Raptor at SpaceX Hawthorne facility | |
| Country of origin | United States |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SpaceX |
| Application | 1st and 2nd stage propulsion of the Starship vehicle |
| Status | Under development |
| Liquid-fuel engine | |
| Propellant | Liquid oxygen / liquid methane |
| Mixture ratio | 3.55 (78% O2, 22% CH4) |
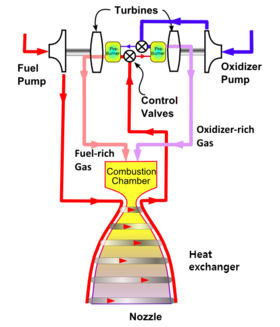
| Cycle | Full-flow staged combustion |
| Pumps | 2 turbopumps |
| Configuration | |
| Chamber | 1 |
| Nozzle ratio | 40 |
| Performance | |
| Thrust | 880–2,210 kN; 200,000–500,000 lbf (90–225 tf) |
| Throttle range | 40–100% |
| Thrust-to-weight ratio |
|
| Chamber pressure |
|
| Isp (vac.) | 380 s (3,700 m/s), goal |
| Isp (SL) | 330 s (3,200 m/s) |
| Mass flow |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 3.1 m (10 ft) |
| Diameter | 1.3 m (4 ft 3 in) |
| Dry weight | 1,500 kg (3,300 lb), goal |
| Used in | |
| Starship | |
The SpaceX Raptor is a full-flow staged combustion, methane-fueled rocket engine manufactured by SpaceX. The engine is powered by cryogenic liquid methane and liquid oxygen (LOX), rather than the RP-1 kerosene and LOX used in SpaceX's prior Merlin and Kestrel rocket engines. The earliest concepts for Raptor considered liquid hydrogen (LH
2) as fuel rather than methane. The Raptor engine has more than twice the thrust of the Merlin 1D engine that powers the current Falcon 9 launch vehicle.
Raptor will be used in both stages of the two-stage-to-orbit, super-heavy-lift Starship system launch vehicle, which is designed to replace all existing SpaceX vehicles, including the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles and the SpaceX Dragon 2. As part of Starship, Raptor engines are expected to be used in various applications, including Earth-orbit satellite delivery market, deployment of a large portion of SpaceX's own Starlink megaconstellation, and the exploration and eventual colonization of Mars.
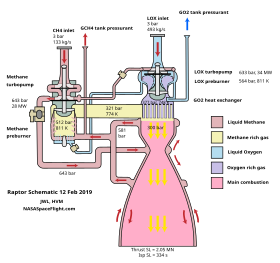
Raptor engines began flight testing on the Starhopper prototype in July 2019 and became the first full-flow staged combustion rocket engine ever flown. As of January Raptor also produces the highest combustion chamber pressure ever reached by an operational rocket engine, at 330 bar (33,000 kilopascals), surpassing the record held by the RD-701 rocket engine at 300 bars.
Description
The Raptor engine is powered by subcooled liquid methane and subcooled liquid oxygen using a more efficient Full Flow Staged Combustion cycle, a departure from the simpler "open-cycle" gas generator system and LOX/kerosene propellants that current Merlin engines use. The RS-25, with hydrolox propellant also used a staged combustion process, as do several Russian rocket engines, including the RD-180 and the 25.74 MPa (3,733 psi) chamber pressure RD-191. The stated design size for the Raptor engine varied widely during 2012–2017 as detailed design continued, from a high target of 8,200 kN (1,800,000 lbf) of vacuum thrust to a more recent, much lower target of 1,900 kN (430,000 lbf). In its 2017 iteration, the operational engine is expected to have a vacuum Isp = 382 s (3,750 m/s) and a sea-level Isp = 334 s (3,280 m/s).
The Raptor engine is designed for the use of deep cryogenic methalox propellants—fluids cooled to near their freezing points, which is typical for cryogenic rocket engines. The use of subcooled propellants increases propellant density to allow more propellant mass in tanks; the engine performance is also improved with subcooled propellants. Specific impulse is increased, and the risk of cavitation at inputs to the turbopumps is reduced due to the higher mass flow rate per unit power generated. Engine ignition for all Raptor engines, both on the pad and in the air, will be by spark ignition, which will eliminate the pyrophoric mixture of triethylaluminum-triethylborane (TEA-TEB) used for engine ignition on the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy.
Raptor has been claimed to be able to deliver "long life ... and more benign turbine environments". Specifically, Raptor utilizes a full-flow staged combustion cycle, where all the oxidizer—with a low-fuel ratio—will power the oxygen turbine pump, and all the fuel—with a low-oxygen ratio—will power the methane turbine pump. Both streams—oxidizer and fuel—will be mixed completely in the gas phase before they enter the combustion chamber. Prior to 2014, only two full-flow staged-combustion rocket engines had ever progressed sufficiently to be tested on test stands: the Soviet RD-270 project in the 1960s and the Aerojet Rocketdyne Integrated Powerhead Demonstrator in the mid-2000s.
Additional characteristics of the full-flow design, projected to further increase performance or reliability include:
- eliminating the fuel–oxidizer turbine interseal, which is a potential point of failure in more traditional engine designs;
- lower pressures are required through the pumping system, increasing life span and further reducing risk of catastrophic failure;
- ability to increase the combustion-chamber pressure, thereby either increasing overall performance or "by using cooler gases, providing the same performance as a standard staged combustion engine but with much less stress on materials, thus significantly reducing material fatigue or [engine] weight".
SpaceX aims at a lifetime of 1000 flights for Raptor.
The turbopump and many of the critical parts of the injectors for the initial engine development testing were, as of 2015, manufactured by using 3D printing, which increases the speed of development and iterative testing. The 2016 1 MN (220,000 lbf) test-stand engine had 40% (by mass) of its parts manufactured by 3D printing.
In 2019 the engine manifolds were cast from SX300 (similar to Inconel), soon to be changed to SX500.
The Raptor engine uses a large number of coaxial swirl injectors to admit propellants to the combustion chamber, rather than pintle injectors used on the previous Merlin rocket engines that SpaceX mass-produced for its Falcon family of launch vehicles. Raptor uses "dual redundant torch igniters".
In 2019 the (marginal) cost of the engine was stated to be less than $1 million. SpaceX plans to mass-produce up to 500 Raptor engines per year, each costing less than $250,000.
History
The engine development from 2009 to 2015 was funded exclusively through private investment by SpaceX, and not as a result of any funding from the US government. In January 2016, SpaceX did agree with the US Air Force to take US$33.6 million in defense department funding in order to develop a particular Raptor model: a prototype of a new upper-stage variant of the Raptor engine designed for potential use as an upper stage on Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy, with SpaceX agreeing to fund at least US$67.3 million on the same upper-stage development project, on a minimum 2:1 private-to-government funding basis.
Initial concept
An advanced rocket engine design project named Raptor—then a hydrolox engine—was first publicly discussed by SpaceX's Max Vozoff at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Commercial Crew/Cargo symposium in 2009. As of April 2011, SpaceX had a small number of staff working on the Raptor upper-stage engine, then still a LH
2/LOX concept, at a low level of priority. Further mention of the development program occurred in 2011. In March 2012, news accounts asserted that the Raptor upper-stage engine development program was underway, but that details were not being publicly released.
In October 2012, SpaceX publicly announced concept work on a rocket engine that would be "several times as powerful as the Merlin 1 series of engines, and won't use Merlin's RP-1 fuel", but declined to specify which fuel would be used. They indicated that details on a new SpaceX rocket would be forthcoming in "one to three years" and that the large engine was intended for the next-generation launch vehicle using multiple of these large engines, that would be expected to launch payload masses of the order of 150 to 200 tonnes (150,000 to 200,000 kg; 330,000 to 440,000 lb) to low Earth orbit, exceeding the payload mass capability of the NASA Space Launch System.
Methane engine announcement and component development
In November 2012, Musk announced a new direction for the propulsion division of SpaceX: developing methane-fueled rocket engines. He further indicated that the engine concept, codenamed Raptor, would now become a methane-based design, and that methane would be the fuel of choice for SpaceX's plans for Mars colonization.
Because of the presence of water underground and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of Mars, methane, a simple hydrocarbon, can easily be synthesized on Mars using the Sabatier reaction. In-situ resource production on Mars has been examined by NASA and found to be viable for oxygen, water, and methane production. According to a study published by researchers from the Colorado School of Mines, in-situ resource utilization such as methane from Mars makes space missions more feasible technically and economically and enables reusability.
When first mentioned by SpaceX in 2009, the term "Raptor" was applied exclusively to an upper-stage engine concept—and 2012 pronouncements indicated that it was then still a concept for an upper stage engine—but in early 2014 SpaceX confirmed that Raptor would be used both on a new second stage, as well as for the large (then, nominally a 10-meter-diameter) core of the Mars Colonial Transporter (subsequently, in 2016, on both stages of the Interplanetary Transport System and then, in 2017 on the Big Falcon Rocket).
The earliest public hints that a staged-combustion methane engine was under consideration at SpaceX were given in May 2011 when SpaceX asked if the Air Force was interested in a methane-fueled engine as an option to compete with the mainline kerosene-fueled engine that had been requested in the USAF Reusable Booster System High Thrust Main Engine solicitation.
Public information released in November 2012 indicated that SpaceX might have a family of Raptor-designated rocket engines in mind; this was confirmed by SpaceX in October 2013. However, in March 2014 SpaceX COO Gwynne Shotwell clarified that the focus of the new engine development program is exclusively on the full-size Raptor engine; smaller subscale methalox engines were not planned on the development path to the very large Raptor engine.
In October 2013, SpaceX announced that they would be performing methane engine tests of Raptor engine components at the John C. Stennis Space Center in Hancock County, Mississippi, and that SpaceX would add equipment to the existing test stand infrastructure in order to support liquid methane and hot gaseous methane engine component testing. In April 2014, SpaceX completed the requisite upgrades and maintenance to the Stennis test stand to prepare for testing of Raptor components, and the engine component testing program began in earnest, focusing on the development of robust startup and shutdown procedures, something that is typically quite difficult to do for full-flow staged combustion cycle engines. Component testing at Stennis also allowed hardware characterization and verification of proprietary analytical software models that SpaceX developed to push the technology on this engine cycle that had little prior development work in the West.
October 2013 was the first time SpaceX disclosed a nominal design thrust of the Raptor engine—2,900 kN (661,000 lbf)—although early in 2014 they announced a Raptor engine with greater thrust, and in 2015, one with lower thrust that might better optimize thrust-to-weight.
In February 2014, Tom Mueller, the head of rocket engine development at SpaceX, revealed in a speech that Raptor was being designed for use on a vehicle where nine engines would "put over 100 tons of cargo up to Mars" and that the rocket would be more powerful than previously released publicly, producing greater than 4,400 kN (1,000,000 lbf). A June 2014 talk by Mueller provided more specific engine performance target specifications indicating 6,900 kN (1,600,000 lbf) of sea-level thrust, 8,200 kN (1,800,000 lbf) of vacuum thrust, and a specific impulse (Isp) of 380 s (3,700 m/s) for a vacuum version. Earlier information had estimated the design Isp under vacuum conditions as only 363 s (3,560 m/s). Jeff Thornburg, who led development of the Raptor engine at SpaceX 2011–2015, noted that methane rocket engines have higher performance than kerosene/RP-1 and lower than hydrogen, with significantly fewer problems for long-term, multi-start engine designs than kerosene—methane is cleaner burning—and significantly lower cost than hydrogen, coupled with the ability to "live off the land" and produce methane directly from extraterrestrial sources.
SpaceX successfully began development testing of injectors in 2014 and completed a full-power test of a full-scale oxygen preburner in 2015. 76 hot fire tests of the preburner, totaling some 400 seconds of test time, were executed from April–August 2015. SpaceX completed its planned testing using NASA Stennis facilities in 2014 and 2015.
In January 2015, Elon Musk stated that the thrust they were currently targeting was around 230 tonnes-force (2,300 kN; 510,000 lbf), much lower than older statements had mentioned. By August 2015, an Elon Musk statement surfaced that indicated the oxidizer to fuel ratio of the Mars-bound engine would be approximately 3.8 to 1.
In January 2016, the US Air Force awarded a US$33.6 million development contract to SpaceX to develop a prototype version of its methane-fueled reusable Raptor engine for use on the upper stage of the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles, which required double-matching funding by SpaceX of at least US$67.3 million. Work under the contract was expected to be completed in 2018, with engine performance testing to be done at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center in Mississippi and Los Angeles Air Force Base, California.
Engine development and testing
Initial development testing of Raptor methane engine components was done at the Stennis Space Center in Hancock County, Mississippi, where SpaceX added equipment to the existing infrastructure in order to support liquid methane engine testing. Initial testing was limited to components of the Raptor engine, since the 440 kN (100,000 lbf) test stands at the E-2 complex at Stennis were not large enough to test the full Raptor engine. The development Raptor engine discussed in the October 2013 time frame relative to Stennis testing was designed to generate more than 2,900 kN (661,000 lbf) vacuum thrust. A revised, higher-thrust, specification was discussed by the company in February 2014, but it was unclear whether that higher thrust was something that would be achieved with the initial development engines. Raptor engine component testing began in May 2014 at the E-2 test complex which SpaceX modified to support methane engine tests. The first items tested were single Raptor injector elements, various designs of high-volume gas injectors. The modifications to the test stands made by SpaceX are now a part of the Stennis test infrastructure and are available to other users of the test facility after the SpaceX facility lease was completed. SpaceX successfully completed a "round of main injector testing in late 2014" and a "full-power test of the oxygen preburner component" for Raptor by June 2015. Tests continued at least into September 2015.
By early 2016, SpaceX had constructed a new engine test stand at their site of McGregor in central Texas that can handle the larger thrust of the full Raptor engine.
By August 2016, the first integrated Raptor rocket engine, manufactured at the SpaceX Hawthorne facility in California, shipped to the McGregor rocket engine test facility in Texas for development testing. The engine had 1 MN (220,000 lbf) thrust, which makes it approximately one-third the size of the full-scale Raptor engine planned for flight tests in 2019/2020 timeframe. It is the first full-flow staged-combustion methalox engine ever to reach a test stand. This 2016 development engine had "an expansion ratio of just 150, the maximum possible within Earth’s atmosphere" to prevent flow separation problems. It performed an initial 9-second firing test on 26 September 2016, the day before Musk's talk at the International Aeronautical Congress.
On 26 September 2016, Elon Musk tweeted two images of the first test firing of an integrated Raptor in SpaceX's McGregor test complex. On the same day Musk revealed that their target performance for Raptor was a vacuum specific impulse of 382 s (3,750 m/s), with a thrust of 3 MN (670,000 lbf), a chamber pressure of 300 bar (30 MPa; 4,400 psi), and an expansion ratio of 150 for an altitude optimized version. When asked if the nozzle diameter for such version was 14 ft (4.3 m), he stated that it was pretty close to that dimension. He also disclosed that it used multi-stage turbopumps. On the 27th he clarified that 150 expansion ratio was for the development version, that the production vacuum version would have an expansion ratio of 200. Substantial additional technical details of the ITS propulsion were summarized in a technical article on the Raptor engine published the next week.
By September 2017, the development Raptor engine—with 200 bars (20 MPa; 2,900 psi) chamber pressure—had undergone 1200 seconds of test fire testing in ground-test stands across 42 main engine tests, with the longest test being 100 seconds (which is limited by the capacity of the ground-test propellant tanks). As of September 2017, the first version of the flight engine is intended to operate at a chamber pressure of 250 bars (25 MPa; 3,600 psi), with the intent to raise it to 300 bars (30 MPa; 4,400 psi) at a later time.
By September 2017, the 200 bars (20 MPa; 2,900 psi) sub-scale test engine, with a thrust of 1 meganewton (220,000 lbf) and "a new alloy to help its oxygen-rich turbopump resist oxidization, ... had completed 1200 seconds of firings across 42 tests." This alloy is known as SX500 which is used to contain hot oxygen gas in the engine at up to 12000 psi. SX500 was created by the SpaceX metallurgy team.
While plans for Raptor flight testing have consistently been on the new-generation fiber-composite-material construction flight vehicles since 2016, the specific vehicle was not clarified until October 2017, when it was indicated that initial suborbital test flights would occur with a Big Falcon Ship. In November 2016, the first flight tests of the Raptor engine were projected to be on the Interplanetary Transport System, no earlier than the early 2020s. By July 2017, the plan had been modified to do flight testing on a much smaller launch vehicle and spacecraft, and the new system architecture had "evolved quite a bit" since the ITS concept from 2016. A key driver of the 2017 architecture was to make the new system useful for substantial Earth-orbit and Cislunar launches so that the new system might pay for itself, in part, through economic spaceflight activities in the near-Earth space zone.
Elon Musk announced in September 2017 that the initial flight platform for any Raptor engine would be some part of the Big Falcon Rocket. BFR was a 9 m (30 ft)-diameter launch vehicle. In October 2017, Musk clarified that "[initial flight testing will be with] a full-scale 9-meter-diameter ship doing short hops of a few hundred kilometers altitude and lateral distance ... [projected to be] fairly easy on the vehicle, as no heat shield is needed, we can have a large amount of reserve propellant and don’t need the high area ratio, deep-space Raptor engines."
Notably, Musk also announced that the new Raptor-powered BFR launch vehicle was planned to entirely replace both Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles as well as the SpaceX Dragon 2 in the existing operational SpaceX fleet in the early 2020s, initially aiming at the Earth-orbit market, but SpaceX is explicitly designing in substantial capability to the spacecraft vehicles to support long-duration spaceflight in the cislunar and Mars mission environment as well. SpaceX intends this approach to bring significant cost savings which will help the company justify the development expense of designing and building the new launch vehicle design. In addition to orbital spaceflight missions, BFR is being considered for the point-to-point Earth transportation market, with ~30–60-minute flights to nearly anywhere on the planet.
The first flight version of the Raptor engine arrived in McGregor, Texas in late January 2019.
On 3 February 2019, SpaceX performed the first test of a flight version engine. The test lasted two seconds with the engine operating at 60 percent of rated thrust at a chamber pressure of 170 bars (17,000 kPa). Just four days later, the test engine achieved the power levels needed for use in SpaceX Starship. The engine reached 172 tonnes-force (1,690 kN; 380,000 lbf) thrust with a chamber pressure of 257 bars (25.7 MPa). The test was conducted using warm propellant, with expectations of a 10% to 20% increase in performance when switching to deep cryogenic temperatures for the propellant. On 10 February 2019, Musk announced on Twitter that the flight version engine had attained the chamber combustion pressure of 268.9 bars (26.89 MPa) on a test stand. On 19 June 2020, Musk announced that the Raptor engine tests achieved the expected chamber combustion pressure of 300 bars (30 MPa) on a test stand.
By March, serial number 2 (SN2) of the flight version Raptor engine had been delivered to the SpaceX South Texas Launch Site east of Brownsville, Texas for system integration testing on the Starhopper, the first test article of Starship, approximately one year ahead of schedule. SN2 was used for two tethered tests of the flight test "hopper" in early April. On 3 April 2019, SpaceX conducted a successful static fire test, which ignited the engine while the vehicle remained tethered to the ground. The firing was a few seconds in duration, and was classed as successful by SpaceX. A second tethered test followed just two days later, on 5 April 2019. Serial numbers 3, 4, 5 and 6 had all made it to the test stand by early July, but the first three had issues of various sorts and SpaceX did not try any flight tests of the Starhopper test vehicle. SN6 was still under test on the ground test stand as of 8 July 2019.
The first flight test of a Raptor engine occurred on 25 July 2019 at the SpaceX South Texas Launch Site. Unusually, for initial flight tests of orbital-class rocket engines, this was not a full-duration burn but just a 22-second test. SpaceX is developing their next-generation rocket to be reusable from the beginning, just like an aircraft, and thus needs to start with narrow flight test objectives, while still aiming to land the rocket successfully to be used subsequently in further tests to expand the flight envelope.
Another flight test of a Raptor engine (probably SN6) occurred on 27 August 2019 from Boca Chica, Texas, test facility. The Starhopper reached an estimated altitude of 150 m (FAA approved). A side step and a landing on a nearby landing pad terminated the roughly 1 minute flight.
On August 4, 2020 a single Raptor engine (SN27) propelled a Starship prototype (SN5) to an altitude of 150 m (FAA approved) at the Boca Chica test facility; this was the first flight of a full-size Starship prototype. The Raptor engine was mounted off center and controlled the Starship during lift off, a traverse of approximately 100 meters, and landing on a secondary pad. The total flight time was approximately 50 seconds.
In August 2020, a ground stand test of a Raptor achieved 330 bar (33,000 kPa) chamber pressure, producing ~225 tf (2,210 kN; 500,000 lbf) of thrust. This achievement surpassed RD-701 engine and set a new world record of the highest pressure ever reached in a rocket engine's combustion chamber. Tests have also shown that the engine—designed to be throttleable from the outset—can throttle engine thrust down to 40 percent of maximum output. The current limitation to decreasing thrust even further is Raptor preburner flameout.
On September 3, 2020, Raptor SN29 propelled the Starship prototype SN6 to around 150 m (FAA approved) at the Boca Chica test facility; as with Starship SN5, the engine was mounted off center and controlled the prototype during the entire flight, which lasted for approximately 45 seconds. Unlike the Raptor engine (SN27) mounted on the SN5 Starship prototype, which suffered a small fire during the flight, Raptor SN29 did not seem to have any issues.
On December 9, 2020, three Raptor engines propelled the Starship prototype SN8 to approximately 12.5 km at the Boca Chica test facility. The three engines were placed in the center of the vehicle, unlike in previous prototypes. During this flight, the engines sequentially shutdown each by each until the final Raptor underwent shutdown, preceding the flop maneuver. The last engine in this flight to shutoff had a final burn-time of approximately 4 minutes and 40 seconds. The SN8 was destroyed upon impact to ground during landing.
On 2 February 2021, Starship prototype SN9, basically similar vehicle as the SN8, was launched to an altitude of about 10 km. The SN9 vehicle was destroyed in landing.
On 3 March 2021, Starship prototype SN10, again a vehicle basically the same as SN8 and SN9, was launched to an altitude of about 10 km (again). The SN10 vehicle did land somewhat successfully but was destroyed minutes after landing in a fire that started in the landing process.
Versions
The Raptor methalox engine for SpaceX next-generation launch vehicles have gone through a number of design concepts for engine thrust, specific impulse, and sea-level-nozzle/vacuum-nozzle sizings, depending on the vehicle design concept SpaceX was working on at the time, and subscale versions of Raptor engines were also built for early testing on ground test stands. After 2013, all engine design concepts were methalox using the full-flow staged combustion (FFSC) cycle. In addition, in 2016–2018, a custom prototype upper-stage methalox FFSC Raptor engine was designed and tested for the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles, strictly for the US Air Force to meet US military space readiness objectives. SpaceX never implemented plans to switch the F9/FH upper stage to methalox propellants.
SpaceX next-generation launch vehicle
In September 2016 at the IAC meetings, Musk mentioned several Raptor engine designs that could be used on the Interplanetary Transport System by late in the decade. In addition, a much smaller subscale engine had already been built for test and validation of the new full-flow staged-combustion cycle engine. At that time, this first subscale Raptor development engine had recently been tested on a ground test stand, but for only one brief firing.
The "Raptor subscale development engine" had approximately 1,000 kN (220,000 lbf) thrust. In order to eliminate flow separation problems while being tested in Earth's atmosphere, the test nozzle expansion ratio had been limited to only 150. The engine began testing in September 2016 on a ground test stand. Sources differed on the performance of the test engine. In reporting during the two weeks following the Musk ITS launch vehicle reveal on 27 September, NASASpaceFlight.com indicated that the development engine was only one-third the size of any of the several larger engine designs that were discussed for the later flight vehicles.
For the flight vehicles, Elon Musk discussed two engines: both a low-expansion ratio (ER40) for the first stage, or ITS booster and a higher-expansion ratio (200) to obtain higher performance with the second stage. 42 of these ER40 engines were envisioned in the high-level design of the first stage, with 3,050 kN (690,000 lbf) of thrust at sea level, and 3,285 kN (738,000 lbf) in vacuum. In addition, three gimbaled short-nozzle ER40 engines were to be used for maneuvering the 2016-design ITS second-stage; and these engines were also expected to be used for retropropulsive landings on Mars (with mean atmospheric pressure on the Martian surface of 600 Pa (0.0060 bar; 0.087 psi)). The higher-efficiency engine for in-space flight in vacuum conditions was envisioned then to target a specific impulse of 382s, using a much larger nozzle giving an expansion ratio of 200. Six of these non-gimbaled engines were planned to provide primary propulsion for the 2016 designs of the Interplanetary Spaceship and the Earth-orbit ITS tanker. As designed, both of those vehicles were to play a short-term role as second stages on launches to Earth orbit, as well as provide high-Isp efficiency on transfer from geocentric to heliocentric orbit for transport to beyond-Earth-orbit celestial bodies. 3,500 kN (790,000 lbf) thrust at vacuum, the only conditions under which the six ER200 engines were expected to be fired.
A year later, at the IAC meetings in September 2017, and following a year of testing and iterative development by the propulsion team, Musk said that a smaller Raptor engine—with slightly over half as much thrust as the previous concept designs for the ITS—would be used on the next-generation rocket, now a 9 m (30 ft)-diameter launch vehicle and publicly referred to as Big Falcon Rocket (BFR). With the much smaller launch vehicle, fewer Raptor engines would be used on each stage. BFR was then slated to have 31 Raptors on the first stage and 6 on the second stage. By mid-2018, SpaceX was publicly stating that the sea-level flight version Raptor engine design, with a nozzle exit diameter of 1.3 m (4.3 ft), was expected to have 1,700 kN (380,000 lbf) thrust at sea level with an Isp of 330 s (3,200 m/s) increasing to an Isp of 356 s (3,490 m/s) in vacuum. The vacuum flight version, with a nozzle exit diameter of 2.4 m (7.9 ft), was expected to exert 1,900 kN (430,000 lbf) force with an Isp of 375 s (3,680 m/s). The earliest versions of the flight engine is designed to operate at 250 bars (25,000 kPa; 3,600 psi) chamber pressure; but SpaceX expects to increase this to 300 bar (30,000 kPa; 4,400 psi) in later iterations. The flight engine is designed for extreme reliability, aiming to support the airline-level of safety required by the point-to-point Earth transportation market.
In the BFR update given in September 2018, Musk showed video of a 71-second hot fire test of a Raptor engine, and stated that "this is the Raptor engine that will power BFR, both the ship and the booster; it's the same engine. ... approximately a 200 tonne engine aiming for roughly 300 bar chamber pressure. ... If you had it at a high expansion ratio, has the potential to have a specific impulse of 380."
Raptor Vacuum
Like its sea-level efficient counterpart, the Raptor Vacuum engine is a methalox full-flow staged combustion (FFSC) engine but is optimized for higher performance under vacuum conditions, most notably, optimized for highest specific impulse given other engine requirements like reusability, reliability, and so forth.
While the optimized Raptor vacuum engine is aiming for an Isp of ~380 s (3,700 m/s), the v1.0 Raptor vac design to support early Starship development has been made more conservative and is projecting an Isp of only 365–370 s (3,580–3,630 m/s), intentionally decreasing engine performance to obtain having test engines sooner. In addition, Raptor Vacuum v1 will have a smaller engine nozzle in order to avoid flow separation when the engine is fired at sea-level atmospheric pressure. A full-duration test of version 1 of the Raptor Vacuum engine was completed in September 2020 at the SpaceX development facility in McGregor, Texas.
Upper stage engine prototype for Falcon 9
In January 2016, the US Air Force (USAF) awarded a US$33.6 million development contract to SpaceX to develop a prototype version of its methane-fueled reusable Raptor engine for use on the upper stage of the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles. The contract required double-matching funding by SpaceX of at least US$67.3 million. Work under the contract was expected to be completed no later than December 2018, and engine performance testing was planned to be completed at NASA's Stennis Space Center in Mississippi under US Air Force supervision. The USAF contract called only for the development and build of a single prototype engine with a series of ground tests, with no upper stage launch vehicle design funded by the contract. The Air Force was working with the US Congress in February 2016 to pursue new launch systems."
In October 2017 the US Air Force (USAF) awarded a US$40.8 million modification for the development of the Raptor rocket propulsion system prototype for the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle program, with work under that contract expected to be completed by April 2018.
Little technical detail was ever publicly released about the USAF second stage engine, as is typical for defense contracts. The prototype however was to be designed:
- to serve the theoretical purpose of servicing an upper stage that could be used on the existing SpaceX Falcon 9 (7,600 kN (1,700,000 lbf)-class) and the existing Falcon Heavy (23,000 kN (5,200,000 lbf)-class) first-stage sea-level thrust launch vehicles.
- with propellants: liquid methane and liquid oxygen (LOX),
- with the Raptor full-flow staged combustion engine cycle,
- explicitly to be a reusable engine.
The USAF contract called only for the development and build of a prototype, to be demonstrated in a USAF-supervised set of tests. No upper stage vehicle design/redesign was funded by the contract. Neither the Air Force nor SpaceX subsequently published any results of this non-Starship oriented rocket engine contract.
Comparison to other engines
Applications
As of September 2016, the Raptor engine was slated to be used in three spaceflight vehicles making up the two launch stages of an ITS stack. The first stage would always be ITS booster while the second stage may be either an Interplanetary Spaceship (for beyond-Earth-orbit missions) or an ITS tanker (for on-orbit propellant transfer operations nearer to Earth).
The SpaceX 2016-design of the Interplanetary booster was announced with 42 sea-level optimized Raptors in the first stage of the ITS with a total of 128 MN (29,000,000 lbf) of thrust. The SpaceX Interplanetary Spaceship—which made up the second stage of the ITS on Earth launches was also an interplanetary spacecraft carrying cargo and passengers to beyond-Earth-orbit destinations after on-orbit refueling—was slated in the 2016 design to use six vacuum-optimized Raptors for primary propulsion plus three Raptors with sea-level nozzles for maneuvering.
The SpaceX design after late 2017 is for a much smaller launch vehicle, 9 meters in diameter rather than 12 meters for the ITS, and is now known as Starship. The Starship first stage (now known as Super Heavy) was slated to have 31 sea-level optimized Raptors in the initial design concept, with a total of 48 MN (11,000,000 lbf) of thrust. The Starship will use three vacuum-optimized Raptors for primary propulsion plus three sea-level Raptors for maneuvering and atmospheric flight. SpaceX is currently building and testing a series of Starship and Super Heavy booster prototypes at the SpaceX South Texas Launch Site.