacts on the population health, ecosystems, and cultures in those countries.
Systemic structures
Furthermore, the conventional food system does not structurally facilitate sustainable patterns of food production and consumption. In decision-making associated with the conventional food system, responsibility is in practice largely thought to rest with consumers and private companies in that they are often anticipated to spend time to – voluntarily and/or without external benefit – seek to educate themselves on which behaviours and specific product-choices are sustainable, in cases where such product-information and education is publicly available, and to subsequently change their respective decision-making related to production and consumption due to prioritized assumed ethical values and sometimes health-benefits, despite substantial drawbacks to such being common. For consumers such drawbacks may include higher prices of organic foods, inappropriate relative monetary price gaps between animal-intensive diets and plant-based ones and inadequate consumer guidance by contemporary valuations. In 2020, an analysis of external climate costs of foods indicated that external greenhouse gas costs are typically highest for animal-based products – conventional and organic to about the same extent within that ecosystem subdomain – followed by conventional dairy products and lowest for organic plant-based foods and concludes contemporary monetary evaluations to be "inadequate" and policy-making that lead to reductions of these costs to be possible, appropriate and urgent.
Agricultural pollution
Agricultural pollution refers to biotic and abiotic byproducts of farming practices that result in contamination or degradation of the environment and surrounding ecosystems, and/or cause injury to humans and their economic interests. The pollution may come from a variety of sources, ranging from point source water pollution (from a single discharge point) to more diffuse, landscape-level causes, also known as non-point source pollution and air pollution. Once in the environment these pollutants can have both direct effects in surrounding ecosystems, i.e. killing local wildlife or contaminating drinking water, and downstream effects such as dead zones caused by agricultural runoff is concentrated in large water bodies.
Management practices, or ignorance of them, play a crucial role in the amount and impact of these pollutants. Management techniques range from animal management and housing to the spread of pesticides and fertilizers in global agricultural practices, which can have major environmental impacts. Bad management practices include poorly managed animal feeding operations, overgrazing, plowing, fertilizer, and improper, excessive, or badly timed use of pesticides.
Pollutants from agriculture greatly affect water quality and can be found in lakes, rivers, wetlands, estuaries, and groundwater. Pollutants from farming include sediments, nutrients, pathogens, pesticides, metals, and salts. Animal agriculture has an outsized impact on pollutants that enter the environment. Bacteria and pathogens in manure can make their way into streams and groundwater if grazing, storing manure in lagoons and applying manure to fields is not properly managed. Air pollution caused by agriculture through land use changes and animal agriculture practices have an outsized impact on climate change, and addressing these concerns was a central part of the IPCC Special Report on Climate Change and Land. Mitigation of agricultural pollution is a key component in the development of a sustainable food system.Sourcing sustainable food
At the global level the environmental impact of agribusiness is being addressed through sustainable agriculture, cellular agriculture and organic farming.
Various alternatives to meat and novel or classes of foods can substantially increase sustainability. There are large potentials and benefits of marine algae-based aquaculture for the development of a future healthy and sustainable food system. Fungiculture, another sector of a growing bioeconomy besides algaculture, may also become a larger component of a sustainable food system. Consumption shares of various other ingredients for meat analogues such as protein from pulses may also rise substantially in a sustainable food system. Optimised dietary scenarios would also see changes in various other types of foods such as nuts and pulses such as beans, which have favorable environmental and health profiles.
Complementary approaches under development include vertical farming of various types of foods and various agricultural technologies, often using digital agriculture.
Sustainable seafood
Sustainable seafood is seafood from either fished or farmed sources that can maintain or increase production in the future without jeopardizing the ecosystems from which it was acquired. The sustainable seafood movement has gained momentum as more people become aware about both overfishing and environmentally destructive fishing methods.
Sustainable animal feed
A study suggests there would be large environmental benefits of using insects for animal feed.
Sustainable pet food
The first review on the topic indicated vegan diets, which are more sustainable, would not have adverse impacts on the health of pet dogs and cats if implemented appropriately.
Substitution of meat and sustainable meat and dairy
Meat reduction strategies
(Large-scale) education and awareness building are important strategies to promote more sustainable consumption styles. In 2022 the city of Haarlem, Netherlands announced that advertisements for factory-farmed meat will be banned in public places, starting in 2024.
Other types of policy interventions could accelerate the shifts and could include "restrictions or fiscal mechanisms such as [meat] taxes". In the case of fiscal mechanisms, such could be based on forms of scientific calculation of external costs (externalities currently not reflected in any way in the monetary price) to make the polluter pay, for example for the damage done by excess nitrogen. In the case of restrictions, such could be based on limited domestic supply or Personal (Carbon) Allowances (certificates and credits which would reward sustainable behavior).
Relevant to such a strategy, estimating the environmental impacts of food products in a standardized way – as has been done with a dataset of more than 57,000 food products in supermarkets – could also be used to inform consumers or in policy and would make consumers more aware of the environmental impacts of animal-based products (or require them to take such into consideration).
A review concluded that "low and moderate meat consumption levels are compatible with the climate targets and broader sustainable development, even for 10 billion people".
The Netherlands is reducing the amount of livestock by buying out some farmers.
A reduction in meat portion sizes could potentially be more beneficial than cutting out meat entirely from ones diet, according to a 2022 study. The study revolved around young Dutch adults, and showed that the adults were more reluctant to cut out meat entirely to make the change to plant-based diets due to habitual behaviours. Increasing, as well as improving, plant-based alternatives, as well as the education behind plant-based alternatives proved to be one of the most effective ways to combat these behaviours. The lack of education behind plant-based alternatives is a road-block for most people - most adults do not know how to properly cook plant-based meals, or know the health risks/benefits associated with a vegetarian diet - which is why education among adults is important in meat-reduction strategies.
Young adults that were faced with new physical or social environments were more likely to make dietary changes, and reduce their meat intake (for example, moving away from home). Increasing the prices of meat, while also reducing the prices of plant-based products could show a significant impact on meat-reduction. In the Netherlands, a meat tax of 15% to 30% could show a reduction of meat consumption by 8% - 16%.Effects and combination of measures
A study quantified climate change mitigation potentials of 'high-income' nations shifting diets – away from meat-consumption – and restoration of the spared land, finding that if these were combined they could "reduce annual agricultural production emissions of high-income nations' diets by 61%".
Measures which increase state revenues from meat consumption/production could enable the use of these funds for related research and development and "to cushion social hardships among low-income consumers". Meat and livestock are important sectors of the contemporary socioeconomic system, with livestock value chains employing an estimated >1.3 billion people."Policy sequencing" to gradually extend regulations once established to other forest risk commodities (e.g. other than beef) and regions and coordinating with other importing countries could prevent ineffectiveness.
Meat and dairy
Despite meat from livestock such as beef and lamb being considered unsustainable, some regenerative agriculture proponents suggest to rear livestock with mixed farming system to restore organic matter in grasslands. Organizations such as the Canadian Roundtable for Sustainable Beef (CRSB) are looking for solutions to reduce the impact of meat production on the environment. In October 2021, 17% of beef sold in Canada was certified as sustainable beef by the CRSB. However, sustainable meat has led to criticism, as environmentalists point out that the meat industry excludes most of its emissions.
Important mitigation options for reducing the greenhouse gas emissions from livestock include genetic selection, introduction of methanotrophic bacteria into the rumen, vaccines, feeds, toilet-training, diet modification and grazing management. Other options include shifting to ruminant-free alternatives, such as to milk substitutes and meat analogues or e.g. poultry, which generates far fewer emissions.
Plant-based meat is proposed for sustainable alternatives to meat consumption. Plant-based meat emits 30%–90% less greenhouse gas than conventional meat (kg-CO2-eq/kg-meat) and 72%–99% less water than conventional meat. Public company Beyond Meat and privately held company Impossible Foods are examples of plant-based food production. However, consulting firm Sustainalytics assured that these companies are not more sustainable than meat-processors competitors such as food processor JBS, and they don't disclose all the CO2 emissions of their supply chain.
Beyond reducing negative impacts of meat production, facilitating shifts towards more sustainable meat, and facilitating reduced meat consumption (including via plant-based meat substitutes), cultured meat may offer a potentially sustainable way to produce real meat without the associated negative environmental impacts.
Phase-outs, co-optimization and environmental standards
In regards to deforestation, a study proposed kinds of "climate clubs" of "as many other states as possible taking similar measures and establishing uniform environmental standards". It suggested that "Otherwise, global problems remain unsolvable, and shifting effects will occur" and that "border adjustments [...] have to be introduced to target those states that do not participate—again, to avoid shifting effects with ecologically and economically detrimental consequences", with such "border adjustments or eco-tariffs" incentivizing other countries to adjust their standards and domestic production to join the climate club. Identified potential barriers to sustainability initiatives may include contemporary trade-policy goals and competition law. Greenhouse gas emissions for countries are often measured according to production, for imported goods that are produced in other countries than where they are consumed "embedded emissions" refers to the emissions of the product. In cases where such products are and remain getting imported, eco-tariffs could over time adjust prices for specific categories of products – or for specific noncollaborative polluting origin countries – such as deforestation-associated meat, foods with intransparent supply-chain origin or foods with high embedded emissions.
Agricultural productivity and environmental efficiency
Agricultural productivity (including e.g. reliability of yields) is an important component of food security and increasing it sustainably (e.g. with high efficiency in terms of environmental impacts) can be a major way to decrease negative environmental impacts such as by decreasing the amount of land needed for farming or reducing environmental degradation like deforestation.
Genetically engineered crops
There is research and development to engineer genetically modified crops with e.g. increased heat/drought/stress resistance, increased yields, lower water requirements, and overall lower environmental impacts.
Novel agricultural technologies
Organic food
From an environmental perspective, fertilizing, overproduction and the use of pesticides in conventional farming has caused, and is causing, enormous damage worldwide to local ecosystems, soil health, biodiversity, groundwater and drinking water supplies, and sometimes farmers' health and fertility.
Organic farming typically reduces some environmental impact relative to conventional farming, but the scale of reduction can be difficult to quantify and varies depending on farming methods. In some cases, reducing food waste and dietary changes might provide greater benefits. A 2020 study at the Technical University of Munich found that the greenhouse gas emissions of organically-farmed plant-based food were lower than conventionally-farmed plant-based food. The greenhouse gas costs of organically produced meat were approximately the same as non-organically produced meat. However, the same paper noted that a shift from conventional to organic practices would likely be beneficial for long-term efficiency and ecosystem services, and probably improve soil over time.Local food systems
Local and regional food systems, commonly confused with direct marketing but both are distinct terms, come in multiple types and definitions. Local food demands from consumers within these systems include organic practices, greater nutritional value, better quality, and fresher product. Sometimes sold at lower prices, local food supply from farmers can also come at higher costs due to the environmentally sustainable production practices and through direct marketing farmers can even receive benefits for business such as consumer desires through fast product feedback. Local and regional food systems also face challenges such as inadequate institutions or programs, geographic limitations, and seasonal fluctuations which can affect product demand within regions. In addition, direct marketing also faces challenges of accessibility, coordination, and awareness. Farmers markets, which have increased over the past two decades, are designed for supporting local farmers in selling their fresh products to consumers who are wishing to buy. Food hubs are also similar locations where farmers deliver products and consumers come to pick them up. Consumers who wish to have weekly produce delivered can buy shares through a system called Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA). However, these farmer markets also face challenges with marketing needs such as starting up, advertisement, payments, processing, and regulations.
There are various movements working towards local food production, more productive use of urban wastelands and domestic gardens including permaculture, guerilla gardening, urban horticulture, local food, slow food, sustainable gardening, and organic gardening.
Debates over local food system efficiency and sustainability have risen as these systems decrease transportation which is a strategy for combating environmental footprints and climate change. A popular argument is the less impactful footprint of food products from local markets on communities and environment. Main factors behind climate change include land use practices and greenhouse emissions as global food systems produce approximately 33% of theses emissions. Compared to transportation in a local food system, a conventional system takes more fuel for energy and emits more pollution such as carbon dioxide. This transportation also includes miles for agricultural products to help with agriculture and depends on factors such as transportation sizes, modes, and fuel types. Some airplane importations have shown to be more efficient than local food systems in some cases. Overall, local food systems can often support better environmental practices.
Environmental impact of food miles
Studies found that food miles are a relatively minor factor of carbon emissions, albeit increased food localization may also enable additional, more significant, environmental benefits such as recycling of energy, water, and nutrients. For specific foods regional differences in harvest seasons may make it more environmentally friendly to import from distant regions than more local production and storage or local production in greenhouses. This may vary depending on the environmental standards in the respective country, the distance of the respective countries and on a case-by-case basis for different foods.
However, a 2022 study suggests global food miles CO2 emissions are 3.5–7.5 times higher than previously estimated, with transport accounting for about 19% of total food-system emissions, albeit shifting towards plant-based diets remains substantially more important. Because of such a shift being needed and because the transport of vegetables, fruits, cereal and flour make up the largest share of the emissions, the study concludes that "a shift towards plant-based foods must be coupled with more locally produced items, mainly in affluent countries".
Food distribution
In food distribution, increasing food supply is a production problem as it takes time for products to get marketed and as they wait to get distributed the food goes to waste. Despite the fact that throughout all food production an estimated 20-30% of food is wasted, there have been efforts to combat this issue such as campaigns conducted to promote limiting food waste. However, due to insufficient facilities and practices as well as huge amounts of food unmarketed or harvested due to prices or quality, food is wasted through each phase of its distribution. Another factor for lack of sustainability within food distribution includes transportation in combination with inadequate methods for food handling throughout the packing process. Additionally, poor or long conditions for food in storage and consumer waste add to this list of factors for inefficiency found in food distribution.
Some modern tendencies in food distribution also create bounds in which problems are created and solutions must be met. One factor includes growth of large-scale producing and selling units in bulk to chain stores which displays merchandising power from large scale market organizations as well as their mergence with manufactures. In response to production, another factor includes large scale distributing and buying units among manufacturers in development of food distribution which also affects producers, distributors, and consumers. Another main factor involves protecting public interest which means better adaptation for product and service which results in rapid development of food distribution. A further factor revolves around price maintenance which creates pressure for lower prices resulting in higher drive for lower cost throughout the whole food distribution process. An additional factor comprises new changes and forms of newly invented technical processes such as developments of freezing food discovered through experiments to help with distribution efficiency. In addition to this, new technical development in distributing machinery to meet the influence of consumer demands and economic factors. Lastly, another factor includes government relation to business those who petition against it in correlation with anti-trust laws due to large scale business organizations and the fear of monopoly contributing to changing public attitude.
Food security, nutrition and diet
The environmental effects of different dietary patterns depend on many factors, including the proportion of animal and plant foods consumed and the method of food production. At the same time, current and future food systems need to be provided with sufficient nutrition for not only the current population, but future population growth in light of a world affected by changing climate in the face of global warming.
Nearly one in four households in the United States have experienced food insecurity in 2020–21. Even before the pandemic hit, some 13.7 million households, or 10.5% of all U.S. households, experienced food insecurity at some point during 2019, according to data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture. That works out to more than 35 million Americans who were either unable to acquire enough food to meet their needs, or uncertain of where their next meal might come from, last year.
The "global land squeeze" for agricultural land also has impacts on food security. Likewise, effects of climate change on agriculture can result in lower crop yields and nutritional quality due to for example drought, heat waves and flooding as well as increases in water scarcity, pests and plant diseases. Soil conservation may be important for food security as well. For sustainability and food security, the food system would need to adapt to such current and future problems.
According to one estimate, "just four corporations control 90% of the global grain trade" and researchers have argued that the food system is too fragile due to various issues, such as "massive food producers" (i.e. market-mechanisms) having too much power and nations "polarising into super-importers and super-exporters". However the impact of market power on the food system is contested with other claiming more complex context dependent outcomes.
Production decision-making
In the food industry, especially in agriculture there has been a rise of problems towards the production of some food products. For instance, growing vegetables and fruits has become more expensive. It is difficult to grow some agricultural crops because some have a preferable climate condition for developing. There has also been an incline on food shortages as production has decreased. However, the world still produces enough food for the population but not everyone receives good quality food because it's not accessible to them since it depends on their location and/or income. In addition, the amount of overweight people has increased and there are about 2 billion people that are underfed worldwide. This shows how the global food system lacks quantity and quality according to the food consumption patterns.
A study estimated that "relocating current croplands to [environmentally] optimal locations, whilst allowing ecosystems in then-abandoned areas to regenerate, could simultaneously decrease the current carbon, biodiversity, and irrigation water footprint of global crop production by 71%, 87%, and 100%", with relocation only within national borders also having substantial potential.
Policies, including policies that affect consumption may affect production-decisions, such as which foods are produced, to various degrees and in various indirect and direct ways. Individual studies have named several proposed options of such and the restricted website Project Drawdown has aggregated and preliminarily evaluated some of such measures.
Nitrogen pollution mitigation
Climate change adaptation
A significant effect of global climate change is the altering of global rainfall patterns, with certain effects on agriculture. Rainfed agriculture constitutes 80% of global agriculture. Many of the 852 million poor people in the world live in parts of Asia and Africa that depend on rainfall to cultivate food crops. Climate change will modify rainfall, evaporation, runoff, and soil moisture storage. Extended drought can cause the failure of small and marginal farms with resultant economic, political and social disruption, more so than this currently occurs.
Agriculture of any kind is strongly influenced by the availability of water. Changes in total seasonal precipitation or in its pattern of variability are both important. The occurrence of moisture stress during flowering, pollination, and grain-filling is harmful to most crops and particularly so to corn, soybeans, and wheat. Increased evaporation from the soil and accelerated transpiration in the plants themselves will cause moisture stress.
Adaptive ideas include:
- Taking advantage of global transportation systems to delivering surplus food to where it is needed (though this does not help subsistence farmers unless aid is given).
- Developing crop varieties with greater drought tolerance.
- Rainwater storage. For example, using small planting basins to 'harvest' water in Zimbabwe has been shown to boost maize yields, whether rainfall is abundant or scarce. And in Niger, they have led to three or fourfold increases in millet yields.
- Falling back from crops to wild edible fruits, roots and leaves. Promoting the growth of forests can provide these backup food supplies, and also provide watershed conservation, carbon sequestration, and aesthetic value.
Food waste
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), food waste is responsible for 8 percent of global human-made greenhouse gas emissions. The FAO concludes that nearly 30 percent of all available agricultural land in the world – 1.4 billion hectares – is used for produced but uneaten food. The global blue water footprint of food waste is 250 km3, that is the amount of water that flows annually through the Volga or 3 times Lake Geneva.
There are several factors that explain how food waste has increased globally in food systems. The main factor is population because as population increases more food production is being made but most food produce goes to waste. In addition, not all countries have the same resources to provide the best quality of food. According to a study done in 2010, private households produce the largest amounts of food waste across the globe. Another major factor is overproduction; the rate of food production is significantly higher than the rate of consumption, leading to a surplus of food waste.
Throughout the world there are different ways that food is being processed. With different priorities different choices are being made to meet their most important needs. Money is another big factor that determines how long the process will take, who is working, and it is treated way differently than low income countries' food systems.
However, high income countries food systems still may deal with other issues such as food security. This demonstrates how all food systems have their weaknesses and strengths. Climate change is affecting food waste to increase because the warm temperature causes crops to dry faster and have a higher risk for fires. Food waste can occur throughout any time of production. According to the World Wild Life Organization, since most food produced goes to landfills when it rots it causes methane to be produced. The disposal of the food has a big impact on our environment and health.
Academic discipline
The study of sustainable food applies systems theory and methods of sustainable design towards food systems. As an interdisciplinary field, the study of sustainable food systems has been growing in the last several decades. University programs focused on sustainable food systems include:
- University of Colorado
- Harvard Extension
- University of Delaware
- Mesa Community College
- University of California, Davis
- University of Vermont
- Sterling College (Vermont)
- University of Michigan
- Portland State University
- University of Sheffield's Institute for Sustainable Food
- University of Georgia's Sustainable Food Systems Initiative
- The Culinary Institute of America's Master's in Sustainable Food Systems
- University of Edinburgh's Global Academy of Agriculture and Food Systems
There is a debate about "establishing a body akin to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) for food systems" which "would respond to questions from policymakers and produce advice based on a synthesis of the available evidence" while identifying "gaps in the science that need addressing".
Public policy
European Union
The European Union's Scientific Advice Mechanism has published a systematic review of all European policies related to sustainable food systems, and their analyses in the academic literature.
In September 2019, the EU's Chief Scientific Advisors stated that adapting the European food system for the future should be a high priority for the EU:
Although availability of food is not perceived as an immediate, major concern in Europe, the challenge to ensure a long-term, safe, nutritious and affordable supply of food, from both land and the oceans, remains. A portfolio of coordinated strategies is called for to address this challenge.
In January 2020, the EU put improvements to the food system at the core of the European Green Deal. The European Commission's 'Farm to Fork strategy for a sustainable food system', due to be published in spring 2020, is expected to lay out how European countries will reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect biodiversity, reduce food waste and chemical pesticide use, and contribute to a circular economy.
In April 2020, the EU's Scientific Advice Mechanism delivered to European Commissioners a Scientific Opinion on how to transition to a sustainable food system, informed by an evidence review report undertaken by European academies.Global
During 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference, 45 countries pledged to give more than 4 billion dollars for transition to sustainable agriculture. The organization "Slow Food" expressed concern about the effectivity of the spendings, as they concentrate on technological solutions and reforestation en place of "a holistic agroecology that transforms food from a mass-produced commodity into part of a sustainable system that works within natural boundaries."
Additionally, the Summit consisted of negotiations that led to heavily reducing CO2 emissions, becoming carbon neutral, ending deforestation and reliance on coal, and limiting methane emissions.
In November, the Climate Action Tracker reported that global efforts are on track to for a 2.7 °C temperature increase with current policies, finding that the current targets will not meet global needs as coal and natural gas consumption are primarily responsible for the gap in progress. Since, like-minded developing countries asked for an addendum to the agreement that removed the obligation for developing countries to meet the same requirements of wealthy nations.Asia
China
In 2016, the Chinese government adopted a plan to reduce China's meat consumption by 50%, for achieving more sustainable and healthy food system.
In 2019, the National Basic Research Program or Program 973 funded research into Science and Technology Backyard (STB). STBs are hubs often created in rural areas with significant rates of small-scale farming that combine knowledge of traditional practices with new innovations and technology implementation. The purpose of this program was to invest in sustainable farming throughout the country and increase food production while achieving few negative environmental effects. The program was ultimately proven to be successful, and the study found that the merging of traditional practices and appropriate technology was instrumental in higher crop yields.
India
In collaboration with the Food and Land Use Coalition (FOLU), CEEW (council for energy, environment and water), has given an overview of the current state of sustainable agriculture practices and systems (SAPSs) in India. India is aiming to scale-up SAPs, through policymakers, administrators, philanthropists, and other which represent a vital alternative to conventional, input-intensive agriculture. In idea these efforts identify 16 SAPSs – including agroforestry, crop rotation, rainwater harvesting, organic farming and natural farming – using agroecology as an investigative lens. In a conclusive understanding it is realised that sustainable agriculture is far from mainstream in India. Further proposals for several measures for promoting SAPSs, including restructured government support and rigorous evidence generation for benefits and implementation of sustainable farming are ongoing progress in Indian Agriculture.
An example of initiatives in India towards exploring the world of sustainable farming has been set by the Sowgood foundation which is a nonprofit founded by educator Pragati Chaswal. It started by teaching primary school children about sustainable farming by helping them farm on small farm strips in suburban farmhouses and gardens. Today many government and private schools in Delhi, India have adopted the sowgood foundation curriculum for sustainable farming for their students.