The history of slavery spans many cultures, nationalities, and religions from ancient times to the present day. Likewise, its victims have come from many different ethnicities and religious groups. The social, economic, and legal positions of slaves have differed vastly in different systems of slavery in different times and places.
Slavery occurs relatively rarely among hunter-gatherer populations because it develops under conditions of social stratification. Slavery operated in the first civilizations (such as Sumer in Mesopotamia, which dates back as far as 3500 BC). Slavery features in the Mesopotamian Code of Hammurabi (c. 1860 BCE), which refers to it as an established institution. Slavery was widespread in the ancient world. It was found in almost every ancient civilization, including the Roman Empire. It became less common throughout Europe during the Early Middle Ages, although it continued to be practiced in some areas. Both Christians and Muslims captured each other as slaves during centuries of warfare in the Mediterranean. Islamic slavery encompassed mainly Western and Central Asia, Northern and Eastern Africa, India, and Europe from the 7th to the 20th century. The Dutch, French, Spanish, Portuguese, British and a number of West African kingdoms played a prominent role in the Atlantic slave trade, especially after 1600.
Although slavery is no longer legal anywhere in the world, human trafficking remains an international problem and an estimated 25-40 million people were enslaved as of 2013, the majority in Asia. During the 1983–2005 Second Sudanese Civil War people were taken into slavery. Evidence emerged in the late 1990s of systematic child-slavery and trafficking on cacao plantations in West Africa.
Slavery in the 21st century continues and generates $150 billion in annual profits; modern transportation has made human trafficking easier. Regions with armed conflict have vulnerable populations. In 2019 there were an estimated 40 million people worldwide subject to some form of slavery, 25% of them children. 61% are used for forced labor, mostly in the private sector. 38% live in forced marriages. Other types of modern slavery are child soldiers, sex trafficking, and sexual slavery.
Origins
Evidences of slavery antedate written records; the practice has existed in many if not most cultures. Mass slavery requires economic surpluses and a high population density to be viable. Due to these factors, the practice of slavery would have only proliferated after the invention of agriculture during the Neolithic Revolution, about 11,000 years ago.
Slavery occurred in civilizations as old as Sumer, as well as in almost every other ancient civilization, including ancient Egypt, ancient China, the Akkadian Empire, Assyria, Babylonia, Persia, ancient Greece, ancient India, the Roman Empire, the Arab Islamic Caliphate and Sultanate, Nubia and the pre-Columbian civilizations of the Americas. Ancient slavery represents a mixture of debt-slavery, punishment for crime, the enslavement of prisoners of war, child abandonment, and the birth of slave children to slaves.
C. 1480 BC, fugitive-slave treaty between Idrimi of Alakakh (now Tell Atchana) and Pillia of Kizzuwatna (now Cilicia).
Slaves in chains during the period of Roman rule at Smyrna (present-day İzmir), 200 CE.
13th-century CE slave market in Yemen.
Africa
French historian Fernand Braudel noted that slavery was endemic in Africa and part of the structure of everyday life. "Slavery came in different guises in different societies: there were court slaves, slaves incorporated into princely armies, domestic and household slaves, slaves working on the land, in industry, as couriers and intermediaries, even as traders". During the 16th century, Europe began to outpace the Arab world in the export traffic, with its slave traffic from Africa to the Americas.[citation needed] The Dutch imported slaves from Asia into their colony at the Cape of Good Hope (now Cape Town) in the 17th century. In 1807 Britain (which already held a small coastal territory, intended for the resettlement of freed slaves, in Freetown, Sierra Leone), made the international slave trade illegal with the Slave Trade Act 1807, as did the United States in 1808.
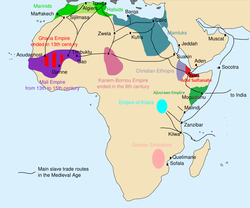
In Senegambia, between 1300 and 1900, close to one-third of the population was enslaved. In early Islamic states of the Western Sudan, including Ghana (750–1076), Mali (1235–1645), Segou (1712–1861), and Songhai (1275–1591), about a third of the population was enslaved. The earliest Akan state of Bonoman which had third of its population being enslaved in the 17th century. In Sierra Leone in the 19th century about half of the population consisted of slaves. In the 19th century at least half the population was enslaved among the Duala of the Cameroon, the Igbo and other peoples of the lower Niger, the Kongo, and the Kasanje kingdom and Chokwe of Angola. Among the Ashanti and Yoruba a third of the population consisted of slaves as well as Bono. The population of the Kanem was about a third slave. It was perhaps 40% in Bornu (1396–1893). Between 1750 and 1900 from one- to two-thirds of the entire population of the Fulani jihad states consisted of slaves. The population of the Sokoto caliphate formed by Hausas in northern Nigeria and Cameroon was half-slave in the 19th century. It is estimated that up to 90% of the population of Arab-Swahili Zanzibar was enslaved. Roughly half the population of Madagascar was enslaved.
Slavery in Ethiopia persisted until 1942. The Anti-Slavery Society estimated that there were 2,000,000 slaves in the early 1930s, out of an estimated population of between 8 and 16 million. It was finally abolished by order of emperor Haile Selassie on 26 August 1942.
When British rule was first imposed on the Sokoto Caliphate and the surrounding areas in northern Nigeria at the turn of the 20th century, approximately 2 million to 2.5 million people there were slaves. Slavery in northern Nigeria was finally outlawed in 1936.
Elikia M'bokolo, April 1998, Le Monde diplomatique. Quote: "The African continent was bled of its human resources via all possible routes. Across the Sahara, through the Red Sea, from the Indian Ocean ports and across the Atlantic. At least ten centuries of slavery for the benefit of the Muslim countries (from the ninth to the nineteenth)." He continues: "Four million slaves exported via the Red Sea, another four million through the Swahili ports of the Indian Ocean, perhaps as many as nine million along the trans-Saharan caravan route, and eleven to twenty million (depending on the author) across the Atlantic Ocean"
Sub-Saharan Africa
Zanzibar was once East Africa's main slave-trading port, during the East African slave trade and under Omani Arabs in the 19th century, as many as 50,000 slaves were passing through the city each year.
Prior to the 16th century, the bulk of slaves exported from Africa were shipped from East Africa to the Arabian peninsula. Zanzibar became a leading port in this trade. Arab slave traders differed from European ones in that they would often conduct raiding expeditions themselves, sometimes penetrating deep into the continent. They also differed in that their market greatly preferred the purchase of female slaves over male ones.
The increased presence of European rivals along the East coast led Arab traders to concentrate on the overland slave caravan routes across the Sahara from the Sahel to North Africa. The German explorer Gustav Nachtigal reported seeing slave caravans departing from Kukawa in Bornu bound for Tripoli and Egypt in 1870. The slave trade represented the major source of revenue for the state of Bornu as late as 1898. The eastern regions of the Central African Republic have never recovered demographically from the impact of 19th-century raids from the Sudan and still have a population density of less than 1 person/km2. During the 1870s, European initiatives against the slave trade caused an economic crisis in northern Sudan, precipitating the rise of Mahdist forces. Mahdi's victory created an Islamic state, one that quickly reinstituted slavery.
European involvement in the East African slave trade began when Portugal established Estado da Índia in the early 16th century. From then until the 1830s, c. 200 slaves were exported from Mozambique annually and similar figures has been estimated for slaves brought from Asia to the Philippines during the Iberian Union (1580–1640).
The Middle Passage, the crossing of the Atlantic to the Americas, endured by slaves laid out in rows in the holds of ships, was only one element of the well-known triangular trade engaged in by Portuguese, American, Dutch, Danish-Norwegians, French, British and others. Ships having landed slaves in Caribbean ports would take on sugar, indigo, raw cotton, and later coffee, and make for Liverpool, Nantes, Lisbon or Amsterdam. Ships leaving European ports for West Africa would carry printed cotton textiles, some originally from India, copper utensils and bangles, pewter plates and pots, iron bars more valued than gold, hats, trinkets, gunpowder and firearms and alcohol. Tropical shipworms were eliminated in the cold Atlantic waters, and at each unloading, a profit was made.
The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the late 18th century when the largest number of slaves were captured on raiding expeditions into the interior of West Africa. These expeditions were typically carried out by African states, such as the Bono State, Oyo empire (Yoruba), Kong Empire, Kingdom of Benin, Imamate of Futa Jallon, Imamate of Futa Toro, Kingdom of Koya, Kingdom of Khasso, Kingdom of Kaabu, Fante Confederacy, Ashanti Confederacy, Aro Confederacy and the kingdom of Dahomey. Europeans rarely entered the interior of Africa, due to fear of disease and moreover fierce African resistance. The slaves were brought to coastal outposts where they were traded for goods. The people captured on these expeditions were shipped by European traders to the colonies of the New World. As a result of the War of the Spanish Succession, the United Kingdom obtained the monopoly (asiento de negros) of transporting captive Africans to Spanish America. It is estimated that over the centuries, twelve to twenty million people were shipped as slaves from Africa by European traders, of whom some 15 percent died during the terrible voyage, many during the arduous journey through the Middle Passage. The great majority were shipped to the Americas, but some also went to Europe and Southern Africa.
While talking about the slave trade in East Africa in his journals, David Livingstone said
To overdraw its evil is a simple impossibility.
While travelling in the African Great Lakes Region in 1866, Livingstone described a trail of slaves:
19th June 1866 – We passed a woman tied by the neck to a tree and dead, the people of the country explained that she had been unable to keep up with the other slaves in a gang, and her master had determined that she should not become anyone's property if she recovered.
26th June. – ...We passed a slave woman shot or stabbed through the body and lying on the path: a group of men stood about a hundred yards off on one side, and another of the women on the other side, looking on; they said an Arab who passed early that morning had done it in anger at losing the price he had given for her, because she was unable to walk any longer.
27th June 1866 – To-day we came upon a man dead from starvation, as he was very thin. One of our men wandered and found many slaves with slave-sticks on, abandoned by their masters from want of food; they were too weak to be able to speak or say where they had come from; some were quite young.
The strangest disease I have seen in this country seems really to be broken-heartedness, and it attacks free men who have been captured and made slaves... Twenty one were unchained, as now safe; however all ran away at once; but eight with many others still in chains, died in three days after the crossing. They described their only pain in the heart, and placed the hand correctly on the spot, though many think the organ stands high up in the breast-bone.
African participation in the slave trade
African states played a key role in the slave trade, and slavery was a common practice among Sub Saharan Africans before the involvement of the Arabs, Berbers and Europeans. There were three types: those who were slaves through conquest, those who were slaves due to unpaid debts, or those whose parents gave them as slaves to tribal chiefs. Chieftains would barter their slaves to Arab, Berber, Ottoman or European buyers for rum, spices, cloth or other goods. Selling captives or prisoners was commonly practiced among Africans, Turks, Berbers and Arabs during that era. However, as the Atlantic slave trade increased its demand, local systems which primarily serviced indentured servitude expanded. European slave trading, as a result, was the most pivotal change in the social, economic, cultural, spiritual, religious, political dynamics of the concept of slave trading. It ultimately undermined local economies and political stability as villages' vital labour forces were shipped overseas as slave raids and civil wars became commonplace. Crimes which were previously punishable by some other means became punishable by enslavement.
Before the arrival of the Portuguese, slavery pre-existed in Kingdom of Kongo. Despite its establishment within his kingdom, Afonso I of Kongo believed that the slave trade should be subject to Kongo law. When he suspected the Portuguese of receiving illegally enslaved persons to sell, he wrote letters to the King João III of Portugal in 1526 imploring him to put a stop to the practice.
The kings of Dahomey sold their war captives into transatlantic slavery, who otherwise may have been killed in a ceremony known as the Annual Customs. As one of West Africa's principal slave states, Dahomey became extremely unpopular with neighbouring peoples. Like the Bambara Empire to the east, the Khasso kingdoms depended heavily on the slave trade for their economy. A family's status was indicated by the number of slaves it owned, leading to wars for the sole purpose of taking more captives. This trade led the Khasso into increasing contact with the European settlements of Africa's west coast, particularly the French. Benin grew increasingly rich during the 16th and 17th centuries on the slave trade with Europe; slaves from enemy states of the interior were sold, and carried to the Americas in Dutch and Portuguese ships. The Bight of Benin's shore soon came to be known as the "Slave Coast".
In the 1840s, King Gezo of Dahomey said:
The slave trade is the ruling principle of my people. It is the source and the glory of their wealth…the mother lulls the child to sleep with notes of triumph over an enemy reduced to slavery…
In 1807, under internal and external pressures[What pressures?], the United Kingdom made illegal the international trade in slaves. The Royal Navy was deployed to prevent slavers from the United States, France, Spain, Portugal, Holland, West Africa and Arabia. The King of Bonny (now in Nigeria) allegedly became dissatisfied of the British intervention in stopping slave trading.
We think this trade must go on. That is the verdict of our oracle and the priests. They say that your country, however great, can never stop a trade ordained by God himself.
Joseph Miller states that African buyers would prefer males, but in reality, women and children would be more easily captured as men fled. Those captured would be sold for various reasons such as food, debts, or servitude. Once captured, the journey to the coast killed many and weakened others. Disease engulfed many, and insufficient food damaged those who made it to the coasts. Scurvy was so common that it was known as mal de Luanda (Luanda sickness). The assumption for those who died on the journey died from malnutrition. As food was limited, water may have been just as bad. Dysentery was widespread and poor sanitary conditions at ports did not help. Since supplies were poor, slaves were not equipped with the best clothing that further exposed to more diseases.
If the fear of disease caused terror, the psyche of slaves for being captured was just as terrifying. The most popular assumption for being captured was Europeans were cannibals. Stories and rumours spread that whites captured Africans to eat them. Olaudah Equiano accounts his experience about the sorrow slaves encountered at the ports. He talks about his first moment on a slave ship and asked if he was going to be eaten. Yet, the worst for slaves has only begun, and the journey on the water proved to be more terrifying. For every 100 Africans captured, only 64 would reach the coast, and only about 50 would reach the New World.
Others believe that slavers had a vested interest in capturing rather than killing, and in keeping their captives alive; and that this coupled with the disproportionate removal of males and the introduction of new crops from the Americas (cassava, maize) would have limited general population decline to particular regions of western Africa around 1760–1810, and in Mozambique and neighbouring areas half a century later. There has also been speculation that within Africa, females were most often captured as brides, with their male protectors being a "bycatch" who would have been killed if there had not been an export market for them.
British explorer Mungo Park encountered a group of slaves when traveling through Mandinka country:
They were all very inquisitive, but they viewed me at first with looks of horror, and repeatedly asked if my countrymen were cannibals. They were very desirous to know what became of the slaves after they had crossed the salt water. I told them that they were employed in cultivation the land; but they would not believe me ... A deeply-rooted idea that the whites purchase negroes for the purpose of devouring them, or of selling them to others that they may be devoured hereafter, naturally makes the slaves contemplate a journey towards the coast with great terror, insomuch that the slatees are forced to keep them constantly in irons, and watch them very closely, to prevent their escape.
During the period from the late 19th century and early 20th century, demand for the labour-intensive harvesting of rubber drove frontier expansion and forced labour. The personal monarchy of Belgian King Leopold II in the Congo Free State saw mass killings and slavery to extract rubber.
Africans on ships
Stephanie Smallwood in her book Saltwater Slavery uses Equiano's account on board ships to describe the general thoughts of most slaves:
"Then," said I, "how comes it in all our country we never heard of them?" They told me because they lived so very far off. I then asked where were their women? Had they any like themselves? I was told that they had. "And why," said I, "do we not see them?" They answered, because they were left behind. I asked how the vessel could go? They told me they could not tell; but that there was cloth put upon the masts by the help of the ropes I saw, and then the vessel went on; and the white men had some spell or magic they put in the water when they liked, in order to stop the vessel. I was exceedingly amazed at this account, and really thought they were spirits. I there-fore wished much to be from amongst them, for I expected they would sacrifice me; but my wishes were vain—for we were so quartered that it was impossible for any of us to make our escape.
Accounts like these raised many questions as some slaves grew philosophical with their journey. Smallwood points out the challenges for slaves were physical and metaphysical. The physical would be obvious as the challenge to overcome capacity, lack of ship room, and food. The metaphysical was unique as the open sea would challenge African slaves' vision of the ocean as habitable. At essence, the journey on the ocean would prove to be an African's biggest fear that would keep them in awe. Combining this with the lack of knowledge of the sea, Africans would be entering a world of anxiety never seen before. Yet, Europeans were also fearful of the sea, but not to the extent of Africans. One of these dilemmas came with the sense of time. Africans used seasonal weather to predict time and days. The moon was a sense of time, but used like in other cultures. On the sea, Africans used the moon to best count the days, but the sea did not provide seasonal changes for them to know how long they were at sea. Counting the days on a ship was not the main priority, however. Surviving the voyage was the main horror. No one escaped diseases as the close quarters infected everyone including the crew. Death was so common that ships were called tumbeiros or floating tombs. What shocked Africans the most was how death was handled in the ships. Smallwood says the traditions for an African death was delicate and community-based. On ships, bodies would be thrown into the sea. Because the sea represented bad omens, bodies in the sea represented a form of purgatory and the ship a form of hell. In the end, the Africans who made the journey would have survived disease, malnutrition, confined space, close death, and the trauma of the ship.
North Africa
In Algiers during the time of the Regency of Algiers in North Africa in the 19th century, up to 1.5 million Christians and Europeans were captured and forced into slavery. This eventually led to the Bombardment of Algiers in 1816 by the British and Dutch, forcing the Dey of Algiers to free many slaves.
Modern times
The trading of children has been reported in modern Nigeria and Benin. In parts of Ghana, a family may be punished for an offense by having to turn over a virgin female to serve as a sex slave within the offended family. In this instance, the woman does not gain the title or status of "wife". In parts of Ghana, Togo, and Benin, shrine slavery persists, despite being illegal in Ghana since 1998. In this system of ritual servitude, sometimes called trokosi (in Ghana) or voodoosi in Togo and Benin, young virgin girls are given as slaves to traditional shrines and are used sexually by the priests in addition to providing free labor for the shrine.
An article in the Middle East Quarterly in 1999 reported that slavery is endemic in Sudan. Estimates of abductions during the Second Sudanese Civil War range from 14,000 to 200,000 people.
During the Second Sudanese Civil War people were taken into slavery; estimates of abductions range from 14,000 to 200,000. Abduction of Dinka women and children was common. In Mauritania it is estimated that up to 600,000 men, women and children, or 20% of the population, are currently enslaved, many of them used as bonded labor. Slavery in Mauritania was criminalized in August 2007.
During the Darfur conflict that began in 2003, many people were kidnapped by Janjaweed and sold into slavery as agricultural labor, domestic servants and sex slaves.
In Niger, slavery is also a current phenomenon. A Nigerien study has found that more than 800,000 people are enslaved, almost 8% of the population. Niger installed an anti-slavery provision in 2003. In a landmark ruling in 2008, the ECOWAS Community Court of Justice declared that the Republic of Niger failed to protect Hadijatou Mani Koraou from slavery, and awarded Mani CFA 10,000,000 (approximately US$20,000) in reparations.
Sexual slavery and forced labor are common in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Many pygmies in the Republic of Congo and Democratic Republic of Congo belong from birth to Bantus in a system of slavery.
Evidence emerged in the late 1990s of systematic slavery in cacao plantations in West Africa; see the chocolate and slavery article.
According to the U.S. State Department, more than 109,000 children were working on cocoa farms alone in Ivory Coast in "the worst forms of child labour" in 2002.
On the night of 14–15 April 2014, a group of militants attacked the Government Girls Secondary School in Chibok, Nigeria. They broke into the school, pretending to be guards, telling the girls to get out and come with them. A large number of students were taken away in trucks, possibly into the Konduga area of the Sambisa Forest where Boko Haram were known to have fortified camps. Houses in Chibok were also burned down in the incident. According to police, approximately 276 children were taken in the attack, of whom 53 had escaped as of 2 May. Other reports said that 329 girls were kidnapped, 53 had escaped and 276 were still missing. The students have been forced to convert to Islam and into marriage with members of Boko Haram, with a reputed "bride price" of ₦2,000 each ($12.50/£7.50). Many of the students were taken to the neighbouring countries of Chad and Cameroon, with sightings reported of the students crossing borders with the militants, and sightings of the students by villagers living in the Sambisa Forest, which is considered a refuge for Boko Haram.
On 5 May 2014 a video in which Boko Haram leader Abubakar Shekau claimed responsibility for the kidnappings emerged. Shekau claimed that "Allah instructed me to sell them...I will carry out his instructions" and "[s]lavery is allowed in my religion, and I shall capture people and make them slaves." He said the girls should not have been in school and instead should have been married since girls as young as nine are suitable for marriage.
Libyan slave trade
During the Second Libyan Civil War Libyans started capturing some of the Sub-Saharan African migrants trying to get to Europe through Libya and selling them on slave markets. Slaves are often ransomed to their families and in the meantime until ransom can be paid, they may be tortured, forced to work, sometimes worked to death, and eventually they may be executed or left to starve if the payment has not been made after a period of time. Women are often raped and used as sex slaves and sold to brothels.
Many child migrants also suffer from abuse and child rape in Libya.
Americas
For the slave trade on Spanish America bankers and trading companies actually had to pay the Spanish king for the license, called the Asiento de Negros, but an unknown amount of the trade was illegal. After 1670 when the Spanish Empire declined substantially they outsourced part of the slave trade to the Dutch (1685-1687), the Portuguese, the French (1698-1713) and the English (1713-1750), also providing Dutch, British and French America from the Caribbean islands were there organized depots. Meanwhile, slave trade became a core business for privately owned enterprises.
Among indigenous peoples
In Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica the most common forms of slavery were those of prisoners of war and debtors. People unable to pay back debts could be sentenced to work as slaves to the persons owed until the debts were worked off. Warfare was important to Maya society, because raids on surrounding areas provided the victims required for human sacrifice, as well as slaves for the construction of temples. Most victims of human sacrifice were prisoners of war or slaves. Slavery was not usually hereditary; children of slaves were born free. In the Inca Empire, workers were subject to a mita in lieu of taxes which they paid by working for the government. Each ayllu, or extended family, would decide which family member to send to do the work. It is unclear if this labor draft or corvée counts as slavery. The Spanish adopted this system, particularly for their silver mines in Bolivia.
Other slave-owning societies and tribes of the New World were, for example, the Tehuelche of Patagonia, the Comanche of Texas, the Caribs of Dominica, the Tupinambá of Brazil, the fishing societies, such as the Yurok, that lived along the coast from what is now Alaska to California, the Pawnee and Klamath. Many of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, such as the Haida and Tlingit, were traditionally known as fierce warriors and slave-traders, raiding as far as California. Slavery was hereditary, the slaves being prisoners of war. Among some Pacific Northwest tribes about a quarter of the population were slaves. One slave narrative was composed by an Englishman, John R. Jewitt, who had been taken alive when his ship was captured in 1802; his memoir provides a detailed look at life as a slave, and asserts that a large number were held.
Brazil
Slavery was a mainstay of the Brazilian colonial economy, especially in mining and sugarcane production. 35.3% of all slaves involved in the Atlantic Slave trade went to Brazil. 4 million slaves were obtained by Brazil, 1.5 million more than any other country. Starting around 1550, the Portuguese began to trade African slaves to work the sugar plantations, once the native Tupi people deteriorated. Although Portuguese Prime Minister Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, 1st Marquis of Pombal abolished slavery in mainland Portugal on 12 February 1761, slavery continued in her overseas colonies. Slavery was practiced among all classes. Slaves were owned by upper and middle classes, by the poor, and even by other slaves.
From São Paulo, the Bandeirantes, adventurers mostly of mixed Portuguese and native ancestry, penetrated steadily westward in their search for Indian slaves. Along the Amazon river and its major tributaries, repeated slaving raids and punitive attacks left their mark. One French traveler in the 1740s described hundreds of miles of river banks with no sign of human life and once-thriving villages that were devastated and empty. In some areas of the Amazon Basin, and particularly among the Guarani of southern Brazil and Paraguay, the Jesuits had organized their Jesuit Reductions along military lines to fight the slavers. In the mid-to-late 19th century, many Amerindians were enslaved to work on rubber plantations.
Resistance and abolition
Escaped slaves formed Maroon communities which played an important role in the histories of Brazil and other countries such as Suriname, Puerto Rico, Cuba, and Jamaica. In Brazil, the Maroon villages were called palenques or quilombos. Maroons survived by growing vegetables and hunting. They also raided plantations. At these attacks, the maroons would burn crops, steal livestock and tools, kill slavemasters, and invite other slaves to join their communities.
Jean-Baptiste Debret, a French painter who was active in Brazil in the first decades of the 19th century, started out with painting portraits of members of the Brazilian Imperial family, but soon became concerned with the slavery of both blacks and indigenous inhabitants. His paintings on the subject (two appear on this page) helped bring attention to the subject in both Europe and Brazil itself.
The Clapham Sect, a group of evangelical reformers, campaigned during much of the 19th century for Britain to use its influence and power to stop the traffic of slaves to Brazil. Besides moral qualms, the low cost of slave-produced Brazilian sugar meant that British colonies in the West Indies were unable to match the market prices of Brazilian sugar, and each Briton was consuming 16 pounds (7 kg) of sugar a year by the 19th century. This combination led to intensive pressure from the British government for Brazil to end this practice, which it did by steps over several decades.
First, foreign slave trade was banned in 1850. Then, in 1871, the sons of the slaves were freed. In 1885, slaves aged over 60 years were freed. The Paraguayan War contributed to ending slavery as many slaves enlisted in exchange for freedom. In Colonial Brazil, slavery was more a social than a racial condition. Some of the greatest figures of the time, like the writer Machado de Assis and the engineer André Rebouças had black ancestry.
Brazil's 1877–78 Grande Seca (Great Drought) in the cotton-growing northeast led to major turmoil, starvation, poverty and internal migration. As wealthy plantation holders rushed to sell their slaves south, popular resistance and resentment grew, inspiring numerous emancipation societies. They succeeded in banning slavery altogether in the province of Ceará by 1884. Slavery was legally ended nationwide on 13 May by the Lei Áurea ("Golden Law") of 1888. It was an institution in decadence at these times, as since the 1880s the country had begun to use European immigrant labor instead. Brazil was the last nation in the Western Hemisphere to abolish slavery. The Republic of Ragusa became the first European country to ban the slave trade in 1416. In modern times Denmark-Norway abolished the trade in 1802.
British and French Caribbean
Slavery was commonly used in the parts of the Caribbean controlled by France and the British Empire. The Lesser Antilles islands of Barbados, St. Kitts, Antigua, Martinique and Guadeloupe, which were the first important slave societies of the Caribbean, began the widespread use of enslaved Africans by the end of the 17th century, as their economies converted from sugar production.
England had multiple sugar islands in the Caribbean, especially Jamaica, Barbados, Nevis, and Antigua, which provided a steady flow of sugar sales; slave labor produced the sugar. By the 1700s, there were more enslaved persons in Barbados than in all the English colonies on the mainland combined. Since Barbados did not have many mountains, the British were able to clear land for sugar cane. Indentured servants were initially sent to Barbados to work in the sugar fields. These indentured servants were treated so poorly that future indentured servants stopped going to Barbados, and there were not enough people to work the fields. This is when the British started bringing in enslaved Africans. For the English planters, reliance on enslaved labor was necessary for them to be able to profit from production of cane-origin sugar for the growing market for sugar in England and elsewhere in Europe.
An important result of Britain's victory in the War of the Spanish Succession (1702–1714) was enlarging its role in the slave trade. Of special importance was the successful secret negotiation with France to obtain thirty-year monopoly on the Spanish slave trade, called the Asiento de Negros. Queen Anne of Great Britain also allowed her North American colonies like Virginia to make laws that promoted black slavery. Anne had secretly negotiated with France to get its approval regarding the Asiento. She boasted to Parliament of her success in taking the Asiento away from France and London celebrated her economic coup. Most of the slave trade involved sales to Spanish colonies in the Caribbean, and to Mexico, as well as sales to British colonies in the Caribbean and in North America. Historian Vinita Ricks says the agreement allotted Queen Anne "22.5% (and King Philip V, of Spain 28%) of all profits collected for her personal fortune." Ricks concludes that the Queen's "connection to slave trade revenue meant that she was no longer a neutral observer. She had a vested interest in what happened on slave ships."
By 1778, the French were importing approximately 13,000 Africans for enslavement yearly to the French West Indies.
To regularise slavery, in 1685 Louis XIV had enacted the code noir, which accorded certain human rights to slaves and responsibilities to the master, who was obliged to feed, clothe and provide for the general well-being of his slaves. Free blacks owned one-third of the plantation property and one-quarter of the slaves in Saint Domingue (later Haiti). Slavery in the French First Republic was abolished on 4 February 1794. When it became clear that Napoleon intended to re-establish slavery in Haiti, Dessalines and Pétion switched sides, in October 1802. On 1 January 1804, Jean-Jacques Dessalines, the new leader under the dictatorial 1801 constitution, declared Haiti a free republic. Thus Haiti became the second independent nation in the Western Hemisphere, after the United States, and the only successful slave rebellion in world history.
Whitehall in England announced in 1833 that slaves in its territories would be totally freed by 1840. In the meantime, the government told slaves they had to remain on their plantations and would have the status of "apprentices" for the next six years.
In Port-of-Spain, Trinidad, on 1 August 1834, an unarmed group of mainly elderly Negroes being addressed by the Governor at Government House about the new laws, began chanting: "Pas de six ans. Point de six ans" ("Not six years. No six years"), drowning out the voice of the Governor. Peaceful protests continued until a resolution to abolish apprenticeship was passed and de facto freedom was achieved. Full emancipation for all was legally granted ahead of schedule on 1 August 1838, making Trinidad the first British colony with slaves to completely abolish slavery.
After Great Britain abolished slavery, it began to pressure other nations to do the same. France, too, abolished slavery. By then Saint-Domingue had already won its independence and formed the independent Republic of Haiti. French-controlled islands were then limited to a few smaller islands in the Lesser Antilles.
Canada
Slavery in Canada was practised by First Nations and continued during the European colonization of Canada. It is estimated that there were 4,200 slaves in the French colony of Canada and later British North America between 1671 and 1831. Two-thirds of these were of indigenous ancestry (typically called panis) whereas the other third were of African descent. They were house servants and farm workers. The number of black slaves increased during British rule, especially with the arrival of United Empire Loyalists after 1783. A small portion of Black Canadians today are descended from these slaves.
The practice of slavery in the Canadas ended through case law; having died out in the early 19th century through judicial actions litigated on behalf of slaves seeking manumission. The courts, to varying degrees, rendered slavery unenforceable in both Lower Canada and Nova Scotia. In Lower Canada, for example, after court decisions in the late 1790s, the "slave could not be compelled to serve longer than he would, and ... might leave his master at will." Upper Canada passed the Act Against Slavery in 1793, one of the earliest anti-slavery acts in the world. The institution was formally banned throughout most of the British Empire, including the Canadas in 1834, after the passage of the Slavery Abolition Act 1833 in the British parliament. These measures resulted in a number of Black people (free and slaves) from the United States moving to Canada after the American Revolution, known as the Black Loyalists; and again after the War of 1812, with a number of Black Refugees settling in Canada. During the mid-19th century, British North America served as a terminus for the Underground Railroad, a network of routes used by enslaved African-Americans to escape a slave state.
Latin America
During the period from the late 19th century and early 20th century, demand for the labor-intensive harvesting of rubber drove frontier expansion and slavery in Latin America and elsewhere. Indigenous peoples were enslaved as part of the rubber boom in Ecuador, Peru, Colombia, and Brazil. In Central America, rubber tappers participated in the enslavement of the indigenous Guatuso-Maleku people for domestic service.
United States
Early events
In late August 1619, the frigate White Lion, a privateer ship owned by Robert Rich, 2nd Earl of Warwick, but flying a Dutch flag arrived at Point Comfort, Virginia (several miles downstream from the colony of Jamestown, Virginia) with the first recorded slaves from Africa to Virginia. The approximately 20 Africans were from the present-day Angola. They had been removed by the White Lion's crew from a Portuguese slave ship, the São João Bautista.
Historians are undecided if the legal practice of slavery began in the colony because at least some of them had the status of indentured servant. Alden T. Vaughn says most agree that both black slaves and indentured servants existed by 1640.
Only a small fraction of the enslaved Africans brought to the New World came to British North America, perhaps as little as 5% of the total. The vast majority of slaves were sent to the Caribbean sugar colonies, Brazil, or Spanish America.
By the 1680s, with the consolidation of England's Royal African Company, enslaved Africans were arriving in English colonies in larger numbers, and the institution continued to be protected by the British government. Colonists now began purchasing slaves in larger numbers.
Slavery in American colonial law
- 1640: Virginia courts sentence John Punch to lifetime slavery, marking the earliest legal sanctioning of slavery in English colonies.
- 1641: Massachusetts legalizes slavery.
- 1650: Connecticut legalizes slavery.
- 1652: Rhode Island bans the enslavement or forced servitude of any white or negro for more than ten years or beyond the age of 24.
- 1654: Virginia sanctions "the right of Negros to own slaves of their own race" after African Anthony Johnson, former indentured servant, sued to have fellow African John Casor declared not an indentured servant but "slave for life."
- 1661: Virginia officially recognizes slavery by statute.
- 1662: A Virginia statute declares that children born would have the same status as their mother.
- 1663: Maryland legalizes slavery.
- 1664: Slavery is legalized in New York and New Jersey.
- 1670: Carolina (later, South Carolina and North Carolina) is founded mainly by planters from the overpopulated British sugar island colony of Barbados, who brought relatively large numbers of African slaves from that island.
- 1676: Rhode Island bans the enslavement of Native Americans.
Development of slavery
The shift from indentured servants to African slaves was prompted by a dwindling class of former servants who had worked through the terms of their indentures and thus became competitors to their former masters. These newly freed servants were rarely able to support themselves comfortably, and the tobacco industry was increasingly dominated by large planters. This caused domestic unrest culminating in Bacon's Rebellion. Eventually, chattel slavery became the norm in regions dominated by plantations.
The Fundamental Constitutions of Carolina established a model in which a rigid social hierarchy placed slaves under the absolute authority of their master. With the rise of a plantation economy in the Carolina Lowcountry based on rice cultivation, a slave society was created that later became the model for the King Cotton economy across the Deep South. The model created by South Carolina was driven by the emergence of a majority slave population that required repressive and often brutal force to control. Justification for such a slave society developed into a conceptual framework of white superiority and aristocratic privilege.
Several local slave rebellions took place during the 17th and 18th centuries: Gloucester County, Virginia Revolt (1663); New York Slave Revolt of 1712; Stono Rebellion (1739); and New York Slave Insurrection of 1741.
Early United States law
Within the British Empire, the Massachusetts courts began to follow England when, in 1772, England became the first country in the world to outlaw the slave trade within its borders (see Somerset v Stewart) followed by the Knight v. Wedderburn decision in Scotland in 1778. Between 1764 and 1774, seventeen slaves appeared in Massachusetts courts to sue their owners for freedom. In 1766, John Adams' colleague Benjamin Kent won the first trial in the present-day United States to free a slave (Slew vs. Whipplee
The Republic of Vermont banned slavery in its constitution of 1777 and continued the ban when it entered the United States in 1791. Through the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 under the Congress of the Confederation, slavery was prohibited in the territories north west of the Ohio River. In 1794, Congress banned American vessels from being used in the slave trade, and also banned the export of American slaves to other countries. However, little effort was made to enforce this legislation. The slave ship owners of Rhode Island were able to continue in trade, and the USA's slaving fleet in 1806 was estimated to be nearly 75% as large as that of Britain, with dominance of the transportation of slaves into Cuba. By 1804, abolitionists succeeded in passing legislation that ended legal slavery in every northern state (with slaves above a certain age legally transformed to indentured servants). Congress passed an Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves as of 1 January 1808; but not the internal slave trade.[]
Despite the actions of abolitionists, free blacks were subject to racial segregation in the Northern states. While the United Kingdom did not ban slavery throughout most of the empire, including British North America till 1833, free blacks found refugee in the Canadas after the America Revolution and again after the War of 1812. Refugees from slavery fled the South across the Ohio River to the North via the Underground Railroad. Midwestern state governments asserted States Rights arguments to refuse federal jurisdiction over fugitives. Some juries exercised their right of jury nullification and refused to convict those indicted under the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850.
After the passage of the Kansas–Nebraska Act in 1854, armed conflict broke out in Kansas Territory, where the question of whether it would be admitted to the Union as a slave state or a free state had been left to the inhabitants. The radical abolitionist John Brown was active in the mayhem and killing in "Bleeding Kansas." The true turning point in public opinion is better fixed at the Lecompton Constitution fraud. Pro-slavery elements in Kansas had arrived first from Missouri and quickly organized a territorial government that excluded abolitionists. Through the machinery of the territory and violence, the pro-slavery faction attempted to force an unpopular pro-slavery constitution through the state. This infuriated Northern Democrats, who supported popular sovereignty, and was exacerbated by the Buchanan administration reneging on a promise to submit the constitution to a referendum—which would surely fail. Anti-slavery legislators took office under the banner of the newly formed Republican Party. The Supreme Court in the Dred Scott decision of 1857 asserted that one could take one's property anywhere, even if one's property was chattel and one crossed into a free territory. It also asserted that African Americans could not be federal citizens. Outraged critics across the North denounced these episodes as the latest of the Slave Power (the politically organized slave owners) taking more control of the nation.
Civil War
The slave population in the United States stood at four million. Ninety-five percent of blacks lived in the South, comprising one third of the population there as opposed to 1% of the population of the North. The central issue in politics in the 1850s involved the extension of slavery into the western territories, which settlers from the Northern states opposed. The Whig Party split and collapsed on the slavery issue, to be replaced in the North by the new Republican Party, which was dedicated to stopping the expansion of slavery. Republicans gained a majority in every northern state by absorbing a faction of anti-slavery Democrats, and warning that slavery was a backward system that undercut democracy and economic modernization. Numerous compromise proposals were put forward, but they all collapsed. A majority of Northern voters were committed to stopping the expansion of slavery, which they believed would ultimately end slavery. Southern voters were overwhelmingly angry that they were being treated as second-class citizens. In the election of 1860, the Republicans swept Abraham Lincoln into the Presidency and his party took control with legislators into Congress. The states of the deep South, convinced that the economic power of what they called "King Cotton" would overwhelm the North and win support from Europe voted to secede from the U.S. (the Union). They formed the Confederate States of America, based on the promise of maintaining slavery. War broke out in April 1861, as both sides sought wave after wave of enthusiasm among young men volunteering to form new regiments and new armies. In the North, the main goal was to preserve the union as an expression of American nationalism.
Rebel leaders Jefferson Davis, Robert E. Lee, Nathan Bedford Forrest and others were slavers and slave-traders.
By 1862 most northern leaders realized that the mainstay of Southern secession, slavery, had to be attacked head-on. All the border states rejected President Lincoln's proposal for compensated emancipation. However, by 1865 all had begun the abolition of slavery, except Kentucky and Delaware. The Emancipation Proclamation was an executive order issued by Lincoln on 1 January 1863. In a single stroke, it changed the legal status, as recognized by the U.S. government, of 3 million slaves in designated areas of the Confederacy from "slave" to "free." It had the practical effect that as soon as a slave escaped the control of the Confederate government, by running away or through advances of Federal troops, the slave became legally and actually free. Plantation owners, realizing that emancipation would destroy their economic system, sometimes moved their slaves as far as possible out of reach of the Union Army. By June 1865, the Union Army controlled all of the Confederacy and liberated all of the designated slaves. The owners were never compensated. About 186,000 free blacks and newly freed slaves fought for the Union in the Army and Navy, thereby validating their claims to full citizenship.
The severe dislocations of war and Reconstruction had a severe negative impact on the black population, with a large amount of sickness and death. After liberation, many of the Freedmen remained on the same plantation. Others fled or crowded into refugee camps operated by the Freedmen's Bureau. The Bureau provided food, housing, clothing, medical care, church services, some schooling, legal support, and arranged for labor contracts. Fierce debates about the rights of the Freedmen, and of the defeated Confederates, often accompanied by killings of black leaders, marked the Reconstruction Era, 1863–77.
Slavery was never reestablished, but after President Ulysses S. Grant left the White House in 1877, white Democrats took control of all the southern states, and blacks lost nearly all the political power they had achieved during Reconstruction. By 1900, they also lost the right to vote – they had become second class citizens. The great majority lived in the rural South in poverty working as laborers, sharecroppers or tenant farmers; a small proportion owned their own land. The black churches, especially the Baptist Church, was the center of community activity and leadership.
Middle East
In the ancient Near East and Asia Minor slavery was common practice, dating back to the very earliest recorded civilisations in the world such as Sumer, Elam, Ancient Egypt, Akkad, Assyria, Ebla and Babylonia, as well as amongst the Hattians, Hittites, Hurrians, Mycenaean Greece, Luwians, Canaanites, Israelites, Amorites, Phoenicians, Arameans, Ammonites, Edomites, Moabites, Byzantines, Philistines, Medes, Phrygians, Lydians, Mitanni, Kassites, Parthians, Urartians, Colchians, Chaldeans and Armenians.
Slavery in the Middle East first developed out of the slavery practices of the Ancient Near East, and these practices were radically different at times, depending on social-political factors such as the Muslim slave trade. Two rough estimates by scholars of the number of slaves held over twelve centuries in Muslim lands are 11.5 million and 14 million.
Under Sharia (Islamic law) children of slaves or prisoners of war could become slaves but only non-Muslims. Manumission of a slave was encouraged as a way of expiating sins. Many early converts to Islam, such as Bilal ibn Rabah al-Habashi, were the poor and former slaves. In theory, slavery in Islamic law does not have a racial or color component, although this has not always been the case in practice.
Bernard Lewis writes: "In one of the sad paradoxes of human history, it was the humanitarian reforms brought by Islam that resulted in a vast development of the slave trade inside, and still more outside, the Islamic empire." He notes that the Islamic injunctions against the enslavement of Muslims led to massive importation of slaves from the outside. According to Patrick Manning, Islam by recognizing and codifying the slavery seems to have done more to protect and expand slavery than the reverse.
Slavery was a legal and important part of the economy of the Ottoman Empire and Ottoman society until the slavery of Caucasians was banned in the early 19th century, although slaves from other groups were allowed. In Constantinople (present-day Istanbul), the administrative and political center of the Empire, about a fifth of the population consisted of slaves in 1609. Even after several measures to ban slavery in the late 19th century, the practice continued largely unfazed into the early 20th century. As late as 1908, female slaves were still sold in the Ottoman Empire. Sexual slavery was a central part of the Ottoman slave system throughout the history of the institution.
A member of the Ottoman slave class, called a kul in Turkish, could achieve high status. Harem guards and janissaries are some of the better-known positions a slave could hold, but slaves were actually often at the forefront of Ottoman politics. The majority of officials in the Ottoman government were bought slaves, raised free, and integral to the success of the Ottoman Empire from the 14th century into the 19th. Many officials themselves owned a large number of slaves, although the Sultan himself owned by far the largest amount. By raising and specially training slaves as officials in palace schools such as Enderun, the Ottomans created administrators with intricate knowledge of government and fanatic loyalty.
Ottomans practiced devşirme, a sort of "blood tax" or "child collection", young Christian boys from the Balkans and Anatolia were taken from their homes and families, brought up as Muslims, and enlisted into the most famous branch of the kapıkulu, the Janissaries, a special soldier class of the Ottoman army that became a decisive faction in the Ottoman invasions of Europe.
During the various 18th and 19th century persecution campaigns against Christians as well as during the culminating Assyrian, Armenian and Greek genocides of World War I, many indigenous Armenian, Assyrian and Greek Christian women and children were carried off as slaves by the Ottoman Turks and their Kurdish allies. Henry Morgenthau, Sr., U.S. Ambassador in Constantinople from 1913 to 1916, reports in his Ambassador Morgenthau's Story that there were gangs trading white slaves during his term in Constantinople. He also reports that Armenian girls were sold as slaves during the Armenian Genocide.
According to Ronald Segal, the male:female gender ratio in the Atlantic slave trade was 2:1, whereas in Islamic lands the ratio was 1:2. Another difference between the two was, he argues, that slavery in the west had a racial component, whereas the Qur'an explicitly condemned racism. This, in Segal's view, eased assimilation of freed slaves into society. Men would often take their female slaves as concubines; in fact, most Ottoman sultans were sons of such concubines.
ISIL slave trade
According to media reports from late 2014, the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) was selling Yazidi and Christian women as slaves. According to Haleh Esfandiari of the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, after ISIL militants have captured an area "[t]hey usually take the older women to a makeshift slave market and try to sell them." In mid-October 2014, the UN estimated that 5,000 to 7,000 Yazidi women and children were abducted by ISIL and sold into slavery. In the digital magazine Dabiq, ISIL claimed religious justification for enslaving Yazidi women whom they consider to be from a heretical sect. ISIL claimed that the Yazidi are idol worshipers and their enslavement is part of the old shariah practice of spoils of war. According to The Wall Street Journal, ISIL appeals to apocalyptic beliefs and claims "justification by a Hadith that they interpret as portraying the revival of slavery as a precursor to the end of the world".
ISIL announced the revival of slavery as an institution. In 2015 the official slave prices set by ISIL were following:
- Children aged 1 to 9 were sold for 200,000 dinars ($169).
- Women and children 10 to 20 years sold for 150,000 dinars ($127).
- Women 20 to 30 years old for 100,000 dinar ($85).
- Women 30 to 40 years old are 75,000 dinar ($63).
- Women 40 to 50 years old for 50,000 dinar ($42).
However some slaves have been sold for as little as a pack of cigarettes. Sex slaves were sold to Saudi Arabia, other Persian Gulf states and Turkey.
Asia
Slavery has existed all throughout Asia, and forms of slavery still exist today.
Classic era
Ancient India
Scholars differ as to whether or not slaves and the institution of slavery existed in ancient India. These English words have no direct, universally accepted equivalent in Sanskrit or other Indian languages, but some scholars translate the word dasa, mentioned in texts like Manu Smriti, as slaves. Ancient historians who visited India offer the closest insights into the nature of Indian society and slavery in other ancient civilizations. For example, the Greek historian Arrian, who chronicled India about the time of Alexander the Great, wrote in his Indika,
The Indians do not even use aliens as slaves, much less a countryman of their own.
— The Indika of Arrian
Ancient China
- Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) Men sentenced to castration became eunuch slaves of the Qin dynasty state and as a result they were made to do forced labor, on projects like the Terracotta Army.
The Qin government confiscated the property and enslaved the families
of those who received castration as a punishment for rape.
- Slaves were deprived of their rights and connections to their families.
- Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD) One of Emperor Gao's first acts was to set free from slavery agricultural workers who were enslaved during the Warring States period, although domestic servants retained their status.
- Men punished with castration during the Han dynasty were also used as slave labor.
- Deriving from earlier Legalist laws, the Han dynasty set in place rules that the property of and families of criminals doing three years of hard labor or sentenced to castration were to have their families seized and kept as property by the government.
During the millennium long Chinese domination of Vietnam, Vietnam was a great source of slave girls who were used as sex slaves in China. The slave girls of Viet were even eroticized in Tang dynasty poetry.
Middle Ages
Indian subcontinent
The Islamic invasions, starting in the 8th century, also resulted in hundreds of thousands of Indians being enslaved by the invading armies, one of the earliest being the armies of the Umayyad commander Muhammad bin Qasim. Qutb-ud-din Aybak, a Turkic slave of Muhammad Ghori rose to power following his master's death. For almost a century, his descendants ruled North-Central India in form of Slave Dynasty. Several slaves were also brought to India by the Indian Ocean trades; for example, the Siddi are descendants of Bantu slaves brought to India by Arab and Portuguese merchants.
Andre Wink summarizes the slavery in 8th and 9th century India as follows,
(During the invasion of Muhammad al-Qasim), invariably numerous women and children were enslaved. The sources insist that now, in dutiful conformity to religious law, 'the one-fifth of the slaves and spoils' were set apart for the caliph's treasury and despatched to Iraq and Syria. The remainder was scattered among the army of Islam. At Rūr, a random 60,000 captives reduced to slavery. At Brahamanabad 30,000 slaves were allegedly taken. At Multan 6,000. Slave raids continued to be made throughout the late Umayyad period in Sindh, but also much further into Hind, as far as Ujjain and Malwa. The Abbasid governors raided Punjab, where many prisoners and slaves were taken.
— Al Hind, André Wink
In the early 11th century Tarikh al-Yamini, the Arab historian Al-Utbi recorded that in 1001 the armies of Mahmud of Ghazna conquered Peshawar and Waihand (capital of Gandhara) after Battle of Peshawar (1001), "in the midst of the land of Hindustan", and captured some 100,000 youths. Later, following his twelfth expedition into India in 1018–19, Mahmud is reported to have returned with such a large number of slaves that their value was reduced to only two to ten dirhams each. This unusually low price made, according to Al-Utbi, "merchants [come] from distant cities to purchase them, so that the countries of Central Asia, Iraq and Khurasan were swelled with them, and the fair and the dark, the rich and the poor, mingled in one common slavery". Elliot and Dowson refer to "five hundred thousand slaves, beautiful men and women.". Later, during the Delhi Sultanate period (1206–1555), references to the abundant availability of low-priced Indian slaves abound. Levi attributes this primarily to the vast human resources of India, compared to its neighbors to the north and west (India's Mughal population being approximately 12 to 20 times that of Turan and Iran at the end of the 16th century).
Slavery and empire-formation tied in particularly well with iqta and it is within this context of Islamic expansion that elite slavery was later commonly found. It became the predominant system in North India in the thirteenth century and retained considerable importance in the fourteenth century. Slavery was still vigorous in fifteenth-century Bengal, while after that date it shifted to the Deccan where it persisted until the seventeenth century. It remained present to a minor extent in the Mughal provinces throughout the seventeenth century and had a notable revival under the Afghans in North India again in the eighteenth century.
— Al Hind, André Wink
The Delhi sultanate obtained thousands of slaves and eunuch servants from the villages of Eastern Bengal (a widespread practice which Mughal emperor Jahangir later tried to stop). Wars, famines, pestilences drove many villagers to sell their children as slaves. The Muslim conquest of Gujarat in Western India had two main objectives. The conquerors demanded and more often forcibly wrested both land owned by Hindus and Hindu women. Enslavement of women invariably led to their conversion to Islam. In battles waged by Muslims against Hindus in Malwa and Deccan plateau, a large number of captives were taken. Muslim soldiers were permitted to retain and enslave POWs as plunder.
The first Bahmani sultan, Alauddin Bahman Shah is noted to have captured 1,000 singing and dancing girls from Hindu temples after he battled the northern Carnatic chieftains. The later Bahmanis also enslaved civilian women and children in wars; many of them were converted to Islam in captivity. About the Mughal empire, W.H. Moreland observed, "it became a fashion to raid a village or group of villages without any obvious justification, and carry off the inhabitants as slaves."
During the rule of Shah Jahan, many peasants were compelled to sell their women and children into slavery to meet the land revenue demand. Slavery was officially abolished in British India by the Indian Slavery Act, 1843. However, in modern India, Pakistan and Nepal, there are millions of bonded laborers, who work as slaves to pay off debts.
China
The Tang dynasty purchased Western slaves from the Radanite Jews. Tang Chinese soldiers and pirates enslaved Koreans, Turks, Persians, Indonesians, and people from Inner Mongolia, Central Asia, and northern India. The greatest source of slaves came from southern tribes, including Thais and aboriginals from the southern provinces of Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Guizhou. Malays, Khmers, Indians, and black Africans were also purchased as slaves in the Tang dynasty. Slavery was prevalent until the late 19th century and early 20th century China. All forms of slavery have been illegal in China since 1910.
Modern era
Iran
Reginald Dyer, recalling operations against tribes in Iranian Baluchistan in 1916, stated in a 1921 memoir that the local Balochi tribes would regularly carry out raids against travellers and small towns. During these raids, women and children would often be abducted to become slaves, and would be sold for prices varying based on quality, age and looks. He stated that the average price for a young woman was 300 rupees, and the average price for a small child 25 rupees. The slaves, it was noted, were often half starved.
Japan
Slavery in Japan was, for most of its history, indigenous, since the export and import of slaves was restricted by Japan being a group of islands. In late-16th-century Japan, slavery was officially banned; but forms of contract and indentured labor persisted alongside the period penal codes' forced labor. During the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Pacific War, the Japanese military used millions of civilians and prisoners of war from several countries as forced laborers.
Korea
In Korea, slavery was officially abolished with the Gabo Reform of 1894. During the Joseon period, in times of poor harvest and famine, many peasants voluntarily sold themselves into the nobi system in order to survive.
Southeast Asia
In Southeast Asia, there was a large slave class in Khmer Empire who built the enduring monuments in Angkor Wat and did most of the heavy work. Between the 17th and the early 20th centuries one-quarter to one-third of the population of some areas of Thailand and Burma were slaves. By the 19th century, Bhutan had developed a slave trade with Sikkim and Tibet, also enslaving British subjects and Brahmins. .According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), during the early 21st century an estimated 800,000 people are subject to forced labor in Myanmar.
Slavery in pre-Spanish Philippines was practiced by the tribal Austronesian peoples who inhabited the culturally diverse islands. The neighbouring Muslim states conducted slave raids from the 1600s into the 1800s in coastal areas of the Gulf of Thailand and the Philippine islands. Slaves in Toraja society in Indonesia were family property. People would become slaves when they incurred a debt. Slaves could also be taken during wars, and slave trading was common. Torajan slaves were sold and shipped out to Java and Siam. Slaves could buy their freedom, but their children still inherited slave status. Slavery was abolished in 1863 in all Dutch colonies.
Europe
Classic era
Ancient Greece
Records of slavery in Ancient Greece go as far back as Mycenaean Greece. The origins are not known, but it appears that slavery became an important part of the economy and society only after the establishment of cities. Slavery was common practice and an integral component of ancient Greece, as it was in other societies of the time, including ancient Israel. It is estimated that in Athens, the majority of citizens owned at least one slave. Most ancient writers considered slavery not only natural but necessary, but some isolated debate began to appear, notably in Socratic dialogues. The Stoics produced the first condemnation of slavery recorded in history.
During the 8th and the 7th centuries BC, in the course of the two Messenian Wars, the Spartans reduced an entire population to a pseudo-slavery called helotry. According to Herodotus (IX, 28–29), helots were seven times as numerous as Spartans. Following several helot revolts around the year 600 BC, the Spartans restructured their city-state along authoritarian lines, for the leaders decided that only by turning their society into an armed camp could they hope to maintain control over the numerically dominant helot population. In some Ancient Greek city-states, about 30% of the population consisted of slaves, but paid and slave labor seem to have been equally important.
Rome
Romans inherited the institution of slavery from the Greeks and the Phoenicians. As the Roman Republic expanded outward, it enslaved entire populations, thus ensuring an ample supply of laborers to work in Rome's farms, quarries and households. The people subjected to Roman slavery came from all over Europe and the Mediterranean. Slaves were used for labor, and also for amusement (e.g. gladiators and sex slaves). In the late Republic, the widespread use of recently enslaved groups on plantations and ranches led to slave revolts on a large scale; the Third Servile War led by Spartacus was the most famous and most threatening to Rome.
Other European tribes
Various tribes of Europe are recorded by Roman sources as owning slaves. Strabo records slaves as an export commodity from Britannia, From Llyn Cerrig Bach in Anglesey, an iron gang chain dated to 100 BCE-50 CE was found, over 3 metres long with neck-rings for five captives.
Middle Ages
The chaos of invasion and frequent warfare also resulted in victorious parties taking slaves throughout Europe in the early Middle Ages. St. Patrick, himself captured and sold as a slave, protested against an attack that enslaved newly baptized Christians in his "Letter to the Soldiers of Coroticus". As a commonly traded commodity, like cattle, slaves could become a form of internal or trans-border currency. Slavery during the Early Middle Ages had several distinct sources.
The Vikings raided across Europe, but took the most slaves in raids on the British Isles and in Eastern Europe. While the Vikings kept some slaves as servants, known as thralls, they sold most captives in the Byzantine or Islamic markets. In the West, their target populations were primarily English, Irish, and Scottish, while in the East they were mainly Slavs. The Viking slave-trade slowly ended in the 11th century, as the Vikings settled in the European territories they had once raided. They converted serfs to Christianity and themselves merged with the local populace.
In central Europe, specifically the Frankish/German/Holy Roman Empire of Charlemagne, raids and wars to the east generated a steady supply of slaves from the Slavic captives of these regions. Because of high demand for slaves in the wealthy Muslim empires of Northern Africa, Spain, and the Near East, especially for slaves of European descent, a market for these slaves rapidly emerged. So lucrative was this market that it spawned an economic boom in central and western Europe, today known as the Carolingian Renaissance. This boom period for slaves stretched from the early Muslim conquests to the High Middle Ages but declined in the later Middle Ages as the Islamic Golden Age waned.
Medieval Spain and Portugal saw almost constant warfare between Muslims and Christians. Al-Andalus sent periodic raiding expeditions to loot the Iberian Christian kingdoms, bringing back booty and slaves. In a raid against Lisbon, Portugal in 1189, for example, the Almohad caliph Yaqub al-Mansur took 3,000 female and child captives. In a subsequent attack upon Silves, Portugal in 1191, his governor of Córdoba took 3,000 Christian slaves.
The Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the Ottoman wars in Europe resulted in the taking of large numbers of Christian slaves and using or selling them in the Islamic world too. After the battle of Lepanto the victors freed approximately 12,000 Christian galley slaves from the Ottoman fleet.
Similarly, Christians sold Muslim slaves captured in war. The Order of the Knights of Malta attacked pirates and Muslim shipping, and their base became a centre for slave trading, selling captured North Africans and Turks. Malta remained a slave market until well into the late 18th century. One thousand slaves were required to man the galleys (ships) of the Order.
Poland banned slavery in the 15th century; in Lithuania, slavery was formally abolished in 1588; the institution was replaced by the second enserfment. Slavery remained a minor institution in Russia until 1723, when Peter the Great converted the household slaves into house serfs. Russian agricultural slaves were formally converted into serfs earlier, in 1679. The escaped Russian serfs and kholops formed autonomous communities in the southern steppes, where they became known as Cossacks (meaning "outlaws").
British Isles
Capture in war, voluntary servitude and debt slavery became common within the British Isles before 1066. The Bodmin manumissions show both that slavery existed in 9th and 10th Century Cornwall and that many Cornish slave owners did set their slaves free. Slaves were routinely bought and sold. Running away was also common and slavery was never a major economic factor in the British Isles during the Middle Ages. Ireland and Denmark provided markets for captured Anglo-Saxon and Celtic slaves. Pope Gregory I reputedly made the pun, Non Angli, sed Angeli ("Not Angles, but Angels"), after a response to his query regarding the identity of a group of fair-haired Angles, slave children whom he had observed in the marketplace. After the Norman Conquest, the law no longer supported chattel slavery and slaves became part of the larger body of serfs.
France
In the early Middle Ages, the city of Verdun was the centre of the thriving European slave trade in young boys who were sold to the Islamic emirates of Iberia where they were enslaved as eunuchs. The Italian ambassador Liutprand of Cremona, as one example in the 10th century, presented a gift of four eunuchs to Emperor Constantine VII.
Barbary pirates and Maltese corsairs
Barbary pirates and Maltese corsairs both raided for slaves and purchased slaves from European merchants, often the Radhanites, one of the few groups who could easily move between the Christian and Islamic worlds.
Genoa and Venice
In the late Middle Ages, from 1100 to 1500, the European slave-trade continued, though with a shift from being centered among the Western Mediterranean Islamic nations to the Eastern Christian and Muslim states. The city-states of Venice and Genoa controlled the Eastern Mediterranean from the 12th century and the Black Sea from the 13th century. They sold both Slavic and Baltic slaves, as well as Georgians, Turks, and other ethnic groups of the Black Sea and Caucasus. The sale of European slaves by Europeans slowly ended as the Slavic and Baltic ethnic groups Christianized by the Late Middle Ages. European slaves did not pass on an inherited status and was thus more akin to forced labor, or indentured servitude.
From the 1440s into the 18th century, Europeans from Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, and England were sold into slavery by North Africans. It has been suggested that "white slavery had been minimised or ignored because academics preferred to treat Europeans as evil colonialists rather than as victims."[307][308] In 1575, the Tatars captured over 35,000 Ukrainians; a 1676 raid took almost 40,000. About 60,000 Ukrainians were captured in 1688; some were ransomed, but most were sold into slavery.[309][310] Some of the Roma people were enslaved over five centuries in Romania until abolition in 1864 (see Slavery in Romania).
Mongols
The Mongol invasions and conquests in the 13th century also resulted in taking numerous captives into slavery. The Mongols enslaved skilled individuals, women and children and marched them to Karakorum or Sarai, whence they were sold throughout Eurasia. Many of these slaves were shipped to the slave market in Novgorod.
Slave commerce during the Late Middle Ages was mainly in the hands of Venetian and Genoese merchants and cartels, who were involved in the slave trade with the Golden Horde. In 1382 the Golden Horde under Khan Tokhtamysh sacked Moscow, burning the city and carrying off thousands of inhabitants as slaves. Between 1414 and 1423, some 10,000 eastern European slaves were sold in Venice. Genoese merchants organized the slave trade from the Crimea to Mamluk Egypt. For years, the Khanates of Kazan and Astrakhan routinely made raids on Russian principalities for slaves and to plunder towns. Russian chronicles record about 40 raids by Kazan Khans on the Russian territories in the first half of the 16th century.
In 1441 Haci I Giray declared independence from the Golden Horde and established the Crimean Khanate. For a long time, until the early 18th century, the khanate maintained an extensive slave-trade with the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East. In a process called the "harvesting of the steppe" they enslaved many Slavic peasants. Muscovy recorded about 30 major Tatar raids into Muscovite territories between 1558 and 1596.
Moscow was repeatedly a target. In 1521, the combined forces of Crimean Khan Mehmed Giray and his Kazan allies attacked the city and captured thousands of slaves. In 1571, the Crimean Tatars attacked and sacked Moscow, burning everything but the Kremlin and taking thousands of captives as slaves. In Crimea, about 75% of the population consisted of slaves.
In the Viking era beginning circa 793, the Norse raiders often captured and enslaved militarily weaker peoples they encountered. The Nordic countries called their slaves thralls (Old Norse: Þræll). The thralls were mostly from Western Europe, among them many Franks, Frisians, Anglo-Saxons, and both Irish and Britonnic Celts. Many Irish slaves travelled in expeditions for the colonization of Iceland. The Norse also took German, Baltic, Slavic and Latin slaves. The slave trade was one of the pillars of Norse commerce during the 9th through 11th centuries. The 10th-century Persian traveller Ibn Rustah described how Swedish Vikings, the Varangians or Rus, terrorized and enslaved the Slavs taken in their raids along the Volga River. The thrall system was finally abolished in the mid-14th century in Scandinavia.
Modern era
Mediterranean powers frequently sentenced convicted criminals to row in the war-galleys of the state (initially only in time of war). After the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685 and Camisard rebellion, the French Crown filled its galleys with French Huguenots, Protestants condemned for resisting the state. Galley-slaves lived and worked in such harsh conditions that many did not survive their terms of sentence, even if they survived shipwreck and slaughter or torture at the hands of enemies or of pirates. Naval forces often turned 'infidel' prisoners-of-war into galley-slaves. Several well-known historical figures served time as galley slaves after being captured by the enemy—the Ottoman corsair and admiral Turgut Reis and the Knights Hospitaller Grand Master Jean Parisot de la Valette among them.
Denmark-Norway was the first European country to ban the slave trade. This happened with a decree issued by King Christian VII of Denmark in 1792, to become fully effective by 1803. Slavery as an institution was not banned until 1848. At this time Iceland was a part of Denmark-Norway but slave trading had been abolished in Iceland in 1117 and had never been reestablished.
Slavery in the French Republic was abolished on 4 February 1794, including in its colonies. The lengthy Haitian Revolution by its slaves and free people of color established Haiti as a free republic in 1804 ruled by blacks, the first of its kind. At the time of the revolution, Haiti was known as Saint-Domingue and was a colony of France. Napoleon Bonaparte gave up on Haiti in 1803, but re-established slavery in Guadeloupe and Martinique in 1804, at the request of planters of the Caribbean colonies. Slavery was permanently abolished in the French empire during the French Revolution of 1848.
Portugal
The 15th-century Portuguese exploration of the African coast is commonly regarded as the harbinger of European colonialism. In 1452, Pope Nicholas V issued the papal bull Dum Diversas, granting Afonso V of Portugal the right to reduce any "Saracens, pagans and any other unbelievers" to hereditary slavery which legitimized slave trade under Catholic beliefs of that time. This approval of slavery was reaffirmed and extended in his Romanus Pontifex bull of 1455. These papal bulls came to serve as a justification for the subsequent era of the slave trade and European colonialism, although for a short period as in 1462 Pius II declared slavery to be "a great crime". The followers of the church of England and Protestants did not use the papal bull as a justification. The position of the church was to condemn the slavery of Christians, but slavery was regarded as an old established and necessary institution which supplied Europe with the necessary workforce. In the 16th century, African slaves had replaced almost all other ethnicities and religious enslaved groups in Europe. Within the Portuguese territory of Brazil, and even beyond its original borders, the enslavement of Native Americans was carried out by the Bandeirantes.
Among many other European slave markets, Genoa, and Venice were some well-known markets, their importance and demand growing after the great plague of the 14th century which decimated much of the European workforce. The maritime town of Lagos, Portugal, was the first slave market created in Portugal for the sale of imported African slaves, the Mercado de Escravos, which opened in 1444In 1441, the first slaves were brought to Portugal from northern Mauritania. Prince Henry the Navigator, major sponsor of the Portuguese African expeditions, as of any other merchandise, taxed one fifth of the selling price of the slaves imported to Portugal. By the year 1552 African slaves made up 10 percent of the population of Lisbon. In the second half of the 16th century, the Crown gave up the monopoly on slave trade and the focus of European trade in African slaves shifted from import to Europe to slave transports directly to tropical colonies in the Americas—in the case of Portugal, especially Brazil. In the 15th century, one-third of the slaves were resold to the African market in exchange of gold. Slavery was abolished in mainland Portugal and Portuguese India in 1761. It was finally abolished in all Portuguese colonies in 1869.
Spain
The Spaniards were the first Europeans to use African slaves in the New World on islands such as Cuba and Hispaniola, due to a shortage of labor caused by the spread of diseases, and so the Spanish colonists gradually became involved in the Atlantic slave trade. The first African slaves arrived in Hispaniola in 1501; by 1517, the natives had been "virtually annihilated" mostly to diseases. The problem of the justness of Native American's slavery was a key issue for the Spanish Crown. It was Charles V who gave a definite answer to this complicated and delicate matter. To that end, on 25 November 1542, the Emperor abolished slavery by decree in his Leyes Nuevas New Laws. This bill was based on the arguments given by the best Spanish theologists and jurists who were unanimous in the condemnation of such slavery as unjust; they declared it illegitimate and outlawed it from America—not just the slavery of Spaniards over Natives—but also the type of slavery practiced among the Natives themselves Thus, Spain became the first country to officially abolish slavery.
However, in the Spanish colonies of Cuba and Puerto Rico, where sugarcane production was highly profitable based on slave labor, African slavery persisted until 1873 in Puerto Rico "with provisions for periods of apprenticeship", and 1886 in Cuba.
Netherlands
Although slavery was illegal inside the Netherlands it flourished throughout the Dutch Empire in the Americas, Africa, Ceylon and Indonesia. The Dutch Slave Coast (Dutch: Slavenkust) referred to the trading posts of the Dutch West India Company on the Slave Coast, which lie in contemporary Ghana, Benin, Togo and Nigeria. Initially the Dutch shipped slaves to northern Brazil, and during the second half of the 17th century they had a controlling interest in the trade to the Spanish colonies. Today's Suriname and Guyana became prominent markets in the 18th century. Between 1612 and 1872, the Dutch operated from some 10 fortresses along the Gold Coast (now Ghana), from which slaves were shipped across the Atlantic. Dutch involvement on the Slave Coast increased with the establishment of a trading post in Offra in 1660. Willem Bosman writes in his Nauwkeurige beschrijving van de Guinese Goud- Tand- en Slavekust (1703) that Allada was also called Grand Ardra, being the larger cousin of Little Ardra, also known as Offra. From 1660 onward, Dutch presence in Allada and especially Offra became more permanent. A report from this year asserts Dutch trading posts, apart from Allada and Offra, in Benin City, Grand-Popo, and Savi.
The Offra trading post soon became the most important Dutch office on the Slave Coast. According to a 1670 report, annually 2,500 to 3,000 slaves were transported from Offra to the Americas. These numbers were only feasible in times of peace, however, and dwindled in time of conflict. From 1688 onward, the struggle between the Aja king of Allada and the peoples on the coastal regions, impeded the supply of slaves. The Dutch West India Company chose the side of the Aja king, causing the Offra office to be destroyed by opposing forces in 1692. By 1650 the Dutch had the pre-eminent slave trade in Europe and South East Asia. Later, trade shifted to Ouidah. On the instigation of Governor-General of the Dutch Gold Coast Willem de la Palma, Jacob van den Broucke was sent in 1703 as "opperkommies" (head merchant) to the Dutch trading post at Ouidah, which according to sources was established around 1670. Political unrest caused the Dutch to abandon their trading post at Ouidah in 1725, and they then moved to Jaquim, at which place they built Fort Zeelandia. The head of the post, Hendrik Hertog, had a reputation for being a successful slave trader. In an attempt to extend his trading area, Hertog negotiated with local tribes and mingled in local political struggles. He sided with the wrong party, however, leading to a conflict with Director-General Jan Pranger and to his exile to the island of Appa in 1732. The Dutch trading post on this island was extended as the new centre of the slave trade. In 1733, Hertog returned to Jaquim, this time extending the trading post into Fort Zeelandia. The revival of the slave trade at Jaquim was only temporary, however, as his superiors at the Dutch West India Company noticed that Hertog's slaves were more expensive than at the Gold Coast. From 1735, Elmina became the preferred spot to trade slaves. As of 1778, it was estimated that the Dutch were shipping approximately 6,000 Africans for enslavement in the Dutch West Indies each year. Slavery also characterised the Dutch possessions in Indonesia, Ceylon and South Africa, where Indonesians have made a significant contribution to the Cape Coloured population of that country. The Dutch part in the Atlantic slave trade is estimated at 5–7 percent, as they shipped about 550,000–600,000 African slaves across the Atlantic, about 75,000 of whom died on board before reaching their destinations. From 1596 to 1829, the Dutch traders sold 250,000 slaves in the Dutch Guianas, 142,000 in the Dutch Caribbean islands, and 28,000 in Dutch Brazil. In addition, tens of thousands of slaves, mostly from India and some from Africa, were carried to the Dutch East Indies. The Netherlands abolished slavery in 1863. Although the decision was made in 1848, it took many years for the law to be implemented. Furthermore, slaves in Suriname would be fully free only in 1873, since the law stipulated that there was to be a mandatory 10-year transition.
Barbary corsairs
Barbary Corsairs continued to trade in European slaves into the Modern time-period. Muslim pirates, primarily Algerians with the support of the Ottoman Empire, raided European coasts and shipping from the 16th to the 19th centuries, and took thousands of captives, whom they sold or enslaved. Many were held for ransom, and European communities raised funds such as Malta's Monte della Redenzione degli Schiavi to buy back their citizens. The raids gradually ended with the naval decline of the Ottoman Empire in the late 16th and 17th centuries, as well as the European conquest of North Africa throughout the 19th century.
From 1609 to 1616, England lost 466 merchant ships to Barbary pirates. 160 English ships were captured by Algerians between 1677 and 1680. Many of the captured sailors were made into slaves and held for ransom. The corsairs were no strangers to the South West of England where raids were known in a number of coastal communities. In 1627 Barbary Pirates under command of the Dutch renegade Jan Janszoon (Murat Reis), operating from the Moroccan port of Salé, occupied the island of Lundy. During this time there were reports of captured slaves being sent to Algiers.
Ireland, despite its northern position, was not immune from attacks by the corsairs. In June 1631 Janszoon, with pirates from Algiers and armed troops of the Ottoman Empire, stormed ashore at the little harbor village of Baltimore, County Cork. They captured almost all the villagers and took them away to a life of slavery in North Africa. The prisoners were destined for a variety of fates—some lived out their days chained to the oars as galley slaves, while others would spend long years in the scented seclusion of the harem or within the walls of the sultan's palace. Only two of them ever saw Ireland again.
The Congress of Vienna (1814–15), which ended the Napoleonic Wars, led to increased European consensus on the need to end Barbary raiding. The sacking of Palma on the island of Sardinia by a Tunisian squadron, which carried off 158 inhabitants, roused widespread indignation. Britain had by this time banned the slave trade and was seeking to induce other countries to do likewise. States that were more vulnerable to the corsairs complained that Britain cared more for ending the trade in African slaves than stopping the enslavement of Europeans and Americans by the Barbary States.
In order to neutralise this objection and further the anti-slavery campaign, in 1816 Britain sent Lord Exmouth to secure new concessions from Tripoli, Tunis, and Algiers, including a pledge to treat Christian captives in any future conflict as prisoners of war rather than slaves. He imposed peace between Algiers and the kingdoms of Sardinia and Sicily. On his first visit, Lord Exmouth negotiated satisfactory treaties and sailed for home. While he was negotiating, a number of Sardinian fishermen who had settled at Bona on the Tunisian coast were brutally treated without his knowledge. As Sardinians they were technically under British protection, and the government sent Exmouth back to secure reparation. On 17 August, in combination with a Dutch squadron under Admiral Van de Capellen, Exmouth bombarded Algiers. Both Algiers and Tunis made fresh concessions as a result.
The Barbary states had difficulty securing uniform compliance with a total prohibition of slave-raiding, as this had been traditionally of central importance to the North African economy. Slavers continued to take captives by preying on less well-protected peoples. Algiers subsequently renewed its slave-raiding, though on a smaller scale. Europeans at the Congress of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1818 discussed possible retaliation. In 1820 a British fleet under Admiral Sir Harry Neal bombarded Algiers. Corsair activity based in Algiers did not entirely cease until France conquered the state in 1830.
Crimean Khanate
The Crimeans frequently mounted raids into the Danubian principalities, Poland-Lithuania, and Muscovy to enslave people whom they could capture; for each captive, the khan received a fixed share (savğa) of 10% or 20%. These campaigns by Crimean forces were either sefers ("sojourns" – officially declared military operations led by the khans themselves), or çapuls ("despoiling" – raids undertaken by groups of noblemen, sometimes illegally because they contravened treaties concluded by the khans with neighbouring rulers).
For a long time, until the early 18th century, the Crimean Khanate maintained a massive slave trade with the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East, exporting about 2 million slaves from Russia and Poland-Lithuania over the period 1500–1700. Caffa (modern Feodosia) became one of the best-known and significant trading ports and slave markets. In 1769 the last major Tatar raid saw the capture of 20,000 Russian and Ruthenian slaves.
Author and historian Brian Glyn Williams writes:
Fisher estimates that in the sixteenth century the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth lost around 20,000 individuals a year and that from 1474 to 1694, as many as a million Commonwealth citizens were carried off into Crimean slavery.
Early modern sources are full of descriptions of sufferings of Christian slaves captured by the Crimean Tatars in the course of their raids:
It seems that the position and everyday conditions of a slave depended largely on his/her owner. Some slaves indeed could spend the rest of their days doing exhausting labor: as the Crimean vizir (minister) Sefer Gazi Aga mentions in one of his letters, the slaves were often "a plough and a scythe" of their owners. Most terrible, perhaps, was the fate of those who became galley-slaves, whose sufferings were poeticized in many Ukrainian dumas (songs). ... Both female and male slaves were often used for sexual purposes.
British slave trade
Britain played a prominent role in the Atlantic slave trade, especially after 1640, when sugar cane was introduced to the region. At first, most were white Britons, or Irish, enslaved as indentured labour – for a fixed period – in the West Indies. These people may have been criminals, political rebels, the poor with no prospects or others who were simply tricked or kidnapped. Slavery was a legal institution in all of the 13 American colonies and Canada (acquired by Britain in 1763). The profits of the slave trade and of West Indian plantations amounted to under 5% of the British economy at the time of the Industrial Revolution.
A little-known incident in the career of Judge Jeffreys refers to an assize in Bristol in 1685 when he made the mayor of the city, then sitting fully robed beside him on the bench, go into the dock and be fined £1000 for being a "kidnapping knave"; some Bristol traders at the time were known at the time to kidnap their own countrymen and ship them away as slaves.
Somersett's case in 1772 was generally taken at the time to have decided that the condition of slavery did not exist under English law in England. In 1785, English poet William Cowper wrote: "We have no slaves at home – Then why abroad? Slaves cannot breathe in England; if their lungs receive our air, that moment they are free. They touch our country, and their shackles fall. That's noble, and bespeaks a nation proud. And jealous of the blessing. Spread it then, And let it circulate through every vein." However, slavery continued to thrive in England itself, much like it did in the British Empire, until full emancipation in the 1830s. In 1807, following many years of lobbying by the abolitionist movement, led primarily by William Wilberforce, the British Parliament voted to make the slave trade illegal anywhere in the Empire with the Slave Trade Act 1807. Thereafter Britain took a prominent role in combating the trade, and slavery itself was abolished in the British Empire (except for India) with the Slavery Abolition Act 1833. Between 1808 and 1860, the West Africa Squadron seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard. Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade. Akitoye, the 11th Oba of Lagos, is famous for having used British involvement to regain his rule in return for suppressing slavery among the Yoruba people of Lagos in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers. In 1839, the world's oldest international human rights organization, British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society (now Anti-Slavery International), was formed in Britain as by Joseph Sturge, which worked to outlaw slavery in other countries.
After 1833, the freed African slaves declined employment in the cane fields. This led to the importation of indentured labour again – mainly from India, and also China.
In 1811, Arthur William Hodge was executed for the murder of a slave in the British West Indies. He was not, however, as some have claimed, the first white person to have been lawfully executed for the murder of a slave.
Modern Europe
Germany
During World War II Nazi Germany operated several categories of Arbeitslager (Labor Camps) for different categories of inmates. The largest number of them held Polish gentiles and Jewish civilians forcibly abducted in occupied countries (see Łapanka) to provide labor in the German war industry, repair bombed railroads and bridges or work on farms. By 1944, 20% of all workers were foreigners, either civilians or prisoners of war
Allied powers
As agreed by the Allies at the Yalta conference, Germans were used as forced labor as part of the reparations to be extracted. By 1947, it is estimated that 400,000 Germans (both civilians and POWs) were being used as forced labor by the U.S., France, the UK and the Soviet Union. German prisoners were for example forced to clear minefields in France and the Low Countries. By December 1945, it was estimated by French authorities that 2,000 German prisoners were being killed or injured each month in accidents. In Norway the last available casualty record, from 29 August 1945, shows that by that time a total of 275 German soldiers died while clearing mines, while 392 had been injured.
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union took over the already extensive katorga system and expanded it immensely, eventually organizing the Gulag to run the camps. In 1954, a year after Stalin's death, the new Soviet government of Nikita Khrushchev began to release political prisoners and close down the camps. By the end of the 1950s, virtually all "corrective labor camps" were reorganized, mostly into the system of corrective labor colonies. Officially, the Gulag was terminated by the MVD order 20 25 January 1960.
During the period of Stalinism, the Gulag labor camps in the Soviet Union were officially called "Corrective labor camps." The term "labor colony"; more exactly, "Corrective labor colony", (Russian: исправительно-трудовая колония, abbr. ИТК), was also in use, most notably the ones for underaged (16 years or younger) convicts and captured besprizorniki (street children, literally, "children without family care"). After the reformation of the camps into the Gulag, the term "corrective labor colony" essentially encompassed labor camps[citation needed].
The Soviet Union had about 14 million people working in Gulags during its existence.
Oceania
In the first half of the 19th century, small-scale slave raids took place across Polynesia to supply labor and sex workers for the whaling and sealing trades, with examples from both the westerly and easterly extremes of the Polynesian triangle. By the 1860s this had grown to a larger scale operation with Peruvian slave raids in the South Sea Islands to collect labor for the guano industry.
Hawaii
Ancient Hawaii was a caste society. People were born into specific social classes. Kauwa were those of the outcast or slave class. They are believed to have been war captives or their descendants. Marriage between higher castes and the kauwa was strictly forbidden. The kauwa worked for the chiefs and were often used as human sacrifices at the luakini heiau. (They were not the only sacrifices; law-breakers of all castes or defeated political opponents were also acceptable as victims.)
The kapu system was abolished during the ʻAi Noa in 1819, and with it the distinction between the kauwā slave class and the makaʻāinana (commoners). The 1852 Constitution of the Kingdom of Hawaii officially made slavery illegal.
New Zealand
Before the arrival of European settlers, each Maori tribe (iwi) considered itself a separate entity equivalent to a nation. In the traditional Maori society of Aotearoa, prisoners of war became taurekareka, slaves – unless released, ransomed or eaten. With some exceptions, the child of a slave remained a slave.
As far as it is possible to tell, slavery seems to have increased in the early-19th century with increased numbers of prisoners being taken by Māori military leaders (such as Hongi Hika and Te Rauparaha) to satisfy the need for labor in the Musket Wars, to supply whalers and traders with food, flax and timber in return for western goods. The intertribal Musket Wars lasted from 1807 to 1843; northern tribes who had acquired muskets captured large numbers of slaves. About 20,000 Maori died in the wars. An unknown number of slaves were captured. Northern tribes used slaves (called mokai) to grow large areas of potatoes for trade with visiting ships. Chiefs started an extensive sex trade in the Bay of Islands in the 1830s, using mainly slave girls. By 1835 about 70 to 80 ships per year called into the port. One French captain described the impossibility of getting rid of the girls who swarmed over his ship, outnumbering his crew of 70 by 3 to 1. All payments to the girls were stolen by the chief. By 1833 Christianity had become established in the north of New Zealand, and large numbers of slaves were freed.
Slavery was outlawed when the British entered into a constitutional arrangement with New Zealand in 1840 via the Treaty of Waitangi, although it did not end completely until government was effectively extended over the whole of the country with the defeat of the King movement in the Wars of the mid-1860s.
Chatham Islands
One group of Polynesians who migrated to the Chatham Islands became the Moriori who developed a largely pacifist culture. It was originally speculated that they settled the Chathams direct from Polynesia, but it is now widely believed they were disaffected Maori who emigrated from the South Island of New Zealand. Their pacifism left the Moriori unable to defend themselves when the islands were invaded by mainland Māori in the 1830s.
Two Taranaki tribes, Ngati Tama and Ngati Mutunga, displaced by the Musket Wars, carried out a carefully planned invasion of the Chatham Islands, 800 km east of Christchurch, in 1835. About 15% of the Polynesian Moriori natives who had migrated to the islands at about 1500 CE were killed, with many women being tortured to death. The remaining population was enslaved for the purpose of growing food, especially potatoes. The Moriori were treated in an inhumane and degrading manner for many years. Their culture was banned and they were forbidden to marry.
Some 300 Moriori men, women and children were massacred and the remaining 1,200 to 1,300 survivors were enslaved.
Some Maori took Moriori partners. The state of enslavement of Moriori lasted until the 1860s although it had been discouraged by CMS missionaries in northern New Zealand from the late 1820s. In 1870 Ngati Mutunga, one of the invading tribes, argued before the Native Land Court in New Zealand that their gross mistreatment of the Moriori was standard Maori practice or tikanga.
Rapa Nui / Easter Island
The isolated island of Rapa Nui/Easter Island was inhabited by the Rapanui, who suffered a series of slave raids from 1805 or earlier, culminating in a near genocidal experience in the 1860s. The 1805 raid was by American sealers and was one of a series that changed the attitude of the islanders to outside visitors, with reports in the 1820s and 1830s that all visitors received a hostile reception. In December 1862, Peruvian slave raiders took between 1,400 and 2,000 islanders back to Peru to work in the guano industry; this was about a third of the island's population and included much of the island's leadership, the last ariki-mau and possibly the last who could read Rongorongo. After intervention by the French ambassador in Lima, the last 15 survivors were returned to the island, but brought with them smallpox, which further devastated the island.
Abolitionist movements
Slavery has existed, in one form or another, throughout the whole of human history. So, too, have movements to free large or distinct groups of slaves. However, abolitionism should be distinguished from efforts to help a particular group of slaves, or to restrict one practice, such as the slave trade.
Drescher (2009) provides a model for the history of the abolition of slavery, emphasizing its origins in Western Europe. Around the year 1500, slavery had virtually died out in Western Europe, but was a normal phenomenon practically everywhere else. The imperial powers – the British, French, Spanish, Portuguese, Dutch, and Belgian empires, and a few others – built worldwide empires based primarily on plantation agriculture using slaves imported from Africa. However, the powers took care to minimize the presence of slavery in their homelands. In 1807 Britain and soon after, the United States also, both criminalized the international slave trade. The Royal Navy was increasingly effective in intercepting slave ships, freeing the captives and taking the crew for trial in courts.
Although there were numerous slave revolts in the Caribbean, the only successful uprising came in the French colony of Haiti in the 1790s, where the slaves rose up, killed the mulattoes and whites, and established the independent Republic of Haiti. Europe recoiled in horror.
The continuing profitability of slave-based plantations and the threats of race war slowed the development of abolition movements during the first half of the 19th century. These movements were strongest in Britain, and after 1840 in the United States. The Northern states of the United States abolished slavery, partly in response to the Declaration of Independence, between 1777 and 1804. Britain ended slavery in its empire in the 1830s. However, the plantation economies of the southern United States, based on cotton, and those in Brazil and Cuba, based on sugar, expanded and grew even more profitable. The bloody American Civil War ended slavery in the United States in 1865. The system ended in Cuba and Brazil in the 1880s because it was no longer profitable for the owners. Slavery continued to exist in Africa, where Arab slave traders raided black areas for new captives to be sold in the system. European colonial rule and diplomatic pressure slowly put an end to the trade, and eventually to the practice of slavery itself.
Britain
In 1772, the Somersett Case (R. v.Knowles, ex parte Somersett) of the English Court of King's Bench ruled that it was unlawful for a slave to be forcibly taken abroad. The case has since been misrepresented as finding that slavery was unlawful in England (although not elsewhere in the British Empire). A similar case, that of Joseph Knight, took place in Scotland five years later and ruled slavery to be contrary to the law of Scotland.
Following the work of campaigners in the United Kingdom, such as William Wilberforce, Henry Dundas, 1st Viscount Melville and Thomas Clarkson, who founded the Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade (Abolition Society) in May 1787, the Act for the Abolition of the Slave Trade was passed by Parliament on 25 March 1807, coming into effect the following year. The act imposed a fine of £100 for every slave found aboard a British ship. The intention was to outlaw entirely the Atlantic slave trade within the whole British Empire.
The significance of the abolition of the British slave trade lay in the number of people hitherto sold and carried by British slave vessels. Britain shipped 2,532,300 Africans across the Atlantic, equalling 41% of the total transport of 6,132,900 individuals. This made the British empire the biggest slave-trade contributor in the world due to the magnitude of the empire, which made the abolition act all the more damaging to the global trade of slaves. Britain used its diplomatic influence to press other nations into treaties to ban their slave trade and to give the Royal Navy the right to interdict slave ships sailing under their national flag.
The Slavery Abolition Act, passed on 1 August 1833, outlawed slavery itself throughout the British Empire, with the exception of India. On 1 August 1834 slaves became indentured to their former owners in an apprenticeship system for six years. Full emancipation was granted ahead of schedule on 1 August 1838. Britain abolished slavery in both Hindu and Muslim India with the Indian Slavery Act, 1843.
The Society for the Mitigation and Gradual Abolition of Slavery Throughout the British Dominions (later London Anti-slavery Society ), was founded in 1823, and existed until 1838.
Domestic slavery practised by the educated African coastal elites (as well as interior traditional rulers) in Sierra Leone was abolished in 1928. A study found practices of domestic slavery still widespread in rural areas in the 1970s.
The British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society, founded in 1839 and having gone several name changes since, still exists as Anti-Slavery International.
France
There were slaves in mainland France (especially in trade ports such as Nantes or Bordeaux).,[citation needed] but the institution was never officially authorized there. The legal case of Jean Boucaux in 1739 clarified the unclear legal position of possible slaves in France, and was followed by laws that established registers for slaves in mainland France, who were limited to a three-year stay, for visits or learning a trade. Unregistered "slaves" in France were regarded as free. However, slavery was of vital importance to the economy of France's Caribbean possessions, especially Saint-Domingue.
Abolition
In 1793, influenced by the French Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen of August 1789 and alarmed as the massive slave revolt of August 1791 that had become the Haitian Revolution threatened to ally itself with the British, the French Revolutionary commissioners Sonthonax and Polverel declared general emancipation to reconcile them with France. In Paris, on 4 February 1794, Abbé Grégoire and the Convention ratified this action by officially abolishing slavery in all French territories outside mainland France, freeing all the slaves both for moral and security reasons.
Napoleon restores slavery
Napoleon came to power in 1799 and soon had grandiose plans for the French sugar colonies; to achieve them he reintroduced slavery. Napoleon's major adventure into the Caribbean—sending 30,000 troops in 1802 to retake Saint Domingue (Haiti) from ex-slaves under Toussaint L'Ouverture who had revolted. Napoleon wanted to preserve France's financial benefits from the colony's sugar and coffee crops; he then planned to establish a major base at New Orleans. He therefore re-established slavery in Haiti and Guadeloupe, where it had been abolished after rebellions. Slaves and black freedmen fought the French for their freedom and independence. Revolutionary ideals played a central role in the fighting for it was the slaves and their allies who were fighting for the revolutionary ideals of freedom and equality, while the French troops under General Charles Leclerc fought to restore the order of the ancien régime. The goal of re-establishing slavery explicitly contradicted the ideals of the French Revolution. The French soldiers were unable to cope with tropical diseases, and most died of yellow fever. Slavery was reimposed in Guadeloupe but not in Haiti, which became an independent black republic. Napoleon's vast colonial dreams for Egypt, India, the Caribbean, Louisiana, and even Australia were all doomed for lack of a fleet capable of matching Britain's Royal Navy. Realizing the fiasco Napoleon liquidated the Haiti project, brought home the survivors and sold off the huge Louisiana territory to the US in 1803.
Napoleon and slavery
In 1794 slavery was abolished in the French Empire. After seizing Lower Egypt in 1798, Napoleon Bonaparte issued a proclamation in Arabic, declaring all men to be free and equal. However, the French bought males as soldiers and females as concubines. Napoleon personally opposed the abolition and restored colonial slavery in 1802, a year after the capitulation of his troops in Egypt.
In a little-known episode, Napoleon decreed the abolition of the slave trade upon his returning from Elba in an attempt to appease Great Britain. His decision was confirmed by the Treaty of Paris on 20 November 1815 and by order of Louis XVIII on 8 January 1817. However, trafficking continued despite sanctions.
Victor Schœlcher and the 1848 abolition
Slavery in the French colonies was finally abolished only in 1848, three months after the beginning of the revolution against the July Monarchy. It was in large part the result of the tireless 18-year campaign of Victor Schœlcher. On 3 March 1848, he had been appointed under-secretary of the navy, and caused a decree to be issued by the provisional government which acknowledged the principle of the enfranchisement of the slaves through the French possessions. He also wrote the decree of 27 April 1848 in which the French government announced that slavery was abolished in all of its colonies.
United States
In 1688, four German Quakers in Germantown presented a protest against the institution of slavery to their local Quaker Meeting. It was ignored for 150 years but in 1844 it was rediscovered and was popularized by the abolitionist movement. The 1688 Petition was the first American public document of its kind to protest slavery, and in addition was one of the first public documents to define universal human rights.
The American Colonization Society, the primary vehicle for returning black Americans to greater freedom in Africa, established the colony of Liberia in 1821–23, on the premise that former American slaves would have greater freedom and equality there. The ACS assisted in the movement of thousands of African Americans to Liberia, with its founder Henry Clay stating; "unconquerable prejudice resulting from their color, they never could amalgamate with the free whites of this country. It was desirable, therefore, as it respected them, and the residue of the population of the country, to drain them off". Abraham Lincoln, an enthusiastic supporter of Clay, adopted his position on returning the blacks to their own land.
Slaves in the United States who escaped ownership would often make their way to Canada via the "Underground Railroad". The more famous of the African American abolitionists include former slaves Harriet Tubman, Sojourner Truth and Frederick Douglass. Many more people who opposed slavery and worked for abolition were northern whites, such as William Lloyd Garrison and John Brown. Slavery was legally abolished in 1865 by the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
While abolitionists agreed on the evils of slavery, there were differing opinions on what should happen after African Americans were freed. By the time of Emancipation, African-Americans were now native to the United States and did not want to leave. Most believed that their labor had made the land theirs as well as that of the whites.
Congress of Vienna
The Declaration of the Powers, on the Abolition of the Slave Trade, of 8 February 1815 (Which also formed ACT, No. XV. of the Final Act of the Congress of Vienna of the same year) included in its first sentence the concept of the "principles of humanity and universal morality" as justification for ending a trade that was "odious in its continuance".
Twentieth century
The 1926 Slavery Convention, an initiative of the League of Nations, was a turning point in banning global slavery. Article 4 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted in 1948 by the UN General Assembly, explicitly banned slavery. The United Nations 1956 Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery was convened to outlaw and ban slavery worldwide, including child slavery. In December 1966, the UN General Assembly adopted the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which was developed from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Article 4 of this international treaty bans slavery. The treaty came into force in March 1976 after it had been ratified by 35 nations.
As of November 2003, 104 nations had ratified the treaty. However, illegal forced labour involves millions of people in the 21st century, 43% for sexual exploitation and 32% for economic exploitation.
In May 2004, the 22 members of the Arab League adopted the Arab Charter on Human Rights, which incorporated the 1990 Cairo Declaration on Human Rights in Islam, which states:
Human beings are born free, and no one has the right to enslave, humiliate, oppress or exploit them, and there can be no subjugation but to God the Most-High.
— Article 11, Cairo Declaration on Human Rights in Islam, 1990
Currently, the Anti-trafficking Coordination Team Initiative (ACT Team Initiative), a coordinated effort between the U.S. departments of justice, homeland security and labor, addresses human trafficking. The International Labour Organization estimates that there are 20.9 million victims of human trafficking globally, including 5.5 million children, of which 55% are women and girls.
Contemporary slavery
Slavery continues into the 21st century. As of 2018, the countries with the most slaves were: India (8 million), China (3.86 million), Pakistan (3.19 million), North Korea (2.64 million), Nigeria (1.39 million), Iran (1.29 million), Indonesia (1.22 million), Democratic Republic of the Congo (1 million), Russia (794,000) and the Philippines (784,000). The countries with highest prevalence of slavery were North Korea (10.5%), Eritrea (9.3%), Burundi (4%), the Central African Republic (2.2%), Afghanistan (2.2%), Mauritania (2.1%), South Sudan (2.1%), Pakistan (1.7%), Cambodia (1.7%) and Iran (1.6%).
Historiography
Historiography in the United States
The history of slavery originally was the history of the government's laws and policies toward slavery, and the political debates about it. Black history was promoted very largely at black colleges. The situation changed dramatically with the coming of the Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s. Attention shifted to the enslaved humans, the free blacks, and the struggles of the black community against adversity.
Peter Kolchin described the state of historiography in the early 20th century as follows:
During the first half of the twentieth century, a major component of this approach was often simply racism, manifest in the belief that blacks were, at best, imitative of whites. Thus Ulrich B. Phillips, the era's most celebrated and influential expert on slavery, combined a sophisticated portrait of the white planters' life and behavior with crude passing generalizations about the life and behavior of their black slaves.
Historians James Oliver Horton and Lois E. Horton described Phillips' mindset, methodology and influence:
His portrayal of blacks as passive, inferior people, whose African origins made them uncivilized, seemed to provide historical evidence for the theories of racial inferiority that supported racial segregation. Drawing evidence exclusively from plantation records, letters, southern newspapers, and other sources reflecting the slaveholder's point of view, Phillips depicted slave masters who provided for the welfare of their slaves and contended that true affection existed between master and slave.
The racist attitude concerning slaves carried over into the historiography of the Dunning School of Reconstruction era history, which dominated in the early 20th century. Writing in 2005, the historian Eric Foner states:
Their account of the era rested, as one member of the Dunning school put it, on the assumption of "negro incapacity." Finding it impossible to believe that blacks could ever be independent actors on the stage of history, with their own aspirations and motivations, Dunning et al. portrayed African Americans either as "children", ignorant dupes manipulated by unscrupulous whites, or as savages, their primal passions unleashed by the end of slavery.
Beginning in the 1950s, historiography moved away from the tone of the Phillips era. Historians still emphasized the slave as an object. Whereas Phillips presented the slave as the object of benign attention by the owners, historians such as Kenneth Stampp emphasized the mistreatment and abuse of the slave.
In the portrayal of the slave as a victim, the historian Stanley M. Elkins in his 1959 work Slavery: A Problem in American Institutional and Intellectual Life compared the effects of United States slavery to that resulting from the brutality of the Nazi concentration camps. He stated the institution destroyed the will of the slave, creating an "emasculated, docile Sambo" who identified totally with the owner. Elkins' thesis was challenged by historians. Gradually historians recognized that in addition to the effects of the owner-slave relationship, slaves did not live in a "totally closed environment but rather in one that permitted the emergence of enormous variety and allowed slaves to pursue important relationships with persons other than their master, including those to be found in their families, churches and communities."
Economic historians Robert W. Fogel and Stanley L. Engerman in the 1970s, through their work Time on the Cross, portrayed slaves as having internalized the Protestant work ethic of their owners. In portraying the more benign version of slavery, they also argue in their 1974 book that the material conditions under which the slaves lived and worked compared favorably to those of free workers in the agriculture and industry of the time. (This was also an argument of Southerners during the 19th century.)
In the 1970s and 1980s, historians made use of sources such as black music and statistical census data to create a more detailed and nuanced picture of slave life. Relying also on 19th-century autobiographies of ex-slaves (known as slave narratives) and the WPA Slave Narrative Collection, a set of interviews conducted with former slaves in the 1930s by the Federal Writers' Project, historians described slavery as the slaves remembered it. Far from slaves' being strictly victims or content, historians showed slaves as both resilient and autonomous in many of their activities. Despite their exercise of autonomy and their efforts to make a life within slavery, current historians recognize the precariousness of the slave's situation. Slave children quickly learned that they were subject to the direction of both their parents and their owners. They saw their parents disciplined just as they came to realize that they also could be physically or verbally abused by their owners. Historians writing during this era include John Blassingame (Slave Community), Eugene Genovese (Roll, Jordan, Roll), Leslie Howard Owens (This Species of Property), and Herbert Gutman (The Black Family in Slavery and Freedom).
Important work on slavery has continued; for instance, in 2003 Steven Hahn published the Pulitzer Prize-winning account, A Nation under Our Feet: Black Political Struggles in the Rural South from Slavery to the Great Migration, which examined how slaves built community and political understanding while enslaved, so they quickly began to form new associations and institutions when emancipated, including black churches separate from white control. In 2010, Robert E. Wright published a model that explains why slavery was more prevalent in some areas than others (e.g. southern than northern Delaware) and why some firms (individuals, corporations, plantation owners) chose slave labor while others used wage, indentured, or family labor instead.
A national Marist Poll of Americans in 2015 asked, "Was slavery the main reason for the Civil War, or not?" 53% said yes and 41% said not. There were sharp cleavages along lines of region and party. In the South, 49% answered not. Nationwide 55 percent said students should be taught slavery was the reason for the Civil War.
In 2018, a conference at the University of Virginia studied the history of slavery and recent views on it.
Economics of slavery in the West Indies
One of the most controversial aspects of the British Empire is its role in first promoting and then ending slavery. In the 18th-century British merchant ships were the largest element in the "Middle Passage" which transported millions of slaves to the Western Hemisphere. Most of those who survived the journey wound up in the Caribbean, where the Empire had highly profitable sugar colonies, and the living conditions were bad (the plantation owners lived in Britain). Parliament ended the international transportation of slaves in 1807 and used the Royal Navy to enforce that ban. In 1833 it bought out the plantation owners and banned slavery. Historians before the 1940s argued that moralistic reformers such as William Wilberforce were primarily responsible.
Historical revisionism arrived when West Indian historian Eric Williams, a Marxist, in Capitalism and Slavery (1944), rejected this moral explanation and argued that abolition was now more profitable, for a century of sugarcane raising had exhausted the soil of the islands, and the plantations had become unprofitable. It was more profitable to sell the slaves to the government than to keep up operations. The 1807 prohibition of the international trade, Williams argued, prevented French expansion on other islands. Meanwhile, British investors turned to Asia, where labor was so plentiful that slavery was unnecessary. Williams went on to argue that slavery played a major role in making Britain prosperous. The high profits from the slave trade, he said, helped finance the Industrial Revolution. Britain enjoyed prosperity because of the capital gained from the unpaid work of slaves.
Since the 1970s numerous historians have challenged Williams from various angles and Gad Heuman has concluded, "More recent research has rejected this conclusion; it is now clear that the colonies of the British Caribbean profited considerably during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars." In his major attack on the Williams's thesis, Seymour Drescher argues that Britain's abolition of the slave trade in 1807 resulted not from the diminishing value of slavery for Britain but instead from the moral outrage of the British voting public. Critics have also argued that slavery remained profitable in the 1830s because of innovations in agriculture so the profit motive was not central to abolition. Richardson (1998) finds Williams's claims regarding the Industrial Revolution are exaggerated, for profits from the slave trade amounted to less than 1% of domestic investment in Britain. Richardson further challenges claims (by African scholars) that the slave trade caused widespread depopulation and economic distress in Africa—indeed that it caused the "underdevelopment" of Africa. Admitting the horrible suffering of slaves, he notes that many Africans benefited directly because the first stage of the trade was always firmly in the hands of Africans. European slave ships waited at ports to purchase cargoes of people who were captured in the hinterland by African dealers and tribal leaders. Richardson finds that the "terms of trade" (how much the ship owners paid for the slave cargo) moved heavily in favor of the Africans after about 1750. That is, indigenous elites inside West and Central Africa made large and growing profits from slavery, thus increasing their wealth and power.
Economic historian Stanley Engerman finds that even without subtracting the associated costs of the slave trade (e.g., shipping costs, slave mortality, mortality of British people in Africa, defense costs) or reinvestment of profits back into the slave trade, the total profits from the slave trade and of West Indian plantations amounted to less than 5% of the British economy during any year of the Industrial Revolution. Engerman's 5% figure gives as much as possible in terms of benefit of the doubt to the Williams argument, not solely because it does not take into account the associated costs of the slave trade to Britain, but also because it carries the full-employment assumption from economics and holds the gross value of slave trade profits as a direct contribution to Britain's national income. Historian Richard Pares, in an article written before Williams's book, dismisses the influence of wealth generated from the West Indian plantations upon the financing of the Industrial Revolution, stating that whatever substantial flow of investment from West Indian profits into industry there was occurred after emancipation, not before.