Spontaneous emission is the process in which a quantum mechanical system (such as an atom, molecule or subatomic particle) transitions from an excited energy state to a lower energy state (e.g., its ground state) and emits a quantum in the form of a photon.
Spontaneous emission is ultimately responsible for most of the light we
see all around us; it is so ubiquitous that there are many names given
to what is essentially the same process. If atoms (or molecules) are
excited by some means other than heating, the spontaneous emission is
called luminescence.
For example, fireflies are luminescent. And there are different forms
of luminescence depending on how excited atoms are produced (electroluminescence, chemiluminescence etc.). If the excitation is affected by the absorption of radiation the spontaneous emission is called fluorescence.
Sometimes molecules have a metastable level and continue to fluoresce
long after the exciting radiation is turned off; this is called phosphorescence. Figurines that glow in the dark are phosphorescent. Lasers start via spontaneous emission, then during continuous operation work by stimulated emission.
Spontaneous emission cannot be explained by classical electromagnetic theory and is fundamentally a quantum process. The first person to derive the rate of spontaneous emission accurately from first principles was Dirac in his quantum theory of radiation,[1] the precursor to the theory which he later coined quantum electrodynamics.[2] Contemporary physicists, when asked to give a physical explanation for spontaneous emission, generally invoke the zero-point energy of the electromagnetic field.[3][4] In 1963 the Jaynes-Cummings model[5] was developed describing the system of a two-level atom interacting with a quantized field mode (i.e. the vacuum) within an optical cavity. It gave the nonintuitive prediction that the rate of spontaneous emission could be controlled depending on the boundary conditions of the surrounding vacuum field. These experiments gave rise to cavity quantum electrodynamics (CQED), the study of effects of mirrors and cavities on radiative corrections.
Spontaneous emission cannot be explained by classical electromagnetic theory and is fundamentally a quantum process. The first person to derive the rate of spontaneous emission accurately from first principles was Dirac in his quantum theory of radiation,[1] the precursor to the theory which he later coined quantum electrodynamics.[2] Contemporary physicists, when asked to give a physical explanation for spontaneous emission, generally invoke the zero-point energy of the electromagnetic field.[3][4] In 1963 the Jaynes-Cummings model[5] was developed describing the system of a two-level atom interacting with a quantized field mode (i.e. the vacuum) within an optical cavity. It gave the nonintuitive prediction that the rate of spontaneous emission could be controlled depending on the boundary conditions of the surrounding vacuum field. These experiments gave rise to cavity quantum electrodynamics (CQED), the study of effects of mirrors and cavities on radiative corrections.
Introduction
If a light source ('the atom') is in an excited state with energy , it may spontaneously decay to a lower lying level (e.g., the ground state) with energy
, it may spontaneously decay to a lower lying level (e.g., the ground state) with energy  , releasing the difference in energy between the two states as a photon. The photon will have angular frequency
, releasing the difference in energy between the two states as a photon. The photon will have angular frequency  and an energy
and an energy  :
: is the reduced Planck constant. Note:
is the reduced Planck constant. Note:  , where
, where  is the Planck constant and
is the Planck constant and  is the linear frequency. The phase of the photon in spontaneous emission is random as is the direction in which the photon propagates. This is not true for stimulated emission. An energy level diagram illustrating the process of spontaneous emission is shown below:
is the linear frequency. The phase of the photon in spontaneous emission is random as is the direction in which the photon propagates. This is not true for stimulated emission. An energy level diagram illustrating the process of spontaneous emission is shown below: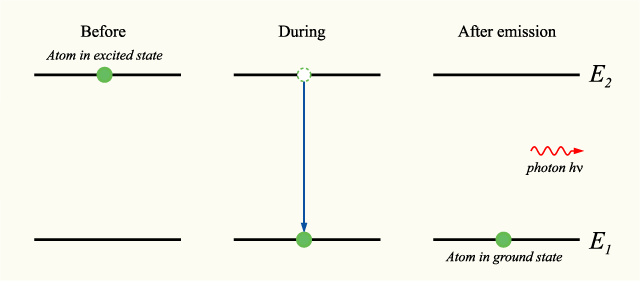
If the number of light sources in the excited state at time
 is given by
is given by  , the rate at which
, the rate at which  decays is:
decays is: is the rate of spontaneous emission. In the rate-equation
is the rate of spontaneous emission. In the rate-equation  is a proportionality constant for this particular transition in this
particular light source. The constant is referred to as the Einstein A coefficient, and has units
is a proportionality constant for this particular transition in this
particular light source. The constant is referred to as the Einstein A coefficient, and has units  .[6] The above equation can be solved to give:
.[6] The above equation can be solved to give: is the initial number of light sources in the excited state,
is the initial number of light sources in the excited state,  is the time and
is the time and  is the radiative decay rate of the transition. The number of excited states
is the radiative decay rate of the transition. The number of excited states  thus decays exponentially with time, similar to radioactive decay. After one lifetime, the number of excited states decays to 36.8% of its original value (
thus decays exponentially with time, similar to radioactive decay. After one lifetime, the number of excited states decays to 36.8% of its original value ( -time). The radiative decay rate
-time). The radiative decay rate  is inversely proportional to the lifetime
is inversely proportional to the lifetime  :
:Theory
Spontaneous transitions were not explainable within the framework of the Schrödinger equation, in which the electronic energy levels were quantized, but the electromagnetic field was not. Given that the eigenstates of an atom are properly diagonalized, the overlap of the wavefunctions between the excited state and the ground state of the atom is zero. Thus, in the absence of a quantized electromagnetic field, the excited state atom cannot decay to the ground state. In order to explain spontaneous transitions, quantum mechanics must be extended to a quantum field theory, wherein the electromagnetic field is quantized at every point in space. The quantum field theory of electrons and electromagnetic fields is known as quantum electrodynamics.In quantum electrodynamics (or QED), the electromagnetic field has a ground state, the QED vacuum, which can mix with the excited stationary states of the atom.[2] As a result of this interaction, the "stationary state" of the atom is no longer a true eigenstate of the combined system of the atom plus electromagnetic field. In particular, the electron transition from the excited state to the electronic ground state mixes with the transition of the electromagnetic field from the ground state to an excited state, a field state with one photon in it. Spontaneous emission in free space depends upon vacuum fluctuations to get started.[7][8]
Although there is only one electronic transition from the excited state to ground state, there are many ways in which the electromagnetic field may go from the ground state to a one-photon state. That is, the electromagnetic field has infinitely more degrees of freedom, corresponding to the different directions in which the photon can be emitted. Equivalently, one might say that the phase space offered by the electromagnetic field is infinitely larger than that offered by the atom. This infinite degree of freedom for the emission of the photon results in the apparent irreversible decay, i.e., spontaneous emission.
In the presence of electromagnetic vacuum modes, the combined atom-vacuum system is explained by the superposition of the wavefunctions of the excited state atom with no photon and the ground state atom with a single emitted photon:
 and
and  are the atomic excited state-electromagnetic vacuum wavefunction and its probability amplitude,
are the atomic excited state-electromagnetic vacuum wavefunction and its probability amplitude,  and
and  are the ground state atom with a single photon (of mode
are the ground state atom with a single photon (of mode  ) wavefunction and its probability amplitude,
) wavefunction and its probability amplitude,  is the atomic transition frequency, and
is the atomic transition frequency, and  is the frequency of the photon. The sum is over
is the frequency of the photon. The sum is over  and
and  ,
which are the wavenumber and polarization of the emitted photon,
respectively. As mentioned above, the emitted photon has a chance to be
emitted with different wavenumbers and polarizations, and the resulting
wavefunction is a superposition of these possibilities. To calculate the
probability of the atom at the ground state (
,
which are the wavenumber and polarization of the emitted photon,
respectively. As mentioned above, the emitted photon has a chance to be
emitted with different wavenumbers and polarizations, and the resulting
wavefunction is a superposition of these possibilities. To calculate the
probability of the atom at the ground state ( ), one needs to solve the time evolution of the wavefunction with an appropriate Hamiltonian.[1]
To solve for the transition amplitude, one needs to average over
(integrate over) all the vacuum modes, since one must consider the
probabilities that the emitted photon occupies various parts of phase
space equally. The "spontaneously" emitted photon has infinite different
modes to propagate into, thus the probability of the atom re-absorbing
the photon and returning to the original state is negligible, making the
atomic decay practically irreversible. Such irreversible time evolution
of the atom-vacuum system is responsible for the apparent spontaneous
decay of an excited atom. If one were to keep track of all the vacuum
modes, the combined atom-vacuum system would undergo unitary time
evolution, making the decay process reversible. Cavity quantum electrodynamics is one such system where the vacuum modes are modified resulting in the reversible decay process, see also Quantum revival. The theory of the spontaneous emission under the QED framework was first calculated by Weisskopf and Wigner.
), one needs to solve the time evolution of the wavefunction with an appropriate Hamiltonian.[1]
To solve for the transition amplitude, one needs to average over
(integrate over) all the vacuum modes, since one must consider the
probabilities that the emitted photon occupies various parts of phase
space equally. The "spontaneously" emitted photon has infinite different
modes to propagate into, thus the probability of the atom re-absorbing
the photon and returning to the original state is negligible, making the
atomic decay practically irreversible. Such irreversible time evolution
of the atom-vacuum system is responsible for the apparent spontaneous
decay of an excited atom. If one were to keep track of all the vacuum
modes, the combined atom-vacuum system would undergo unitary time
evolution, making the decay process reversible. Cavity quantum electrodynamics is one such system where the vacuum modes are modified resulting in the reversible decay process, see also Quantum revival. The theory of the spontaneous emission under the QED framework was first calculated by Weisskopf and Wigner.In spectroscopy one can frequently find that atoms or molecules in the excited states dissipate their energy in the absence of any external source of photons. This is not spontaneous emission, but is actually nonradiative relaxation of the atoms or molecules caused by the fluctuation of the surrounding molecules present inside the bulk.[clarification needed]
Rate of spontaneous emission
The rate of spontaneous emission (i.e., the radiative rate) can be described by Fermi's golden rule.[9] The rate of emission depends on two factors: an 'atomic part', which describes the internal structure of the light source and a 'field part', which describes the density of electromagnetic modes of the environment. The atomic part describes the strength of a transition between two states in terms of transition moments. In a homogeneous medium, such as free space, the rate of spontaneous emission in the dipole approximation is given by: is the emission frequency,
is the emission frequency,  is the index of refraction,
is the index of refraction,  is the transition dipole moment,
is the transition dipole moment,  is the vacuum permittivity,
is the vacuum permittivity,  is the reduced Planck constant,
is the reduced Planck constant,  is the vacuum speed of light, and
is the vacuum speed of light, and  is the fine structure constant.[clarification needed]
(This approximation breaks down in the case of inner shell electrons in
high-Z atoms.) The above equation clearly shows that the rate of
spontaneous emission in free space increases proportionally to
is the fine structure constant.[clarification needed]
(This approximation breaks down in the case of inner shell electrons in
high-Z atoms.) The above equation clearly shows that the rate of
spontaneous emission in free space increases proportionally to  .
.In contrast with atoms, which have a discrete emission spectrum, quantum dots can be tuned continuously by changing their size. This property has been used to check the
 -frequency dependence of the spontaneous emission rate as described by Fermi's golden rule.[10]
-frequency dependence of the spontaneous emission rate as described by Fermi's golden rule.[10]Radiative and nonradiative decay: the quantum efficiency
In the rate-equation above, it is assumed that decay of the number of excited states only occurs under emission of light. In this case one speaks of full
radiative decay and this means that the quantum efficiency is 100%.
Besides radiative decay, which occurs under the emission of light, there
is a second decay mechanism; nonradiative decay. To determine the total
decay rate
only occurs under emission of light. In this case one speaks of full
radiative decay and this means that the quantum efficiency is 100%.
Besides radiative decay, which occurs under the emission of light, there
is a second decay mechanism; nonradiative decay. To determine the total
decay rate  , radiative and nonradiative rates should be summed:
, radiative and nonradiative rates should be summed: is the total decay rate,
is the total decay rate,  is the radiative decay rate and
is the radiative decay rate and  the nonradiative decay rate. The quantum efficiency (QE) is defined as
the fraction of emission processes in which emission of light is
involved:
the nonradiative decay rate. The quantum efficiency (QE) is defined as
the fraction of emission processes in which emission of light is
involved:















